Assignment 1. ECSE-487 Computer archecture Lab. Due date: September 21, 2007, Trottier Assignment Box by 14:30
|
|
|
- Charlene Easter McDaniel
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Assignment 1 ECSE-487 Computer archecture Lab Due date: September 21, 2007, Trottier Assignment Box by 14:30 1 Introduction The purpose of this assignment is to re-familiarize the student with VHDL and to learn how to use industrial electronic design automation (EDA) software such as ModelSim for simulation and Precision RTL for synthesis. The arithmetic logic unit (ALU) is a core component of any CPU. The ALU performs arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction and multiplication and many more. You can read more about the ALU by following this Wikipedia link ( logic unit) or by referencing a textbook on computer architecture 2 Functional Requirements You are required to implement a complex 8-bit ALU that has a similar architecture as that shown in Figure 1. A description of each port and their type (in/out) is shown in Table 1. Each complex numbers is represented by a 16-bit vector. The most significant byte (8 bits) represents the real part. The least significant byte (8 bits) represents the imaginary part. The real and imaginary parts of the complex number are signed integers. The ALU will also perform basic operations on a finite field (also named Galois Field (GF)). Galois fields are used in many applications such as cryptography and coding theory. For example, they are used in Reed-Solomon codes which are in turn used about everywhere. CD-ROMs, hard disks, deep space probes and many more use Reed-Solomon codes to prevent corruption of the information. You can get more information on finite fields on the Wikipedia links ( field and 1
2 field arithmetic). The specific Galois field that you will operate on will be GF(2 8 ) or GF(256). It contains 256 elements and therefore only needs 8 bits to represent all possible members. The primitive polynomial is the standard x 8 + x 4 + x 3 + x + 1 (do not worry too much about that, you only need to use it for the multiplication operation). In this field, the addition and the substraction are actually the same operation and they are very easy to implement: it is a simple XOR operation. The multiplication is a bit more complicated and can either be computed physically or precomputed and loaded in a lookup table (LUT), the choice is yours. If you opt for the LUT implementation, I suggest writing a small script in C or in Matlab to generate the VHDL code, 256 elements is a bit tedious to enter manually. Detailed instruction on the multiplication algorithm can be found in the links provided above. The operations that your ALU implementation should be able to perform are listed in Table 2.The ALU is synchronous. The inputs must be latched into registers before the computation takes place and the correct output must be latched into a register once it is ready. You are free to add any extra input or output signals that are deemed necessary. It is also up to you to decide how many bits to use for each input and output. You will be required to explain your design decisions in your report. 2.1 Behavioral Description A VHDL behavioral model specifies a module s function using VHDL programming constructs such as ifthen-else clauses, etc. It does not specify any internal structure. A VHDL structural model specifies a module s internal structure by identifying all internal modules or units (call these sub-modules) and defining how they are interconnected using the portmap construct. It does not specify any internal behavior. In this assignment your will learn to use both behavioral and structural models. 2.2 ALU Design Hardware systems can be optimized for various performance measures depending on the goals of the design. In this assignment 3 different goals are of interest: minimum hardware, minimum latency and maximum throughput. The minimum hardware design must reuse components as much as possible. The minimum latency design must reduce the delay required to execute a computation by exploiting parallelism. The maximum throughput design must increase the rate at which results are produced through pipelining. Start by implementing the ALU using a behavioral VHDL model aiming for maximum throughput. Next, select between one of the 2 design optimization (minimum hardware or minimum latency) and implement the ALU using a structural model. Both models should be simulated and synthesized. 2
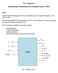
3 Figure 1: Proposed ALU architecture 2.3 Simulations and Testing Testing is a very important part of the hardware design process that is often neglected. You are expected to thoroughly test your VHDL models to ensure correct operation. Make sure that all special cases are tested. Your benchmark should be included in your report to convince the reader that the design is functioning correctly. Provide a waveform trace showing the execution of 2 operations. The trace should be properly annotated and easy to understand without needing to consult your source code. Describe the important features of the simulation and annotate your traces to improve readability. Remove any irrelevant signals from the traces. Lengthy simulations can be included, if necessary, in an appendix. 2.4 Source Code Your VHDL code should be well documented. Each file should start with a header including the filename, the authors, the date, the last revision date and a meaningful description. A description for mux2.vhd such as this is the mux2 implementation doesn t add any information and is not considered meaningful. All the ports of an entity should be briefly described. Comments should be used to indicate interesting parts of the code or parts that could be improved. Use good names for your variables and signals to improve the readability of your code. Imagine that someone who isn t familiar with this assignment is reading your code and trying to understand it. 3
4 Name Type Description OPCODE In Operation to be performed by the ALU DATA0 In First operand DATA1 In Second operand RESET In Reset the ALU to initial state CLOCK In Input clock DATAOUT Out Result of the operation STATUS Out Status of the DATAOUT port Table 1: Description of the ALU ports Operation Type Complex Arithmetic Galois Field Operation Addition, Substraction, Multiplication Addition/Substraction, Multiplication Table 2: Supported ALU operations 3 Assignment Tasks Here is a recap of what is to be done in this first assignment. 1. Implement an ALU as described in Section 2: (a) Behavioral model aiming for maximum throughput. (b) Structural model aiming either for minimum hardware or minimum latency. 2. Simulate and test your designs. You might need 2 different testbenches for your 2 designs. Your testbenchs should be in a separate file. 3. Your source code should be properly commented so that the marker can follow your design. 4. Provide a waveform trace showing the execution of 2 operations. The trace should be properly annotated and easy to understand without needing to consult your source code. 5. Synthesize your designs without the testbench. In your report, describe the results of the synthesis, including the number of logic cells, look-up tables, and the latency of your circuit. Identify in your designs the piece that consumes the most space and the longest path. 4 Submission Guidelines A hardcopy version of your report excluding VHDL source code is to be submitted either in-class or in the assignment box in the Trottier building. 4
5 An electronic copy of your report including your VHDL source files is to be submitted through WebCT in the form of a compressed archive. The archive should have the following properties: the name of the archive should be of the form firstname lastname.zip or.rar or.tgz. the archive should extract to a directory named firstname lastname. Your report should be no longer than 4 pages (excluding the title page, diagrams and appendices) and should include the following: front page (course number, lab title, student name, ID, date) design description: diagram and brief description of your ALU. brief summary of any important design choices. simulation results: description of testing strategy. simulation traces and discussion of results. synthesis results: critical path. estimated clock speed. resource usage. 5 Marking Scheme 35 : Working ALU implementation. 20 : Automated testbench. 05 : Simulation traces showing two operations. 10 : Synthesis results. 10 : Well structured code including meaningful comments. 20 : Report (discussion of design decisions etc) 5
Assignment 01 Computer Architecture Lab ECSE
 Assignment 01 Computer Architecture Lab ECSE 487-001 Date due: September 22, 2006, Trottier Assignment Box by 14:30 1 Introduction The purpose of this assignment is to re-familiarize the student with VHDL
Assignment 01 Computer Architecture Lab ECSE 487-001 Date due: September 22, 2006, Trottier Assignment Box by 14:30 1 Introduction The purpose of this assignment is to re-familiarize the student with VHDL
CprE 381 Computer Organization and Assembly Level Programming
 CprE 381 Computer Organization and Assembly Level Programming Mini-Project B, Version 1.0 Last update: 10/21/2013 This is a three-week project. You will design and implement two versions of a single-cycle
CprE 381 Computer Organization and Assembly Level Programming Mini-Project B, Version 1.0 Last update: 10/21/2013 This is a three-week project. You will design and implement two versions of a single-cycle
VHDL for Synthesis. Course Description. Course Duration. Goals
 VHDL for Synthesis Course Description This course provides all necessary theoretical and practical know how to write an efficient synthesizable HDL code through VHDL standard language. The course goes
VHDL for Synthesis Course Description This course provides all necessary theoretical and practical know how to write an efficient synthesizable HDL code through VHDL standard language. The course goes
Verilog for High Performance
 Verilog for High Performance Course Description This course provides all necessary theoretical and practical know-how to write synthesizable HDL code through Verilog standard language. The course goes
Verilog for High Performance Course Description This course provides all necessary theoretical and practical know-how to write synthesizable HDL code through Verilog standard language. The course goes
FPGA for Software Engineers
 FPGA for Software Engineers Course Description This course closes the gap between hardware and software engineers by providing the software engineer all the necessary FPGA concepts and terms. The course
FPGA for Software Engineers Course Description This course closes the gap between hardware and software engineers by providing the software engineer all the necessary FPGA concepts and terms. The course
ANALYSIS OF AN AREA EFFICIENT VLSI ARCHITECTURE FOR FLOATING POINT MULTIPLIER AND GALOIS FIELD MULTIPLIER*
 IJVD: 3(1), 2012, pp. 21-26 ANALYSIS OF AN AREA EFFICIENT VLSI ARCHITECTURE FOR FLOATING POINT MULTIPLIER AND GALOIS FIELD MULTIPLIER* Anbuselvi M. and Salivahanan S. Department of Electronics and Communication
IJVD: 3(1), 2012, pp. 21-26 ANALYSIS OF AN AREA EFFICIENT VLSI ARCHITECTURE FOR FLOATING POINT MULTIPLIER AND GALOIS FIELD MULTIPLIER* Anbuselvi M. and Salivahanan S. Department of Electronics and Communication
ECEU530. Schedule. ECE U530 Digital Hardware Synthesis. Datapath for the Calculator (HW 5) HW 5 Datapath Entity
 ECE U530 Digital Hardware Synthesis Prof. Miriam Leeser mel@coe.neu.edu November 6, 2006 Classes November 6 and 8 are in 429 Dana! Lecture 15: Homework 5: Datapath How to write a testbench for synchronous
ECE U530 Digital Hardware Synthesis Prof. Miriam Leeser mel@coe.neu.edu November 6, 2006 Classes November 6 and 8 are in 429 Dana! Lecture 15: Homework 5: Datapath How to write a testbench for synchronous
University of California, Davis Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. EEC180B DIGITAL SYSTEMS Spring Quarter 2018
 University of California, Davis Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EEC180B DIGITAL SYSTEMS Spring Quarter 2018 LAB 2: FPGA Synthesis and Combinational Logic Design Objective: This lab covers
University of California, Davis Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EEC180B DIGITAL SYSTEMS Spring Quarter 2018 LAB 2: FPGA Synthesis and Combinational Logic Design Objective: This lab covers
CPEN 230L: Introduction to Digital Logic Laboratory Lab 7: Multiplexers, Decoders, and Seven Segment Displays
 CPEN 230L: Introduction to Digital Logic Laboratory Lab 7: Multiplexers, Decoders, and Seven Segment Displays Purpose Learn about multiplexers (MUXs), decoders and seven segment displays. Learn about hierarchical
CPEN 230L: Introduction to Digital Logic Laboratory Lab 7: Multiplexers, Decoders, and Seven Segment Displays Purpose Learn about multiplexers (MUXs), decoders and seven segment displays. Learn about hierarchical
Part 4: VHDL for sequential circuits. Introduction to Modeling and Verification of Digital Systems. Memory elements. Sequential circuits
 M1 Informatique / MOSIG Introduction to Modeling and erification of Digital Systems Part 4: HDL for sequential circuits Laurence PIERRE http://users-tima.imag.fr/amfors/lpierre/m1arc 2017/2018 81 Sequential
M1 Informatique / MOSIG Introduction to Modeling and erification of Digital Systems Part 4: HDL for sequential circuits Laurence PIERRE http://users-tima.imag.fr/amfors/lpierre/m1arc 2017/2018 81 Sequential
EE577A FINAL PROJECT REPORT Design of a General Purpose CPU
 EE577A FINAL PROJECT REPORT Design of a General Purpose CPU Submitted By Youngseok Lee - 4930239194 Narayana Reddy Lekkala - 9623274062 Chirag Ahuja - 5920609598 Phase 2 Part 1 A. Introduction The core
EE577A FINAL PROJECT REPORT Design of a General Purpose CPU Submitted By Youngseok Lee - 4930239194 Narayana Reddy Lekkala - 9623274062 Chirag Ahuja - 5920609598 Phase 2 Part 1 A. Introduction The core
Digital Design LU. Lab Exercise 1
 Digital Design LU Lab Exercise 1 Jakob Lechner, Thomas Polzer {lechner, tpolzer}@ecs.tuwien.ac.at Department of Computer Engineering University of Technology Vienna Vienna, October 4, 2010 1 Overview 1
Digital Design LU Lab Exercise 1 Jakob Lechner, Thomas Polzer {lechner, tpolzer}@ecs.tuwien.ac.at Department of Computer Engineering University of Technology Vienna Vienna, October 4, 2010 1 Overview 1
VHDL Essentials Simulation & Synthesis
 VHDL Essentials Simulation & Synthesis Course Description This course provides all necessary theoretical and practical know-how to design programmable logic devices using VHDL standard language. The course
VHDL Essentials Simulation & Synthesis Course Description This course provides all necessary theoretical and practical know-how to design programmable logic devices using VHDL standard language. The course
קורס VHDL for High Performance. VHDL
 קורס VHDL for High Performance תיאור הקורס קורסזהמספקאתכלהידע התיאורטיוהמעשילכתיבתקודHDL. VHDL לסינתזה בעזרת שפת הסטנדרט הקורסמעמיקמאודומלמדאת הדרךהיעילהלכתיבתקודVHDL בכדילקבלאתמימושתכןהלוגי המדויק. הקורסמשלב
קורס VHDL for High Performance תיאור הקורס קורסזהמספקאתכלהידע התיאורטיוהמעשילכתיבתקודHDL. VHDL לסינתזה בעזרת שפת הסטנדרט הקורסמעמיקמאודומלמדאת הדרךהיעילהלכתיבתקודVHDL בכדילקבלאתמימושתכןהלוגי המדויק. הקורסמשלב
LAB 1: Combinational Logic: Designing and Simulation of Arithmetic Logic Unit ALU using VHDL
 LAB 1: Combinational Logic: Designing and Simulation of Arithmetic Logic Unit ALU using VHDL Outcome: 1) Identify the operation techniques 2) Demonstrate the use of architecture types 3) Identify and describe
LAB 1: Combinational Logic: Designing and Simulation of Arithmetic Logic Unit ALU using VHDL Outcome: 1) Identify the operation techniques 2) Demonstrate the use of architecture types 3) Identify and describe
TEACHING COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE THROUGH DESIGN PRACTICE. Guoping Wang 1. INTRODUCTION
 TEACHING COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE THROUGH DESIGN PRACTICE Guoping Wang Indiana University Purdue University Fort Wayne, Indiana; Email:wang@engr.ipfw.edu 1. INTRODUCTION Computer Architecture is a common
TEACHING COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE THROUGH DESIGN PRACTICE Guoping Wang Indiana University Purdue University Fort Wayne, Indiana; Email:wang@engr.ipfw.edu 1. INTRODUCTION Computer Architecture is a common
Lab Assignment 1. Developing and Using Testbenches
 Lab Assignment 1 Developing and Using Testbenches Task 1 Develop a testbench in VHDL to test and verify the operation of an ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit), specified using Fig. 1 and Tables 1 and 2. The ALU
Lab Assignment 1 Developing and Using Testbenches Task 1 Develop a testbench in VHDL to test and verify the operation of an ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit), specified using Fig. 1 and Tables 1 and 2. The ALU
Don t expect to be able to write and debug your code during the lab session.
 EECS150 Spring 2002 Lab 4 Verilog Simulation Mapping UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Lab 4 Verilog Simulation Mapping
EECS150 Spring 2002 Lab 4 Verilog Simulation Mapping UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Lab 4 Verilog Simulation Mapping
Hardware Design Environments. Dr. Mahdi Abbasi Computer Engineering Department Bu-Ali Sina University
 Hardware Design Environments Dr. Mahdi Abbasi Computer Engineering Department Bu-Ali Sina University Outline Welcome to COE 405 Digital System Design Design Domains and Levels of Abstractions Synthesis
Hardware Design Environments Dr. Mahdi Abbasi Computer Engineering Department Bu-Ali Sina University Outline Welcome to COE 405 Digital System Design Design Domains and Levels of Abstractions Synthesis
Chapter 2 Basic Logic Circuits and VHDL Description
 Chapter 2 Basic Logic Circuits and VHDL Description We cannot solve our problems with the same thinking we used when we created them. ----- Albert Einstein Like a C or C++ programmer don t apply the logic.
Chapter 2 Basic Logic Circuits and VHDL Description We cannot solve our problems with the same thinking we used when we created them. ----- Albert Einstein Like a C or C++ programmer don t apply the logic.
structure syntax different levels of abstraction
 This and the next lectures are about Verilog HDL, which, together with another language VHDL, are the most popular hardware languages used in industry. Verilog is only a tool; this course is about digital
This and the next lectures are about Verilog HDL, which, together with another language VHDL, are the most popular hardware languages used in industry. Verilog is only a tool; this course is about digital
Here is a list of lecture objectives. They are provided for you to reflect on what you are supposed to learn, rather than an introduction to this
 This and the next lectures are about Verilog HDL, which, together with another language VHDL, are the most popular hardware languages used in industry. Verilog is only a tool; this course is about digital
This and the next lectures are about Verilog HDL, which, together with another language VHDL, are the most popular hardware languages used in industry. Verilog is only a tool; this course is about digital
ENGG3380: Computer Organization and Design Lab5: Microprogrammed Control
 ENGG330: Computer Organization and Design Lab5: Microprogrammed Control School of Engineering, University of Guelph Winter 201 1 Objectives: The objectives of this lab are to: Start Date: Week #5 201 Due
ENGG330: Computer Organization and Design Lab5: Microprogrammed Control School of Engineering, University of Guelph Winter 201 1 Objectives: The objectives of this lab are to: Start Date: Week #5 201 Due
Verilog Design Entry, Synthesis, and Behavioral Simulation
 ------------------------------------------------------------- PURPOSE - This lab will present a brief overview of a typical design flow and then will start to walk you through some typical tasks and familiarize
------------------------------------------------------------- PURPOSE - This lab will present a brief overview of a typical design flow and then will start to walk you through some typical tasks and familiarize
EITF35 - Introduction to Structured VLSI Design (Fall ) 7. Assignment 3 - Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
 EITF35 - Introduction to Structured VLSI Design (Fall 2018 2016 2015) 7 Assignment 3 - Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) v.1.1.0 Introduction In this lab assignment, a simple arithmetic logic unit (ALU) will
EITF35 - Introduction to Structured VLSI Design (Fall 2018 2016 2015) 7 Assignment 3 - Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) v.1.1.0 Introduction In this lab assignment, a simple arithmetic logic unit (ALU) will
Binary Adders. Ripple-Carry Adder
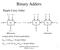 Ripple-Carry Adder Binary Adders x n y n x y x y c n FA c n - c 2 FA c FA c s n MSB position Longest delay (Critical-path delay): d c(n) = n d carry = 2n gate delays d s(n-) = (n-) d carry +d sum = 2n
Ripple-Carry Adder Binary Adders x n y n x y x y c n FA c n - c 2 FA c FA c s n MSB position Longest delay (Critical-path delay): d c(n) = n d carry = 2n gate delays d s(n-) = (n-) d carry +d sum = 2n
4DM4 Lab. #1 A: Introduction to VHDL and FPGAs B: An Unbuffered Crossbar Switch (posted Thursday, Sept 19, 2013)
 1 4DM4 Lab. #1 A: Introduction to VHDL and FPGAs B: An Unbuffered Crossbar Switch (posted Thursday, Sept 19, 2013) Lab #1: ITB Room 157, Thurs. and Fridays, 2:30-5:20, EOW Demos to TA: Thurs, Fri, Sept.
1 4DM4 Lab. #1 A: Introduction to VHDL and FPGAs B: An Unbuffered Crossbar Switch (posted Thursday, Sept 19, 2013) Lab #1: ITB Room 157, Thurs. and Fridays, 2:30-5:20, EOW Demos to TA: Thurs, Fri, Sept.
AES Core Specification. Author: Homer Hsing
 AES Core Specification Author: Homer Hsing homer.hsing@gmail.com Rev. 0.1.1 October 30, 2012 This page has been intentionally left blank. www.opencores.org Rev 0.1.1 ii Revision History Rev. Date Author
AES Core Specification Author: Homer Hsing homer.hsing@gmail.com Rev. 0.1.1 October 30, 2012 This page has been intentionally left blank. www.opencores.org Rev 0.1.1 ii Revision History Rev. Date Author
CSE 141L Computer Architecture Lab Fall Lecture 3
 CSE 141L Computer Architecture Lab Fall 2005 Lecture 3 Pramod V. Argade November 1, 2005 Fall 2005 CSE 141L Course Schedule Lecture # Date Day Lecture Topic Lab Due 1 9/27 Tuesday No Class 2 10/4 Tuesday
CSE 141L Computer Architecture Lab Fall 2005 Lecture 3 Pramod V. Argade November 1, 2005 Fall 2005 CSE 141L Course Schedule Lecture # Date Day Lecture Topic Lab Due 1 9/27 Tuesday No Class 2 10/4 Tuesday
V1 - VHDL Language. FPGA Programming with VHDL and Simulation (through the training Xilinx, Lattice or Actel FPGA are targeted) Objectives
 Formation VHDL Language: FPGA Programming with VHDL and Simulation (through the training Xilinx, Lattice or Actel FPGA are targeted) - Programmation: Logique Programmable V1 - VHDL Language FPGA Programming
Formation VHDL Language: FPGA Programming with VHDL and Simulation (through the training Xilinx, Lattice or Actel FPGA are targeted) - Programmation: Logique Programmable V1 - VHDL Language FPGA Programming
Design of a Simple Pipeline (RTL Coding)
 EE457 Computer Systems Organization Lab #7 Part#3 Subparts #3 and #4 Objective Design of a Simple Pipeline (RTL Coding) To understand and appreciate the improved readability provided by RTL coding (Register
EE457 Computer Systems Organization Lab #7 Part#3 Subparts #3 and #4 Objective Design of a Simple Pipeline (RTL Coding) To understand and appreciate the improved readability provided by RTL coding (Register
Design and Implementation of VLSI 8 Bit Systolic Array Multiplier
 Design and Implementation of VLSI 8 Bit Systolic Array Multiplier Khumanthem Devjit Singh, K. Jyothi MTech student (VLSI & ES), GIET, Rajahmundry, AP, India Associate Professor, Dept. of ECE, GIET, Rajahmundry,
Design and Implementation of VLSI 8 Bit Systolic Array Multiplier Khumanthem Devjit Singh, K. Jyothi MTech student (VLSI & ES), GIET, Rajahmundry, AP, India Associate Professor, Dept. of ECE, GIET, Rajahmundry,
CSE140L: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Lab
 CSE140L: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Lab Tajana Simunic Rosing Source: Vahid, Katz, Culler 1 Announcements & Outline Lab 4 due; demo signup times listed on the cse140l site Check
CSE140L: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Lab Tajana Simunic Rosing Source: Vahid, Katz, Culler 1 Announcements & Outline Lab 4 due; demo signup times listed on the cse140l site Check
isplever Reed-Solomon Encoder User s Guide October 2005 ipug05_03.0
 isplever TM CORE Reed-Solomon Encoder User s Guide October 2005 ipug05_03.0 Introduction Lattice s Reed-Solomon Encoder core provides an ideal solution that meets the needs of today s Reed-Solomon applications.
isplever TM CORE Reed-Solomon Encoder User s Guide October 2005 ipug05_03.0 Introduction Lattice s Reed-Solomon Encoder core provides an ideal solution that meets the needs of today s Reed-Solomon applications.
ARM 64-bit Register File
 ARM 64-bit Register File Introduction: In this class we will develop and simulate a simple, pipelined ARM microprocessor. Labs #1 & #2 build some basic components of the processor, then labs #3 and #4
ARM 64-bit Register File Introduction: In this class we will develop and simulate a simple, pipelined ARM microprocessor. Labs #1 & #2 build some basic components of the processor, then labs #3 and #4
Lecture 7. Standard ICs FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) VHDL (Very-high-speed integrated circuits. Hardware Description Language)
 Standard ICs FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) VHDL (Very-high-speed integrated circuits Hardware Description Language) 1 Standard ICs PLD: Programmable Logic Device CPLD: Complex PLD FPGA: Field Programmable
Standard ICs FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) VHDL (Very-high-speed integrated circuits Hardware Description Language) 1 Standard ICs PLD: Programmable Logic Device CPLD: Complex PLD FPGA: Field Programmable
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 10 Logic Synthesis
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 10 Logic Synthesis September 26, 2002 John Wawrzynek Fall 2002 EECS150 Lec10-synthesis Page 1 Logic Synthesis Verilog and VHDL stated out as simulation languages, but quickly
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 10 Logic Synthesis September 26, 2002 John Wawrzynek Fall 2002 EECS150 Lec10-synthesis Page 1 Logic Synthesis Verilog and VHDL stated out as simulation languages, but quickly
Computer Science 324 Computer Architecture Mount Holyoke College Fall Topic Notes: Data Paths and Microprogramming
 Computer Science 324 Computer Architecture Mount Holyoke College Fall 2007 Topic Notes: Data Paths and Microprogramming We have spent time looking at the MIPS instruction set architecture and building
Computer Science 324 Computer Architecture Mount Holyoke College Fall 2007 Topic Notes: Data Paths and Microprogramming We have spent time looking at the MIPS instruction set architecture and building
INTRODUCTION TO CATAPULT C
 INTRODUCTION TO CATAPULT C Vijay Madisetti, Mohanned Sinnokrot Georgia Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering with adaptations and updates by: Dongwook Lee, Andreas Gerstlauer
INTRODUCTION TO CATAPULT C Vijay Madisetti, Mohanned Sinnokrot Georgia Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering with adaptations and updates by: Dongwook Lee, Andreas Gerstlauer
EKT 422/4 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE. MINI PROJECT : Design of an Arithmetic Logic Unit
 EKT 422/4 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE MINI PROJECT : Design of an Arithmetic Logic Unit Objective Students will design and build a customized Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU). It will perform 16 different operations
EKT 422/4 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE MINI PROJECT : Design of an Arithmetic Logic Unit Objective Students will design and build a customized Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU). It will perform 16 different operations
CSE/ESE 260M Introduction to Digital Logic and Computer Design. Lab 3 Supplement
 CSE/ESE 260M Introduction to Digital Logic and Computer Design Due 11/13/2013 and 11/20/2013 Lab 3 Supplement Recall and follow the General notes from lab 1. You may work in groups of up to 2 (but no more
CSE/ESE 260M Introduction to Digital Logic and Computer Design Due 11/13/2013 and 11/20/2013 Lab 3 Supplement Recall and follow the General notes from lab 1. You may work in groups of up to 2 (but no more
Sequential VHDL. Katarzyna Radecka. DSD COEN 313
 Sequential VHDL Katarzyna Radecka DSD COEN 313 kasiar@ece.concordia.ca Overview Process Sensitivity List Wait Statements If Statements Case Statements Loop Statements Three Styles of VHDL Behavioral Structural
Sequential VHDL Katarzyna Radecka DSD COEN 313 kasiar@ece.concordia.ca Overview Process Sensitivity List Wait Statements If Statements Case Statements Loop Statements Three Styles of VHDL Behavioral Structural
Timing Analysis in Xilinx ISE
 Timing Analysis in Xilinx ISE For each design which is to be implemented, constraints should be defined to get predictable results. The first important class of constraints was already introduced in the
Timing Analysis in Xilinx ISE For each design which is to be implemented, constraints should be defined to get predictable results. The first important class of constraints was already introduced in the
Field Programmable Gate Array
 Field Programmable Gate Array System Arch 27 (Fire Tom Wada) What is FPGA? System Arch 27 (Fire Tom Wada) 2 FPGA Programmable (= reconfigurable) Digital System Component Basic components Combinational
Field Programmable Gate Array System Arch 27 (Fire Tom Wada) What is FPGA? System Arch 27 (Fire Tom Wada) 2 FPGA Programmable (= reconfigurable) Digital System Component Basic components Combinational
Laboratory Memory Components
 Laboratory 3 3. Memory Components 3.1 Objectives Design, implement and test Register File Read only Memories ROMs Random Access Memories RAMs Familiarize the students with Xilinx ISE WebPack Xilinx Synthesis
Laboratory 3 3. Memory Components 3.1 Objectives Design, implement and test Register File Read only Memories ROMs Random Access Memories RAMs Familiarize the students with Xilinx ISE WebPack Xilinx Synthesis
VHDL simulation and synthesis
 VHDL simulation and synthesis How we treat VHDL in this course You will not become an expert in VHDL after taking this course The goal is that you should learn how VHDL can be used for simulation and synthesis
VHDL simulation and synthesis How we treat VHDL in this course You will not become an expert in VHDL after taking this course The goal is that you should learn how VHDL can be used for simulation and synthesis
EN2911X: Reconfigurable Computing Topic 02: Hardware Definition Languages
 EN2911X: Reconfigurable Computing Topic 02: Hardware Definition Languages Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu School of Engineering Brown University Spring 2014 1 Introduction to Verilog
EN2911X: Reconfigurable Computing Topic 02: Hardware Definition Languages Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu School of Engineering Brown University Spring 2014 1 Introduction to Verilog
Final Project: MIPS-like Microprocessor
 Final Project: MIPS-like Microprocessor Objective: The objective of this project is to design, simulate, and implement a simple 32-bit microprocessor with an instruction set that is similar to a MIPS.
Final Project: MIPS-like Microprocessor Objective: The objective of this project is to design, simulate, and implement a simple 32-bit microprocessor with an instruction set that is similar to a MIPS.
ZBT SRAM Controller Reference Design
 ZBT SRAM Controller Reference Design for APEX II Devices December 2001, ver. 1.0 Application Note 183 Introduction As communication systems require more low-latency, high-bandwidth interfaces for peripheral
ZBT SRAM Controller Reference Design for APEX II Devices December 2001, ver. 1.0 Application Note 183 Introduction As communication systems require more low-latency, high-bandwidth interfaces for peripheral
Design of a High-Level Data Link Controller
 ECE 551 Course Project Design of a High-Level Data Link Controller Interim Report - Due Wednesday, November 28, 2001, 4:00 PM Final Report - Due Wednesday, December 12, 2001, 4:00 PM Project Teams and
ECE 551 Course Project Design of a High-Level Data Link Controller Interim Report - Due Wednesday, November 28, 2001, 4:00 PM Final Report - Due Wednesday, December 12, 2001, 4:00 PM Project Teams and
Reed-Solomon Compiler User Guide
 Reed-Solomon Compiler Reed-Solomon Compiler 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com UG-RSCOMPILER-12.0 Feedback Subscribe 2012 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE,
Reed-Solomon Compiler Reed-Solomon Compiler 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com UG-RSCOMPILER-12.0 Feedback Subscribe 2012 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE,
Lab 3 Verilog Simulation Mapping
 University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences 1. Motivation Lab 3 Verilog Simulation Mapping In this lab you will learn how to use
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences 1. Motivation Lab 3 Verilog Simulation Mapping In this lab you will learn how to use
ZedBoard Tutorial. EEL 4720/5721 Reconfigurable Computing
 Introduction: In this lab, you will be learning how to create a custom peripheral in the programmable logic on the ZedBoard and how to communicate with that peripheral from software running on the ARM
Introduction: In this lab, you will be learning how to create a custom peripheral in the programmable logic on the ZedBoard and how to communicate with that peripheral from software running on the ARM
ALTERA FPGA Design Using Verilog
 ALTERA FPGA Design Using Verilog Course Description This course provides all necessary theoretical and practical know-how to design ALTERA FPGA/CPLD using Verilog standard language. The course intention
ALTERA FPGA Design Using Verilog Course Description This course provides all necessary theoretical and practical know-how to design ALTERA FPGA/CPLD using Verilog standard language. The course intention
ALTERA FPGAs Architecture & Design
 ALTERA FPGAs Architecture & Design Course Description This course provides all theoretical and practical know-how to design programmable devices of ALTERA with QUARTUS-II design software. The course combines
ALTERA FPGAs Architecture & Design Course Description This course provides all theoretical and practical know-how to design programmable devices of ALTERA with QUARTUS-II design software. The course combines
90A John Muir Drive Buffalo, New York Tel: Fax:
 Reed Solomon Coding The VOCAL implementation of Reed Solomon (RS) Forward Error Correction (FEC) algorithms is available in several forms. The forms include pure software and software with varying levels
Reed Solomon Coding The VOCAL implementation of Reed Solomon (RS) Forward Error Correction (FEC) algorithms is available in several forms. The forms include pure software and software with varying levels
Lab 3 Sequential Logic for Synthesis. FPGA Design Flow.
 Lab 3 Sequential Logic for Synthesis. FPGA Design Flow. Task 1 Part 1 Develop a VHDL description of a Debouncer specified below. The following diagram shows the interface of the Debouncer. The following
Lab 3 Sequential Logic for Synthesis. FPGA Design Flow. Task 1 Part 1 Develop a VHDL description of a Debouncer specified below. The following diagram shows the interface of the Debouncer. The following
Chapter 4. The Processor
 Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS implementations A simplified
Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS implementations A simplified
Advanced module: Video en/decoder on Virtex 5
 Advanced module: Video en/decoder on Virtex 5 Content 1. Advanced module: Video en/decoder on Virtex 5... 2 1.1. Introduction to the lab environment... 3 1.1.1. Remote control... 4 1.2. Getting started
Advanced module: Video en/decoder on Virtex 5 Content 1. Advanced module: Video en/decoder on Virtex 5... 2 1.1. Introduction to the lab environment... 3 1.1.1. Remote control... 4 1.2. Getting started
VHDL: RTL Synthesis Basics. 1 of 59
 VHDL: RTL Synthesis Basics 1 of 59 Goals To learn the basics of RTL synthesis. To be able to synthesize a digital system, given its VHDL model. To be able to relate VHDL code to its synthesized output.
VHDL: RTL Synthesis Basics 1 of 59 Goals To learn the basics of RTL synthesis. To be able to synthesize a digital system, given its VHDL model. To be able to relate VHDL code to its synthesized output.
High Performance Computing Lecture 26. Matthew Jacob Indian Institute of Science
 High Performance Computing Lecture 26 Matthew Jacob Indian Institute of Science Agenda 1. Program execution: Compilation, Object files, Function call and return, Address space, Data & its representation
High Performance Computing Lecture 26 Matthew Jacob Indian Institute of Science Agenda 1. Program execution: Compilation, Object files, Function call and return, Address space, Data & its representation
How to use the IP generator from Xilinx to instantiate IP cores
 ÁÌ ¹ ÁÒØÖÓ ÙØ ÓÒ ØÓ ËØÖÙØÙÖ ÎÄËÁ Ò ÐÐ ¾¼½ µ ÓÙÖ ÔÖÓ Ø Úº½º¼º¼ 1 Introduction This document describes the course projects provided in EITF35 Introduction to Structured VLSI Design conducted at EIT, LTH.
ÁÌ ¹ ÁÒØÖÓ ÙØ ÓÒ ØÓ ËØÖÙØÙÖ ÎÄËÁ Ò ÐÐ ¾¼½ µ ÓÙÖ ÔÖÓ Ø Úº½º¼º¼ 1 Introduction This document describes the course projects provided in EITF35 Introduction to Structured VLSI Design conducted at EIT, LTH.
Synthesis vs. Compilation Descriptions mapped to hardware Verilog design patterns for best synthesis. Spring 2007 Lec #8 -- HW Synthesis 1
 Verilog Synthesis Synthesis vs. Compilation Descriptions mapped to hardware Verilog design patterns for best synthesis Spring 2007 Lec #8 -- HW Synthesis 1 Logic Synthesis Verilog and VHDL started out
Verilog Synthesis Synthesis vs. Compilation Descriptions mapped to hardware Verilog design patterns for best synthesis Spring 2007 Lec #8 -- HW Synthesis 1 Logic Synthesis Verilog and VHDL started out
CprE 583 Reconfigurable Computing
 Recap Moore FSM Example CprE / ComS 583 Reconfigurable Computing Moore FSM that recognizes sequence 10 0 1 0 1 S0 / 0 S1 / 0 1 S2 / 1 Prof. Joseph Zambreno Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Recap Moore FSM Example CprE / ComS 583 Reconfigurable Computing Moore FSM that recognizes sequence 10 0 1 0 1 S0 / 0 S1 / 0 1 S2 / 1 Prof. Joseph Zambreno Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
EGC221: Digital Logic Lab
 EGC221: Digital Logic Lab Experiment #7 Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) Schematic Implementation Student s Name: Student s Name: Reg. no.: Reg. no.: Semester: Spring 2017 Date: 04 April 2017 Assessment: Assessment
EGC221: Digital Logic Lab Experiment #7 Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) Schematic Implementation Student s Name: Student s Name: Reg. no.: Reg. no.: Semester: Spring 2017 Date: 04 April 2017 Assessment: Assessment
EECS150 Lab Lecture 2 Design Verification
 EECS150 Lab Lecture 2 Design Verification Vincent Lee Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley 9/7/2012 EECS150-Fa12-lab1 1 Lab Logistics T minus three weeks-ish
EECS150 Lab Lecture 2 Design Verification Vincent Lee Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley 9/7/2012 EECS150-Fa12-lab1 1 Lab Logistics T minus three weeks-ish
CSE140L: Components and Design
 CSE140L: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Lab Tajana Simunic Rosing Source: Vahid, Katz, Culler 1 Grade distribution: 70% Labs 35% Lab 4 30% Lab 3 20% Lab 2 15% Lab 1 30% Final exam
CSE140L: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Lab Tajana Simunic Rosing Source: Vahid, Katz, Culler 1 Grade distribution: 70% Labs 35% Lab 4 30% Lab 3 20% Lab 2 15% Lab 1 30% Final exam
Implementation of Low Power High Speed 32 bit ALU using FPGA
 Implementation of Low Power High Speed 32 bit ALU using FPGA J.P. Verma Assistant Professor (Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering) Maaz Arif; Brij Bhushan Choudhary& Nitish Kumar Electronics
Implementation of Low Power High Speed 32 bit ALU using FPGA J.P. Verma Assistant Professor (Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering) Maaz Arif; Brij Bhushan Choudhary& Nitish Kumar Electronics
Reed-Solomon Decoder Group 3
 Reed-Solomon Decoder Group 3 Report 5 Abhinav Agarwal Final Report Grant Elliott 17 th May 2007 S. R. K. Branavan The objective of this project is to design & implement a Reed-Solomon decoder for GF(256)
Reed-Solomon Decoder Group 3 Report 5 Abhinav Agarwal Final Report Grant Elliott 17 th May 2007 S. R. K. Branavan The objective of this project is to design & implement a Reed-Solomon decoder for GF(256)
ENGN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 02: Design/Lab Foundations
 ENGN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 02: Design/Lab Foundations Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu School of Engineering Brown University Spring 2017 1 Topics 1. Programmable logic
ENGN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 02: Design/Lab Foundations Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu School of Engineering Brown University Spring 2017 1 Topics 1. Programmable logic
Logic Synthesis. EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Synthesis
 Logic Synthesis Verilog and VHDL started out as simulation languages, but quickly people wrote programs to automatically convert Verilog code into low-level circuit descriptions (netlists). EECS150 - Digital
Logic Synthesis Verilog and VHDL started out as simulation languages, but quickly people wrote programs to automatically convert Verilog code into low-level circuit descriptions (netlists). EECS150 - Digital
Design of Decode, Control and Associated Datapath Units
 1 Design of Decode, Control and Associated Datapath Units ECE/CS 3710 - Computer Design Lab Lab 3 - Due Date: Thu Oct 18 I. OVERVIEW In the previous lab, you have designed the ALU and hooked it up with
1 Design of Decode, Control and Associated Datapath Units ECE/CS 3710 - Computer Design Lab Lab 3 - Due Date: Thu Oct 18 I. OVERVIEW In the previous lab, you have designed the ALU and hooked it up with
OUTLINE SYSTEM-ON-CHIP DESIGN. GETTING STARTED WITH VHDL September 3, 2018 GAJSKI S Y-CHART (1983) TOP-DOWN DESIGN (1)
 September 3, 2018 GETTING STARTED WITH VHDL 2 Top-down design VHDL history Main elements of VHDL Entities and architectures Signals and processes Data types Configurations Simulator basics The testbench
September 3, 2018 GETTING STARTED WITH VHDL 2 Top-down design VHDL history Main elements of VHDL Entities and architectures Signals and processes Data types Configurations Simulator basics The testbench
1-D Time-Domain Convolution. for (i=0; i < outputsize; i++) { y[i] = 0; for (j=0; j < kernelsize; j++) { y[i] += x[i - j] * h[j]; } }
![1-D Time-Domain Convolution. for (i=0; i < outputsize; i++) { y[i] = 0; for (j=0; j < kernelsize; j++) { y[i] += x[i - j] * h[j]; } } 1-D Time-Domain Convolution. for (i=0; i < outputsize; i++) { y[i] = 0; for (j=0; j < kernelsize; j++) { y[i] += x[i - j] * h[j]; } }](/thumbs/81/82997720.jpg) Introduction: Convolution is a common operation in digital signal processing. In this project, you will be creating a custom circuit implemented on the Nallatech board that exploits a significant amount
Introduction: Convolution is a common operation in digital signal processing. In this project, you will be creating a custom circuit implemented on the Nallatech board that exploits a significant amount
FPGA Design Challenge :Techkriti 14 Digital Design using Verilog Part 1
 FPGA Design Challenge :Techkriti 14 Digital Design using Verilog Part 1 Anurag Dwivedi Digital Design : Bottom Up Approach Basic Block - Gates Digital Design : Bottom Up Approach Gates -> Flip Flops Digital
FPGA Design Challenge :Techkriti 14 Digital Design using Verilog Part 1 Anurag Dwivedi Digital Design : Bottom Up Approach Basic Block - Gates Digital Design : Bottom Up Approach Gates -> Flip Flops Digital
Analysis of the MIPS 32-bit, pipelined processor using synthesized VHDL
 Analysis of the MIPS 32-bit, pipelined processor using synthesized VHDL Aaron Arthurs (ajarthu@uark.edu), Linh Ngo (lngo@uark.edu) Department of Computer Science and Engineering, University of Arkansas
Analysis of the MIPS 32-bit, pipelined processor using synthesized VHDL Aaron Arthurs (ajarthu@uark.edu), Linh Ngo (lngo@uark.edu) Department of Computer Science and Engineering, University of Arkansas
Circuit Design and Simulation with VHDL 2nd edition Volnei A. Pedroni MIT Press, 2010 Book web:
 Circuit Design and Simulation with VHDL 2nd edition Volnei A. Pedroni MIT Press, 2010 Book web: www.vhdl.us Appendix C Xilinx ISE Tutorial (ISE 11.1) This tutorial is based on ISE 11.1 WebPack (free at
Circuit Design and Simulation with VHDL 2nd edition Volnei A. Pedroni MIT Press, 2010 Book web: www.vhdl.us Appendix C Xilinx ISE Tutorial (ISE 11.1) This tutorial is based on ISE 11.1 WebPack (free at
DIGITAL VS. ANALOG SIGNAL PROCESSING Digital signal processing (DSP) characterized by: OUTLINE APPLICATIONS OF DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING
 1 DSP applications DSP platforms The synthesis problem Models of computation OUTLINE 2 DIGITAL VS. ANALOG SIGNAL PROCESSING Digital signal processing (DSP) characterized by: Time-discrete representation
1 DSP applications DSP platforms The synthesis problem Models of computation OUTLINE 2 DIGITAL VS. ANALOG SIGNAL PROCESSING Digital signal processing (DSP) characterized by: Time-discrete representation
White Paper. Floating-Point FFT Processor (IEEE 754 Single Precision) Radix 2 Core. Introduction. Parameters & Ports
 White Paper Introduction Floating-Point FFT Processor (IEEE 754 Single Precision) Radix 2 Core The floating-point fast fourier transform (FFT) processor calculates FFTs with IEEE 754 single precision (1
White Paper Introduction Floating-Point FFT Processor (IEEE 754 Single Precision) Radix 2 Core The floating-point fast fourier transform (FFT) processor calculates FFTs with IEEE 754 single precision (1
EEL 4783: HDL in Digital System Design
 EEL 4783: HDL in Digital System Design Lecture 15: Logic Synthesis with Verilog Prof. Mingjie Lin 1 Verilog Synthesis Synthesis vs. Compilation Descriptions mapped to hardware Verilog design patterns for
EEL 4783: HDL in Digital System Design Lecture 15: Logic Synthesis with Verilog Prof. Mingjie Lin 1 Verilog Synthesis Synthesis vs. Compilation Descriptions mapped to hardware Verilog design patterns for
1 Design Process HOME CONTENTS INDEX. For further assistance, or call your local support center
 1 Design Process VHDL Compiler, a member of the Synopsys HDL Compiler family, translates and optimizes a VHDL description to an internal gate-level equivalent. This representation is then compiled with
1 Design Process VHDL Compiler, a member of the Synopsys HDL Compiler family, translates and optimizes a VHDL description to an internal gate-level equivalent. This representation is then compiled with
International Journal of Innovations in Engineering and Technology (IJIET)
 RTL Design and Implementation of Erasure Code for RAID system Chethan.K 1, Dr.Srividya.P 2, Mr.Sivashanmugam Krishnan 3 1 PG Student, Department Of ECE, R. V. College Engineering, Bangalore, India. 2 Associate
RTL Design and Implementation of Erasure Code for RAID system Chethan.K 1, Dr.Srividya.P 2, Mr.Sivashanmugam Krishnan 3 1 PG Student, Department Of ECE, R. V. College Engineering, Bangalore, India. 2 Associate
Control and Datapath 8
 Control and Datapath 8 Engineering attempts to develop design methods that break a problem up into separate steps to simplify the design and increase the likelihood of a correct solution. Digital system
Control and Datapath 8 Engineering attempts to develop design methods that break a problem up into separate steps to simplify the design and increase the likelihood of a correct solution. Digital system
EITF35: Introduction to Structured VLSI Design
 EITF35: Introduction to Structured VLSI Design Part 1.2.2: VHDL-1 Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline VHDL Background Basic VHDL Component An example FSM Design with VHDL Simulation & TestBench 2
EITF35: Introduction to Structured VLSI Design Part 1.2.2: VHDL-1 Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline VHDL Background Basic VHDL Component An example FSM Design with VHDL Simulation & TestBench 2
Novel Design of Dual Core RISC Architecture Implementation
 Journal From the SelectedWorks of Kirat Pal Singh Spring May 18, 2015 Novel Design of Dual Core RISC Architecture Implementation Akshatha Rai K, VTU University, MITE, Moodbidri, Karnataka Basavaraj H J,
Journal From the SelectedWorks of Kirat Pal Singh Spring May 18, 2015 Novel Design of Dual Core RISC Architecture Implementation Akshatha Rai K, VTU University, MITE, Moodbidri, Karnataka Basavaraj H J,
Lab Assignment 2. Implementing Combinational and Sequential Logic in VHDL
 Lab Assignment 2 Implementing Combinational and Sequential Logic in VHDL Task 1 Draw a detailed block diagram of the ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit), specified using Fig. 1 and Tables 1 and 2. Then develop
Lab Assignment 2 Implementing Combinational and Sequential Logic in VHDL Task 1 Draw a detailed block diagram of the ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit), specified using Fig. 1 and Tables 1 and 2. Then develop
An easy to read reference is:
 1. Synopsis: Timing Analysis and Timing Constraints The objective of this lab is to make you familiar with two critical reports produced by the Xilinx ISE during your design synthesis and implementation.
1. Synopsis: Timing Analysis and Timing Constraints The objective of this lab is to make you familiar with two critical reports produced by the Xilinx ISE during your design synthesis and implementation.
Tiny Tate Bilinear Pairing Core Specification. Author: Homer Hsing
 Tiny Tate Bilinear Pairing Core Specification Author: Homer Hsing homer.hsing@gmail.com Rev. 0.1 May 3, 2012 This page has been intentionally left blank. www.opencores.org Rev 0.1 ii Rev. Date Author Description
Tiny Tate Bilinear Pairing Core Specification Author: Homer Hsing homer.hsing@gmail.com Rev. 0.1 May 3, 2012 This page has been intentionally left blank. www.opencores.org Rev 0.1 ii Rev. Date Author Description
EITF35 - Introduction to Structured VLSI Design (Fall 2017) Course projects
 1 EITF35 - Introduction to Structured VLSI Design (Fall 2017) Course projects v.1.0.0 1 Introduction This document describes the course projects provided in EITF35 Introduction to Structured VLSI Design
1 EITF35 - Introduction to Structured VLSI Design (Fall 2017) Course projects v.1.0.0 1 Introduction This document describes the course projects provided in EITF35 Introduction to Structured VLSI Design
In this lecture, we will focus on two very important digital building blocks: counters which can either count events or keep time information, and
 In this lecture, we will focus on two very important digital building blocks: counters which can either count events or keep time information, and shift registers, which is most useful in conversion between
In this lecture, we will focus on two very important digital building blocks: counters which can either count events or keep time information, and shift registers, which is most useful in conversion between
ENGN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 02: Lab Foundations
 ENGN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 02: Lab Foundations Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu School of Engineering Brown University Spring 2014 1 Topics 1. Programmable logic 2.
ENGN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 02: Lab Foundations Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu School of Engineering Brown University Spring 2014 1 Topics 1. Programmable logic 2.
Lab #1. Topics. 3. Introduction to Verilog 2/8/ Programmable logic. 2. Design Flow. 3. Verilog --- A Hardware Description Language
 Lab #1 Lecture 8, 9, &10: FPGA Dataflow and Verilog Modeling February 9, 11, 13, 2015 Prof R Iris Bahar Lab #1 is posted on the webpage wwwbrownedu/departments/engineering/courses/engn1640 Note for problem
Lab #1 Lecture 8, 9, &10: FPGA Dataflow and Verilog Modeling February 9, 11, 13, 2015 Prof R Iris Bahar Lab #1 is posted on the webpage wwwbrownedu/departments/engineering/courses/engn1640 Note for problem
a, b sum module add32 sum vector bus sum[31:0] sum[0] sum[31]. sum[7:0] sum sum overflow module add32_carry assign
![a, b sum module add32 sum vector bus sum[31:0] sum[0] sum[31]. sum[7:0] sum sum overflow module add32_carry assign a, b sum module add32 sum vector bus sum[31:0] sum[0] sum[31]. sum[7:0] sum sum overflow module add32_carry assign](/thumbs/91/106466219.jpg) I hope you have completed Part 1 of the Experiment. This lecture leads you to Part 2 of the experiment and hopefully helps you with your progress to Part 2. It covers a number of topics: 1. How do we specify
I hope you have completed Part 1 of the Experiment. This lecture leads you to Part 2 of the experiment and hopefully helps you with your progress to Part 2. It covers a number of topics: 1. How do we specify
Lecture 9. VHDL, part IV. Hierarchical and parameterized design. Section 1 HIERARCHICAL DESIGN
 Lecture 9 VHDL, part IV Hierarchical and parameterized design Section 1 HIERARCHICAL DESIGN 2 1 Dealing with Large Digital System Design 1. Apply hierarchy to the design At the highest level use larger
Lecture 9 VHDL, part IV Hierarchical and parameterized design Section 1 HIERARCHICAL DESIGN 2 1 Dealing with Large Digital System Design 1. Apply hierarchy to the design At the highest level use larger
A Tutorial Introduction 1
 Preface From the Old to the New Acknowledgments xv xvii xxi 1 Verilog A Tutorial Introduction 1 Getting Started A Structural Description Simulating the binarytoeseg Driver Creating Ports For the Module
Preface From the Old to the New Acknowledgments xv xvii xxi 1 Verilog A Tutorial Introduction 1 Getting Started A Structural Description Simulating the binarytoeseg Driver Creating Ports For the Module
: : (91-44) (Office) (91-44) (Residence)
 Course: VLSI Circuits (Video Course) Faculty Coordinator(s) : Prof. S. Srinivasan Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai 600036 Email Telephone : srinis@iitm.ac.in,
Course: VLSI Circuits (Video Course) Faculty Coordinator(s) : Prof. S. Srinivasan Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai 600036 Email Telephone : srinis@iitm.ac.in,
Introduction to VHDL #3
 ECE 322 Digital Design with VHDL Introduction to VHDL #3 Lecture 7 & 8 VHDL Modeling Styles VHDL Modeling Styles Dataflow Concurrent statements Structural Components and interconnects Behavioral (sequential)
ECE 322 Digital Design with VHDL Introduction to VHDL #3 Lecture 7 & 8 VHDL Modeling Styles VHDL Modeling Styles Dataflow Concurrent statements Structural Components and interconnects Behavioral (sequential)
Lab 6 : Introduction to Verilog
 Lab 6 : Introduction to Verilog Name: Sign the following statement: On my honor, as an Aggie, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this academic work 1 Objective The main objective of
Lab 6 : Introduction to Verilog Name: Sign the following statement: On my honor, as an Aggie, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this academic work 1 Objective The main objective of
CAD4 The ALU Fall 2009 Assignment. Description
 CAD4 The ALU Fall 2009 Assignment To design a 16-bit ALU which will be used in the datapath of the microprocessor. This ALU must support two s complement arithmetic and the instructions in the baseline
CAD4 The ALU Fall 2009 Assignment To design a 16-bit ALU which will be used in the datapath of the microprocessor. This ALU must support two s complement arithmetic and the instructions in the baseline
A Brief Introduction to Verilog Hardware Definition Language (HDL)
 www.realdigital.org A Brief Introduction to Verilog Hardware Definition Language (HDL) Forward Verilog is a Hardware Description language (HDL) that is used to define the structure and/or behavior of digital
www.realdigital.org A Brief Introduction to Verilog Hardware Definition Language (HDL) Forward Verilog is a Hardware Description language (HDL) that is used to define the structure and/or behavior of digital
