Sequential Circuit Testing 3
|
|
|
- Brent Heath
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sequential Circuit Testing 3 Recap: Approaches State table analysis Machine identification (checking sequence) method Time-frame expansion Misc. Issues Controlling and observing internal states of a sequential circuit Scan design solves this problem Establishing a known initial state Need for backtrace through multiple time-frames Need for nine-valued logic Easy special case: cycle-free circuits John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 21 Lecture13: Page 1 Nine-Valued Logic For sequential testing we need may to consider all pairs of,1, signals for the good/faulty machines Roth s 5-valued algebra: 1 1/ /1 / 1/1 / Muth s 9-valued algebra: 1 1/ /1 / 1/1 / / 1/ / /1 John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 21 Lecture13: Page 2
2 Example: Need for 9 values Nine-Valued Logic FF1 Q B A Q FF2 Fault A/1 John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 21 Lecture13: Page 3 Nine-Valued Logic Example: ATPG with 5 values A A s-a-1 s-a-1 FF1 FF1 FF2 FF2 B Time-frame -1 Time-frame B John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 21 Lecture13: Page 4
3 Nine-Valued Logic Example: ATPG with 9 values A A FF1 s-a-1 /1 s-a-1 /1 / / FF1 FF2 /1 /1 FF2 B Time-frame -1 Time-frame B /1 John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 21 Lecture13: Page 5 Cycle-Free Circuits Characterized by absence of cycles among flip-flops and a sequential depth dseq dseq is the maximum number of flip-flops on any path between PIs and POs Special testing properties Both good and faulty circuits are initializable Test sequence length for a fault is bounded by dseq + 1 John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 21 Lecture13: Page 6
4 Cycle-Free Circuits Circuit F2 2 F1 Level = 1 F2 F3 3 s - graph F1 2 F3 dseq = 3 Level = 1 3 John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 21 Lecture13: Page 7 Simulation-Based ATPG Possible Methods irected search Genetic algorithms Spectral techniques Advantages Fault simulation technology is very well-developed Many types of test methods (deterministic, functional, random) can be used John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 21 Lecture13: Page 8
5 Simulation-Based ATPG No Generate new trial vectors Vector source (functional, heuristic, random, etc.) Yes Stop Stopping criteria (fault coverage,cpu runtime, etc) met? No Restore Circuit state Fault simulator New faults detected? Trial vectors Yes Fault list Update fault list Append vectors Test vectors John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 21 Lecture13: Page 9 CONTEST Algorithm Simulation-based ATPG program for sequential circuits developed at Bell Labs (1989) Searches for tests guided by cost functions Uses a 3-phase test generation method: Initialization phase: No faults are targeted. Cost function is computed by true-value simulation. Concurrent phase: All faults are targeted. Cost function is computed by concurrent fault simulation. Single fault phase: Faults are targeted one at a time. Cost function is computed by true-value simulation and dynamic testability analysis John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 21 Lecture13: Page 1
6 CONTEST Algorithm Trial vectors Vector space Tests Initial vector Cost= John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 21 Lecture13: Page 11 CONTEST Algorithm Cost Functions Functions are defined for specific current objectives (initialization or fault detection) Each function numerically grades a test vector for suitability to meet the current objective Cost function = for any vector that exactly meets the objective Cost is computed for an input vector via either true-value or fault simulation John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 21 Lecture13: Page 12
7 CONTEST Algorithm Phase I: Initialization Initialize test sequence with random or given vector (sequence) Set all flip-flops in unknown () state Cost functions used: Number of flip-flops in the state Cost computed from true-value simulation of trial vectors Trial vector generation: Heuristically generate trial vector set from the previous vector(s) in the test sequence, e.g., all vectors at Hamming distance one from the last vector Vector selection: Add the minimum-cost trial vector to the test sequence. Repeat trial vector generation and vector selection until cost given limit. John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 21 Lecture13: Page 13 CONTEST Algorithm Phase II: Concurrent Fault etection Initial test sequence uses vectors from Phase I Simulate all faults and drop detected faults Compute a distance cost function for trial vectors: For each undetected fault, find the shortest fault distance (no. of gates) between its fault effect and a primary output Cost function = sum of fault distances for all undetected faults Trial vectors: Generate trial vectors, e.g., using unit distance Vector selection: Add trial vector with the minimum cost function to test sequence Remove faults with zero fault distance from the fault list. Repeat trial vector generation and vector selection until fault list reduces to given size John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 21 Lecture13: Page 14
8 Need for Phase III CONTEST Algorithm Vector space Initial vector John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 21 Lecture13: Page 15 CONTEST Algorithm Phase III: Single Fault Target Cost (fault, input vector) = K AC + PC Activation cost (AC) is the dynamic controllability of the faulty line Propagation cost (PC) is the minimum (over all paths to POs) dynamic observability of the faulty line. K is a large weighting factor, e.g., K = 1. ynamic testability measures (controllability and observability) are specific to the present signal values in the circuit. Cost of a vector is computed for a fault from the true-value simulation result. Cost = means fault is detected. Trial vector generation and vector selection are similar to the other phases John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 21 Lecture13: Page 16
9 CONTEST Algorithm Test Results: Benchmark circuit: 35 PIs, 49 POs, 179 flip-flops, 4,63 faults, synchronous CONTEST Random Tests Gentest** Fault coverage 75.5% 67.6% 72.6% Untestable faults 122 Test vectors 1,722 57, Trial vectors used 57, Test gen. CPU time# 3 min.* 4.5 hrs. Fault sim. CPU time# 9 min.* 9 min. 1 sec. # Sun Ultra II, 2 MHz CPU *Estimated time **Time-frame expansion (higher coverage possible with more CPU time) John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 21 Lecture13: Page 17 Genetic Algorithm Heuristic algorithms that mimic the biological mechanisms underlying the theory of evolution by natural selection (arwin 1859) Key idea: Populations improve with each generation. Genetic ATPG algorithms Population: Set of input vectors or vector sequences. Fitness function: Quantitative measures of testing success in tasks like initialization and fault detection Regeneration rules: Tests with higher fitness values are selected to produce new tests via transformations like mutation and crossover. John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 21 Lecture13: Page 18
10 High-Level Test Generation Goals Speed up test generation Generate tests for circuits without complete structural models Methods Use structural hierarchy and circuit and fault modeling Use functional descriptions of modules and circuits istinguish data and control functions Exploit high-level (expert) information about circuit operation John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 21 Lecture13: Page 19 High-Level Test Generation Precomputed Tests for Modules Hierarchical circuit CT S Primary input... T S Scan path... MUT... / M 1 /... Register 8 4 Module under test T R / 8 M 2 / 4... CT R2 Primary output Primary output CT R1 John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 21 Lecture13: Page 2
VLSI Test Technology and Reliability (ET4076)
 VLSI Test Technology and Reliability (ET4076) Lecture 4(part 2) Testability Measurements (Chapter 6) Said Hamdioui Computer Engineering Lab Delft University of Technology 2009-2010 1 Previous lecture What
VLSI Test Technology and Reliability (ET4076) Lecture 4(part 2) Testability Measurements (Chapter 6) Said Hamdioui Computer Engineering Lab Delft University of Technology 2009-2010 1 Previous lecture What
Preizkušanje elektronskih vezij
 Laboratorij za načrtovanje integriranih vezij Univerza v Ljubljani Fakulteta za elektrotehniko Preizkušanje elektronskih vezij Generacija testnih vzorcev Test pattern generation Overview Introduction Theoretical
Laboratorij za načrtovanje integriranih vezij Univerza v Ljubljani Fakulteta za elektrotehniko Preizkušanje elektronskih vezij Generacija testnih vzorcev Test pattern generation Overview Introduction Theoretical
VLSI Test Technology and Reliability (ET4076)
 VLSI Test Technology and Reliability (ET4076) Lecture 8 (1) Delay Test (Chapter 12) Said Hamdioui Computer Engineering Lab Delft University of Technology 2009-2010 1 Learning aims Define a path delay fault
VLSI Test Technology and Reliability (ET4076) Lecture 8 (1) Delay Test (Chapter 12) Said Hamdioui Computer Engineering Lab Delft University of Technology 2009-2010 1 Learning aims Define a path delay fault
Testing Digital Systems I
 Testing Digital Systems I Lecture 6: Fault Simulation Instructor: M. Tahoori Copyright 2, M. Tahoori TDS I: Lecture 6 Definition Fault Simulator A program that models a design with fault present Inputs:
Testing Digital Systems I Lecture 6: Fault Simulation Instructor: M. Tahoori Copyright 2, M. Tahoori TDS I: Lecture 6 Definition Fault Simulator A program that models a design with fault present Inputs:
l Some materials from various sources! n Current course textbook! Soma 1! Soma 3!
 Ackwledgements! Test generation algorithms! Mani Soma! l Some materials from various sources! n r. Phil Nigh, IBM! n Principles of Testing Electronic Systems by S. Mourad & Y. Zorian! n Essentials of Electronic
Ackwledgements! Test generation algorithms! Mani Soma! l Some materials from various sources! n r. Phil Nigh, IBM! n Principles of Testing Electronic Systems by S. Mourad & Y. Zorian! n Essentials of Electronic
Chapter 9. Design for Testability
 Chapter 9 Design for Testability Testability CUT = Circuit Under Test A design property that allows: cost-effective development of tests to be applied to the CUT determining the status of the CUT (normal
Chapter 9 Design for Testability Testability CUT = Circuit Under Test A design property that allows: cost-effective development of tests to be applied to the CUT determining the status of the CUT (normal
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison. Fall Midterm Examination CLOSED BOOK
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison ECE 553: Testing and Testable Design of Digital Systems Fall 2013-2014 Midterm Examination CLOSED BOOK Kewal K. Saluja
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison ECE 553: Testing and Testable Design of Digital Systems Fall 2013-2014 Midterm Examination CLOSED BOOK Kewal K. Saluja
VLSI Test Technology and Reliability (ET4076)
 VLSI Test Technology and Reliability (ET476) Lecture 5 Combinational Circuit Test Generation (Chapter 7) Said Hamdioui Computer Engineering Lab elft University of Technology 29-2 Learning aims of today
VLSI Test Technology and Reliability (ET476) Lecture 5 Combinational Circuit Test Generation (Chapter 7) Said Hamdioui Computer Engineering Lab elft University of Technology 29-2 Learning aims of today
Fault Simulation. Problem and Motivation
 Fault Simulation Problem and Motivation Fault Simulation Problem: Given A circuit A sequence of test vectors A fault model Determine Fault coverage Fraction (or percentage) of modeled faults detected by
Fault Simulation Problem and Motivation Fault Simulation Problem: Given A circuit A sequence of test vectors A fault model Determine Fault coverage Fraction (or percentage) of modeled faults detected by
12. Use of Test Generation Algorithms and Emulation
 12. Use of Test Generation Algorithms and Emulation 1 12. Use of Test Generation Algorithms and Emulation Jacob Abraham Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin
12. Use of Test Generation Algorithms and Emulation 1 12. Use of Test Generation Algorithms and Emulation Jacob Abraham Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin
Lecture 3 - Fault Simulation
 Lecture 3 - Fault Simulation Fault simulation Algorithms Serial Parallel Deductive Random Fault Sampling Problem and Motivation Fault simulation Problem: Given A circuit A sequence of test vectors A fault
Lecture 3 - Fault Simulation Fault simulation Algorithms Serial Parallel Deductive Random Fault Sampling Problem and Motivation Fault simulation Problem: Given A circuit A sequence of test vectors A fault
236 Chapter 8. SEQUENTIAL CIRCUIT TEST GENERATION
 236 Chapter 8. SEQUENTIAL CIRCUIT TEST GENERATION PI vector k 1 PI vector k Feedback set PPI C C C C C C C C (CK) FMCK FMCK FMCK (CK) FMCK FMCK FMCK PPO PPO Asynchronous signal stabilization Asynchronous
236 Chapter 8. SEQUENTIAL CIRCUIT TEST GENERATION PI vector k 1 PI vector k Feedback set PPI C C C C C C C C (CK) FMCK FMCK FMCK (CK) FMCK FMCK FMCK PPO PPO Asynchronous signal stabilization Asynchronous
Design and Synthesis for Test
 TDTS 80 Lecture 6 Design and Synthesis for Test Zebo Peng Embedded Systems Laboratory IDA, Linköping University Testing and its Current Practice To meet user s quality requirements. Testing aims at the
TDTS 80 Lecture 6 Design and Synthesis for Test Zebo Peng Embedded Systems Laboratory IDA, Linköping University Testing and its Current Practice To meet user s quality requirements. Testing aims at the
CPE 628 Chapter 4 Test Generation. Dr. Rhonda Kay Gaede UAH. CPE Introduction Conceptual View. UAH Chapter 4
 Chapter 4 Test Generation Dr. Rhonda Kay Gaede UAH 1 4.1 Introduction Conceptual View Generate an input vector that can the - circuit from the one Page 2 1 4.1 Introduction Simple Illustration Consider
Chapter 4 Test Generation Dr. Rhonda Kay Gaede UAH 1 4.1 Introduction Conceptual View Generate an input vector that can the - circuit from the one Page 2 1 4.1 Introduction Simple Illustration Consider
Lecture 7 Fault Simulation
 Lecture 7 Fault Simulation Problem and motivation Fault simulation algorithms Serial Parallel Deductive Concurrent Random Fault Sampling Summary Copyright 2, Agrawal & Bushnell VLSI Test: Lecture 7 Problem
Lecture 7 Fault Simulation Problem and motivation Fault simulation algorithms Serial Parallel Deductive Concurrent Random Fault Sampling Summary Copyright 2, Agrawal & Bushnell VLSI Test: Lecture 7 Problem
Origins of Stuck-Faults. Combinational Automatic Test-Pattern Generation (ATPG) Basics. Functional vs. Structural ATPG.
 Combinational Automatic Test-Pattern Generation (ATPG) Basics Algorithms and representations Structural vs functional test efinitions Search spaces Completeness Algebras Types of Algorithms Origins of
Combinational Automatic Test-Pattern Generation (ATPG) Basics Algorithms and representations Structural vs functional test efinitions Search spaces Completeness Algebras Types of Algorithms Origins of
Overview ECE 753: FAULT-TOLERANT COMPUTING 1/23/2014. Recap. Introduction. Introduction (contd.) Introduction (contd.)
 ECE 753: FAULT-TOLERANT COMPUTING Kewal K.Saluja Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Test Generation and Fault Simulation Lectures Set 3 Overview Introduction Basics of testing Complexity
ECE 753: FAULT-TOLERANT COMPUTING Kewal K.Saluja Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Test Generation and Fault Simulation Lectures Set 3 Overview Introduction Basics of testing Complexity
Advanced Digital Logic Design EECS 303
 Advanced igital Logic esign EECS 33 http://ziyang.eecs.northwestern.edu/eecs33/ Teacher: Robert ick Office: L477 Tech Email: dickrp@northwestern.edu Phone: 847 467 2298 Outline. 2. 2 Robert ick Advanced
Advanced igital Logic esign EECS 33 http://ziyang.eecs.northwestern.edu/eecs33/ Teacher: Robert ick Office: L477 Tech Email: dickrp@northwestern.edu Phone: 847 467 2298 Outline. 2. 2 Robert ick Advanced
VLSI System Testing. Fault Simulation
 ECE 538 VLSI System Testing Krish Chakrabarty Fault Simulation ECE 538 Krish Chakrabarty Fault Simulation Problem and motivation Fault simulation algorithms Serial Parallel Deductive Concurrent Random
ECE 538 VLSI System Testing Krish Chakrabarty Fault Simulation ECE 538 Krish Chakrabarty Fault Simulation Problem and motivation Fault simulation algorithms Serial Parallel Deductive Concurrent Random
Exploiting Off-Line Hierarchical Test Paths in Module Diagnosis and On-Line Test
 Exploiting Off-Line Hierarchical Paths in Diagnosis and On-Line lu Reliable Systems Synthesis Lab Computer Science & Engineering Department University of California San Diego 9500 Gilman Drive MC-0114
Exploiting Off-Line Hierarchical Paths in Diagnosis and On-Line lu Reliable Systems Synthesis Lab Computer Science & Engineering Department University of California San Diego 9500 Gilman Drive MC-0114
CONTEST : A CONCURRENT TEST GENERATOR FOR SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS
 CONTEST : A CONCURRENT TEST GENERATOR FOR SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS Vishwani D. Agrawal AT&T Bell Laboratories, Murray Hill, NJ 07974 Kwang-Ting Cheng University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720 Prathima Agrawal
CONTEST : A CONCURRENT TEST GENERATOR FOR SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS Vishwani D. Agrawal AT&T Bell Laboratories, Murray Hill, NJ 07974 Kwang-Ting Cheng University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720 Prathima Agrawal
UMBC. space and introduced backtrace. Fujiwara s FAN efficiently constrained the backtrace to speed up search and further limited the search space.
 ATPG Algorithms Characteristics of the three main algorithms: Roth s -Algorithm (-ALG) defined the calculus and algorithms for ATPG using -cubes. Goel s POEM used path propagation constraints to limit
ATPG Algorithms Characteristics of the three main algorithms: Roth s -Algorithm (-ALG) defined the calculus and algorithms for ATPG using -cubes. Goel s POEM used path propagation constraints to limit
VLSI Testing. Virendra Singh. Bangalore E0 286: Test & Verification of SoC Design Lecture - 7. Jan 27,
 VLSI Testing Fault Simulation Virendra Singh Indian Institute t of Science Bangalore virendra@computer.org E 286: Test & Verification of SoC Design Lecture - 7 Jan 27, 2 E-286@SERC Fault Simulation Jan
VLSI Testing Fault Simulation Virendra Singh Indian Institute t of Science Bangalore virendra@computer.org E 286: Test & Verification of SoC Design Lecture - 7 Jan 27, 2 E-286@SERC Fault Simulation Jan
Sequential Circuit Test Generation Using Decision Diagram Models
 Sequential Circuit Test Generation Using Decision Diagram Models Jaan Raik, Raimund Ubar Department of Computer Engineering Tallinn Technical University, Estonia Abstract A novel approach to testing sequential
Sequential Circuit Test Generation Using Decision Diagram Models Jaan Raik, Raimund Ubar Department of Computer Engineering Tallinn Technical University, Estonia Abstract A novel approach to testing sequential
PROOFS Fault Simulation Algorithm
 PROOFS Fault Simulation Algorithm Pratap S.Prasad Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Auburn University, Auburn, AL prasaps@auburn.edu Term Paper for ELEC 7250 (Spring 2005) Abstract This paper
PROOFS Fault Simulation Algorithm Pratap S.Prasad Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Auburn University, Auburn, AL prasaps@auburn.edu Term Paper for ELEC 7250 (Spring 2005) Abstract This paper
Digital VLSI Testing Prof. Santanu Chattopadhyay Department of Electronics and EC Engineering India Institute of Technology, Kharagpur.
 Digital VLSI Testing Prof. Santanu Chattopadhyay Department of Electronics and EC Engineering India Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 05 DFT Next we will look into the topic design for testability,
Digital VLSI Testing Prof. Santanu Chattopadhyay Department of Electronics and EC Engineering India Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 05 DFT Next we will look into the topic design for testability,
An Efficient Test Relaxation Technique for Synchronous Sequential Circuits
 An Efficient Test Relaxation Technique for Synchronous Sequential Circuits Aiman El-Maleh and Khaled Al-Utaibi King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Dhahran 326, Saudi Arabia emails:{aimane, alutaibi}@ccse.kfupm.edu.sa
An Efficient Test Relaxation Technique for Synchronous Sequential Circuits Aiman El-Maleh and Khaled Al-Utaibi King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Dhahran 326, Saudi Arabia emails:{aimane, alutaibi}@ccse.kfupm.edu.sa
EECS 579: Built-in Self-Test 3. Regular Circuits
 EECS 579: Built-in Self-Test 3 Outline Implementing BIST by regularization Adder ALU RAM Commercial BIST approaches LOCSD STUMPS CSTP Case Study Bosch AE11 microcontroller John P. Hayes University of Michigan
EECS 579: Built-in Self-Test 3 Outline Implementing BIST by regularization Adder ALU RAM Commercial BIST approaches LOCSD STUMPS CSTP Case Study Bosch AE11 microcontroller John P. Hayes University of Michigan
Evaluation of FPGA Resources for Built-In Self-Test of Programmable Logic Blocks
 Evaluation of FPGA Resources for Built-In Self-Test of Programmable Logic Blocks Charles Stroud, Ping Chen, Srinivasa Konala, Dept. of Electrical Engineering University of Kentucky and Miron Abramovici
Evaluation of FPGA Resources for Built-In Self-Test of Programmable Logic Blocks Charles Stroud, Ping Chen, Srinivasa Konala, Dept. of Electrical Engineering University of Kentucky and Miron Abramovici
Testing Embedded Cores Using Partial Isolation Rings
 Testing Embedded Cores Using Partial Isolation Rings Nur A. Touba and Bahram Pouya Computer Engineering Research Center Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Texas, Austin, TX
Testing Embedded Cores Using Partial Isolation Rings Nur A. Touba and Bahram Pouya Computer Engineering Research Center Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Texas, Austin, TX
Diagnostic Test Vectors for Combinational and Sequential
 Compaction of Pass/Fail-based Diagnostic Test Vectors for Combinational and Sequential Circuits Yoshinobu Higami, Hiroshi Takahashi, Shin-ya Kobayashi and Yuzo Takamatsu(Ehime University) Kewal K. Saluja
Compaction of Pass/Fail-based Diagnostic Test Vectors for Combinational and Sequential Circuits Yoshinobu Higami, Hiroshi Takahashi, Shin-ya Kobayashi and Yuzo Takamatsu(Ehime University) Kewal K. Saluja
Pinaki Mazumder. Digital Testing 1 PODEM. PODEM Algorithm. PODEM Flow Chart
 POEM Algorithm POEM IBM introduced semiconductor RAM memory into its mainframes late 970 s Memory had error correction and translation circuits improved reliability -ALG unable to test these circuits!
POEM Algorithm POEM IBM introduced semiconductor RAM memory into its mainframes late 970 s Memory had error correction and translation circuits improved reliability -ALG unable to test these circuits!
Functional extension of structural logic optimization techniques
 Functional extension of structural logic optimization techniques J. A. Espejo, L. Entrena, E. San Millán, E. Olías Universidad Carlos III de Madrid # e-mail: { ppespejo, entrena, quique, olias}@ing.uc3m.es
Functional extension of structural logic optimization techniques J. A. Espejo, L. Entrena, E. San Millán, E. Olías Universidad Carlos III de Madrid # e-mail: { ppespejo, entrena, quique, olias}@ing.uc3m.es
Automatic Test Program Generation from RT-level microprocessor descriptions
 Automatic Test Program Generation from RT-level microprocessor descriptions F. Corno, G. Cumani, M. Sonza Reorda, G. Squillero Politecnico di Torino Dipartimento di Automatica e Informatica Torino, Italy
Automatic Test Program Generation from RT-level microprocessor descriptions F. Corno, G. Cumani, M. Sonza Reorda, G. Squillero Politecnico di Torino Dipartimento di Automatica e Informatica Torino, Italy
VLSI System Testing. Outline
 ECE 538 VLSI System Testing Krish Chakrabarty Test Generation: 2 ECE 538 Krish Chakrabarty Outline Problem with -Algorithm POEM FAN Fault-independent ATPG Critical path tracing Random test generation Redundancy
ECE 538 VLSI System Testing Krish Chakrabarty Test Generation: 2 ECE 538 Krish Chakrabarty Outline Problem with -Algorithm POEM FAN Fault-independent ATPG Critical path tracing Random test generation Redundancy
Adaptive Techniques for Improving Delay Fault Diagnosis
 Adaptive Techniques for Improving Delay Fault Diagnosis Jayabrata Ghosh-Dastidar and Nur A. Touba Computer Engineering Research Center Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Texas,
Adaptive Techniques for Improving Delay Fault Diagnosis Jayabrata Ghosh-Dastidar and Nur A. Touba Computer Engineering Research Center Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Texas,
PROR compaction scheme for larger circuits and longer vectors with deterministic ATPG
 PROR compaction scheme for larger circuits and longer vectors with deterministic ATPG Suresh k Devanathan Michael L Bushnell Abstract Reverse order restoration ROR techniques have found great use in sequential
PROR compaction scheme for larger circuits and longer vectors with deterministic ATPG Suresh k Devanathan Michael L Bushnell Abstract Reverse order restoration ROR techniques have found great use in sequential
Multiple Fault Models Using Concurrent Simulation 1
 Multiple Fault Models Using Concurrent Simulation 1 Evan Weststrate and Karen Panetta Tufts University Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 161 College Avenue Medford, MA 02155 Email:
Multiple Fault Models Using Concurrent Simulation 1 Evan Weststrate and Karen Panetta Tufts University Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 161 College Avenue Medford, MA 02155 Email:
IMPLEMENTATION OF AN ATPG USING PODEM ALGORITHM
 IMPLEMENTATION OF AN ATPG USING PODEM ALGORITHM SACHIN DHINGRA ELEC 7250: VLSI testing OBJECTIVE: Write a test pattern generation program using the PODEM algorithm. ABSTRACT: PODEM (Path-Oriented Decision
IMPLEMENTATION OF AN ATPG USING PODEM ALGORITHM SACHIN DHINGRA ELEC 7250: VLSI testing OBJECTIVE: Write a test pattern generation program using the PODEM algorithm. ABSTRACT: PODEM (Path-Oriented Decision
On Using Machine Learning for Logic BIST
 On Using Machine Learning for Logic BIST Christophe FAGOT Patrick GIRARD Christian LANDRAULT Laboratoire d Informatique de Robotique et de Microélectronique de Montpellier, UMR 5506 UNIVERSITE MONTPELLIER
On Using Machine Learning for Logic BIST Christophe FAGOT Patrick GIRARD Christian LANDRAULT Laboratoire d Informatique de Robotique et de Microélectronique de Montpellier, UMR 5506 UNIVERSITE MONTPELLIER
Test Set Compaction Algorithms for Combinational Circuits
 Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer-Aided Design, November 1998 Set Compaction Algorithms for Combinational Circuits Ilker Hamzaoglu and Janak H. Patel Center for Reliable & High-Performance
Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer-Aided Design, November 1998 Set Compaction Algorithms for Combinational Circuits Ilker Hamzaoglu and Janak H. Patel Center for Reliable & High-Performance
Extraction Error Diagnosis and Correction in High-Performance Designs
 Extraction Error iagnosis and Correction in High-Performance esigns Yu-Shen Yang 1 J. Brandon Liu 1 Paul Thadikaran 3 Andreas Veneris 1,2 Abstract Test model generation is crucial in the test generation
Extraction Error iagnosis and Correction in High-Performance esigns Yu-Shen Yang 1 J. Brandon Liu 1 Paul Thadikaran 3 Andreas Veneris 1,2 Abstract Test model generation is crucial in the test generation
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction The advent of synthesis systems for Very Large Scale Integrated Circuits (VLSI) and automated design environments for Application Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC) have allowed
Chapter 1 Introduction The advent of synthesis systems for Very Large Scale Integrated Circuits (VLSI) and automated design environments for Application Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC) have allowed
Report on benchmark identification and planning of experiments to be performed
 COTEST/D1 Report on benchmark identification and planning of experiments to be performed Matteo Sonza Reorda, Massimo Violante Politecnico di Torino Dipartimento di Automatica e Informatica Torino, Italy
COTEST/D1 Report on benchmark identification and planning of experiments to be performed Matteo Sonza Reorda, Massimo Violante Politecnico di Torino Dipartimento di Automatica e Informatica Torino, Italy
REDI: An Efficient Fault Oriented Procedure to Identify Redundant Faults in Combinational Logic Circuits *
 REDI: An Efficient Fault Oriented Procedure to Identify Redundant Faults in Combinational Logic Circuits * Chen Wang, Irith Pomeranz and Sudhakar M. Reddy Electrical and Computer Engineering Department
REDI: An Efficient Fault Oriented Procedure to Identify Redundant Faults in Combinational Logic Circuits * Chen Wang, Irith Pomeranz and Sudhakar M. Reddy Electrical and Computer Engineering Department
VLSI Testing. Fault Simulation. Virendra Singh. Indian Institute of Science Bangalore
 VLSI Testing Fault Simulation Virendra Singh Indian Institute of Science Bangalore virendra@computer.org E0 286: Test & Verification of SoC Design Lecture - 4 Jan 25, 2008 E0-286@SERC 1 Fault Model - Summary
VLSI Testing Fault Simulation Virendra Singh Indian Institute of Science Bangalore virendra@computer.org E0 286: Test & Verification of SoC Design Lecture - 4 Jan 25, 2008 E0-286@SERC 1 Fault Model - Summary
Recitation Session 6
 Recitation Session 6 CSE341 Computer Organization University at Buffalo radhakri@buffalo.edu March 11, 2016 CSE341 Computer Organization Recitation Session 6 1/26 Recitation Session Outline 1 Overview
Recitation Session 6 CSE341 Computer Organization University at Buffalo radhakri@buffalo.edu March 11, 2016 CSE341 Computer Organization Recitation Session 6 1/26 Recitation Session Outline 1 Overview
Mentor Graphics Tools for DFT. DFTAdvisor, FastScan and FlexTest
 Mentor Graphics Tools for DFT DFTAdvisor, FastScan and FlexTest 1 DFT Advisor Synthesis tool capable of doing DRC, Scan Insertion and Test point Synthesis Creates a do file and a test procedure file after
Mentor Graphics Tools for DFT DFTAdvisor, FastScan and FlexTest 1 DFT Advisor Synthesis tool capable of doing DRC, Scan Insertion and Test point Synthesis Creates a do file and a test procedure file after
A Module Diagnosis and Design-for-Debug Methodology Based on Hierarchical Test Paths
 A Diagnosis and Design-for-Debug Methodology ased on Hierarchical Test s
A Diagnosis and Design-for-Debug Methodology ased on Hierarchical Test s
Design for Testability
 Design for Testability Sungho Kang Yonsei University Outline Introduction Testability Measure Design for Testability Ad-Hoc Testable Design Conclusion 2 Merging Design and Test Design and Test become closer
Design for Testability Sungho Kang Yonsei University Outline Introduction Testability Measure Design for Testability Ad-Hoc Testable Design Conclusion 2 Merging Design and Test Design and Test become closer
High-level Variable Selection for Partial-Scan Implementation
 High-level Variable Selection for Partial-Scan Implementation FrankF.Hsu JanakH.Patel Center for Reliable & High-Performance Computing University of Illinois, Urbana, IL Abstract In this paper, we propose
High-level Variable Selection for Partial-Scan Implementation FrankF.Hsu JanakH.Patel Center for Reliable & High-Performance Computing University of Illinois, Urbana, IL Abstract In this paper, we propose
Test Generation for Asynchronous Sequential Digital Circuits
 Test Generation for Asynchronous Sequential Digital Circuits Roland Dobai Institute of Informatics Slovak Academy of Sciences Dúbravská cesta 9, 845 07 Bratislava, Slovakia roland.dobai@savba.sk Abstract
Test Generation for Asynchronous Sequential Digital Circuits Roland Dobai Institute of Informatics Slovak Academy of Sciences Dúbravská cesta 9, 845 07 Bratislava, Slovakia roland.dobai@savba.sk Abstract
Witold Pedrycz. University of Alberta Edmonton, Alberta, Canada
 2017 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC) Banff Center, Banff, Canada, October 5-8, 2017 Analysis of Optimization Algorithms in Automated Test Pattern Generation for Sequential
2017 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC) Banff Center, Banff, Canada, October 5-8, 2017 Analysis of Optimization Algorithms in Automated Test Pattern Generation for Sequential
Efficient Sequential ATPG for Functional RTL Circuits
 Efficient Sequential ATPG for Functional RTL Circuits Liang Zhang, Indradeep Ghosh, and Michael Hsiao Department of ECE, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA, liang, hsiao @vt.edu Fujitsu Labs. of America Inc.,
Efficient Sequential ATPG for Functional RTL Circuits Liang Zhang, Indradeep Ghosh, and Michael Hsiao Department of ECE, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA, liang, hsiao @vt.edu Fujitsu Labs. of America Inc.,
Metodologie di progetto HW Il test di circuiti digitali
 Metodologie di progetto HW Il test di circuiti digitali Introduzione Versione del 9/4/8 Metodologie di progetto HW Il test di circuiti digitali Introduction VLSI Realization Process Customer s need Determine
Metodologie di progetto HW Il test di circuiti digitali Introduzione Versione del 9/4/8 Metodologie di progetto HW Il test di circuiti digitali Introduction VLSI Realization Process Customer s need Determine
Scan Chain Operation for Stuck at Test
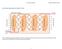 Scan Chain Operation for Stuck at Test Scan Enable Here is an example design under test (DUT). I have shown a single scan chain (in red color) in the circuit, with and ports. Assume that all scan flip
Scan Chain Operation for Stuck at Test Scan Enable Here is an example design under test (DUT). I have shown a single scan chain (in red color) in the circuit, with and ports. Assume that all scan flip
ECE 2300 Digital Logic & Computer Organization. More Sequential Logic Verilog
 ECE 2300 Digital Logic & Computer Organization Spring 2018 More Sequential Logic Verilog Lecture 7: 1 Announcements HW3 will be posted tonight Prelim 1 Thursday March 1, in class Coverage: Lectures 1~7
ECE 2300 Digital Logic & Computer Organization Spring 2018 More Sequential Logic Verilog Lecture 7: 1 Announcements HW3 will be posted tonight Prelim 1 Thursday March 1, in class Coverage: Lectures 1~7
Metodologie di progetto HW Il test di circuiti digitali
 Metodologie di progetto HW Il test di circuiti digitali Introduzione Versione del 9/4/8 Metodologie di progetto HW Il test di circuiti digitali Introduction Pag. 2 VLSI Realization Process Customer s need
Metodologie di progetto HW Il test di circuiti digitali Introduzione Versione del 9/4/8 Metodologie di progetto HW Il test di circuiti digitali Introduction Pag. 2 VLSI Realization Process Customer s need
Contents 1 Basic of Test and Role of HDLs 2 Verilog HDL for Design and Test
 1 Basic of Test and Role of HDLs... 1.1 Design and Test... 1.1.1 RTL Design Process... 1.1.2 Postmanufacturing Test... 1.2 Test Concerns... 1.2.1 Test Methods... 1.2.2 Testability Methods... 1.2.3 Testing
1 Basic of Test and Role of HDLs... 1.1 Design and Test... 1.1.1 RTL Design Process... 1.1.2 Postmanufacturing Test... 1.2 Test Concerns... 1.2.1 Test Methods... 1.2.2 Testability Methods... 1.2.3 Testing
Digital Systems Testing
 Digital Systems Testing Verilog HDL for Design and Test Moslem Amiri, Václav Přenosil Embedded Systems Laboratory Faculty of Informatics, Masaryk University Brno, Czech Republic amiri@mail.muni.cz prenosil@fi.muni.cz
Digital Systems Testing Verilog HDL for Design and Test Moslem Amiri, Václav Přenosil Embedded Systems Laboratory Faculty of Informatics, Masaryk University Brno, Czech Republic amiri@mail.muni.cz prenosil@fi.muni.cz
Faults, Testing & Test Generation
 Faults, Testing & Test Generation Smith Text: Chapter 14.1,14.3, 14.4 Mentor Graphics/Tessent: Scan and ATPG Process Guide ATPG and Failure Diagnosis Tools Reference Manual (access via mgcdocs ) ASIC Design
Faults, Testing & Test Generation Smith Text: Chapter 14.1,14.3, 14.4 Mentor Graphics/Tessent: Scan and ATPG Process Guide ATPG and Failure Diagnosis Tools Reference Manual (access via mgcdocs ) ASIC Design
FACTOR: A Hierarchical Methodology for Functional Test Generation and Testability Analysis
 FACTOR: A Hierarchical Methodology for Functional Test Generation and Testability Analysis Vivekananda M. Vedula and Jacob A. Abraham Computer Engineering Research Center The University of Texas at Austin
FACTOR: A Hierarchical Methodology for Functional Test Generation and Testability Analysis Vivekananda M. Vedula and Jacob A. Abraham Computer Engineering Research Center The University of Texas at Austin
Ripple Counters. Lecture 30 1
 Ripple Counters A register that goes through a prescribed sequence of states upon the application of input pulses is called a counter. The input pulses may be clock pulses, or they may originate from some
Ripple Counters A register that goes through a prescribed sequence of states upon the application of input pulses is called a counter. The input pulses may be clock pulses, or they may originate from some
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 20 - Finite State Machines Revisited
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 20 - Finite State Machines Revisited April 2, 2009 John Wawrzynek Spring 2009 EECS150 - Lec20-fsm Page 1 Finite State Machines (FSMs) FSM circuits are a type of sequential
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 20 - Finite State Machines Revisited April 2, 2009 John Wawrzynek Spring 2009 EECS150 - Lec20-fsm Page 1 Finite State Machines (FSMs) FSM circuits are a type of sequential
EECS 151/251A Fall 2017 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits. Instructor: John Wawrzynek and Nicholas Weaver. Lecture 14 EE141
 EECS 151/251A Fall 2017 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits Instructor: John Wawrzynek and Nicholas Weaver Lecture 14 EE141 Outline Parallelism EE141 2 Parallelism Parallelism is the act of doing more
EECS 151/251A Fall 2017 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits Instructor: John Wawrzynek and Nicholas Weaver Lecture 14 EE141 Outline Parallelism EE141 2 Parallelism Parallelism is the act of doing more
Combinational Test Generation for Various Classes of Acyclic Sequential Circuits
 ombinational Test Generation for Various lasses of cyclic Sequential ircuits Yong hang Kim y Vishwani. grawal Kewal K. Saluja University of Wisconsin-Madison S Res. Lab, gere Systems University of Wisconsin-Madison
ombinational Test Generation for Various lasses of cyclic Sequential ircuits Yong hang Kim y Vishwani. grawal Kewal K. Saluja University of Wisconsin-Madison S Res. Lab, gere Systems University of Wisconsin-Madison
Full Chip False Timing Path Identification: Applications to the PowerPC TM Microprocessors
 Full Chip False Timing Path Identification: Applications to the PowerPC TM Microprocessors Jing Zeng yz, Magdy S. Abadir y, Jayanta Bhadra yz, and Jacob A. Abraham z y EDA Tools and Methodology, Motorola
Full Chip False Timing Path Identification: Applications to the PowerPC TM Microprocessors Jing Zeng yz, Magdy S. Abadir y, Jayanta Bhadra yz, and Jacob A. Abraham z y EDA Tools and Methodology, Motorola
Application of Binary Decision Diagram in digital circuit analysis.
 Application of Binary Decision Diagram in digital circuit analysis. Jyoti Kukreja University of Southern California For Dr. James Ellison Abstract: Binary Decision Diagrams (BDDs) are one of the biggest
Application of Binary Decision Diagram in digital circuit analysis. Jyoti Kukreja University of Southern California For Dr. James Ellison Abstract: Binary Decision Diagrams (BDDs) are one of the biggest
outline Reliable State Machines MER Mission example
 outline Reliable State Machines Dr. Gary R Burke California Institute of Technology Jet Propulsion Laboratory Background JPL MER example JPL FPGA/ASIC Process Procedure Guidelines State machines Traditional
outline Reliable State Machines Dr. Gary R Burke California Institute of Technology Jet Propulsion Laboratory Background JPL MER example JPL FPGA/ASIC Process Procedure Guidelines State machines Traditional
EECS 366: Computer Architecure. Memory Technology. Lecture Notes # 15. University of Illinois at Chicago. Instructor: Shantanu Dutt Department of EECS
 EECS 366: Computer Architecure Instructor: Shantanu Dutt Department of EECS University of Illinois at Chicago Lecture Notes # 15 Memory Technology c Shantanu Dutt MEMORY ORGANIZATION Physical Characteristics
EECS 366: Computer Architecure Instructor: Shantanu Dutt Department of EECS University of Illinois at Chicago Lecture Notes # 15 Memory Technology c Shantanu Dutt MEMORY ORGANIZATION Physical Characteristics
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Logic Simulation
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Logic Simulation Sep. 17, 013 Prof. Ronald Fearing Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley (slides courtesy of Prof. John Wawrzynek)
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Logic Simulation Sep. 17, 013 Prof. Ronald Fearing Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley (slides courtesy of Prof. John Wawrzynek)
The Embedded computing platform. Four-cycle handshake. Bus protocol. Typical bus signals. Four-cycle example. CPU bus.
 The Embedded computing platform CPU bus. Memory. I/O devices. CPU bus Connects CPU to: memory; devices. Protocol controls communication between entities. Bus protocol Determines who gets to use the bus
The Embedded computing platform CPU bus. Memory. I/O devices. CPU bus Connects CPU to: memory; devices. Protocol controls communication between entities. Bus protocol Determines who gets to use the bus
EEL 4744C: Microprocessor Applications. Lecture 7. Part 1. Interrupt. Dr. Tao Li 1
 EEL 4744C: Microprocessor Applications Lecture 7 Part 1 Interrupt Dr. Tao Li 1 M&M: Chapter 8 Or Reading Assignment Software and Hardware Engineering (new version): Chapter 12 Dr. Tao Li 2 Interrupt An
EEL 4744C: Microprocessor Applications Lecture 7 Part 1 Interrupt Dr. Tao Li 1 M&M: Chapter 8 Or Reading Assignment Software and Hardware Engineering (new version): Chapter 12 Dr. Tao Li 2 Interrupt An
Reading Assignment. Interrupt. Interrupt. Interrupt. EEL 4744C: Microprocessor Applications. Lecture 7. Part 1
 Reading Assignment EEL 4744C: Microprocessor Applications Lecture 7 M&M: Chapter 8 Or Software and Hardware Engineering (new version): Chapter 12 Part 1 Interrupt Dr. Tao Li 1 Dr. Tao Li 2 Interrupt An
Reading Assignment EEL 4744C: Microprocessor Applications Lecture 7 M&M: Chapter 8 Or Software and Hardware Engineering (new version): Chapter 12 Part 1 Interrupt Dr. Tao Li 1 Dr. Tao Li 2 Interrupt An
Philadelphia University Department of Computer Science. By Dareen Hamoudeh
 Philadelphia University Department of Computer Science By Dareen Hamoudeh 1.REGISTERS WHAT IS REGISTER? register is a quickly accessible location available to a computer's central processing unit (CPU).
Philadelphia University Department of Computer Science By Dareen Hamoudeh 1.REGISTERS WHAT IS REGISTER? register is a quickly accessible location available to a computer's central processing unit (CPU).
TEST FUNCTION SPECIFICATION IN SYNTHESIS
 TEST FUNCTION SPECIFICATION IN SYNTHESIS Vishwani D. Agrawal and Kwang-Ting Cbeng AT&T Bell Laboratories Murray Hill, New Jersey 07974 ABSTRACT - We present a new synthesis for testability method in which
TEST FUNCTION SPECIFICATION IN SYNTHESIS Vishwani D. Agrawal and Kwang-Ting Cbeng AT&T Bell Laboratories Murray Hill, New Jersey 07974 ABSTRACT - We present a new synthesis for testability method in which
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Rapid advances in integrated circuit technology have made it possible to fabricate digital circuits with large number of devices on a single chip. The advantages of integrated circuits
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Rapid advances in integrated circuit technology have made it possible to fabricate digital circuits with large number of devices on a single chip. The advantages of integrated circuits
Fault Tolerant Computing CS 530 Testing Sequential Circuits
 CS 530 Testing Sequential Circuits Yashwant K. Malaiya Colorado State University 1 Why Testing Sequential Circuits is Hard To test a sequential circuit we need to Initialize it into a known state (reset
CS 530 Testing Sequential Circuits Yashwant K. Malaiya Colorado State University 1 Why Testing Sequential Circuits is Hard To test a sequential circuit we need to Initialize it into a known state (reset
Focus On Structural Test: AC Scan
 Focus On Structural Test: AC Scan Alfred L. Crouch Chief Scientist Inovys Corporation al.crouch@inovys.com The DFT Equation The Problem What is Driving Modern Test Technology? 300mm Wafers Volume Silicon/Test
Focus On Structural Test: AC Scan Alfred L. Crouch Chief Scientist Inovys Corporation al.crouch@inovys.com The DFT Equation The Problem What is Driving Modern Test Technology? 300mm Wafers Volume Silicon/Test
Transition Faults and Transition Path Delay Faults: Test Generation, Path Selection, and Built-In Generation of Functional Broadside Tests
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Open Access Dissertations Theses and Dissertations Fall 2013 Transition Faults and Transition Path Delay Faults: Test Generation, Path Selection, and Built-In Generation
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Open Access Dissertations Theses and Dissertations Fall 2013 Transition Faults and Transition Path Delay Faults: Test Generation, Path Selection, and Built-In Generation
A Toolbox for Counter-Example Analysis and Optimization
 A Toolbox for Counter-Example Analysis and Optimization Alan Mishchenko Niklas Een Robert Brayton Department of EECS, University of California, Berkeley {alanmi, een, brayton}@eecs.berkeley.edu Abstract
A Toolbox for Counter-Example Analysis and Optimization Alan Mishchenko Niklas Een Robert Brayton Department of EECS, University of California, Berkeley {alanmi, een, brayton}@eecs.berkeley.edu Abstract
A Parallel Implementation of Fault Simulation on a Cluster of. Workstations
 A Parallel Implementation of Fault Simulation on a Cluster of Workstations Except where reference is made to the work of others, the work described in this thesis is my own or was done in collaboration
A Parallel Implementation of Fault Simulation on a Cluster of Workstations Except where reference is made to the work of others, the work described in this thesis is my own or was done in collaboration
Digital Integrated Circuits
 Digital Integrated Circuits Introduction to the course Jaeyong Chung SoC Laboratory Incheon National University Course Information Schedule (EPC6055001) Mon 6:55pm - 8:40pm (SI433), Tue 7:50pm - 9:35pm
Digital Integrated Circuits Introduction to the course Jaeyong Chung SoC Laboratory Incheon National University Course Information Schedule (EPC6055001) Mon 6:55pm - 8:40pm (SI433), Tue 7:50pm - 9:35pm
Characteristics of the ITC 99 Benchmark Circuits
 Characteristics of the ITC 99 Benchmark Circuits Scott Davidson Sun Microsystems, Inc. ITC 99 Benchmarks - Scott Davidson Page 1 Outline Why Benchmark? Some History. Soliciting Benchmarks Benchmark Characteristics
Characteristics of the ITC 99 Benchmark Circuits Scott Davidson Sun Microsystems, Inc. ITC 99 Benchmarks - Scott Davidson Page 1 Outline Why Benchmark? Some History. Soliciting Benchmarks Benchmark Characteristics
Using Genetic Algorithms to Solve the Box Stacking Problem
 Using Genetic Algorithms to Solve the Box Stacking Problem Jenniffer Estrada, Kris Lee, Ryan Edgar October 7th, 2010 Abstract The box stacking or strip stacking problem is exceedingly difficult to solve
Using Genetic Algorithms to Solve the Box Stacking Problem Jenniffer Estrada, Kris Lee, Ryan Edgar October 7th, 2010 Abstract The box stacking or strip stacking problem is exceedingly difficult to solve
Non-Enumerative Path Delay Fault Diagnosis
 Non-Enumerative Path Delay Fault Diagnosis Saravanan Padmanaban Spyros Tragoudas Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Southern Illinois University Carbondale, IL 6901 Abstract The first non-enumerative
Non-Enumerative Path Delay Fault Diagnosis Saravanan Padmanaban Spyros Tragoudas Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Southern Illinois University Carbondale, IL 6901 Abstract The first non-enumerative
QUESTION BANK FOR TEST
 CSCI 2121 Computer Organization and Assembly Language PRACTICE QUESTION BANK FOR TEST 1 Note: This represents a sample set. Please study all the topics from the lecture notes. Question 1. Multiple Choice
CSCI 2121 Computer Organization and Assembly Language PRACTICE QUESTION BANK FOR TEST 1 Note: This represents a sample set. Please study all the topics from the lecture notes. Question 1. Multiple Choice
ECE 156B Fault Model and Fault Simulation
 ECE 156B Fault Model and Fault Simulation Lecture 6 ECE 156B 1 What is a fault A fault is a hypothesis of what may go wrong in the manufacturing process In fact, a fault model is not trying to model the
ECE 156B Fault Model and Fault Simulation Lecture 6 ECE 156B 1 What is a fault A fault is a hypothesis of what may go wrong in the manufacturing process In fact, a fault model is not trying to model the
Digital Integrated Circuits
 Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture Jaeyong Chung System-on-Chips (SoC) Laboratory Incheon National University Design/manufacture Process Chung EPC655 2 Design/manufacture Process Chung EPC655 3 Layout
Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture Jaeyong Chung System-on-Chips (SoC) Laboratory Incheon National University Design/manufacture Process Chung EPC655 2 Design/manufacture Process Chung EPC655 3 Layout
ATPG for Faults Analysis in VLSI Circuits Using Immune Genetic Algorithm
 ATPG for Faults Analysis in VLSI Circuits Using Immune Genetic Algorithm P.K.Chakrabarty 1, S.N.Patnaik 2 1Professor, Department of CSE., IT,BHU, India 2Asst.Professor, ECE Department, DRIEMS, Cuttack,
ATPG for Faults Analysis in VLSI Circuits Using Immune Genetic Algorithm P.K.Chakrabarty 1, S.N.Patnaik 2 1Professor, Department of CSE., IT,BHU, India 2Asst.Professor, ECE Department, DRIEMS, Cuttack,
March 19, Heuristics for Optimization. Outline. Problem formulation. Genetic algorithms
 Olga Galinina olga.galinina@tut.fi ELT-53656 Network Analysis and Dimensioning II Department of Electronics and Communications Engineering Tampere University of Technology, Tampere, Finland March 19, 2014
Olga Galinina olga.galinina@tut.fi ELT-53656 Network Analysis and Dimensioning II Department of Electronics and Communications Engineering Tampere University of Technology, Tampere, Finland March 19, 2014
Introduction to Genetic Algorithms. Genetic Algorithms
 Introduction to Genetic Algorithms Genetic Algorithms We ve covered enough material that we can write programs that use genetic algorithms! More advanced example of using arrays Could be better written
Introduction to Genetic Algorithms Genetic Algorithms We ve covered enough material that we can write programs that use genetic algorithms! More advanced example of using arrays Could be better written
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 09 - Parallelism
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 09 - Parallelism Feb 19, 2013 John Wawrzynek Spring 2013 EECS150 - Lec09-parallel Page 1 Parallelism Parallelism is the act of doing more than one thing at a time. Optimization
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 09 - Parallelism Feb 19, 2013 John Wawrzynek Spring 2013 EECS150 - Lec09-parallel Page 1 Parallelism Parallelism is the act of doing more than one thing at a time. Optimization
Sequential Circuit Design: Principle
 Sequential Circuit Design: Principle Chapter 8 1 Outline 1. Overview on sequential circuits 2. Synchronous circuits 3. Danger of synthesizing asynchronous circuit 4. Inference of basic memory elements
Sequential Circuit Design: Principle Chapter 8 1 Outline 1. Overview on sequential circuits 2. Synchronous circuits 3. Danger of synthesizing asynchronous circuit 4. Inference of basic memory elements
Lecture 28 IEEE JTAG Boundary Scan Standard
 Lecture 28 IEEE 49. JTAG Boundary Scan Standard Motivation Bed-of-nails tester System view of boundary scan hardware Elementary scan cell Test Access Port (TAP) controller Boundary scan instructions Summary
Lecture 28 IEEE 49. JTAG Boundary Scan Standard Motivation Bed-of-nails tester System view of boundary scan hardware Elementary scan cell Test Access Port (TAP) controller Boundary scan instructions Summary
Digital System Design with SystemVerilog
 Digital System Design with SystemVerilog Mark Zwolinski AAddison-Wesley Upper Saddle River, NJ Boston Indianapolis San Francisco New York Toronto Montreal London Munich Paris Madrid Capetown Sydney Tokyo
Digital System Design with SystemVerilog Mark Zwolinski AAddison-Wesley Upper Saddle River, NJ Boston Indianapolis San Francisco New York Toronto Montreal London Munich Paris Madrid Capetown Sydney Tokyo
Compaction mechanism to reduce test pattern counts and segmented delay fault testing for path delay faults
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Spring 2013 Compaction mechanism to reduce test pattern counts and segmented delay fault testing for path delay faults Sharada Jha University
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Spring 2013 Compaction mechanism to reduce test pattern counts and segmented delay fault testing for path delay faults Sharada Jha University
Driving Toward Higher I DDQ Test Quality for Sequential Circuits: A Generalized Fault Model and Its ATPG
 Driving Toward Higher I DDQ Test Quality for Sequential Circuits: A Generalized Fault Model and Its ATPG Hisashi Kondo Kwang-Ting Cheng y Kawasaki Steel Corp., LSI Division Electrical and Computer Engineering
Driving Toward Higher I DDQ Test Quality for Sequential Circuits: A Generalized Fault Model and Its ATPG Hisashi Kondo Kwang-Ting Cheng y Kawasaki Steel Corp., LSI Division Electrical and Computer Engineering
ANALYSIS AND EVALUATION OF SEQUENTIAL REDUNDANCY IDENTIFICATION ALGORITHMS. Master of Science Thesis In Electronic System Design By
 TRITA-ICT-EX-2011:239 ANALYSIS AND EVALUATION OF SEQUENTIAL REDUNDANCY IDENTIFICATION ALGORITHMS Master of Science Thesis In Electronic System Design By Yulia Kuznetsova Stockholm, [October 2011] Supervisor
TRITA-ICT-EX-2011:239 ANALYSIS AND EVALUATION OF SEQUENTIAL REDUNDANCY IDENTIFICATION ALGORITHMS Master of Science Thesis In Electronic System Design By Yulia Kuznetsova Stockholm, [October 2011] Supervisor
RTL Scan Design for Skewed-Load At-Speed Test under Power Constraints
 RTL Scan Design for Skewed-Load At-Speed Test under Power Constraints Ho Fai Ko and Nicola Nicolici Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, L8S 4K1, Canada
RTL Scan Design for Skewed-Load At-Speed Test under Power Constraints Ho Fai Ko and Nicola Nicolici Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, L8S 4K1, Canada
