Thinking in Frequency
|
|
|
- Mark Bridges
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Thinking in Frequency Computer Vision Jia-Bin Huang, Virginia Tech Dali: Gala Contemplating the Mediterranean Sea (1976)
2 Administrative stuffs Course website: Office hours - Jia-Bin (440 Whittemore Hall ) Friday at 11:00 AM 12:00 PM; 1:30 PM 2:00 PM Office hours Yuliang (344 Whittemore) Wednesday 2:30 PM - 3:30 PM Monday (on HW due date) HW 1 will be posted next Tue (Sept 12). Due date: Sept 25.
3 Using ARC Cluster: NewRiver g/newriver/ Using MATLAB on NewRiver /matlab/
4 Previous class: Image Filtering Linear filtering is sum of dot product at each position Can smooth, sharpen, translate (among many other uses) Gaussian filters Low pass filters, separability, variance Attend to details: filter size, extrapolation, cropping Applications: Noise models and nonlinear image filters Texture representation
5 Today s class Review of image filtering in spatial domain Fourier transform and frequency domain Frequency view of filtering Image downsizing and interpolation Goals: Understand 2D Fourier transform Understand how to implement filtering in Fourier domain Understand aliasing and how to prevent aliasing
6 Demo
7 Questions Write as filtering operations, plus some pointwise operations: +, -,.*,> out( m, n) 1 out( m, n) k, l { 1,1} k, l { 1,0,1} out( m, n) 0 if in( m, n) in( m k, n l) out = 1 + in*h1; in( m k, n l) 2 out = (in.^2)*h2; out( m, n) 1 if in( m, n) ( in( m, n 1) in( m, n 1)) / 2 ( in( m, n 1) in( m, n 1)) / out = in > in*h3;
8 Review: questions Fill in the blanks: a) _ = D * B b) A = _ * _ c) F = D * _ d) _ = D * D Filtering Operator A E B F G C H I D Slide: Hoiem
9 Hybrid Images Slide credit: Derek Hoiem A. Oliva, A. Torralba, P.G. Schyns, Hybrid Images, SIGGRAPH 2006
10 Why do we get different, distance-dependent interpretations of hybrid images?? Slide credit: Derek Hoiem
11 Why does a lower resolution image still make sense to us? What do we lose? Slide credit: Derek Hoiem Image:
12 Thinking in terms of frequency
13 Jean Baptiste Joseph Fourier ( ) had crazy idea (1807): Any univariate function can be rewritten as a weighted sum of sines and cosines of different frequencies. Don t believe it? Neither did Lagrange, Laplace, Poisson and other big wigs Not translated into English until 1878! But it s (mostly) true! called Fourier Series there are some subtle restrictions...the manner in which the author arrives at these equations is not exempt of difficulties and...his analysis to integrate them still leaves something to be desired on the score of generality and even rigour. Laplace Lagrange Legendre Slides: Efros
14 How would math have changed if the Slanket or Snuggie had been invented? Slide credit: James Hays
15 A sum of sines Our building block: Asin( x Add enough of them to get any signal f(x) you want!
16 Frequency Spectra example : g(t) = sin(2πf t) + (1/3)sin(2π(3f) t) = + Slides: Efros
17 Frequency Spectra
18 Frequency Spectra = + =
19 Frequency Spectra = + =
20 Frequency Spectra = + =
21 Frequency Spectra = + =
22 Frequency Spectra = + =
23 Frequency Spectra = A k 1 1 sin(2 kt ) k
24 Example: Music We think of music in terms of frequencies at different magnitudes
25 Other signals We can also think of all kinds of other signals the same way Cats(?) xkcd.com
26 Fourier analysis in images Intensity Image Fourier Image
27 Signals can be composed + = More:
28 Fourier Transform Teases away fast vs. slow changes in the image. Slide credit: A Efros Image as a sum of basis images
29 Extension to 2D in Matlab, check out: imagesc(log(abs(fftshift(fft2(im)))));
30 Fourier Transform Fourier transform stores the magnitude and phase at each frequency Magnitude encodes how much signal there is at a particular frequency Phase encodes spatial information (indirectly) For mathematical convenience, this is often notated in terms of real and complex numbers Amplitude: A R I 2 2 ( ) ( ) Phase: tan 1 I( ) R( ) Euler s formula:
31 Salvador Dali invented Hybrid Images? Salvador Dali Gala Contemplating the Mediterranean Sea, which at 30 meters becomes the portrait of Abraham Lincoln, 1976
32
33
34 Strong Vertical Frequency (Sharp Horizontal Edge) Diagonal Frequencies Strong Horz. Frequency (Sharp Vert. Edge) Log Magnitude Low Frequencies
35 Man-made Scene
36 Can change spectrum, then reconstruct
37 Low and High Pass filtering
38 Computing the Fourier Transform Continuous Discrete k = -N/2..N/2 Fast Fourier Transform (FFT): NlogN
39 The Convolution Theorem The Fourier transform of the convolution of two functions is the product of their Fourier transforms F[ g h] F[ g]f[ h] The inverse Fourier transform of the product of two Fourier transforms is the convolution of the two inverse Fourier transforms F 1 [ gh] F 1 [ g] [ h] Convolution in spatial domain is equivalent to multiplication in frequency domain! F 1
40 Properties of Fourier Transforms Linearity Fourier transform of a real signal is symmetric about the origin The energy of the signal is the same as the energy of its Fourier transform See Szeliski Book (3.4)
41 Filtering in spatial domain * =
42 Spatial domain * = FFT FFT Inverse FFT = Frequency domain
43 FFT in Matlab Filtering with fft im = % im: gray-scale floating point image [imh, imw] = size(im); fftsize = 1024; % fftsize: should be order of 2 (for speed) and include padding hs = 50; % fil: Gaussian filter fil = fspecial('gaussian', hs*2+1, 10); % im_fft = fft2(im, fftsize, fftsize); % 1) fft im with padding fil_fft = fft2(fil, fftsize, fftsize); % 2) fft fil, pad to same size as image im_fil_fft = im_fft.* fil_fft; % 3) multiply fft images im_fil = ifft2(im_fil_fft); % 4) inverse fft2 im_fil = im_fil(1+hs:size(im,1)+hs, 1+hs:size(im, 2)+hs); % 5) remove padding Displaying with fft figure(1), imagesc(log(abs(fftshift(im_fft)))), axis image, colormap jet
44 Questions Which has more information, the phase or the magnitude? What happens if you take the phase from one image and combine it with the magnitude from another image?
45 Phase vs. Magnitude Intensity image FFT Use random magnitude Inverse FFT Use random phase Inverse FFT Magnitude Phase
46 Filtering Why does the Gaussian give a nice smooth image, but the square filter give edgy artifacts? Gaussian Box filter
47 Gaussian
48 Box Filter
49 Question Match the spatial domain image to the Fourier magnitude image B A C D E
50 Image half-sizing This image is too big to fit on the screen. How can we reduce it? How to generate a halfsized version?
51 Image sub-sampling 1/8 1/4 Throw away every other row and column to create a 1/2 size image - called image sub-sampling Slide by Steve Seitz
52 Image sub-sampling 1/2 Why does this look so crufty? Aliasing! What do we do? 1/4 (2x zoom) 1/8 (4x zoom) Slide by Steve Seitz
53 Image sub-sampling Source: F. Durand
54 Even worse for synthetic images Source: L. Zhang
55 Aliasing problem 1D example (sinewave): Source: S. Marschner
56 Aliasing problem 1D example (sinewave): Source: S. Marschner
57 Aliasing problem Sub-sampling may be dangerous. Characteristic errors may appear: Wagon wheels rolling the wrong way in movies Checkerboards disintegrate in ray tracing Striped shirts look funny on color television Source: D. Forsyth
58 Aliasing Occurs when your sampling rate is not high enough to capture the amount of detail in your image Can give you the wrong signal/image an alias To do sampling right, need to understand the structure of your signal/image To avoid aliasing: sampling rate 2 * max frequency in the image said another way: two samples per cycle This minimum sampling rate is called the Nyquist rate Source: L. Zhang
59 Wagon-wheel effect (See Source: L. Zhang
60 Wagon-wheel effect
61 Sampling an image Examples of GOOD sampling
62 Undersampling Examples of BAD sampling -> Aliasing
63 Anti-aliasing Forsyth and Ponce 2002
64 Gaussian (low-pass) pre-filtering G 1/4 G 1/8 Gaussian 1/2 Solution: filter the image, then subsample Source: S. Seitz
65 Subsampling with Gaussian pre-filtering Gaussian 1/2 G 1/4 G 1/8 Solution: filter the image, then subsample Source: S. Seitz
66 Compare with... 1/2 1/4 (2x zoom) 1/8 (4x zoom) Source: S. Seitz
67 Why does a lower resolution image still make sense to us? What do we lose? Image:
68 Why do we get different, distance-dependent interpretations of hybrid images??
69 Clues from Human Perception Early processing in humans filters for various orientations and scales of frequency Perceptual cues in the mid-high frequencies dominate perception When we see an image from far away, we are effectively subsampling it Early Visual Processing: Multi-scale edge and blob filters
70 Hybrid Image in FFT Hybrid Image Low-passed Image High-passed Image
71 Upsampling This image is too small for this screen: How can we make it 10 times as big? Simplest approach: repeat each row and column 10 times ( Nearest neighbor interpolation )
72 Image interpolation d = 1 in this example Recall how a digital image is formed It is a discrete point-sampling of a continuous function If we could somehow reconstruct the original function, any new image could be generated, at any resolution and scale Adapted from: S. Seitz
73 Image interpolation d = 1 in this example Recall how a digital image is formed It is a discrete point-sampling of a continuous function If we could somehow reconstruct the original function, any new image could be generated, at any resolution and scale Adapted from: S. Seitz
74 Image interpolation 1 d = 1 in this example What if we don t know? Guess an approximation: Can be done in a principled way: filtering Convert to a continuous function: Reconstruct by convolution with a reconstruction filter, h Adapted from: S. Seitz
75 Image interpolation Ideal reconstruction Nearest-neighbor interpolation Linear interpolation Gaussian reconstruction Source: B. Curless
76 Reconstruction filters What does the 2D version of this hat function look like? performs linear interpolation (tent function) performs bilinear interpolation Often implemented without cross-correlation E.g., Better filters give better resampled images Bicubic is common choice Cubic reconstruction filter
77 Image interpolation Original image: x 10 Nearest-neighbor interpolation Bilinear interpolation Bicubic interpolation
78 Image interpolation Also used for resampling
79 Things to Remember Sometimes it makes sense to think of images and filtering in the frequency domain Fourier analysis Can be faster to filter using FFT for large images (N logn vs. N 2 for auto-correlation) Images are mostly smooth Basis for compression Remember to low-pass before sampling
80 Thank you Next class: Pyramid, template matching
Applications of Image Filters
 02/04/0 Applications of Image Filters Computer Vision CS 543 / ECE 549 University of Illinois Derek Hoiem Review: Image filtering g[, ] f [.,.] h[.,.] 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 90
02/04/0 Applications of Image Filters Computer Vision CS 543 / ECE 549 University of Illinois Derek Hoiem Review: Image filtering g[, ] f [.,.] h[.,.] 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 90
EEM 561 Machine Vision. Week 3: Fourier Transform and Image Pyramids
 EEM 561 Machine Vision Week 3: Fourier Transform and Image Pyramids Spring 2015 Instructor: Hatice Çınar Akakın, Ph.D. haticecinarakakin@anadolu.edu.tr Anadolu University Linear Image Transformations In
EEM 561 Machine Vision Week 3: Fourier Transform and Image Pyramids Spring 2015 Instructor: Hatice Çınar Akakın, Ph.D. haticecinarakakin@anadolu.edu.tr Anadolu University Linear Image Transformations In
Does everyone have an override code?
 Does everyone have an override code? Project 1 due Friday 9pm Review of Filtering Filtering in frequency domain Can be faster than filtering in spatial domain (for large filters) Can help understand effect
Does everyone have an override code? Project 1 due Friday 9pm Review of Filtering Filtering in frequency domain Can be faster than filtering in spatial domain (for large filters) Can help understand effect
Texture and Other Uses of Filters
 CS 1699: Intro to Computer Vision Texture and Other Uses of Filters Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh September 10, 2015 Slides from Kristen Grauman (12-52) and Derek Hoiem (54-83) Plan for
CS 1699: Intro to Computer Vision Texture and Other Uses of Filters Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh September 10, 2015 Slides from Kristen Grauman (12-52) and Derek Hoiem (54-83) Plan for
Filtering in frequency domain
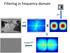 Filtering in frequency domain FFT FFT = Inverse FFT Filtering in frequency domain Can be faster than filtering in spatial domain (for large filters) Can help understand effect of filter Algorithm: 1. Convert
Filtering in frequency domain FFT FFT = Inverse FFT Filtering in frequency domain Can be faster than filtering in spatial domain (for large filters) Can help understand effect of filter Algorithm: 1. Convert
Texture Representation + Image Pyramids
 CS 1674: Intro to Computer Vision Texture Representation + Image Pyramids Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh September 14, 2016 Reminders/Announcements HW2P due tonight, 11:59pm HW3W, HW3P
CS 1674: Intro to Computer Vision Texture Representation + Image Pyramids Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh September 14, 2016 Reminders/Announcements HW2P due tonight, 11:59pm HW3W, HW3P
Image Pyramids and Applications
 Image Pyramids and Applications Computer Vision Jia-Bin Huang, Virginia Tech Golconda, René Magritte, 1953 Administrative stuffs HW 1 will be posted tonight, due 11:59 PM Sept 25 Anonymous feedback Previous
Image Pyramids and Applications Computer Vision Jia-Bin Huang, Virginia Tech Golconda, René Magritte, 1953 Administrative stuffs HW 1 will be posted tonight, due 11:59 PM Sept 25 Anonymous feedback Previous
FOURIER TRANSFORM GABOR FILTERS. and some textons
 FOURIER TRANSFORM GABOR FILTERS and some textons Thank you for the slides. They come mostly from the following sources Alexei Efros CMU Martial Hebert CMU Image sub-sampling 1/8 1/4 Throw away every other
FOURIER TRANSFORM GABOR FILTERS and some textons Thank you for the slides. They come mostly from the following sources Alexei Efros CMU Martial Hebert CMU Image sub-sampling 1/8 1/4 Throw away every other
Templates, Image Pyramids, and Filter Banks
 Templates, Image Pyramids, and Filter Banks Computer Vision James Hays, Brown Slides: Hoiem and others Reminder Project due Friday Fourier Bases Teases away fast vs. slow changes in the image. This change
Templates, Image Pyramids, and Filter Banks Computer Vision James Hays, Brown Slides: Hoiem and others Reminder Project due Friday Fourier Bases Teases away fast vs. slow changes in the image. This change
Lecture 2: 2D Fourier transforms and applications
 Lecture 2: 2D Fourier transforms and applications B14 Image Analysis Michaelmas 2017 Dr. M. Fallon Fourier transforms and spatial frequencies in 2D Definition and meaning The Convolution Theorem Applications
Lecture 2: 2D Fourier transforms and applications B14 Image Analysis Michaelmas 2017 Dr. M. Fallon Fourier transforms and spatial frequencies in 2D Definition and meaning The Convolution Theorem Applications
Computer Vision: 4. Filtering. By I-Chen Lin Dept. of CS, National Chiao Tung University
 Computer Vision: 4. Filtering By I-Chen Lin Dept. of CS, National Chiao Tung University Outline Impulse response and convolution. Linear filter and image pyramid. Textbook: David A. Forsyth and Jean Ponce,
Computer Vision: 4. Filtering By I-Chen Lin Dept. of CS, National Chiao Tung University Outline Impulse response and convolution. Linear filter and image pyramid. Textbook: David A. Forsyth and Jean Ponce,
CPSC 425: Computer Vision
 CPSC 425: Computer Vision Image Credit: https://docs.adaptive-vision.com/4.7/studio/machine_vision_guide/templatematching.html Lecture 9: Template Matching (cont.) and Scaled Representations ( unless otherwise
CPSC 425: Computer Vision Image Credit: https://docs.adaptive-vision.com/4.7/studio/machine_vision_guide/templatematching.html Lecture 9: Template Matching (cont.) and Scaled Representations ( unless otherwise
Review of Filtering. Filtering in frequency domain
 Review of Filtering Filtering in frequency domain Can be faster than filtering in spatial domain (for large filters) Can help understand effect of filter Algorithm: 1. Convert image and filter to fft (fft2
Review of Filtering Filtering in frequency domain Can be faster than filtering in spatial domain (for large filters) Can help understand effect of filter Algorithm: 1. Convert image and filter to fft (fft2
Sampling and Reconstruction. Most slides from Steve Marschner
 Sampling and Reconstruction Most slides from Steve Marschner 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2008 Sampling and Reconstruction Sampled representations How to store and compute
Sampling and Reconstruction Most slides from Steve Marschner 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2008 Sampling and Reconstruction Sampled representations How to store and compute
Scaled representations
 Scaled representations Big bars (resp. spots, hands, etc.) and little bars are both interesting Stripes and hairs, say Inefficient to detect big bars with big filters And there is superfluous detail in
Scaled representations Big bars (resp. spots, hands, etc.) and little bars are both interesting Stripes and hairs, say Inefficient to detect big bars with big filters And there is superfluous detail in
Filters and Pyramids. CSC320: Introduction to Visual Computing Michael Guerzhoy. Many slides from Steve Marschner, Alexei Efros
 Filters and Pyramids Wassily Kandinsky, "Accent in Pink" Many slides from Steve Marschner, Alexei Efros CSC320: Introduction to Visual Computing Michael Guerzhoy Moving Average In 2D What are the weights
Filters and Pyramids Wassily Kandinsky, "Accent in Pink" Many slides from Steve Marschner, Alexei Efros CSC320: Introduction to Visual Computing Michael Guerzhoy Moving Average In 2D What are the weights
CS4442/9542b Artificial Intelligence II prof. Olga Veksler
 CS4442/9542b Artificial Intelligence II prof. Olga Veksler Lecture 8 Computer Vision Introduction, Filtering Some slides from: D. Jacobs, D. Lowe, S. Seitz, A.Efros, X. Li, R. Fergus, J. Hayes, S. Lazebnik,
CS4442/9542b Artificial Intelligence II prof. Olga Veksler Lecture 8 Computer Vision Introduction, Filtering Some slides from: D. Jacobs, D. Lowe, S. Seitz, A.Efros, X. Li, R. Fergus, J. Hayes, S. Lazebnik,
CS4442/9542b Artificial Intelligence II prof. Olga Veksler
 CS4442/9542b Artificial Intelligence II prof. Olga Veksler Lecture 2 Computer Vision Introduction, Filtering Some slides from: D. Jacobs, D. Lowe, S. Seitz, A.Efros, X. Li, R. Fergus, J. Hayes, S. Lazebnik,
CS4442/9542b Artificial Intelligence II prof. Olga Veksler Lecture 2 Computer Vision Introduction, Filtering Some slides from: D. Jacobs, D. Lowe, S. Seitz, A.Efros, X. Li, R. Fergus, J. Hayes, S. Lazebnik,
Filters (cont.) CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University
 Filters (cont.) CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University Today s topics Image Formation Image filters in spatial domain Filter is a mathematical operation of a grid of numbers Smoothing,
Filters (cont.) CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University Today s topics Image Formation Image filters in spatial domain Filter is a mathematical operation of a grid of numbers Smoothing,
Filtering Applications & Edge Detection. GV12/3072 Image Processing.
 Filtering Applications & Edge Detection GV12/3072 1 Outline Sampling & Reconstruction Revisited Anti-Aliasing Edges Edge detection Simple edge detector Canny edge detector Performance analysis Hough Transform
Filtering Applications & Edge Detection GV12/3072 1 Outline Sampling & Reconstruction Revisited Anti-Aliasing Edges Edge detection Simple edge detector Canny edge detector Performance analysis Hough Transform
Low-level Vision Processing Algorithms Speaker: Ito, Dang Supporter: Ishii, Toyama and Y. Murakami
 Low-level Vision Processing Algorithms Speaker: Ito, Dang Supporter: Ishii, Toyama and Y. Murakami Adaptive Systems Lab The University of Aizu Overview Introduction What is Vision Processing? Basic Knowledge
Low-level Vision Processing Algorithms Speaker: Ito, Dang Supporter: Ishii, Toyama and Y. Murakami Adaptive Systems Lab The University of Aizu Overview Introduction What is Vision Processing? Basic Knowledge
Image transformations. Prof. Noah Snavely CS Administrivia
 Image transformations Prof. Noah Snavely CS1114 http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs1114/ Administrivia 2 Last time: Interpolation 3 Nearest neighbor interpolation 4 Bilinear interpolation 5 Bicubic interpolation
Image transformations Prof. Noah Snavely CS1114 http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs1114/ Administrivia 2 Last time: Interpolation 3 Nearest neighbor interpolation 4 Bilinear interpolation 5 Bicubic interpolation
Introduction to Computer Vision. Week 3, Fall 2010 Instructor: Prof. Ko Nishino
 Introduction to Computer Vision Week 3, Fall 2010 Instructor: Prof. Ko Nishino Last Week! Image Sensing " Our eyes: rods and cones " CCD, CMOS, Rolling Shutter " Sensing brightness and sensing color! Projective
Introduction to Computer Vision Week 3, Fall 2010 Instructor: Prof. Ko Nishino Last Week! Image Sensing " Our eyes: rods and cones " CCD, CMOS, Rolling Shutter " Sensing brightness and sensing color! Projective
Announcements. Image Matching! Source & Destination Images. Image Transformation 2/ 3/ 16. Compare a big image to a small image
 2/3/ Announcements PA is due in week Image atching! Leave time to learn OpenCV Think of & implement something creative CS 50 Lecture #5 February 3 rd, 20 2/ 3/ 2 Compare a big image to a small image So
2/3/ Announcements PA is due in week Image atching! Leave time to learn OpenCV Think of & implement something creative CS 50 Lecture #5 February 3 rd, 20 2/ 3/ 2 Compare a big image to a small image So
Texture. Outline. Image representations: spatial and frequency Fourier transform Frequency filtering Oriented pyramids Texture representation
 Texture Outline Image representations: spatial and frequency Fourier transform Frequency filtering Oriented pyramids Texture representation 1 Image Representation The standard basis for images is the set
Texture Outline Image representations: spatial and frequency Fourier transform Frequency filtering Oriented pyramids Texture representation 1 Image Representation The standard basis for images is the set
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps
 Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps Last Time? Monte-Carlo Integration Importance Sampling Ray Tracing vs. Path Tracing source hemisphere What is a Pixel? Sampling & Reconstruction Filters in Computer Graphics
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps Last Time? Monte-Carlo Integration Importance Sampling Ray Tracing vs. Path Tracing source hemisphere What is a Pixel? Sampling & Reconstruction Filters in Computer Graphics
Prof. Feng Liu. Winter /15/2019
 Prof. Feng Liu Winter 2019 http://www.cs.pdx.edu/~fliu/courses/cs410/ 01/15/2019 Last Time Filter 2 Today More on Filter Feature Detection 3 Filter Re-cap noisy image naïve denoising Gaussian blur better
Prof. Feng Liu Winter 2019 http://www.cs.pdx.edu/~fliu/courses/cs410/ 01/15/2019 Last Time Filter 2 Today More on Filter Feature Detection 3 Filter Re-cap noisy image naïve denoising Gaussian blur better
Computer Vision and Graphics (ee2031) Digital Image Processing I
 Computer Vision and Graphics (ee203) Digital Image Processing I Dr John Collomosse J.Collomosse@surrey.ac.uk Centre for Vision, Speech and Signal Processing University of Surrey Learning Outcomes After
Computer Vision and Graphics (ee203) Digital Image Processing I Dr John Collomosse J.Collomosse@surrey.ac.uk Centre for Vision, Speech and Signal Processing University of Surrey Learning Outcomes After
CS5670: Computer Vision
 CS5670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 4: Harris corner detection Szeliski: 4.1 Reading Announcements Project 1 (Hybrid Images) code due next Wednesday, Feb 14, by 11:59pm Artifacts due Friday, Feb
CS5670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 4: Harris corner detection Szeliski: 4.1 Reading Announcements Project 1 (Hybrid Images) code due next Wednesday, Feb 14, by 11:59pm Artifacts due Friday, Feb
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps
 Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps Last Time? Monte-Carlo Integration Importance Sampling Ray Tracing vs. Path Tracing source hemisphere Sampling sensitive to choice of samples less sensitive to choice of samples
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps Last Time? Monte-Carlo Integration Importance Sampling Ray Tracing vs. Path Tracing source hemisphere Sampling sensitive to choice of samples less sensitive to choice of samples
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING
 The image part with relationship ID rid2 was not found in the file. DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING Lecture 6 Wavelets (cont), Lines and edges Tammy Riklin Raviv Electrical and Computer Engineering Ben-Gurion
The image part with relationship ID rid2 was not found in the file. DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING Lecture 6 Wavelets (cont), Lines and edges Tammy Riklin Raviv Electrical and Computer Engineering Ben-Gurion
Fourier analysis and sampling theory
 Reading Required: Shirley, Ch. 9 Recommended: Fourier analysis and sampling theory Ron Bracewell, The Fourier Transform and Its Applications, McGraw-Hill. Don P. Mitchell and Arun N. Netravali, Reconstruction
Reading Required: Shirley, Ch. 9 Recommended: Fourier analysis and sampling theory Ron Bracewell, The Fourier Transform and Its Applications, McGraw-Hill. Don P. Mitchell and Arun N. Netravali, Reconstruction
Why is computer vision difficult?
 Why is computer vision difficult? Viewpoint variation Illumination Scale Why is computer vision difficult? Intra-class variation Motion (Source: S. Lazebnik) Background clutter Occlusion Challenges: local
Why is computer vision difficult? Viewpoint variation Illumination Scale Why is computer vision difficult? Intra-class variation Motion (Source: S. Lazebnik) Background clutter Occlusion Challenges: local
Reading. 2. Fourier analysis and sampling theory. Required: Watt, Section 14.1 Recommended:
 Reading Required: Watt, Section 14.1 Recommended: 2. Fourier analysis and sampling theory Ron Bracewell, The Fourier Transform and Its Applications, McGraw-Hill. Don P. Mitchell and Arun N. Netravali,
Reading Required: Watt, Section 14.1 Recommended: 2. Fourier analysis and sampling theory Ron Bracewell, The Fourier Transform and Its Applications, McGraw-Hill. Don P. Mitchell and Arun N. Netravali,
convolution shift invariant linear system Fourier Transform Aliasing and sampling scale representation edge detection corner detection
 COS 429: COMPUTER VISON Linear Filters and Edge Detection convolution shift invariant linear system Fourier Transform Aliasing and sampling scale representation edge detection corner detection Reading:
COS 429: COMPUTER VISON Linear Filters and Edge Detection convolution shift invariant linear system Fourier Transform Aliasing and sampling scale representation edge detection corner detection Reading:
Texture. Texture. 2) Synthesis. Objectives: 1) Discrimination/Analysis
 Texture Texture D. Forsythe and J. Ponce Computer Vision modern approach Chapter 9 (Slides D. Lowe, UBC) Key issue: How do we represent texture? Topics: Texture segmentation Texture-based matching Texture
Texture Texture D. Forsythe and J. Ponce Computer Vision modern approach Chapter 9 (Slides D. Lowe, UBC) Key issue: How do we represent texture? Topics: Texture segmentation Texture-based matching Texture
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps
 Last Time? Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps 2D Texture Mapping Perspective Correct Interpolation Common Texture Coordinate Projections Bump Mapping Displacement Mapping Environment Mapping Texture Maps for
Last Time? Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps 2D Texture Mapping Perspective Correct Interpolation Common Texture Coordinate Projections Bump Mapping Displacement Mapping Environment Mapping Texture Maps for
Theoretically Perfect Sensor
 Sampling 1/60 Sampling The ray tracer samples the geometry, only gathering information from the parts of the world that interact with a finite number of rays In contrast, a scanline renderer can push all
Sampling 1/60 Sampling The ray tracer samples the geometry, only gathering information from the parts of the world that interact with a finite number of rays In contrast, a scanline renderer can push all
Filtering, scale, orientation, localization, and texture. Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD (with thanks to David Forsyth)
 Filtering, scale, orientation, localization, and texture Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD (with thanks to David Forsyth) Beyond edges we have talked a lot about edges while they are important, it
Filtering, scale, orientation, localization, and texture Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD (with thanks to David Forsyth) Beyond edges we have talked a lot about edges while they are important, it
Digital Image Processing. Lecture 6
 Digital Image Processing Lecture 6 (Enhancement in the Frequency domain) Bu-Ali Sina University Computer Engineering Dep. Fall 2016 Image Enhancement In The Frequency Domain Outline Jean Baptiste Joseph
Digital Image Processing Lecture 6 (Enhancement in the Frequency domain) Bu-Ali Sina University Computer Engineering Dep. Fall 2016 Image Enhancement In The Frequency Domain Outline Jean Baptiste Joseph
Theoretically Perfect Sensor
 Sampling 1/67 Sampling The ray tracer samples the geometry, only gathering information from the parts of the world that interact with a finite number of rays In contrast, a scanline renderer can push all
Sampling 1/67 Sampling The ray tracer samples the geometry, only gathering information from the parts of the world that interact with a finite number of rays In contrast, a scanline renderer can push all
Computer Vision 2. SS 18 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Professur für Bildverarbeitung. Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier
 Computer Vision 2 SS 18 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Professur für Bildverarbeitung Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier 1. IMAGE PROCESSING Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Content of this Chapter Non-linear
Computer Vision 2 SS 18 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Professur für Bildverarbeitung Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier 1. IMAGE PROCESSING Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Content of this Chapter Non-linear
Drawing a Triangle (and an introduction to sampling)
 Lecture 4: Drawing a Triangle (and an introduction to sampling) Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Spring 2017 Assignment 1 is out! https://15462-s17.github.io/asst1_drawsvg/ Let s draw some triangles
Lecture 4: Drawing a Triangle (and an introduction to sampling) Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Spring 2017 Assignment 1 is out! https://15462-s17.github.io/asst1_drawsvg/ Let s draw some triangles
Image gradients and edges April 11 th, 2017
 4//27 Image gradients and edges April th, 27 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis PS due this Friday Announcements Questions? 2 Last time Image formation Linear filters and convolution useful for Image smoothing, removing
4//27 Image gradients and edges April th, 27 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis PS due this Friday Announcements Questions? 2 Last time Image formation Linear filters and convolution useful for Image smoothing, removing
Image gradients and edges April 10 th, 2018
 Image gradients and edges April th, 28 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis PS due this Friday Announcements Questions? 2 Last time Image formation Linear filters and convolution useful for Image smoothing, removing
Image gradients and edges April th, 28 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis PS due this Friday Announcements Questions? 2 Last time Image formation Linear filters and convolution useful for Image smoothing, removing
Edges, interpolation, templates. Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD (with thanks to David Forsyth)
 Edges, interpolation, templates Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD (with thanks to David Forsyth) Gradients and edges edges are points of large gradient magnitude edge detection strategy 1. determine
Edges, interpolation, templates Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD (with thanks to David Forsyth) Gradients and edges edges are points of large gradient magnitude edge detection strategy 1. determine
Broad field that includes low-level operations as well as complex high-level algorithms
 Image processing About Broad field that includes low-level operations as well as complex high-level algorithms Low-level image processing Computer vision Computational photography Several procedures and
Image processing About Broad field that includes low-level operations as well as complex high-level algorithms Low-level image processing Computer vision Computational photography Several procedures and
EECS 556 Image Processing W 09. Image enhancement. Smoothing and noise removal Sharpening filters
 EECS 556 Image Processing W 09 Image enhancement Smoothing and noise removal Sharpening filters What is image processing? Image processing is the application of 2D signal processing methods to images Image
EECS 556 Image Processing W 09 Image enhancement Smoothing and noise removal Sharpening filters What is image processing? Image processing is the application of 2D signal processing methods to images Image
Edge Detection. Computer Vision Shiv Ram Dubey, IIIT Sri City
 Edge Detection Computer Vision Shiv Ram Dubey, IIIT Sri City Previous two classes: Image Filtering Spatial domain Smoothing, sharpening, measuring texture * = FFT FFT Inverse FFT = Frequency domain Denoising,
Edge Detection Computer Vision Shiv Ram Dubey, IIIT Sri City Previous two classes: Image Filtering Spatial domain Smoothing, sharpening, measuring texture * = FFT FFT Inverse FFT = Frequency domain Denoising,
CS1114 Section 8: The Fourier Transform March 13th, 2013
 CS1114 Section 8: The Fourier Transform March 13th, 2013 http://xkcd.com/26 Today you will learn about an extremely useful tool in image processing called the Fourier transform, and along the way get more
CS1114 Section 8: The Fourier Transform March 13th, 2013 http://xkcd.com/26 Today you will learn about an extremely useful tool in image processing called the Fourier transform, and along the way get more
Image pyramids and their applications Bill Freeman and Fredo Durand Feb. 28, 2006
 Image pyramids and their applications 6.882 Bill Freeman and Fredo Durand Feb. 28, 2006 Image pyramids Gaussian Laplacian Wavelet/QMF Steerable pyramid http://www-bcs.mit.edu/people/adelson/pub_pdfs/pyramid83.pdf
Image pyramids and their applications 6.882 Bill Freeman and Fredo Durand Feb. 28, 2006 Image pyramids Gaussian Laplacian Wavelet/QMF Steerable pyramid http://www-bcs.mit.edu/people/adelson/pub_pdfs/pyramid83.pdf
Edge and Texture. CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University
 Edge and Texture CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University Filters for features Previously, thinking of filtering as a way to remove or reduce noise Now, consider how filters will allow us
Edge and Texture CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University Filters for features Previously, thinking of filtering as a way to remove or reduce noise Now, consider how filters will allow us
Anno accademico 2006/2007. Davide Migliore
 Robotica Anno accademico 6/7 Davide Migliore migliore@elet.polimi.it Today What is a feature? Some useful information The world of features: Detectors Edges detection Corners/Points detection Descriptors?!?!?
Robotica Anno accademico 6/7 Davide Migliore migliore@elet.polimi.it Today What is a feature? Some useful information The world of features: Detectors Edges detection Corners/Points detection Descriptors?!?!?
Edges, interpolation, templates. Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD (with thanks to David Forsyth)
 Edges, interpolation, templates Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD (with thanks to David Forsyth) Edge detection edge detection has many applications in image processing an edge detector implements
Edges, interpolation, templates Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD (with thanks to David Forsyth) Edge detection edge detection has many applications in image processing an edge detector implements
Mosaics. Today s Readings
 Mosaics VR Seattle: http://www.vrseattle.com/ Full screen panoramas (cubic): http://www.panoramas.dk/ Mars: http://www.panoramas.dk/fullscreen3/f2_mars97.html Today s Readings Szeliski and Shum paper (sections
Mosaics VR Seattle: http://www.vrseattle.com/ Full screen panoramas (cubic): http://www.panoramas.dk/ Mars: http://www.panoramas.dk/fullscreen3/f2_mars97.html Today s Readings Szeliski and Shum paper (sections
Computer Vision I. Announcements. Fourier Tansform. Efficient Implementation. Edge and Corner Detection. CSE252A Lecture 13.
 Announcements Edge and Corner Detection HW3 assigned CSE252A Lecture 13 Efficient Implementation Both, the Box filter and the Gaussian filter are separable: First convolve each row of input image I with
Announcements Edge and Corner Detection HW3 assigned CSE252A Lecture 13 Efficient Implementation Both, the Box filter and the Gaussian filter are separable: First convolve each row of input image I with
Image Filtering, Warping and Sampling
 Image Filtering, Warping and Sampling Connelly Barnes CS 4810 University of Virginia Acknowledgement: slides by Jason Lawrence, Misha Kazhdan, Allison Klein, Tom Funkhouser, Adam Finkelstein and David
Image Filtering, Warping and Sampling Connelly Barnes CS 4810 University of Virginia Acknowledgement: slides by Jason Lawrence, Misha Kazhdan, Allison Klein, Tom Funkhouser, Adam Finkelstein and David
Lecture 4: Spatial Domain Transformations
 # Lecture 4: Spatial Domain Transformations Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Reminder 2 nd Quiz on the manipulator Part is this Fri, April 7 205, :5 AM to :0 PM Open Book, Open Notes, Focus on the material
# Lecture 4: Spatial Domain Transformations Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Reminder 2 nd Quiz on the manipulator Part is this Fri, April 7 205, :5 AM to :0 PM Open Book, Open Notes, Focus on the material
Drawing a Triangle (and an Intro to Sampling)
 Lecture 4: Drawing a Triangle (and an Intro to Sampling) Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Spring 2018 HW 0.5 Due, HW 1 Out Today! GOAL: Implement a basic rasterizer - (Topic of today s lecture) - We
Lecture 4: Drawing a Triangle (and an Intro to Sampling) Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Spring 2018 HW 0.5 Due, HW 1 Out Today! GOAL: Implement a basic rasterizer - (Topic of today s lecture) - We
Local Image Features
 Local Image Features Computer Vision Read Szeliski 4.1 James Hays Acknowledgment: Many slides from Derek Hoiem and Grauman&Leibe 2008 AAAI Tutorial Flashed Face Distortion 2nd Place in the 8th Annual Best
Local Image Features Computer Vision Read Szeliski 4.1 James Hays Acknowledgment: Many slides from Derek Hoiem and Grauman&Leibe 2008 AAAI Tutorial Flashed Face Distortion 2nd Place in the 8th Annual Best
Local Image Features
 Local Image Features Computer Vision CS 143, Brown Read Szeliski 4.1 James Hays Acknowledgment: Many slides from Derek Hoiem and Grauman&Leibe 2008 AAAI Tutorial This section: correspondence and alignment
Local Image Features Computer Vision CS 143, Brown Read Szeliski 4.1 James Hays Acknowledgment: Many slides from Derek Hoiem and Grauman&Leibe 2008 AAAI Tutorial This section: correspondence and alignment
Lecture 6 Basic Signal Processing
 Lecture 6 Basic Signal Processing Copyright c1996, 1997 by Pat Hanrahan Motivation Many aspects of computer graphics and computer imagery differ from aspects of conventional graphics and imagery because
Lecture 6 Basic Signal Processing Copyright c1996, 1997 by Pat Hanrahan Motivation Many aspects of computer graphics and computer imagery differ from aspects of conventional graphics and imagery because
Peripheral drift illusion
 Peripheral drift illusion Does it work on other animals? Computer Vision Motion and Optical Flow Many slides adapted from J. Hays, S. Seitz, R. Szeliski, M. Pollefeys, K. Grauman and others Video A video
Peripheral drift illusion Does it work on other animals? Computer Vision Motion and Optical Flow Many slides adapted from J. Hays, S. Seitz, R. Szeliski, M. Pollefeys, K. Grauman and others Video A video
ME/CS 132: Introduction to Vision-based Robot Navigation! Low-level Image Processing" Larry Matthies"
 ME/CS 132: Introduction to Vision-based Robot Navigation! Low-level Image Processing" Larry Matthies" lhm@jpl.nasa.gov, 818-354-3722" Announcements" First homework grading is done! Second homework is due
ME/CS 132: Introduction to Vision-based Robot Navigation! Low-level Image Processing" Larry Matthies" lhm@jpl.nasa.gov, 818-354-3722" Announcements" First homework grading is done! Second homework is due
Biomedical Image Analysis. Spatial Filtering
 Biomedical Image Analysis Contents: Spatial Filtering The mechanics of Spatial Filtering Smoothing and sharpening filters BMIA 15 V. Roth & P. Cattin 1 The Mechanics of Spatial Filtering Spatial filter:
Biomedical Image Analysis Contents: Spatial Filtering The mechanics of Spatial Filtering Smoothing and sharpening filters BMIA 15 V. Roth & P. Cattin 1 The Mechanics of Spatial Filtering Spatial filter:
Image gradients and edges
 Image gradients and edges April 7 th, 2015 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis Announcements PS0 due this Friday Questions? 2 Last time Image formation Linear filters and convolution useful for Image smoothing, removing
Image gradients and edges April 7 th, 2015 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis Announcements PS0 due this Friday Questions? 2 Last time Image formation Linear filters and convolution useful for Image smoothing, removing
CS 4495 Computer Vision. Linear Filtering 2: Templates, Edges. Aaron Bobick. School of Interactive Computing. Templates/Edges
 CS 4495 Computer Vision Linear Filtering 2: Templates, Edges Aaron Bobick School of Interactive Computing Last time: Convolution Convolution: Flip the filter in both dimensions (right to left, bottom to
CS 4495 Computer Vision Linear Filtering 2: Templates, Edges Aaron Bobick School of Interactive Computing Last time: Convolution Convolution: Flip the filter in both dimensions (right to left, bottom to
Sampling and Reconstruction
 Sampling and Reconstruction Sampling and Reconstruction Sampling and Spatial Resolution Spatial Aliasing Problem: Spatial aliasing is insufficient sampling of data along the space axis, which occurs because
Sampling and Reconstruction Sampling and Reconstruction Sampling and Spatial Resolution Spatial Aliasing Problem: Spatial aliasing is insufficient sampling of data along the space axis, which occurs because
Lecture 5: Frequency Domain Transformations
 #1 Lecture 5: Frequency Domain Transformations Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu From Last Lecture Spatial Domain Transformation Point Processing for Enhancement Area/Mask Processing Transformations Image
#1 Lecture 5: Frequency Domain Transformations Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu From Last Lecture Spatial Domain Transformation Point Processing for Enhancement Area/Mask Processing Transformations Image
UNIT-2 IMAGE REPRESENTATION IMAGE REPRESENTATION IMAGE SENSORS IMAGE SENSORS- FLEX CIRCUIT ASSEMBLY
 18-08-2016 UNIT-2 In the following slides we will consider what is involved in capturing a digital image of a real-world scene Image sensing and representation Image Acquisition Sampling and quantisation
18-08-2016 UNIT-2 In the following slides we will consider what is involved in capturing a digital image of a real-world scene Image sensing and representation Image Acquisition Sampling and quantisation
Computer Vision. Fourier Transform. 20 January Copyright by NHL Hogeschool and Van de Loosdrecht Machine Vision BV All rights reserved
 Van de Loosdrecht Machine Vision Computer Vision Fourier Transform 20 January 2017 Copyright 2001 2017 by NHL Hogeschool and Van de Loosdrecht Machine Vision BV All rights reserved j.van.de.loosdrecht@nhl.nl,
Van de Loosdrecht Machine Vision Computer Vision Fourier Transform 20 January 2017 Copyright 2001 2017 by NHL Hogeschool and Van de Loosdrecht Machine Vision BV All rights reserved j.van.de.loosdrecht@nhl.nl,
Introduction to Computer Vision
 Introduction to Computer Vision Michael J. Black Sept 2009 Lecture 9: Image gradients, feature detection, correlation Goals Image gradient Filtering as feature detection Convolution vs correlation Time
Introduction to Computer Vision Michael J. Black Sept 2009 Lecture 9: Image gradients, feature detection, correlation Goals Image gradient Filtering as feature detection Convolution vs correlation Time
Digital Image Processing. Image Enhancement in the Frequency Domain
 Digital Image Processing Image Enhancement in the Frequency Domain Topics Frequency Domain Enhancements Fourier Transform Convolution High Pass Filtering in Frequency Domain Low Pass Filtering in Frequency
Digital Image Processing Image Enhancement in the Frequency Domain Topics Frequency Domain Enhancements Fourier Transform Convolution High Pass Filtering in Frequency Domain Low Pass Filtering in Frequency
Aliasing and Antialiasing. ITCS 4120/ Aliasing and Antialiasing
 Aliasing and Antialiasing ITCS 4120/5120 1 Aliasing and Antialiasing What is Aliasing? Errors and Artifacts arising during rendering, due to the conversion from a continuously defined illumination field
Aliasing and Antialiasing ITCS 4120/5120 1 Aliasing and Antialiasing What is Aliasing? Errors and Artifacts arising during rendering, due to the conversion from a continuously defined illumination field
Image processing in frequency Domain
 Image processing in frequency Domain Introduction to Frequency Domain Deal with images in: -Spatial domain -Frequency domain Frequency Domain In the frequency or Fourier domain, the value and location
Image processing in frequency Domain Introduction to Frequency Domain Deal with images in: -Spatial domain -Frequency domain Frequency Domain In the frequency or Fourier domain, the value and location
What will we learn? Neighborhood processing. Convolution and correlation. Neighborhood processing. Chapter 10 Neighborhood Processing
 What will we learn? Lecture Slides ME 4060 Machine Vision and Vision-based Control Chapter 10 Neighborhood Processing By Dr. Debao Zhou 1 What is neighborhood processing and how does it differ from point
What will we learn? Lecture Slides ME 4060 Machine Vision and Vision-based Control Chapter 10 Neighborhood Processing By Dr. Debao Zhou 1 What is neighborhood processing and how does it differ from point
Sampling and Monte-Carlo Integration
 Sampling and Monte-Carlo Integration Sampling and Monte-Carlo Integration Last Time Pixels are samples Sampling theorem Convolution & multiplication Aliasing: spectrum replication Ideal filter And its
Sampling and Monte-Carlo Integration Sampling and Monte-Carlo Integration Last Time Pixels are samples Sampling theorem Convolution & multiplication Aliasing: spectrum replication Ideal filter And its
CS 2770: Computer Vision. Edges and Segments. Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh February 21, 2017
 CS 2770: Computer Vision Edges and Segments Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh February 21, 2017 Edges vs Segments Figure adapted from J. Hays Edges vs Segments Edges More low-level Don t
CS 2770: Computer Vision Edges and Segments Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh February 21, 2017 Edges vs Segments Figure adapted from J. Hays Edges vs Segments Edges More low-level Don t
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393
 Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 21 Nov 16 th, 2017 Pranav Mantini Ack: Shah. M Image Processing Geometric Transformation Point Operations Filtering (spatial, Frequency) Input Restoration/
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 21 Nov 16 th, 2017 Pranav Mantini Ack: Shah. M Image Processing Geometric Transformation Point Operations Filtering (spatial, Frequency) Input Restoration/
Video Mosaics for Virtual Environments, R. Szeliski. Review by: Christopher Rasmussen
 Video Mosaics for Virtual Environments, R. Szeliski Review by: Christopher Rasmussen September 19, 2002 Announcements Homework due by midnight Next homework will be assigned Tuesday, due following Tuesday.
Video Mosaics for Virtual Environments, R. Szeliski Review by: Christopher Rasmussen September 19, 2002 Announcements Homework due by midnight Next homework will be assigned Tuesday, due following Tuesday.
Frequency analysis, pyramids, texture analysis, applications (face detection, category recognition)
 Frequency analysis, pyramids, texture analysis, applications (face detection, category recognition) Outline Measuring frequencies in images: Definitions, properties Sampling issues Relation with Gaussian
Frequency analysis, pyramids, texture analysis, applications (face detection, category recognition) Outline Measuring frequencies in images: Definitions, properties Sampling issues Relation with Gaussian
Ulrik Söderström 17 Jan Image Processing. Introduction
 Ulrik Söderström ulrik.soderstrom@tfe.umu.se 17 Jan 2017 Image Processing Introduction Image Processsing Typical goals: Improve images for human interpretation Image processing Processing of images for
Ulrik Söderström ulrik.soderstrom@tfe.umu.se 17 Jan 2017 Image Processing Introduction Image Processsing Typical goals: Improve images for human interpretation Image processing Processing of images for
Edge and corner detection
 Edge and corner detection Prof. Stricker Doz. G. Bleser Computer Vision: Object and People Tracking Goals Where is the information in an image? How is an object characterized? How can I find measurements
Edge and corner detection Prof. Stricker Doz. G. Bleser Computer Vision: Object and People Tracking Goals Where is the information in an image? How is an object characterized? How can I find measurements
Edge Detection CSC 767
 Edge Detection CSC 767 Edge detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Most semantic and shape information from the image can be encoded in the edges More compact than pixels
Edge Detection CSC 767 Edge detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Most semantic and shape information from the image can be encoded in the edges More compact than pixels
CS 558: Computer Vision 3 rd Set of Notes
 1 CS 558: Computer Vision 3 rd Set of Notes Instructor: Philippos Mordohai Webpage: www.cs.stevens.edu/~mordohai E-mail: Philippos.Mordohai@stevens.edu Office: Lieb 215 Overview Denoising Based on slides
1 CS 558: Computer Vision 3 rd Set of Notes Instructor: Philippos Mordohai Webpage: www.cs.stevens.edu/~mordohai E-mail: Philippos.Mordohai@stevens.edu Office: Lieb 215 Overview Denoising Based on slides
Fourier Transform in Image Processing. CS/BIOEN 6640 U of Utah Guido Gerig (slides modified from Marcel Prastawa 2012)
 Fourier Transform in Image Processing CS/BIOEN 6640 U of Utah Guido Gerig (slides modified from Marcel Prastawa 2012) 1D: Common Transform Pairs Summary source FT Properties: Convolution See book DIP 4.2.5:
Fourier Transform in Image Processing CS/BIOEN 6640 U of Utah Guido Gerig (slides modified from Marcel Prastawa 2012) 1D: Common Transform Pairs Summary source FT Properties: Convolution See book DIP 4.2.5:
CS 534: Computer Vision Texture
 CS 534: Computer Vision Texture Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science CS 534 Texture - 1 Outlines Finding templates by convolution What is Texture Co-occurrence matrices for texture Spatial Filtering
CS 534: Computer Vision Texture Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science CS 534 Texture - 1 Outlines Finding templates by convolution What is Texture Co-occurrence matrices for texture Spatial Filtering
Schedule for Rest of Semester
 Schedule for Rest of Semester Date Lecture Topic 11/20 24 Texture 11/27 25 Review of Statistics & Linear Algebra, Eigenvectors 11/29 26 Eigenvector expansions, Pattern Recognition 12/4 27 Cameras & calibration
Schedule for Rest of Semester Date Lecture Topic 11/20 24 Texture 11/27 25 Review of Statistics & Linear Algebra, Eigenvectors 11/29 26 Eigenvector expansions, Pattern Recognition 12/4 27 Cameras & calibration
Learning and Inferring Depth from Monocular Images. Jiyan Pan April 1, 2009
 Learning and Inferring Depth from Monocular Images Jiyan Pan April 1, 2009 Traditional ways of inferring depth Binocular disparity Structure from motion Defocus Given a single monocular image, how to infer
Learning and Inferring Depth from Monocular Images Jiyan Pan April 1, 2009 Traditional ways of inferring depth Binocular disparity Structure from motion Defocus Given a single monocular image, how to infer
Sampling and Reconstruction
 Page 1 Sampling and Reconstruction The sampling and reconstruction process Real world: continuous Digital world: discrete Basic signal processing Fourier transforms The convolution theorem The sampling
Page 1 Sampling and Reconstruction The sampling and reconstruction process Real world: continuous Digital world: discrete Basic signal processing Fourier transforms The convolution theorem The sampling
Vision: From Eye to Brain (Chap 3)
 Vision: From Eye to Brain (Chap 3) Lecture 7 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 early visual pathway eye eye optic nerve optic chiasm optic tract
Vision: From Eye to Brain (Chap 3) Lecture 7 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 early visual pathway eye eye optic nerve optic chiasm optic tract
CPSC 425: Computer Vision
 1 / 92 CPSC 425: Computer Vision Instructor: Jim Little little@cs.ubc.ca Department of Computer Science University of British Columbia Lecture Notes 2016/2017 Term 2 2 / 92 Menu February 14, 2017 Topics:
1 / 92 CPSC 425: Computer Vision Instructor: Jim Little little@cs.ubc.ca Department of Computer Science University of British Columbia Lecture Notes 2016/2017 Term 2 2 / 92 Menu February 14, 2017 Topics:
Wikipedia - Mysid
 Wikipedia - Mysid Erik Brynjolfsson, MIT Filtering Edges Corners Feature points Also called interest points, key points, etc. Often described as local features. Szeliski 4.1 Slides from Rick Szeliski,
Wikipedia - Mysid Erik Brynjolfsson, MIT Filtering Edges Corners Feature points Also called interest points, key points, etc. Often described as local features. Szeliski 4.1 Slides from Rick Szeliski,
Computer Graphics. Sampling Theory & Anti-Aliasing. Philipp Slusallek
 Computer Graphics Sampling Theory & Anti-Aliasing Philipp Slusallek Dirac Comb (1) Constant & δ-function flash Comb/Shah function 2 Dirac Comb (2) Constant & δ-function Duality f(x) = K F(ω) = K (ω) And
Computer Graphics Sampling Theory & Anti-Aliasing Philipp Slusallek Dirac Comb (1) Constant & δ-function flash Comb/Shah function 2 Dirac Comb (2) Constant & δ-function Duality f(x) = K F(ω) = K (ω) And
Image Transformation Techniques Dr. Rajeev Srivastava Dept. of Computer Engineering, ITBHU, Varanasi
 Image Transformation Techniques Dr. Rajeev Srivastava Dept. of Computer Engineering, ITBHU, Varanasi 1. Introduction The choice of a particular transform in a given application depends on the amount of
Image Transformation Techniques Dr. Rajeev Srivastava Dept. of Computer Engineering, ITBHU, Varanasi 1. Introduction The choice of a particular transform in a given application depends on the amount of
CS448f: Image Processing For Photography and Vision. Fast Filtering
 CS448f: Image Processing For Photography and Vision Fast Filtering Problems in Computer Vision Computer Vision in One Slide 1) Extract some features from some images 2) Use these to formulate some (hopefully
CS448f: Image Processing For Photography and Vision Fast Filtering Problems in Computer Vision Computer Vision in One Slide 1) Extract some features from some images 2) Use these to formulate some (hopefully
Image Stitching. Slides from Rick Szeliski, Steve Seitz, Derek Hoiem, Ira Kemelmacher, Ali Farhadi
 Image Stitching Slides from Rick Szeliski, Steve Seitz, Derek Hoiem, Ira Kemelmacher, Ali Farhadi Combine two or more overlapping images to make one larger image Add example Slide credit: Vaibhav Vaish
Image Stitching Slides from Rick Szeliski, Steve Seitz, Derek Hoiem, Ira Kemelmacher, Ali Farhadi Combine two or more overlapping images to make one larger image Add example Slide credit: Vaibhav Vaish
Edge detection. Winter in Kraków photographed by Marcin Ryczek
 Edge detection Winter in Kraków photographed by Marcin Ryczek Edge detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, most semantic and shape information from the image
Edge detection Winter in Kraków photographed by Marcin Ryczek Edge detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, most semantic and shape information from the image
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 14 FIFO 2 and SIFT. Recap and Outline
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 14 FIFO 2 and SIFT Oct. 15, 2013 Prof. Ronald Fearing Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley (slides courtesy of Prof. John Wawrzynek)
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 14 FIFO 2 and SIFT Oct. 15, 2013 Prof. Ronald Fearing Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley (slides courtesy of Prof. John Wawrzynek)
Category vs. instance recognition
 Category vs. instance recognition Category: Find all the people Find all the buildings Often within a single image Often sliding window Instance: Is this face James? Find this specific famous building
Category vs. instance recognition Category: Find all the people Find all the buildings Often within a single image Often sliding window Instance: Is this face James? Find this specific famous building
