The assignments will help you learn Verilog as a Hardware Description Language and how hardware circuits can be developed using Verilog and FPGA.
|
|
|
- Emil Dennis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 General Instructions The assignments will help you learn Verilog as a Hardware Description Language and how hardware circuits can be developed using Verilog and FPGA. You have to come to the lab during your lab session to carry out the experiments using the FPGA board. You are expected to write the Verilog modules before coming to the lab. Your TAs will check your results and grade your work during the lab session. You have to submit the code artifacts through CANVAS. Only one member of each group has to submit the assignment. Please Make sure that there is no duplicate submission from your group. The maximum possible deadline extension is 2 days. For the extension for one day after the deadline, there will be a penalty of 10% of the grade. For the second day extension, the penalty is another 20% of the grade. No assignment submission will be accepted after 48 hours of the deadline. Sharing of the solution outside the group is strictly prohibited. groups will get 0 in the assignment. If found guilty, both the involved Each group member should equally contribute to every assignment and should fully understand the submitted solution. The TAs may ask any group member to explain the solution.
2 Resources Xilinx Spartan 3E FPGA Starter Board You will use Xilinx Spartan 3E FPGA Starter Board for your Verilog Assignments. Here is the manual for the FPGA Kit: and kits/ug230.pdf Xilinx ISE WebPACK Design Software You can use Xilinx ISE WebPACK Design Software for writing and simulating your Verilog programs. The software can be downloaded from the following location: Here are some resources to install the software: Verilog Textbook Pong P. Chu. FPGA Prototyping by Verilog Examples: Xilinx Spartan-3 Version, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., marcondes/netfpga/fpgaprototypingbyverilogexamples.pdf Page 2 of 7
3 Assignmnet 1 (10 points) Lab Session: (during the week of March 06, March 10, 2017) Deadline for submission: 11:59 pm on March 10, 2017 Objectives: To learn how to use Xilinx ISE WebPACK design software to develop a Verilog module for a hardware circuit, simulate and test it, and program the FPGA chip to implement the hardware. To get familiar with the input-output mechanisms of the Xilinx Spartan 3E FPGA kit: slide switches, push-button switches, LEDs and LCD Screen. Problems: 1. Blinking a LED (2 points) Follow the instructions in the following tutorial to blink a LED in your FPGA Board. This tutorial illustrates how to use the ISE Webpack design software and describes all the steps to develop a hardware circuit using FPGA. (1) Xilinx Spartan 3E FPGA board Manual (Chapter 2, Chapter 3) 2. Printing in the LCD display (3 points) Write a Verilog module and a constraint file to display Computer Organization in the LCD screen of your FPGA Fit. The LCD display has two rows. The word Computer should be displayed in the first row and the word Organization should be displayed in the second row. (1) The following Quora post discusses how to display Hello World on the LCD display of the Spartan 3E FPGA board: 3E-XC3S400-FPGA-kit (2) Xilinx Spartan 3E FPGA board Manual (Chapter 5) 3a. Comparing two 2-bits binary number (2 points) (a) Write a Verilog module eq1 to compare two bits. The output should be 1 if the two bis are equal. Write a Verilog module eq2 to compare two 2-bit binary numbers. The program should return 1 if the two numbers are equal. Use the module eq1 to implement the module eq2. (c) Write a constraint file to use the 4 sliding switches to input two 2-bit binary numbers. Use one of the LEDs to indicate the output. (d) Synthesize and implement your Verilog module to generate a configuration file and download the configuration file to the FPGA chip. Move the sliding switches to on and off positions to generate different 2-bit binary numbers as input and check the LED output to ensure that your circuit is correct. (1) Xilinx Spartan 3E FPGA board Manual (Chapter 2) (2) Your Verilog Textbook (Chapter 2) 3b. Comparing two 4-bits binary number (3 points) (a) Write a Verilog module eq4 to compare two 4-bit binary numbers. The program should return 1 if the two numbers are equal. Use the module eq2 to implement the module eq4. Page 3 of 7
4 (c) The Xilinx Spartan 3E FPGA board has only four sliding switches. That allows you to input only one 4-bit binary number. To input more data you use push-button switches. You can position the slide switches and press a push button to enter a binary number. You repeat the process with another push button to enter the second number. Update the Verilog module to incorporate the input mechanism using slide switches and push-button switches. (d) Write a constraint file to use 4 sliding switches and two push buttons to input the two 4-bit binary numbers. Use one of the LEDs to indicate the output. configuration file to the FPGA kit. Move the sliding switches to on or off position to generate different 4-bit binary numbers. Use the two push buttons to capture the numbers. Check the LED output to ensure that your circuit is correct. (1) Xilinx Spartan 3E FPGA board Manual (Chapter 2) (2) Your Verilog Textbook (Chapter 4, Section for an example of using slide switch and push-button switch together to input multiple binary numbers) Page 4 of 7
5 Assignmnet 2 (10 points) Lab Session: (during the week of March 27, March 31, 2017) Deadline for submission: 11:59 pm on March 31, 2017 Problems: 1. Adding two 4-bits binary number ( = 6 points) (a) Write a Verilog module add4 to add two 4-bit binary numbers. The program should return the sum as a four bit number and the carry bit. (c) The Xilinx Spartan 3E FPGA board has only four sliding switches. That allows you to input only one 4-bit binary number. To input more data you use push-button switches. You can position the slide switches and press a push button to enter a binary number. You repeat the process with another push button to enter the second number. Update the Verilog module to incorporate the input mechanism using slide switches and push-button switches. (d) Write a constraint file to use 4 sliding switches and two push buttons to input the two 4-bit binary numbers. Display the sum as a hexadecimal character on the LCD Display. Use one of the LEDs to indicate the carry output. configuration file to the FPGA kit. Move the sliding switches to on or off position to generate different 4-bit binary numbers. Use the two push buttons to capture the numbers. Check the LCD and LED output to ensure that your circuit is correct. 2. Counter with set and reset ( = 4 points) (a) Write a Verilog module that counts from 0 to 15 repetitively. The counting should happen in every second. The module should have three inputs: (i) init, a four bit number that provides the value from which the counting gets started, (ii) set, a one bit input that sets the counter to start the counting from the number provided in init, and (iii) reset, a one bit input that makes the counting start from 0. The module has one four bit output out that outputs the current value of the counter. You should use state machine in designing your module. (b) Write a constraint file to include clock constraints, 4 sliding switches to input the init value, two push buttons to generate the set and reset inputs, and 4 LEDs to display the output value. (c) Synthesize and implement your Verilog module to generate a configuration file and download the configuration file to the FPGA kit. Check if the LED outputs are changing as desired. Now press the button corresponding to the reset input and see if the counting starts from 0. Next, set the slide switches to a desired value, press the button corresponding to the set input and check if the counting starts from the value provided by the sliding switches. Page 5 of 7
6 Assignmnet 3 (20 points) Lab Session: (during the week of April 3, April 7, 2017 and April 10, April 14, 2017) Deadline for submission: 11:59 pm on April 14, 2017 Objective: In this lab assignment, you will design a simple processor involving an ALU and a register file. Problems: 1. 4-bit ALU ( = 7 points) (a) Write a Verilog module alu4 to perform arithmetic and logical operations on two 4-bit binary numbers. The ALU should support the following operations: and, or, add and sub. It should produce the result of the arithmetic or logical operation as output. Moreover, it should also output three flags CF, ZF and SF to indicate if there is carry generated, if the result is zero and if the result is negative, respectively. For arithmetic operations, assume that the inputs are signed numbers. (c) Update the Verilog module to incorporate the input mechanism using slide switches and push-button switches. Three different push buttons can be used to input the operation (using two slide switches) and the two operands (using four slide switches in each case). (d) Write a constraint file to use sliding switches and three push buttons to input the two bit opcode and two 4-bit binary numbers and display the result as a hexadecimal character on the LCD Display. Use three of the LEDs to indicate the CF, ZF and SF flags. configuration file to the FPGA kit. Move the sliding switches to on or off position to generate different 2-bit numbers for operations and 4-bit binary numbers for operands. Use the push buttons to capture the inputs. Check the LCD screen and LED output to ensure that your ALU is operating correctly. 2. Register File ( = 6 points) (a) Write a Verilog module regfile to implement a register file that contains 16 registers each of size 4 bits. The register file module should have six inputs: the clock, two read registers (RR1 and RR2), one write register (WR), one write data (WData) port and one write enable (WEnable) port. The module should have two output ports providing the data stored in the two registers given in the two read register input ports. The data provided in the write data port is written to the write register on the positive edge of the clock when the write enable signal is on. (b) Update the Verilog module to incorporate the input mechanism using slide switches and push-buttons. The four 4-bit inputs RR1, RR2, WR and WData can be obtained using the four slide switches and four push buttons, one for each input. The write enable signal can be generated using the Rotary Push-Button Switch (See page 17 of Spartan-3E FPGA Starter Kit Board User Guide for details). (c) Write a constraint file to use the sliding switches and four push buttons to input the 4-bit read registers, 4-bit write register and the 4-bit write data. Display the results in two read data ports using eight LEDs. (d) Synthesize and implement your Verilog module to generate a configuration file and download the configuration file to the FPGA kit. Move the sliding switches to on or off position to generate different 4-bit binary numbers and use the push buttons to capture the register numbers and write data. Check the LED outputs to ensure that the data are written to the registers and read from the registers correctly. 3. A simple processor ( = 7 points) (a) Write a Verilog module processor that combines modules alu4 and regfile to design a simple processor. The processor has two modes: In one mode, it accepts data to be written to a given register in the register file and in another mode it performs arithmetic and logical operations on the values in the two registers given by the user as input. The processor accepts a 3-bit opcode, two 4-bits inputs and a one bit input used as register write enable signal. If the opcode is 100 then the processor works in the register write mode. In that case one of the 4-bit Page 6 of 7
7 inputs works as the destination register to be written, and the other 4-bit input is the data to be written to that register. If the opcode is 000, 001, 010 or 011, the processor should perform and, or, add and subtract operations respectively with the help of the arithmetic logic unit. In this case the two 4-bit inputs provide the two registers that contain the operands. In this mode, the processor should output the result and status flags obtained from ALU. The processor should use an invalid bit as output to indicate the validity of the given opcode. For example, if the input opcode is 110, then the value of invalid bit should be 1. (b) Update the Verilog module to incorporate the input mechanism using the slide switches and push buttons. The 3-bit opcode and the two 4-bit inputs should be obtained by using the slide switches and three different push buttons. The fourth push button can be used to generate the register write enable signal. (c) Write a constraint file to use sliding switches and three push buttons to input the 3-bit opcode and two 4-bit binary numbers, and a push button to input the register write enable signal. Include constraints to display the result of the ALU operation as a hexadecimal character on the LCD Display and use three of the LEDs to indicate the CF, ZF and SF flags. configuration file to the FPGA kit. First use the opcode 100 to store some values in a few registers. Then try different opcodes for the ALU operations and check the LCD screen and LED output to ensure that your ALU is operating correctly. Page 7 of 7
General Instructions. You can use QtSpim simulator to work on these assignments.
 General Instructions You can use QtSpim simulator to work on these assignments. Only one member of each group has to submit the assignment. Please Make sure that there is no duplicate submission from your
General Instructions You can use QtSpim simulator to work on these assignments. Only one member of each group has to submit the assignment. Please Make sure that there is no duplicate submission from your
ELCT501 Digital System Design Winter Tutorial #11 FPGA Complete Design Flow with LCD Example
 ELCT501 Digital System Design Winter 2014 Tutorial #11 FPGA Complete Design Flow with LCD Example Design a 4-bit Up-Counter with Enable Design Flow Steps: 1. Write VHDL code for the counter. 2. Test the
ELCT501 Digital System Design Winter 2014 Tutorial #11 FPGA Complete Design Flow with LCD Example Design a 4-bit Up-Counter with Enable Design Flow Steps: 1. Write VHDL code for the counter. 2. Test the
ECE 491 Laboratory 1 Introducing FPGA Design with Verilog September 6, 2004
 Goals ECE 491 Laboratory 1 Introducing FPGA Design with Verilog September 6, 2004 1. To review the use of Verilog for combinational logic design. 2. To become familiar with using the Xilinx ISE software
Goals ECE 491 Laboratory 1 Introducing FPGA Design with Verilog September 6, 2004 1. To review the use of Verilog for combinational logic design. 2. To become familiar with using the Xilinx ISE software
EE 1315 DIGITAL LOGIC LAB EE Dept, UMD
 EE 1315 DIGITAL LOGIC LAB EE Dept, UMD EXPERIMENT # 1: Logic building blocks The main objective of this experiment is to let you familiarize with the lab equipment and learn about the operation of the
EE 1315 DIGITAL LOGIC LAB EE Dept, UMD EXPERIMENT # 1: Logic building blocks The main objective of this experiment is to let you familiarize with the lab equipment and learn about the operation of the
Digital Design Using Verilog and FPGAs An Experiment Manual. Chirag Sangani Abhishek Kasina
 Digital Design Using Verilog and FPGAs An Experiment Manual Chirag Sangani Abhishek Kasina ii Contents I Combinatorial and Sequential Circuits 1 1 Seven-Segment Decoder 3 1.1 Concept.........................................
Digital Design Using Verilog and FPGAs An Experiment Manual Chirag Sangani Abhishek Kasina ii Contents I Combinatorial and Sequential Circuits 1 1 Seven-Segment Decoder 3 1.1 Concept.........................................
EECE.2160: ECE Application Programming
 Spring 2018 Programming Assignment #10: Instruction Decoding and File I/O Due Wednesday, 5/9/18, 11:59:59 PM (Extra credit ( 4 pts on final average), no late submissions or resubmissions) 1. Introduction
Spring 2018 Programming Assignment #10: Instruction Decoding and File I/O Due Wednesday, 5/9/18, 11:59:59 PM (Extra credit ( 4 pts on final average), no late submissions or resubmissions) 1. Introduction
TEACHING COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE THROUGH DESIGN PRACTICE. Guoping Wang 1. INTRODUCTION
 TEACHING COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE THROUGH DESIGN PRACTICE Guoping Wang Indiana University Purdue University Fort Wayne, Indiana; Email:wang@engr.ipfw.edu 1. INTRODUCTION Computer Architecture is a common
TEACHING COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE THROUGH DESIGN PRACTICE Guoping Wang Indiana University Purdue University Fort Wayne, Indiana; Email:wang@engr.ipfw.edu 1. INTRODUCTION Computer Architecture is a common
CSE 140L Spring 2010 Bonus Final
 CSE 140L Spring 2010 Bonus Final Logistics for Bonus Final: This final should be done in individually. Use Xilinx tools version 10.1. What is due: - Report: o Submit a single report in.pdf form via email
CSE 140L Spring 2010 Bonus Final Logistics for Bonus Final: This final should be done in individually. Use Xilinx tools version 10.1. What is due: - Report: o Submit a single report in.pdf form via email
CSE 141L Computer Architecture Lab Fall Lecture 3
 CSE 141L Computer Architecture Lab Fall 2005 Lecture 3 Pramod V. Argade November 1, 2005 Fall 2005 CSE 141L Course Schedule Lecture # Date Day Lecture Topic Lab Due 1 9/27 Tuesday No Class 2 10/4 Tuesday
CSE 141L Computer Architecture Lab Fall 2005 Lecture 3 Pramod V. Argade November 1, 2005 Fall 2005 CSE 141L Course Schedule Lecture # Date Day Lecture Topic Lab Due 1 9/27 Tuesday No Class 2 10/4 Tuesday
LAB 9 The Performance of MIPS
 LAB 9 The Performance of MIPS Goals Learn how the performance of the processor is determined. Improve the processor performance by adding new instructions. To Do Determine the speed of the processor in
LAB 9 The Performance of MIPS Goals Learn how the performance of the processor is determined. Improve the processor performance by adding new instructions. To Do Determine the speed of the processor in
CS/EE Prerequsites. Hardware Infrastructure. Class Goal CS/EE Computer Design Lab. Computer Design Lab Fall 2010
 CS/EE 3710 Computer Design Lab Fall 2010 CS/EE 3710 Computer Design Lab T Th 3:40pm-5:00pm Lectures in WEB 110, Labs in MEB 3133 (DSL) Instructor: Erik Brunvand MEB 3142 Office Hours: After class, when
CS/EE 3710 Computer Design Lab Fall 2010 CS/EE 3710 Computer Design Lab T Th 3:40pm-5:00pm Lectures in WEB 110, Labs in MEB 3133 (DSL) Instructor: Erik Brunvand MEB 3142 Office Hours: After class, when
CS/EE Computer Design Lab Fall 2010 CS/EE T Th 3:40pm-5:00pm Lectures in WEB 110, Labs in MEB 3133 (DSL) Instructor: Erik Brunvand
 CS/EE 3710 Computer Design Lab Fall 2010 CS/EE 3710 Computer Design Lab T Th 3:40pm-5:00pm Lectures in WEB 110, Labs in MEB 3133 (DSL) Instructor: Erik Brunvand MEB 3142 Office Hours: After class, when
CS/EE 3710 Computer Design Lab Fall 2010 CS/EE 3710 Computer Design Lab T Th 3:40pm-5:00pm Lectures in WEB 110, Labs in MEB 3133 (DSL) Instructor: Erik Brunvand MEB 3142 Office Hours: After class, when
University of Hawaii EE 361L. Getting Started with Spartan 3E Digilent Basys2 Board. Lab 4.1
 University of Hawaii EE 361L Getting Started with Spartan 3E Digilent Basys2 Board Lab 4.1 I. Test Basys2 Board Attach the Basys2 board to the PC or laptop with the USB connector. Make sure the blue jumper
University of Hawaii EE 361L Getting Started with Spartan 3E Digilent Basys2 Board Lab 4.1 I. Test Basys2 Board Attach the Basys2 board to the PC or laptop with the USB connector. Make sure the blue jumper
Design of Digital Circuits
 Design of Digital Circuits Lecture 3: Introduction to the Labs and FPGAs Prof. Onur Mutlu (Lecture by Hasan Hassan) ETH Zurich Spring 2018 1 March 2018 1 Lab Sessions Where? HG E 19, HG E 26.1, HG E 26.3,
Design of Digital Circuits Lecture 3: Introduction to the Labs and FPGAs Prof. Onur Mutlu (Lecture by Hasan Hassan) ETH Zurich Spring 2018 1 March 2018 1 Lab Sessions Where? HG E 19, HG E 26.1, HG E 26.3,
Lab Assignment 1. Developing and Using Testbenches
 Lab Assignment 1 Developing and Using Testbenches Task 1 Develop a testbench in VHDL to test and verify the operation of an ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit), specified using Fig. 1 and Tables 1 and 2. The ALU
Lab Assignment 1 Developing and Using Testbenches Task 1 Develop a testbench in VHDL to test and verify the operation of an ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit), specified using Fig. 1 and Tables 1 and 2. The ALU
CSE/ESE 260M Introduction to Digital Logic and Computer Design. Lab 3 Supplement
 CSE/ESE 260M Introduction to Digital Logic and Computer Design Due 11/13/2013 and 11/20/2013 Lab 3 Supplement Recall and follow the General notes from lab 1. You may work in groups of up to 2 (but no more
CSE/ESE 260M Introduction to Digital Logic and Computer Design Due 11/13/2013 and 11/20/2013 Lab 3 Supplement Recall and follow the General notes from lab 1. You may work in groups of up to 2 (but no more
ECE 473 Computer Architecture and Organization Project: Design of a Five Stage Pipelined MIPS-like Processor Project Team TWO Objectives
 ECE 473 Computer Architecture and Organization Project: Design of a Five Stage Pipelined MIPS-like Processor Due: December 8, 2011 Instructor: Dr. Yifeng Zhu Project Team This is a team project. All teams
ECE 473 Computer Architecture and Organization Project: Design of a Five Stage Pipelined MIPS-like Processor Due: December 8, 2011 Instructor: Dr. Yifeng Zhu Project Team This is a team project. All teams
ECE 4305 Computer Architecture Lab #1
 ECE 4305 Computer Architecture Lab #1 The objective of this lab is for students to familiarize with the FPGA prototyping system board (Nexys-2) and the Xilinx software development environment that will
ECE 4305 Computer Architecture Lab #1 The objective of this lab is for students to familiarize with the FPGA prototyping system board (Nexys-2) and the Xilinx software development environment that will
DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF MOD-6 SYNCHRONOUS COUNTER USING VHDL
 Arid Zone Journal of Engineering, Technology and Environment. August, 2013; Vol. 9, 17-26 DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF MOD-6 SYNCHRONOUS COUNTER USING VHDL Dibal, P.Y. (Department of Computer Engineering,
Arid Zone Journal of Engineering, Technology and Environment. August, 2013; Vol. 9, 17-26 DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF MOD-6 SYNCHRONOUS COUNTER USING VHDL Dibal, P.Y. (Department of Computer Engineering,
MICROPROCESSOR B.Tech. th ECE
 MICROPROCESSOR B.Tech. th ECE Submitted by: Er. Amita Sharma Dept. of ECE 11/24/2014 2 Microprocessor Architecture The microprocessor can be programmed to perform functions on given data by writing specific
MICROPROCESSOR B.Tech. th ECE Submitted by: Er. Amita Sharma Dept. of ECE 11/24/2014 2 Microprocessor Architecture The microprocessor can be programmed to perform functions on given data by writing specific
Circuit design with configurable devices (FPGA)
 1 Material Circuit design with configurable devices (FPGA) Computer with Xilinx's ISE software installed. Digilent's Basys2 prototype board and documentation. Sample design files (lab kit). Files and documents
1 Material Circuit design with configurable devices (FPGA) Computer with Xilinx's ISE software installed. Digilent's Basys2 prototype board and documentation. Sample design files (lab kit). Files and documents
Lab 6: Intro to FPGAs
 Lab 6: Intro to FPGAs UC Davis Physics 116B Rev 2/22/2018 There s a saying when dealing with complex electronic systems: If you can make the LED blink, you re 90% of the way there., so in this lab you
Lab 6: Intro to FPGAs UC Davis Physics 116B Rev 2/22/2018 There s a saying when dealing with complex electronic systems: If you can make the LED blink, you re 90% of the way there., so in this lab you
Lab 7: RPN Calculator
 University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE171 - Digital Design Laboratory Lab 7: RPN Calculator The purpose of this lab is: Purpose 1. To get familiar with the use
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE171 - Digital Design Laboratory Lab 7: RPN Calculator The purpose of this lab is: Purpose 1. To get familiar with the use
Lab Assignment 2. Implementing Combinational and Sequential Logic in VHDL
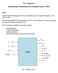 Lab Assignment 2 Implementing Combinational and Sequential Logic in VHDL Task 1 Draw a detailed block diagram of the ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit), specified using Fig. 1 and Tables 1 and 2. Then develop
Lab Assignment 2 Implementing Combinational and Sequential Logic in VHDL Task 1 Draw a detailed block diagram of the ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit), specified using Fig. 1 and Tables 1 and 2. Then develop
Lab Manual for COE 203: Digital Design Lab
 Lab Manual for COE 203: Digital Design Lab 1 Table of Contents 1. Prototyping of Logic Circuits using Discrete Components...3 2. Prototyping of Logic Circuits using EEPROMs...9 3. Introduction to FPGA
Lab Manual for COE 203: Digital Design Lab 1 Table of Contents 1. Prototyping of Logic Circuits using Discrete Components...3 2. Prototyping of Logic Circuits using EEPROMs...9 3. Introduction to FPGA
CSE 591: Advanced Hardware Design and Verification (2012 Spring) LAB #0
 Lab 0: Tutorial on Xilinx Project Navigator & ALDEC s Active-HDL Simulator CSE 591: Advanced Hardware Design and Verification Assigned: 01/05/2011 Due: 01/19/2011 Table of Contents 1 Overview... 2 1.1
Lab 0: Tutorial on Xilinx Project Navigator & ALDEC s Active-HDL Simulator CSE 591: Advanced Hardware Design and Verification Assigned: 01/05/2011 Due: 01/19/2011 Table of Contents 1 Overview... 2 1.1
Tutorial: ISE 12.2 and the Spartan3e Board v August 2010
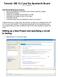 Tutorial: ISE 12.2 and the Spartan3e Board v12.2.1 August 2010 This tutorial will show you how to: Use a combination of schematics and Verilog to specify a design Simulate that design Define pin constraints
Tutorial: ISE 12.2 and the Spartan3e Board v12.2.1 August 2010 This tutorial will show you how to: Use a combination of schematics and Verilog to specify a design Simulate that design Define pin constraints
To design a 4-bit ALU To experimentally check the operation of the ALU
 1 Experiment # 11 Design and Implementation of a 4 - bit ALU Objectives: The objectives of this lab are: To design a 4-bit ALU To experimentally check the operation of the ALU Overview An Arithmetic Logic
1 Experiment # 11 Design and Implementation of a 4 - bit ALU Objectives: The objectives of this lab are: To design a 4-bit ALU To experimentally check the operation of the ALU Overview An Arithmetic Logic
Xilinx Project Navigator Reference Guide
 31 July 2003 Author: David M. Sendek Xilinx Project Navigator Reference Guide Background: This guide provides you with step-by-step procedures in using the Xilinx Project Navigator to perform the following:
31 July 2003 Author: David M. Sendek Xilinx Project Navigator Reference Guide Background: This guide provides you with step-by-step procedures in using the Xilinx Project Navigator to perform the following:
EE 459/500 HDL Based Digital Design with Programmable Logic
 EE 459/500 HDL Based Digital Design with Programmable Logic Lecture 17 From special-purpose FSMD to general-purpose microcontroller: Xilinx s PicoBlaze 1 Overview From FSMD to Microcontroller PicoBlaze
EE 459/500 HDL Based Digital Design with Programmable Logic Lecture 17 From special-purpose FSMD to general-purpose microcontroller: Xilinx s PicoBlaze 1 Overview From FSMD to Microcontroller PicoBlaze
Designing an Improved 64 Bit Arithmetic and Logical Unit for Digital Signaling Processing Purposes
 Available Online at- http://isroj.net/index.php/issue/current-issue ISROJ Index Copernicus Value for 2015: 49.25 Volume 02 Issue 01, 2017 e-issn- 2455 8818 Designing an Improved 64 Bit Arithmetic and Logical
Available Online at- http://isroj.net/index.php/issue/current-issue ISROJ Index Copernicus Value for 2015: 49.25 Volume 02 Issue 01, 2017 e-issn- 2455 8818 Designing an Improved 64 Bit Arithmetic and Logical
CS/EE 3710 Computer Architecture Lab Checkpoint #2 Datapath Infrastructure
 CS/EE 3710 Computer Architecture Lab Checkpoint #2 Datapath Infrastructure Overview In order to complete the datapath for your insert-name-here machine, the register file and ALU that you designed in checkpoint
CS/EE 3710 Computer Architecture Lab Checkpoint #2 Datapath Infrastructure Overview In order to complete the datapath for your insert-name-here machine, the register file and ALU that you designed in checkpoint
EITF35 - Introduction to Structured VLSI Design (Fall ) 7. Assignment 3 - Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
 EITF35 - Introduction to Structured VLSI Design (Fall 2018 2016 2015) 7 Assignment 3 - Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) v.1.1.0 Introduction In this lab assignment, a simple arithmetic logic unit (ALU) will
EITF35 - Introduction to Structured VLSI Design (Fall 2018 2016 2015) 7 Assignment 3 - Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) v.1.1.0 Introduction In this lab assignment, a simple arithmetic logic unit (ALU) will
ELEC 326: Class project
 ELEC 326: Class project Kartik Mohanram 1 Introduction For this project you will design and test a three-digit binary-coded-decimal (BCD) adder capable of adding positive and negative BCD numbers. In the
ELEC 326: Class project Kartik Mohanram 1 Introduction For this project you will design and test a three-digit binary-coded-decimal (BCD) adder capable of adding positive and negative BCD numbers. In the
Changes in timetable (changes in GREEN)
 Changes in timetable (changes in GREEN) Wk12: May25 29 HLAB5 PICOBLAZE assembly Wk13: Jun1 5 Still hand in assignment on Wk13 Jun5 C.O.B. Wks14 15 (Jun8 19) Hardware tests Exam on Jun 22 Project lab I
Changes in timetable (changes in GREEN) Wk12: May25 29 HLAB5 PICOBLAZE assembly Wk13: Jun1 5 Still hand in assignment on Wk13 Jun5 C.O.B. Wks14 15 (Jun8 19) Hardware tests Exam on Jun 22 Project lab I
ECT 224: Digital Computer Fundamentals Using Xilinx StateCAD
 ECT 224: Digital Computer Fundamentals Using Xilinx StateCAD 1) Sequential circuit design often starts with a problem statement tat can be realized in the form of a state diagram or state table a) Xilinx
ECT 224: Digital Computer Fundamentals Using Xilinx StateCAD 1) Sequential circuit design often starts with a problem statement tat can be realized in the form of a state diagram or state table a) Xilinx
Setup/Hold. Set Up time (t su ):
 Lecture 10 Agenda Set Up time (t su ): Setup/Hold Minimum amount of time the data is to be held steady prior to the clock event Hold time (t h ): Minimum amount of time the data is to be held steady after
Lecture 10 Agenda Set Up time (t su ): Setup/Hold Minimum amount of time the data is to be held steady prior to the clock event Hold time (t h ): Minimum amount of time the data is to be held steady after
LAB#2 ( Due Date & Time: See course web page )
 UCSD CSE140L Fall 2014 LAB#2 ( Due Date & Time: See course web page ) Instructor: Dr. Choon Kim Objective Based on the experience gained from LAB#1, learn how to design, simulate, synthesize, program on
UCSD CSE140L Fall 2014 LAB#2 ( Due Date & Time: See course web page ) Instructor: Dr. Choon Kim Objective Based on the experience gained from LAB#1, learn how to design, simulate, synthesize, program on
ECE/CS Computer Design Lab
 ECE/CS 3710 Computer Design Lab Ken Stevens Fall 2009 ECE/CS 3710 Computer Design Lab Tue & Thu 3:40pm 5:00pm Lectures in WEB 110, Labs in MEB 3133 (DSL) Instructor: Ken Stevens MEB 4506 Office Hours:
ECE/CS 3710 Computer Design Lab Ken Stevens Fall 2009 ECE/CS 3710 Computer Design Lab Tue & Thu 3:40pm 5:00pm Lectures in WEB 110, Labs in MEB 3133 (DSL) Instructor: Ken Stevens MEB 4506 Office Hours:
Digital Logic Design Lab
 Digital Logic Design Lab DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LAB BROCHURE DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN LABORATORY CONTENTS Lab Venue... 3 Lab Objectives & Courses... 3 Lab Description & Experiments... 4 Hardware
Digital Logic Design Lab DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LAB BROCHURE DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN LABORATORY CONTENTS Lab Venue... 3 Lab Objectives & Courses... 3 Lab Description & Experiments... 4 Hardware
ECE 448 FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL. Spring 2018
 ECE 448 FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL Spring 2018 Kris Gaj Research and teaching interests: reconfigurable computing cryptography computer arithmetic network security Contact: The Engineering Building,
ECE 448 FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL Spring 2018 Kris Gaj Research and teaching interests: reconfigurable computing cryptography computer arithmetic network security Contact: The Engineering Building,
Processor, Assembler, and Compiler Design Education using an FPGA
 Processor, Assembler, and Compiler Design Education using an FPGA Koji Nakano and Yasuaki Ito Department of Information Engineering, Hiroshima University Kagamiyama 1-4-1, Higashi-Hiroshima, 739-8527,
Processor, Assembler, and Compiler Design Education using an FPGA Koji Nakano and Yasuaki Ito Department of Information Engineering, Hiroshima University Kagamiyama 1-4-1, Higashi-Hiroshima, 739-8527,
FPGA Implementation of MIPS RISC Processor
 FPGA Implementation of MIPS RISC Processor S. Suresh 1 and R. Ganesh 2 1 CVR College of Engineering/PG Student, Hyderabad, India 2 CVR College of Engineering/ECE Department, Hyderabad, India Abstract The
FPGA Implementation of MIPS RISC Processor S. Suresh 1 and R. Ganesh 2 1 CVR College of Engineering/PG Student, Hyderabad, India 2 CVR College of Engineering/ECE Department, Hyderabad, India Abstract The
FPGA Implementation of a High Speed Multiplier Employing Carry Lookahead Adders in Reduction Phase
 FPGA Implementation of a High Speed Multiplier Employing Carry Lookahead Adders in Reduction Phase Abhay Sharma M.Tech Student Department of ECE MNNIT Allahabad, India ABSTRACT Tree Multipliers are frequently
FPGA Implementation of a High Speed Multiplier Employing Carry Lookahead Adders in Reduction Phase Abhay Sharma M.Tech Student Department of ECE MNNIT Allahabad, India ABSTRACT Tree Multipliers are frequently
Tutorial: Working with Verilog and the Xilinx FPGA in ISE 9.2i
 Tutorial: Working with Verilog and the Xilinx FPGA in ISE 9.2i This tutorial will show you how to: Use Verilog to specify a design Simulate that Verilog design Define pin constraints for the FPGA (.ucf
Tutorial: Working with Verilog and the Xilinx FPGA in ISE 9.2i This tutorial will show you how to: Use Verilog to specify a design Simulate that Verilog design Define pin constraints for the FPGA (.ucf
Mark II Aiken Relay Calculator
 Introduction to Embedded Microcomputer Systems Lecture 6.1 Mark II Aiken Relay Calculator 2.12. Tutorial 2. Arithmetic and logical operations format descriptions examples h 8-bit unsigned hexadecimal $00
Introduction to Embedded Microcomputer Systems Lecture 6.1 Mark II Aiken Relay Calculator 2.12. Tutorial 2. Arithmetic and logical operations format descriptions examples h 8-bit unsigned hexadecimal $00
Chapter 5 Embedded Soft Core Processors
 Embedded Soft Core Processors Coarse Grained Architecture. The programmable gate array (PGA) has provided the opportunity for the design and implementation of a soft core processor in embedded design.
Embedded Soft Core Processors Coarse Grained Architecture. The programmable gate array (PGA) has provided the opportunity for the design and implementation of a soft core processor in embedded design.
Note that none of the above MAY be a VALID ANSWER.
 ECE 270 Learning Outcome 4-1 - Practice Exam / Solution OUTCOME #4: An ability to design and implement computer logic circuits. Multiple Choice select the single most appropriate response for each question.
ECE 270 Learning Outcome 4-1 - Practice Exam / Solution OUTCOME #4: An ability to design and implement computer logic circuits. Multiple Choice select the single most appropriate response for each question.
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, DAVIS Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. EEC180B DIGITAL SYSTEMS II Fall 1999
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, DAVIS Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EEC180B DIGITAL SYSTEMS II Fall 1999 Lab 7-10: Micro-processor Design: Minimal Instruction Set Processor (MISP) Objective:
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, DAVIS Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EEC180B DIGITAL SYSTEMS II Fall 1999 Lab 7-10: Micro-processor Design: Minimal Instruction Set Processor (MISP) Objective:
Building Combinatorial Circuit Using Behavioral Modeling Lab
 Building Combinatorial Circuit Using Behavioral Modeling Lab Overview: In this lab you will learn how to model a combinatorial circuit using behavioral modeling style of Verilog HDL. You will model a combinatorial
Building Combinatorial Circuit Using Behavioral Modeling Lab Overview: In this lab you will learn how to model a combinatorial circuit using behavioral modeling style of Verilog HDL. You will model a combinatorial
Architecture & Instruction set of 8085 Microprocessor and 8051 Micro Controller
 of 8085 microprocessor 8085 is pronounced as "eighty-eighty-five" microprocessor. It is an 8-bit microprocessor designed by Intel in 1977 using NMOS technology. It has the following configuration 8-bit
of 8085 microprocessor 8085 is pronounced as "eighty-eighty-five" microprocessor. It is an 8-bit microprocessor designed by Intel in 1977 using NMOS technology. It has the following configuration 8-bit
CSE140 L. Instructor: Thomas Y. P. Lee January 18,2006. CSE140L Course Info
 CSE4 L Instructor: Thomas Y. P. Lee January 8,26 CSE4L Course Info Lectures Wedesday :-:2AM, HSS33 Lab Assignment egins TA s JinHua Liu (jhliu@cs.ucsd.edu) Contact TAs if you re still looking for a lab
CSE4 L Instructor: Thomas Y. P. Lee January 8,26 CSE4L Course Info Lectures Wedesday :-:2AM, HSS33 Lab Assignment egins TA s JinHua Liu (jhliu@cs.ucsd.edu) Contact TAs if you re still looking for a lab
Lab 2: Barrel Shifter Design
 EGR 400 A Advanced Digital System Design Using FPGAs Lab 2: Barrel Shifter Design Prepared for: Dr. Foist Christopher Parisi College of Engineering California Baptist University 10/05/12 Introduction The
EGR 400 A Advanced Digital System Design Using FPGAs Lab 2: Barrel Shifter Design Prepared for: Dr. Foist Christopher Parisi College of Engineering California Baptist University 10/05/12 Introduction The
Introduction. About this tutorial. How to use this tutorial
 Basic Entry & not About this tutorial This tutorial consists of an introduction to creating simple circuits on an FPGA using a variety of methods. There are two ways to create the circuit: using or by
Basic Entry & not About this tutorial This tutorial consists of an introduction to creating simple circuits on an FPGA using a variety of methods. There are two ways to create the circuit: using or by
Experiment 3. Digital Circuit Prototyping Using FPGAs
 Experiment 3. Digital Circuit Prototyping Using FPGAs Masud ul Hasan Muhammad Elrabaa Ahmad Khayyat Version 151, 11 September 2015 Table of Contents 1. Objectives 2. Materials Required 3. Background 3.1.
Experiment 3. Digital Circuit Prototyping Using FPGAs Masud ul Hasan Muhammad Elrabaa Ahmad Khayyat Version 151, 11 September 2015 Table of Contents 1. Objectives 2. Materials Required 3. Background 3.1.
CS 31: Intro to Systems ISAs and Assembly. Martin Gagné Swarthmore College February 7, 2017
 CS 31: Intro to Systems ISAs and Assembly Martin Gagné Swarthmore College February 7, 2017 ANNOUNCEMENT All labs will meet in SCI 252 (the robot lab) tomorrow. Overview How to directly interact with hardware
CS 31: Intro to Systems ISAs and Assembly Martin Gagné Swarthmore College February 7, 2017 ANNOUNCEMENT All labs will meet in SCI 252 (the robot lab) tomorrow. Overview How to directly interact with hardware
EITF35 - Introduction to Structured VLSI Design (Fall 2017) Course projects
 1 EITF35 - Introduction to Structured VLSI Design (Fall 2017) Course projects v.1.0.0 1 Introduction This document describes the course projects provided in EITF35 Introduction to Structured VLSI Design
1 EITF35 - Introduction to Structured VLSI Design (Fall 2017) Course projects v.1.0.0 1 Introduction This document describes the course projects provided in EITF35 Introduction to Structured VLSI Design
Xilinx ISE8.1 and Spartan-3 Tutorial EE3810
 Xilinx ISE8.1 and Spartan-3 Tutorial EE3810 1 Part1) Starting a new project Simple 3-to-8 Decoder Start the Xilinx ISE 8.1i Project Navigator: Select File > New Project in the opened window 2 Select a
Xilinx ISE8.1 and Spartan-3 Tutorial EE3810 1 Part1) Starting a new project Simple 3-to-8 Decoder Start the Xilinx ISE 8.1i Project Navigator: Select File > New Project in the opened window 2 Select a
Faculty of Engineering Systems & Biomedical Dept. First Year Cairo University Sheet 6 Computer I
 aculty of Engineering Systems & Biomedical Dept. irst Year Cairo University Sheet 6 Computer I 1. Choose rue or alse for each of the following statements a) In a direct addressing mode instruction, the
aculty of Engineering Systems & Biomedical Dept. irst Year Cairo University Sheet 6 Computer I 1. Choose rue or alse for each of the following statements a) In a direct addressing mode instruction, the
Elec 326: Digital Logic Design
 Elec 326: Digital Logic Design Project Requirements Fall 2005 For this project you will design and test a three-digit binary-coded-decimal (BCD) adder capable of adding positive and negative BCD numbers.
Elec 326: Digital Logic Design Project Requirements Fall 2005 For this project you will design and test a three-digit binary-coded-decimal (BCD) adder capable of adding positive and negative BCD numbers.
Number Systems. Readings: , Problem: Implement simple pocket calculator Need: Display, adders & subtractors, inputs
 Number Systems Readings: 3-3.3.3, 3.3.5 Problem: Implement simple pocket calculator Need: Display, adders & subtractors, inputs Display: Seven segment displays Inputs: Switches Missing: Way to implement
Number Systems Readings: 3-3.3.3, 3.3.5 Problem: Implement simple pocket calculator Need: Display, adders & subtractors, inputs Display: Seven segment displays Inputs: Switches Missing: Way to implement
ECEN 651: Microprogrammed Control of Digital Systems Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University
 ECEN 651: Microprogrammed Control of Digital Systems Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University Prof. Mi Lu TA: Ehsan Rohani Laboratory Exercise #3 Storage Elements in Verilog
ECEN 651: Microprogrammed Control of Digital Systems Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University Prof. Mi Lu TA: Ehsan Rohani Laboratory Exercise #3 Storage Elements in Verilog
Design a three-input, two-output sequential digital circuit which functions as a digital locking mechanism. LOCK ALARM
 Department of Computing Course 112 Hardware First Year Laboratory Assignment Dates for the session 2005-2006: Hand out Date: 10 th January 2006 Hand in deadline (electronic and written report): 17.00 Monday
Department of Computing Course 112 Hardware First Year Laboratory Assignment Dates for the session 2005-2006: Hand out Date: 10 th January 2006 Hand in deadline (electronic and written report): 17.00 Monday
EXPERIMENT NO. 1 THE MKT 8085 MICROPROCESSOR TRAINER
 OBJECT: EXPERIMENT NO. 1 THE MKT 8085 MICROPROCESSOR TRAINER To understand the structure and operating instruction of the microprocessor trainer. INTRODUCTION: The MKT 8085 is a single-board microcomputer,
OBJECT: EXPERIMENT NO. 1 THE MKT 8085 MICROPROCESSOR TRAINER To understand the structure and operating instruction of the microprocessor trainer. INTRODUCTION: The MKT 8085 is a single-board microcomputer,
Lab 3 Sequential Logic for Synthesis. FPGA Design Flow.
 Lab 3 Sequential Logic for Synthesis. FPGA Design Flow. Task 1 Part 1 Develop a VHDL description of a Debouncer specified below. The following diagram shows the interface of the Debouncer. The following
Lab 3 Sequential Logic for Synthesis. FPGA Design Flow. Task 1 Part 1 Develop a VHDL description of a Debouncer specified below. The following diagram shows the interface of the Debouncer. The following
CMPEN 331 Computer Organization and Design, Lab 4 Due Wednesday April 5, 2017 at 7:0 am (Drop box on Canvas)
 Penn State University School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Page 1 of 5 CMPEN 331 Computer Organization and Design, Lab 4 Due Wednesday April 5, 2017 at 7:0 am (Drop box on Canvas) This
Penn State University School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Page 1 of 5 CMPEN 331 Computer Organization and Design, Lab 4 Due Wednesday April 5, 2017 at 7:0 am (Drop box on Canvas) This
Microprocessors and Microcontrollers Prof. Santanu Chattopadhyay Department of E & EC Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Microprocessors and Microcontrollers Prof. Santanu Chattopadhyay Department of E & EC Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 09 8085 Microprocessors (Contd.) (Refer Slide Time:
Microprocessors and Microcontrollers Prof. Santanu Chattopadhyay Department of E & EC Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 09 8085 Microprocessors (Contd.) (Refer Slide Time:
EMBEDDED SOPC DESIGN WITH NIOS II PROCESSOR AND VHDL EXAMPLES
 EMBEDDED SOPC DESIGN WITH NIOS II PROCESSOR AND VHDL EXAMPLES Pong P. Chu Cleveland State University A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION PREFACE An SoC (system on a chip) integrates a processor, memory
EMBEDDED SOPC DESIGN WITH NIOS II PROCESSOR AND VHDL EXAMPLES Pong P. Chu Cleveland State University A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION PREFACE An SoC (system on a chip) integrates a processor, memory
Computer Organization II CMSC 3833 Lecture 33
 Term MARIE Definition Machine Architecture that is Really Intuitive and Easy 4.8.1 The Architecture Figure s Architecture Characteristics: Binary, two s complement Stored program, fixed word length Word
Term MARIE Definition Machine Architecture that is Really Intuitive and Easy 4.8.1 The Architecture Figure s Architecture Characteristics: Binary, two s complement Stored program, fixed word length Word
LAB 9 The Performance of MIPS
 Goals To Do LAB 9 The Performance of MIPS Learn how the performance of the processor is determined. Improve the processor performance by adding new instructions. Determine the speed of the processor in
Goals To Do LAB 9 The Performance of MIPS Learn how the performance of the processor is determined. Improve the processor performance by adding new instructions. Determine the speed of the processor in
EGC221: Digital Logic Lab
 EGC221: Digital Logic Lab Experiment #7 Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) Schematic Implementation Student s Name: Student s Name: Reg. no.: Reg. no.: Semester: Spring 2017 Date: 04 April 2017 Assessment: Assessment
EGC221: Digital Logic Lab Experiment #7 Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) Schematic Implementation Student s Name: Student s Name: Reg. no.: Reg. no.: Semester: Spring 2017 Date: 04 April 2017 Assessment: Assessment
Adding the ILA Core to an Existing Design Lab
 Adding the ILA Core to an Existing Introduction This lab consists of adding a ChipScope Pro software ILA core with the Core Inserter tool and debugging a nonfunctioning design. The files for this lab are
Adding the ILA Core to an Existing Introduction This lab consists of adding a ChipScope Pro software ILA core with the Core Inserter tool and debugging a nonfunctioning design. The files for this lab are
FPGA Interfacing of HD44780 Based LCD Using Delayed Finite State Machine (FSM)
 FPGA Interfacing of HD44780 Based LCD Using Delayed Finite State Machine (FSM) Edwin NC Mui Custom R & D Engineer Texco Enterprise Ptd. Ltd. {blackgrail2000@hotmail.com} Abstract This paper presents a
FPGA Interfacing of HD44780 Based LCD Using Delayed Finite State Machine (FSM) Edwin NC Mui Custom R & D Engineer Texco Enterprise Ptd. Ltd. {blackgrail2000@hotmail.com} Abstract This paper presents a
CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture
 CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr. Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Last updated: January 2, 2018 at 11:23 CS429 Slideset 5: 1 Topics of this Slideset
CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr. Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Last updated: January 2, 2018 at 11:23 CS429 Slideset 5: 1 Topics of this Slideset
Intel 8086 MICROPROCESSOR. By Y V S Murthy
 Intel 8086 MICROPROCESSOR By Y V S Murthy 1 Features It is a 16-bit μp. 8086 has a 20 bit address bus can access up to 2 20 memory locations (1 MB). It can support up to 64K I/O ports. It provides 14,
Intel 8086 MICROPROCESSOR By Y V S Murthy 1 Features It is a 16-bit μp. 8086 has a 20 bit address bus can access up to 2 20 memory locations (1 MB). It can support up to 64K I/O ports. It provides 14,
ENEE245 Digital Circuits and Systems Lab Manual
 ENEE245 Digital Circuits and Systems Lab Manual Department of Engineering, Physical & Computer Sciences Montgomery College Version 1.1 Copyright Prof. Lan Xiang (Do not distribute without permission) 1
ENEE245 Digital Circuits and Systems Lab Manual Department of Engineering, Physical & Computer Sciences Montgomery College Version 1.1 Copyright Prof. Lan Xiang (Do not distribute without permission) 1
Addendum # 2 Guidelines to the Design Project
 1. Motivation: Addendum # 2 Guidelines to the Design Project Throughout the semester, you have done various lab exercises and built simple circuits. In the process, you have learnt many different techniques
1. Motivation: Addendum # 2 Guidelines to the Design Project Throughout the semester, you have done various lab exercises and built simple circuits. In the process, you have learnt many different techniques
EE 2700 Project 2 Microprocessor Design
 EE 2700 Project 2 Microprocessor Design This project may be done individually or in teams of two. You may consult others for general questions but not for specific issues. Cheating will not be tolerated
EE 2700 Project 2 Microprocessor Design This project may be done individually or in teams of two. You may consult others for general questions but not for specific issues. Cheating will not be tolerated
Verilog Lab. Two s Complement Add/Sub Unit. TA: Xin-Yu Shi
 Verilog Lab. Two s Complement Add/Sub Unit TA: Xin-Yu Shi genius@access.ee.ntu.edu.tw Introduction In previous lecture, what you have learned : Complete representation for binary negative number Arithmetic
Verilog Lab. Two s Complement Add/Sub Unit TA: Xin-Yu Shi genius@access.ee.ntu.edu.tw Introduction In previous lecture, what you have learned : Complete representation for binary negative number Arithmetic
Verilog Design Entry, Synthesis, and Behavioral Simulation
 ------------------------------------------------------------- PURPOSE - This lab will present a brief overview of a typical design flow and then will start to walk you through some typical tasks and familiarize
------------------------------------------------------------- PURPOSE - This lab will present a brief overview of a typical design flow and then will start to walk you through some typical tasks and familiarize
Advanced Computer Architecture-CS501
 Advanced Computer Architecture Lecture No. 34 Reading Material Vincent P. Heuring & Harry F. Jordan Chapter 6 Computer Systems Design and Architecture 6.1, 6.2 Summary Introduction to ALSU Radix Conversion
Advanced Computer Architecture Lecture No. 34 Reading Material Vincent P. Heuring & Harry F. Jordan Chapter 6 Computer Systems Design and Architecture 6.1, 6.2 Summary Introduction to ALSU Radix Conversion
ENEE245 Digital Circuits and Systems Lab Manual
 ENEE245 Digital Circuits and Systems Lab Manual Department of Engineering, Physical & Computer Sciences Montgomery College Modified Fall 2017 Copyright Prof. Lan Xiang (Do not distribute without permission)
ENEE245 Digital Circuits and Systems Lab Manual Department of Engineering, Physical & Computer Sciences Montgomery College Modified Fall 2017 Copyright Prof. Lan Xiang (Do not distribute without permission)
Physics 364, Fall 2014, reading due your answers to by 11pm on Sunday
 Physics 364, Fall 2014, reading due 2014-11-23. Email your answers to ashmansk@hep.upenn.edu by 11pm on Sunday Course materials and schedule are at positron.hep.upenn.edu/p364 Assignment: (a) First read
Physics 364, Fall 2014, reading due 2014-11-23. Email your answers to ashmansk@hep.upenn.edu by 11pm on Sunday Course materials and schedule are at positron.hep.upenn.edu/p364 Assignment: (a) First read
More complicated than addition. Let's look at 3 versions based on grade school algorithm (multiplicand) More time and more area
 Multiplication More complicated than addition accomplished via shifting and addition More time and more area Let's look at 3 versions based on grade school algorithm 01010010 (multiplicand) x01101101 (multiplier)
Multiplication More complicated than addition accomplished via shifting and addition More time and more area Let's look at 3 versions based on grade school algorithm 01010010 (multiplicand) x01101101 (multiplier)
 Chapter 1 Microprocessor architecture ECE 3120 Dr. Mohamed Mahmoud http://iweb.tntech.edu/mmahmoud/ mmahmoud@tntech.edu Outline 1.1 Computer hardware organization 1.1.1 Number System 1.1.2 Computer hardware
Chapter 1 Microprocessor architecture ECE 3120 Dr. Mohamed Mahmoud http://iweb.tntech.edu/mmahmoud/ mmahmoud@tntech.edu Outline 1.1 Computer hardware organization 1.1.1 Number System 1.1.2 Computer hardware
ECE/CS Computer Design Lab Lab 1 - Completion by Sept 13. Lab 2 will be assigned during the 2nd week of September.
 1 Design of the ALU ECE/CS 3710 - Computer Design Lab Lab 1 - Completion by Sept 13. Lab 2 will be assigned during the 2nd week of September. I. OVERVIEW The instruction set of the CR16 uses standard 16-bit
1 Design of the ALU ECE/CS 3710 - Computer Design Lab Lab 1 - Completion by Sept 13. Lab 2 will be assigned during the 2nd week of September. I. OVERVIEW The instruction set of the CR16 uses standard 16-bit
Introduction to Verilog. Mitch Trope EECS 240 Spring 2004
 Introduction to Verilog Mitch Trope mtrope@ittc.ku.edu EECS 240 Spring 2004 Overview What is Verilog? Verilog History Max+Plus II Schematic entry Verilog entry System Design Using Verilog: Sum of Products
Introduction to Verilog Mitch Trope mtrope@ittc.ku.edu EECS 240 Spring 2004 Overview What is Verilog? Verilog History Max+Plus II Schematic entry Verilog entry System Design Using Verilog: Sum of Products
Design and Implementation of a FPGA-based Pipelined Microcontroller
 Design and Implementation of a FPGA-based Pipelined Microcontroller Rainer Bermbach, Martin Kupfer University of Applied Sciences Braunschweig / Wolfenbüttel Germany Embedded World 2009, Nürnberg, 03.03.09
Design and Implementation of a FPGA-based Pipelined Microcontroller Rainer Bermbach, Martin Kupfer University of Applied Sciences Braunschweig / Wolfenbüttel Germany Embedded World 2009, Nürnberg, 03.03.09
REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE
 REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE The operations executed on the data stored in the registers are called micro operations. Classifications of micro operations Register transfer micro operations Arithmetic micro
REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE The operations executed on the data stored in the registers are called micro operations. Classifications of micro operations Register transfer micro operations Arithmetic micro
How to Integrate FPGAs into a Computer Organization Course
 How to Integrate FPGAs into a Computer Organization Course Michael J Jipping jipping@cs.hope.edu Sara Henry sara.henry@hope.edu Kathleen Ludewig kathleen.ludewig@hope.edu Leslie Tableman leslie.tableman@hope.edu
How to Integrate FPGAs into a Computer Organization Course Michael J Jipping jipping@cs.hope.edu Sara Henry sara.henry@hope.edu Kathleen Ludewig kathleen.ludewig@hope.edu Leslie Tableman leslie.tableman@hope.edu
Please put your cellphone on vibrate
 week 1 Page 1 Introduction Administration Overview of this course Assignment #1 Examples Download design tool Get into groups of 3 Please put your cellphone on vibrate week 1 Page 2 Administration http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/su09/cse141l/index.html
week 1 Page 1 Introduction Administration Overview of this course Assignment #1 Examples Download design tool Get into groups of 3 Please put your cellphone on vibrate week 1 Page 2 Administration http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/su09/cse141l/index.html
Lab 3: Standard Combinational Components
 Lab 3: Standard Combinational Components Purpose In this lab you will implement several combinational circuits on the DE1 development board to test and verify their operations. Introduction Using a high-level
Lab 3: Standard Combinational Components Purpose In this lab you will implement several combinational circuits on the DE1 development board to test and verify their operations. Introduction Using a high-level
CECS LAB 1 Introduction to Xilinx EDA Tools
 NAME: DUE DATE: STUDENT ID: POSSIBLE POINTS: 10 COURSE DATE & TIME: OBJECTIVE: To familiarize ourselves with the Xilinx Electronic Design Aid (EDA) Tools. We will simulate a simple 4-to-1 Multiplexor using
NAME: DUE DATE: STUDENT ID: POSSIBLE POINTS: 10 COURSE DATE & TIME: OBJECTIVE: To familiarize ourselves with the Xilinx Electronic Design Aid (EDA) Tools. We will simulate a simple 4-to-1 Multiplexor using
Design of a High-Level Data Link Controller
 ECE 551 Course Project Design of a High-Level Data Link Controller Interim Report - Due Wednesday, November 28, 2001, 4:00 PM Final Report - Due Wednesday, December 12, 2001, 4:00 PM Project Teams and
ECE 551 Course Project Design of a High-Level Data Link Controller Interim Report - Due Wednesday, November 28, 2001, 4:00 PM Final Report - Due Wednesday, December 12, 2001, 4:00 PM Project Teams and
How to use the IP generator from Xilinx to instantiate IP cores
 ÁÌ ¹ ÁÒØÖÓ ÙØ ÓÒ ØÓ ËØÖÙØÙÖ ÎÄËÁ Ò ÐÐ ¾¼½ µ ÓÙÖ ÔÖÓ Ø Úº½º¼º¼ 1 Introduction This document describes the course projects provided in EITF35 Introduction to Structured VLSI Design conducted at EIT, LTH.
ÁÌ ¹ ÁÒØÖÓ ÙØ ÓÒ ØÓ ËØÖÙØÙÖ ÎÄËÁ Ò ÐÐ ¾¼½ µ ÓÙÖ ÔÖÓ Ø Úº½º¼º¼ 1 Introduction This document describes the course projects provided in EITF35 Introduction to Structured VLSI Design conducted at EIT, LTH.
cs281: Computer Systems CPUlab ALU and Datapath Assigned: Oct. 30, Due: Nov. 8 at 11:59 pm
 cs281: Computer Systems CPUlab ALU and Datapath Assigned: Oct. 30, Due: Nov. 8 at 11:59 pm The objective of this exercise is twofold to complete a combinational circuit for an ALU that we can use with
cs281: Computer Systems CPUlab ALU and Datapath Assigned: Oct. 30, Due: Nov. 8 at 11:59 pm The objective of this exercise is twofold to complete a combinational circuit for an ALU that we can use with
THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLEDGE
 THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLEDGE Assertion Based Verification of I2C Master Bus Controller with RTC Sagar T. D. M.Tech Student, VLSI Design and Embedded Systems BGS Institute of Technology,
THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLEDGE Assertion Based Verification of I2C Master Bus Controller with RTC Sagar T. D. M.Tech Student, VLSI Design and Embedded Systems BGS Institute of Technology,
CHAPTER 5 : Introduction to Intel 8085 Microprocessor Hardware BENG 2223 MICROPROCESSOR TECHNOLOGY
 CHAPTER 5 : Introduction to Intel 8085 Hardware BENG 2223 MICROPROCESSOR TECHNOLOGY The 8085A(commonly known as the 8085) : Was first introduced in March 1976 is an 8-bit microprocessor with 16-bit address
CHAPTER 5 : Introduction to Intel 8085 Hardware BENG 2223 MICROPROCESSOR TECHNOLOGY The 8085A(commonly known as the 8085) : Was first introduced in March 1976 is an 8-bit microprocessor with 16-bit address
Assignment 01 Computer Architecture Lab ECSE
 Assignment 01 Computer Architecture Lab ECSE 487-001 Date due: September 22, 2006, Trottier Assignment Box by 14:30 1 Introduction The purpose of this assignment is to re-familiarize the student with VHDL
Assignment 01 Computer Architecture Lab ECSE 487-001 Date due: September 22, 2006, Trottier Assignment Box by 14:30 1 Introduction The purpose of this assignment is to re-familiarize the student with VHDL
The Instruction Set. Chapter 5
 The Instruction Set Architecture Level(ISA) Chapter 5 1 ISA Level The ISA level l is the interface between the compilers and the hardware. (ISA level code is what a compiler outputs) 2 Memory Models An
The Instruction Set Architecture Level(ISA) Chapter 5 1 ISA Level The ISA level l is the interface between the compilers and the hardware. (ISA level code is what a compiler outputs) 2 Memory Models An
