POS-PHY Level 4 MegaCore Function (POSPHY4)
|
|
|
- Alyson Gilbert
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 POS-PHY Level 4 MegaCore Function (POSPHY4) August 2001; ver Data Sheet Introduction Optimized for the Altera APEX TM II device architecture, the POS-PHY level 4 MegaCore function (POSPHY4) interfaces cell and packet transfers between physical (PHY) and link layer devices. The POSPHY4 supports rates of up to SONET OC-192, and 10 gigabits per second (Gbps) Ethernet rates. Features SPI-4 Phase 2 interface data width of 16 bits (True-LVDS TM solution) Supports up to 832 Mbps on each LVDS channel Operates in single-phy (SPHY), or multi-phy (MPHY) mode with up to 256 ports Fixed start of packet (SOP) alignment significantly eases subsequent packet processing Configurable for receive or transmit directions FIFO buffer status management and indications Configurable FIFO buffer options (including port address optionally passed through FIFO buffer, adjustable FIFO buffer depth) Static alignment (training sequence required for word alignment in the receiver) Configurable Atlantic TM slave interface data width of 8, 16, 32, 64, 128 or 256 bits for simplified bridging with other Atlantic interface compatible cores Complies with all applicable standards, including: Optical Internetworking Forum (OIF), System Packet Level 4 (SPI-4) Phase 2: OC-192 System for Physical and Link Layer Devices, OIF-SPI4-02.0, January PMC-Sierra Inc., POS-PHY TM Level 4 A Saturn Packet and Cell Specification for OC-192 SONET/SDH and 10 GB/s Ethernet Applications, Issue 5 (Draft): June Altera Corporation, Atlantic Specification. Functional Description The POSPHY4 functions as a transmitter () master where data flows from the Atlantic interface to the SPI-4 interface, or as a receiver () slave where data flows from the SPI-4 interface to the Atlantic interface. 1 Altera Corporation A-DS-IPPOSPHY4-1.00
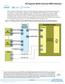
2 Figure 1 shows a block diagram of the and the. Figure 1. Block Diagram rrefclk SPI-4 Phase 2 Core Status Signals rxreset_n rdclk rctl rdat[15:0] rsclk rstat[1:0] dip4_err train_lck train_en msop_err meop_err sop8_err paddr_err rxfifo_oflw arxclk arxreset_n arxena arxdav arxadr[7:0] arxdat[255/127/63/31/15/7:0] arxval arxsop arxeop arxmty[4/3/2/1:0] arxerr rxfifo_uflw Atlantic RX dip2_err Core Status Signals SPI-4 Phase 2 tstat_sync txfifo_uflw idle_ins trefclk trefreset_n tdclk tctl tdat[15:0] tsclk tstat[1:0] atxclk atxreset_n atxena atxdav atxadr[7:0] atxdat[255/127/63/31/15/7:0] atxsop atxeop atxmty[4/3/2/1:0] atxerr Atlantic TX txfifo_oflw global or fast clock Altera Corporation 2
3 The following lists the features for the and, assuming a full-feature configuration. Static alignment for bit sampling (training sequence required for word alignment) Accepts packets (or cells) from the SPI-4 Phase 2 interface Control word processing Diagonal interleaved parity (DIP-4) parity error detection Fixed SOP alignment Adjustable FIFO buffer depth FIFO buffer status management Port address optionally passed through FIFO buffer Inserts training sequence Sends data packets (or cells) on the SPI-4 Phase 2 interface Inserts control words Generates DIP-4 parity Adjustable FIFO buffer depth FIFO buffer status management s & Protocols Two interfaces support the POSPHY4: the SPI-4 Phase 2 interface and the Atlantic interface. While multiple Atlantic interfaces can be used, the SPI- 4 Phase 2 interface can only support a single transmitter, and/or a single receiver. SPI-4 Phase 2 The SPI-4 Phase 2 interface is an external interface protocol developed by the Optical Internetworking Forum (OIF). The POSPHY4 complies with the static alignment requirements specified by this protocol. This interface passes data and control words in both the TX (master) and RX (slave) directions. It features a high-speed portion and a FIFO buffer status portion. The high-speed portion comprises a 16-bit data bus, a 1-bit control line, and a double data rate (DDR) clock. The FIFO buffer status portion comprises a 2-bit status channel and a clock. This interface supports a data width of 16 bits. The interface can be a PHY-link, link-link, link-phy, or PHY-PHY connection. 1 For the purpose of this document, the POSPHY4 is implemented as a link layer device. 3 Altera Corporation
4 Figure 2 shows an SPI-4 Phase 2 PHY link configuration, including a TX (master) and an RX (slave). Figure 2. SPI-4 Phase 2 Top Level View TX Master Link Layer tdclk tdctl tdat[15:0] tsclk tstat[1:0] RX Slave PHY Layer RX Slave Link Layer rdclk rdctl rdat[15:0] rsclk rstat[1:0] TX Master PHY Layer f For further information on this interface, refer to the System Packet Level 4 (SPI-4) Phase 2: OC-192 System for Physical and Link Layer Devices, available at Atlantic The Atlantic interface is a full-duplex synchronous bus protocol supporting both packets and cells. The POSPHY4 is an Atlantic interface slave using a configurable data path of 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, or 256 bits to deliver packets to the slave. The Atlantic interface provides a connection between the FIFO buffer and neighboring logic. The width of the output bus (to FIFO buffer) is always as wide as, or wider than, the width of the input bus (Atlantic interface). The POSPHY4 FIFO buffer is used for crossing the clock domain from the Atlantic interface to the POSPHY4 reference clock. f For further information on this interface, refer to the Atlantic Functional Specification, available at Altera Corporation 4
5 Generating Variants Table 1 lists the optional features available to generate/request all POSPHY4 variants. Table 1. Optional Features Options Parameters Choices Data Flow Direction Receive (RX) data flows from the SPI-4 interface to the Atlantic interface. Transmit (TX) data flows from the Atlantic interface to the SPI-4 interface. DFLOW RX/TX Atlantic Data Width Atlantic data bus width ATLDW 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256 Calender_ Length Number of ports and FIFO buffers (1) CALLEN Embedded Address Send/receive address with data through the FIFO buffer (2) EADDR Yes /No FIFO Buffer Depth Number of elements FDEPTH 0, 256, 512 FIFO Pipeline FIFO buffer is pipelined for increased performance. FPIPELINE Yes/No Almost Empty Starving to Hungry threshold indications for each PHY AE 0<AE<FDEPTH/2 port (2) Almost Full Hungry to Satisfied threshold indications for each PHY port AF FDEPTH/2<AF<FDEPTH (2) FIFO_Threshold Low FIFO buffer low watermark FTL 0<FTL<FDEPTH/2 FIFO_Threshold High FIFO buffer high watermark FTH FDEPTH/2<FTH<FDEPTH Calender_M Number of repeated FIFO buffer calculations before DIP-2 CALM and framing occurs. (2) Maxburst 1 Number of 16-byte words that can be transmitted when the MB FIFO buffer is Starving. (2) Maxburst 2 Number of 16-byte words that can be transmitted when the FIFO buffer is Hungry. This number must be less than or equal to MB1. (2) MB MaxT Training Sequence Interval. The interval depends on the internal trefclk cycle. If the chosen interval is 1, the sequence occurs every trefclk cycle; if the chosen interval is 2, the sequence occurs every 2 trefclk cycles. (2) Training Pattern Repetitions ALPHA (α) is the number of repetitions of the training pattern sequence. (2) Transmit Bandwidth Optimization Yes inserts a single EOP/SOP control word between packets. No inserts of an EOP control word followed by a maximum of six IDLEs and a SOP control word between packets. (3) MAXT 8-2,048 ALPHA TXBOPT Yes/No Notes: (1) If one port is chosen, the POSPHY4 operates in SPHY mode; if 2 to 256 ports are chosen, the POSPHY4 operates in MPHY mode. (The MPHY mode is not supported in version 1.0.0p1.) (2) These parameters do not materially affect the size of the POSPHY4. (3) TXBOPT=Yes is not supported in version 1.0.0p1. 5 Altera Corporation
6 Performance Table 2 lists the estimated resources and speed of a SPHY POSPHY4 MegaCore function. These timing results were obtained using the Quartus II software version 1.1, and an APEX II EP2A15-7 device. Table 2. SPHY Configuration Utilization Performance Direction Parameters LE ESB f MAX (MHz) ATLDW=128, CALLEN=1, EADDR=No, FDEPTH=256, FTL=5, FTH=251, AE=30, AF=200, CALM=10, MB1=61, MB2=50, MAXT=2048, ALPHA=1, FPIPELINE=Yes 7, ATLDW=128, CALLEN=1, EADDR=No, FDEPTH=256, FTL=5, FTH=251, AE=30, AF=200, CALM=10, MB1=61, MB2=50, MAXT=2048, ALPHA=1, TXBOPT=No, FPIPELINE=Yes 2, Typical Applications Figure 3 shows a POSPHY4 configured for link layer, in an APEX II device. Figure 3. POSPHY4 as Link Layer Configuration SPI-4 Phase 2 Atlantic OC-192 or 10G MAC User Packet Processing Switch Switch Fabric APEX II Device Figure 4 illustrates the POSPHY4 configured for PHY layer, in an APEX II device. Figure 4. POSPHY4 as PHY Layer Configuration Atlantic SPI-4 Phase 2 OC-192 or 10G Ethernet Framer or MAC Logic Traffic Manager APEX II Device Altera Corporation 6
7 Licensing A license is not required to perform the following trial operations using your own custom logic: Instantiation Place-and-route Static timing analysis Simulation on third-party simulator Only when you are ready to generate programming files, do you need to obtain a license through your local Altera sales representative. 1 All current variants use a single license with ordering code: PLSM-POSPHY4. Deliverables The following elements are provided with the POSPHY4 package: Data sheet User guide Atlantic interface functional specification Encrypted gate level netlist Place-and-route constraints (where necessary) Secure RTL simulation model Demo testbench Access to problem reporting system 1 If your chosen variant (configuration) is not included as part of the downloaded package, the MegaWizard Plug-In generates the necessary text to request this variant. Forward this text to telecom@altera.com for processing. 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA (408) Applications Hotline: (800) 800-EPLD Customer Marketing: (408) Literature Services: lit_req@altera.com Copyright 2001 Altera Corporation. Altera, The Programmable Solutions Company, the stylized Altera logo, specific device designations, and all other words and logos that are identified as trademarks and/or service marks are, unless noted otherwise, the trademarks and service marks of Altera Corporation in the U.S. and other countries. All other product or service names are the property of their respective holders. Altera products are protected under numerous U.S. and foreign patents and pending applications, maskwork rights, and copyrights. Altera warrants performance of its semiconductor products to current specifications in accordance with Altera s standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any products and services at any time without notice. Altera assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any information, product, or service described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Altera Corporation. Altera customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device specifications before relying on any published information and before placing orders for products or services. All rights reserved. 7 Altera Corporation
POS-PHY Level 4 POS-PHY Level 3 Bridge Reference Design
 Level 4 Bridge Reference Design October 2001; ver. 1.02 Application Note 180 General Description This application note describes how the Level 4 Bridge reference design can be used to bridge packet or
Level 4 Bridge Reference Design October 2001; ver. 1.02 Application Note 180 General Description This application note describes how the Level 4 Bridge reference design can be used to bridge packet or
POS-PHY Level 4 MegaCore Function v2.1.0 Wrapper Features
 POS-PHY Level 4 MegaCore Function v2.1.0 Wrapper Features January 2004, ver. 1.0 Application Note 335 Introduction The Altera POS-PHY Level 4 MegaCore function provides high-speed cell and packet transfers
POS-PHY Level 4 MegaCore Function v2.1.0 Wrapper Features January 2004, ver. 1.0 Application Note 335 Introduction The Altera POS-PHY Level 4 MegaCore function provides high-speed cell and packet transfers
E3 Mapper MegaCore Function (E3MAP)
 MegaCore Function (E3MAP) March 9, 2001; ver. 1.0 Data Sheet Features Easy-to-use MegaWizard Plug-In generates MegaCore variants Quartus TM II software and OpenCore TM feature allow place-androute, and
MegaCore Function (E3MAP) March 9, 2001; ver. 1.0 Data Sheet Features Easy-to-use MegaWizard Plug-In generates MegaCore variants Quartus TM II software and OpenCore TM feature allow place-androute, and
SONET/SDH STS-12c/STM-4 Framer MegaCore Function (STS12CFRM)
 July 2001; ver. 1.01 SONET/SDH STS-12c/STM-4 Framer MegaCore Function (STS12CFRM) Data Sheet Features Performs synchronous optical network (SONET)/synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) framing and transport
July 2001; ver. 1.01 SONET/SDH STS-12c/STM-4 Framer MegaCore Function (STS12CFRM) Data Sheet Features Performs synchronous optical network (SONET)/synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) framing and transport
T3 Framer MegaCore Function (T3FRM)
 MegaCore Function August 2001; ver. 1.02 Data Sheet Features Achieving optimum performance in the Altera APEX TM 20K device architecture, the multi-featured MegaCore Function meets your innovative design
MegaCore Function August 2001; ver. 1.02 Data Sheet Features Achieving optimum performance in the Altera APEX TM 20K device architecture, the multi-featured MegaCore Function meets your innovative design
SPI-4.2 Interoperability with. in Stratix GX Devices. Introduction. PMC-Sierra XENON Family
 SPI-4.2 Interoperability with PMC-Sierra XENON Family in Stratix GX Devices May 2003, ver. 1.0 Application Note 228 Introduction The system packet interface level 4 phase 2 (SPI-4.2) specification, defined
SPI-4.2 Interoperability with PMC-Sierra XENON Family in Stratix GX Devices May 2003, ver. 1.0 Application Note 228 Introduction The system packet interface level 4 phase 2 (SPI-4.2) specification, defined
SPI-4.2 Interoperability with the Intel IXF1110 in Stratix GX Devices
 SPI-4.2 Interoperability with the Intel IXF1110 in Stratix GX Devices May 2003, ver. 1.0 Application Note 227 Introduction The system packet interface level 4 phase 2 (SPI-4.2) specification, defined by
SPI-4.2 Interoperability with the Intel IXF1110 in Stratix GX Devices May 2003, ver. 1.0 Application Note 227 Introduction The system packet interface level 4 phase 2 (SPI-4.2) specification, defined by
POS-PHY Level 4 MegaCore Function
 POS-PHY Level 4 MegaCore Function November 2004, MegaCore Version 2.2.2 Errata Sheet Introduction This document addresses known errata and documentation changes for version v2.2.2 of the POS-PHY Level
POS-PHY Level 4 MegaCore Function November 2004, MegaCore Version 2.2.2 Errata Sheet Introduction This document addresses known errata and documentation changes for version v2.2.2 of the POS-PHY Level
POS-PHY Level 2 and 3 Compiler User Guide
 POS-PHY Level 2 and 3 Compiler User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com MegaCore Version: 8.1 Document Date: November 2008 Copyright 2008 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved.
POS-PHY Level 2 and 3 Compiler User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com MegaCore Version: 8.1 Document Date: November 2008 Copyright 2008 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved.
POS-PHY Level 4 IP Core User Guide
 JulyPOS-PHY Level 4 IP Core User Guide POS-PHY Level 4 IP Core User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com UG-IPPOSPHY4-2014.07.07 Document last updated for Altera Complete Design
JulyPOS-PHY Level 4 IP Core User Guide POS-PHY Level 4 IP Core User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com UG-IPPOSPHY4-2014.07.07 Document last updated for Altera Complete Design
UTOPIA Level 3 Master MegaCore Function
 UTOPIA Level 3 Master MegaCore Function UTOPIA3MS User Guide November 21 11 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 (48) 544-7 http://www.altera.com A-UG-IPUTOPIA3MS-1. UTOPIA Level 3 Master MegaCore Function
UTOPIA Level 3 Master MegaCore Function UTOPIA3MS User Guide November 21 11 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 (48) 544-7 http://www.altera.com A-UG-IPUTOPIA3MS-1. UTOPIA Level 3 Master MegaCore Function
UTOPIA Level 3 Slave. MegaCore Function UTOPIA3SL. User Guide September 2001
 UTOPIA Level 3 Slave MegaCore Function UTOPIA3SL User Guide September 21 11 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 (48) 544-7 http://www.altera.com A-UG-IPUTOPIA3SL-1.1 UTOPIA Level 3 Slave MegaCore Function
UTOPIA Level 3 Slave MegaCore Function UTOPIA3SL User Guide September 21 11 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 (48) 544-7 http://www.altera.com A-UG-IPUTOPIA3SL-1.1 UTOPIA Level 3 Slave MegaCore Function
Nios Soft Core Embedded Processor
 Nios Soft Core Embedded Processor June 2000, ver. 1 Data Sheet Features... Preliminary Information Part of Altera s Excalibur TM embedded processor solutions, the Nios TM soft core embedded processor is
Nios Soft Core Embedded Processor June 2000, ver. 1 Data Sheet Features... Preliminary Information Part of Altera s Excalibur TM embedded processor solutions, the Nios TM soft core embedded processor is
White Paper The Need for a High-Bandwidth Memory Architecture in Programmable Logic Devices
 Introduction White Paper The Need for a High-Bandwidth Memory Architecture in Programmable Logic Devices One of the challenges faced by engineers designing communications equipment is that memory devices
Introduction White Paper The Need for a High-Bandwidth Memory Architecture in Programmable Logic Devices One of the challenges faced by engineers designing communications equipment is that memory devices
The implementation of these interfaces may assume any of the following forms:
 Draft Standard Contribution2 1. Physical Sublayer Interface 1.1 SONNET/SDH Physical Sublayer 1.1.1 Overview This clause defines the logical and electrical characteris tics for the SPI interfaces between
Draft Standard Contribution2 1. Physical Sublayer Interface 1.1 SONNET/SDH Physical Sublayer 1.1.1 Overview This clause defines the logical and electrical characteris tics for the SPI interfaces between
RapidIO Physical Layer MegaCore Function
 RapidIO Physical Layer MegaCore Function April 2005, MegaCore version 2.2.1 Errata Sheet Introduction This document addresses known errata and documentation changes for version 2.2.1 of the RapidIO Physical
RapidIO Physical Layer MegaCore Function April 2005, MegaCore version 2.2.1 Errata Sheet Introduction This document addresses known errata and documentation changes for version 2.2.1 of the RapidIO Physical
ZBT SRAM Controller Reference Design
 ZBT SRAM Controller Reference Design for APEX II Devices December 2001, ver. 1.0 Application Note 183 Introduction As communication systems require more low-latency, high-bandwidth interfaces for peripheral
ZBT SRAM Controller Reference Design for APEX II Devices December 2001, ver. 1.0 Application Note 183 Introduction As communication systems require more low-latency, high-bandwidth interfaces for peripheral
AIRbus Interface. Features Fixed width (8-, 16-, or 32-bit) data transfers (dependent on the width. Functional Description. General Arrangement
 AIRbus Interface December 22, 2000; ver. 1.00 Functional Specification 9 Features Fixed width (8-, 16-, or 32-bit) data transfers (dependent on the width of the data bus) Read and write access Four-way
AIRbus Interface December 22, 2000; ver. 1.00 Functional Specification 9 Features Fixed width (8-, 16-, or 32-bit) data transfers (dependent on the width of the data bus) Read and write access Four-way
Estimating Nios Resource Usage & Performance
 Estimating Nios Resource Usage & Performance in Altera Devices September 2001, ver. 1.0 Application Note 178 Introduction The Excalibur Development Kit, featuring the Nios embedded processor, includes
Estimating Nios Resource Usage & Performance in Altera Devices September 2001, ver. 1.0 Application Note 178 Introduction The Excalibur Development Kit, featuring the Nios embedded processor, includes
Simulating the PCI MegaCore Function Behavioral Models
 Simulating the PCI MegaCore Function Behavioral Models August 2001, ver. 1.0 Application Note 169 Introduction Altera intellectual property (IP) MegaCore functions are developed and pre-tested by Altera,
Simulating the PCI MegaCore Function Behavioral Models August 2001, ver. 1.0 Application Note 169 Introduction Altera intellectual property (IP) MegaCore functions are developed and pre-tested by Altera,
White Paper Understanding 40-nm FPGA Solutions for SATA/SAS
 White Paper Understanding 40-nm Solutions for /SAS This white paper describes the and SAS protocols, how the protocols are used, explains the value and SAS in terms of usage in an, and illustrates how
White Paper Understanding 40-nm Solutions for /SAS This white paper describes the and SAS protocols, how the protocols are used, explains the value and SAS in terms of usage in an, and illustrates how
Table 1 shows the issues that affect the FIR Compiler v7.1.
 May 2007, Version 7.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the Altera, v7.1. Errata are functional defects or errors, which may cause an Altera MegaCore function
May 2007, Version 7.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the Altera, v7.1. Errata are functional defects or errors, which may cause an Altera MegaCore function
LatticeSCM SPI4.2 Interoperability with PMC-Sierra PM3388
 August 2006 Technical Note TN1121 Introduction The System Packet Interface, Level 4, Phase 2 (SPI4.2) is a system level interface, published in 2001 by the Optical Internetworking Forum (OIF), for packet
August 2006 Technical Note TN1121 Introduction The System Packet Interface, Level 4, Phase 2 (SPI4.2) is a system level interface, published in 2001 by the Optical Internetworking Forum (OIF), for packet
SONET/SDH Compiler. Introduction. SONET/SDH Compiler v2.3.0 Issues
 January 2005, Compiler Version 2.3.0 Errata Sheet Introduction This document addresses known errata and documentation changes for version 2.3.0 of the SONET/SDH Compiler. Errata are design functional defects
January 2005, Compiler Version 2.3.0 Errata Sheet Introduction This document addresses known errata and documentation changes for version 2.3.0 of the SONET/SDH Compiler. Errata are design functional defects
Nios Embedded Processor UART Peripheral
 Nios Embedded Processor UART Peripheral March 2001, ver. 1.1 Data Sheet General Description The Nios universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter UART implements simple RS-232 asynchronous transmit and
Nios Embedded Processor UART Peripheral March 2001, ver. 1.1 Data Sheet General Description The Nios universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter UART implements simple RS-232 asynchronous transmit and
Using MAX 3000A Devices as a Microcontroller I/O Expander
 Using MAX 3000A Devices as a Microcontroller I/O Expander August 2003, Ver 1.0 Application Note 265 Introduction Advantages of Using MAX 3000A Devices Many microcontrollers and microprocessors limit I/O
Using MAX 3000A Devices as a Microcontroller I/O Expander August 2003, Ver 1.0 Application Note 265 Introduction Advantages of Using MAX 3000A Devices Many microcontrollers and microprocessors limit I/O
Active Serial Memory Interface
 Active Serial Memory Interface October 2002, Version 1.0 Data Sheet Introduction Altera Cyclone TM devices can be configured in active serial configuration mode. This mode reads a configuration bitstream
Active Serial Memory Interface October 2002, Version 1.0 Data Sheet Introduction Altera Cyclone TM devices can be configured in active serial configuration mode. This mode reads a configuration bitstream
System Packet Interface Level 4 (SPI-4) Phase 2 Revision 1: OC-192 System Interface for Physical and Link Layer Devices.
 System Packet Interface Level 4 (SPI-4) Phase 2 Revision 1: OC-192 System Interface for Physical and Link Layer Devices. OIF-SPI-4-02.1 October 15, 2003 Implementation Agreement Created and Approved by
System Packet Interface Level 4 (SPI-4) Phase 2 Revision 1: OC-192 System Interface for Physical and Link Layer Devices. OIF-SPI-4-02.1 October 15, 2003 Implementation Agreement Created and Approved by
AN 610: Implementing Deterministic Latency for CPRI and OBSAI Protocols in Altera Devices
 AN 610: Implementing Deterministic Latency for CPRI and OBSAI Protocols in Altera Devices July 2010 AN-610-1.0 This application note describes how to implement deterministic latency for Common Public Radio
AN 610: Implementing Deterministic Latency for CPRI and OBSAI Protocols in Altera Devices July 2010 AN-610-1.0 This application note describes how to implement deterministic latency for Common Public Radio
Excalibur Solutions DPRAM Reference Design
 Excalibur Solutions DPRAM Reference Design August 22, ver. 2.3 Application Note 173 Introduction The Excalibur devices are excellent system development platforms, offering flexibility, performance, and
Excalibur Solutions DPRAM Reference Design August 22, ver. 2.3 Application Note 173 Introduction The Excalibur devices are excellent system development platforms, offering flexibility, performance, and
UTOPIA Level 2 Slave MegaCore Function
 UTOPIA Level 2 Slave MegaCore Function October 2005, Version 2.5.0 Release Notes These release notes for the UTOPIA Level 2 Slave MegaCore function contain the following information: System Requirements
UTOPIA Level 2 Slave MegaCore Function October 2005, Version 2.5.0 Release Notes These release notes for the UTOPIA Level 2 Slave MegaCore function contain the following information: System Requirements
Recommended Protocol Configurations for Stratix IV GX FPGAs
 Recommended Protocol s for Stratix IV GX FPGAs AN-577-3.0 Application Note The architecture of the Altera Stratix IV GX FPGA is designed to accommodate the widest range of protocol standards spread over
Recommended Protocol s for Stratix IV GX FPGAs AN-577-3.0 Application Note The architecture of the Altera Stratix IV GX FPGA is designed to accommodate the widest range of protocol standards spread over
Table 1 shows the issues that affect the FIR Compiler, v6.1. Table 1. FIR Compiler, v6.1 Issues.
 December 2006, Version 6.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the Altera FIR Compiler, v6.1. Errata are functional defects or errors, which may cause an Altera
December 2006, Version 6.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the Altera FIR Compiler, v6.1. Errata are functional defects or errors, which may cause an Altera
Using Flexible-LVDS I/O Pins in
 Using Flexible-LVDS I/O Pins in APEX II Devices August 2002, ver. 1.1 Application Note 167 Introduction Recent expansion in the telecommunications market and growth in Internet use have created a demand
Using Flexible-LVDS I/O Pins in APEX II Devices August 2002, ver. 1.1 Application Note 167 Introduction Recent expansion in the telecommunications market and growth in Internet use have created a demand
DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler User Guide
 DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com Operations Part Number Compiler Version: 8.1 Document Date: November 2008 Copyright 2008 Altera
DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com Operations Part Number Compiler Version: 8.1 Document Date: November 2008 Copyright 2008 Altera
Stratix vs. Virtex-II Pro FPGA Performance Analysis
 White Paper Stratix vs. Virtex-II Pro FPGA Performance Analysis The Stratix TM and Stratix II architecture provides outstanding performance for the high performance design segment, providing clear performance
White Paper Stratix vs. Virtex-II Pro FPGA Performance Analysis The Stratix TM and Stratix II architecture provides outstanding performance for the high performance design segment, providing clear performance
RapidIO MegaCore Function
 March 2007, MegaCore Function Version 3.1.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the Altera RapidIO MegaCore function version 3.1.1. Errata are functional defects
March 2007, MegaCore Function Version 3.1.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the Altera RapidIO MegaCore function version 3.1.1. Errata are functional defects
Simulating the Reed-Solomon Model
 July 2000, ver. 1 Simulating the Reed-Solomon Model with the Visual IP Software User Guide Introduction Altera intellectual property (IP) MegaCore functions are developed and pre-tested by Altera, and
July 2000, ver. 1 Simulating the Reed-Solomon Model with the Visual IP Software User Guide Introduction Altera intellectual property (IP) MegaCore functions are developed and pre-tested by Altera, and
RapidIO MegaCore Function
 RapidIO MegaCore Function October 2007, MegaCore Function Version 7.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the Altera RapidIO MegaCore function version 7.0. Errata
RapidIO MegaCore Function October 2007, MegaCore Function Version 7.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the Altera RapidIO MegaCore function version 7.0. Errata
Using MAX II & MAX 3000A Devices as a Microcontroller I/O Expander
 Using MAX II & MAX 3000A Devices as a Microcontroller I/O Expander March 2004, ver 2.0 Application Note 265 Introduction Advantages of Using MAX II & MAX 3000A Devices Many microcontroller and microprocessors
Using MAX II & MAX 3000A Devices as a Microcontroller I/O Expander March 2004, ver 2.0 Application Note 265 Introduction Advantages of Using MAX II & MAX 3000A Devices Many microcontroller and microprocessors
Video and Image Processing Suite
 Video and Image Processing Suite December 2006, Version 7.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the MegaCore functions in the Video and Image Processing Suite,
Video and Image Processing Suite December 2006, Version 7.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the MegaCore functions in the Video and Image Processing Suite,
Introduction. Design Hierarchy. FPGA Compiler II BLIS & the Quartus II LogicLock Design Flow
 FPGA Compiler II BLIS & the Quartus II LogicLock Design Flow February 2002, ver. 2.0 Application Note 171 Introduction To maximize the benefits of the LogicLock TM block-based design methodology in the
FPGA Compiler II BLIS & the Quartus II LogicLock Design Flow February 2002, ver. 2.0 Application Note 171 Introduction To maximize the benefits of the LogicLock TM block-based design methodology in the
DSP Development Kit, Stratix II Edition
 DSP Development Kit, Stratix II Edition August 2005, Development Kit version 1.1.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation changes the DSP Development Kit, Stratix II Edition
DSP Development Kit, Stratix II Edition August 2005, Development Kit version 1.1.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation changes the DSP Development Kit, Stratix II Edition
Nios DMA. General Description. Functional Description
 Nios DMA January 2003, Version 1.1 Data Sheet General Functional The Nios DMA module is an Altera SOPC Builder library component included in the Nios development kit. The DMA module allows for efficient
Nios DMA January 2003, Version 1.1 Data Sheet General Functional The Nios DMA module is an Altera SOPC Builder library component included in the Nios development kit. The DMA module allows for efficient
Cyclone II FPGA Family
 ES-030405-1.3 Errata Sheet Introduction This errata sheet provides updated information on Cyclone II devices. This document addresses known device issues and includes methods to work around the issues.
ES-030405-1.3 Errata Sheet Introduction This errata sheet provides updated information on Cyclone II devices. This document addresses known device issues and includes methods to work around the issues.
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler
 DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler march 2007, Compiler Version 7.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version 7.0.
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler march 2007, Compiler Version 7.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version 7.0.
White Paper Enabling Quality of Service With Customizable Traffic Managers
 White Paper Enabling Quality of Service With Customizable Traffic s Introduction Communications networks are changing dramatically as lines blur between traditional telecom, wireless, and cable networks.
White Paper Enabling Quality of Service With Customizable Traffic s Introduction Communications networks are changing dramatically as lines blur between traditional telecom, wireless, and cable networks.
Simple Excalibur System
 Excalibur Solutions Simple Excalibur System August 2002, ver. 1.0 Application Note 242 Introduction This application note describes a simple Excalibur system design that consists of software running on
Excalibur Solutions Simple Excalibur System August 2002, ver. 1.0 Application Note 242 Introduction This application note describes a simple Excalibur system design that consists of software running on
PCI Express Compiler. System Requirements. New Features & Enhancements
 April 2006, Compiler Version 2.1.0 Release Notes These release notes for the PCI Express Compiler version 2.1.0 contain the following information: System Requirements New Features & Enhancements Errata
April 2006, Compiler Version 2.1.0 Release Notes These release notes for the PCI Express Compiler version 2.1.0 contain the following information: System Requirements New Features & Enhancements Errata
Introduction. Synchronous vs. Asynchronous Memory. Converting Memory from Asynchronous to Synchronous for Stratix & Stratix GX Designs
 Converting from synchronous to Synchronous for Stratix & Stratix GX esigns November 2002, ver. 2.0 pplication Note 210 Introduction The Stratix TM and Stratix GX device families provide a unique memory
Converting from synchronous to Synchronous for Stratix & Stratix GX esigns November 2002, ver. 2.0 pplication Note 210 Introduction The Stratix TM and Stratix GX device families provide a unique memory
PCI Express Multi-Channel DMA Interface
 2014.12.15 UG-01160 Subscribe The PCI Express DMA Multi-Channel Controller Example Design provides multi-channel support for the Stratix V Avalon Memory-Mapped (Avalon-MM) DMA for PCI Express IP Core.
2014.12.15 UG-01160 Subscribe The PCI Express DMA Multi-Channel Controller Example Design provides multi-channel support for the Stratix V Avalon Memory-Mapped (Avalon-MM) DMA for PCI Express IP Core.
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller
 DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller December 2005, Compiler Version 3.3.1 Release Notes These release notes for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version 3.3.1 contain the following information: System
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller December 2005, Compiler Version 3.3.1 Release Notes These release notes for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version 3.3.1 contain the following information: System
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler
 DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler May 2006, Compiler Version 3.3.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version 3.3.1.
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler May 2006, Compiler Version 3.3.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version 3.3.1.
Using the Nios Development Board Configuration Controller Reference Designs
 Using the Nios Development Board Controller Reference Designs July 2006 - ver 1.1 Application Note 346 Introduction Many modern embedded systems utilize flash memory to store processor configuration information
Using the Nios Development Board Controller Reference Designs July 2006 - ver 1.1 Application Note 346 Introduction Many modern embedded systems utilize flash memory to store processor configuration information
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller
 DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller October 2005, Compiler Version 3.3.0 Release Notes These release notes for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version 3.3.0 contain the following information: System
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller October 2005, Compiler Version 3.3.0 Release Notes These release notes for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version 3.3.0 contain the following information: System
DSP Builder. DSP Builder v6.1 Issues. Error When Directory Pathname is a Network UNC Path
 March 2007, Version 6.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation changes for DSP Builder version 6.1. Errata are functional defects or errors which may cause DSP Builder to deviate
March 2007, Version 6.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation changes for DSP Builder version 6.1. Errata are functional defects or errors which may cause DSP Builder to deviate
Legacy SDRAM Controller with Avalon Interface
 Legacy SDRAM Controller with Avalon Interface January 2003, Version 1.0 Data Sheet Introduction PTF Assignments SDRAM is commonly used in cost-sensitive applications requiring large amounts of memory.
Legacy SDRAM Controller with Avalon Interface January 2003, Version 1.0 Data Sheet Introduction PTF Assignments SDRAM is commonly used in cost-sensitive applications requiring large amounts of memory.
Matrices in MAX II & MAX 3000A Devices
 Crosspoint Switch Matrices in MAX II & MAX 3000A Devices March 200, ver. 2.0 Application Note 29 Introduction With a high level of flexibility, performance, and programmability, you can use crosspoint
Crosspoint Switch Matrices in MAX II & MAX 3000A Devices March 200, ver. 2.0 Application Note 29 Introduction With a high level of flexibility, performance, and programmability, you can use crosspoint
On-Chip Memory Implementations
 On-Chip Memory Implementations Using Cyclone Memory Blocks March 2003, ver. 1.1 Application Note 252 Introduction Cyclone devices feature embedded memory blocks that can be easily configured to support
On-Chip Memory Implementations Using Cyclone Memory Blocks March 2003, ver. 1.1 Application Note 252 Introduction Cyclone devices feature embedded memory blocks that can be easily configured to support
LogiCORE IP SPI-4.2 v12.2
 DS823 July 25, 2012 Introduction The Xilinx SPI-4.2 (PL4) core implements and is compliant with the OIF-SPI4-02.1 System Packet Phase 2 standard. This fully verified solution interconnects physical-layer
DS823 July 25, 2012 Introduction The Xilinx SPI-4.2 (PL4) core implements and is compliant with the OIF-SPI4-02.1 System Packet Phase 2 standard. This fully verified solution interconnects physical-layer
Design Verification Using the SignalTap II Embedded
 Design Verification Using the SignalTap II Embedded Logic Analyzer January 2003, ver. 1.0 Application Note 280 Introduction The SignalTap II embedded logic analyzer, available exclusively in the Altera
Design Verification Using the SignalTap II Embedded Logic Analyzer January 2003, ver. 1.0 Application Note 280 Introduction The SignalTap II embedded logic analyzer, available exclusively in the Altera
White Paper Using the MAX II altufm Megafunction I 2 C Interface
 White Paper Using the MAX II altufm Megafunction I 2 C Interface Introduction Inter-Integrated Circuit (I 2 C) is a bidirectional two-wire interface protocol, requiring only two bus lines; a serial data/address
White Paper Using the MAX II altufm Megafunction I 2 C Interface Introduction Inter-Integrated Circuit (I 2 C) is a bidirectional two-wire interface protocol, requiring only two bus lines; a serial data/address
Implementing LED Drivers in MAX Devices
 Implementing LE rivers in MAX evices ecember 2002, ver. 1.0 Application Note 286 Introduction Commercial LE river Chips iscrete light-emitting diode (LE) driver chips are common on many system boards.
Implementing LE rivers in MAX evices ecember 2002, ver. 1.0 Application Note 286 Introduction Commercial LE river Chips iscrete light-emitting diode (LE) driver chips are common on many system boards.
Designing with ESBs in APEX II Devices
 Designing with ESBs in APEX II Devices March 2002, ver. 1.0 Application Note 179 Introduction In APEX TM II devices, enhanced embedded system blocks (ESBs) support memory structures, such as single-port
Designing with ESBs in APEX II Devices March 2002, ver. 1.0 Application Note 179 Introduction In APEX TM II devices, enhanced embedded system blocks (ESBs) support memory structures, such as single-port
Arria II GX FPGA Development Kit HSMC Loopback Tests Rev 0.1
 Arria II GX FPGA Development Kit HSMC Loopback Tests Rev 0.1 High Speed Design Team, San Diego Thursday, July 23, 2009 1 2009 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. Altera, The Programmable Solutions
Arria II GX FPGA Development Kit HSMC Loopback Tests Rev 0.1 High Speed Design Team, San Diego Thursday, July 23, 2009 1 2009 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. Altera, The Programmable Solutions
100G Interlaken MegaCore Function User Guide
 00G Interlaken MegaCore Function User Guide Subscribe UG-028 05.06.203 0 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 9534 www.altera.com TOC-2 00G Interlaken MegaCore Function User Guide Contents About This MegaCore
00G Interlaken MegaCore Function User Guide Subscribe UG-028 05.06.203 0 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 9534 www.altera.com TOC-2 00G Interlaken MegaCore Function User Guide Contents About This MegaCore
CORDIC Reference Design. Introduction. Background
 CORDIC Reference Design June 2005, ver. 1.4 Application Note 263 Introduction The co-ordinate rotation digital computer (CORDIC) reference design implements the CORDIC algorithm, which converts cartesian
CORDIC Reference Design June 2005, ver. 1.4 Application Note 263 Introduction The co-ordinate rotation digital computer (CORDIC) reference design implements the CORDIC algorithm, which converts cartesian
RLDRAM II Controller MegaCore Function
 RLDRAM II Controller MegaCore Function November 2006, MegaCore Version 1.0.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the RLDRAM II Controller MegaCore function version
RLDRAM II Controller MegaCore Function November 2006, MegaCore Version 1.0.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the RLDRAM II Controller MegaCore function version
Simulating the PCI MegaCore Function Behavioral Models
 Simulating the PCI MegaCore Function Behavioral Models February 2003, ver. 1.2 Application Note 169 Introduction Altera intellectual property (IP) MegaCore functions are developed and pre-tested by Altera,
Simulating the PCI MegaCore Function Behavioral Models February 2003, ver. 1.2 Application Note 169 Introduction Altera intellectual property (IP) MegaCore functions are developed and pre-tested by Altera,
December 2002, ver. 1.3 Application Note 191. Six individual interrupts Six-bit priority scheme Five-bit priority scheme plus one individual interrupt
 Excalibur Solutions Using the Interrupt Controller December 22, ver..3 Application Note 9 Introduction This document describes the operation of the interrupt controller for the Excalibur devices, particularly
Excalibur Solutions Using the Interrupt Controller December 22, ver..3 Application Note 9 Introduction This document describes the operation of the interrupt controller for the Excalibur devices, particularly
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler
 DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler August 2007, Compiler Version 7.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version
DDR & DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler August 2007, Compiler Version 7.1 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler version
Exercise 1 In this exercise you will review the DSSS modem design using the Quartus II software.
 White Paper DSSS Modem Lab Background The direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) digital modem reference design is a hardware design that has been optimized for the Altera APEX DSP development board (starter
White Paper DSSS Modem Lab Background The direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) digital modem reference design is a hardware design that has been optimized for the Altera APEX DSP development board (starter
Using the Serial FlashLoader With the Quartus II Software
 Using the Serial FlashLoader With the Quartus II Software July 2006, ver. 3.0 Application Note 370 Introduction Using the Joint Test Action Group () interface, the Altera Serial FlashLoader (SFL) is the
Using the Serial FlashLoader With the Quartus II Software July 2006, ver. 3.0 Application Note 370 Introduction Using the Joint Test Action Group () interface, the Altera Serial FlashLoader (SFL) is the
Using DCFIFO for Data Transfer between Asynchronous Clock Domains
 Using DCFIFO for Data Transfer between Asynchronous Clock Domains, version 1.0 Application Note 473 Introduction In the design world, there are very few designs with a single clock domain. With increasingly
Using DCFIFO for Data Transfer between Asynchronous Clock Domains, version 1.0 Application Note 473 Introduction In the design world, there are very few designs with a single clock domain. With increasingly
Dynamic Reconfiguration of PMA Controls in Stratix V Devices
 Dynamic Reconfiguration of PMA Controls in Stratix V Devices AN-645-1.0 Application Note This application note describes how to use the transceiver reconfiguration controller to dynamically reconfigure
Dynamic Reconfiguration of PMA Controls in Stratix V Devices AN-645-1.0 Application Note This application note describes how to use the transceiver reconfiguration controller to dynamically reconfigure
AN 547: Putting the MAX II CPLD in Hibernation Mode to Achieve Zero Standby Current
 AN 547: Putting the MAX II CPLD in Hibernation Mode to Achieve Zero Standby Current January 2009 AN-547-10 Introduction To save power, the MAX II CPLD can be completely powered down into hibernation mode
AN 547: Putting the MAX II CPLD in Hibernation Mode to Achieve Zero Standby Current January 2009 AN-547-10 Introduction To save power, the MAX II CPLD can be completely powered down into hibernation mode
Toolflow for ARM-Based Embedded Processor PLDs
 Toolflow for ARM-Based Embedded Processor PLDs December 2000, ver. 1 Application Note Introduction The Excalibur embedded processor devices achieve a new level of system integration from the inclusion
Toolflow for ARM-Based Embedded Processor PLDs December 2000, ver. 1 Application Note Introduction The Excalibur embedded processor devices achieve a new level of system integration from the inclusion
RapidIO MegaCore Function
 March 2007, MegaCore Function Version 3.1.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the Altera RapidIO MegaCore function version 3.1.0. Errata are functional defects
March 2007, MegaCore Function Version 3.1.0 Errata Sheet This document addresses known errata and documentation issues for the Altera RapidIO MegaCore function version 3.1.0. Errata are functional defects
Excalibur Solutions Using the Expansion Bus Interface. Introduction. EBI Characteristics
 Excalibur Solutions Using the Expansion Bus Interface October 2002, ver. 1.0 Application Note 143 Introduction In the Excalibur family of devices, an ARM922T processor, memory and peripherals are embedded
Excalibur Solutions Using the Expansion Bus Interface October 2002, ver. 1.0 Application Note 143 Introduction In the Excalibur family of devices, an ARM922T processor, memory and peripherals are embedded
Using Flexible-LVDS Circuitry in Mercury Devices
 Using Flexible-LVDS Circuitry in Mercury Devices November 2002, ver. 1.1 Application Note 186 Introduction With the ever increasing demand for high bandwidth and low power consumption in the telecommunications
Using Flexible-LVDS Circuitry in Mercury Devices November 2002, ver. 1.1 Application Note 186 Introduction With the ever increasing demand for high bandwidth and low power consumption in the telecommunications
Benefits of Embedded RAM in FLEX 10K Devices
 Benefits of Embedded RAM in FLEX 1K Devices January 1996, ver. 1 Product Information Bulletin 2 Introduction Driven by the demand to integrate many more digital functions in a single device, custom logic
Benefits of Embedded RAM in FLEX 1K Devices January 1996, ver. 1 Product Information Bulletin 2 Introduction Driven by the demand to integrate many more digital functions in a single device, custom logic
FPGAs Provide Reconfigurable DSP Solutions
 FPGAs Provide Reconfigurable DSP Solutions Razak Mohammedali Product Marketing Engineer Altera Corporation DSP processors are widely used for implementing many DSP applications. Although DSP processors
FPGAs Provide Reconfigurable DSP Solutions Razak Mohammedali Product Marketing Engineer Altera Corporation DSP processors are widely used for implementing many DSP applications. Although DSP processors
ByteBlaster II Parallel Port Download Cable
 ByteBlaster II Parallel Port Download Cable December 2002, Version 1.0 Data Sheet Features Allows PC users to perform the following functions: Program MAX 9000, MAX 7000S, MAX 7000AE, MAX 7000B, MAX 3000A,
ByteBlaster II Parallel Port Download Cable December 2002, Version 1.0 Data Sheet Features Allows PC users to perform the following functions: Program MAX 9000, MAX 7000S, MAX 7000AE, MAX 7000B, MAX 3000A,
White Paper AHB to Avalon & Avalon to AHB Bridges
 White Paper AHB to & to AHB s Introduction For years, system designers have been manually connecting IP peripheral functions to embedded processors, taking anywhere from weeks to months to accomplish.
White Paper AHB to & to AHB s Introduction For years, system designers have been manually connecting IP peripheral functions to embedded processors, taking anywhere from weeks to months to accomplish.
Avalon Streaming Interface Specification
 Avalon Streaming Interface Specification 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com Document Version: 1.3 Document Date: June 2007 Copyright 2005 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. Altera,
Avalon Streaming Interface Specification 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com Document Version: 1.3 Document Date: June 2007 Copyright 2005 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. Altera,
Figure 1. Device Package Ordering Information for Stratix, Stratix GX, Cyclone, APEX 20KC, APEX II, Mercury & Excalibur Devices EP1S 25 F 780 C 5 N
 April 2003, ver. 15 Altera Devices Figures 1 and 2 explain the ordering codes for Altera devices. Devices that have multiple pin counts for the same package include the pin count in their ordering codes.
April 2003, ver. 15 Altera Devices Figures 1 and 2 explain the ordering codes for Altera devices. Devices that have multiple pin counts for the same package include the pin count in their ordering codes.
SERDES Transmitter/Receiver (ALTLVDS) Megafunction User Guide
 SERDES Transmitter/Receiver (ALTLVDS) Megafunction User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com Software Version: 8.1 Document Version: 4.0 Document Date: November 2008 UG-MF9504-4.0
SERDES Transmitter/Receiver (ALTLVDS) Megafunction User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com Software Version: 8.1 Document Version: 4.0 Document Date: November 2008 UG-MF9504-4.0
IMPLEMENTATION AGREEMENT: OIF-SPI SPI-5. System Packet Interface Level 5 (SPI-5): OC-768 System Interface for Physical and Link Layer Devices.
 Working Group: Physical and Link Layer (PLL) TITLE: System Packet Interface Level 5 (SPI-5): OC-768 System Interface for Physical and Link Layer Devices. SOURCE: Karl Gass Russ Tuck Technical Editor Sandia
Working Group: Physical and Link Layer (PLL) TITLE: System Packet Interface Level 5 (SPI-5): OC-768 System Interface for Physical and Link Layer Devices. SOURCE: Karl Gass Russ Tuck Technical Editor Sandia
APEX II The Complete I/O Solution
 APEX II The Complete I/O Solution July 2002 Altera introduces the APEX II device family: highperformance, high-bandwidth programmable logic devices (PLDs) targeted towards emerging network communications
APEX II The Complete I/O Solution July 2002 Altera introduces the APEX II device family: highperformance, high-bandwidth programmable logic devices (PLDs) targeted towards emerging network communications
FPGA Design Security Solution Using MAX II Devices
 White Paper FPGA Solution Using MAX II Devices Introduction SRAM-based FPGAs are volatile devices. They require external memory to store the configuration data that is sent to them at power up. It is possible
White Paper FPGA Solution Using MAX II Devices Introduction SRAM-based FPGAs are volatile devices. They require external memory to store the configuration data that is sent to them at power up. It is possible
Using Verplex Conformal LEC for Formal Verification of Design Functionality
 Using Verplex Conformal LEC for Formal Verification of Design Functionality January 2003, ver. 1.0 Application Note 296 Introduction The Altera Quartus II software, version 2.2, easily interfaces with
Using Verplex Conformal LEC for Formal Verification of Design Functionality January 2003, ver. 1.0 Application Note 296 Introduction The Altera Quartus II software, version 2.2, easily interfaces with
POS-PHY Level 2 & 3 Compiler
 POS-PHY Level 2 & 3 Compiler User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 (408) 544-7000 www.altera.com Core Version: 1.1.1 Document Version: 1.1.1 rev1 Document Date: July 2003 Copyright 2003 Altera
POS-PHY Level 2 & 3 Compiler User Guide 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 (408) 544-7000 www.altera.com Core Version: 1.1.1 Document Version: 1.1.1 rev1 Document Date: July 2003 Copyright 2003 Altera
Nios II Embedded Design Suite 6.1 Release Notes
 December 2006, Version 6.1 Release Notes This document lists the release notes for the Nios II Embedded Design Suite (EDS) version 6.1. Table of Contents: New Features & Enhancements...2 Device & Host
December 2006, Version 6.1 Release Notes This document lists the release notes for the Nios II Embedded Design Suite (EDS) version 6.1. Table of Contents: New Features & Enhancements...2 Device & Host
Using TriMatrix Embedded Memory Blocks
 Using TriMatrix Embedded Memory Blocks in Stratix & Stratix GX evices November 2002, ver. 2.0 Application Note 203 Introduction TriMatrix Memory Stratix and Stratix GX devices feature the TriMatrix memory
Using TriMatrix Embedded Memory Blocks in Stratix & Stratix GX evices November 2002, ver. 2.0 Application Note 203 Introduction TriMatrix Memory Stratix and Stratix GX devices feature the TriMatrix memory
4. TriMatrix Embedded Memory Blocks in HardCopy IV Devices
 January 2011 HIV51004-2.2 4. TriMatrix Embedded Memory Blocks in HardCopy IV Devices HIV51004-2.2 This chapter describes TriMatrix memory blocks, modes, features, and design considerations in HardCopy
January 2011 HIV51004-2.2 4. TriMatrix Embedded Memory Blocks in HardCopy IV Devices HIV51004-2.2 This chapter describes TriMatrix memory blocks, modes, features, and design considerations in HardCopy
Arria II GX FPGA Development Board
 Arria II GX FPGA Development Board DDR2 SODIMM Interface 2011 Help Document DDR2 SODIMM Interface Measurements were made on the DDR2 SODIMM interface using the Board Test System user interface. The Address,
Arria II GX FPGA Development Board DDR2 SODIMM Interface 2011 Help Document DDR2 SODIMM Interface Measurements were made on the DDR2 SODIMM interface using the Board Test System user interface. The Address,
Implementing 9.8G CPRI in Arria V GT and ST FPGAs
 03..06 AN 686 Subscribe This application note describes the implementation of 9.8304 Gbps Common Public Radio Interface (CPRI) using the Arria V GT and Arria V ST FPGA transceivers. The hard physical coding
03..06 AN 686 Subscribe This application note describes the implementation of 9.8304 Gbps Common Public Radio Interface (CPRI) using the Arria V GT and Arria V ST FPGA transceivers. The hard physical coding
24K FFT for 3GPP LTE RACH Detection
 24K FFT for GPP LTE RACH Detection ovember 2008, version 1.0 Application ote 515 Introduction In GPP Long Term Evolution (LTE), the user equipment (UE) transmits a random access channel (RACH) on the uplink
24K FFT for GPP LTE RACH Detection ovember 2008, version 1.0 Application ote 515 Introduction In GPP Long Term Evolution (LTE), the user equipment (UE) transmits a random access channel (RACH) on the uplink
Practical Hardware Debugging: Quick Notes On How to Simulate Altera s Nios II Multiprocessor Systems Using Mentor Graphics ModelSim
 Practical Hardware Debugging: Quick Notes On How to Simulate Altera s Nios II Multiprocessor Systems Using Mentor Graphics ModelSim Ray Duran Staff Design Specialist FAE, Altera Corporation 408-544-7937
Practical Hardware Debugging: Quick Notes On How to Simulate Altera s Nios II Multiprocessor Systems Using Mentor Graphics ModelSim Ray Duran Staff Design Specialist FAE, Altera Corporation 408-544-7937
White Paper Configuring the MicroBlaster Passive Serial Software Driver
 White Paper Configuring the MicroBlaster Passive Serial Software Driver Introduction The MicroBlaster TM software driver is designed to configure Altera programmable logic devices (PLDs) through the ByteBlasterMV
White Paper Configuring the MicroBlaster Passive Serial Software Driver Introduction The MicroBlaster TM software driver is designed to configure Altera programmable logic devices (PLDs) through the ByteBlasterMV
