Grundlagen Microcontroller Processor Core. Günther Gridling Bettina Weiss
|
|
|
- Flora Hamilton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Grundlagen Microcontroller Processor Core Günther Gridling Bettina Weiss 1
2 Processor Core Architecture Instruction Set Lecture Overview 2
3 Processor Core Architecture Computes things > ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit) arithmetic and logic operations shifting and rotation ADD SUB AND OR NOT... 2 data inputs, 1 data output 3
4 Architecture Interesting information about ALU result: Status Register (Condition Code Register) zero (Z) negative (N) overflow (V) carry (C) 4
5 Architecture Status Register Flags: Z, N, V, C whenever the result of an operation is zero, the Z flag is set, otherwise it is cleared if the result of an operation is negative (msb = 1), the N flag is set, otherwise it is cleared the V flag alerts that in a 2's complement operation, the sign bit has changed irregularly The carry bit is used for multi word operations 5
6 Architecture Where do operands come from? > Register File many general purpose registers some dedicated registers (accumulator) 6
7 Architecture Where do operands come from? > Data Memory the data memory is not part of the CPU! memory access is slower than register access 7
8 Architecture Who controls ALU? > Control Unit interprets instructions controls datapath 8
9 Architecture Which instruction should be executed? > Program Counter (PC) contains address of next instruction instruction is loaded into instruction register (IR), PC is incremented 9
10 Architecture What is the next instruction? mostly sequential (PC = PC + 1) sometimes a jump (PC = address, PC = PC + offset) sometimes a subroutine call > want to jump back after subroutine is finished have to store the return address 10
11 Architecture Where is return address stored? > Stack Stack: consecutive area in data memory used by CPU: store return addresses, sometimes registers User: store data, save register contents Stack Pointer (SP): points to first free (or last used) location in stack 11
12 Stack Initialization Architecture stack grows down, from higher address to lower address initial SP value is often the end of the data memory (0xFF here) SP is initialized by the user! 12
13 Architecture Stack Example PUSH #1 PUSH #2 POP R0 13
14 Architecture Subroutine Call: 0x0A: JSR MyFunc 0x0C: NOP... start: PC = 0x0A SP = 0xFF MyFunc: 0x50: NOP 0x52: RET 14
15 Architecture Subroutine Call: 0x0A: JSR MyFunc 0x0C: NOP... MyFunc: 0x50: NOP 0x52: RET start: PC = 0x0A SP = 0xFF JSR is loaded PC = 0x0C JSR is interpreted PUSH PC ( > SP = 0xFE) PC = 0x50 15
16 Architecture Subroutine Call: 0x0A: JSR MyFunc 0x0C: NOP... MyFunc: 0x50: NOP 0x52: RET start: PC = 0x50 SP = 0xFE NOP is loaded PC = 0x52 NOP is interpreted 16
17 Architecture Subroutine Call: 0x0A: JSR MyFunc 0x0C: NOP... MyFunc: 0x50: NOP 0x52: RET start: PC = 0x52 SP = 0xFE RET is loaded PC = 0x54 RET is interpreted POP PC ( > PC = 0x0C) ( > SP = 0xFF) 17
18 Architecture Subroutine Call: 0x0A: JSR MyFunc 0x0C: NOP... MyFunc: 0x50: NOP 0x52: RET start: PC = 0x0C SP = 0xFF NOP is loaded PC = 0x0E NOP is interpreted...and so on... 18
19 Finally: our CPU is complete Datapath: ALU SR/CCR Register File PC contains next instr. SP for storing ret. addr. Control Architecture 19
20 Processor Core Architecture Instruction Set Lecture Overview 20
21 What can we do with the CPU? Instruction Format: Opcode [Operand]* Interesting information: types of instructions instruction size number of operands types of operands Instruction Set 21
22 Instruction Set Types of instructions: arithmetic and logic instructions branch instructions data transfer instructions bit instructions control instructions 22
23 Instruction Set Arithmetic and logic instructions ADD, SUB, MUL, INC, DEC,... AND, OR, NOT,... possibly special instructions for BCD arithmetic 23
24 Branch instructions Instruction Set everything that influences the program flow unconditional branches: JUMP (relative or absolute) conditional branches: BEQ, BNEQ subroutine calls: JSR, RET 24
25 Instruction Set Data transfer instructions instructions that move data, access memory load to/from registers: LD, ST copy data in memory: MOV tend to take many cycles (memory access) 25
26 Bit instructions Instruction Set an important feature of microcontrollers set/clear bits: BSET, BCLR test bits: BTST bit instructions are extremely important, they ensure that you can access a single output line without influencing other lines never access a bit you don't have to! 26
27 Control instructions are used to control the microcontroller simplest instruction: NOP (no operation, do nothing) control sleep mode: SLEEP, IDLE control watchdog Instruction Set cause a reset, enter debug mode,... 27
28 Interesting things: types of instructions instruction size number of operands types of operands Instruction Set 28
29 Instruction Size: 8 32 bits, fixed or variable long size has advantages and drawbacks: + many different instructions + many explicit operands, many different operand types large code size complex hardware CISC vs. RISC Instruction Set 29
30 Instruction Set CISC: Complex Instruction Set Computer complex (microcoded) instructions take many clock cycles to execute larger and often variable code size many addressing modes many instructions very powerful instructions 30
31 Instruction Set But: Study: 20% of instructions are responsible for 80% of code (80/20 rule) it is possible to simulate complex instructions with several simple ones 31
32 Instruction Set RISC: Reduced Instruction Set Computer simple (hardwired) instructions often take only one or few clock cycles to execute small fixed code size few addressing modes few instructions very fast execution of instructions 32
33 Instruction Set Which is better: RISC or CISC? depends on what you need! frequently need a powerful instruction/complex addressing mode > use CISC mostly need simple instructions and addressing modes > use RISC You must know which instructions/addr. modes you need to select the appropriate controller! 33
34 Interesting things: types of instructions instruction size number of operands types of operands Instruction Set 34
35 Instructions may require 0 3 operands, depending on their type: 0 operands: e.g. RET Instruction Set 1 operand: e.g. JUMP <addr> 2 operands: e.g. LOAD <dest>, <source> 3 operands: e.g. ADD <dest>, <source1>, <source2> 35
36 Instruction Set How many explicit operands does an instruction with 3 operands need? depends on the architecture, may be from 0 to 3! few operands imply short instructions, but it is not very flexible many operands allow for powerful instructions 36
37 0 Operands: 0 Address Format, Stack Architecture source operands are on the stack result is put on the stack Example: z = x + y PUSH x PUSH y ADD POP z Instruction Set ; push 1 st operand on stack ; push 2 nd operand on stack ; pop operands, add them, push result ; pop result 37
38 Instruction Set 1 Operand: 1 Address Format, Accumulator one source operand is implicit (accumulator register) result is saved in accumulator Example: z = x + y LDA x ADD y STA z ; load x into accumulator A ; add y to accu, store result in accu ; store value of accu A back to z 38
39 Instruction Set 2 Operands: 2 Address Format destination register is one of the source registers we assume that it is the first source Example: z = x + y LD R0, x ADD R0, y ST R0, z ; load x into register R0 ; add y to R0, store result in R0 ; store value of register R0 in z 39
40 Instruction Set 3 Operands: 3 Address Format sources and destination are explicit very powerful, but large instruction size Example: z = x + y ADD z, x, y ; add x and y, store result in z 40
41 Instruction Set Important Term: Load/Store Architecture memory access is slow > only do it with data transfer instructions arithmetic and logic instructions use registers register file contains many general purpose registers (i.e., all registers have the same functions) RISC architectures are load/store (register access is fast and easy compared to memory access) 41
42 Interesting things: types of instructions instruction size number of operands types of operands Instruction Set 42
43 Operand Types: constants registers memory locations Instruction Set 43
44 How do we specify the location of the operand? > Addressing Mode implicit immediate (constant) register direct/absolute... Instruction Set 44
45 Instruction Set Implicit Addressing Mode do not specify anything e.g. Stack Architecture: operands on stack 45
46 Instruction Set Immediate Addressing Mode for constants no data location, just a value how to distinguish from addresses? prefix, e.g. LD R0, #5 dedicated instructions, e.g. LDI R0, 5 (load immediate) 46
47 Register Addressing Mode operand is a register Instruction Set LD R0, R1 47
48 Instruction Set Direct/Absolute Addressing Mode operand is a memory address LD R0, 0x0FF M [0x0FF] 48
49 Register Indirect Instruction Set register contains memory address LD R0, (R1) M [R1] 49
50 Instruction Set Register Indirect with Autoincrement register contains memory address post increment, pre decrement (good for arrays) LD R0, (R1)+ M [R1], R1 < R1 + 1 LD R0, (R1) R1 < R1 1, M [R1] 50
51 Instruction Set Displacement/Based Register + Constant are address nice for arrays, data records LD R0, C(R1) M [C + R1] 51
52 Instruction Set Indexed Register + Register are address nice for arrays: one is base, one is index especially nice with autoincrement LD R0, (R1 + RX) M [R1+RX] 52
53 Memory Indirect Instruction Set memory contains address nice for jump tables LD M [M [R1]] 53
54 Instruction Set there are many more addressing modes for special accesses a given controller implements a subset of the addressing modes CISC controllers have more and more powerful addressing modes than RISC controllers 54
55 Instruction Set Summary types of instructions arithm./logic, branch, data transfer, bit, control instruction size CISC vs. RISC number of operands stack, accumulator, 2 address, 3 address types of operands constants/registers/memory, addressing modes 55
56 Processor Core Lecture Summary Architecture: datapath + control; ALU, reg. file, SR, PC, SP Instruction Set: different types of instructions (datasheet), CISC vs. RISC, addressing modes 56
Instruction-set Design Issues: what is the ML instruction format(s) ML instruction Opcode Dest. Operand Source Operand 1...
 Instruction-set Design Issues: what is the format(s) Opcode Dest. Operand Source Operand 1... 1) Which instructions to include: How many? Complexity - simple ADD R1, R2, R3 complex e.g., VAX MATCHC substrlength,
Instruction-set Design Issues: what is the format(s) Opcode Dest. Operand Source Operand 1... 1) Which instructions to include: How many? Complexity - simple ADD R1, R2, R3 complex e.g., VAX MATCHC substrlength,
Instruction-set Design Issues: what is the ML instruction format(s) ML instruction Opcode Dest. Operand Source Operand 1...
 Instruction-set Design Issues: what is the format(s) Opcode Dest. Operand Source Operand 1... 1) Which instructions to include: How many? Complexity - simple ADD R1, R2, R3 complex e.g., VAX MATCHC substrlength,
Instruction-set Design Issues: what is the format(s) Opcode Dest. Operand Source Operand 1... 1) Which instructions to include: How many? Complexity - simple ADD R1, R2, R3 complex e.g., VAX MATCHC substrlength,
CN310 Microprocessor Systems Design
 CN310 Microprocessor Systems Design Instruction Set (AVR) Nawin Somyat Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Thammasat University Outline Course Contents 1 Introduction 2 Simple Computer 3
CN310 Microprocessor Systems Design Instruction Set (AVR) Nawin Somyat Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Thammasat University Outline Course Contents 1 Introduction 2 Simple Computer 3
OSIAC Read OSIAC 5362 posted on the course website
 OSIAC 5362 Read OSIAC 5362 posted on the course website The Basic Structure of Control Unit m CLK Run/Inhibit Control Step Counter m Preset (to any new state) Reset IR Decoder/Encoder (combinational logic)
OSIAC 5362 Read OSIAC 5362 posted on the course website The Basic Structure of Control Unit m CLK Run/Inhibit Control Step Counter m Preset (to any new state) Reset IR Decoder/Encoder (combinational logic)
CHAPTER 8: Central Processing Unit (CPU)
 CS 224: Computer Organization S.KHABET CHAPTER 8: Central Processing Unit (CPU) Outline Introduction General Register Organization Stack Organization Instruction Formats Addressing Modes 1 Major Components
CS 224: Computer Organization S.KHABET CHAPTER 8: Central Processing Unit (CPU) Outline Introduction General Register Organization Stack Organization Instruction Formats Addressing Modes 1 Major Components
TYPES OF INTERRUPTS: -
 There are 3 types of interrupts. TYPES OF INTERRUPTS: - External Interrupts. Internal Interrupts. Software interrupts. Hardware Interrupts (1) External interrupts come from I/O devices, from a timing device
There are 3 types of interrupts. TYPES OF INTERRUPTS: - External Interrupts. Internal Interrupts. Software interrupts. Hardware Interrupts (1) External interrupts come from I/O devices, from a timing device
ก AVR Microcontrollers
 ก AVR Microcontrollers. ก ก AVR Microcontrollers Architecture 1 Instruction Execution Timing The Parallel Instruction Fetches and Instruction Executions Single Cycle ALU Operation AVR Microcontrollers
ก AVR Microcontrollers. ก ก AVR Microcontrollers Architecture 1 Instruction Execution Timing The Parallel Instruction Fetches and Instruction Executions Single Cycle ALU Operation AVR Microcontrollers
Computer Organization CS 206 T Lec# 2: Instruction Sets
 Computer Organization CS 206 T Lec# 2: Instruction Sets Topics What is an instruction set Elements of instruction Instruction Format Instruction types Types of operations Types of operand Addressing mode
Computer Organization CS 206 T Lec# 2: Instruction Sets Topics What is an instruction set Elements of instruction Instruction Format Instruction types Types of operations Types of operand Addressing mode
The von Neumann Architecture. IT 3123 Hardware and Software Concepts. The Instruction Cycle. Registers. LMC Executes a Store.
 IT 3123 Hardware and Software Concepts February 11 and Memory II Copyright 2005 by Bob Brown The von Neumann Architecture 00 01 02 03 PC IR Control Unit Command Memory ALU 96 97 98 99 Notice: This session
IT 3123 Hardware and Software Concepts February 11 and Memory II Copyright 2005 by Bob Brown The von Neumann Architecture 00 01 02 03 PC IR Control Unit Command Memory ALU 96 97 98 99 Notice: This session
Microcomputer Architecture and Programming
 IUST-EE (Chapter 1) Microcomputer Architecture and Programming 1 Outline Basic Blocks of Microcomputer Typical Microcomputer Architecture The Single-Chip Microprocessor Microprocessor vs. Microcontroller
IUST-EE (Chapter 1) Microcomputer Architecture and Programming 1 Outline Basic Blocks of Microcomputer Typical Microcomputer Architecture The Single-Chip Microprocessor Microprocessor vs. Microcontroller
CPU: SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE INSTRUCTION SET (PART
 General Introduction CPU: SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE INSTRUCTION SET (PART 1) General Introduction (1/5): On Instructions Instruction operate with data or with the flow of the program The following information
General Introduction CPU: SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE INSTRUCTION SET (PART 1) General Introduction (1/5): On Instructions Instruction operate with data or with the flow of the program The following information
CSIS1120A. 10. Instruction Set & Addressing Mode. CSIS1120A 10. Instruction Set & Addressing Mode 1
 CSIS1120A 10. Instruction Set & Addressing Mode CSIS1120A 10. Instruction Set & Addressing Mode 1 Elements of a Machine Instruction Operation Code specifies the operation to be performed, e.g. ADD, SUB
CSIS1120A 10. Instruction Set & Addressing Mode CSIS1120A 10. Instruction Set & Addressing Mode 1 Elements of a Machine Instruction Operation Code specifies the operation to be performed, e.g. ADD, SUB
CPE 323 MSP430 INSTRUCTION SET ARCHITECTURE (ISA)
 CPE 323 MSP430 INSTRUCTION SET ARCHITECTURE (ISA) Aleksandar Milenković Email: milenka@uah.edu Web: http://www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka Objective Introduce MSP430 Instruction Set Architecture (Class of ISA,
CPE 323 MSP430 INSTRUCTION SET ARCHITECTURE (ISA) Aleksandar Milenković Email: milenka@uah.edu Web: http://www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka Objective Introduce MSP430 Instruction Set Architecture (Class of ISA,
AVR ISA & AVR Programming (I) Lecturer: Sri Parameswaran Notes by: Annie Guo
 AVR ISA & AVR Programming (I) Lecturer: Sri Parameswaran Notes by: Annie Guo 1 Lecture Overview AVR ISA AVR Instructions & Programming (I) Basic construct implementation 2 Atmel AVR 8-bit RISC architecture
AVR ISA & AVR Programming (I) Lecturer: Sri Parameswaran Notes by: Annie Guo 1 Lecture Overview AVR ISA AVR Instructions & Programming (I) Basic construct implementation 2 Atmel AVR 8-bit RISC architecture
Instruction Set Architecture. "Speaking with the computer"
 Instruction Set Architecture "Speaking with the computer" The Instruction Set Architecture Application Compiler Instr. Set Proc. Operating System I/O system Instruction Set Architecture Digital Design
Instruction Set Architecture "Speaking with the computer" The Instruction Set Architecture Application Compiler Instr. Set Proc. Operating System I/O system Instruction Set Architecture Digital Design
Assembly Language Programming of 8085
 Assembly Language Programming of 8085 Topics 1. Introduction 2. Programming model of 8085 3. Instruction set of 8085 4. Example Programs 5. Addressing modes of 8085 6. Instruction & Data Formats of 8085
Assembly Language Programming of 8085 Topics 1. Introduction 2. Programming model of 8085 3. Instruction set of 8085 4. Example Programs 5. Addressing modes of 8085 6. Instruction & Data Formats of 8085
UNIT-II. Part-2: CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT
 Page1 UNIT-II Part-2: CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT Stack Organization Instruction Formats Addressing Modes Data Transfer And Manipulation Program Control Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) Introduction:
Page1 UNIT-II Part-2: CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT Stack Organization Instruction Formats Addressing Modes Data Transfer And Manipulation Program Control Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) Introduction:
Assembly Language Programming of 8085
 Assembly Language Programming of 8085 1. Introduction A microprocessor executes instructions given by the user Instructions should be in a language known to the microprocessor Microprocessor understands
Assembly Language Programming of 8085 1. Introduction A microprocessor executes instructions given by the user Instructions should be in a language known to the microprocessor Microprocessor understands
Instruction Sets: Characteristics and Functions Addressing Modes
 Instruction Sets: Characteristics and Functions Addressing Modes Chapters 10 and 11, William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 th Edition What is an Instruction Set? The complete collection
Instruction Sets: Characteristics and Functions Addressing Modes Chapters 10 and 11, William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 th Edition What is an Instruction Set? The complete collection
Mechatronics and Microcomputers. Stipendium Hungaricum 2018/2019 Autumn Semester Szilárd Aradi, PhD
 Mechatronics and Microcomputers Stipendium Hungaricum 2018/2019 Autumn Semester Szilárd Aradi, PhD ATmega128 CPU Single-level pipelining Egyciklusú ALU működés Reg. reg., reg. konst. közötti műveletek
Mechatronics and Microcomputers Stipendium Hungaricum 2018/2019 Autumn Semester Szilárd Aradi, PhD ATmega128 CPU Single-level pipelining Egyciklusú ALU működés Reg. reg., reg. konst. közötti műveletek
Instruction Sets Ch 9-10
 Instruction Sets Ch 9-10 Characteristics Operands Operations Addressing Instruction Formats 1 Instruction Set (käskykanta) Collection of instructions that CPU understands Only interface to CPU from outside
Instruction Sets Ch 9-10 Characteristics Operands Operations Addressing Instruction Formats 1 Instruction Set (käskykanta) Collection of instructions that CPU understands Only interface to CPU from outside
Instruction Sets Ch 9-10
 Instruction Sets Ch 9-10 Characteristics Operands Operations Addressing Instruction Formats 1 Instruction Set (käskykanta) Collection of instructions that CPU understands Only interface to CPU from outside
Instruction Sets Ch 9-10 Characteristics Operands Operations Addressing Instruction Formats 1 Instruction Set (käskykanta) Collection of instructions that CPU understands Only interface to CPU from outside
MOS 6502 Architecture
 MOS 6502 Architecture Lecture 3 Fall 17 1 History Origins lie in the Motorola 6800. Was very expensive for consumers. ($300, or about $1500 in 2017 $s) Chuck Peddle proposes lower-cost, lower-area 6800
MOS 6502 Architecture Lecture 3 Fall 17 1 History Origins lie in the Motorola 6800. Was very expensive for consumers. ($300, or about $1500 in 2017 $s) Chuck Peddle proposes lower-cost, lower-area 6800
Introduction to Microcontrollers
 Introduction to Microcontrollers Courses 182.064 & 182.074 Vienna University of Technology Institute of Computer Engineering Embedded Computing Systems Group March 19, 2006 Version 1.3 Günther Gridling,
Introduction to Microcontrollers Courses 182.064 & 182.074 Vienna University of Technology Institute of Computer Engineering Embedded Computing Systems Group March 19, 2006 Version 1.3 Günther Gridling,
Module 8: Atmega32 Stack & Subroutine. Stack Pointer Subroutine Call function
 Module 8: Atmega32 Stack & Subroutine Stack Pointer Subroutine Call function Stack Stack o Stack is a section of RAM used by the CPU to store information temporarily (i.e. data or address). o The CPU needs
Module 8: Atmega32 Stack & Subroutine Stack Pointer Subroutine Call function Stack Stack o Stack is a section of RAM used by the CPU to store information temporarily (i.e. data or address). o The CPU needs
Lecture1: introduction. Outline: History overview Central processing unite Register set Special purpose address registers Datapath Control unit
 Lecture1: introduction Outline: History overview Central processing unite Register set Special purpose address registers Datapath Control unit 1 1. History overview Computer systems have conventionally
Lecture1: introduction Outline: History overview Central processing unite Register set Special purpose address registers Datapath Control unit 1 1. History overview Computer systems have conventionally
It is possible to define a number using a character or multiple numbers (see instruction DB) by using a string.
 1 od 5 17. 12. 2017 23:53 (https://github.com/schweigi/assembler-simulator) Introduction This simulator provides a simplified assembler syntax (based on NASM (http://www.nasm.us)) and is simulating a x86
1 od 5 17. 12. 2017 23:53 (https://github.com/schweigi/assembler-simulator) Introduction This simulator provides a simplified assembler syntax (based on NASM (http://www.nasm.us)) and is simulating a x86
SOEN228, Winter Revision 1.2 Date: October 25,
 SOEN228, Winter 2003 Revision 1.2 Date: October 25, 2003 1 Contents Flags Mnemonics Basic I/O Exercises Overview of sample programs 2 Flag Register The flag register stores the condition flags that retain
SOEN228, Winter 2003 Revision 1.2 Date: October 25, 2003 1 Contents Flags Mnemonics Basic I/O Exercises Overview of sample programs 2 Flag Register The flag register stores the condition flags that retain
By: Dr. Hamed Saghaei
 By: Dr. Hamed Saghaei The AVR RISC Microcontroller supports powerful and efficient addressing modes for access to the program memory (Flash) and data memory (SRAM). This section describes the different
By: Dr. Hamed Saghaei The AVR RISC Microcontroller supports powerful and efficient addressing modes for access to the program memory (Flash) and data memory (SRAM). This section describes the different
Register Files. Single Bus Architecture. Register Files. Single Bus Processor. Term Project: using VHDL. Accumulator based architecture
 Register Files DR 3 SelS Design and simulate the LC-3 processor using VHDL Term Project: Single Processor Decoder... R R3 R6...... mux mux S S SelDR 3 DRin Clock 3 SelS LC-3 Architecture 3 Register File
Register Files DR 3 SelS Design and simulate the LC-3 processor using VHDL Term Project: Single Processor Decoder... R R3 R6...... mux mux S S SelDR 3 DRin Clock 3 SelS LC-3 Architecture 3 Register File
ISA and RISCV. CASS 2018 Lavanya Ramapantulu
 ISA and RISCV CASS 2018 Lavanya Ramapantulu Program Program =?? Algorithm + Data Structures Niklaus Wirth Program (Abstraction) of processor/hardware that executes 3-Jul-18 CASS18 - ISA and RISCV 2 Program
ISA and RISCV CASS 2018 Lavanya Ramapantulu Program Program =?? Algorithm + Data Structures Niklaus Wirth Program (Abstraction) of processor/hardware that executes 3-Jul-18 CASS18 - ISA and RISCV 2 Program
Digital System Design Using Verilog. - Processing Unit Design
 Digital System Design Using Verilog - Processing Unit Design 1.1 CPU BASICS A typical CPU has three major components: (1) Register set, (2) Arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and (3) Control unit (CU) The register
Digital System Design Using Verilog - Processing Unit Design 1.1 CPU BASICS A typical CPU has three major components: (1) Register set, (2) Arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and (3) Control unit (CU) The register
Grundlagen Microcontroller Interrupts. Günther Gridling Bettina Weiss
 Grundlagen Microcontroller Interrupts Günther Gridling Bettina Weiss 1 Interrupts Lecture Overview Definition Sources ISR Priorities & Nesting 2 Definition Interrupt: reaction to (asynchronous) external
Grundlagen Microcontroller Interrupts Günther Gridling Bettina Weiss 1 Interrupts Lecture Overview Definition Sources ISR Priorities & Nesting 2 Definition Interrupt: reaction to (asynchronous) external
Computer Organization and Technology Processor and System Structures
 Computer Organization and Technology Processor and System Structures Assoc. Prof. Dr. Wattanapong Kurdthongmee Division of Computer Engineering, School of Engineering and Resources, Walailak University
Computer Organization and Technology Processor and System Structures Assoc. Prof. Dr. Wattanapong Kurdthongmee Division of Computer Engineering, School of Engineering and Resources, Walailak University
AVR ISA & AVR Programming (I) Lecturer: Sri Parameswaran Notes by: Annie Guo
 AVR ISA & AVR Programming (I) Lecturer: Sri Parameswaran Notes by: Annie Guo 1 Lecture Overview AVR ISA AVR Instructions & Programming (I) Basic construct implementation 2 Atmel AVR 8-bit RISC architecture
AVR ISA & AVR Programming (I) Lecturer: Sri Parameswaran Notes by: Annie Guo 1 Lecture Overview AVR ISA AVR Instructions & Programming (I) Basic construct implementation 2 Atmel AVR 8-bit RISC architecture
Fig: Computer memory with Program, data, and Stack. Blog - NEC (Autonomous) 1
 Central Processing Unit 1. Stack Organization A useful feature that is included in the CPU of most computers is a stack or last in, first out (LIFO) list. A stack is a storage device that stores information
Central Processing Unit 1. Stack Organization A useful feature that is included in the CPU of most computers is a stack or last in, first out (LIFO) list. A stack is a storage device that stores information
Lecture 04: Machine Instructions
 CSCI2510 Computer Organization Lecture 04: Machine Instructions Ming-Chang YANG mcyang@cse.cuhk.edu.hk Reading: Chap. 2.3~2.4, 2.10~2.11 Recall: Instructions & Program A computer is governed by instructions.
CSCI2510 Computer Organization Lecture 04: Machine Instructions Ming-Chang YANG mcyang@cse.cuhk.edu.hk Reading: Chap. 2.3~2.4, 2.10~2.11 Recall: Instructions & Program A computer is governed by instructions.
COMPUTER HARDWARE. Instruction Set Architecture
 COMPUTER HARDWARE Instruction Set Architecture Overview Computer architecture Operand addressing Addressing architecture Addressing modes Elementary instructions Data transfer instructions Data manipulation
COMPUTER HARDWARE Instruction Set Architecture Overview Computer architecture Operand addressing Addressing architecture Addressing modes Elementary instructions Data transfer instructions Data manipulation
3.0 Instruction Set. 3.1 Overview
 3.0 Instruction Set 3.1 Overview There are 16 different P8 instructions. Research on instruction set usage was the basis for instruction selection. Each instruction has at least two addressing modes, with
3.0 Instruction Set 3.1 Overview There are 16 different P8 instructions. Research on instruction set usage was the basis for instruction selection. Each instruction has at least two addressing modes, with
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 th Edition. Chapter 11 Instruction Sets: Addressing Modes and Formats
 William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 th Edition Chapter 11 Instruction Sets: Addressing Modes and Formats Addressing Modes Immediate Direct Indirect Register Register Indirect Displacement
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 th Edition Chapter 11 Instruction Sets: Addressing Modes and Formats Addressing Modes Immediate Direct Indirect Register Register Indirect Displacement
Programming of 8085 microprocessor and 8051 micro controller Study material
 8085 Demo Programs Now, let us take a look at some program demonstrations using the above instructions Adding Two 8-bit Numbers Write a program to add data at 3005H & 3006H memory location and store the
8085 Demo Programs Now, let us take a look at some program demonstrations using the above instructions Adding Two 8-bit Numbers Write a program to add data at 3005H & 3006H memory location and store the
Computer Architecture
 Computer Architecture Lecture 1: Digital logic circuits The digital computer is a digital system that performs various computational tasks. Digital computers use the binary number system, which has two
Computer Architecture Lecture 1: Digital logic circuits The digital computer is a digital system that performs various computational tasks. Digital computers use the binary number system, which has two
AVR ISA & AVR Programming (I)
 AVR ISA & AVR Programming (I) Lecturer: Sri Parameswaran Notes by: Annie Guo Week 1 1 Lecture Overview AVR ISA AVR Instructions & Programming (I) Basic construct implementation Week 1 2 1 Atmel AVR 8-bit
AVR ISA & AVR Programming (I) Lecturer: Sri Parameswaran Notes by: Annie Guo Week 1 1 Lecture Overview AVR ISA AVR Instructions & Programming (I) Basic construct implementation Week 1 2 1 Atmel AVR 8-bit
Example of A Microprogrammed Computer
 Example of A Microprogrammed omputer The purpose of this example is to demonstrate some of the concepts of microprogramming. We are going to create a simple 16-bit computer that uses three buses A, B,
Example of A Microprogrammed omputer The purpose of this example is to demonstrate some of the concepts of microprogramming. We are going to create a simple 16-bit computer that uses three buses A, B,
COSC 243. Instruction Sets And Addressing Modes. Lecture 7&8 Instruction Sets and Addressing Modes. COSC 243 (Computer Architecture)
 COSC 243 Instruction Sets And Addressing Modes 1 Overview This Lecture Source Chapters 12 & 13 (10 th editition) Textbook uses x86 and ARM (we use 6502) Next 2 Lectures Assembly language programming 2
COSC 243 Instruction Sets And Addressing Modes 1 Overview This Lecture Source Chapters 12 & 13 (10 th editition) Textbook uses x86 and ARM (we use 6502) Next 2 Lectures Assembly language programming 2
Chapter 7 Central Processor Unit (S08CPUV2)
 Chapter 7 Central Processor Unit (S08CPUV2) 7.1 Introduction This section provides summary information about the registers, addressing modes, and instruction set of the CPU of the HCS08 Family. For a more
Chapter 7 Central Processor Unit (S08CPUV2) 7.1 Introduction This section provides summary information about the registers, addressing modes, and instruction set of the CPU of the HCS08 Family. For a more
EC-801 Advanced Computer Architecture
 EC-801 Advanced Computer Architecture Lecture 5 Instruction Set Architecture I Dr Hashim Ali Fall 2018 Department of Computer Science and Engineering HITEC University Taxila!1 Instruction Set Architecture
EC-801 Advanced Computer Architecture Lecture 5 Instruction Set Architecture I Dr Hashim Ali Fall 2018 Department of Computer Science and Engineering HITEC University Taxila!1 Instruction Set Architecture
Architecture & Instruction set of 8085 Microprocessor and 8051 Micro Controller
 of 8085 microprocessor 8085 is pronounced as "eighty-eighty-five" microprocessor. It is an 8-bit microprocessor designed by Intel in 1977 using NMOS technology. It has the following configuration 8-bit
of 8085 microprocessor 8085 is pronounced as "eighty-eighty-five" microprocessor. It is an 8-bit microprocessor designed by Intel in 1977 using NMOS technology. It has the following configuration 8-bit
8051 Overview and Instruction Set
 8051 Overview and Instruction Set Curtis A. Nelson Engr 355 1 Microprocessors vs. Microcontrollers Microprocessors are single-chip CPUs used in microcomputers Microcontrollers and microprocessors are different
8051 Overview and Instruction Set Curtis A. Nelson Engr 355 1 Microprocessors vs. Microcontrollers Microprocessors are single-chip CPUs used in microcomputers Microcontrollers and microprocessors are different
 Chapter 1 Microprocessor architecture ECE 3120 Dr. Mohamed Mahmoud http://iweb.tntech.edu/mmahmoud/ mmahmoud@tntech.edu Outline 1.1 Computer hardware organization 1.1.1 Number System 1.1.2 Computer hardware
Chapter 1 Microprocessor architecture ECE 3120 Dr. Mohamed Mahmoud http://iweb.tntech.edu/mmahmoud/ mmahmoud@tntech.edu Outline 1.1 Computer hardware organization 1.1.1 Number System 1.1.2 Computer hardware
LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture
 CMPE12 Notes LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture (Textbookʼs Chapter 5 and 6)# Instruction Set Architecture# ISA is all of the programmer-visible components and operations of the computer.# memory organization#
CMPE12 Notes LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture (Textbookʼs Chapter 5 and 6)# Instruction Set Architecture# ISA is all of the programmer-visible components and operations of the computer.# memory organization#
LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture. Textbook Chapter 5
 LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture Textbook Chapter 5 Instruction set architecture What is an instruction set architecture (ISA)? It is all of the programmer-visible components and operations of the computer
LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture Textbook Chapter 5 Instruction set architecture What is an instruction set architecture (ISA)? It is all of the programmer-visible components and operations of the computer
We briefly explain an instruction cycle now, before proceeding with the details of addressing modes.
 Addressing Modes This is an important feature of computers. We start with the known fact that many instructions have to include addresses; the instructions should be short, but addresses tend to be long.
Addressing Modes This is an important feature of computers. We start with the known fact that many instructions have to include addresses; the instructions should be short, but addresses tend to be long.
THE MICROPROCESSOR Von Neumann s Architecture Model
 THE ICROPROCESSOR Von Neumann s Architecture odel Input/Output unit Provides instructions and data emory unit Stores both instructions and data Arithmetic and logic unit Processes everything Control unit
THE ICROPROCESSOR Von Neumann s Architecture odel Input/Output unit Provides instructions and data emory unit Stores both instructions and data Arithmetic and logic unit Processes everything Control unit
Chapter 4. MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer
 Chapter 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer Chapter 4 Objectives Learn the components common to every modern computer system. Be able to explain how each component contributes to program execution.
Chapter 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer Chapter 4 Objectives Learn the components common to every modern computer system. Be able to explain how each component contributes to program execution.
CHAPTER ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMMING
 CHAPTER 2 8051 ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMMING Registers Register are used to store information temporarily: A byte of data to be processed An address pointing to the data to be fetched The vast majority
CHAPTER 2 8051 ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMMING Registers Register are used to store information temporarily: A byte of data to be processed An address pointing to the data to be fetched The vast majority
Instruction Set. Instruction Sets Ch Instruction Representation. Machine Instruction. Instruction Set Design (5) Operation types
 Instruction Sets Ch 10-11 Characteristics Operands Operations Addressing Instruction Formats Instruction Set Collection of instructions that CPU understands Only interface to CPU from outside CPU executes
Instruction Sets Ch 10-11 Characteristics Operands Operations Addressing Instruction Formats Instruction Set Collection of instructions that CPU understands Only interface to CPU from outside CPU executes
Problem with Scanning an Infix Expression
 Operator Notation Consider the infix expression (X Y) + (W U), with parentheses added to make the evaluation order perfectly obvious. This is an arithmetic expression written in standard form, called infix
Operator Notation Consider the infix expression (X Y) + (W U), with parentheses added to make the evaluation order perfectly obvious. This is an arithmetic expression written in standard form, called infix
The Assembly Language of the Boz 5
 The Assembly Language of the Boz 5 The Boz 5 uses bits 31 27 of the IR as a five bit opcode. Of the possible 32 opcodes, only 26 are implemented. Op-Code Mnemonic Description 00000 HLT Halt the Computer
The Assembly Language of the Boz 5 The Boz 5 uses bits 31 27 of the IR as a five bit opcode. Of the possible 32 opcodes, only 26 are implemented. Op-Code Mnemonic Description 00000 HLT Halt the Computer
Microcontroller Intel [Instruction Set]
![Microcontroller Intel [Instruction Set] Microcontroller Intel [Instruction Set]](/thumbs/82/86620819.jpg) Microcontroller Intel 8051 [Instruction Set] Structure of Assembly Language [ label: ] mnemonic [operands] [ ;comment ] Example: MOV R1, #25H ; load data 25H into R1 2 8051 Assembly Language Registers
Microcontroller Intel 8051 [Instruction Set] Structure of Assembly Language [ label: ] mnemonic [operands] [ ;comment ] Example: MOV R1, #25H ; load data 25H into R1 2 8051 Assembly Language Registers
Computer Organization
 Computer Organization (Instruction set Architecture & Assembly Language Programming) KR Chowdhary Professor & Head Email: kr.chowdhary@gmail.com webpage: krchowdhary.com Department of Computer Science
Computer Organization (Instruction set Architecture & Assembly Language Programming) KR Chowdhary Professor & Head Email: kr.chowdhary@gmail.com webpage: krchowdhary.com Department of Computer Science
Central Processing Unit
 Central Processing Unit Networks and Embedded Software Module.. by Wolfgang Neff Components () lock diagram Execution Unit Control Unit Registers rithmetic logic unit DD, SU etc. NOT, ND etc. us Interface
Central Processing Unit Networks and Embedded Software Module.. by Wolfgang Neff Components () lock diagram Execution Unit Control Unit Registers rithmetic logic unit DD, SU etc. NOT, ND etc. us Interface
Computer System Architecture
 CSC 203 1.5 Computer System Architecture Department of Statistics and Computer Science University of Sri Jayewardenepura Addressing 2 Addressing Subject of specifying where the operands (addresses) are
CSC 203 1.5 Computer System Architecture Department of Statistics and Computer Science University of Sri Jayewardenepura Addressing 2 Addressing Subject of specifying where the operands (addresses) are
Instruction Set II. COMP 212 Computer Organization & Architecture. COMP 212 Fall Lecture 7. Instruction Set. Quiz. What is an Instruction Set?
 COMP 212 Computer Organization & Architecture Quiz COMP 212 Fall 2008 Lecture 7 Fill in your student number only, do NOT write down your name Open book, but NO calculator, NO discussions, Relax and have
COMP 212 Computer Organization & Architecture Quiz COMP 212 Fall 2008 Lecture 7 Fill in your student number only, do NOT write down your name Open book, but NO calculator, NO discussions, Relax and have
ECE 375 Computer Organization and Assembly Language Programming Winter 2018 Solution Set #2
 ECE 375 Computer Organization and Assembly Language Programming Winter 2018 Set #2 1- Consider the internal structure of the pseudo-cpu discussed in class augmented with a single-port register file (i.e.,
ECE 375 Computer Organization and Assembly Language Programming Winter 2018 Set #2 1- Consider the internal structure of the pseudo-cpu discussed in class augmented with a single-port register file (i.e.,
ELEG3924 Microprocessor
 Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG3924 Microprocessor Ch.3 Jump, Loop, and Call Dr. Jing Yang jingyang@uark.edu 1 OUTLINE Loop and Jump instructions Call instructions Time
Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG3924 Microprocessor Ch.3 Jump, Loop, and Call Dr. Jing Yang jingyang@uark.edu 1 OUTLINE Loop and Jump instructions Call instructions Time
Chapter 7 Subroutines. Richard P. Paul, SPARC Architecture, Assembly Language Programming, and C
 Chapter 7 Subroutines Richard P. Paul, SPARC Architecture, Assembly Language Programming, and C 2 Subroutines Subroutines allow us to either to repeat a computation or to repeat the computation with different
Chapter 7 Subroutines Richard P. Paul, SPARC Architecture, Assembly Language Programming, and C 2 Subroutines Subroutines allow us to either to repeat a computation or to repeat the computation with different
Accumulator and memory instructions 1. Loads, stores, and transfers 2. Arithmetic operations 3. Multiply and divide 4. Logical operations 5. Data test
 HC11 Instruction Set Instruction classes 1. 2. 3. 4. Accumulator and Memory Stack and Index Register Condition Code Register Program control instructions 2 1 Accumulator and memory instructions 1. Loads,
HC11 Instruction Set Instruction classes 1. 2. 3. 4. Accumulator and Memory Stack and Index Register Condition Code Register Program control instructions 2 1 Accumulator and memory instructions 1. Loads,
DR bit RISC Microcontroller. Instructions set details ver 3.10
 DR80390 8-bit RISC Microcontroller Instructions set details ver 3.10 DR80390 Instructions set details - 2 - Contents 1. Overview 7 1.1. Document structure. 7 2. Instructions set brief 7 2.1. Instruction
DR80390 8-bit RISC Microcontroller Instructions set details ver 3.10 DR80390 Instructions set details - 2 - Contents 1. Overview 7 1.1. Document structure. 7 2. Instructions set brief 7 2.1. Instruction
(2) Explain the addressing mode of OR What do you mean by addressing mode? Explain diff. addressing mode for 8085 with examples.
 (1) Explain instruction format and Opcode format of 8085 μp with example. OR With help of examples, explain the formation of opcodes of 8085 OR What is an instruction? List type of instruction based on
(1) Explain instruction format and Opcode format of 8085 μp with example. OR With help of examples, explain the formation of opcodes of 8085 OR What is an instruction? List type of instruction based on
Microprocessors 1. The 8051 Instruction Set. Microprocessors 1 1. Msc. Ivan A. Escobar Broitman
 Microprocessors 1 The 8051 Instruction Set Microprocessors 1 1 Instruction Groups The 8051 has 255 instructions Every 8-bit opcode from 00 to FF is used except for A5. The instructions are grouped into
Microprocessors 1 The 8051 Instruction Set Microprocessors 1 1 Instruction Groups The 8051 has 255 instructions Every 8-bit opcode from 00 to FF is used except for A5. The instructions are grouped into
VARDHAMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS) Shamshabad, Hyderabad
 Introduction to MS-DOS Debugger DEBUG In this laboratory, we will use DEBUG program and learn how to: 1. Examine and modify the contents of the 8086 s internal registers, and dedicated parts of the memory
Introduction to MS-DOS Debugger DEBUG In this laboratory, we will use DEBUG program and learn how to: 1. Examine and modify the contents of the 8086 s internal registers, and dedicated parts of the memory
Advanced Parallel Architecture Lesson 3. Annalisa Massini /2015
 Advanced Parallel Architecture Lesson 3 Annalisa Massini - 2014/2015 Von Neumann Architecture 2 Summary of the traditional computer architecture: Von Neumann architecture http://williamstallings.com/coa/coa7e.html
Advanced Parallel Architecture Lesson 3 Annalisa Massini - 2014/2015 Von Neumann Architecture 2 Summary of the traditional computer architecture: Von Neumann architecture http://williamstallings.com/coa/coa7e.html
Chapter 5. Computer Architecture Organization and Design. Computer System Architecture Database Lab, SANGJI University
 Chapter 5. Computer Architecture Organization and Design Computer System Architecture Database Lab, SANGJI University Computer Architecture Organization and Design Instruction Codes Computer Registers
Chapter 5. Computer Architecture Organization and Design Computer System Architecture Database Lab, SANGJI University Computer Architecture Organization and Design Instruction Codes Computer Registers
Lecture 11: Control Unit and Instruction Encoding
 CSCI25 Computer Organization Lecture : Control Unit and Instruction Encoding Ming-Chang YANG mcyang@cse.cuhk.edu.hk Reading: Chap. 7.4~7.5 (5 th Ed.) Recall: Components of a Processor Register file: a
CSCI25 Computer Organization Lecture : Control Unit and Instruction Encoding Ming-Chang YANG mcyang@cse.cuhk.edu.hk Reading: Chap. 7.4~7.5 (5 th Ed.) Recall: Components of a Processor Register file: a
 Instruction Set Instruction set of 8085 can be classified in following groups: Data Transfer Instructions These instructions can perform data transfer operations between Registers of 8085 e.g. MOV 8085
Instruction Set Instruction set of 8085 can be classified in following groups: Data Transfer Instructions These instructions can perform data transfer operations between Registers of 8085 e.g. MOV 8085
General Purpose Processors
 Calcolatori Elettronici e Sistemi Operativi Specifications Device that executes a program General Purpose Processors Program list of instructions Instructions are stored in an external memory Stored program
Calcolatori Elettronici e Sistemi Operativi Specifications Device that executes a program General Purpose Processors Program list of instructions Instructions are stored in an external memory Stored program
INSTRUCTION SET ARCHITECTURE
 INSTRUCTION SET ARCHITECTURE Slides by: Pedro Tomás Additional reading: Computer Architecture: A Quantitative Approach, 5th edition, Appendix A, John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Morgan Kaufmann,
INSTRUCTION SET ARCHITECTURE Slides by: Pedro Tomás Additional reading: Computer Architecture: A Quantitative Approach, 5th edition, Appendix A, John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Morgan Kaufmann,
Programming. A. Assembly Language Programming. A.1 Machine Code. Machine Code Example: Motorola ADD
 A. Assembly Language Programming Programming of a computer system: Machine code direct execution Assembly language tool: assembler High level programming language tool: interpreter tool: compiler Programming
A. Assembly Language Programming Programming of a computer system: Machine code direct execution Assembly language tool: assembler High level programming language tool: interpreter tool: compiler Programming
8051 Microcontrollers
 8051 Microcontrollers Richa Upadhyay Prabhu NMIMS s MPSTME richa.upadhyay@nmims.edu March 15, 2016 8051 INSTRUCTIONS JUMP, LOOP AND CALL INSTRUCTIONS 8051 INSTRUCTIONS Repeating a sequence of instructions
8051 Microcontrollers Richa Upadhyay Prabhu NMIMS s MPSTME richa.upadhyay@nmims.edu March 15, 2016 8051 INSTRUCTIONS JUMP, LOOP AND CALL INSTRUCTIONS 8051 INSTRUCTIONS Repeating a sequence of instructions
COMP2121: Microprocessors and Interfacing. Instruction Set Architecture (ISA)
 COMP2121: Microprocessors and Interfacing Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs2121 Lecturer: Hui Wu Session 2, 2017 1 Contents Memory models Registers Data types Instructions
COMP2121: Microprocessors and Interfacing Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs2121 Lecturer: Hui Wu Session 2, 2017 1 Contents Memory models Registers Data types Instructions
ARM Cortex A9. ARM Cortex A9
 ARM Cortex A9 Four dedicated registers are used for special purposes. The IP register works around the limitations of the ARM functional call instruction (BL) which cannot fully address all of its 2 32
ARM Cortex A9 Four dedicated registers are used for special purposes. The IP register works around the limitations of the ARM functional call instruction (BL) which cannot fully address all of its 2 32
9/25/ Software & Hardware Architecture
 8086 Software & Hardware Architecture 1 INTRODUCTION It is a multipurpose programmable clock drive register based integrated electronic device, that reads binary instructions from a storage device called
8086 Software & Hardware Architecture 1 INTRODUCTION It is a multipurpose programmable clock drive register based integrated electronic device, that reads binary instructions from a storage device called
CN310 Microprocessor Systems Design
 CN310 Microprocessor Systems Design Micro Architecture Nawin Somyat Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Thammasat University 28 August 2018 Outline Course Contents 1 Introduction 2 Simple
CN310 Microprocessor Systems Design Micro Architecture Nawin Somyat Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Thammasat University 28 August 2018 Outline Course Contents 1 Introduction 2 Simple
Introduction to Computer. Chapter 5 The LC-3. Instruction Set Architecture
 Introduction to Computer Engineering ECE/CS 252, Fall 2010 Prof. Mikko Lipasti Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 5 The LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture
Introduction to Computer Engineering ECE/CS 252, Fall 2010 Prof. Mikko Lipasti Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 5 The LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture
SISTEMI EMBEDDED. Computer Organization Central Processing Unit (CPU) Federico Baronti Last version:
 SISTEMI EMBEDDED Computer Organization Central Processing Unit (CPU) Federico Baronti Last version: 20170516 Processing Unit A processor reads program instructions from the computer s memory and executes
SISTEMI EMBEDDED Computer Organization Central Processing Unit (CPU) Federico Baronti Last version: 20170516 Processing Unit A processor reads program instructions from the computer s memory and executes
Chapter 17. Microprogrammed Control. Yonsei University
 Chapter 17 Microprogrammed Control Contents Basic Concepts Microinstruction Sequencing Microinstruction Execution TI 8800 Applications of Microprogramming 17-2 Introduction Basic Concepts An alternative
Chapter 17 Microprogrammed Control Contents Basic Concepts Microinstruction Sequencing Microinstruction Execution TI 8800 Applications of Microprogramming 17-2 Introduction Basic Concepts An alternative
CPE300: Digital System Architecture and Design
 CPE300: Digital System Architecture and Design Fall 2011 MW 17:30-18:45 CBC C316 Arithmetic Unit 10032011 http://www.egr.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe300/ 2 Outline Recap Chapter 3 Number Systems Fixed Point
CPE300: Digital System Architecture and Design Fall 2011 MW 17:30-18:45 CBC C316 Arithmetic Unit 10032011 http://www.egr.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe300/ 2 Outline Recap Chapter 3 Number Systems Fixed Point
ELEG3923 Microprocessor Ch.3 Jump, Loop, and Call
 Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG3923 Microprocessor Ch.3 Jump, Loop, and Call Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Loop and Jump instructions Call instructions Time delay
Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG3923 Microprocessor Ch.3 Jump, Loop, and Call Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Loop and Jump instructions Call instructions Time delay
The CPU and Memory. How does a computer work? How does a computer interact with data? How are instructions performed? Recall schematic diagram:
 The CPU and Memory How does a computer work? How does a computer interact with data? How are instructions performed? Recall schematic diagram: 1 Registers A register is a permanent storage location within
The CPU and Memory How does a computer work? How does a computer interact with data? How are instructions performed? Recall schematic diagram: 1 Registers A register is a permanent storage location within
CPU Design John D. Carpinelli, All Rights Reserved 1
 CPU Design 1997 John D. Carpinelli, All Rights Reserved 1 Outline Register organization ALU design Stacks Instruction formats and types Addressing modes 1997 John D. Carpinelli, All Rights Reserved 2 We
CPU Design 1997 John D. Carpinelli, All Rights Reserved 1 Outline Register organization ALU design Stacks Instruction formats and types Addressing modes 1997 John D. Carpinelli, All Rights Reserved 2 We
CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture
 CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Warren Hunt, Jr. and Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Last updated: October 1, 2014 at 12:03 CS429 Slideset 6: 1 Topics
CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Warren Hunt, Jr. and Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Last updated: October 1, 2014 at 12:03 CS429 Slideset 6: 1 Topics
Practical Malware Analysis
 Practical Malware Analysis Ch 4: A Crash Course in x86 Disassembly Revised 1-16-7 Basic Techniques Basic static analysis Looks at malware from the outside Basic dynamic analysis Only shows you how the
Practical Malware Analysis Ch 4: A Crash Course in x86 Disassembly Revised 1-16-7 Basic Techniques Basic static analysis Looks at malware from the outside Basic dynamic analysis Only shows you how the
INSTRUCTION SET OF 8085
 INSTRUCTION SET OF 8085 Instruction Set of 8085 An instruction is a binary pattern designed inside a microprocessor to perform a specific function. The entire group of instructions that a microprocessor
INSTRUCTION SET OF 8085 Instruction Set of 8085 An instruction is a binary pattern designed inside a microprocessor to perform a specific function. The entire group of instructions that a microprocessor
Lecture 4: Instruction Set Architecture
 Lecture 4: Instruction Set Architecture ISA types, register usage, memory addressing, endian and alignment, quantitative evaluation Reading: Textbook (5 th edition) Appendix A Appendix B (4 th edition)
Lecture 4: Instruction Set Architecture ISA types, register usage, memory addressing, endian and alignment, quantitative evaluation Reading: Textbook (5 th edition) Appendix A Appendix B (4 th edition)
8085 INSTRUCTION SET INSTRUCTION DETAILS
 8085 INSTRUCTION SET INSTRUCTION DETAILS DATA TRANSFER INSTRUCTIONS MOV Rd, Rs Copy from source to destination This instruction copies the contents of the source register Rs into the destination register
8085 INSTRUCTION SET INSTRUCTION DETAILS DATA TRANSFER INSTRUCTIONS MOV Rd, Rs Copy from source to destination This instruction copies the contents of the source register Rs into the destination register
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies Unit - 1
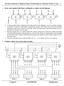 Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies Unit - 1 1. Draw and explain 4 bit binary arithmetic or adder circuit diagram. A binary parallel adder is digital function that produces
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies Unit - 1 1. Draw and explain 4 bit binary arithmetic or adder circuit diagram. A binary parallel adder is digital function that produces
Page 1. Structure of von Nuemann machine. Instruction Set - the type of Instructions
 Structure of von Nuemann machine Arithmetic and Logic Unit Input Output Equipment Main Memory Program Control Unit 1 1 Instruction Set - the type of Instructions Arithmetic + Logical (ADD, SUB, MULT, DIV,
Structure of von Nuemann machine Arithmetic and Logic Unit Input Output Equipment Main Memory Program Control Unit 1 1 Instruction Set - the type of Instructions Arithmetic + Logical (ADD, SUB, MULT, DIV,
Disassembly of MC9S12 op codes Decimal, Hexadecimal and Binary Numbers
 Disassembly of MC9S12 op codes Decimal, Hexadecimal and Binary Numbers o How to disassemble an MC9S12 instruction sequence o Binary numbers are a code and represent what the programmer intends for the
Disassembly of MC9S12 op codes Decimal, Hexadecimal and Binary Numbers o How to disassemble an MC9S12 instruction sequence o Binary numbers are a code and represent what the programmer intends for the
Disassembly of MC9S12 op codes Decimal, Hexadecimal and Binary Numbers
 Disassembly of MC9S12 op codes Decimal, Hexadecimal and Binary Numbers o How to disassemble an MC9S12 instruction sequence o Binary numbers are a code and represent what the programmer intends for the
Disassembly of MC9S12 op codes Decimal, Hexadecimal and Binary Numbers o How to disassemble an MC9S12 instruction sequence o Binary numbers are a code and represent what the programmer intends for the
