Positioning Lesion from Breast MRI and Mammogram using Registration Method
|
|
|
- Morgan Wells
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Positioning Lesion from Breast MRI and Mammogram using Registration Method Rugma M. *, Malu G., C. Gopakumar, Elizabeth Sherly * PG Scholar, Dept. of CE, College of Engineering, Chengannur. Alapuzha, India Research Scholar, IIITM-K, Technopark, Trivandrum, India Associate Professor, Dept. of ECE, College of Engineering, Karunagappally. Kollam, India Professor, IIITM-K, Techopark, Trivandrum, India Abstract The mammogram and MRI used for detection of cancerous cells in breast, requires overlaying the approach to get the best out of two or a combined effort. However, the varying intensity of breast in both modalities make the automatic segmentation of such lesions extremely challenging as both the modalities are different. This paper presents a new approach for automatic registration of mammograms and MR images. The registration of images taken from MRI and mammography is carried out to locate the position of lesion present in breast followed by noise removal, edge enhancement and morphological operations. The chest wall removal is done to extract the breast area, for obtaining the mass area and micro-calcifications to locate its position. The locations of lesions in both images are extracted out using region growing algorithm and thresholding method. Registering the images provide the most accurate location of masses and micro-calcification that is missed in any of the modalities, into single image. The results show that the method gives fast and accurate registration that can be effectively used for detecting masses and micro-calcifications with high level of accuracy. The accuracy obtained in the proposed method is about 87%. Keywords image pre-processing, chest wall removal, nipple localization, segmentation, registration. I. INTRODUCTION Breast cancer continues to be a significant public health problem in the world. Early detection is the better method for improving breast cancer prognosis. Various researches were carried out for the automatic detection of breast cancer independently, but work on combining both MRI and mammogram is very less. In this paper we propose a technique for locating the cancerous lesions present in breast from multimodality images such as: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and mammogram images using image registration [1]. The goal is to attain the accurate position of breast lesion by combining both the multi-modal images. The processes involved are image pre-processing, chest wall removal, nipple localization, segmentation and registration. The proposed technique has the potential to support clinical diagnosis, which helps medical practitioner in correctly identifying the position of breast lesion. Mammography is currently the primary method of early detection. But recent research has shown that many cases missed by mammography can be detected in Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). In proposed system, the Medio- Lateral Oblique (MLO) view of (X-ray) mammograms [2] is considered for registering with the MR images. Since, the mammogram images considered for registration is oblique i.e., MLO mammograms, the MR slices for the proposed system should be of side to side lengthwise (sagitall) images. These images are comparable and used in registration to locate the breast lesion. MRI provides good tissue specificity via Gadolinium Diethylene Triamine Penta-Acetic Acid (Gd- DTPA) of contrast enhancement, whilst mammography has spatial resolution and image formation capable of providing information about curvilinear structures, tumour spiculation and micro calcifications. The objective of this paper is to register the MLO mammograms to equivalent projections of a contrast enhanced MR slices to enable feature correspondence to be made between modalities. Here, the MR images are obtained from Signa Hdxt Magnetic Resonance Scanner and the mammograms are obtained from selenia dimensions. The image that is obtained through diagnosis is in DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) format which is three dimensional images. The MLO images considered consist of chest wall which is comparable with the chest walls in MR images. The chest wall removal plays an important part in lesion localization. Otherwise, the presence of nodes at the walls of the breast gives a false identification of lesion making segmentation more complex. Registering both the images provides high quality resolution images and the details lost in either of the image during diagnosis can be retained. The overall organization of the paper is as described below. The general problem in finding the breast lesion from a single image is mentioned in section II. Section III describes the proposed methodology for registration and in each subsection it has been explained in details. Section IV demonstrates some simulation results and their performance evaluation. Finally conclusions are presented in section V which also narrates the advantages of the proposed registration technique. II. PROBLEM FORMULATION Mammography [8] is the most popular and cost effective image diagnosis for breast cancer detection. However, it is not 1365
2 possible to record all types of lesion using mammogram alone. Sometimes the physician has to rely on some other imaging techniques along with mammography for better identification of lesion. Mammography is good in micro calcification and tumor specifications, but tissues with hard nature are not prominent in it. In such cases, MRI is preferred due to its noninvasive nature and tissue specificity. Though, MRI is bit expensive, it provides good details on masses missed by mammography. In the case of large amount of data, relaying on both images for lesion prediction is not appropriate for operator assisted method. In such cases, a co-registration process to combine both the images provides much easiness, but is challenging mainly because of the multimodality of two images. Here an attempt is made to construct co-registration of two multimodality images to extract more information, so that diagnosis will be more accurate and easy. In previous work, most of the authors considered the carnio caudal (CC) view of mammogram for registration with MRI. The CC mammogram gives an ellipsoidal shape to compare it with the MR images. But the complete breast capturing in such images is still a daunting problem. The patients with low breast volume will only be able to produce the complete structure of breast during mammography, while patients with high breast volume fails doing so. As a result, registering such images becomes tedious and there is a high chance for missing relevant information. To overcome this situation, the MLO mammograms [2] are considered for registration with MR images. The presence of chest wall in MLO images indicates complete capture of breast during mammography. Since, the MLO views of mammogram and sagitall images of MR are comparable; these views can be used for registration activity. The chest wall removal in proposed method helps to improve the flawless working of the system. III. PROPOSED METHOD The proposed system aims to develop an efficient method to register the multi-modal images for detecting the masses and micro-calcifications present in breast. The system is designed as five stage process as which is evolved from the existing system [7]. In the first stage, the input image is preprocessed to get more accurate feature points. During the second stage, the chest walls of MR and MLO images are detected to remove the pectoral muscles. The above image is considered as third stage for nipple localization by finding out the minimal object distance from the coordinate system with the help of boundaries obtained from boundary tracing. The fourth stage is the detection of masses and micro-calcifications from MRI and Mammogram using image segmentation through region growing and thresholding. The last stage is the registration where the images are registered to get the most detailed image to obtain the accurate location of masses and microcalcifications into single image. These stages are pictorially represented using block diagram shown in Fig. 1. Fig. 1. Block diagram of the proposed system A. Pre-processing Method The input images (Fig. 2) MRI and MLO mammograms are subjected to several processing methods before it is used for registration activity. The image pre-processing step [3] helps to increase the robustness of the system under varying conditions. Initially, the images are converted into gray scale images and resized into a specific size, 512x512. This helps to reduce computational complexity of the system. Fig. 2. The Input images (MRI and MLO mammogram) The MR images and MLO mammograms undergo filtering to remove the noise present in the image. Since the medical images contain black and white noise, the most 1366
3 efficient filtering used in MRI is median filter and in mammogram bilateral filtering is more suited to remove the noise. During noise removal some details in the image is lost; to reproduce that information without noise, edge enhancement method is applied. For this, Gaussian filtering and intensity adjustments are used. To obtain smooth surfaces, morphological operation [3] is performed. These techniques help to improve the detection accuracy of the breast from boundary. is used for registration activity. The pectoral muscle removal in mammogram and MR images is illustrated in figures 2 and 3. B. Chest wall Removal and Nipple Localization The pectoral muscle region [4] (in MLO mammograms) has a predominantly high density that may interfere with the analysis of mammograms. The prior detection and removal of this region could lead to improved results in lesion localization. The high density of the pectoral muscle results in strong edge separating breast area from chest wall. This strong edge can be approximated by a straight line. The region other than the breast area is removed to obtain the breast region alone. The pectoral muscle removal steps are as follows: 1. Object Extraction Object extraction is used to extract the object (breast with chest wall) part from background for its use in pectoral muscle removal. In MR images, the object extraction is done through binary thresholding. Thresholding results in extraction of object area from the background. In MLO mammograms, gradient edge detection method is applied. These binary conversions will help in extracting the object area devoid of background. 2. Boundary Tracing Boundary Tracing is performed to find out the boundary points of breast region in both images. From previous step, breast is extracted in the form of binary image and is ready for boundary tracing. Boundary tracing algorithm is used for drawing the boundary along edges of breast region. The boundary tracing begins from start point of the object boundary and traverse through edges of object by drawing curve. The obtained boundary points are used for drawing line segments. 3. Pectoral Muscle Removal The pectoral muscles should be deleted from the breast image to avoid complexity in lesion identification. The node present in chest wall appears as lesion and they have similar intensity as that of cancerous lesion. The pectoral muscles in MR images and MLO are removed with the help of line segments drawn from boundary points. The boundary points obtained from boundary tracing is used for constructing line segments. The longest line segment that passes the boundary points is considered as the edge that separates pectoral muscles from breast area. The lift image toolbox provided by Matlab is used in MLO mammograms to remove the chest wall from the object. Lift image toolbox is useful in the case of irregular shapes with any number of edge points. Similarly, the breast area is obtained and Fig. 2. Pectoral muscle removal in mammogram: (a) plotting of line segments, (b) pectoral muscle detected and (c) chest wall removed. Fig. 3. Pectoral muscle removal in MR images: (a) plotting of line segments, (b) pectoral muscle detected and (c) chest wall removed. 4. Nipple Localization In order to locate nipple position during registration, matching control point selection is the first step to be made. For this, some standard points be selected in which nipple location is the one among them. The boundary point with the least displacement from coordinating axis is generally considered as nipple. It is followed that the object is always aligned to the 1367
4 right of the image when locating nipple position. The lesion position is localized in terms of clock face position. The location of masses and micro-calcifications can be described by dividing the breast into four quadrants: the upper outer quadrant (UOQ), the upper inner quadrant (UIQ), the lower outer quadrant (LOQ) and the lower inner quadrant (LIQ). Each quadrant is further subdivided to locate the position of masses and micro-calcification using clock face model. C. Lesion Localization To identify the exact location of masses and microcalcifications from MR images and MLO mammograms can easily be made when considered separately. To include both the information on a single image can be achieved only through registration method. The breast extracted image obtained from previous step provides highly detailed image carrying the information on masses present in MRI and micro-calcifications in MLO mammograms. The identified masses in MRI are segmented out using the region growing method and the micro-calcifications are identified using thresholding. Their location in breast can be calculated from clock face model. The positions of micro-calcifications in MLO mammogram are obtained from MLO and CC images together. The MLO view gives the information on upper or lower part of breast and the CC view provides the inner or outer region of breast where microcalcifications are found. Including both the information the clock position of masses and micro-calcification can be obtained (Fig. 4). The concept of registration is pictorially represented below (Fig. 5). Initially, matching control points are picked from MRI and MLO mammograms to align them in position. The control points in MRI slices are taken from multiple slices as the MRI slice containing nipple may not possess details of masses present. The visibility of masses in breast may depend upon the depth of occurrences. Also the MRI slice that is taken from inner breast region having masses may not contain the nipple position visible. In such cases, more than one slice is used for locating the control points. These points are marked in the image slice having masses are used for registration with MLO images. The registration overlaps the MRI and MLO images by applying some spatial transformations. The different types of transformations used are projective, affine, etc. Some resampling methods are done to align the images during registration time and the resulting image gives better information on features in registered image. The registration algorithm for the proposed system is explained as: 1. Consider input image I(x,y) and base image B(x,y) 2. Use cpselect to select matching control points (CP) 3. Pass CP to infer spatial transformation 4. Apply spatial transform and register it with B(x,y) Fig. 4. The micro-calcifications are found to the right lower inner quadrant (LOQ) around 4 o clock position and to the left upper inner quadrant (UIQ) around 10 o clock position. D. Registration Image registration [5][6] is the process of overlaying two or more images of the same object taken at different times, from two modalities. It geometrically aligns two images the base (MRI) and input (MLO mammogram) images. In proposed system, the medical images of breast taken from different imaging techniques are considered for registration activity. Selection of control points is the key factor in image registration. The control points used in the proposed model are the nipple position and the end points of the breast line. These points are automatically located from MRI slices and MLO images for its use in registration activity. Fig. 5. Registration steps 1368
5 IV. RESULT AND DISCUSSION The data is collected from Regional Cancer Centre (RCC), Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, India. The dataset composed of MRI and Mammogram images (MLO) of different patients. The MRI dataset consists of more than 728 slices from a single patient at different time interval: containing masses as well as lesion free slices. The number of slices containing lesion vary for different patients with different type of lesion present. The mammogram dataset consists of 6 images from a single patient. The image resolution of MRI is 512x512x3 and the size of the MR image is 116 kb. The mammogram (MLO) image resolution is and the size varies from 226kB to 3.32 MB. The size and resolution can vary for different patients. The MR images and MLO mammograms undergo preprocessing steps such as: Gaussian filtering, edge enhancement and morphological operations, to obtain noise free edge enhanced smoothened image. After pre-processing, the chest wall removal and nipple localization is performed using gradient method and boundary tracing method. This preprocessed set is used for enhancing the quality of MRI and mammogram images. The registration method helps to localize the masses and micro-calcification into single breast image. The position of masses and micro-calcifications in breast is identified using clock face model. The proposed technique is implemented in the working platform MATLAB 2010 and it is evaluated using 10 cases having breast cancer as testing set. Among the 10 patient profiles, 7 profiles contain lesion, 2 are falsely missed lesion and 1 containing no lesion. The precision is obtained a value of 87.5%, i.e. it shows the correctness of the system in detecting the lesion from breast image. The recall is obtained as 77.8%, i.e. it denotes the probability that a lesion is detected and the F1 score is obtained as % i.e. combines both precision n recall values. Fig. 7. Nipple localization Fig. 8. Lesion segmented from MRI and micro- Mammogram calcifications from Fig. 9. Registered Image Fig. 6. Chest Wall Removal (a) MRI boundary with pectoral muscle detection, (b) chest wall removes MR image, (c) MLO boundary with pectoral muscle detection and (d) Chest wall removed MLO image. Fig. 10. Lesion localization in registered image 1369
6 The results of lesion position detection using registration are shown in figures 6 to 10. All processing methods can have an error rate and in some occasion it may either fail to identify the lesion present or falsely identify the lesion that is not present. It is common to describe this error rate by the terms true and false positive and true and false negative. The registration works for images from clinical routine helps the experts in identifying the position of masses and micro-calcification. The accuracy in locating their position in breast shows promising results even when the clinical variability of datasets is large. The obtained results are in the same range as the accuracies achieved in literature though in this work fully automated approach was used. This method is able to register images from different modalities with MLO mammogram. The registration does not take gravity into account. This is motivated from other literatures reporting insignificant influence of gravity in diagnoses. Lesion positions were not used as landmarks for registration. The patient profile set included a large variety of lesions, either in size, location or contrast enhancement. Image similarity based optimization seems not to be influenced by the nature of the lesion. This leads to the conclusion that registration approach in the proposed system does not strongly depend on the type of lesion and the visibility of lesion. The nipple position and the points near the breast and the chest walls are used as standard points for registration. V. CONCLUSION In this paper, an automatic method for positioning masses, micro-calcifications in MRI and MLO mammograms using registration method is proposed. This approach helps in localizing the position of masses and micro-calcifications in breast from a large number of clinical datasets. The MLO view of Mammogram and the MR images are used for locating the masses and micro-calcification present with the help of registration activity. In the proposed system, the test images undergone Gaussian filtering, edge enhancement and morphological operation resulted in enhanced data images for computational operations. The chest wall removal and nipple localization is successfully achieved through boundary tracing method. The different test data are correctly overlapped in one coordinate system through registration activity. The registered images provide information as a combination of details obtained from MRI and MLO mammograms. The position of masses in MRI and micro-calcification in MLO mammograms are included in a registered image helps medical practitioners to examine the details to provide better treatment to the patients. REFERENCES [1] Nicole V. Ruiter, Rainer Stotzka, Tim-Oliver Müller, Hartmut Gemmeke, Jürgen R. Reichenbach, and Werner A. Kaiser, Model- Based Registration of X-Ray Mammograms and MR Images of the Female Breast,IEEE Transaction on Nuclear Science, Vol. 53, No. 1, [2] C. P. Behrenbruch, M. Yam, M. Brady, and R. E. English, The use of magnetic resonance imaging to model breast compression in X-ray mammography for MR/X-ray data fusion, in 5th Proc. Int. Works. Digital Mammography, Toronto, Canada, pp , [3] T. Hoppa, M. Dietzelb, P. A. Baltzerc, P. Kreiseld,W. A. Kaiserd, H.Gemmekea, N. V. Ruiter, Automatic Multimodal 2D/3D Breast Image Registration using Biomechanical FEM Models and Intensity- Based Optimization, Medical Image Analysis, vol.17, pp , 2013 [4] S. K. Kinoshita, P. M. Azevedo-Marques, R. R. Pereira Jr, J. A. H. Rodrigues, and R. M.Rangayyan, Radon-Domain Detection of the Nipple and the Pectoral Muscle in Mammograms, Journal of Digital Imaging, Vol 21, No. 1 (March), [5] Barbara Zitova, Jan Flusser, Image registration methods: a survey, Image and Vision Computing, Vol. 21, issue 11, pp , [6] Tran Duy Linh, Huynh Quang Linh, Department of Biomedical Engineering Faculty of Applied Science HCMC University of Technology, Vietnam, Medical Image Registration In Matlab. [7] Torsten Hopp, Pascal Baltzer, Matthias Dietzel, Werner A. Kaiser, Nicole V. Ruiter, 2D/3D Image Fusion of X-ray Mammograms with Breast MRI: Visualizing Dynamic Contrast Enhancement in Mammograms, International journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, Vol. 7, issue 3, pp , [8] [Online]. Available:
TUMOR DETECTION IN MRI IMAGES
 TUMOR DETECTION IN MRI IMAGES Prof. Pravin P. Adivarekar, 2 Priyanka P. Khatate, 3 Punam N. Pawar Prof. Pravin P. Adivarekar, 2 Priyanka P. Khatate, 3 Punam N. Pawar Asst. Professor, 2,3 BE Student,,2,3
TUMOR DETECTION IN MRI IMAGES Prof. Pravin P. Adivarekar, 2 Priyanka P. Khatate, 3 Punam N. Pawar Prof. Pravin P. Adivarekar, 2 Priyanka P. Khatate, 3 Punam N. Pawar Asst. Professor, 2,3 BE Student,,2,3
3D Surface Reconstruction of the Brain based on Level Set Method
 3D Surface Reconstruction of the Brain based on Level Set Method Shijun Tang, Bill P. Buckles, and Kamesh Namuduri Department of Computer Science & Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering University
3D Surface Reconstruction of the Brain based on Level Set Method Shijun Tang, Bill P. Buckles, and Kamesh Namuduri Department of Computer Science & Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering University
CHAPTER 6 DETECTION OF MASS USING NOVEL SEGMENTATION, GLCM AND NEURAL NETWORKS
 130 CHAPTER 6 DETECTION OF MASS USING NOVEL SEGMENTATION, GLCM AND NEURAL NETWORKS A mass is defined as a space-occupying lesion seen in more than one projection and it is described by its shapes and margin
130 CHAPTER 6 DETECTION OF MASS USING NOVEL SEGMENTATION, GLCM AND NEURAL NETWORKS A mass is defined as a space-occupying lesion seen in more than one projection and it is described by its shapes and margin
Available Online through
 Available Online through www.ijptonline.com ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Research Article ANALYSIS OF CT LIVER IMAGES FOR TUMOUR DIAGNOSIS BASED ON CLUSTERING TECHNIQUE AND TEXTURE FEATURES M.Krithika
Available Online through www.ijptonline.com ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Research Article ANALYSIS OF CT LIVER IMAGES FOR TUMOUR DIAGNOSIS BASED ON CLUSTERING TECHNIQUE AND TEXTURE FEATURES M.Krithika
Hybrid Approach for MRI Human Head Scans Classification using HTT based SFTA Texture Feature Extraction Technique
 Volume 118 No. 17 2018, 691-701 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Hybrid Approach for MRI Human Head Scans Classification using HTT
Volume 118 No. 17 2018, 691-701 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Hybrid Approach for MRI Human Head Scans Classification using HTT
MIXTURE MODELING FOR DIGITAL MAMMOGRAM DISPLAY AND ANALYSIS 1
 MIXTURE MODELING FOR DIGITAL MAMMOGRAM DISPLAY AND ANALYSIS 1 Stephen R. Aylward, Bradley M. Hemminger, and Etta D. Pisano Department of Radiology Medical Image Display and Analysis Group University of
MIXTURE MODELING FOR DIGITAL MAMMOGRAM DISPLAY AND ANALYSIS 1 Stephen R. Aylward, Bradley M. Hemminger, and Etta D. Pisano Department of Radiology Medical Image Display and Analysis Group University of
Tumor Detection and classification of Medical MRI UsingAdvance ROIPropANN Algorithm
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Advanced Technology (IJERAT) DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.31695/IJERAT.2018.3273 E-ISSN : 2454-6135 Volume.4, Issue 6 June -2018 Tumor Detection and classification
International Journal of Engineering Research and Advanced Technology (IJERAT) DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.31695/IJERAT.2018.3273 E-ISSN : 2454-6135 Volume.4, Issue 6 June -2018 Tumor Detection and classification
Mammogram Segmentation using Region based Method with Split and Merge Technique
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 9(40), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i40/99589, October 2016 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Mammogram Segmentation using Region based Method
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 9(40), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i40/99589, October 2016 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Mammogram Segmentation using Region based Method
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Proc Soc Photo Opt Instrum Eng. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2014 October 07.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Proc Soc Photo Opt Instrum Eng. 2014 March 21; 9034: 903442. doi:10.1117/12.2042915. MRI Brain Tumor Segmentation and Necrosis Detection
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Proc Soc Photo Opt Instrum Eng. 2014 March 21; 9034: 903442. doi:10.1117/12.2042915. MRI Brain Tumor Segmentation and Necrosis Detection
Automated segmentation methods for liver analysis in oncology applications
 University of Szeged Department of Image Processing and Computer Graphics Automated segmentation methods for liver analysis in oncology applications Ph. D. Thesis László Ruskó Thesis Advisor Dr. Antal
University of Szeged Department of Image Processing and Computer Graphics Automated segmentation methods for liver analysis in oncology applications Ph. D. Thesis László Ruskó Thesis Advisor Dr. Antal
Hybrid Spline-based Multimodal Registration using a Local Measure for Mutual Information
 Hybrid Spline-based Multimodal Registration using a Local Measure for Mutual Information Andreas Biesdorf 1, Stefan Wörz 1, Hans-Jürgen Kaiser 2, Karl Rohr 1 1 University of Heidelberg, BIOQUANT, IPMB,
Hybrid Spline-based Multimodal Registration using a Local Measure for Mutual Information Andreas Biesdorf 1, Stefan Wörz 1, Hans-Jürgen Kaiser 2, Karl Rohr 1 1 University of Heidelberg, BIOQUANT, IPMB,
Predicting Tumour Location by Simulating Large Deformations of the Breast using a 3D Finite Element Model and Nonlinear Elasticity
 Predicting Tumour Location by Simulating Large Deformations of the Breast using a 3D Finite Element Model and Nonlinear Elasticity P. Pathmanathan 1 D. Gavaghan 1 J. Whiteley 1 M. Brady 2 M. Nash 3 P.
Predicting Tumour Location by Simulating Large Deformations of the Breast using a 3D Finite Element Model and Nonlinear Elasticity P. Pathmanathan 1 D. Gavaghan 1 J. Whiteley 1 M. Brady 2 M. Nash 3 P.
Introduction to Medical Image Processing
 Introduction to Medical Image Processing Δ Essential environments of a medical imaging system Subject Image Analysis Energy Imaging System Images Image Processing Feature Images Image processing may be
Introduction to Medical Image Processing Δ Essential environments of a medical imaging system Subject Image Analysis Energy Imaging System Images Image Processing Feature Images Image processing may be
MEDICAL IMAGE ANALYSIS
 SECOND EDITION MEDICAL IMAGE ANALYSIS ATAM P. DHAWAN g, A B IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Sponsor IEEE Press Series in Biomedical Engineering Metin Akay, Series Editor +IEEE IEEE PRESS
SECOND EDITION MEDICAL IMAGE ANALYSIS ATAM P. DHAWAN g, A B IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Sponsor IEEE Press Series in Biomedical Engineering Metin Akay, Series Editor +IEEE IEEE PRESS
Object Identification in Ultrasound Scans
 Object Identification in Ultrasound Scans Wits University Dec 05, 2012 Roadmap Introduction to the problem Motivation Related Work Our approach Expected Results Introduction Nowadays, imaging devices like
Object Identification in Ultrasound Scans Wits University Dec 05, 2012 Roadmap Introduction to the problem Motivation Related Work Our approach Expected Results Introduction Nowadays, imaging devices like
Morphometric Analysis of Biomedical Images. Sara Rolfe 10/9/17
 Morphometric Analysis of Biomedical Images Sara Rolfe 10/9/17 Morphometric Analysis of Biomedical Images Object surface contours Image difference features Compact representation of feature differences
Morphometric Analysis of Biomedical Images Sara Rolfe 10/9/17 Morphometric Analysis of Biomedical Images Object surface contours Image difference features Compact representation of feature differences
Analysis of classifier to improve Medical diagnosis for Breast Cancer Detection using Data Mining Techniques A.subasini 1
 2117 Analysis of classifier to improve Medical diagnosis for Breast Cancer Detection using Data Mining Techniques A.subasini 1 1 Research Scholar, R.D.Govt college, Sivagangai Nirase Fathima abubacker
2117 Analysis of classifier to improve Medical diagnosis for Breast Cancer Detection using Data Mining Techniques A.subasini 1 1 Research Scholar, R.D.Govt college, Sivagangai Nirase Fathima abubacker
PROSTATE CANCER DETECTION USING LABEL IMAGE CONSTRAINED MULTIATLAS SELECTION
 PROSTATE CANCER DETECTION USING LABEL IMAGE CONSTRAINED MULTIATLAS SELECTION Ms. Vaibhavi Nandkumar Jagtap 1, Mr. Santosh D. Kale 2 1 PG Scholar, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics and Telecommunication,
PROSTATE CANCER DETECTION USING LABEL IMAGE CONSTRAINED MULTIATLAS SELECTION Ms. Vaibhavi Nandkumar Jagtap 1, Mr. Santosh D. Kale 2 1 PG Scholar, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics and Telecommunication,
ISSN: X Impact factor: 4.295
 ISSN: 2454-132X Impact factor: 4.295 (Volume3, Issue1) Available online at: www.ijariit.com Performance Analysis of Image Clustering Algorithm Applied to Brain MRI Kalyani R.Mandlik 1, Dr. Suresh S. Salankar
ISSN: 2454-132X Impact factor: 4.295 (Volume3, Issue1) Available online at: www.ijariit.com Performance Analysis of Image Clustering Algorithm Applied to Brain MRI Kalyani R.Mandlik 1, Dr. Suresh S. Salankar
Blood Microscopic Image Analysis for Acute Leukemia Detection
 I J C T A, 9(9), 2016, pp. 3731-3735 International Science Press Blood Microscopic Image Analysis for Acute Leukemia Detection V. Renuga, J. Sivaraman, S. Vinuraj Kumar, S. Sathish, P. Padmapriya and R.
I J C T A, 9(9), 2016, pp. 3731-3735 International Science Press Blood Microscopic Image Analysis for Acute Leukemia Detection V. Renuga, J. Sivaraman, S. Vinuraj Kumar, S. Sathish, P. Padmapriya and R.
A fast breast nonlinear elastography reconstruction technique using the Veronda-Westman model
 A fast breast nonlinear elastography reconstruction technique using the Veronda-Westman model Mohammadhosein Amooshahi a and Abbas Samani abc a Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, University
A fast breast nonlinear elastography reconstruction technique using the Veronda-Westman model Mohammadhosein Amooshahi a and Abbas Samani abc a Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, University
A ranklet-based CAD for digital mammography
 A ranklet-based CAD for digital mammography Enrico Angelini 1, Renato Campanini 1, Emiro Iampieri 1, Nico Lanconelli 1, Matteo Masotti 1, Todor Petkov 1, and Matteo Roffilli 2 1 Physics Department, University
A ranklet-based CAD for digital mammography Enrico Angelini 1, Renato Campanini 1, Emiro Iampieri 1, Nico Lanconelli 1, Matteo Masotti 1, Todor Petkov 1, and Matteo Roffilli 2 1 Physics Department, University
Classification of Subject Motion for Improved Reconstruction of Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 1 CS 9 Final Project Classification of Subject Motion for Improved Reconstruction of Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging Feiyu Chen Department of Electrical Engineering ABSTRACT Subject motion is a significant
1 CS 9 Final Project Classification of Subject Motion for Improved Reconstruction of Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging Feiyu Chen Department of Electrical Engineering ABSTRACT Subject motion is a significant
Whole Body MRI Intensity Standardization
 Whole Body MRI Intensity Standardization Florian Jäger 1, László Nyúl 1, Bernd Frericks 2, Frank Wacker 2 and Joachim Hornegger 1 1 Institute of Pattern Recognition, University of Erlangen, {jaeger,nyul,hornegger}@informatik.uni-erlangen.de
Whole Body MRI Intensity Standardization Florian Jäger 1, László Nyúl 1, Bernd Frericks 2, Frank Wacker 2 and Joachim Hornegger 1 1 Institute of Pattern Recognition, University of Erlangen, {jaeger,nyul,hornegger}@informatik.uni-erlangen.de
AUTOMATED EVALUATION OF BREAST CANCER DETECTION USING SVM CLASSIFIER
 International Journal of Computer Science Engineering and Information Technology Research (IJCSEITR) ISSN(P): 2249-6831; ISSN(E): 2249-7943 Vol. 5, Issue 1, Feb 2015, 7-16 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. AUTOMATED EVALUATION
International Journal of Computer Science Engineering and Information Technology Research (IJCSEITR) ISSN(P): 2249-6831; ISSN(E): 2249-7943 Vol. 5, Issue 1, Feb 2015, 7-16 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. AUTOMATED EVALUATION
Semi-Automatic Detection of Cervical Vertebrae in X-ray Images Using Generalized Hough Transform
 Semi-Automatic Detection of Cervical Vertebrae in X-ray Images Using Generalized Hough Transform Mohamed Amine LARHMAM, Saïd MAHMOUDI and Mohammed BENJELLOUN Faculty of Engineering, University of Mons,
Semi-Automatic Detection of Cervical Vertebrae in X-ray Images Using Generalized Hough Transform Mohamed Amine LARHMAM, Saïd MAHMOUDI and Mohammed BENJELLOUN Faculty of Engineering, University of Mons,
Medicale Image Analysis
 Medicale Image Analysis Registration Validation Prof. Dr. Philippe Cattin MIAC, University of Basel Prof. Dr. Philippe Cattin: Registration Validation Contents 1 Validation 1.1 Validation of Registration
Medicale Image Analysis Registration Validation Prof. Dr. Philippe Cattin MIAC, University of Basel Prof. Dr. Philippe Cattin: Registration Validation Contents 1 Validation 1.1 Validation of Registration
Mass Classification Method in Mammogram Using Fuzzy K-Nearest Neighbour Equality
 Mass Classification Method in Mammogram Using Fuzzy K-Nearest Neighbour Equality Abstract: Mass classification of objects is an important area of research and application in a variety of fields. In this
Mass Classification Method in Mammogram Using Fuzzy K-Nearest Neighbour Equality Abstract: Mass classification of objects is an important area of research and application in a variety of fields. In this
ISSN: (Online) Volume 3, Issue 6, June 2015 International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies
 ISSN: 2321-7782 (Online) Volume 3, Issue 6, June 2015 International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies Research Article / Survey Paper / Case Study Available online
ISSN: 2321-7782 (Online) Volume 3, Issue 6, June 2015 International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies Research Article / Survey Paper / Case Study Available online
3-D Compounding of B-Scan Ultrasound Images
 3-D Compounding of B-Scan Ultrasound Images Jochen F. Krücker, Charles R. Meyer, Theresa A. Tuthill, Gerald L. LeCarpentier, J. Brian Fowlkes, Paul L. Carson University of Michigan, Dept. of Radiology,
3-D Compounding of B-Scan Ultrasound Images Jochen F. Krücker, Charles R. Meyer, Theresa A. Tuthill, Gerald L. LeCarpentier, J. Brian Fowlkes, Paul L. Carson University of Michigan, Dept. of Radiology,
WorkstationOne. - a diagnostic breast imaging workstation. User Training Presentation. doc #24 (v2.0) Let MammoOne Assist You in Digital Mammography
 WorkstationOne - a diagnostic breast imaging workstation User Training Presentation WorkstationOne Unique streamlined workflow for efficient digital mammography reading Let MammoOne Let MammoOne Assist
WorkstationOne - a diagnostic breast imaging workstation User Training Presentation WorkstationOne Unique streamlined workflow for efficient digital mammography reading Let MammoOne Let MammoOne Assist
RADIOMICS: potential role in the clinics and challenges
 27 giugno 2018 Dipartimento di Fisica Università degli Studi di Milano RADIOMICS: potential role in the clinics and challenges Dr. Francesca Botta Medical Physicist Istituto Europeo di Oncologia (Milano)
27 giugno 2018 Dipartimento di Fisica Università degli Studi di Milano RADIOMICS: potential role in the clinics and challenges Dr. Francesca Botta Medical Physicist Istituto Europeo di Oncologia (Milano)
Machine Learning for Medical Image Analysis. A. Criminisi
 Machine Learning for Medical Image Analysis A. Criminisi Overview Introduction to machine learning Decision forests Applications in medical image analysis Anatomy localization in CT Scans Spine Detection
Machine Learning for Medical Image Analysis A. Criminisi Overview Introduction to machine learning Decision forests Applications in medical image analysis Anatomy localization in CT Scans Spine Detection
Global Thresholding Techniques to Classify Dead Cells in Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonant Images
 Global Thresholding Techniques to Classify Dead Cells in Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonant Images Ravi S 1, A. M. Khan 2 1 Research Student, Department of Electronics, Mangalore University, Karnataka
Global Thresholding Techniques to Classify Dead Cells in Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonant Images Ravi S 1, A. M. Khan 2 1 Research Student, Department of Electronics, Mangalore University, Karnataka
Parameter Optimization for Mammogram Image Classification with Support Vector Machine
 , March 15-17, 2017, Hong Kong Parameter Optimization for Mammogram Image Classification with Support Vector Machine Keerachart Suksut, Ratiporn Chanklan, Nuntawut Kaoungku, Kedkard Chaiyakhan, Nittaya
, March 15-17, 2017, Hong Kong Parameter Optimization for Mammogram Image Classification with Support Vector Machine Keerachart Suksut, Ratiporn Chanklan, Nuntawut Kaoungku, Kedkard Chaiyakhan, Nittaya
Chapter 7 UNSUPERVISED LEARNING TECHNIQUES FOR MAMMOGRAM CLASSIFICATION
 UNSUPERVISED LEARNING TECHNIQUES FOR MAMMOGRAM CLASSIFICATION Supervised and unsupervised learning are the two prominent machine learning algorithms used in pattern recognition and classification. In this
UNSUPERVISED LEARNING TECHNIQUES FOR MAMMOGRAM CLASSIFICATION Supervised and unsupervised learning are the two prominent machine learning algorithms used in pattern recognition and classification. In this
Optimizing Flip Angle Selection in Breast MRI for Accurate Extraction and Visualization of T1 Tissue Relaxation Time
 Optimizing Flip Angle Selection in Breast MRI for Accurate Extraction and Visualization of T1 Tissue Relaxation Time GEORGIOS KETSETZIS AND MICHAEL BRADY Medical Vision Laboratory Department of Engineering
Optimizing Flip Angle Selection in Breast MRI for Accurate Extraction and Visualization of T1 Tissue Relaxation Time GEORGIOS KETSETZIS AND MICHAEL BRADY Medical Vision Laboratory Department of Engineering
Automatic Detection and Segmentation of Kidneys in Magnetic Resonance Images Using Image Processing Techniques
 Biomedical Statistics and Informatics 2017; 2(1): 22-26 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/bsi doi: 10.11648/j.bsi.20170201.15 Automatic Detection and Segmentation of Kidneys in Magnetic Resonance
Biomedical Statistics and Informatics 2017; 2(1): 22-26 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/bsi doi: 10.11648/j.bsi.20170201.15 Automatic Detection and Segmentation of Kidneys in Magnetic Resonance
Spatio-Temporal Registration of Biomedical Images by Computational Methods
 Spatio-Temporal Registration of Biomedical Images by Computational Methods Francisco P. M. Oliveira, João Manuel R. S. Tavares tavares@fe.up.pt, www.fe.up.pt/~tavares Outline 1. Introduction 2. Spatial
Spatio-Temporal Registration of Biomedical Images by Computational Methods Francisco P. M. Oliveira, João Manuel R. S. Tavares tavares@fe.up.pt, www.fe.up.pt/~tavares Outline 1. Introduction 2. Spatial
Global Journal of Engineering Science and Research Management
 ADVANCED K-MEANS ALGORITHM FOR BRAIN TUMOR DETECTION USING NAIVE BAYES CLASSIFIER Veena Bai K*, Dr. Niharika Kumar * MTech CSE, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, B.N.M. Institute of Technology,
ADVANCED K-MEANS ALGORITHM FOR BRAIN TUMOR DETECTION USING NAIVE BAYES CLASSIFIER Veena Bai K*, Dr. Niharika Kumar * MTech CSE, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, B.N.M. Institute of Technology,
Predicting Tumour Location by Modelling the Deformation of the Breast using Nonlinear Elasticity
 Predicting Tumour Location by Modelling the Deformation of the Breast using Nonlinear Elasticity November 8th, 2006 Outline Motivation Motivation Motivation for Modelling Breast Deformation Mesh Generation
Predicting Tumour Location by Modelling the Deformation of the Breast using Nonlinear Elasticity November 8th, 2006 Outline Motivation Motivation Motivation for Modelling Breast Deformation Mesh Generation
MR-Guided Mixed Reality for Breast Conserving Surgical Planning
 MR-Guided Mixed Reality for Breast Conserving Surgical Planning Suba Srinivasan (subashini7@gmail.com) March 30 th 2017 Mentors: Prof. Brian A. Hargreaves, Prof. Bruce L. Daniel MEDICINE MRI Guided Mixed
MR-Guided Mixed Reality for Breast Conserving Surgical Planning Suba Srinivasan (subashini7@gmail.com) March 30 th 2017 Mentors: Prof. Brian A. Hargreaves, Prof. Bruce L. Daniel MEDICINE MRI Guided Mixed
An Improved Modified Tracking Algorithm Hybrid with Fuzzy C Means Clustering In Digital Mammograms
 An Improved Modified Tracking Algorithm Hybrid with Fuzzy C Means Clustering In Digital Mammograms R.Sivakumar 1, Marcus Karnan 2, G.Gokila Deepa 3 1 Research Scholar, Dept. of R&D Centre, Bharathiar University,
An Improved Modified Tracking Algorithm Hybrid with Fuzzy C Means Clustering In Digital Mammograms R.Sivakumar 1, Marcus Karnan 2, G.Gokila Deepa 3 1 Research Scholar, Dept. of R&D Centre, Bharathiar University,
Methodological progress in image registration for ventilation estimation, segmentation propagation and multi-modal fusion
 Methodological progress in image registration for ventilation estimation, segmentation propagation and multi-modal fusion Mattias P. Heinrich Julia A. Schnabel, Mark Jenkinson, Sir Michael Brady 2 Clinical
Methodological progress in image registration for ventilation estimation, segmentation propagation and multi-modal fusion Mattias P. Heinrich Julia A. Schnabel, Mark Jenkinson, Sir Michael Brady 2 Clinical
A METHODICAL WAY OF IMAGE REGISTRATION IN DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING
 International Journal of Technical Research and Applications e-issn: 2320-8163, www.ijtra.com Volume 2, Issue 1 (jan-feb 2014), PP. 40-44 A METHODICAL WAY OF IMAGE REGISTRATION IN DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING
International Journal of Technical Research and Applications e-issn: 2320-8163, www.ijtra.com Volume 2, Issue 1 (jan-feb 2014), PP. 40-44 A METHODICAL WAY OF IMAGE REGISTRATION IN DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING
Computational Medical Imaging Analysis Chapter 4: Image Visualization
 Computational Medical Imaging Analysis Chapter 4: Image Visualization Jun Zhang Laboratory for Computational Medical Imaging & Data Analysis Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky Lexington,
Computational Medical Imaging Analysis Chapter 4: Image Visualization Jun Zhang Laboratory for Computational Medical Imaging & Data Analysis Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky Lexington,
Extraction and recognition of the thoracic organs based on 3D CT images and its application
 1 Extraction and recognition of the thoracic organs based on 3D CT images and its application Xiangrong Zhou, PhD a, Takeshi Hara, PhD b, Hiroshi Fujita, PhD b, Yoshihiro Ida, RT c, Kazuhiro Katada, MD
1 Extraction and recognition of the thoracic organs based on 3D CT images and its application Xiangrong Zhou, PhD a, Takeshi Hara, PhD b, Hiroshi Fujita, PhD b, Yoshihiro Ida, RT c, Kazuhiro Katada, MD
Available online Journal of Scientific and Engineering Research, 2019, 6(1): Research Article
 Available online www.jsaer.com, 2019, 6(1):193-197 Research Article ISSN: 2394-2630 CODEN(USA): JSERBR An Enhanced Application of Fuzzy C-Mean Algorithm in Image Segmentation Process BAAH Barida 1, ITUMA
Available online www.jsaer.com, 2019, 6(1):193-197 Research Article ISSN: 2394-2630 CODEN(USA): JSERBR An Enhanced Application of Fuzzy C-Mean Algorithm in Image Segmentation Process BAAH Barida 1, ITUMA
The BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING Series Series Editor Michael R. Neuman. Uriiwsity of Calßy ülgaiy, Nbeitai, Cart. (g) CRC PRESS
 The BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING Series Series Editor Michael R. Neuman Biomedical Image Analysis Uriiwsity of Calßy ülgaiy, Nbeitai, Cart (g) CRC PRESS Boca Raton London New York Washington, D.C. Contents Preface
The BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING Series Series Editor Michael R. Neuman Biomedical Image Analysis Uriiwsity of Calßy ülgaiy, Nbeitai, Cart (g) CRC PRESS Boca Raton London New York Washington, D.C. Contents Preface
Compression, Noise Removal and Comparison in Digital Mammography using LabVIEW
 Compression, Noise Removal and Comparison in Digital Mammography using LabVIEW MIHAELA LASCU, DAN LASCU IOAN LIE, MIHAIL TĂNASE Department of Measurements and Optical Electronics Faculty of Electronics
Compression, Noise Removal and Comparison in Digital Mammography using LabVIEW MIHAELA LASCU, DAN LASCU IOAN LIE, MIHAIL TĂNASE Department of Measurements and Optical Electronics Faculty of Electronics
CHAPTER 6 ENHANCEMENT USING HYPERBOLIC TANGENT DIRECTIONAL FILTER BASED CONTOURLET
 93 CHAPTER 6 ENHANCEMENT USING HYPERBOLIC TANGENT DIRECTIONAL FILTER BASED CONTOURLET 6.1 INTRODUCTION Mammography is the most common technique for radiologists to detect and diagnose breast cancer. This
93 CHAPTER 6 ENHANCEMENT USING HYPERBOLIC TANGENT DIRECTIONAL FILTER BASED CONTOURLET 6.1 INTRODUCTION Mammography is the most common technique for radiologists to detect and diagnose breast cancer. This
Idle Object Detection in Video for Banking ATM Applications
 Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 4(24): 5350-5356, 2012 ISSN: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2012 Submitted: March 18, 2012 Accepted: April 06, 2012 Published:
Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 4(24): 5350-5356, 2012 ISSN: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2012 Submitted: March 18, 2012 Accepted: April 06, 2012 Published:
Development of an Automated Method for Detecting Mammographic Masses With a Partial Loss of Region
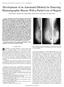 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 20, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2001 1209 Development of an Automated Method for Detecting Mammographic Masses With a Partial Loss of Region Yuji Hatanaka*, Takeshi Hara,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 20, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2001 1209 Development of an Automated Method for Detecting Mammographic Masses With a Partial Loss of Region Yuji Hatanaka*, Takeshi Hara,
Advanced Visual Medicine: Techniques for Visual Exploration & Analysis
 Advanced Visual Medicine: Techniques for Visual Exploration & Analysis Interactive Visualization of Multimodal Volume Data for Neurosurgical Planning Felix Ritter, MeVis Research Bremen Multimodal Neurosurgical
Advanced Visual Medicine: Techniques for Visual Exploration & Analysis Interactive Visualization of Multimodal Volume Data for Neurosurgical Planning Felix Ritter, MeVis Research Bremen Multimodal Neurosurgical
Edge-Preserving Denoising for Segmentation in CT-Images
 Edge-Preserving Denoising for Segmentation in CT-Images Eva Eibenberger, Anja Borsdorf, Andreas Wimmer, Joachim Hornegger Lehrstuhl für Mustererkennung, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg
Edge-Preserving Denoising for Segmentation in CT-Images Eva Eibenberger, Anja Borsdorf, Andreas Wimmer, Joachim Hornegger Lehrstuhl für Mustererkennung, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg
A Systematic Analysis System for CT Liver Image Classification and Image Segmentation by Local Entropy Method
 A Systematic Analysis System for CT Liver Image Classification and Image Segmentation by Local Entropy Method A.Anuja Merlyn 1, A.Anuba Merlyn 2 1 PG Scholar, Department of Computer Science and Engineering,
A Systematic Analysis System for CT Liver Image Classification and Image Segmentation by Local Entropy Method A.Anuja Merlyn 1, A.Anuba Merlyn 2 1 PG Scholar, Department of Computer Science and Engineering,
Object Detection in Video Streams
 Object Detection in Video Streams Sandhya S Deore* *Assistant Professor Dept. of Computer Engg., SRES COE Kopargaon *sandhya.deore@gmail.com ABSTRACT Object Detection is the most challenging area in video
Object Detection in Video Streams Sandhya S Deore* *Assistant Professor Dept. of Computer Engg., SRES COE Kopargaon *sandhya.deore@gmail.com ABSTRACT Object Detection is the most challenging area in video
Context-sensitive Classification Forests for Segmentation of Brain Tumor Tissues
 Context-sensitive Classification Forests for Segmentation of Brain Tumor Tissues D. Zikic, B. Glocker, E. Konukoglu, J. Shotton, A. Criminisi, D. H. Ye, C. Demiralp 3, O. M. Thomas 4,5, T. Das 4, R. Jena
Context-sensitive Classification Forests for Segmentation of Brain Tumor Tissues D. Zikic, B. Glocker, E. Konukoglu, J. Shotton, A. Criminisi, D. H. Ye, C. Demiralp 3, O. M. Thomas 4,5, T. Das 4, R. Jena
Department of Computer Engineering, Punjabi University, Patiala, Punjab, India 2
 Volume 6, Issue 8, August 2016 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Comparison of
Volume 6, Issue 8, August 2016 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Comparison of
MR IMAGE SEGMENTATION
 MR IMAGE SEGMENTATION Prepared by : Monil Shah What is Segmentation? Partitioning a region or regions of interest in images such that each region corresponds to one or more anatomic structures Classification
MR IMAGE SEGMENTATION Prepared by : Monil Shah What is Segmentation? Partitioning a region or regions of interest in images such that each region corresponds to one or more anatomic structures Classification
AN EFFICIENT BINARIZATION TECHNIQUE FOR FINGERPRINT IMAGES S. B. SRIDEVI M.Tech., Department of ECE
 AN EFFICIENT BINARIZATION TECHNIQUE FOR FINGERPRINT IMAGES S. B. SRIDEVI M.Tech., Department of ECE sbsridevi89@gmail.com 287 ABSTRACT Fingerprint identification is the most prominent method of biometric
AN EFFICIENT BINARIZATION TECHNIQUE FOR FINGERPRINT IMAGES S. B. SRIDEVI M.Tech., Department of ECE sbsridevi89@gmail.com 287 ABSTRACT Fingerprint identification is the most prominent method of biometric
A MORPHOLOGY-BASED FILTER STRUCTURE FOR EDGE-ENHANCING SMOOTHING
 Proceedings of the 1994 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP-94), pp. 530-534. (Austin, Texas, 13-16 November 1994.) A MORPHOLOGY-BASED FILTER STRUCTURE FOR EDGE-ENHANCING SMOOTHING
Proceedings of the 1994 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP-94), pp. 530-534. (Austin, Texas, 13-16 November 1994.) A MORPHOLOGY-BASED FILTER STRUCTURE FOR EDGE-ENHANCING SMOOTHING
Comparison of Vessel Segmentations using STAPLE
 Comparison of Vessel Segmentations using STAPLE Julien Jomier, Vincent LeDigarcher, and Stephen R. Aylward Computer-Aided Diagnosis and Display Lab The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Department
Comparison of Vessel Segmentations using STAPLE Julien Jomier, Vincent LeDigarcher, and Stephen R. Aylward Computer-Aided Diagnosis and Display Lab The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Department
Medical Image Feature, Extraction, Selection And Classification
 Medical Image Feature, Extraction, Selection And Classification 1 M.VASANTHA *, 2 DR.V.SUBBIAH BHARATHI, 3 R.DHAMODHARAN 1. Research Scholar, Mother Teresa Women s University, KodaiKanal, and Asst.Professor,
Medical Image Feature, Extraction, Selection And Classification 1 M.VASANTHA *, 2 DR.V.SUBBIAH BHARATHI, 3 R.DHAMODHARAN 1. Research Scholar, Mother Teresa Women s University, KodaiKanal, and Asst.Professor,
CHAPTER-1 INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER-1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Fuzzy concept, digital image processing and application in medicine With the advancement of digital computers, it has become easy to store large amount of data and carry out
CHAPTER-1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Fuzzy concept, digital image processing and application in medicine With the advancement of digital computers, it has become easy to store large amount of data and carry out
Computer-Aided Diagnosis in Abdominal and Cardiac Radiology Using Neural Networks
 Computer-Aided Diagnosis in Abdominal and Cardiac Radiology Using Neural Networks Du-Yih Tsai, Masaru Sekiya and Yongbum Lee Department of Radiological Technology, School of Health Sciences, Faculty of
Computer-Aided Diagnosis in Abdominal and Cardiac Radiology Using Neural Networks Du-Yih Tsai, Masaru Sekiya and Yongbum Lee Department of Radiological Technology, School of Health Sciences, Faculty of
I. INTRODUCTION. Figure-1 Basic block of text analysis
 ISSN: 2349-7637 (Online) (RHIMRJ) Research Paper Available online at: www.rhimrj.com Detection and Localization of Texts from Natural Scene Images: A Hybrid Approach Priyanka Muchhadiya Post Graduate Fellow,
ISSN: 2349-7637 (Online) (RHIMRJ) Research Paper Available online at: www.rhimrj.com Detection and Localization of Texts from Natural Scene Images: A Hybrid Approach Priyanka Muchhadiya Post Graduate Fellow,
Nonrigid Registration using Free-Form Deformations
 Nonrigid Registration using Free-Form Deformations Hongchang Peng April 20th Paper Presented: Rueckert et al., TMI 1999: Nonrigid registration using freeform deformations: Application to breast MR images
Nonrigid Registration using Free-Form Deformations Hongchang Peng April 20th Paper Presented: Rueckert et al., TMI 1999: Nonrigid registration using freeform deformations: Application to breast MR images
Biomedical Image Processing
 Biomedical Image Processing Jason Thong Gabriel Grant 1 2 Motivation from the Medical Perspective MRI, CT and other biomedical imaging devices were designed to assist doctors in their diagnosis and treatment
Biomedical Image Processing Jason Thong Gabriel Grant 1 2 Motivation from the Medical Perspective MRI, CT and other biomedical imaging devices were designed to assist doctors in their diagnosis and treatment
Detection of Ductus in Mammary Gland Tissue by Computer Vision
 Detection of Ductus in Mammary Gland Tissue by Computer Vision Katarina Mele and Aleš Leonardis Computer Vision Laboratory Faculty of Computer and Information Science University of Ljubljana Tržaška 25,
Detection of Ductus in Mammary Gland Tissue by Computer Vision Katarina Mele and Aleš Leonardis Computer Vision Laboratory Faculty of Computer and Information Science University of Ljubljana Tržaška 25,
Digital breast tomosynthesis: comparison of different methods to calculate patient doses
 Digital breast tomosynthesis: comparison of different methods to calculate patient doses Poster No.: C-2220 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: A. Jacobs 1, L. Cockmartin 1, D. R. Dance
Digital breast tomosynthesis: comparison of different methods to calculate patient doses Poster No.: C-2220 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: A. Jacobs 1, L. Cockmartin 1, D. R. Dance
Computer-aided detection of clustered microcalcifications in digital mammograms.
 Computer-aided detection of clustered microcalcifications in digital mammograms. Stelios Halkiotis, John Mantas & Taxiarchis Botsis. University of Athens Faculty of Nursing- Health Informatics Laboratory.
Computer-aided detection of clustered microcalcifications in digital mammograms. Stelios Halkiotis, John Mantas & Taxiarchis Botsis. University of Athens Faculty of Nursing- Health Informatics Laboratory.
A Study of Medical Image Analysis System
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 8(25), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2015/v8i25/80492, October 2015 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 A Study of Medical Image Analysis System Kim Tae-Eun
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 8(25), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2015/v8i25/80492, October 2015 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 A Study of Medical Image Analysis System Kim Tae-Eun
Medical Image Registration by Maximization of Mutual Information
 Medical Image Registration by Maximization of Mutual Information EE 591 Introduction to Information Theory Instructor Dr. Donald Adjeroh Submitted by Senthil.P.Ramamurthy Damodaraswamy, Umamaheswari Introduction
Medical Image Registration by Maximization of Mutual Information EE 591 Introduction to Information Theory Instructor Dr. Donald Adjeroh Submitted by Senthil.P.Ramamurthy Damodaraswamy, Umamaheswari Introduction
Mammograms Feature Extraction using Fuzzy Surface
 Article ID: 2046-1690 Mammograms Feature Extraction using Fuzzy Surface Corresponding Author: Dr. Rash B Dubey, Professor, ECE Dept, Hindu College of Engg, Sonepat, 121003 - India Submitting Author: Dr.
Article ID: 2046-1690 Mammograms Feature Extraction using Fuzzy Surface Corresponding Author: Dr. Rash B Dubey, Professor, ECE Dept, Hindu College of Engg, Sonepat, 121003 - India Submitting Author: Dr.
Lesion Segmentation and Bias Correction in Breast Ultrasound B-mode Images Including Elastography Information
 Lesion Segmentation and Bias Correction in Breast Ultrasound B-mode Images Including Elastography Information Gerard Pons a, Joan Martí a, Robert Martí a, Mariano Cabezas a, Andrew di Battista b, and J.
Lesion Segmentation and Bias Correction in Breast Ultrasound B-mode Images Including Elastography Information Gerard Pons a, Joan Martí a, Robert Martí a, Mariano Cabezas a, Andrew di Battista b, and J.
4/19/2016. Deborah Thames R.T. (R)(M)(QM) Theory & Technology and advancement in 3D imaging DBT
 Deborah Thames R.T. (R)(M)(QM) Theory & Technology and advancement in 3D imaging DBT 1 Three manufacturers approved for Tomo Hologic and GE, and Siemens Why 2D Digital Mammography 2D FFDM it appears to
Deborah Thames R.T. (R)(M)(QM) Theory & Technology and advancement in 3D imaging DBT 1 Three manufacturers approved for Tomo Hologic and GE, and Siemens Why 2D Digital Mammography 2D FFDM it appears to
Intraoperative Prostate Tracking with Slice-to-Volume Registration in MR
 Intraoperative Prostate Tracking with Slice-to-Volume Registration in MR Sean Gill a, Purang Abolmaesumi a,b, Siddharth Vikal a, Parvin Mousavi a and Gabor Fichtinger a,b,* (a) School of Computing, Queen
Intraoperative Prostate Tracking with Slice-to-Volume Registration in MR Sean Gill a, Purang Abolmaesumi a,b, Siddharth Vikal a, Parvin Mousavi a and Gabor Fichtinger a,b,* (a) School of Computing, Queen
Mouse Pointer Tracking with Eyes
 Mouse Pointer Tracking with Eyes H. Mhamdi, N. Hamrouni, A. Temimi, and M. Bouhlel Abstract In this article, we expose our research work in Human-machine Interaction. The research consists in manipulating
Mouse Pointer Tracking with Eyes H. Mhamdi, N. Hamrouni, A. Temimi, and M. Bouhlel Abstract In this article, we expose our research work in Human-machine Interaction. The research consists in manipulating
Semi-Automatic Segmentation of the Patellar Cartilage in MRI
 Semi-Automatic Segmentation of the Patellar Cartilage in MRI Lorenz König 1, Martin Groher 1, Andreas Keil 1, Christian Glaser 2, Maximilian Reiser 2, Nassir Navab 1 1 Chair for Computer Aided Medical
Semi-Automatic Segmentation of the Patellar Cartilage in MRI Lorenz König 1, Martin Groher 1, Andreas Keil 1, Christian Glaser 2, Maximilian Reiser 2, Nassir Navab 1 1 Chair for Computer Aided Medical
ENGLISH. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
 ENGLISH Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Medical imaging excellence Planmed is strongly committed to improving the early detection of breast cancer. Our mission is to provide top quality imaging systems for
ENGLISH Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Medical imaging excellence Planmed is strongly committed to improving the early detection of breast cancer. Our mission is to provide top quality imaging systems for
Edge Detection in Angiogram Images Using Modified Classical Image Processing Technique
 Edge Detection in Angiogram Images Using Modified Classical Image Processing Technique S. Deepak Raj 1 Harisha D S 2 1,2 Asst. Prof, Dept Of ISE, Sai Vidya Institute of Technology, Bangalore, India Deepak
Edge Detection in Angiogram Images Using Modified Classical Image Processing Technique S. Deepak Raj 1 Harisha D S 2 1,2 Asst. Prof, Dept Of ISE, Sai Vidya Institute of Technology, Bangalore, India Deepak
Automatic System For Brain Tumor Detection And Classification Using Level Set And ANN
 Automatic System For Brain Tumor Detection And Classification Using Level Set And ANN Nisha Babu A Computer Science Department LBSITW Trivandrum, India nisthesweet@gmail.com Agoma Martin Computer Science
Automatic System For Brain Tumor Detection And Classification Using Level Set And ANN Nisha Babu A Computer Science Department LBSITW Trivandrum, India nisthesweet@gmail.com Agoma Martin Computer Science
IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 10 March 2015 ISSN (online):
 IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 10 March 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Counting of Micro-Organisms for Medical Diagnosis using Image Processing
IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 10 March 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Counting of Micro-Organisms for Medical Diagnosis using Image Processing
Using Probability Maps for Multi organ Automatic Segmentation
 Using Probability Maps for Multi organ Automatic Segmentation Ranveer Joyseeree 1,2, Óscar Jiménez del Toro1, and Henning Müller 1,3 1 University of Applied Sciences Western Switzerland (HES SO), Sierre,
Using Probability Maps for Multi organ Automatic Segmentation Ranveer Joyseeree 1,2, Óscar Jiménez del Toro1, and Henning Müller 1,3 1 University of Applied Sciences Western Switzerland (HES SO), Sierre,
Edge Detection for Dental X-ray Image Segmentation using Neural Network approach
 Volume 1, No. 7, September 2012 ISSN 2278-1080 The International Journal of Computer Science & Applications (TIJCSA) RESEARCH PAPER Available Online at http://www.journalofcomputerscience.com/ Edge Detection
Volume 1, No. 7, September 2012 ISSN 2278-1080 The International Journal of Computer Science & Applications (TIJCSA) RESEARCH PAPER Available Online at http://www.journalofcomputerscience.com/ Edge Detection
Local Independent Projection Based Classification Using Fuzzy Clustering
 www.ijecs.in International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science ISSN:2319-7242 Volume 4 Issue 6 June 2015, Page No. 12306-12311 Local Independent Projection Based Classification Using Fuzzy Clustering
www.ijecs.in International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science ISSN:2319-7242 Volume 4 Issue 6 June 2015, Page No. 12306-12311 Local Independent Projection Based Classification Using Fuzzy Clustering
Normalization for clinical data
 Normalization for clinical data Christopher Rorden, Leonardo Bonilha, Julius Fridriksson, Benjamin Bender, Hans-Otto Karnath (2012) Agespecific CT and MRI templates for spatial normalization. NeuroImage
Normalization for clinical data Christopher Rorden, Leonardo Bonilha, Julius Fridriksson, Benjamin Bender, Hans-Otto Karnath (2012) Agespecific CT and MRI templates for spatial normalization. NeuroImage
Detection of Bone Fracture using Image Processing Methods
 Detection of Bone Fracture using Image Processing Methods E Susmitha, M.Tech Student, Susmithasrinivas3@gmail.com Mr. K. Bhaskar Assistant Professor bhasi.adc@gmail.com MVR college of engineering and Technology
Detection of Bone Fracture using Image Processing Methods E Susmitha, M.Tech Student, Susmithasrinivas3@gmail.com Mr. K. Bhaskar Assistant Professor bhasi.adc@gmail.com MVR college of engineering and Technology
Deformable Registration Using Scale Space Keypoints
 Deformable Registration Using Scale Space Keypoints Mehdi Moradi a, Purang Abolmaesoumi a,b and Parvin Mousavi a a School of Computing, Queen s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada K7L 3N6; b Department
Deformable Registration Using Scale Space Keypoints Mehdi Moradi a, Purang Abolmaesoumi a,b and Parvin Mousavi a a School of Computing, Queen s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada K7L 3N6; b Department
Approaches For Automated Detection And Classification Of Masses In Mammograms
 www.ijecs.in International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science ISSN:2319-7242 Volume 3, Issue 11 November, 2014 Page No. 9097-9011 Approaches For Automated Detection And Classification Of Masses
www.ijecs.in International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science ISSN:2319-7242 Volume 3, Issue 11 November, 2014 Page No. 9097-9011 Approaches For Automated Detection And Classification Of Masses
Refraction Corrected Transmission Ultrasound Computed Tomography for Application in Breast Imaging
 Refraction Corrected Transmission Ultrasound Computed Tomography for Application in Breast Imaging Joint Research With Trond Varslot Marcel Jackowski Shengying Li and Klaus Mueller Ultrasound Detection
Refraction Corrected Transmission Ultrasound Computed Tomography for Application in Breast Imaging Joint Research With Trond Varslot Marcel Jackowski Shengying Li and Klaus Mueller Ultrasound Detection
Foveal Algorithm for the Detection of Microcalcification Clusters: a FROC Analysis
 Foveal Algorithm for the Detection of Microcalcification Clusters: a FROC Analysis Marius George Linguraru a,b, Michael Brady a and Ruth English c a Medical Vision Laboratory, University of Oxford, Ewert
Foveal Algorithm for the Detection of Microcalcification Clusters: a FROC Analysis Marius George Linguraru a,b, Michael Brady a and Ruth English c a Medical Vision Laboratory, University of Oxford, Ewert
A Review on Label Image Constrained Multiatlas Selection
 A Review on Label Image Constrained Multiatlas Selection Ms. VAIBHAVI NANDKUMAR JAGTAP 1, Mr. SANTOSH D. KALE 2 1PG Scholar, Department of Electronics and Telecommunication, SVPM College of Engineering,
A Review on Label Image Constrained Multiatlas Selection Ms. VAIBHAVI NANDKUMAR JAGTAP 1, Mr. SANTOSH D. KALE 2 1PG Scholar, Department of Electronics and Telecommunication, SVPM College of Engineering,
An Enhanced Mammogram Image Classification Using Fuzzy Association Rule Mining
 An Enhanced Mammogram Image Classification Using Fuzzy Association Rule Mining Dr.K.Meenakshi Sundaram 1, P.Aarthi Rani 2, D.Sasikala 3 Associate Professor, Department of Computer Science, Erode Arts and
An Enhanced Mammogram Image Classification Using Fuzzy Association Rule Mining Dr.K.Meenakshi Sundaram 1, P.Aarthi Rani 2, D.Sasikala 3 Associate Professor, Department of Computer Science, Erode Arts and
Skin Infection Recognition using Curvelet
 IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 2278-2834, p- ISSN: 2278-8735. Volume 4, Issue 6 (Jan. - Feb. 2013), PP 37-41 Skin Infection Recognition using Curvelet Manisha
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 2278-2834, p- ISSN: 2278-8735. Volume 4, Issue 6 (Jan. - Feb. 2013), PP 37-41 Skin Infection Recognition using Curvelet Manisha
Biomedical Image Processing for Human Elbow
 Biomedical Image Processing for Human Elbow Akshay Vishnoi, Sharad Mehta, Arpan Gupta Department of Mechanical Engineering Graphic Era University Dehradun, India akshaygeu001@gmail.com, sharadm158@gmail.com
Biomedical Image Processing for Human Elbow Akshay Vishnoi, Sharad Mehta, Arpan Gupta Department of Mechanical Engineering Graphic Era University Dehradun, India akshaygeu001@gmail.com, sharadm158@gmail.com
Volume visualization. Volume visualization. Volume visualization methods. Sources of volume visualization. Sources of volume visualization
 Volume visualization Volume visualization Volumes are special cases of scalar data: regular 3D grids of scalars, typically interpreted as density values. Each data value is assumed to describe a cubic
Volume visualization Volume visualization Volumes are special cases of scalar data: regular 3D grids of scalars, typically interpreted as density values. Each data value is assumed to describe a cubic
Implementation of Hybrid Model Image Fusion Algorithm
 IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 2278-2834,p- ISSN: 2278-8735.Volume 9, Issue 5, Ver. V (Sep - Oct. 2014), PP 17-22 Implementation of Hybrid Model Image Fusion
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 2278-2834,p- ISSN: 2278-8735.Volume 9, Issue 5, Ver. V (Sep - Oct. 2014), PP 17-22 Implementation of Hybrid Model Image Fusion
8/3/2017. Contour Assessment for Quality Assurance and Data Mining. Objective. Outline. Tom Purdie, PhD, MCCPM
 Contour Assessment for Quality Assurance and Data Mining Tom Purdie, PhD, MCCPM Objective Understand the state-of-the-art in contour assessment for quality assurance including data mining-based techniques
Contour Assessment for Quality Assurance and Data Mining Tom Purdie, PhD, MCCPM Objective Understand the state-of-the-art in contour assessment for quality assurance including data mining-based techniques
