PACE figforth Implementation
|
|
|
- Elaine Leonard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PACE figforth Implementation Adapting the figforth Glossary to a word-addressing computer David Kilbridge FORTH Day 2009 November 21, 2009
2 Review of implementation project Nine reference implementations All written to a common API specification, the figforth glossary which evolved during the project Published and released into the public domain at 1979 WCCF
3 Design issues How are data to be represented in memory? What is the connection between the Forth virtual machine and the actual hardware?
4 Data representation: obvious choices One stack cell per 16-bit word Stack pointers are native addresses Change by 1 to push or pop One dictionary field per 16-bit word Compiler stores one address per word Inner interpreter deals with native addresses
5 How to store text data? Two choices: One character per word Two characters packed into 1 word
6 One character per word Probably the best choice today Storage is cheap Allows i18n via UTF-16 encoding Each character gets a native address Possible issues with data exchange May have to unpack characters on input, pack on output
7 Two characters per word My choice at the time Most efficient use of expensive storage Unicode, ISO-8859 didn t exist Allowed (FIND) to compare 2 bytes at a time WORD aligns strings consistently with count in the MSB Used existing I/O subsystem transferring packed characters
8 Implications of packed characters Need a way to address each byte of a word Forced to add abstract addresses for bytes How does byte addressing work?
9 New conversion words BYTE addr --- baddr (= addr * 2) Returns address of most-significant byte of word (big-endian) Used ~ 15x in figforth nucleus CELL baddr --- addr (= baddr / 2) Returns address of word containing byte Used ~ 7x in figforth nucleus
10 Words that use byte addresses C! CMOVE COUNT ENCLOSE EXPECT (LINE) (NUMBER) TOGGLE TRAVERSE -TRAILING TYPE #>
11 Elaborations to Glossary, part 1 C@ baddr --- b C! b baddr --- CMOVE baddr1 baddr2 count --- COUNT addr1 --- baddr2 n ENCLOSE baddr1 c --- baddr1 n1 n2 n3 EXPECT baddr count --- HLD (contains a byte address)
12 Elaborations to Glossary, part 2 (LINE) n1 n2 --- baddr count (NUMBER) d1 baddr1 --- d2 baddr2 TOGGLE baddr b --- TRAVERSE baddr1 n --- baddr2 -TRAILING baddr n1 --- baddr n2 TYPE baddr count --- #> d --- baddr count
13 Word addresses used for: SP, RP, IP, W, DP and all dictionary fields TIB, PAD, disk buffers Most words in the figforth glossary
14 Objections to byte addressing Creates a 32K-word barrier in memory A problem we wished we had! No worse off than with a byte-addressed machine with 64K bytes of memory Schizophrenic API Have two distinct pointer types without strong-typing support from the language Forces programmer to remember which type of address to use where
15 PACE architecture Unit of addressing = 16-bit word All machine instructions are 1 word long - No inline addresses or extension words - All EAs are short offsets from a base or indirectly from there (LD, ST, JMP, JSR) Memory-mapped (and bit-banging) I/O 6-level priority interrupts
16 Programmer s model AC0 Program Counter AC1 Ten-Word LIFO Stack AC2 AC3 LINK CRY OVF
17 Typical memory reference instruction: OPCODE xr displacement Four pages directly addressable xr = 0: 0000 to 00FF (or FF80 to 007F) xr = 1: (PC) - 80 to (PC) + 7F xr = 2: (AC2) - 80 to (AC2) + 7F xr = 3: (AC3) - 80 to (AC3) + 7F
18 Capabilities of all registers flags, stack, other registers, memory Equality test with memory Add from memory Load immed., Complement, Add immed. Add w/wo carry, And, Xor other registers Shift and rotate
19 Special register capabilities AC0: Test =0, 0, 0, <0, and bits 0, 1, 2 Additional operations with memory operands: And, Or, Subtract w/borrow, Decimal add, Greater-than test, Mask test, Load byte Load and store Indirect AC2 and AC3: Serve as base or index registers
20 Forth register assignment AC0 Working accumulator Program Counter AC1 IP Ten-Word LIFO Stack Scratch AC2 W AC3 SP LINK CRY OVF RP, UP in memory page 0
21 Use internal stack as parameter or return stack? Only 10 words deep Only top word is accessible Not easily extended into memory Would need to enable and service stack full/empty interrupts Just use for register saving, JSRs and interrupts (if required by the installation)
22 SP, IP, W usage LIT:.WORD.+1 RCPY IP,X ; PICK UP LD 0,(X) ; VALUE AISZ IP,1 ; STEP IP OVER PUSH: AISZ SP,-1 ; EXTEND STACK PUT: ST 0,(SP) ; STORE VALUE NEXT: RCPY IP,X AISZ IP,1 ; INCREMENT IP LD W,(X) ; ADDR OF NEXT WORD ; JUMP THRU CODE ADDR
23 RP usage TOR:.WORD.+1 DSZ RP ; EXTEND RETURN STACK LD 0,(SP) ; GET DATA ITEM ST 0,@RP ; PUT ON RETURN STACK JMP POP ; POP FROM DATA STACK FROMR:.WORD.+1 LD 0,@RP ; GET FROM RETURN STK ISZ RP ; POP RETURN STACK JMP PUSH ; PUSH ON DATA STACK R:.WORD.+1 LD 0,@RP ; GET NONDESTRUCTIVE JMP PUSH ; PUSH ON DATA STACK
24 Summary The PACE implementation split the figforth Glossary s concept of a single type of address into two: Most addresses in the Forth virtual machine are native word addresses, allowing efficient execution Byte addresses are used for packed text handling and compatibility with 8-bit algorithms
CSIS1120A. 10. Instruction Set & Addressing Mode. CSIS1120A 10. Instruction Set & Addressing Mode 1
 CSIS1120A 10. Instruction Set & Addressing Mode CSIS1120A 10. Instruction Set & Addressing Mode 1 Elements of a Machine Instruction Operation Code specifies the operation to be performed, e.g. ADD, SUB
CSIS1120A 10. Instruction Set & Addressing Mode CSIS1120A 10. Instruction Set & Addressing Mode 1 Elements of a Machine Instruction Operation Code specifies the operation to be performed, e.g. ADD, SUB
When an instruction is initially read from memory it goes to the Instruction register.
 CS 320 Ch. 12 Instruction Sets Computer instructions are written in mnemonics. Mnemonics typically have a 1 to 1 correspondence between a mnemonic and the machine code. Mnemonics are the assembly language
CS 320 Ch. 12 Instruction Sets Computer instructions are written in mnemonics. Mnemonics typically have a 1 to 1 correspondence between a mnemonic and the machine code. Mnemonics are the assembly language
2. ADDRESSING METHODS
 2 Addressing Methods STUDY MATERIALS ON COMPUTER ORGANIZATION (As per the curriculum of Third semester BSc Electronics of Mahatma Gandh Uniiversity) Compiled by Sam Kollannore U Lecturer in Electronics
2 Addressing Methods STUDY MATERIALS ON COMPUTER ORGANIZATION (As per the curriculum of Third semester BSc Electronics of Mahatma Gandh Uniiversity) Compiled by Sam Kollannore U Lecturer in Electronics
Instruction Sets: Characteristics and Functions Addressing Modes
 Instruction Sets: Characteristics and Functions Addressing Modes Chapters 10 and 11, William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 th Edition What is an Instruction Set? The complete collection
Instruction Sets: Characteristics and Functions Addressing Modes Chapters 10 and 11, William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 th Edition What is an Instruction Set? The complete collection
Page 1. Structure of von Nuemann machine. Instruction Set - the type of Instructions
 Structure of von Nuemann machine Arithmetic and Logic Unit Input Output Equipment Main Memory Program Control Unit 1 1 Instruction Set - the type of Instructions Arithmetic + Logical (ADD, SUB, MULT, DIV,
Structure of von Nuemann machine Arithmetic and Logic Unit Input Output Equipment Main Memory Program Control Unit 1 1 Instruction Set - the type of Instructions Arithmetic + Logical (ADD, SUB, MULT, DIV,
Computer Organization CS 206 T Lec# 2: Instruction Sets
 Computer Organization CS 206 T Lec# 2: Instruction Sets Topics What is an instruction set Elements of instruction Instruction Format Instruction types Types of operations Types of operand Addressing mode
Computer Organization CS 206 T Lec# 2: Instruction Sets Topics What is an instruction set Elements of instruction Instruction Format Instruction types Types of operations Types of operand Addressing mode
Instruction Set Architecture
 C Fortran Ada etc. Basic Java Instruction Set Architecture Compiler Assembly Language Compiler Byte Code Nizamettin AYDIN naydin@yildiz.edu.tr http://www.yildiz.edu.tr/~naydin http://akademik.bahcesehir.edu.tr/~naydin
C Fortran Ada etc. Basic Java Instruction Set Architecture Compiler Assembly Language Compiler Byte Code Nizamettin AYDIN naydin@yildiz.edu.tr http://www.yildiz.edu.tr/~naydin http://akademik.bahcesehir.edu.tr/~naydin
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture. Instruction Set Architectures
 COSC 6385 Computer Architecture Instruction Set Architectures Spring 2012 Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) Definition on Wikipedia: Part of the Computer Architecture related to programming Defines set
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture Instruction Set Architectures Spring 2012 Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) Definition on Wikipedia: Part of the Computer Architecture related to programming Defines set
Chapter 9. Programming Framework
 Chapter 9 Programming Framework Lesson 1 Registers Registers Pointers Accumulator Status General Purpose Outline CPU Registers Examples 8-bitA (Accumulator) Register 8-bit B Register 8-bitPSW (Processor
Chapter 9 Programming Framework Lesson 1 Registers Registers Pointers Accumulator Status General Purpose Outline CPU Registers Examples 8-bitA (Accumulator) Register 8-bit B Register 8-bitPSW (Processor
MOS 6502 Architecture
 MOS 6502 Architecture Lecture 3 Fall 17 1 History Origins lie in the Motorola 6800. Was very expensive for consumers. ($300, or about $1500 in 2017 $s) Chuck Peddle proposes lower-cost, lower-area 6800
MOS 6502 Architecture Lecture 3 Fall 17 1 History Origins lie in the Motorola 6800. Was very expensive for consumers. ($300, or about $1500 in 2017 $s) Chuck Peddle proposes lower-cost, lower-area 6800
Microcontroller Intel [Instruction Set]
![Microcontroller Intel [Instruction Set] Microcontroller Intel [Instruction Set]](/thumbs/82/86620819.jpg) Microcontroller Intel 8051 [Instruction Set] Structure of Assembly Language [ label: ] mnemonic [operands] [ ;comment ] Example: MOV R1, #25H ; load data 25H into R1 2 8051 Assembly Language Registers
Microcontroller Intel 8051 [Instruction Set] Structure of Assembly Language [ label: ] mnemonic [operands] [ ;comment ] Example: MOV R1, #25H ; load data 25H into R1 2 8051 Assembly Language Registers
Topics Power tends to corrupt; absolute power corrupts absolutely. Computer Organization CS Data Representation
 Computer Organization CS 231-01 Data Representation Dr. William H. Robinson November 12, 2004 Topics Power tends to corrupt; absolute power corrupts absolutely. Lord Acton British historian, late 19 th
Computer Organization CS 231-01 Data Representation Dr. William H. Robinson November 12, 2004 Topics Power tends to corrupt; absolute power corrupts absolutely. Lord Acton British historian, late 19 th
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 th Edition. Chapter 11 Instruction Sets: Addressing Modes and Formats
 William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 th Edition Chapter 11 Instruction Sets: Addressing Modes and Formats Addressing Modes Immediate Direct Indirect Register Register Indirect Displacement
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 th Edition Chapter 11 Instruction Sets: Addressing Modes and Formats Addressing Modes Immediate Direct Indirect Register Register Indirect Displacement
TYPES OF INTERRUPTS: -
 There are 3 types of interrupts. TYPES OF INTERRUPTS: - External Interrupts. Internal Interrupts. Software interrupts. Hardware Interrupts (1) External interrupts come from I/O devices, from a timing device
There are 3 types of interrupts. TYPES OF INTERRUPTS: - External Interrupts. Internal Interrupts. Software interrupts. Hardware Interrupts (1) External interrupts come from I/O devices, from a timing device
Microprocessors 1. The 8051 Instruction Set. Microprocessors 1 1. Msc. Ivan A. Escobar Broitman
 Microprocessors 1 The 8051 Instruction Set Microprocessors 1 1 Instruction Groups The 8051 has 255 instructions Every 8-bit opcode from 00 to FF is used except for A5. The instructions are grouped into
Microprocessors 1 The 8051 Instruction Set Microprocessors 1 1 Instruction Groups The 8051 has 255 instructions Every 8-bit opcode from 00 to FF is used except for A5. The instructions are grouped into
Instruction Set II. COMP 212 Computer Organization & Architecture. COMP 212 Fall Lecture 7. Instruction Set. Quiz. What is an Instruction Set?
 COMP 212 Computer Organization & Architecture Quiz COMP 212 Fall 2008 Lecture 7 Fill in your student number only, do NOT write down your name Open book, but NO calculator, NO discussions, Relax and have
COMP 212 Computer Organization & Architecture Quiz COMP 212 Fall 2008 Lecture 7 Fill in your student number only, do NOT write down your name Open book, but NO calculator, NO discussions, Relax and have
Assembly Language Programming of 8085
 Assembly Language Programming of 8085 Topics 1. Introduction 2. Programming model of 8085 3. Instruction set of 8085 4. Example Programs 5. Addressing modes of 8085 6. Instruction & Data Formats of 8085
Assembly Language Programming of 8085 Topics 1. Introduction 2. Programming model of 8085 3. Instruction set of 8085 4. Example Programs 5. Addressing modes of 8085 6. Instruction & Data Formats of 8085
The CPU and Memory. How does a computer work? How does a computer interact with data? How are instructions performed? Recall schematic diagram:
 The CPU and Memory How does a computer work? How does a computer interact with data? How are instructions performed? Recall schematic diagram: 1 Registers A register is a permanent storage location within
The CPU and Memory How does a computer work? How does a computer interact with data? How are instructions performed? Recall schematic diagram: 1 Registers A register is a permanent storage location within
STRUCTURE OF DESKTOP COMPUTERS
 Page no: 1 UNIT 1 STRUCTURE OF DESKTOP COMPUTERS The desktop computers are the computers which are usually found on a home or office desk. They consist of processing unit, storage unit, visual display
Page no: 1 UNIT 1 STRUCTURE OF DESKTOP COMPUTERS The desktop computers are the computers which are usually found on a home or office desk. They consist of processing unit, storage unit, visual display
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture
 William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture Chapter 16 Control Unit Operations Rev. 3.2 (2009-10) by Enrico Nardelli 16-1 Execution of the Instruction Cycle It has many elementary phases,
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture Chapter 16 Control Unit Operations Rev. 3.2 (2009-10) by Enrico Nardelli 16-1 Execution of the Instruction Cycle It has many elementary phases,
Rui Wang, Assistant professor Dept. of Information and Communication Tongji University.
 Instructions: ti Language of the Computer Rui Wang, Assistant professor Dept. of Information and Communication Tongji University it Email: ruiwang@tongji.edu.cn Computer Hierarchy Levels Language understood
Instructions: ti Language of the Computer Rui Wang, Assistant professor Dept. of Information and Communication Tongji University it Email: ruiwang@tongji.edu.cn Computer Hierarchy Levels Language understood
Instruction Set Principles and Examples. Appendix B
 Instruction Set Principles and Examples Appendix B Outline What is Instruction Set Architecture? Classifying ISA Elements of ISA Programming Registers Type and Size of Operands Addressing Modes Types of
Instruction Set Principles and Examples Appendix B Outline What is Instruction Set Architecture? Classifying ISA Elements of ISA Programming Registers Type and Size of Operands Addressing Modes Types of
CHAPTER 8: Central Processing Unit (CPU)
 CS 224: Computer Organization S.KHABET CHAPTER 8: Central Processing Unit (CPU) Outline Introduction General Register Organization Stack Organization Instruction Formats Addressing Modes 1 Major Components
CS 224: Computer Organization S.KHABET CHAPTER 8: Central Processing Unit (CPU) Outline Introduction General Register Organization Stack Organization Instruction Formats Addressing Modes 1 Major Components
CS 261 Fall Binary Information (convert to hex) Mike Lam, Professor
 CS 261 Fall 2018 Mike Lam, Professor 3735928559 (convert to hex) Binary Information Binary information Topics Base conversions (bin/dec/hex) Data sizes Byte ordering Character and program encodings Bitwise
CS 261 Fall 2018 Mike Lam, Professor 3735928559 (convert to hex) Binary Information Binary information Topics Base conversions (bin/dec/hex) Data sizes Byte ordering Character and program encodings Bitwise
CPU: SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE INSTRUCTION SET (PART
 General Introduction CPU: SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE INSTRUCTION SET (PART 1) General Introduction (1/5): On Instructions Instruction operate with data or with the flow of the program The following information
General Introduction CPU: SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE INSTRUCTION SET (PART 1) General Introduction (1/5): On Instructions Instruction operate with data or with the flow of the program The following information
Assembly Language Programming of 8085
 Assembly Language Programming of 8085 1. Introduction A microprocessor executes instructions given by the user Instructions should be in a language known to the microprocessor Microprocessor understands
Assembly Language Programming of 8085 1. Introduction A microprocessor executes instructions given by the user Instructions should be in a language known to the microprocessor Microprocessor understands
UNIT-II. Part-2: CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT
 Page1 UNIT-II Part-2: CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT Stack Organization Instruction Formats Addressing Modes Data Transfer And Manipulation Program Control Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) Introduction:
Page1 UNIT-II Part-2: CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT Stack Organization Instruction Formats Addressing Modes Data Transfer And Manipulation Program Control Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) Introduction:
(2) Explain the addressing mode of OR What do you mean by addressing mode? Explain diff. addressing mode for 8085 with examples.
 (1) Explain instruction format and Opcode format of 8085 μp with example. OR With help of examples, explain the formation of opcodes of 8085 OR What is an instruction? List type of instruction based on
(1) Explain instruction format and Opcode format of 8085 μp with example. OR With help of examples, explain the formation of opcodes of 8085 OR What is an instruction? List type of instruction based on
8051 Overview and Instruction Set
 8051 Overview and Instruction Set Curtis A. Nelson Engr 355 1 Microprocessors vs. Microcontrollers Microprocessors are single-chip CPUs used in microcomputers Microcontrollers and microprocessors are different
8051 Overview and Instruction Set Curtis A. Nelson Engr 355 1 Microprocessors vs. Microcontrollers Microprocessors are single-chip CPUs used in microcomputers Microcontrollers and microprocessors are different
SN8F5000 Family Instruction Set
 SONiX Technology Co., Ltd. 8051-based Microcontroller 1 Overview SN8F5000 is 8051 Flash Type microcontroller supports comprehensive assembly instructions and which are fully compatible with standard 8051.
SONiX Technology Co., Ltd. 8051-based Microcontroller 1 Overview SN8F5000 is 8051 Flash Type microcontroller supports comprehensive assembly instructions and which are fully compatible with standard 8051.
3.0 Instruction Set. 3.1 Overview
 3.0 Instruction Set 3.1 Overview There are 16 different P8 instructions. Research on instruction set usage was the basis for instruction selection. Each instruction has at least two addressing modes, with
3.0 Instruction Set 3.1 Overview There are 16 different P8 instructions. Research on instruction set usage was the basis for instruction selection. Each instruction has at least two addressing modes, with
 Instruction Set Instruction set of 8085 can be classified in following groups: Data Transfer Instructions These instructions can perform data transfer operations between Registers of 8085 e.g. MOV 8085
Instruction Set Instruction set of 8085 can be classified in following groups: Data Transfer Instructions These instructions can perform data transfer operations between Registers of 8085 e.g. MOV 8085
Grundlagen Microcontroller Processor Core. Günther Gridling Bettina Weiss
 Grundlagen Microcontroller Processor Core Günther Gridling Bettina Weiss 1 Processor Core Architecture Instruction Set Lecture Overview 2 Processor Core Architecture Computes things > ALU (Arithmetic Logic
Grundlagen Microcontroller Processor Core Günther Gridling Bettina Weiss 1 Processor Core Architecture Instruction Set Lecture Overview 2 Processor Core Architecture Computes things > ALU (Arithmetic Logic
8/26/2010. Introduction to 8085 BLOCK DIAGRAM OF INTEL Introduction to Introduction to Three Units of 8085
 BLOCK DIAGRAM OF INTEL 8085 GURSHARAN SINGH TATLA Introduction to 8085 It was introduced in 1977. It is 8-bit microprocessor. Its actual name is 8085 A. It is single NMOS device. It contains 6200 transistors
BLOCK DIAGRAM OF INTEL 8085 GURSHARAN SINGH TATLA Introduction to 8085 It was introduced in 1977. It is 8-bit microprocessor. Its actual name is 8085 A. It is single NMOS device. It contains 6200 transistors
SOME ASSEMBLY REQUIRED
 SOME ASSEMBLY REQUIRED Assembly Language Programming with the AVR Microcontroller TIMOTHY S. MARGUSH CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Croup an Informa business
SOME ASSEMBLY REQUIRED Assembly Language Programming with the AVR Microcontroller TIMOTHY S. MARGUSH CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Croup an Informa business
The von Neumann Architecture. IT 3123 Hardware and Software Concepts. The Instruction Cycle. Registers. LMC Executes a Store.
 IT 3123 Hardware and Software Concepts February 11 and Memory II Copyright 2005 by Bob Brown The von Neumann Architecture 00 01 02 03 PC IR Control Unit Command Memory ALU 96 97 98 99 Notice: This session
IT 3123 Hardware and Software Concepts February 11 and Memory II Copyright 2005 by Bob Brown The von Neumann Architecture 00 01 02 03 PC IR Control Unit Command Memory ALU 96 97 98 99 Notice: This session
12-Dec-11. Gursharan Singh Maninder Kaur. Introduction to 8085 BLOCK DIAGRAM OF INTEL Introduction to Introduction to 8085
 mailme@gursharansingh.in BLOCK DIAGRAM OF INTEL 8085 mailme@maninderkaur.in Introduction to 8085 It was introduced in 1977. It is 8-bit microprocessor. Its actual name is 8085 A. It is single NMOS device.
mailme@gursharansingh.in BLOCK DIAGRAM OF INTEL 8085 mailme@maninderkaur.in Introduction to 8085 It was introduced in 1977. It is 8-bit microprocessor. Its actual name is 8085 A. It is single NMOS device.
Address Modes effective address
 Address Modes The MARIE supports only three addressing modes: immediate, direct, and indirect. We are now going to discuss addressing modes in general. Most computers support quite a few of these modes.
Address Modes The MARIE supports only three addressing modes: immediate, direct, and indirect. We are now going to discuss addressing modes in general. Most computers support quite a few of these modes.
Microcomputer Architecture and Programming
 IUST-EE (Chapter 1) Microcomputer Architecture and Programming 1 Outline Basic Blocks of Microcomputer Typical Microcomputer Architecture The Single-Chip Microprocessor Microprocessor vs. Microcontroller
IUST-EE (Chapter 1) Microcomputer Architecture and Programming 1 Outline Basic Blocks of Microcomputer Typical Microcomputer Architecture The Single-Chip Microprocessor Microprocessor vs. Microcontroller
Reverse Engineering II: Basics. Gergely Erdélyi Senior Antivirus Researcher
 Reverse Engineering II: Basics Gergely Erdélyi Senior Antivirus Researcher Agenda Very basics Intel x86 crash course Basics of C Binary Numbers Binary Numbers 1 Binary Numbers 1 0 1 1 Binary Numbers 1
Reverse Engineering II: Basics Gergely Erdélyi Senior Antivirus Researcher Agenda Very basics Intel x86 crash course Basics of C Binary Numbers Binary Numbers 1 Binary Numbers 1 0 1 1 Binary Numbers 1
CS401 - Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Programming Glossary By
 CS401 - Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Programming Glossary By absolute address : A virtual (not physical) address within the process address space that is computed as an absolute number.
CS401 - Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Programming Glossary By absolute address : A virtual (not physical) address within the process address space that is computed as an absolute number.
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION & ARCHITECTURE
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION & ARCHITECTURE Instructions Sets Architecture Lesson 5a 1 What are Instruction Sets The complete collection of instructions that are understood by a CPU Can be considered as a functional
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION & ARCHITECTURE Instructions Sets Architecture Lesson 5a 1 What are Instruction Sets The complete collection of instructions that are understood by a CPU Can be considered as a functional
Instruction set of 8085
 Instruction set of 05 /23/2016 ptkarule@rediffmail.com 1 Instruction set of 05 Instruction set is divided into various groups depending on the operations performed: 1. Data transfer 2. rithmetic 3. Logical
Instruction set of 05 /23/2016 ptkarule@rediffmail.com 1 Instruction set of 05 Instruction set is divided into various groups depending on the operations performed: 1. Data transfer 2. rithmetic 3. Logical
CHAPTER 5 : Introduction to Intel 8085 Microprocessor Hardware BENG 2223 MICROPROCESSOR TECHNOLOGY
 CHAPTER 5 : Introduction to Intel 8085 Hardware BENG 2223 MICROPROCESSOR TECHNOLOGY The 8085A(commonly known as the 8085) : Was first introduced in March 1976 is an 8-bit microprocessor with 16-bit address
CHAPTER 5 : Introduction to Intel 8085 Hardware BENG 2223 MICROPROCESSOR TECHNOLOGY The 8085A(commonly known as the 8085) : Was first introduced in March 1976 is an 8-bit microprocessor with 16-bit address
Chapter. Computer Architecture
 Chapter 4 Computer Architecture Figure 4.1 Input device Central processing unit Main memory Output device Bus Data flow Control Figure 4.2 Central processing unit () Status bits ( ) Accumulator ( ) Index
Chapter 4 Computer Architecture Figure 4.1 Input device Central processing unit Main memory Output device Bus Data flow Control Figure 4.2 Central processing unit () Status bits ( ) Accumulator ( ) Index
Operations On Data CHAPTER 4. (Solutions to Odd-Numbered Problems) Review Questions
 CHAPTER 4 Operations On Data (Solutions to Odd-Numbered Problems) Review Questions 1. Arithmetic operations interpret bit patterns as numbers. Logical operations interpret each bit as a logical values
CHAPTER 4 Operations On Data (Solutions to Odd-Numbered Problems) Review Questions 1. Arithmetic operations interpret bit patterns as numbers. Logical operations interpret each bit as a logical values
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture. Defining Computer Architecture
 COSC 6385 Computer rchitecture Defining Computer rchitecture Fall 007 icro-processors in today s world arkets Desktop computing Servers Embedded computers Characteristics Price vailability Reliability
COSC 6385 Computer rchitecture Defining Computer rchitecture Fall 007 icro-processors in today s world arkets Desktop computing Servers Embedded computers Characteristics Price vailability Reliability
Virtual Machine Tutorial
 Virtual Machine Tutorial CSA2201 Compiler Techniques Gordon Mangion Virtual Machine A software implementation of a computing environment in which an operating system or program can be installed and run.
Virtual Machine Tutorial CSA2201 Compiler Techniques Gordon Mangion Virtual Machine A software implementation of a computing environment in which an operating system or program can be installed and run.
Math 230 Assembly Programming (AKA Computer Organization) Spring 2008
 Math 230 Assembly Programming (AKA Computer Organization) Spring 2008 MIPS Intro II Lect 10 Feb 15, 2008 Adapted from slides developed for: Mary J. Irwin PSU CSE331 Dave Patterson s UCB CS152 M230 L10.1
Math 230 Assembly Programming (AKA Computer Organization) Spring 2008 MIPS Intro II Lect 10 Feb 15, 2008 Adapted from slides developed for: Mary J. Irwin PSU CSE331 Dave Patterson s UCB CS152 M230 L10.1
CS4617 Computer Architecture
 1/27 CS4617 Computer Architecture Lecture 7: Instruction Set Architectures Dr J Vaughan October 1, 2014 2/27 ISA Classification Stack architecture: operands on top of stack Accumulator architecture: 1
1/27 CS4617 Computer Architecture Lecture 7: Instruction Set Architectures Dr J Vaughan October 1, 2014 2/27 ISA Classification Stack architecture: operands on top of stack Accumulator architecture: 1
CHAPTER 5 A Closer Look at Instruction Set Architectures
 CHAPTER 5 A Closer Look at Instruction Set Architectures 5.1 Introduction 5.2 Instruction Formats 5.2.1 Design Decisions for Instruction Sets 5.2.2 Little versus Big Endian 5.2.3 Internal Storage in the
CHAPTER 5 A Closer Look at Instruction Set Architectures 5.1 Introduction 5.2 Instruction Formats 5.2.1 Design Decisions for Instruction Sets 5.2.2 Little versus Big Endian 5.2.3 Internal Storage in the
SCRAM Introduction. Philipp Koehn. 19 February 2018
 SCRAM Introduction Philipp Koehn 19 February 2018 This eek 1 Fully work through a computer circuit assembly code Simple but Complete Random Access Machine (SCRAM) every instruction is 8 bit 4 bit for op-code:
SCRAM Introduction Philipp Koehn 19 February 2018 This eek 1 Fully work through a computer circuit assembly code Simple but Complete Random Access Machine (SCRAM) every instruction is 8 bit 4 bit for op-code:
We briefly explain an instruction cycle now, before proceeding with the details of addressing modes.
 Addressing Modes This is an important feature of computers. We start with the known fact that many instructions have to include addresses; the instructions should be short, but addresses tend to be long.
Addressing Modes This is an important feature of computers. We start with the known fact that many instructions have to include addresses; the instructions should be short, but addresses tend to be long.
94 CPU (CM8051) Incompatible Instruction ERRATA AND DATASHEET CLARIFICATION V1.0. Leader of Microcontroller Technology A Fabless Semiconductor Company
 94 CPU (CM8051) Incompatible Instruction ERRATA AND DATASHEET CLARIFICATION V1.0 Leader of Microcontroller Technology A Fabless Semiconductor Company Document information Info Keywords Abstract Content
94 CPU (CM8051) Incompatible Instruction ERRATA AND DATASHEET CLARIFICATION V1.0 Leader of Microcontroller Technology A Fabless Semiconductor Company Document information Info Keywords Abstract Content
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Instruction Set Principles
 COSC 6385 Computer rchitecture - Instruction Set Principles Fall 2006 Organizational Issues September 4th: no class (labor day holiday) Classes of onday Sept. 11 th and Wednesday Sept. 13 th have to be
COSC 6385 Computer rchitecture - Instruction Set Principles Fall 2006 Organizational Issues September 4th: no class (labor day holiday) Classes of onday Sept. 11 th and Wednesday Sept. 13 th have to be
Reverse Engineering II: The Basics
 Reverse Engineering II: The Basics Gergely Erdélyi Senior Manager, Anti-malware Research Protecting the irreplaceable f-secure.com Binary Numbers 1 0 1 1 - Nibble B 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 - Byte B D 1 0 1 1 1
Reverse Engineering II: The Basics Gergely Erdélyi Senior Manager, Anti-malware Research Protecting the irreplaceable f-secure.com Binary Numbers 1 0 1 1 - Nibble B 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 - Byte B D 1 0 1 1 1
The CS5600 micro-computer
 The CS5600 micro-computer The CS5600 is a fictional computer that will be used for examples in class. The architecture of the system is shown in Figure 1, below. 8 general-purpose registers R0-R7 R7 FFFF
The CS5600 micro-computer The CS5600 is a fictional computer that will be used for examples in class. The architecture of the system is shown in Figure 1, below. 8 general-purpose registers R0-R7 R7 FFFF
SOEN228, Winter Revision 1.2 Date: October 25,
 SOEN228, Winter 2003 Revision 1.2 Date: October 25, 2003 1 Contents Flags Mnemonics Basic I/O Exercises Overview of sample programs 2 Flag Register The flag register stores the condition flags that retain
SOEN228, Winter 2003 Revision 1.2 Date: October 25, 2003 1 Contents Flags Mnemonics Basic I/O Exercises Overview of sample programs 2 Flag Register The flag register stores the condition flags that retain
Chapter 3 Machine Instructions & Programs. Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan
 Chapter 3 Machine Instructions & Programs Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Outline Numbers, Arithmetic Operations, and Characters Memory Locations
Chapter 3 Machine Instructions & Programs Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Outline Numbers, Arithmetic Operations, and Characters Memory Locations
Lesson 2. Instruction set design
 Exercises Lesson 2. Computer Structure and Organization Graduate in Computer Sciences Graduate in Computer Engineering Lesson 2: Page: 2 / 6 1. Lets a 32 bits word computer with a register file of 16 registers
Exercises Lesson 2. Computer Structure and Organization Graduate in Computer Sciences Graduate in Computer Engineering Lesson 2: Page: 2 / 6 1. Lets a 32 bits word computer with a register file of 16 registers
OSIAC Read OSIAC 5362 posted on the course website
 OSIAC 5362 Read OSIAC 5362 posted on the course website The Basic Structure of Control Unit m CLK Run/Inhibit Control Step Counter m Preset (to any new state) Reset IR Decoder/Encoder (combinational logic)
OSIAC 5362 Read OSIAC 5362 posted on the course website The Basic Structure of Control Unit m CLK Run/Inhibit Control Step Counter m Preset (to any new state) Reset IR Decoder/Encoder (combinational logic)
reply db y prompt db Enter your favourite colour:, 0 colour db 80 dup(?) i db 20 k db? num dw 4000 large dd 50000
 Declaring Variables in Assembly Language As in Java, variables must be declared before they can be used Unlike Java, we do not specify a variable type in the declaration in assembly language Instead we
Declaring Variables in Assembly Language As in Java, variables must be declared before they can be used Unlike Java, we do not specify a variable type in the declaration in assembly language Instead we
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 th Edition. Chapter 10 Instruction Sets: Characteristics and Functions
 William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 th Edition Chapter 10 Instruction Sets: Characteristics and Functions Instruction Set = The complete collection of instructions that are recognized
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 th Edition Chapter 10 Instruction Sets: Characteristics and Functions Instruction Set = The complete collection of instructions that are recognized
Chapter 2. Instruction Set. RISC vs. CISC Instruction set. The University of Adelaide, School of Computer Science 18 September 2017
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface RISC-V Edition Chapter 2 Instructions: Language of the Computer These slides are based on the slides by the authors. The slides doesn t
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface RISC-V Edition Chapter 2 Instructions: Language of the Computer These slides are based on the slides by the authors. The slides doesn t
PESIT Bangalore South Campus
 INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST I Date: 30/08/2017 Max Marks: 40 Subject & Code: Computer Organization 15CS34 Semester: III (A & B) Name of the faculty: Mrs.Sharmila Banu.A Time: 8.30 am 10.00 am Answer any FIVE
INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST I Date: 30/08/2017 Max Marks: 40 Subject & Code: Computer Organization 15CS34 Semester: III (A & B) Name of the faculty: Mrs.Sharmila Banu.A Time: 8.30 am 10.00 am Answer any FIVE
Memory organization Programming model - Program status word - register banks - Addressing modes - instruction set Programming examples.
 MICROCONTROLLERS AND APPLICATIONS 1 Module 2 Module-2 Contents: Memory organization Programming model - Program status word - register banks - Addressing modes - instruction set Programming examples. MEMORY
MICROCONTROLLERS AND APPLICATIONS 1 Module 2 Module-2 Contents: Memory organization Programming model - Program status word - register banks - Addressing modes - instruction set Programming examples. MEMORY
 Chapter 1 Microprocessor architecture ECE 3120 Dr. Mohamed Mahmoud http://iweb.tntech.edu/mmahmoud/ mmahmoud@tntech.edu Outline 1.1 Computer hardware organization 1.1.1 Number System 1.1.2 Computer hardware
Chapter 1 Microprocessor architecture ECE 3120 Dr. Mohamed Mahmoud http://iweb.tntech.edu/mmahmoud/ mmahmoud@tntech.edu Outline 1.1 Computer hardware organization 1.1.1 Number System 1.1.2 Computer hardware
Exam I Review February 2017
 Exam I Review February 2017 Binary Number Representations Conversion of binary to hexadecimal and decimal. Convert binary number 1000 1101 to hexadecimal: Make groups of 4 bits to convert to hexadecimal,
Exam I Review February 2017 Binary Number Representations Conversion of binary to hexadecimal and decimal. Convert binary number 1000 1101 to hexadecimal: Make groups of 4 bits to convert to hexadecimal,
CPE 323 MSP430 INSTRUCTION SET ARCHITECTURE (ISA)
 CPE 323 MSP430 INSTRUCTION SET ARCHITECTURE (ISA) Aleksandar Milenković Email: milenka@uah.edu Web: http://www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka Objective Introduce MSP430 Instruction Set Architecture (Class of ISA,
CPE 323 MSP430 INSTRUCTION SET ARCHITECTURE (ISA) Aleksandar Milenković Email: milenka@uah.edu Web: http://www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka Objective Introduce MSP430 Instruction Set Architecture (Class of ISA,
Accumulator and memory instructions 1. Loads, stores, and transfers 2. Arithmetic operations 3. Multiply and divide 4. Logical operations 5. Data test
 HC11 Instruction Set Instruction classes 1. 2. 3. 4. Accumulator and Memory Stack and Index Register Condition Code Register Program control instructions 2 1 Accumulator and memory instructions 1. Loads,
HC11 Instruction Set Instruction classes 1. 2. 3. 4. Accumulator and Memory Stack and Index Register Condition Code Register Program control instructions 2 1 Accumulator and memory instructions 1. Loads,
CSc 453 Interpreters & Interpretation
 CSc 453 Interpreters & Interpretation Saumya Debray The University of Arizona Tucson Interpreters An interpreter is a program that executes another program. An interpreter implements a virtual machine,
CSc 453 Interpreters & Interpretation Saumya Debray The University of Arizona Tucson Interpreters An interpreter is a program that executes another program. An interpreter implements a virtual machine,
8085 INSTRUCTION SET INSTRUCTION DETAILS
 8085 INSTRUCTION SET INSTRUCTION DETAILS DATA TRANSFER INSTRUCTIONS MOV Rd, Rs Copy from source to destination This instruction copies the contents of the source register Rs into the destination register
8085 INSTRUCTION SET INSTRUCTION DETAILS DATA TRANSFER INSTRUCTIONS MOV Rd, Rs Copy from source to destination This instruction copies the contents of the source register Rs into the destination register
Full file at
 Chapter Two DATA MANIPULATION Formatted Chapter Summary This chapter introduces the role of a computer's CPU. It describes the machine cycle and the various operations (or, and, exclusive or, add, shift,
Chapter Two DATA MANIPULATION Formatted Chapter Summary This chapter introduces the role of a computer's CPU. It describes the machine cycle and the various operations (or, and, exclusive or, add, shift,
Chapter 2. Instruction Set Principles and Examples. In-Cheol Park Dept. of EE, KAIST
 Chapter 2. Instruction Set Principles and Examples In-Cheol Park Dept. of EE, KAIST Stack architecture( 0-address ) operands are on the top of the stack Accumulator architecture( 1-address ) one operand
Chapter 2. Instruction Set Principles and Examples In-Cheol Park Dept. of EE, KAIST Stack architecture( 0-address ) operands are on the top of the stack Accumulator architecture( 1-address ) one operand
Wednesday, September 13, Chapter 4
 Wednesday, September 13, 2017 Topics for today Introduction to Computer Systems Static overview Operation Cycle Introduction to Pep/9 Features of the system Operational cycle Program trace Categories of
Wednesday, September 13, 2017 Topics for today Introduction to Computer Systems Static overview Operation Cycle Introduction to Pep/9 Features of the system Operational cycle Program trace Categories of
Computer Architecture
 Computer Architecture Lecture 1: Digital logic circuits The digital computer is a digital system that performs various computational tasks. Digital computers use the binary number system, which has two
Computer Architecture Lecture 1: Digital logic circuits The digital computer is a digital system that performs various computational tasks. Digital computers use the binary number system, which has two
8088/8086 Programming Integer Instructions and Computations
 Unit3 reference 2 8088/8086 Programming Integer Instructions and Computations Introduction Up to this point we have studied the software architecture of the 8088 and 8086 microprocessors, their instruction
Unit3 reference 2 8088/8086 Programming Integer Instructions and Computations Introduction Up to this point we have studied the software architecture of the 8088 and 8086 microprocessors, their instruction
Course Schedule. CS 221 Computer Architecture. Week 3: Plan. I. Hexadecimals and Character Representations. Hexadecimal Representation
 Course Schedule CS 221 Computer Architecture Week 3: Information Representation (2) Fall 2001 W1 Sep 11- Sep 14 Introduction W2 Sep 18- Sep 21 Information Representation (1) (Chapter 3) W3 Sep 25- Sep
Course Schedule CS 221 Computer Architecture Week 3: Information Representation (2) Fall 2001 W1 Sep 11- Sep 14 Introduction W2 Sep 18- Sep 21 Information Representation (1) (Chapter 3) W3 Sep 25- Sep
COS 140: Foundations of Computer Science
 COS 140: Foundations of Computer Science CPU Organization and Assembly Language Fall 2018 CPU 3 Components of the CPU..................................................... 4 Registers................................................................
COS 140: Foundations of Computer Science CPU Organization and Assembly Language Fall 2018 CPU 3 Components of the CPU..................................................... 4 Registers................................................................
CHAPTER 5 A Closer Look at Instruction Set Architectures
 CHAPTER 5 A Closer Look at Instruction Set Architectures 5.1 Introduction 199 5.2 Instruction Formats 199 5.2.1 Design Decisions for Instruction Sets 200 5.2.2 Little versus Big Endian 201 5.2.3 Internal
CHAPTER 5 A Closer Look at Instruction Set Architectures 5.1 Introduction 199 5.2 Instruction Formats 199 5.2.1 Design Decisions for Instruction Sets 200 5.2.2 Little versus Big Endian 201 5.2.3 Internal
10-1 C D Pearson Education, Inc. M. Morris Mano & Charles R. Kime LOGIC AND COMPUTER DESIGN FUNDAMENTALS, 4e
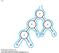 10-1 C D E A B 10-2 A B A B C (A B) C D A A B (A B) C E D (A B) C D E (A B) C + D E (A B) C 10-3 Opcode Mode Address or operand 10-4 Memory 250 Opcode Mode PC = 250 251 ADRS 252 Next instruction ACC Opcode:
10-1 C D E A B 10-2 A B A B C (A B) C D A A B (A B) C E D (A B) C D E (A B) C + D E (A B) C 10-3 Opcode Mode Address or operand 10-4 Memory 250 Opcode Mode PC = 250 251 ADRS 252 Next instruction ACC Opcode:
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 4: Logic Operations and Introduction to Conditionals Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Previously examined
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 4: Logic Operations and Introduction to Conditionals Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Previously examined
Delhi Noida Bhopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow Indore Pune Bhubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: Ph:
 Serial : LS2_EE_S_Microprocessors_2688 Delhi Noida Bhopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow Indore Pune Bhubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: E-mail: info@madeeasy.in Ph: -452462 CLASS TEST 28-9 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
Serial : LS2_EE_S_Microprocessors_2688 Delhi Noida Bhopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow Indore Pune Bhubaneswar Kolkata Patna Web: E-mail: info@madeeasy.in Ph: -452462 CLASS TEST 28-9 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
Fig: Computer memory with Program, data, and Stack. Blog - NEC (Autonomous) 1
 Central Processing Unit 1. Stack Organization A useful feature that is included in the CPU of most computers is a stack or last in, first out (LIFO) list. A stack is a storage device that stores information
Central Processing Unit 1. Stack Organization A useful feature that is included in the CPU of most computers is a stack or last in, first out (LIFO) list. A stack is a storage device that stores information
Chapter 7 Central Processor Unit (S08CPUV2)
 Chapter 7 Central Processor Unit (S08CPUV2) 7.1 Introduction This section provides summary information about the registers, addressing modes, and instruction set of the CPU of the HCS08 Family. For a more
Chapter 7 Central Processor Unit (S08CPUV2) 7.1 Introduction This section provides summary information about the registers, addressing modes, and instruction set of the CPU of the HCS08 Family. For a more
Problem with Scanning an Infix Expression
 Operator Notation Consider the infix expression (X Y) + (W U), with parentheses added to make the evaluation order perfectly obvious. This is an arithmetic expression written in standard form, called infix
Operator Notation Consider the infix expression (X Y) + (W U), with parentheses added to make the evaluation order perfectly obvious. This is an arithmetic expression written in standard form, called infix
Instruction Sets: Characteristics and Functions
 Instruction Sets: Characteristics and Functions Chapter 10 Lesson 15 Slide 1/22 Machine instruction set Computer designer: The machine instruction set provides the functional requirements for the CPU.
Instruction Sets: Characteristics and Functions Chapter 10 Lesson 15 Slide 1/22 Machine instruction set Computer designer: The machine instruction set provides the functional requirements for the CPU.
Computer Architecture
 Computer Architecture Chapter 2 Instructions: Language of the Computer Fall 2005 Department of Computer Science Kent State University Assembly Language Encodes machine instructions using symbols and numbers
Computer Architecture Chapter 2 Instructions: Language of the Computer Fall 2005 Department of Computer Science Kent State University Assembly Language Encodes machine instructions using symbols and numbers
Introduction to Microprocessor
 Introduction to Microprocessor The microprocessor is a general purpose programmable logic device. It is the brain of the computer and it performs all the computational tasks, calculations data processing
Introduction to Microprocessor The microprocessor is a general purpose programmable logic device. It is the brain of the computer and it performs all the computational tasks, calculations data processing
Problem with Scanning an Infix Expression
 Operator Notation Consider the infix expression (X Y) + (W U), with parentheses added to make the evaluation order perfectly obvious. This is an arithmetic expression written in standard form, called infix
Operator Notation Consider the infix expression (X Y) + (W U), with parentheses added to make the evaluation order perfectly obvious. This is an arithmetic expression written in standard form, called infix
Introduction to Computers - Chapter 4
 Introduction to Computers - Chapter 4 Since the invention of the transistor and the first digital computer of the 1940s, computers have been increasing in complexity and performance; however, their overall
Introduction to Computers - Chapter 4 Since the invention of the transistor and the first digital computer of the 1940s, computers have been increasing in complexity and performance; however, their overall
Computer Architecture and Organization. Instruction Sets: Addressing Modes and Formats
 Computer Architecture and Organization Instruction Sets: Addressing Modes and Formats Addressing Modes Immediate Direct Indirect Register Register Indirect Displacement (Indexed) Stack Immediate Addressing
Computer Architecture and Organization Instruction Sets: Addressing Modes and Formats Addressing Modes Immediate Direct Indirect Register Register Indirect Displacement (Indexed) Stack Immediate Addressing
Chapter 3. Z80 Instructions & Assembly Language. Von Neumann Architecture. Memory. instructions. program. data
 Von Neumann Architecture The von Neumann architecture is a computer design model that uses a processing unit and a separate storage to hold both instructions and data To run a machine, program and data
Von Neumann Architecture The von Neumann architecture is a computer design model that uses a processing unit and a separate storage to hold both instructions and data To run a machine, program and data
Register-Level Design
 Register-Level Design A digital system can be treated at different level of abstraction or compleity. So far, we have seen it at the gate level and the transistor level. At a higher level than the gate
Register-Level Design A digital system can be treated at different level of abstraction or compleity. So far, we have seen it at the gate level and the transistor level. At a higher level than the gate
Keeping pace with a single-chip I6-bit microprocessor
 Keeping pace with a single-chip I6-bit microprocessor by ALAN J. WEISSBERGER National Semiconductor Corporation Santa Clara, California INTRODUCTION The emphasis in contemporary microprocessor development
Keeping pace with a single-chip I6-bit microprocessor by ALAN J. WEISSBERGER National Semiconductor Corporation Santa Clara, California INTRODUCTION The emphasis in contemporary microprocessor development
The Instruction Set. Chapter 5
 The Instruction Set Architecture Level(ISA) Chapter 5 1 ISA Level The ISA level l is the interface between the compilers and the hardware. (ISA level code is what a compiler outputs) 2 Memory Models An
The Instruction Set Architecture Level(ISA) Chapter 5 1 ISA Level The ISA level l is the interface between the compilers and the hardware. (ISA level code is what a compiler outputs) 2 Memory Models An
INSTRUCTION SET OF 8085
 INSTRUCTION SET OF 8085 Instruction Set of 8085 An instruction is a binary pattern designed inside a microprocessor to perform a specific function. The entire group of instructions that a microprocessor
INSTRUCTION SET OF 8085 Instruction Set of 8085 An instruction is a binary pattern designed inside a microprocessor to perform a specific function. The entire group of instructions that a microprocessor
Chapter 2 Instruction Set Architecture
 Chapter 2 Instruction Set Architecture Course Outcome (CO) - CO2 Describe the architecture and organization of computer systems Program Outcome (PO) PO1 Apply knowledge of mathematics, science and engineering
Chapter 2 Instruction Set Architecture Course Outcome (CO) - CO2 Describe the architecture and organization of computer systems Program Outcome (PO) PO1 Apply knowledge of mathematics, science and engineering
Computer Architecture 1 ح 303
 Lecture 4 A. Addressing MODES 1. Introduction to assembly language programming: Program is a sequence of commands used to tell a microcomputer what to do. Each command in a program is an instruction Programs
Lecture 4 A. Addressing MODES 1. Introduction to assembly language programming: Program is a sequence of commands used to tell a microcomputer what to do. Each command in a program is an instruction Programs
Chapter 1. Microprocessor architecture ECE Dr. Mohamed Mahmoud.
 Chapter 1 Microprocessor architecture ECE 3130 Dr. Mohamed Mahmoud The slides are copyright protected. It is not permissible to use them without a permission from Dr Mahmoud http://www.cae.tntech.edu/~mmahmoud/
Chapter 1 Microprocessor architecture ECE 3130 Dr. Mohamed Mahmoud The slides are copyright protected. It is not permissible to use them without a permission from Dr Mahmoud http://www.cae.tntech.edu/~mmahmoud/
