C E N T R. Introduction to bioinformatics 2007 E B I O I N F O R M A T I C S V U F O R I N T. Lecture 13 G R A T I V. Iterative homology searching,
|
|
|
- Clifton Oscar Kennedy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 C E N T R E F O R I N T E G R A T I V E B I O I N F O R M A T I C S V U Introduction to bioinformatics 2007 Lecture 13 Iterative homology searching,
2 PSI (Position Specific Iterated) BLAST basic idea use results from BLAST query to construct a profile matrix search database with profile instead of query sequence iterate
3 A Profile Matrix (Position Specific Scoring Matrix PSSM) This is the same as a profile without position-specific gap penalties
4 Searching with a Profile PSI BLAST aligning profile matrix to a simple sequence like aligning two sequences except score for aligning a character with a matrix position is given by the matrix itself not a substitution matrix
5 PSI BLAST: Constructing the Profile Matrix Figure from: Altschul et al. Nucleic Acids Research 25, 1997
6 PSI BLAST: Determining Profile Elements the value for a given element of the profile matrix is given by: where the probability of seeing amino acid a i in column j is estimated as: Observed frequency Pseudocount e.g. α = number of sequences in profile, β=1
7 Q Q PSI-BLAST iteration xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Gapped BLAST search Query sequence Query sequence Database hits iterate A C D.. Y Pi Px A C D.. Y Pi Px Gapped BLAST search PSSM PSSM Database hits
8 PSI-BLAST steps in words Query sequences are first scanned for the presence of so-called low-complexity regions (Wooton and Federhen, 1996 next slide), i.e. regions with a biased composition likely to lead to spurious hits; are excluded from alignment. The program then initially operates on a single query sequence by performing a gapped BLAST search Then, the program takes significant local alignments (hits) found, constructs a multiple alignment (masterslave alignment) and abstracts a position-specific scoring matrix (PSSM) from this alignment. Rescan the database in a subsequent round, using the PSSM, to find more homologous sequences. Iteration continues until user decides to stop or search has converged
9 Low-complexity sequences xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Query sequence For example: AAAAA or AYLAYLAYL or AYLLYAALY Low-complexity (sub)sequences have a biased composition and contain less information than high-complexity sequences Because of the low information content, they often lead to spurious hits without a biological basis (for example, you can t tell whether a poly-a sequence is more similar to a globin, an immunoglobulin or a kinase sequence).
10 The innovation and power of BLAST is the statistical scoring system (PSI-)BLAST converts raw alignment scores based on the (query-database) sequence lengths the size of the data base the (amino acid or nucleotide) composition of the database It also checks to what extend a hit score is higher than randomly expected BLAST has a clever and fast way for this This makes the scores really comparable, so that the hit list can be ordered based on their statistical scores (bit-scores and E-values)
11 Statistics and thresholds Simple idea: accept only hits above a certain threshold value T The likelihood of random sequences to yield a score >T increases linearly with the logarithm of the search space n*m This gives the following formula for accepting hits: S > T + log(m*n)/λ, where λ is depending upon the scoring scheme (substitution matrix, gap penalties)
12 Alignment Bit Score B = (λs ln K) / ln 2 S is the raw alignment score The bit score ( bits ) B has a standard set of units The bit score B is calculated from the number of gaps and substitutions associated with each aligned sequence. The higher the score, the more significant the alignment λ and K and are the statistical parameters of the scoring system (BLOSUM62 in Blast). See Altschul and Gish, 1996, for a collection of values for λ and K over a set of widely used scoring matrices. Because bit scores are normalized with respect to the scoring system, they can be used to compare alignment scores from different searches based on different scoring schemes (a.a. exchange matrices)
13 Normalised sequence similarity The p-value is defined as the probability of seeing at least one unrelated score S greater than or equal to a given score x in a database search over n sequences. This probability follows the Poisson distribution (Waterman and Vingron, 1994): P(x, n) = 1 e -n P(S x), where n is the number of sequences in the database Depending on x and n (fixed)
14 Normalised sequence similarity Statistical significance The E-value is defined as the expected number of nonhomologous sequences with score greater than or equal to a score x in a database of n sequences: E(x, n) = n P(S x) For example, if E-value = 0.01, then the expected number of random hits with score S xis 0.01, which means that this E-value is expected by chance only once in 100 independent searches over the database. if the E-value of a hit is 5, then five fortuitous hits with S x are expected within a single database search, which renders the hit not significant.
15 A model for database searching score probabilities Scores resulting from searching with a query sequence against a database follow the Extreme Value Distribution (EDV) (Gumbel, 1955). Using the EDV, the raw alignment scores are converted to a statistical score (E value) that keeps track of the database amino acid composition and the scoring scheme (a.a. exchange matrix)
16 Extreme Value Distribution y = 1 exp(-e -λ(x-µ) ) Probability density function for the extreme value distribution resulting from parameter values µ = 0 and λ = 1, [y = 1 exp(-e -x )], where µ is the characteristic value and λ is the decay constant.
17 Extreme Value Distribution (EDV) EDV approximation real data You know that an optimal alignment of two sequences is selected out of many suboptimal alignments, and that a database search is also about selecting the best alignment(s). This bodes well with the EDV which has a right tail that falls off more slowly than the left tail. Compared to using the normal distribution, when using the EDV an alignment has to score further away from the expected mean value to become a significant hit.
18 Extreme Value Distribution The probability of a score S to be larger than a given value x can be approximated following the EDV as: E-value: P(S x) = 1 exp(-e -λ(x-µ) ), where µ =(ln Kmn)/λ, and K a constant that can be estimated from the background amino acid distribution and scoring matrix (see Altschul and Gish, 1996, for a collection of values for λ and K over a set of widely used scoring matrices).
19 Extreme Value Distribution Using the equation for µ (preceding slide), the probability for the raw alignment score S becomes P(S x) = 1 exp(-kmne -λx ). In practice, the probability P(S x) is estimated using the approximation 1 exp(-e -x ) e -x, which is valid for large values of x. This leads to a simplification of the equation for P(S x): P(S x) e -λ(x-µ) = Kmne -λx. The lower the probability (E value) for a given threshold value x, the more significant the score S.
20 Normalised sequence similarity Statistical significance Database searching is commonly performed using an E-value in between 0.1 and Low E-values decrease the number of false positives in a database search, but increase the number of false negatives, thereby lowering the sensitivity of the search.
21 Words of Encouragement There are three kinds of lies: lies, damned lies, and statistics Benjamin Disraeli Statistics in the hands of an engineer are like a lamppost to a drunk they re used more for support than illumination Then there is the man who drowned crossing a stream with an average depth of six inches. W.I.E. Gates
22 PSI-BLAST entry page Paste your query sequence Switch this off for default run
23
24 1 - This portion of each description links to the sequence record for a particular hit. 2 - Score or bit score is a value calculated from the number of gaps and substitutions associated with each aligned sequence. The higher the score, the more significant the alignment. Each score links to the corresponding pairwise alignment between query sequence and hit sequence (also referred to as subject or target sequence). 3 - E Value (Expect Value) describes the likelihood that a sequence with a similar score will occur in the database by chance. The smaller the E Value, the more significant the alignment. For example, the first alignment has a very low E value of e -117 meaning that a sequence with a similar score is very unlikely to occur simply by chance. 4 - These links provide the user with direct access from BLAST results to related entries in other databases. L links to LocusLink records and S links to structure records in NCBI's Molecular Modeling DataBase.
25 X residues denote low-complexity sequence fragments that are ignored
26 HMM-based homology searching Most widely used HMM-based profile searching tools currently are SAM-T2K (Karplus et al., 2000) and HMMER2 (Eddy, 1998) Formal probabilistic basis and consistent theory behind gap and insertion scores HMMs good for profile searches, not as good for alignment HMMs are slow
27
28 Profile wander
29 A B B C C D
30 Multi-domain Proteins (cont.) A common conserved protein domain such as the tyrosine kinase domain can make weak but relevant matches to other domain types appear very low in the hit list, so that they are missed (e.g. only appearing after 5000 kinase hits) Sequences containing low-complexity regions, such as coiled coils and transmembrane regions, can cause an explosion of the search rather than convergence because of the absence of any strong sequence signals. Conversely, some searches may lead to premature convergence; this occurs when the PSSM is too strict only allowing matches to very similar proteins, i.e., sequences with the same domain organization as the query are detected but no homologues with different domain combinations. In this case the power of iteration is not used fully.
31 How to assess homology search methods We need an annotated database, so we know which sequences belong to what homologous families Examples of databases of homologous families are PFAM, Homstrad or Astral The idea is to take a protein sequence from a given homologous family, then run the search method, and then assess how well the method has carried out the search This should be repeated for many query sequences and then the overall performance can be measured
32 Sequence searching QUERY True Positive DATABASE True Positive True Negative POSITIVES T False Positive NEGATIVES True Negative False Negative
33 Predicted P N So what have we got Observed P N TP FP FN TN
34 + T e s t - Sensitivity and Specificity medical world True Positive (TP) 10 False Negative (FN) All with Disease 10,000 Sensitivity= TP/(TP+ FN) 9990/( ) False Positive (FP) 989,010 True Negative (TN) All without Disease 999,000 Specificity= TN/(FP+TN ) 989,010/ (989, ) All with Positive Test TP+FP All with Negative Test FN+TN Positive Predictive Value= TP/(TP+FP) 9990/( ) =91% Negative Predictive Value= TN/(FN+TN) 989,010/(10+989,0 10) =99.999% Everyone= TP+FP+FN+TN Pre-Test Probability= (TP+FN)/(TP+FP+FN+TN) (in this case = prevalence) 10,000/1,000,000 = 1%
35 Receiver Operator Curve (ROC) Plot Sensitivity (TP/(TP+FN)) against 1- specificity (1-TN/(FP+TN)), where the latter is called error Sensitivity Sensitivity is also called Coverage Error = 1 - specificity
36
37
38
39
40
41 Sequence identity scoring zones >25-30%: homology zone 15-25%: twilight zone <15%: midnight zone (Rost, 1999) Is midnight zone properly definable?
BLAST - Basic Local Alignment Search Tool
 Lecture for ic Bioinformatics (DD2450) April 11, 2013 Searching 1. Input: Query Sequence 2. Database of sequences 3. Subject Sequence(s) 4. Output: High Segment Pairs (HSPs) Sequence Similarity Measures:
Lecture for ic Bioinformatics (DD2450) April 11, 2013 Searching 1. Input: Query Sequence 2. Database of sequences 3. Subject Sequence(s) 4. Output: High Segment Pairs (HSPs) Sequence Similarity Measures:
As of August 15, 2008, GenBank contained bases from reported sequences. The search procedure should be
 48 Bioinformatics I, WS 09-10, S. Henz (script by D. Huson) November 26, 2009 4 BLAST and BLAT Outline of the chapter: 1. Heuristics for the pairwise local alignment of two sequences 2. BLAST: search and
48 Bioinformatics I, WS 09-10, S. Henz (script by D. Huson) November 26, 2009 4 BLAST and BLAT Outline of the chapter: 1. Heuristics for the pairwise local alignment of two sequences 2. BLAST: search and
Sequence alignment theory and applications Session 3: BLAST algorithm
 Sequence alignment theory and applications Session 3: BLAST algorithm Introduction to Bioinformatics online course : IBT Sonal Henson Learning Objectives Understand the principles of the BLAST algorithm
Sequence alignment theory and applications Session 3: BLAST algorithm Introduction to Bioinformatics online course : IBT Sonal Henson Learning Objectives Understand the principles of the BLAST algorithm
COS 551: Introduction to Computational Molecular Biology Lecture: Oct 17, 2000 Lecturer: Mona Singh Scribe: Jacob Brenner 1. Database Searching
 COS 551: Introduction to Computational Molecular Biology Lecture: Oct 17, 2000 Lecturer: Mona Singh Scribe: Jacob Brenner 1 Database Searching In database search, we typically have a large sequence database
COS 551: Introduction to Computational Molecular Biology Lecture: Oct 17, 2000 Lecturer: Mona Singh Scribe: Jacob Brenner 1 Database Searching In database search, we typically have a large sequence database
BLAST: Basic Local Alignment Search Tool Altschul et al. J. Mol Bio CS 466 Saurabh Sinha
 BLAST: Basic Local Alignment Search Tool Altschul et al. J. Mol Bio. 1990. CS 466 Saurabh Sinha Motivation Sequence homology to a known protein suggest function of newly sequenced protein Bioinformatics
BLAST: Basic Local Alignment Search Tool Altschul et al. J. Mol Bio. 1990. CS 466 Saurabh Sinha Motivation Sequence homology to a known protein suggest function of newly sequenced protein Bioinformatics
Heuristic methods for pairwise alignment:
 Bi03c_1 Unit 03c: Heuristic methods for pairwise alignment: k-tuple-methods k-tuple-methods for alignment of pairs of sequences Bi03c_2 dynamic programming is too slow for large databases Use heuristic
Bi03c_1 Unit 03c: Heuristic methods for pairwise alignment: k-tuple-methods k-tuple-methods for alignment of pairs of sequences Bi03c_2 dynamic programming is too slow for large databases Use heuristic
24 Grundlagen der Bioinformatik, SS 10, D. Huson, April 26, This lecture is based on the following papers, which are all recommended reading:
 24 Grundlagen der Bioinformatik, SS 10, D. Huson, April 26, 2010 3 BLAST and FASTA This lecture is based on the following papers, which are all recommended reading: D.J. Lipman and W.R. Pearson, Rapid
24 Grundlagen der Bioinformatik, SS 10, D. Huson, April 26, 2010 3 BLAST and FASTA This lecture is based on the following papers, which are all recommended reading: D.J. Lipman and W.R. Pearson, Rapid
CS313 Exercise 4 Cover Page Fall 2017
 CS313 Exercise 4 Cover Page Fall 2017 Due by the start of class on Thursday, October 12, 2017. Name(s): In the TIME column, please estimate the time you spent on the parts of this exercise. Please try
CS313 Exercise 4 Cover Page Fall 2017 Due by the start of class on Thursday, October 12, 2017. Name(s): In the TIME column, please estimate the time you spent on the parts of this exercise. Please try
BLAST, Profile, and PSI-BLAST
 BLAST, Profile, and PSI-BLAST Jianlin Cheng, PhD School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Central Florida 26 Free for academic use Copyright @ Jianlin Cheng & original sources
BLAST, Profile, and PSI-BLAST Jianlin Cheng, PhD School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Central Florida 26 Free for academic use Copyright @ Jianlin Cheng & original sources
Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST)
 BLAST 26.04.2018 Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) BLAST (Altshul-1990) is an heuristic Pairwise Alignment composed by six-steps that search for local similarities. The most used access point to
BLAST 26.04.2018 Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) BLAST (Altshul-1990) is an heuristic Pairwise Alignment composed by six-steps that search for local similarities. The most used access point to
An Analysis of Pairwise Sequence Alignment Algorithm Complexities: Needleman-Wunsch, Smith-Waterman, FASTA, BLAST and Gapped BLAST
 An Analysis of Pairwise Sequence Alignment Algorithm Complexities: Needleman-Wunsch, Smith-Waterman, FASTA, BLAST and Gapped BLAST Alexander Chan 5075504 Biochemistry 218 Final Project An Analysis of Pairwise
An Analysis of Pairwise Sequence Alignment Algorithm Complexities: Needleman-Wunsch, Smith-Waterman, FASTA, BLAST and Gapped BLAST Alexander Chan 5075504 Biochemistry 218 Final Project An Analysis of Pairwise
CISC 636 Computational Biology & Bioinformatics (Fall 2016)
 CISC 636 Computational Biology & Bioinformatics (Fall 2016) Sequence pairwise alignment Score statistics: E-value and p-value Heuristic algorithms: BLAST and FASTA Database search: gene finding and annotations
CISC 636 Computational Biology & Bioinformatics (Fall 2016) Sequence pairwise alignment Score statistics: E-value and p-value Heuristic algorithms: BLAST and FASTA Database search: gene finding and annotations
CS 284A: Algorithms for Computational Biology Notes on Lecture: BLAST. The statistics of alignment scores.
 CS 284A: Algorithms for Computational Biology Notes on Lecture: BLAST. The statistics of alignment scores. prepared by Oleksii Kuchaiev, based on presentation by Xiaohui Xie on February 20th. 1 Introduction
CS 284A: Algorithms for Computational Biology Notes on Lecture: BLAST. The statistics of alignment scores. prepared by Oleksii Kuchaiev, based on presentation by Xiaohui Xie on February 20th. 1 Introduction
Bioinformatics. Sequence alignment BLAST Significance. Next time Protein Structure
 Bioinformatics Sequence alignment BLAST Significance Next time Protein Structure 1 Experimental origins of sequence data The Sanger dideoxynucleotide method F Each color is one lane of an electrophoresis
Bioinformatics Sequence alignment BLAST Significance Next time Protein Structure 1 Experimental origins of sequence data The Sanger dideoxynucleotide method F Each color is one lane of an electrophoresis
Bioinformatics for Biologists
 Bioinformatics for Biologists Sequence Analysis: Part I. Pairwise alignment and database searching Fran Lewitter, Ph.D. Director Bioinformatics & Research Computing Whitehead Institute Topics to Cover
Bioinformatics for Biologists Sequence Analysis: Part I. Pairwise alignment and database searching Fran Lewitter, Ph.D. Director Bioinformatics & Research Computing Whitehead Institute Topics to Cover
Bioinformatics explained: BLAST. March 8, 2007
 Bioinformatics Explained Bioinformatics explained: BLAST March 8, 2007 CLC bio Gustav Wieds Vej 10 8000 Aarhus C Denmark Telephone: +45 70 22 55 09 Fax: +45 70 22 55 19 www.clcbio.com info@clcbio.com Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics Explained Bioinformatics explained: BLAST March 8, 2007 CLC bio Gustav Wieds Vej 10 8000 Aarhus C Denmark Telephone: +45 70 22 55 09 Fax: +45 70 22 55 19 www.clcbio.com info@clcbio.com Bioinformatics
Profiles and Multiple Alignments. COMP 571 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University
 Profiles and Multiple Alignments COMP 571 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University Outline Profiles and sequence logos Profile hidden Markov models Aligning profiles Multiple sequence alignment by gradual sequence
Profiles and Multiple Alignments COMP 571 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University Outline Profiles and sequence logos Profile hidden Markov models Aligning profiles Multiple sequence alignment by gradual sequence
B L A S T! BLAST: Basic local alignment search tool. Copyright notice. February 6, Pairwise alignment: key points. Outline of tonight s lecture
 February 6, 2008 BLAST: Basic local alignment search tool B L A S T! Jonathan Pevsner, Ph.D. Introduction to Bioinformatics pevsner@jhmi.edu 4.633.0 Copyright notice Many of the images in this powerpoint
February 6, 2008 BLAST: Basic local alignment search tool B L A S T! Jonathan Pevsner, Ph.D. Introduction to Bioinformatics pevsner@jhmi.edu 4.633.0 Copyright notice Many of the images in this powerpoint
Compares a sequence of protein to another sequence or database of a protein, or a sequence of DNA to another sequence or library of DNA.
 Compares a sequence of protein to another sequence or database of a protein, or a sequence of DNA to another sequence or library of DNA. Fasta is used to compare a protein or DNA sequence to all of the
Compares a sequence of protein to another sequence or database of a protein, or a sequence of DNA to another sequence or library of DNA. Fasta is used to compare a protein or DNA sequence to all of the
Computational Genomics and Molecular Biology, Fall
 Computational Genomics and Molecular Biology, Fall 2015 1 Sequence Alignment Dannie Durand Pairwise Sequence Alignment The goal of pairwise sequence alignment is to establish a correspondence between the
Computational Genomics and Molecular Biology, Fall 2015 1 Sequence Alignment Dannie Durand Pairwise Sequence Alignment The goal of pairwise sequence alignment is to establish a correspondence between the
Mismatch String Kernels for SVM Protein Classification
 Mismatch String Kernels for SVM Protein Classification by C. Leslie, E. Eskin, J. Weston, W.S. Noble Athina Spiliopoulou Morfoula Fragopoulou Ioannis Konstas Outline Definitions & Background Proteins Remote
Mismatch String Kernels for SVM Protein Classification by C. Leslie, E. Eskin, J. Weston, W.S. Noble Athina Spiliopoulou Morfoula Fragopoulou Ioannis Konstas Outline Definitions & Background Proteins Remote
Chapter 8 Multiple sequence alignment. Chaochun Wei Spring 2018
 1896 1920 1987 2006 Chapter 8 Multiple sequence alignment Chaochun Wei Spring 2018 Contents 1. Reading materials 2. Multiple sequence alignment basic algorithms and tools how to improve multiple alignment
1896 1920 1987 2006 Chapter 8 Multiple sequence alignment Chaochun Wei Spring 2018 Contents 1. Reading materials 2. Multiple sequence alignment basic algorithms and tools how to improve multiple alignment
Sequence analysis Pairwise sequence alignment
 UMF11 Introduction to bioinformatics, 25 Sequence analysis Pairwise sequence alignment 1. Sequence alignment Lecturer: Marina lexandersson 12 September, 25 here are two types of sequence alignments, global
UMF11 Introduction to bioinformatics, 25 Sequence analysis Pairwise sequence alignment 1. Sequence alignment Lecturer: Marina lexandersson 12 September, 25 here are two types of sequence alignments, global
Biology 644: Bioinformatics
 Find the best alignment between 2 sequences with lengths n and m, respectively Best alignment is very dependent upon the substitution matrix and gap penalties The Global Alignment Problem tries to find
Find the best alignment between 2 sequences with lengths n and m, respectively Best alignment is very dependent upon the substitution matrix and gap penalties The Global Alignment Problem tries to find
Multiple Sequence Alignment Based on Profile Alignment of Intermediate Sequences
 Multiple Sequence Alignment Based on Profile Alignment of Intermediate Sequences Yue Lu and Sing-Hoi Sze RECOMB 2007 Presented by: Wanxing Xu March 6, 2008 Content Biology Motivation Computation Problem
Multiple Sequence Alignment Based on Profile Alignment of Intermediate Sequences Yue Lu and Sing-Hoi Sze RECOMB 2007 Presented by: Wanxing Xu March 6, 2008 Content Biology Motivation Computation Problem
Chapter 6. Multiple sequence alignment (week 10)
 Course organization Introduction ( Week 1,2) Part I: Algorithms for Sequence Analysis (Week 1-11) Chapter 1-3, Models and theories» Probability theory and Statistics (Week 3)» Algorithm complexity analysis
Course organization Introduction ( Week 1,2) Part I: Algorithms for Sequence Analysis (Week 1-11) Chapter 1-3, Models and theories» Probability theory and Statistics (Week 3)» Algorithm complexity analysis
Computational Molecular Biology
 Computational Molecular Biology Erwin M. Bakker Lecture 3, mainly from material by R. Shamir [2] and H.J. Hoogeboom [4]. 1 Pairwise Sequence Alignment Biological Motivation Algorithmic Aspect Recursive
Computational Molecular Biology Erwin M. Bakker Lecture 3, mainly from material by R. Shamir [2] and H.J. Hoogeboom [4]. 1 Pairwise Sequence Alignment Biological Motivation Algorithmic Aspect Recursive
.. Fall 2011 CSC 570: Bioinformatics Alexander Dekhtyar..
 .. Fall 2011 CSC 570: Bioinformatics Alexander Dekhtyar.. PAM and BLOSUM Matrices Prepared by: Jason Banich and Chris Hoover Background As DNA sequences change and evolve, certain amino acids are more
.. Fall 2011 CSC 570: Bioinformatics Alexander Dekhtyar.. PAM and BLOSUM Matrices Prepared by: Jason Banich and Chris Hoover Background As DNA sequences change and evolve, certain amino acids are more
FASTA. Besides that, FASTA package provides SSEARCH, an implementation of the optimal Smith- Waterman algorithm.
 FASTA INTRODUCTION Definition (by David J. Lipman and William R. Pearson in 1985) - Compares a sequence of protein to another sequence or database of a protein, or a sequence of DNA to another sequence
FASTA INTRODUCTION Definition (by David J. Lipman and William R. Pearson in 1985) - Compares a sequence of protein to another sequence or database of a protein, or a sequence of DNA to another sequence
BLAST MCDB 187. Friday, February 8, 13
 BLAST MCDB 187 BLAST Basic Local Alignment Sequence Tool Uses shortcut to compute alignments of a sequence against a database very quickly Typically takes about a minute to align a sequence against a database
BLAST MCDB 187 BLAST Basic Local Alignment Sequence Tool Uses shortcut to compute alignments of a sequence against a database very quickly Typically takes about a minute to align a sequence against a database
CAP BLAST. BIOINFORMATICS Su-Shing Chen CISE. 8/20/2005 Su-Shing Chen, CISE 1
 CAP 5510-6 BLAST BIOINFORMATICS Su-Shing Chen CISE 8/20/2005 Su-Shing Chen, CISE 1 BLAST Basic Local Alignment Prof Search Su-Shing Chen Tool A Fast Pair-wise Alignment and Database Searching Tool 8/20/2005
CAP 5510-6 BLAST BIOINFORMATICS Su-Shing Chen CISE 8/20/2005 Su-Shing Chen, CISE 1 BLAST Basic Local Alignment Prof Search Su-Shing Chen Tool A Fast Pair-wise Alignment and Database Searching Tool 8/20/2005
A NEW GENERATION OF HOMOLOGY SEARCH TOOLS BASED ON PROBABILISTIC INFERENCE
 205 A NEW GENERATION OF HOMOLOGY SEARCH TOOLS BASED ON PROBABILISTIC INFERENCE SEAN R. EDDY 1 eddys@janelia.hhmi.org 1 Janelia Farm Research Campus, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, 19700 Helix Drive,
205 A NEW GENERATION OF HOMOLOGY SEARCH TOOLS BASED ON PROBABILISTIC INFERENCE SEAN R. EDDY 1 eddys@janelia.hhmi.org 1 Janelia Farm Research Campus, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, 19700 Helix Drive,
Bioinformatics explained: Smith-Waterman
 Bioinformatics Explained Bioinformatics explained: Smith-Waterman May 1, 2007 CLC bio Gustav Wieds Vej 10 8000 Aarhus C Denmark Telephone: +45 70 22 55 09 Fax: +45 70 22 55 19 www.clcbio.com info@clcbio.com
Bioinformatics Explained Bioinformatics explained: Smith-Waterman May 1, 2007 CLC bio Gustav Wieds Vej 10 8000 Aarhus C Denmark Telephone: +45 70 22 55 09 Fax: +45 70 22 55 19 www.clcbio.com info@clcbio.com
Principles of Bioinformatics. BIO540/STA569/CSI660 Fall 2010
 Principles of Bioinformatics BIO540/STA569/CSI660 Fall 2010 Lecture 11 Multiple Sequence Alignment I Administrivia Administrivia The midterm examination will be Monday, October 18 th, in class. Closed
Principles of Bioinformatics BIO540/STA569/CSI660 Fall 2010 Lecture 11 Multiple Sequence Alignment I Administrivia Administrivia The midterm examination will be Monday, October 18 th, in class. Closed
Database Searching Using BLAST
 Mahidol University Objectives SCMI512 Molecular Sequence Analysis Database Searching Using BLAST Lecture 2B After class, students should be able to: explain the FASTA algorithm for database searching explain
Mahidol University Objectives SCMI512 Molecular Sequence Analysis Database Searching Using BLAST Lecture 2B After class, students should be able to: explain the FASTA algorithm for database searching explain
Similarity Searches on Sequence Databases
 Similarity Searches on Sequence Databases Lorenza Bordoli Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics EMBnet Course, Zürich, October 2004 Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics Swiss EMBnet node Outline Importance of
Similarity Searches on Sequence Databases Lorenza Bordoli Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics EMBnet Course, Zürich, October 2004 Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics Swiss EMBnet node Outline Importance of
PROTEIN MULTIPLE ALIGNMENT MOTIVATION: BACKGROUND: Marina Sirota
 Marina Sirota MOTIVATION: PROTEIN MULTIPLE ALIGNMENT To study evolution on the genetic level across a wide range of organisms, biologists need accurate tools for multiple sequence alignment of protein
Marina Sirota MOTIVATION: PROTEIN MULTIPLE ALIGNMENT To study evolution on the genetic level across a wide range of organisms, biologists need accurate tools for multiple sequence alignment of protein
A Coprocessor Architecture for Fast Protein Structure Prediction
 A Coprocessor Architecture for Fast Protein Structure Prediction M. Marolia, R. Khoja, T. Acharya, C. Chakrabarti Department of Electrical Engineering Arizona State University, Tempe, USA. Abstract Predicting
A Coprocessor Architecture for Fast Protein Structure Prediction M. Marolia, R. Khoja, T. Acharya, C. Chakrabarti Department of Electrical Engineering Arizona State University, Tempe, USA. Abstract Predicting
Introduction to Computational Molecular Biology
 18.417 Introduction to Computational Molecular Biology Lecture 13: October 21, 2004 Scribe: Eitan Reich Lecturer: Ross Lippert Editor: Peter Lee 13.1 Introduction We have been looking at algorithms to
18.417 Introduction to Computational Molecular Biology Lecture 13: October 21, 2004 Scribe: Eitan Reich Lecturer: Ross Lippert Editor: Peter Lee 13.1 Introduction We have been looking at algorithms to
New String Kernels for Biosequence Data
 Workshop on Kernel Methods in Bioinformatics New String Kernels for Biosequence Data Christina Leslie Department of Computer Science Columbia University Biological Sequence Classification Problems Protein
Workshop on Kernel Methods in Bioinformatics New String Kernels for Biosequence Data Christina Leslie Department of Computer Science Columbia University Biological Sequence Classification Problems Protein
Introduction to BLAST with Protein Sequences. Utah State University Spring 2014 STAT 5570: Statistical Bioinformatics Notes 6.2
 Introduction to BLAST with Protein Sequences Utah State University Spring 2014 STAT 5570: Statistical Bioinformatics Notes 6.2 1 References Chapter 2 of Biological Sequence Analysis (Durbin et al., 2001)
Introduction to BLAST with Protein Sequences Utah State University Spring 2014 STAT 5570: Statistical Bioinformatics Notes 6.2 1 References Chapter 2 of Biological Sequence Analysis (Durbin et al., 2001)
L4: Blast: Alignment Scores etc.
 L4: Blast: Alignment Scores etc. Why is Blast Fast? Silly Question Prove or Disprove: There are two people in New York City with exactly the same number of hairs. Large database search Database (n) Query
L4: Blast: Alignment Scores etc. Why is Blast Fast? Silly Question Prove or Disprove: There are two people in New York City with exactly the same number of hairs. Large database search Database (n) Query
Lecture 5 Advanced BLAST
 Introduction to Bioinformatics for Medical Research Gideon Greenspan gdg@cs.technion.ac.il Lecture 5 Advanced BLAST BLAST Recap Sequence Alignment Complexity and indexing BLASTN and BLASTP Basic parameters
Introduction to Bioinformatics for Medical Research Gideon Greenspan gdg@cs.technion.ac.il Lecture 5 Advanced BLAST BLAST Recap Sequence Alignment Complexity and indexing BLASTN and BLASTP Basic parameters
Using Hybrid Alignment for Iterative Sequence Database Searches
 Using Hybrid Alignment for Iterative Sequence Database Searches Yuheng Li, Mario Lauria, Department of Computer and Information Science The Ohio State University 2015 Neil Avenue #395 Columbus, OH 43210-1106
Using Hybrid Alignment for Iterative Sequence Database Searches Yuheng Li, Mario Lauria, Department of Computer and Information Science The Ohio State University 2015 Neil Avenue #395 Columbus, OH 43210-1106
Evaluating Machine Learning Methods: Part 1
 Evaluating Machine Learning Methods: Part 1 CS 760@UW-Madison Goals for the lecture you should understand the following concepts bias of an estimator learning curves stratified sampling cross validation
Evaluating Machine Learning Methods: Part 1 CS 760@UW-Madison Goals for the lecture you should understand the following concepts bias of an estimator learning curves stratified sampling cross validation
Lecture Overview. Sequence search & alignment. Searching sequence databases. Sequence Alignment & Search. Goals: Motivations:
 Lecture Overview Sequence Alignment & Search Karin Verspoor, Ph.D. Faculty, Computational Bioscience Program University of Colorado School of Medicine With credit and thanks to Larry Hunter for creating
Lecture Overview Sequence Alignment & Search Karin Verspoor, Ph.D. Faculty, Computational Bioscience Program University of Colorado School of Medicine With credit and thanks to Larry Hunter for creating
Lecture 5: Markov models
 Master s course Bioinformatics Data Analysis and Tools Lecture 5: Markov models Centre for Integrative Bioinformatics Problem in biology Data and patterns are often not clear cut When we want to make a
Master s course Bioinformatics Data Analysis and Tools Lecture 5: Markov models Centre for Integrative Bioinformatics Problem in biology Data and patterns are often not clear cut When we want to make a
Sequence Alignment & Search
 Sequence Alignment & Search Karin Verspoor, Ph.D. Faculty, Computational Bioscience Program University of Colorado School of Medicine With credit and thanks to Larry Hunter for creating the first version
Sequence Alignment & Search Karin Verspoor, Ph.D. Faculty, Computational Bioscience Program University of Colorado School of Medicine With credit and thanks to Larry Hunter for creating the first version
Module: Sequence Alignment Theory and Applica8ons Session: BLAST
 Module: Sequence Alignment Theory and Applica8ons Session: BLAST Learning Objec8ves and Outcomes v Understand the principles of the BLAST algorithm v Understand the different BLAST algorithms, parameters
Module: Sequence Alignment Theory and Applica8ons Session: BLAST Learning Objec8ves and Outcomes v Understand the principles of the BLAST algorithm v Understand the different BLAST algorithms, parameters
15-780: Graduate Artificial Intelligence. Computational biology: Sequence alignment and profile HMMs
 5-78: Graduate rtificial Intelligence omputational biology: Sequence alignment and profile HMMs entral dogma DN GGGG transcription mrn UGGUUUGUG translation Protein PEPIDE 2 omparison of Different Organisms
5-78: Graduate rtificial Intelligence omputational biology: Sequence alignment and profile HMMs entral dogma DN GGGG transcription mrn UGGUUUGUG translation Protein PEPIDE 2 omparison of Different Organisms
Scoring and heuristic methods for sequence alignment CG 17
 Scoring and heuristic methods for sequence alignment CG 17 Amino Acid Substitution Matrices Used to score alignments. Reflect evolution of sequences. Unitary Matrix: M ij = 1 i=j { 0 o/w Genetic Code Matrix:
Scoring and heuristic methods for sequence alignment CG 17 Amino Acid Substitution Matrices Used to score alignments. Reflect evolution of sequences. Unitary Matrix: M ij = 1 i=j { 0 o/w Genetic Code Matrix:
USING AN EXTENDED SUFFIX TREE TO SPEED-UP SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT
 IADIS International Conference Applied Computing 2006 USING AN EXTENDED SUFFIX TREE TO SPEED-UP SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT Divya R. Singh Software Engineer Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA 98052, USA Abdullah
IADIS International Conference Applied Computing 2006 USING AN EXTENDED SUFFIX TREE TO SPEED-UP SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT Divya R. Singh Software Engineer Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA 98052, USA Abdullah
AlignMe Manual. Version 1.1. Rene Staritzbichler, Marcus Stamm, Kamil Khafizov and Lucy R. Forrest
 AlignMe Manual Version 1.1 Rene Staritzbichler, Marcus Stamm, Kamil Khafizov and Lucy R. Forrest Max Planck Institute of Biophysics Frankfurt am Main 60438 Germany 1) Introduction...3 2) Using AlignMe
AlignMe Manual Version 1.1 Rene Staritzbichler, Marcus Stamm, Kamil Khafizov and Lucy R. Forrest Max Planck Institute of Biophysics Frankfurt am Main 60438 Germany 1) Introduction...3 2) Using AlignMe
Chapter 4: Blast. Chaochun Wei Fall 2014
 Course organization Introduction ( Week 1-2) Course introduction A brief introduction to molecular biology A brief introduction to sequence comparison Part I: Algorithms for Sequence Analysis (Week 3-11)
Course organization Introduction ( Week 1-2) Course introduction A brief introduction to molecular biology A brief introduction to sequence comparison Part I: Algorithms for Sequence Analysis (Week 3-11)
Semi-supervised protein classification using cluster kernels
 Semi-supervised protein classification using cluster kernels Jason Weston Max Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics, 72076 Tübingen, Germany weston@tuebingen.mpg.de Dengyong Zhou, Andre Elisseeff
Semi-supervised protein classification using cluster kernels Jason Weston Max Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics, 72076 Tübingen, Germany weston@tuebingen.mpg.de Dengyong Zhou, Andre Elisseeff
Searching Sequence Databases
 Wright State University CORE Scholar Computer Science and Engineering Faculty Publications Computer Science & Engineering 2003 Searching Sequence Databases Dan E. Krane Wright State University - Main Campus,
Wright State University CORE Scholar Computer Science and Engineering Faculty Publications Computer Science & Engineering 2003 Searching Sequence Databases Dan E. Krane Wright State University - Main Campus,
3.4 Multiple sequence alignment
 3.4 Multiple sequence alignment Why produce a multiple sequence alignment? Using more than two sequences results in a more convincing alignment by revealing conserved regions in ALL of the sequences Aligned
3.4 Multiple sequence alignment Why produce a multiple sequence alignment? Using more than two sequences results in a more convincing alignment by revealing conserved regions in ALL of the sequences Aligned
Alignments BLAST, BLAT
 Alignments BLAST, BLAT Genome Genome Gene vs Built of DNA DNA Describes Organism Protein gene Stored as Circular/ linear Single molecule, or a few of them Both (depending on the species) Part of genome
Alignments BLAST, BLAT Genome Genome Gene vs Built of DNA DNA Describes Organism Protein gene Stored as Circular/ linear Single molecule, or a few of them Both (depending on the species) Part of genome
JET 2 User Manual 1 INSTALLATION 2 EXECUTION AND FUNCTIONALITIES. 1.1 Download. 1.2 System requirements. 1.3 How to install JET 2
 JET 2 User Manual 1 INSTALLATION 1.1 Download The JET 2 package is available at www.lcqb.upmc.fr/jet2. 1.2 System requirements JET 2 runs on Linux or Mac OS X. The program requires some external tools
JET 2 User Manual 1 INSTALLATION 1.1 Download The JET 2 package is available at www.lcqb.upmc.fr/jet2. 1.2 System requirements JET 2 runs on Linux or Mac OS X. The program requires some external tools
Application of Support Vector Machine In Bioinformatics
 Application of Support Vector Machine In Bioinformatics V. K. Jayaraman Scientific and Engineering Computing Group CDAC, Pune jayaramanv@cdac.in Arun Gupta Computational Biology Group AbhyudayaTech, Indore
Application of Support Vector Machine In Bioinformatics V. K. Jayaraman Scientific and Engineering Computing Group CDAC, Pune jayaramanv@cdac.in Arun Gupta Computational Biology Group AbhyudayaTech, Indore
Alignment of Pairs of Sequences
 Bi03a_1 Unit 03a: Alignment of Pairs of Sequences Partners for alignment Bi03a_2 Protein 1 Protein 2 =amino-acid sequences (20 letter alphabeth + gap) LGPSSKQTGKGS-SRIWDN LN-ITKSAGKGAIMRLGDA -------TGKG--------
Bi03a_1 Unit 03a: Alignment of Pairs of Sequences Partners for alignment Bi03a_2 Protein 1 Protein 2 =amino-acid sequences (20 letter alphabeth + gap) LGPSSKQTGKGS-SRIWDN LN-ITKSAGKGAIMRLGDA -------TGKG--------
Today s Lecture. Multiple sequence alignment. Improved scoring of pairwise alignments. Affine gap penalties Profiles
 Today s Lecture Multiple sequence alignment Improved scoring of pairwise alignments Affine gap penalties Profiles 1 The Edit Graph for a Pair of Sequences G A C G T T G A A T G A C C C A C A T G A C G
Today s Lecture Multiple sequence alignment Improved scoring of pairwise alignments Affine gap penalties Profiles 1 The Edit Graph for a Pair of Sequences G A C G T T G A A T G A C C C A C A T G A C G
Remote Homolog Detection Using Local Sequence Structure Correlations
 PROTEINS: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics 57:518 530 (2004) Remote Homolog Detection Using Local Sequence Structure Correlations Yuna Hou, 1 * Wynne Hsu, 1 Mong Li Lee, 1 and Christopher Bystroff
PROTEINS: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics 57:518 530 (2004) Remote Homolog Detection Using Local Sequence Structure Correlations Yuna Hou, 1 * Wynne Hsu, 1 Mong Li Lee, 1 and Christopher Bystroff
Evaluating Machine-Learning Methods. Goals for the lecture
 Evaluating Machine-Learning Methods Mark Craven and David Page Computer Sciences 760 Spring 2018 www.biostat.wisc.edu/~craven/cs760/ Some of the slides in these lectures have been adapted/borrowed from
Evaluating Machine-Learning Methods Mark Craven and David Page Computer Sciences 760 Spring 2018 www.biostat.wisc.edu/~craven/cs760/ Some of the slides in these lectures have been adapted/borrowed from
2) NCBI BLAST tutorial This is a users guide written by the education department at NCBI.
 Web resources -- Tour. page 1 of 8 This is a guided tour. Any homework is separate. In fact, this exercise is used for multiple classes and is publicly available to everyone. The entire tour will take
Web resources -- Tour. page 1 of 8 This is a guided tour. Any homework is separate. In fact, this exercise is used for multiple classes and is publicly available to everyone. The entire tour will take
Biologically significant sequence alignments using Boltzmann probabilities
 Biologically significant sequence alignments using Boltzmann probabilities P Clote Department of Biology, Boston College Gasson Hall 16, Chestnut Hill MA 0267 clote@bcedu Abstract In this paper, we give
Biologically significant sequence alignments using Boltzmann probabilities P Clote Department of Biology, Boston College Gasson Hall 16, Chestnut Hill MA 0267 clote@bcedu Abstract In this paper, we give
INTRODUCTION TO BIOINFORMATICS
 Molecular Biology-2019 1 INTRODUCTION TO BIOINFORMATICS In this section, we want to provide a simple introduction to using the web site of the National Center for Biotechnology Information NCBI) to obtain
Molecular Biology-2019 1 INTRODUCTION TO BIOINFORMATICS In this section, we want to provide a simple introduction to using the web site of the National Center for Biotechnology Information NCBI) to obtain
GLOBEX Bioinformatics (Summer 2015) Multiple Sequence Alignment
 GLOBEX Bioinformatics (Summer 2015) Multiple Sequence Alignment Scoring Dynamic Programming algorithms Heuristic algorithms CLUSTAL W Courtesy of jalview Motivations Collective (or aggregate) statistic
GLOBEX Bioinformatics (Summer 2015) Multiple Sequence Alignment Scoring Dynamic Programming algorithms Heuristic algorithms CLUSTAL W Courtesy of jalview Motivations Collective (or aggregate) statistic
Algorithms in Bioinformatics: A Practical Introduction. Database Search
 Algorithms in Bioinformatics: A Practical Introduction Database Search Biological databases Biological data is double in size every 15 or 16 months Increasing in number of queries: 40,000 queries per day
Algorithms in Bioinformatics: A Practical Introduction Database Search Biological databases Biological data is double in size every 15 or 16 months Increasing in number of queries: 40,000 queries per day
False Discovery Rate for Homology Searches
 False Discovery Rate for Homology Searches Hyrum D. Carroll 1,AlexC.Williams 1, Anthony G. Davis 1,andJohnL.Spouge 2 1 Middle Tennessee State University Department of Computer Science Murfreesboro, TN
False Discovery Rate for Homology Searches Hyrum D. Carroll 1,AlexC.Williams 1, Anthony G. Davis 1,andJohnL.Spouge 2 1 Middle Tennessee State University Department of Computer Science Murfreesboro, TN
Hybrid alignment: high-performance with universal statistics
 BIOINFORMATICS Vol. 18 no. 6 2002 Pages 864 872 Hybrid alignment: high-performance with universal statistics Yi-Kuo Yu 1, Ralf Bundschuh 2, and Terence Hwa 2 1 Department of Physics, Florida Atlantic University,
BIOINFORMATICS Vol. 18 no. 6 2002 Pages 864 872 Hybrid alignment: high-performance with universal statistics Yi-Kuo Yu 1, Ralf Bundschuh 2, and Terence Hwa 2 1 Department of Physics, Florida Atlantic University,
Finding data. HMMER Answer key
 Finding data HMMER Answer key HMMER input is prepared using VectorBase ClustalW, which runs a Java application for the graphical representation of the results. If you get an error message that blocks this
Finding data HMMER Answer key HMMER input is prepared using VectorBase ClustalW, which runs a Java application for the graphical representation of the results. If you get an error message that blocks this
Data Mining Technologies for Bioinformatics Sequences
 Data Mining Technologies for Bioinformatics Sequences Deepak Garg Computer Science and Engineering Department Thapar Institute of Engineering & Tecnology, Patiala Abstract Main tool used for sequence alignment
Data Mining Technologies for Bioinformatics Sequences Deepak Garg Computer Science and Engineering Department Thapar Institute of Engineering & Tecnology, Patiala Abstract Main tool used for sequence alignment
Multiple Sequence Alignment: Multidimensional. Biological Motivation
 Multiple Sequence Alignment: Multidimensional Dynamic Programming Boston University Biological Motivation Compare a new sequence with the sequences in a protein family. Proteins can be categorized into
Multiple Sequence Alignment: Multidimensional Dynamic Programming Boston University Biological Motivation Compare a new sequence with the sequences in a protein family. Proteins can be categorized into
FastA and the chaining problem, Gunnar Klau, December 1, 2005, 10:
 FastA and the chaining problem, Gunnar Klau, December 1, 2005, 10:56 4001 4 FastA and the chaining problem We will discuss: Heuristics used by the FastA program for sequence alignment Chaining problem
FastA and the chaining problem, Gunnar Klau, December 1, 2005, 10:56 4001 4 FastA and the chaining problem We will discuss: Heuristics used by the FastA program for sequence alignment Chaining problem
Multiple Sequence Alignment II
 Multiple Sequence Alignment II Lectures 20 Dec 5, 2011 CSE 527 Computational Biology, Fall 2011 Instructor: Su-In Lee TA: Christopher Miles Monday & Wednesday 12:00-1:20 Johnson Hall (JHN) 022 1 Outline
Multiple Sequence Alignment II Lectures 20 Dec 5, 2011 CSE 527 Computational Biology, Fall 2011 Instructor: Su-In Lee TA: Christopher Miles Monday & Wednesday 12:00-1:20 Johnson Hall (JHN) 022 1 Outline
FastA & the chaining problem
 FastA & the chaining problem We will discuss: Heuristics used by the FastA program for sequence alignment Chaining problem 1 Sources for this lecture: Lectures by Volker Heun, Daniel Huson and Knut Reinert,
FastA & the chaining problem We will discuss: Heuristics used by the FastA program for sequence alignment Chaining problem 1 Sources for this lecture: Lectures by Volker Heun, Daniel Huson and Knut Reinert,
Giri Narasimhan. CAP 5510: Introduction to Bioinformatics. ECS 254; Phone: x3748
 CAP 5510: Introduction to Bioinformatics Giri Narasimhan ECS 254; Phone: x3748 giri@cis.fiu.edu www.cis.fiu.edu/~giri/teach/bioinfs07.html 1/30/07 CAP5510 1 BLAST & FASTA FASTA [Lipman, Pearson 85, 88]
CAP 5510: Introduction to Bioinformatics Giri Narasimhan ECS 254; Phone: x3748 giri@cis.fiu.edu www.cis.fiu.edu/~giri/teach/bioinfs07.html 1/30/07 CAP5510 1 BLAST & FASTA FASTA [Lipman, Pearson 85, 88]
Lab 4: Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA)
 Lab 4: Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA) The objective of this lab is to become familiar with the features of several multiple alignment and visualization tools, including the data input and output, basic
Lab 4: Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA) The objective of this lab is to become familiar with the features of several multiple alignment and visualization tools, including the data input and output, basic
Today s Lecture. Edit graph & alignment algorithms. Local vs global Computational complexity of pairwise alignment Multiple sequence alignment
 Today s Lecture Edit graph & alignment algorithms Smith-Waterman algorithm Needleman-Wunsch algorithm Local vs global Computational complexity of pairwise alignment Multiple sequence alignment 1 Sequence
Today s Lecture Edit graph & alignment algorithms Smith-Waterman algorithm Needleman-Wunsch algorithm Local vs global Computational complexity of pairwise alignment Multiple sequence alignment 1 Sequence
BGGN 213 Foundations of Bioinformatics Barry Grant
 BGGN 213 Foundations of Bioinformatics Barry Grant http://thegrantlab.org/bggn213 Recap From Last Time: 25 Responses: https://tinyurl.com/bggn213-02-f17 Why ALIGNMENT FOUNDATIONS Why compare biological
BGGN 213 Foundations of Bioinformatics Barry Grant http://thegrantlab.org/bggn213 Recap From Last Time: 25 Responses: https://tinyurl.com/bggn213-02-f17 Why ALIGNMENT FOUNDATIONS Why compare biological
Stephen Scott.
 1 / 33 sscott@cse.unl.edu 2 / 33 Start with a set of sequences In each column, residues are homolgous Residues occupy similar positions in 3D structure Residues diverge from a common ancestral residue
1 / 33 sscott@cse.unl.edu 2 / 33 Start with a set of sequences In each column, residues are homolgous Residues occupy similar positions in 3D structure Residues diverge from a common ancestral residue
Initiate a PSI-BLAST search simply by choosing the option on the BLAST input form.
 1 2 Initiate a PSI-BLAST search simply by choosing the option on the BLAST input form. But note: invoking the algorithm is trivial. Using it correctly and interpreting the results, perhaps not so much.
1 2 Initiate a PSI-BLAST search simply by choosing the option on the BLAST input form. But note: invoking the algorithm is trivial. Using it correctly and interpreting the results, perhaps not so much.
Biochemistry 324 Bioinformatics. Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA)
 Biochemistry 324 Bioinformatics Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA) Big- Οh notation Greek omicron symbol Ο The Big-Oh notation indicates the complexity of an algorithm in terms of execution speed and storage
Biochemistry 324 Bioinformatics Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA) Big- Οh notation Greek omicron symbol Ο The Big-Oh notation indicates the complexity of an algorithm in terms of execution speed and storage
Sequence Alignment Heuristics
 Sequence Alignment Heuristics Some slides from: Iosif Vaisman, GMU mason.gmu.edu/~mmasso/binf630alignment.ppt Serafim Batzoglu, Stanford http://ai.stanford.edu/~serafim/ Geoffrey J. Barton, Oxford Protein
Sequence Alignment Heuristics Some slides from: Iosif Vaisman, GMU mason.gmu.edu/~mmasso/binf630alignment.ppt Serafim Batzoglu, Stanford http://ai.stanford.edu/~serafim/ Geoffrey J. Barton, Oxford Protein
Highly Scalable and Accurate Seeds for Subsequence Alignment
 Highly Scalable and Accurate Seeds for Subsequence Alignment Abhijit Pol Tamer Kahveci Department of Computer and Information Science and Engineering, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA, 32611
Highly Scalable and Accurate Seeds for Subsequence Alignment Abhijit Pol Tamer Kahveci Department of Computer and Information Science and Engineering, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA, 32611
Dynamic Programming User Manual v1.0 Anton E. Weisstein, Truman State University Aug. 19, 2014
 Dynamic Programming User Manual v1.0 Anton E. Weisstein, Truman State University Aug. 19, 2014 Dynamic programming is a group of mathematical methods used to sequentially split a complicated problem into
Dynamic Programming User Manual v1.0 Anton E. Weisstein, Truman State University Aug. 19, 2014 Dynamic programming is a group of mathematical methods used to sequentially split a complicated problem into
Sequence Alignment (chapter 6) p The biological problem p Global alignment p Local alignment p Multiple alignment
 Sequence lignment (chapter 6) p The biological problem p lobal alignment p Local alignment p Multiple alignment Local alignment: rationale p Otherwise dissimilar proteins may have local regions of similarity
Sequence lignment (chapter 6) p The biological problem p lobal alignment p Local alignment p Multiple alignment Local alignment: rationale p Otherwise dissimilar proteins may have local regions of similarity
Jyoti Lakhani 1, Ajay Khunteta 2, Dharmesh Harwani *3 1 Poornima University, Jaipur & Maharaja Ganga Singh University, Bikaner, Rajasthan, India
 International Journal of Scientific Research in Computer Science, Engineering and Information Technology 2017 IJSRCSEIT Volume 2 Issue 6 ISSN : 2456-3307 Improvisation of Global Pairwise Sequence Alignment
International Journal of Scientific Research in Computer Science, Engineering and Information Technology 2017 IJSRCSEIT Volume 2 Issue 6 ISSN : 2456-3307 Improvisation of Global Pairwise Sequence Alignment
Phase4 automatic evaluation of database search methods
 Phase4 automatic evaluation of database search methods Marc Rehmsmeier Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum (DKFZ) Theoretische Bioinformatik Heidelberg, Germany revised version, 11th September 2002 Abstract
Phase4 automatic evaluation of database search methods Marc Rehmsmeier Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum (DKFZ) Theoretische Bioinformatik Heidelberg, Germany revised version, 11th September 2002 Abstract
INTRODUCTION TO BIOINFORMATICS
 Molecular Biology-2017 1 INTRODUCTION TO BIOINFORMATICS In this section, we want to provide a simple introduction to using the web site of the National Center for Biotechnology Information NCBI) to obtain
Molecular Biology-2017 1 INTRODUCTION TO BIOINFORMATICS In this section, we want to provide a simple introduction to using the web site of the National Center for Biotechnology Information NCBI) to obtain
Salvador Capella-Gutiérrez, Jose M. Silla-Martínez and Toni Gabaldón
 trimal: a tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetics analyses Salvador Capella-Gutiérrez, Jose M. Silla-Martínez and Toni Gabaldón Version 1.2b Index of contents 1. General features
trimal: a tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetics analyses Salvador Capella-Gutiérrez, Jose M. Silla-Martínez and Toni Gabaldón Version 1.2b Index of contents 1. General features
Algorithmic Approaches for Biological Data, Lecture #20
 Algorithmic Approaches for Biological Data, Lecture #20 Katherine St. John City University of New York American Museum of Natural History 20 April 2016 Outline Aligning with Gaps and Substitution Matrices
Algorithmic Approaches for Biological Data, Lecture #20 Katherine St. John City University of New York American Museum of Natural History 20 April 2016 Outline Aligning with Gaps and Substitution Matrices
Utility of Sliding Window FASTA in Predicting Cross- Reactivity with Allergenic Proteins. Bob Cressman Pioneer Crop Genetics
 Utility of Sliding Window FASTA in Predicting Cross- Reactivity with Allergenic Proteins Bob Cressman Pioneer Crop Genetics The issue FAO/WHO 2001 Step 2: prepare a complete set of 80-amino acid length
Utility of Sliding Window FASTA in Predicting Cross- Reactivity with Allergenic Proteins Bob Cressman Pioneer Crop Genetics The issue FAO/WHO 2001 Step 2: prepare a complete set of 80-amino acid length
BIOL591: Introduction to Bioinformatics Alignment of pairs of sequences
 BIOL591: Introduction to Bioinformatics Alignment of pairs of sequences Reading in text (Mount Bioinformatics): I must confess that the treatment in Mount of sequence alignment does not seem to me a model
BIOL591: Introduction to Bioinformatics Alignment of pairs of sequences Reading in text (Mount Bioinformatics): I must confess that the treatment in Mount of sequence alignment does not seem to me a model
From Smith-Waterman to BLAST
 From Smith-Waterman to BLAST Jeremy Buhler July 23, 2015 Smith-Waterman is the fundamental tool that we use to decide how similar two sequences are. Isn t that all that BLAST does? In principle, it is
From Smith-Waterman to BLAST Jeremy Buhler July 23, 2015 Smith-Waterman is the fundamental tool that we use to decide how similar two sequences are. Isn t that all that BLAST does? In principle, it is
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining. Non-Parametric Models Fall 2016
 CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining Non-Parametric Models Fall 2016 Admin Course add/drop deadline tomorrow. Assignment 1 is due Friday. Setup your CS undergrad account ASAP to use Handin: https://www.cs.ubc.ca/getacct
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining Non-Parametric Models Fall 2016 Admin Course add/drop deadline tomorrow. Assignment 1 is due Friday. Setup your CS undergrad account ASAP to use Handin: https://www.cs.ubc.ca/getacct
Lectures by Volker Heun, Daniel Huson and Knut Reinert, in particular last years lectures
 4 FastA and the chaining problem We will discuss: Heuristics used by the FastA program for sequence alignment Chaining problem 4.1 Sources for this lecture Lectures by Volker Heun, Daniel Huson and Knut
4 FastA and the chaining problem We will discuss: Heuristics used by the FastA program for sequence alignment Chaining problem 4.1 Sources for this lecture Lectures by Volker Heun, Daniel Huson and Knut
CISC 889 Bioinformatics (Spring 2003) Multiple Sequence Alignment
 CISC 889 Bioinformatics (Spring 2003) Multiple Sequence Alignment Courtesy of jalview 1 Motivations Collective statistic Protein families Identification and representation of conserved sequence features
CISC 889 Bioinformatics (Spring 2003) Multiple Sequence Alignment Courtesy of jalview 1 Motivations Collective statistic Protein families Identification and representation of conserved sequence features
EECS730: Introduction to Bioinformatics
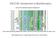 EECS730: Introduction to Bioinformatics Lecture 06: Multiple Sequence Alignment https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/79/rplp0_90_clustalw_aln.gif/575px-rplp0_90_clustalw_aln.gif Slides
EECS730: Introduction to Bioinformatics Lecture 06: Multiple Sequence Alignment https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/79/rplp0_90_clustalw_aln.gif/575px-rplp0_90_clustalw_aln.gif Slides
