CSC 372, Spring 2014 Assignment 2 Due: Wednesday, February 26 at 23:00
|
|
|
- Gillian Walsh
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ASSIGNMENT-WIDE RESTRICTIONS There re two ssignment-wide restrictions: CSC 372, Spring 2014 Assignment 2 Due: Wednesdy, Februry 26 t 23:00 1. The only module you my use is Dt.Chr. 2. Except for problem 1, wrmup.hs, you my not write ny recursive functions! Insted, use higher-order functions like mp, filter, nd foldl. Note tht there is both direct nd indirect recursion. With direct recursion, function f clls itself. With indirect recursion, f might cll g nd then g might cll f. Problem 1. (6 points) wrmup.hs This problem is like wrmup.hs on ssignment 1 I'd like you to write your own version of some functions from the Prelude: mp, filter, foldl, foldr, ny, nd ll. The code for mp, filter, nd foldr re in the slides; the others re esy to find but I'd like you strt with blnk piece of pper nd try to write them from scrtch. If you hve trouble, go hed nd look for the code. Study it but then put it wy nd try to write the function from scrtch. Repet s needed. To void conflicts with the Prelude functions of the sme nme, use these nmes for your versions: Your function mp filt fldl fldr myny myll Prelude function mp filter foldl foldr ny ll You should be ble to write these functions using only pttern mtching, comprisons in gurds, list literls, cons (:), subtrction, nd recursive clls to the function itself. Experiment with the Prelude functions to see how they work. You might find foldl nd foldr to be tough. Don't get stuck on them! This problem, wrmup.hs, is the only problem on this ssignment in which you cn write recursive functions. Pge 1
2 Problem 2. (3 points) dezip.hs Write function dezip list tht seprtes list of 2-tuples into two lists. The first list holds the first element of ech tuple. The second list holds the second element of ech tuple. Don't overlook the problem restrictions following the exmples. > :t dezip dezip :: [(, b)] -> ([], [b]) > dezip [(1,10),(2,20),(3,30)] ([1,2,3],[10,20,30]) > dezip [("just","testing")] (["just"],["testing"]) > dezip [] ([],[]) RESTRICTIONS for dezip.hs: Your solution my only use mp, fst, the composition opertor, nd this function: swp (x,y) = (y,x) Remember tht writing recursive function is prohibited. This function is just like the Prelude function unzip, but with hopefully different enough nme tht you don't test with unzip by mistke! Problem 3. (2 points) repl.hs Write function repl tht works just like replicte in the Prelude. > :t repl repl :: Int -> -> [] > repl 3 7 [7,7,7] > repl 5 '' "" > repl 2 it ["",""] RESTRICTIONS for repl.hs: You my not use replicte. Remember the ssignment-wide prohibition on recursion. This is n esy problem; there re severl wys to solve it using vrious functions from the Prelude. Just for fun you might see how mny distinct solutions you cn come up with. Pge 2
3 Problem 4. (3 points) doubler.hs Crete function nmed doubler tht duplictes ech vlue in list: > :t doubler doubler :: [] -> [] > doubler [1..5] [1,1,2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5] > doubler "bet" "bbeett" > doubler [[]] [[],[]] > doubler [] [] RESTRICTION: Your solution must look like this: doubler = foldr... Tht is, you re to crete doubler using prtil ppliction of foldr. Think bout using n nonymous function. Replce the... with code tht mkes it work. Thirty chrcters should be bout enough but it cn be s long s you need. Problem 5. (2 points) revwords.hs Using point-free style (slide 240), crete function revwords tht reverses the words in sentence. Assume the sentence contins only letters nd spces. > revwords "Reverse the words in this sentence" "esrever eht sdrow ni siht ecnetnes" > revwords "testing" "gnitset" > revwords "" "" Problem 6. (3 points) cpfx.hs is my solution for cpfx from ssignment 1. The cpfx function is recursive. Rewrite tht function to be nonrecursive but still mke use of the cpfx' function. See the ssignment 1 write-up for exmples of using cpfx. Pge 3
4 Problem 7. (10 points) mfilter.hs Write function mfilter tht ccepts list of rnges represented s 2-tuples nd produces function tht when pplied to list of vlues produces the vlues tht do not fll into ny of the rnges. Rnges re inclusive, s the exmples below demonstrte. Note tht mfilter is typed in terms of the Ord type clss, so mfilter works with mny different types of vlues. > :type mfilter mfilter :: Ord => [(, )] -> [] -> [] > mfilter [(3,7)] [1..10] [1,2,8,9,10] > mfilter [(10,18), (2,5), (20,20)] [1..25] [1,6,7,8,9,19,21,22,23,24,25] > mfilter [] [1..3] [1,2,3] > mfilter [('0','9')] "St Feb 8 20:34: " "St Feb :: " > mfilter [('A','Z'), (' ', ' ')] it "teb::" > let f = mfilter [(5,20),(-100,0)] > f [1..30] [1,2,3,4,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30] > f [-10,-9..21] [1,2,3,4,21] Assume for rnge (x, y) tht x <= y, i.e, you won't see rnge like (10,1) or ('z', ''). As you cn see bove, rnges re inclusive. A rnge like (1,3) blocks 1, 2, nd 3. Just for fun...here's n instnce declrtion from the Prelude: instnce (Ord, Ord b) => Ord (, b) It sys tht if the vlues in 2-tuple re orderble, then the 2-tuple is orderble. With tht in mind, consider this mfilter exmple: > mfilter [((3,'z'),(25,''))] (zip [1..] [''..'z']) [(1,''),(2,'b'),(3,'c'),(25,'y'),(26,'z')] Remember: No explicit recursion! NOTE: This problem requires somewht cretive lep. I won't sy more bout tht here so I don't spoil it for nybody but don't feel bd bout sking for hint on this one. Pge 4
5 Problem 8. (10 points) nnn.hs The behvior of the function you re to write for this problem is best shown with n exmple: > nnn [3,1,5] ["3-3-3","1"," "] The first element is 3 nd tht cuses corresponding vlue in the result to be string of three 3s, seprted by dshes. Then we hve one 1. Then five 5s. More exmples: > :t nnn nnn :: [Int] -> [[Chr]] > nnn [1,3..10] ["1","3-3-3"," "," "," "] > nnn [10,2,4] [" ","2-2"," "] > length (hed (nnn [100])) 399 Note the mth for the lst exmple: 100 copies of "100" nd 99 copies of "-" to seprte them. Assume tht the vlues re greter thn zero. Remember: No explicit recursion! Problem 9. (10 points) expnd.hs Consider the following two entries tht specify the spelling of word nd spelling of forms of the word with suffixes: progrm,s,#ed,#ing,'s code,s,d,@ing If suffix begins with pound sign (#), it indictes tht the lst letter of the word should be doubled when dding the suffix. If suffix begins with t-sign (@), it indictes tht the lst letter of the word should be dropped when dding the suffix. In other cses, including the possessive ('s), the suffix is simply dded. The bove two entries represent the following words: progrm progrms progrmmed progrmming progrm's code codes coded coding Pge 5
6 For this problem you re to write function expnd entry tht returns list tht begins with the word with no suffix nd followed by ll the suffixed forms in turn. > :t expnd expnd :: [Chr] -> [String] > expnd ["code","codes","coded","coding"] > expnd "progrm,s,#ed,#ing,'s" ["progrm","progrms","progrmmed","progrmming","progrm's"] > expnd "drift" (If no suffixes, produce just the word.) ["drift"] > expnd ",b,c,d,e,f" ["","b","c","d","e","f"] > expnd ["","b","c","d","x","y","z","1","2","3"] > expnd ["b","bbc","bd","e","bf","b::x"] A word my hve ny number of suffixes with n rbitrry combintion of types. Words nd suffixes my be rbitrrily long. The only chrcters with specil mening re comm, #, Everything is just text. Assume tht the entry is well-formed. You won't see things like zero-length word or suffix. Here re some exmples of entries we will not test with: ",", "test,", "test,s,#,@" Remember: No explicit recursion! Problem 10. (18 points) pnckes.hs In this problem you re to print representtion of series of stcks of pnckes. Let's strt with n exmple: > :t pnckes pnckes :: [[Int]] -> IO () > pnckes [[3,1],[3,1,5]] *** *** * * ***** > The list specifies two stcks of pnckes: the first stck hs two pnckes, of widths 3 nd 1, respectively. The second stck hs three pnckes. Pnckes re lwys centered on their stck. A single spce seprtes ech stck. Pnckes re lwys represented with sterisks. Pge 6
7 Here's nother exmple: > pnckes [[1,5],[1,1,1],[11,3,15],[3,3,3,3],[1]] *** * *********** *** * * *** *** ***** * *************** *** * > There re opportunities for cretive cooking: > pnckes [[7,1,1,1,1,1],[5,7,7,7,7,5],[7,5,3,1,1,1], [5,7,7,7,7,5], [7,1,1,1,1,1],[1,3,3,5,5,7]] ******* ***** ******* ***** ******* * * ******* ***** ******* * *** * ******* *** ******* * *** * ******* * ******* * ***** * ******* * ******* * ***** * ***** * ***** * ******* > Assume tht there is t lest one stck. Assume ll stcks hve t lest one pncke. Assume ll widths re greter thn zero. The smllest order you'll see is this: > pnckes [[1]] * > To void problems with centering, ssume ll pncke widths re odd. Like street on ssignment 1, pnckes produces output. (Now we know to sy tht street nd pnckes re functions tht produce ctions see slide 276 nd following.) My solution is structured like this: pnckes stcks = putstr result where... result =... Remember: No explicit recursion! Problem 11. (18 points) group.hs For this problem you re to write progrm tht reds text file nd prints the file with line of dshes inserted whenever the first chrcter on line differs from the first chrcter on the previous line. Additionlly, the lines from the input file re to be numbered. % ct group.1 ble cdemi lge crton firwy hex hockshop Pge 7
8 % runghc group.hs group.1 1 ble 2 cdemi 3 lge 4 crton 5 firwy 6 hex 7 hockshop % Note tht only the lines from the input file re numbed the seprtors re not numbered. Lines with length of zero (i.e., length line == 0) re discrded s first step. Another exmple: % ct group.2 elempos' _ [] = -1 elempos' x ((vl,pos):vps) x == vl = pos otherwise = elempos' x vps f x y z = (x == chr y) == z dd_c x y = x + y dd_t(x,y) = x + y fromtomn 'I' = 1 fromromn 'V' = 5 fromromn 'X' = 10 p 1 (x:xs) = 10 % runghc group.hs group.2 1 elempos' _ [] = -1 2 elempos' x ((vl,pos):vps) 3 x == vl = pos 4 otherwise = elempos' x vps 5 f x y z = (x == chr y) == z 6 dd_c x y = x + y 7 dd_t(x,y) = x + y 8 fromtomn 'I' = 1 9 fromromn 'V' = 5 10 fromromn 'X' = p 1 (x:xs) = 10 % Pge 8
9 Note tht when the line numbers grow to two digits the line contents re shifted column to the right. Tht's ok. If ll lines strt with the sme chrcter, no seprtors re printed. % ct group.3 test tests testing % runghc group.hs group.3 1 test 2 tests 3 testing % One finl exmple: % ct group.4 b b b b % runghc group.hs group b 3 4 b b b % The seprtor lines re six dshes (minus signs). Assume tht there is t lest one line in the input file. (A one-line file will produce no seprtors, of course.) hs the group.[1234] Pge 9
10 files shown bove. (Tht's /cs/www/clsses/cs372/spring14/2 if you're on lectur.) Implementtion note: Unlike everything else you've done with Hskell, this is whole progrm, not just function run t the ghci prompt. Follow the exmple of longest on slides nd hve binding for min tht hs do block tht sequences getting the commnd line rguments with getargs, reding the whole file with redfile, nd then clling putstr with result of function nmed group, which does ll the computtion. Your group.hs might look like this: import System.Environment (getargs) min = do rgs <- getargs bytes <- redfile (hed rgs) putstr (group bytes)...your functions here... Note tht to run group.hs, you use runghc on the commnd line. If you've instlled The Hskell Pltform for Windows using the defults, I believe you'll find tht you hve runghc commnd t your disposl. Here's wht running it t Windows XP commnd prompt looks like: W:\372>runghc group.hs group.1 1 ble 2 cdemi 3 lge 4 crton 5 firwy 6 hex 7 hockshop W:\372> Note tht the blnk line following "7 hockshop" is produced by Windows, not group. If you're working on your own mchine I recommend tht you do simple test of runghc ASAP, so tht if problems turn up, we'll hve plenty of time to help you get it working. Just try version check: W:\372>runghc --version runghc Remember: No explicit recursion! Problem 12. Extr Credit observtions.txt Submit plin text file nmed observtions.txt with... () (1 point extr credit) An estimte of how long it took you to complete this ssignment. To fcilitte progrmmtic extrction of the hours from ll submissions hve n estimte of hours on line by itself, Pge 10
11 more or less like one of these: Hours: 10 Hours: Hours: 15+ Other comments bout the ssignment re welcome, too. Ws it too long, too hrd, too detiled? Spek up! I pprecite ll feedbck, fvorble or not. (b) (1-3 points extr credit) Cite n interesting course-relted observtion (or observtions) tht you mde while working on the ssignment. The observtion should hve t lest little bit of depth. Think of me sying "Good!" s one point, "Interesting!" s two points, nd "Wow!" s three points. I'm looking for qulity, not quntity. Turning in your work Use the D2L Dropbox nmed 2 to submit single zip file nmed 2.zip tht contins ll your work. If you submit more thn one 2.zip, we'll grde your finl submission. Here's the full list of deliverbles: wrmup.hs dezip.hs repl.hs doubler.hs revwords.hs cpfx.hs mfilter.hs nnn.hs expnd.hs pnckes.hs group.hs observtions.txt (for extr credit) DO NOT SUBMIT INDIVIDUAL FILES submit file nmed 2.zip tht contins ech of the bove files. Note tht ll chrcters in the file nmes re lowercse. Hve ll the deliverbles in the uppermost level of the zip. It's ok if your zip includes other files, too. Miscellneous This ssignment is bsed on the mteril on Hskell slides Point vlues of problems correspond directly to ssignment points in the syllbus. For exmple, 10-point problem on this ssignment corresponds to 1% of your finl grde in the course. Feel free to use comments to document your code s you see fit, but note tht no comments re required, nd no points will be wrded for documenttion itself. (In other words, no prt of your score will be bsed on documenttion.) Two minus signs (--) is comment to end of line; {- nd -} re used to enclose block comments, like /* nd */ in Jv. Remember tht lte ssignments re not ccepted nd tht there re no lte dys; but if circumstnces Pge 11
12 beyond your control interfere with your work on this ssignment, there my be grounds for n extension. See the syllbus for detils. My estimte is tht it will tke typicl CS junior from 10 to 15 hours to complete this ssignment. Keep in mind the point vlue of ech problem; don't invest n inordinte mount of time in problem or become incredibly frustrted before you sk for hint or help. Remember tht the purpose of the ssignments is to build understnding of the course mteril by pplying it to solve problems. If you rech the eight-hour mrk, regrdless of whether you hve specific questions, it's probbly time to touch bse with us. Give us chnce to speed you up! Our gol is tht everybody gets 100% on this ssignment AND gets it done in n mount of time tht is resonble for them. When developing code tht performs complex series of trnsformtions on dt I recommend the technique shown for longest, strting on slide 226. Tht is, work through series of lets to check the trnsformtion mde by ech step. I hte to hve to mention it but keep in mind tht cheters don't get second chnce. If you give your code to somebody else nd they turn it in, you'll both likely fil the clss, nd more. (See the syllbus for the detils.) REMEMBER: Except for wrmup.hs you re not permitted to write ny recursive functions on this ssignment! Pge 12
CSC 372, Spring 2015 Assignment 3 Due: Thursday, February 26 at 23:59:59
 ASSIGNMENT-WIDE RESTRICTIONS There are three assignment-wide restrictions: Use the tester! CSC 372, Spring 2015 Assignment 3 Due: Thursday, February 26 at 23:59:59 1. Minus a couple of exceptions that
ASSIGNMENT-WIDE RESTRICTIONS There are three assignment-wide restrictions: Use the tester! CSC 372, Spring 2015 Assignment 3 Due: Thursday, February 26 at 23:59:59 1. Minus a couple of exceptions that
CSC 372, Spring 2016 Assignment 4 Due: Friday, February 26 at 23:59:59
 ASSIGNMENT-WIDE RESTRICTIONS There are three assignment-wide restrictions: CSC 372, Spring 2016 Assignment 4 Due: Friday, February 26 at 23:59:59 1. Minus some exceptions that are noted for group.hs and
ASSIGNMENT-WIDE RESTRICTIONS There are three assignment-wide restrictions: CSC 372, Spring 2016 Assignment 4 Due: Friday, February 26 at 23:59:59 1. Minus some exceptions that are noted for group.hs and
Functor (1A) Young Won Lim 10/5/17
 Copyright (c) 2016-2017 Young W. Lim. Permission is grnted to copy, distribute nd/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documenttion License, Version 1.2 or ny lter version published
Copyright (c) 2016-2017 Young W. Lim. Permission is grnted to copy, distribute nd/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documenttion License, Version 1.2 or ny lter version published
Functor (1A) Young Won Lim 8/2/17
 Copyright (c) 2016-2017 Young W. Lim. Permission is grnted to copy, distribute nd/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documenttion License, Version 1.2 or ny lter version published
Copyright (c) 2016-2017 Young W. Lim. Permission is grnted to copy, distribute nd/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documenttion License, Version 1.2 or ny lter version published
CS201 Discussion 10 DRAWTREE + TRIES
 CS201 Discussion 10 DRAWTREE + TRIES DrwTree First instinct: recursion As very generic structure, we could tckle this problem s follows: drw(): Find the root drw(root) drw(root): Write the line for the
CS201 Discussion 10 DRAWTREE + TRIES DrwTree First instinct: recursion As very generic structure, we could tckle this problem s follows: drw(): Find the root drw(root) drw(root): Write the line for the
Fall 2018 Midterm 1 October 11, ˆ You may not ask questions about the exam except for language clarifications.
 15-112 Fll 2018 Midterm 1 October 11, 2018 Nme: Andrew ID: Recittion Section: ˆ You my not use ny books, notes, extr pper, or electronic devices during this exm. There should be nothing on your desk or
15-112 Fll 2018 Midterm 1 October 11, 2018 Nme: Andrew ID: Recittion Section: ˆ You my not use ny books, notes, extr pper, or electronic devices during this exm. There should be nothing on your desk or
Fig.25: the Role of LEX
 The Lnguge for Specifying Lexicl Anlyzer We shll now study how to uild lexicl nlyzer from specifiction of tokens in the form of list of regulr expressions The discussion centers round the design of n existing
The Lnguge for Specifying Lexicl Anlyzer We shll now study how to uild lexicl nlyzer from specifiction of tokens in the form of list of regulr expressions The discussion centers round the design of n existing
ECE 468/573 Midterm 1 September 28, 2012
 ECE 468/573 Midterm 1 September 28, 2012 Nme:! Purdue emil:! Plese sign the following: I ffirm tht the nswers given on this test re mine nd mine lone. I did not receive help from ny person or mteril (other
ECE 468/573 Midterm 1 September 28, 2012 Nme:! Purdue emil:! Plese sign the following: I ffirm tht the nswers given on this test re mine nd mine lone. I did not receive help from ny person or mteril (other
CS321 Languages and Compiler Design I. Winter 2012 Lecture 5
 CS321 Lnguges nd Compiler Design I Winter 2012 Lecture 5 1 FINITE AUTOMATA A non-deterministic finite utomton (NFA) consists of: An input lphet Σ, e.g. Σ =,. A set of sttes S, e.g. S = {1, 3, 5, 7, 11,
CS321 Lnguges nd Compiler Design I Winter 2012 Lecture 5 1 FINITE AUTOMATA A non-deterministic finite utomton (NFA) consists of: An input lphet Σ, e.g. Σ =,. A set of sttes S, e.g. S = {1, 3, 5, 7, 11,
COMPUTER SCIENCE 123. Foundations of Computer Science. 6. Tuples
 COMPUTER SCIENCE 123 Foundtions of Computer Science 6. Tuples Summry: This lecture introduces tuples in Hskell. Reference: Thompson Sections 5.1 2 R.L. While, 2000 3 Tuples Most dt comes with structure
COMPUTER SCIENCE 123 Foundtions of Computer Science 6. Tuples Summry: This lecture introduces tuples in Hskell. Reference: Thompson Sections 5.1 2 R.L. While, 2000 3 Tuples Most dt comes with structure
Spring 2018 Midterm Exam 1 March 1, You may not use any books, notes, or electronic devices during this exam.
 15-112 Spring 2018 Midterm Exm 1 Mrch 1, 2018 Nme: Andrew ID: Recittion Section: You my not use ny books, notes, or electronic devices during this exm. You my not sk questions bout the exm except for lnguge
15-112 Spring 2018 Midterm Exm 1 Mrch 1, 2018 Nme: Andrew ID: Recittion Section: You my not use ny books, notes, or electronic devices during this exm. You my not sk questions bout the exm except for lnguge
CSE 401 Midterm Exam 11/5/10 Sample Solution
 Question 1. egulr expressions (20 points) In the Ad Progrmming lnguge n integer constnt contins one or more digits, but it my lso contin embedded underscores. Any underscores must be preceded nd followed
Question 1. egulr expressions (20 points) In the Ad Progrmming lnguge n integer constnt contins one or more digits, but it my lso contin embedded underscores. Any underscores must be preceded nd followed
CS143 Handout 07 Summer 2011 June 24 th, 2011 Written Set 1: Lexical Analysis
 CS143 Hndout 07 Summer 2011 June 24 th, 2011 Written Set 1: Lexicl Anlysis In this first written ssignment, you'll get the chnce to ply round with the vrious constructions tht come up when doing lexicl
CS143 Hndout 07 Summer 2011 June 24 th, 2011 Written Set 1: Lexicl Anlysis In this first written ssignment, you'll get the chnce to ply round with the vrious constructions tht come up when doing lexicl
CPSC 213. Polymorphism. Introduction to Computer Systems. Readings for Next Two Lectures. Back to Procedure Calls
 Redings for Next Two Lectures Text CPSC 213 Switch Sttements, Understnding Pointers - 2nd ed: 3.6.7, 3.10-1st ed: 3.6.6, 3.11 Introduction to Computer Systems Unit 1f Dynmic Control Flow Polymorphism nd
Redings for Next Two Lectures Text CPSC 213 Switch Sttements, Understnding Pointers - 2nd ed: 3.6.7, 3.10-1st ed: 3.6.6, 3.11 Introduction to Computer Systems Unit 1f Dynmic Control Flow Polymorphism nd
ΕΠΛ323 - Θεωρία και Πρακτική Μεταγλωττιστών
 ΕΠΛ323 - Θωρία και Πρακτική Μταγλωττιστών Lecture 3 Lexicl Anlysis Elis Athnsopoulos elisthn@cs.ucy.c.cy Recognition of Tokens if expressions nd reltionl opertors if è if then è then else è else relop
ΕΠΛ323 - Θωρία και Πρακτική Μταγλωττιστών Lecture 3 Lexicl Anlysis Elis Athnsopoulos elisthn@cs.ucy.c.cy Recognition of Tokens if expressions nd reltionl opertors if è if then è then else è else relop
COMP 423 lecture 11 Jan. 28, 2008
 COMP 423 lecture 11 Jn. 28, 2008 Up to now, we hve looked t how some symols in n lphet occur more frequently thn others nd how we cn sve its y using code such tht the codewords for more frequently occuring
COMP 423 lecture 11 Jn. 28, 2008 Up to now, we hve looked t how some symols in n lphet occur more frequently thn others nd how we cn sve its y using code such tht the codewords for more frequently occuring
Midterm I Solutions CS164, Spring 2006
 Midterm I Solutions CS164, Spring 2006 Februry 23, 2006 Plese red ll instructions (including these) crefully. Write your nme, login, SID, nd circle the section time. There re 8 pges in this exm nd 4 questions,
Midterm I Solutions CS164, Spring 2006 Februry 23, 2006 Plese red ll instructions (including these) crefully. Write your nme, login, SID, nd circle the section time. There re 8 pges in this exm nd 4 questions,
Reducing a DFA to a Minimal DFA
 Lexicl Anlysis - Prt 4 Reducing DFA to Miniml DFA Input: DFA IN Assume DFA IN never gets stuck (dd ded stte if necessry) Output: DFA MIN An equivlent DFA with the minimum numer of sttes. Hrry H. Porter,
Lexicl Anlysis - Prt 4 Reducing DFA to Miniml DFA Input: DFA IN Assume DFA IN never gets stuck (dd ded stte if necessry) Output: DFA MIN An equivlent DFA with the minimum numer of sttes. Hrry H. Porter,
box Boxes and Arrows 3 true 7.59 'X' An object is drawn as a box that contains its data members, for example:
 Boxes nd Arrows There re two kinds of vriles in Jv: those tht store primitive vlues nd those tht store references. Primitive vlues re vlues of type long, int, short, chr, yte, oolen, doule, nd flot. References
Boxes nd Arrows There re two kinds of vriles in Jv: those tht store primitive vlues nd those tht store references. Primitive vlues re vlues of type long, int, short, chr, yte, oolen, doule, nd flot. References
Section 3.1: Sequences and Series
 Section.: Sequences d Series Sequences Let s strt out with the definition of sequence: sequence: ordered list of numbers, often with definite pttern Recll tht in set, order doesn t mtter so this is one
Section.: Sequences d Series Sequences Let s strt out with the definition of sequence: sequence: ordered list of numbers, often with definite pttern Recll tht in set, order doesn t mtter so this is one
Some Thoughts on Grad School. Undergraduate Compilers Review and Intro to MJC. Structure of a Typical Compiler. Lexing and Parsing
 Undergrdute Compilers Review nd Intro to MJC Announcements Miling list is in full swing Tody Some thoughts on grd school Finish prsing Semntic nlysis Visitor pttern for bstrct syntx trees Some Thoughts
Undergrdute Compilers Review nd Intro to MJC Announcements Miling list is in full swing Tody Some thoughts on grd school Finish prsing Semntic nlysis Visitor pttern for bstrct syntx trees Some Thoughts
HW Stereotactic Targeting
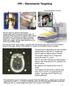 HW Stereotctic Trgeting We re bout to perform stereotctic rdiosurgery with the Gmm Knife under CT guidnce. We instrument the ptient with bse ring nd for CT scnning we ttch fiducil cge (FC). Above: bse
HW Stereotctic Trgeting We re bout to perform stereotctic rdiosurgery with the Gmm Knife under CT guidnce. We instrument the ptient with bse ring nd for CT scnning we ttch fiducil cge (FC). Above: bse
In the last lecture, we discussed how valid tokens may be specified by regular expressions.
 LECTURE 5 Scnning SYNTAX ANALYSIS We know from our previous lectures tht the process of verifying the syntx of the progrm is performed in two stges: Scnning: Identifying nd verifying tokens in progrm.
LECTURE 5 Scnning SYNTAX ANALYSIS We know from our previous lectures tht the process of verifying the syntx of the progrm is performed in two stges: Scnning: Identifying nd verifying tokens in progrm.
Fall 2018 Midterm 2 November 15, 2018
 Nme: 15-112 Fll 2018 Midterm 2 November 15, 2018 Andrew ID: Recittion Section: ˆ You my not use ny books, notes, extr pper, or electronic devices during this exm. There should be nothing on your desk or
Nme: 15-112 Fll 2018 Midterm 2 November 15, 2018 Andrew ID: Recittion Section: ˆ You my not use ny books, notes, extr pper, or electronic devices during this exm. There should be nothing on your desk or
2014 Haskell January Test Regular Expressions and Finite Automata
 0 Hskell Jnury Test Regulr Expressions nd Finite Automt This test comprises four prts nd the mximum mrk is 5. Prts I, II nd III re worth 3 of the 5 mrks vilble. The 0 Hskell Progrmming Prize will be wrded
0 Hskell Jnury Test Regulr Expressions nd Finite Automt This test comprises four prts nd the mximum mrk is 5. Prts I, II nd III re worth 3 of the 5 mrks vilble. The 0 Hskell Progrmming Prize will be wrded
LING/C SC/PSYC 438/538. Lecture 21 Sandiway Fong
 LING/C SC/PSYC 438/538 Lecture 21 Sndiwy Fong Tody's Topics Homework 8 Review Optionl Homework 9 (mke up on Homework 7) Homework 8 Review Question1: write Prolog regulr grmmr for the following lnguge:
LING/C SC/PSYC 438/538 Lecture 21 Sndiwy Fong Tody's Topics Homework 8 Review Optionl Homework 9 (mke up on Homework 7) Homework 8 Review Question1: write Prolog regulr grmmr for the following lnguge:
Mid-term exam. Scores. Fall term 2012 KAIST EE209 Programming Structures for EE. Thursday Oct 25, Student's name: Student ID:
 Fll term 2012 KAIST EE209 Progrmming Structures for EE Mid-term exm Thursdy Oct 25, 2012 Student's nme: Student ID: The exm is closed book nd notes. Red the questions crefully nd focus your nswers on wht
Fll term 2012 KAIST EE209 Progrmming Structures for EE Mid-term exm Thursdy Oct 25, 2012 Student's nme: Student ID: The exm is closed book nd notes. Red the questions crefully nd focus your nswers on wht
Fall 2017 Midterm Exam 1 October 19, You may not use any books, notes, or electronic devices during this exam.
 15-112 Fll 2017 Midterm Exm 1 October 19, 2017 Nme: Andrew ID: Recittion Section: You my not use ny books, notes, or electronic devices during this exm. You my not sk questions bout the exm except for
15-112 Fll 2017 Midterm Exm 1 October 19, 2017 Nme: Andrew ID: Recittion Section: You my not use ny books, notes, or electronic devices during this exm. You my not sk questions bout the exm except for
What are suffix trees?
 Suffix Trees 1 Wht re suffix trees? Allow lgorithm designers to store very lrge mount of informtion out strings while still keeping within liner spce Allow users to serch for new strings in the originl
Suffix Trees 1 Wht re suffix trees? Allow lgorithm designers to store very lrge mount of informtion out strings while still keeping within liner spce Allow users to serch for new strings in the originl
Midterm 2 Sample solution
 Nme: Instructions Midterm 2 Smple solution CMSC 430 Introduction to Compilers Fll 2012 November 28, 2012 This exm contins 9 pges, including this one. Mke sure you hve ll the pges. Write your nme on the
Nme: Instructions Midterm 2 Smple solution CMSC 430 Introduction to Compilers Fll 2012 November 28, 2012 This exm contins 9 pges, including this one. Mke sure you hve ll the pges. Write your nme on the
CSc 453. Compilers and Systems Software. 4 : Lexical Analysis II. Department of Computer Science University of Arizona
 CSc 453 Compilers nd Systems Softwre 4 : Lexicl Anlysis II Deprtment of Computer Science University of Arizon collerg@gmil.com Copyright c 2009 Christin Collerg Implementing Automt NFAs nd DFAs cn e hrd-coded
CSc 453 Compilers nd Systems Softwre 4 : Lexicl Anlysis II Deprtment of Computer Science University of Arizon collerg@gmil.com Copyright c 2009 Christin Collerg Implementing Automt NFAs nd DFAs cn e hrd-coded
Dr. D.M. Akbar Hussain
 Dr. D.M. Akr Hussin Lexicl Anlysis. Bsic Ide: Red the source code nd generte tokens, it is similr wht humns will do to red in; just tking on the input nd reking it down in pieces. Ech token is sequence
Dr. D.M. Akr Hussin Lexicl Anlysis. Bsic Ide: Red the source code nd generte tokens, it is similr wht humns will do to red in; just tking on the input nd reking it down in pieces. Ech token is sequence
Unit #9 : Definite Integral Properties, Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
 Unit #9 : Definite Integrl Properties, Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus Gols: Identify properties of definite integrls Define odd nd even functions, nd reltionship to integrl vlues Introduce the Fundmentl
Unit #9 : Definite Integrl Properties, Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus Gols: Identify properties of definite integrls Define odd nd even functions, nd reltionship to integrl vlues Introduce the Fundmentl
Suffix Tries. Slides adapted from the course by Ben Langmead
 Suffix Tries Slides dpted from the course y Ben Lngmed en.lngmed@gmil.com Indexing with suffixes Until now, our indexes hve een sed on extrcting sustrings from T A very different pproch is to extrct suffixes
Suffix Tries Slides dpted from the course y Ben Lngmed en.lngmed@gmil.com Indexing with suffixes Until now, our indexes hve een sed on extrcting sustrings from T A very different pproch is to extrct suffixes
CSEP 573 Artificial Intelligence Winter 2016
 CSEP 573 Artificil Intelligence Winter 2016 Luke Zettlemoyer Problem Spces nd Serch slides from Dn Klein, Sturt Russell, Andrew Moore, Dn Weld, Pieter Abbeel, Ali Frhdi Outline Agents tht Pln Ahed Serch
CSEP 573 Artificil Intelligence Winter 2016 Luke Zettlemoyer Problem Spces nd Serch slides from Dn Klein, Sturt Russell, Andrew Moore, Dn Weld, Pieter Abbeel, Ali Frhdi Outline Agents tht Pln Ahed Serch
4452 Mathematical Modeling Lecture 4: Lagrange Multipliers
 Mth Modeling Lecture 4: Lgrnge Multipliers Pge 4452 Mthemticl Modeling Lecture 4: Lgrnge Multipliers Lgrnge multipliers re high powered mthemticl technique to find the mximum nd minimum of multidimensionl
Mth Modeling Lecture 4: Lgrnge Multipliers Pge 4452 Mthemticl Modeling Lecture 4: Lgrnge Multipliers Lgrnge multipliers re high powered mthemticl technique to find the mximum nd minimum of multidimensionl
Lecture T4: Pattern Matching
 Introduction to Theoreticl CS Lecture T4: Pttern Mtching Two fundmentl questions. Wht cn computer do? How fst cn it do it? Generl pproch. Don t tlk bout specific mchines or problems. Consider miniml bstrct
Introduction to Theoreticl CS Lecture T4: Pttern Mtching Two fundmentl questions. Wht cn computer do? How fst cn it do it? Generl pproch. Don t tlk bout specific mchines or problems. Consider miniml bstrct
CMPSC 470: Compiler Construction
 CMPSC 47: Compiler Construction Plese complete the following: Midterm (Type A) Nme Instruction: Mke sure you hve ll pges including this cover nd lnk pge t the end. Answer ech question in the spce provided.
CMPSC 47: Compiler Construction Plese complete the following: Midterm (Type A) Nme Instruction: Mke sure you hve ll pges including this cover nd lnk pge t the end. Answer ech question in the spce provided.
Section 10.4 Hyperbolas
 66 Section 10.4 Hyperbols Objective : Definition of hyperbol & hyperbols centered t (0, 0). The third type of conic we will study is the hyperbol. It is defined in the sme mnner tht we defined the prbol
66 Section 10.4 Hyperbols Objective : Definition of hyperbol & hyperbols centered t (0, 0). The third type of conic we will study is the hyperbol. It is defined in the sme mnner tht we defined the prbol
Scanner Termination. Multi Character Lookahead. to its physical end. Most parsers require an end of file token. Lex and Jlex automatically create an
 Scnner Termintion A scnner reds input chrcters nd prtitions them into tokens. Wht hppens when the end of the input file is reched? It my be useful to crete n Eof pseudo-chrcter when this occurs. In Jv,
Scnner Termintion A scnner reds input chrcters nd prtitions them into tokens. Wht hppens when the end of the input file is reched? It my be useful to crete n Eof pseudo-chrcter when this occurs. In Jv,
If you are at the university, either physically or via the VPN, you can download the chapters of this book as PDFs.
 Lecture 5 Wlks, Trils, Pths nd Connectedness Reding: Some of the mteril in this lecture comes from Section 1.2 of Dieter Jungnickel (2008), Grphs, Networks nd Algorithms, 3rd edition, which is ville online
Lecture 5 Wlks, Trils, Pths nd Connectedness Reding: Some of the mteril in this lecture comes from Section 1.2 of Dieter Jungnickel (2008), Grphs, Networks nd Algorithms, 3rd edition, which is ville online
CS 340, Fall 2014 Dec 11 th /13 th Final Exam Note: in all questions, the special symbol ɛ (epsilon) is used to indicate the empty string.
 CS 340, Fll 2014 Dec 11 th /13 th Finl Exm Nme: Note: in ll questions, the specil symol ɛ (epsilon) is used to indicte the empty string. Question 1. [5 points] Consider the following regulr expression;
CS 340, Fll 2014 Dec 11 th /13 th Finl Exm Nme: Note: in ll questions, the specil symol ɛ (epsilon) is used to indicte the empty string. Question 1. [5 points] Consider the following regulr expression;
Implementing Automata. CSc 453. Compilers and Systems Software. 4 : Lexical Analysis II. Department of Computer Science University of Arizona
 Implementing utomt Sc 5 ompilers nd Systems Softwre : Lexicl nlysis II Deprtment of omputer Science University of rizon collerg@gmil.com opyright c 009 hristin ollerg NFs nd DFs cn e hrd-coded using this
Implementing utomt Sc 5 ompilers nd Systems Softwre : Lexicl nlysis II Deprtment of omputer Science University of rizon collerg@gmil.com opyright c 009 hristin ollerg NFs nd DFs cn e hrd-coded using this
Topic 2: Lexing and Flexing
 Topic 2: Lexing nd Flexing COS 320 Compiling Techniques Princeton University Spring 2016 Lennrt Beringer 1 2 The Compiler Lexicl Anlysis Gol: rek strem of ASCII chrcters (source/input) into sequence of
Topic 2: Lexing nd Flexing COS 320 Compiling Techniques Princeton University Spring 2016 Lennrt Beringer 1 2 The Compiler Lexicl Anlysis Gol: rek strem of ASCII chrcters (source/input) into sequence of
Reducing Costs with Duck Typing. Structural
 Reducing Costs with Duck Typing Structurl 1 Duck Typing In computer progrmming with object-oriented progrmming lnguges, duck typing is lyer of progrmming lnguge nd design rules on top of typing. Typing
Reducing Costs with Duck Typing Structurl 1 Duck Typing In computer progrmming with object-oriented progrmming lnguges, duck typing is lyer of progrmming lnguge nd design rules on top of typing. Typing
1 Quad-Edge Construction Operators
 CS48: Computer Grphics Hndout # Geometric Modeling Originl Hndout #5 Stnford University Tuesdy, 8 December 99 Originl Lecture #5: 9 November 99 Topics: Mnipultions with Qud-Edge Dt Structures Scribe: Mike
CS48: Computer Grphics Hndout # Geometric Modeling Originl Hndout #5 Stnford University Tuesdy, 8 December 99 Originl Lecture #5: 9 November 99 Topics: Mnipultions with Qud-Edge Dt Structures Scribe: Mike
Solving Problems by Searching. CS 486/686: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Winter 2016
 Solving Prolems y Serching CS 486/686: Introduction to Artificil Intelligence Winter 2016 1 Introduction Serch ws one of the first topics studied in AI - Newell nd Simon (1961) Generl Prolem Solver Centrl
Solving Prolems y Serching CS 486/686: Introduction to Artificil Intelligence Winter 2016 1 Introduction Serch ws one of the first topics studied in AI - Newell nd Simon (1961) Generl Prolem Solver Centrl
Reference types and their characteristics Class Definition Constructors and Object Creation Special objects: Strings and Arrays
 Objects nd Clsses Reference types nd their chrcteristics Clss Definition Constructors nd Object Cretion Specil objects: Strings nd Arrys OOAD 1999/2000 Cludi Niederée, Jochim W. Schmidt Softwre Systems
Objects nd Clsses Reference types nd their chrcteristics Clss Definition Constructors nd Object Cretion Specil objects: Strings nd Arrys OOAD 1999/2000 Cludi Niederée, Jochim W. Schmidt Softwre Systems
Today. Search Problems. Uninformed Search Methods. Depth-First Search Breadth-First Search Uniform-Cost Search
 Uninformed Serch [These slides were creted by Dn Klein nd Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI t UC Berkeley. All CS188 mterils re vilble t http://i.berkeley.edu.] Tody Serch Problems Uninformed Serch Methods
Uninformed Serch [These slides were creted by Dn Klein nd Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI t UC Berkeley. All CS188 mterils re vilble t http://i.berkeley.edu.] Tody Serch Problems Uninformed Serch Methods
Data sharing in OpenMP
 Dt shring in OpenMP Polo Burgio polo.burgio@unimore.it Outline Expressing prllelism Understnding prllel threds Memory Dt mngement Dt cluses Synchroniztion Brriers, locks, criticl sections Work prtitioning
Dt shring in OpenMP Polo Burgio polo.burgio@unimore.it Outline Expressing prllelism Understnding prllel threds Memory Dt mngement Dt cluses Synchroniztion Brriers, locks, criticl sections Work prtitioning
MIPS I/O and Interrupt
 MIPS I/O nd Interrupt Review Floting point instructions re crried out on seprte chip clled coprocessor 1 You hve to move dt to/from coprocessor 1 to do most common opertions such s printing, clling functions,
MIPS I/O nd Interrupt Review Floting point instructions re crried out on seprte chip clled coprocessor 1 You hve to move dt to/from coprocessor 1 to do most common opertions such s printing, clling functions,
Ray surface intersections
 Ry surfce intersections Some primitives Finite primitives: polygons spheres, cylinders, cones prts of generl qudrics Infinite primitives: plnes infinite cylinders nd cones generl qudrics A finite primitive
Ry surfce intersections Some primitives Finite primitives: polygons spheres, cylinders, cones prts of generl qudrics Infinite primitives: plnes infinite cylinders nd cones generl qudrics A finite primitive
Stack. A list whose end points are pointed by top and bottom
 4. Stck Stck A list whose end points re pointed by top nd bottom Insertion nd deletion tke plce t the top (cf: Wht is the difference between Stck nd Arry?) Bottom is constnt, but top grows nd shrinks!
4. Stck Stck A list whose end points re pointed by top nd bottom Insertion nd deletion tke plce t the top (cf: Wht is the difference between Stck nd Arry?) Bottom is constnt, but top grows nd shrinks!
INTRODUCTION TO SIMPLICIAL COMPLEXES
 INTRODUCTION TO SIMPLICIAL COMPLEXES CASEY KELLEHER AND ALESSANDRA PANTANO 0.1. Introduction. In this ctivity set we re going to introduce notion from Algebric Topology clled simplicil homology. The min
INTRODUCTION TO SIMPLICIAL COMPLEXES CASEY KELLEHER AND ALESSANDRA PANTANO 0.1. Introduction. In this ctivity set we re going to introduce notion from Algebric Topology clled simplicil homology. The min
Problem Set 2 Fall 16 Due: Wednesday, September 21th, in class, before class begins.
 Problem Set 2 Fll 16 Due: Wednesdy, September 21th, in clss, before clss begins. 1. LL Prsing For the following sub-problems, consider the following context-free grmmr: S T$ (1) T A (2) T bbb (3) A T (4)
Problem Set 2 Fll 16 Due: Wednesdy, September 21th, in clss, before clss begins. 1. LL Prsing For the following sub-problems, consider the following context-free grmmr: S T$ (1) T A (2) T bbb (3) A T (4)
CMSC 331 First Midterm Exam
 0 00/ 1 20/ 2 05/ 3 15/ 4 15/ 5 15/ 6 20/ 7 30/ 8 30/ 150/ 331 First Midterm Exm 7 October 2003 CMC 331 First Midterm Exm Nme: mple Answers tudent ID#: You will hve seventy-five (75) minutes to complete
0 00/ 1 20/ 2 05/ 3 15/ 4 15/ 5 15/ 6 20/ 7 30/ 8 30/ 150/ 331 First Midterm Exm 7 October 2003 CMC 331 First Midterm Exm Nme: mple Answers tudent ID#: You will hve seventy-five (75) minutes to complete
CS 241. Fall 2017 Midterm Review Solutions. October 24, Bits and Bytes 1. 3 MIPS Assembler 6. 4 Regular Languages 7.
 CS 241 Fll 2017 Midterm Review Solutions Octoer 24, 2017 Contents 1 Bits nd Bytes 1 2 MIPS Assemly Lnguge Progrmming 2 3 MIPS Assemler 6 4 Regulr Lnguges 7 5 Scnning 9 1 Bits nd Bytes 1. Give two s complement
CS 241 Fll 2017 Midterm Review Solutions Octoer 24, 2017 Contents 1 Bits nd Bytes 1 2 MIPS Assemly Lnguge Progrmming 2 3 MIPS Assemler 6 4 Regulr Lnguges 7 5 Scnning 9 1 Bits nd Bytes 1. Give two s complement
CSCE 531, Spring 2017, Midterm Exam Answer Key
 CCE 531, pring 2017, Midterm Exm Answer Key 1. (15 points) Using the method descried in the ook or in clss, convert the following regulr expression into n equivlent (nondeterministic) finite utomton: (
CCE 531, pring 2017, Midterm Exm Answer Key 1. (15 points) Using the method descried in the ook or in clss, convert the following regulr expression into n equivlent (nondeterministic) finite utomton: (
Lexical Analysis: Constructing a Scanner from Regular Expressions
 Lexicl Anlysis: Constructing Scnner from Regulr Expressions Gol Show how to construct FA to recognize ny RE This Lecture Convert RE to n nondeterministic finite utomton (NFA) Use Thompson s construction
Lexicl Anlysis: Constructing Scnner from Regulr Expressions Gol Show how to construct FA to recognize ny RE This Lecture Convert RE to n nondeterministic finite utomton (NFA) Use Thompson s construction
9 Graph Cutting Procedures
 9 Grph Cutting Procedures Lst clss we begn looking t how to embed rbitrry metrics into distributions of trees, nd proved the following theorem due to Brtl (1996): Theorem 9.1 (Brtl (1996)) Given metric
9 Grph Cutting Procedures Lst clss we begn looking t how to embed rbitrry metrics into distributions of trees, nd proved the following theorem due to Brtl (1996): Theorem 9.1 (Brtl (1996)) Given metric
Quiz2 45mins. Personal Number: Problem 1. (20pts) Here is an Table of Perl Regular Ex
 Long Quiz2 45mins Nme: Personl Numer: Prolem. (20pts) Here is n Tle of Perl Regulr Ex Chrcter Description. single chrcter \s whitespce chrcter (spce, t, newline) \S non-whitespce chrcter \d digit (0-9)
Long Quiz2 45mins Nme: Personl Numer: Prolem. (20pts) Here is n Tle of Perl Regulr Ex Chrcter Description. single chrcter \s whitespce chrcter (spce, t, newline) \S non-whitespce chrcter \d digit (0-9)
Geometric transformations
 Geometric trnsformtions Computer Grphics Some slides re bsed on Shy Shlom slides from TAU mn n n m m T A,,,,,, 2 1 2 22 12 1 21 11 Rows become columns nd columns become rows nm n n m m A,,,,,, 1 1 2 22
Geometric trnsformtions Computer Grphics Some slides re bsed on Shy Shlom slides from TAU mn n n m m T A,,,,,, 2 1 2 22 12 1 21 11 Rows become columns nd columns become rows nm n n m m A,,,,,, 1 1 2 22
Compilers Spring 2013 PRACTICE Midterm Exam
 Compilers Spring 2013 PRACTICE Midterm Exm This is full length prctice midterm exm. If you wnt to tke it t exm pce, give yourself 7 minutes to tke the entire test. Just like the rel exm, ech question hs
Compilers Spring 2013 PRACTICE Midterm Exm This is full length prctice midterm exm. If you wnt to tke it t exm pce, give yourself 7 minutes to tke the entire test. Just like the rel exm, ech question hs
Today. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Recap: Search. Example: Pancake Problem. Example: Pancake Problem. General Tree Search.
 CS 88: Artificil Intelligence Fll 00 Lecture : A* Serch 9//00 A* Serch rph Serch Tody Heuristic Design Dn Klein UC Berkeley Multiple slides from Sturt Russell or Andrew Moore Recp: Serch Exmple: Pncke
CS 88: Artificil Intelligence Fll 00 Lecture : A* Serch 9//00 A* Serch rph Serch Tody Heuristic Design Dn Klein UC Berkeley Multiple slides from Sturt Russell or Andrew Moore Recp: Serch Exmple: Pncke
Digital Design. Chapter 1: Introduction. Digital Design. Copyright 2006 Frank Vahid
 Chpter : Introduction Copyright 6 Why Study?. Look under the hood of computers Solid understnding --> confidence, insight, even better progrmmer when wre of hrdwre resource issues Electronic devices becoming
Chpter : Introduction Copyright 6 Why Study?. Look under the hood of computers Solid understnding --> confidence, insight, even better progrmmer when wre of hrdwre resource issues Electronic devices becoming
Algorithm Design (5) Text Search
 Algorithm Design (5) Text Serch Tkshi Chikym School of Engineering The University of Tokyo Text Serch Find sustring tht mtches the given key string in text dt of lrge mount Key string: chr x[m] Text Dt:
Algorithm Design (5) Text Serch Tkshi Chikym School of Engineering The University of Tokyo Text Serch Find sustring tht mtches the given key string in text dt of lrge mount Key string: chr x[m] Text Dt:
File Manager Quick Reference Guide. June Prepared for the Mayo Clinic Enterprise Kahua Deployment
 File Mnger Quick Reference Guide June 2018 Prepred for the Myo Clinic Enterprise Khu Deployment NVIGTION IN FILE MNGER To nvigte in File Mnger, users will mke use of the left pne to nvigte nd further pnes
File Mnger Quick Reference Guide June 2018 Prepred for the Myo Clinic Enterprise Khu Deployment NVIGTION IN FILE MNGER To nvigte in File Mnger, users will mke use of the left pne to nvigte nd further pnes
Engineer To Engineer Note
 Engineer To Engineer Note EE-186 Technicl Notes on using Anlog Devices' DSP components nd development tools Contct our technicl support by phone: (800) ANALOG-D or e-mil: dsp.support@nlog.com Or visit
Engineer To Engineer Note EE-186 Technicl Notes on using Anlog Devices' DSP components nd development tools Contct our technicl support by phone: (800) ANALOG-D or e-mil: dsp.support@nlog.com Or visit
CS 430 Spring Mike Lam, Professor. Parsing
 CS 430 Spring 2015 Mike Lm, Professor Prsing Syntx Anlysis We cn now formlly descrie lnguge's syntx Using regulr expressions nd BNF grmmrs How does tht help us? Syntx Anlysis We cn now formlly descrie
CS 430 Spring 2015 Mike Lm, Professor Prsing Syntx Anlysis We cn now formlly descrie lnguge's syntx Using regulr expressions nd BNF grmmrs How does tht help us? Syntx Anlysis We cn now formlly descrie
pdfapilot Server 2 Manual
 pdfpilot Server 2 Mnul 2011 by clls softwre gmbh Schönhuser Allee 6/7 D 10119 Berlin Germny info@cllssoftwre.com www.cllssoftwre.com Mnul clls pdfpilot Server 2 Pge 2 clls pdfpilot Server 2 Mnul Lst modified:
pdfpilot Server 2 Mnul 2011 by clls softwre gmbh Schönhuser Allee 6/7 D 10119 Berlin Germny info@cllssoftwre.com www.cllssoftwre.com Mnul clls pdfpilot Server 2 Pge 2 clls pdfpilot Server 2 Mnul Lst modified:
Slides for Data Mining by I. H. Witten and E. Frank
 Slides for Dt Mining y I. H. Witten nd E. Frnk Simplicity first Simple lgorithms often work very well! There re mny kinds of simple structure, eg: One ttriute does ll the work All ttriutes contriute eqully
Slides for Dt Mining y I. H. Witten nd E. Frnk Simplicity first Simple lgorithms often work very well! There re mny kinds of simple structure, eg: One ttriute does ll the work All ttriutes contriute eqully
CSCI 446: Artificial Intelligence
 CSCI 446: Artificil Intelligence Serch Instructor: Michele Vn Dyne [These slides were creted by Dn Klein nd Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI t UC Berkeley. All CS188 mterils re vilble t http://i.berkeley.edu.]
CSCI 446: Artificil Intelligence Serch Instructor: Michele Vn Dyne [These slides were creted by Dn Klein nd Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI t UC Berkeley. All CS188 mterils re vilble t http://i.berkeley.edu.]
What do all those bits mean now? Number Systems and Arithmetic. Introduction to Binary Numbers. Questions About Numbers
 Wht do ll those bits men now? bits (...) Number Systems nd Arithmetic or Computers go to elementry school instruction R-formt I-formt... integer dt number text chrs... floting point signed unsigned single
Wht do ll those bits men now? bits (...) Number Systems nd Arithmetic or Computers go to elementry school instruction R-formt I-formt... integer dt number text chrs... floting point signed unsigned single
MATH 25 CLASS 5 NOTES, SEP
 MATH 25 CLASS 5 NOTES, SEP 30 2011 Contents 1. A brief diversion: reltively prime numbers 1 2. Lest common multiples 3 3. Finding ll solutions to x + by = c 4 Quick links to definitions/theorems Euclid
MATH 25 CLASS 5 NOTES, SEP 30 2011 Contents 1. A brief diversion: reltively prime numbers 1 2. Lest common multiples 3 3. Finding ll solutions to x + by = c 4 Quick links to definitions/theorems Euclid
CS 321 Programming Languages and Compilers. Bottom Up Parsing
 CS 321 Progrmming nguges nd Compilers Bottom Up Prsing Bottom-up Prsing: Shift-reduce prsing Grmmr H: fi ; fi b Input: ;;b hs prse tree ; ; b 2 Dt for Shift-reduce Prser Input string: sequence of tokens
CS 321 Progrmming nguges nd Compilers Bottom Up Prsing Bottom-up Prsing: Shift-reduce prsing Grmmr H: fi ; fi b Input: ;;b hs prse tree ; ; b 2 Dt for Shift-reduce Prser Input string: sequence of tokens
Math 142, Exam 1 Information.
 Mth 14, Exm 1 Informtion. 9/14/10, LC 41, 9:30-10:45. Exm 1 will be bsed on: Sections 7.1-7.5. The corresponding ssigned homework problems (see http://www.mth.sc.edu/ boyln/sccourses/14f10/14.html) At
Mth 14, Exm 1 Informtion. 9/14/10, LC 41, 9:30-10:45. Exm 1 will be bsed on: Sections 7.1-7.5. The corresponding ssigned homework problems (see http://www.mth.sc.edu/ boyln/sccourses/14f10/14.html) At
Physics 208: Electricity and Magnetism Exam 1, Secs Feb IMPORTANT. Read these directions carefully:
 Physics 208: Electricity nd Mgnetism Exm 1, Secs. 506 510 11 Feb. 2004 Instructor: Dr. George R. Welch, 415 Engineering-Physics, 845-7737 Print your nme netly: Lst nme: First nme: Sign your nme: Plese
Physics 208: Electricity nd Mgnetism Exm 1, Secs. 506 510 11 Feb. 2004 Instructor: Dr. George R. Welch, 415 Engineering-Physics, 845-7737 Print your nme netly: Lst nme: First nme: Sign your nme: Plese
ΕΠΛ323 - Θεωρία και Πρακτική Μεταγλωττιστών. Lecture 3b Lexical Analysis Elias Athanasopoulos
 ΕΠΛ323 - Θωρία και Πρακτική Μταγλωττιστών Lecture 3 Lexicl Anlysis Elis Athnsopoulos elisthn@cs.ucy.c.cy RecogniNon of Tokens if expressions nd relnonl opertors if è if then è then else è else relop è
ΕΠΛ323 - Θωρία και Πρακτική Μταγλωττιστών Lecture 3 Lexicl Anlysis Elis Athnsopoulos elisthn@cs.ucy.c.cy RecogniNon of Tokens if expressions nd relnonl opertors if è if then è then else è else relop è
2 Computing all Intersections of a Set of Segments Line Segment Intersection
 15-451/651: Design & Anlysis of Algorithms Novemer 14, 2016 Lecture #21 Sweep-Line nd Segment Intersection lst chnged: Novemer 8, 2017 1 Preliminries The sweep-line prdigm is very powerful lgorithmic design
15-451/651: Design & Anlysis of Algorithms Novemer 14, 2016 Lecture #21 Sweep-Line nd Segment Intersection lst chnged: Novemer 8, 2017 1 Preliminries The sweep-line prdigm is very powerful lgorithmic design
5 Regular 4-Sided Composition
 Xilinx-Lv User Guide 5 Regulr 4-Sided Composition This tutoril shows how regulr circuits with 4-sided elements cn be described in Lv. The type of regulr circuits tht re discussed in this tutoril re those
Xilinx-Lv User Guide 5 Regulr 4-Sided Composition This tutoril shows how regulr circuits with 4-sided elements cn be described in Lv. The type of regulr circuits tht re discussed in this tutoril re those
Stack Manipulation. Other Issues. How about larger constants? Frame Pointer. PowerPC. Alternative Architectures
 Other Issues Stck Mnipultion support for procedures (Refer to section 3.6), stcks, frmes, recursion mnipulting strings nd pointers linkers, loders, memory lyout Interrupts, exceptions, system clls nd conventions
Other Issues Stck Mnipultion support for procedures (Refer to section 3.6), stcks, frmes, recursion mnipulting strings nd pointers linkers, loders, memory lyout Interrupts, exceptions, system clls nd conventions
Announcements. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Recap: Search. Today. Example: Pancake Problem. Example: Pancake Problem
 Announcements Project : erch It s live! Due 9/. trt erly nd sk questions. It s longer thn most! Need prtner? Come up fter clss or try Pizz ections: cn go to ny, ut hve priority in your own C 88: Artificil
Announcements Project : erch It s live! Due 9/. trt erly nd sk questions. It s longer thn most! Need prtner? Come up fter clss or try Pizz ections: cn go to ny, ut hve priority in your own C 88: Artificil
INDIAN COMMUNITY SCHOOL INFORMATICS PRACTICES 2012
 INDIAN COMMUNITY SCHOOL INFORMATICS PRACTICES 0. Write corresponding C ++ expression for the following mthemticl expression: i) (-b) + (c-d) ii) e x x. Write C++ expression for the following: ) All possible
INDIAN COMMUNITY SCHOOL INFORMATICS PRACTICES 0. Write corresponding C ++ expression for the following mthemticl expression: i) (-b) + (c-d) ii) e x x. Write C++ expression for the following: ) All possible
MA1008. Calculus and Linear Algebra for Engineers. Course Notes for Section B. Stephen Wills. Department of Mathematics. University College Cork
 MA1008 Clculus nd Liner Algebr for Engineers Course Notes for Section B Stephen Wills Deprtment of Mthemtics University College Cork s.wills@ucc.ie http://euclid.ucc.ie/pges/stff/wills/teching/m1008/ma1008.html
MA1008 Clculus nd Liner Algebr for Engineers Course Notes for Section B Stephen Wills Deprtment of Mthemtics University College Cork s.wills@ucc.ie http://euclid.ucc.ie/pges/stff/wills/teching/m1008/ma1008.html
Math 464 Fall 2012 Notes on Marginal and Conditional Densities October 18, 2012
 Mth 464 Fll 2012 Notes on Mrginl nd Conditionl Densities klin@mth.rizon.edu October 18, 2012 Mrginl densities. Suppose you hve 3 continuous rndom vribles X, Y, nd Z, with joint density f(x,y,z. The mrginl
Mth 464 Fll 2012 Notes on Mrginl nd Conditionl Densities klin@mth.rizon.edu October 18, 2012 Mrginl densities. Suppose you hve 3 continuous rndom vribles X, Y, nd Z, with joint density f(x,y,z. The mrginl
On String Matching in Chunked Texts
 On String Mtching in Chunked Texts Hnnu Peltol nd Jorm Trhio {hpeltol, trhio}@cs.hut.fi Deprtment of Computer Science nd Engineering Helsinki University of Technology P.O. Box 5400, FI-02015 HUT, Finlnd
On String Mtching in Chunked Texts Hnnu Peltol nd Jorm Trhio {hpeltol, trhio}@cs.hut.fi Deprtment of Computer Science nd Engineering Helsinki University of Technology P.O. Box 5400, FI-02015 HUT, Finlnd
Lists in Lisp and Scheme
 Lists in Lisp nd Scheme Lists in Lisp nd Scheme Lists re Lisp s fundmentl dt structures, ut there re others Arrys, chrcters, strings, etc. Common Lisp hs moved on from eing merely LISt Processor However,
Lists in Lisp nd Scheme Lists in Lisp nd Scheme Lists re Lisp s fundmentl dt structures, ut there re others Arrys, chrcters, strings, etc. Common Lisp hs moved on from eing merely LISt Processor However,
Misrepresentation of Preferences
 Misrepresenttion of Preferences Gicomo Bonnno Deprtment of Economics, University of Cliforni, Dvis, USA gfbonnno@ucdvis.edu Socil choice functions Arrow s theorem sys tht it is not possible to extrct from
Misrepresenttion of Preferences Gicomo Bonnno Deprtment of Economics, University of Cliforni, Dvis, USA gfbonnno@ucdvis.edu Socil choice functions Arrow s theorem sys tht it is not possible to extrct from
10/9/2012. Operator is an operation performed over data at runtime. Arithmetic, Logical, Comparison, Assignment, Etc. Operators have precedence
 /9/22 P f Performing i Si Simple l Clcultions C l l ti with ith C#. Opertors in C# nd Opertor Precedence 2. Arithmetic Opertors 3. Logicl Opertors 4. Bitwise Opertors 5. Comprison Opertors 6. Assignment
/9/22 P f Performing i Si Simple l Clcultions C l l ti with ith C#. Opertors in C# nd Opertor Precedence 2. Arithmetic Opertors 3. Logicl Opertors 4. Bitwise Opertors 5. Comprison Opertors 6. Assignment
Unit 5 Vocabulary. A function is a special relationship where each input has a single output.
 MODULE 3 Terms Definition Picture/Exmple/Nottion 1 Function Nottion Function nottion is n efficient nd effective wy to write functions of ll types. This nottion llows you to identify the input vlue with
MODULE 3 Terms Definition Picture/Exmple/Nottion 1 Function Nottion Function nottion is n efficient nd effective wy to write functions of ll types. This nottion llows you to identify the input vlue with
Lexical analysis, scanners. Construction of a scanner
 Lexicl nlysis scnners (NB. Pges 4-5 re for those who need to refresh their knowledge of DFAs nd NFAs. These re not presented during the lectures) Construction of scnner Tools: stte utomt nd trnsition digrms.
Lexicl nlysis scnners (NB. Pges 4-5 re for those who need to refresh their knowledge of DFAs nd NFAs. These re not presented during the lectures) Construction of scnner Tools: stte utomt nd trnsition digrms.
Definition of Regular Expression
 Definition of Regulr Expression After the definition of the string nd lnguges, we re redy to descrie regulr expressions, the nottion we shll use to define the clss of lnguges known s regulr sets. Recll
Definition of Regulr Expression After the definition of the string nd lnguges, we re redy to descrie regulr expressions, the nottion we shll use to define the clss of lnguges known s regulr sets. Recll
vcloud Director Service Provider Admin Portal Guide vcloud Director 9.1
 vcloud Director Service Provider Admin Portl Guide vcloud Director 9. vcloud Director Service Provider Admin Portl Guide You cn find the most up-to-dte technicl documenttion on the VMwre website t: https://docs.vmwre.com/
vcloud Director Service Provider Admin Portl Guide vcloud Director 9. vcloud Director Service Provider Admin Portl Guide You cn find the most up-to-dte technicl documenttion on the VMwre website t: https://docs.vmwre.com/
CS 221: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011
 CS 221: Artificil Intelligence Fll 2011 Lecture 2: Serch (Slides from Dn Klein, with help from Sturt Russell, Andrew Moore, Teg Grenger, Peter Norvig) Problem types! Fully observble, deterministic! single-belief-stte
CS 221: Artificil Intelligence Fll 2011 Lecture 2: Serch (Slides from Dn Klein, with help from Sturt Russell, Andrew Moore, Teg Grenger, Peter Norvig) Problem types! Fully observble, deterministic! single-belief-stte
Dynamic Programming. Andreas Klappenecker. [partially based on slides by Prof. Welch] Monday, September 24, 2012
![Dynamic Programming. Andreas Klappenecker. [partially based on slides by Prof. Welch] Monday, September 24, 2012 Dynamic Programming. Andreas Klappenecker. [partially based on slides by Prof. Welch] Monday, September 24, 2012](/thumbs/96/127090604.jpg) Dynmic Progrmming Andres Klppenecker [prtilly bsed on slides by Prof. Welch] 1 Dynmic Progrmming Optiml substructure An optiml solution to the problem contins within it optiml solutions to subproblems.
Dynmic Progrmming Andres Klppenecker [prtilly bsed on slides by Prof. Welch] 1 Dynmic Progrmming Optiml substructure An optiml solution to the problem contins within it optiml solutions to subproblems.
How to Design REST API? Written Date : March 23, 2015
 Visul Prdigm How Design REST API? Turil How Design REST API? Written Dte : Mrch 23, 2015 REpresenttionl Stte Trnsfer, n rchitecturl style tht cn be used in building networked pplictions, is becoming incresingly
Visul Prdigm How Design REST API? Turil How Design REST API? Written Dte : Mrch 23, 2015 REpresenttionl Stte Trnsfer, n rchitecturl style tht cn be used in building networked pplictions, is becoming incresingly
Very sad code. Abstraction, List, & Cons. CS61A Lecture 7. Happier Code. Goals. Constructors. Constructors 6/29/2011. Selectors.
 6/9/ Abstrction, List, & Cons CS6A Lecture 7-6-9 Colleen Lewis Very sd code (define (totl hnd) (if (empty? hnd) (+ (butlst (lst hnd)) (totl (butlst hnd))))) STk> (totl (h c d)) 7 STk> (totl (h ks d)) ;;;EEEK!
6/9/ Abstrction, List, & Cons CS6A Lecture 7-6-9 Colleen Lewis Very sd code (define (totl hnd) (if (empty? hnd) (+ (butlst (lst hnd)) (totl (butlst hnd))))) STk> (totl (h c d)) 7 STk> (totl (h ks d)) ;;;EEEK!
6.2 Volumes of Revolution: The Disk Method
 mth ppliction: volumes by disks: volume prt ii 6 6 Volumes of Revolution: The Disk Method One of the simplest pplictions of integrtion (Theorem 6) nd the ccumultion process is to determine so-clled volumes
mth ppliction: volumes by disks: volume prt ii 6 6 Volumes of Revolution: The Disk Method One of the simplest pplictions of integrtion (Theorem 6) nd the ccumultion process is to determine so-clled volumes
A Tautology Checker loosely related to Stålmarck s Algorithm by Martin Richards
 A Tutology Checker loosely relted to Stålmrck s Algorithm y Mrtin Richrds mr@cl.cm.c.uk http://www.cl.cm.c.uk/users/mr/ University Computer Lortory New Museum Site Pemroke Street Cmridge, CB2 3QG Mrtin
A Tutology Checker loosely relted to Stålmrck s Algorithm y Mrtin Richrds mr@cl.cm.c.uk http://www.cl.cm.c.uk/users/mr/ University Computer Lortory New Museum Site Pemroke Street Cmridge, CB2 3QG Mrtin
COMBINATORIAL PATTERN MATCHING
 COMBINATORIAL PATTERN MATCHING Genomic Repets Exmple of repets: ATGGTCTAGGTCCTAGTGGTC Motivtion to find them: Genomic rerrngements re often ssocited with repets Trce evolutionry secrets Mny tumors re chrcterized
COMBINATORIAL PATTERN MATCHING Genomic Repets Exmple of repets: ATGGTCTAGGTCCTAGTGGTC Motivtion to find them: Genomic rerrngements re often ssocited with repets Trce evolutionry secrets Mny tumors re chrcterized
