Smart GIS Course. Developed By. Mohamed Elsayed Elshayal. Elshayal Smart GIS Map Editor and Surface Analysis. First Arabian GIS Software
|
|
|
- Hope Curtis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Smart GIS Course Developed By Mohamed Elsayed Elshayal Elshayal Smart GIS Map Editor and Surface Analysis First Arabian GIS Software Cairo Egypt Copyright Free for None Commercial Use This Software is Independent of any Commercial Software Package, or Code Library This Software is Built by Individuals and Not Supported by any Organization Page 1 of 36
2 GIS Course Syllabus 1) INTRODUCTION... 4 A) Q. WHAT IS A GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM?... 4 B) THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN RASTER AND VECTOR MAPS... 4 C) THE RELATION BETWEEN VECTOR SPATIAL LOCATION AND ATTRIBUTE DATA BASE... 5 D) GIS SHAPE FILE TYPES 2D & 3D (POINT POLYLINE POLYGON) ) COORDINATES SYSTEMS... 6 A) LON AND LAT GEOGRAPHIC COORDINATE SYSTEM... 6 B) UNIVERSAL TRANSVERSE MERCATOR COORDINATE SYSTEM UTM... 6 C) CONVERTING COORDINATES BETWEEN LON LAT AND UTM... 6 D) UTM MAP PROJECTION ) SPATIAL DIGITIZING AND EDITING... 8 A) BUILDING NEW SHAPE FILE SPATIAL AND DATA STRUCTURE... 8 B) DIGITIZING SPATIAL SHAPE FILE ( FEATURE PART VERTEX )... 9 C) EDITING SHAPE FILE ( FEATURE PART VERTEX ) D) MOVE SETTINGS E) MAP VIEW F) CONVERTING BETWEEN SHAPE FILE TYPES 2D & 3D (POINT POLYLINE POLYGON) G) LAYER PROPERTIES ) ATTRIBUTE DATA TABLE A) MODIFYING DBF FILE DATA STRUCTURE B) EDITING DATA TABLE C) RUNNING VB SCRIPT IN DATA TABLE FIELDS D) EDITING ONE FEATURE (RECORD) ) GIS ANALYSIS AND SELECTION A) SPATIAL LOCATION ANALYSIS AND SELECTION B) ATTRIBUTE DATA BASE ANALYSIS AND SELECTION C) NESTED ATTRIBUTE DATA BASE ANALYSIS AND SELECTION D) SPATIAL FEATURES SNAPPING AND DIVIDING E) SHORTEST PATH ANALYSIS ) SATELLITES IMAGES A) GOOGLE EARTH SETTINGS B) DOWNLOAD FROM GOOGLE EARTH C) SAVE IMAGES Page 2 of 36
3 7) SURFACE ANALYSIS A) DOWNLOADING (ASTER AND SRTM) NASA GEO DEM HEIGHT FILES B) CONVERT (ASTER AND SRTM) NASA GEO DEM HEIGHT FILES TO TIN SHAPE FILE C) CONVERT ASTER NASA GEO DEM TO COLOR VALUE BMP FILE D) BUILDING CONTOURS FROM ASTER NASA GEO DEM E) BUILDING TIN SURFACE ANALYSIS F) BUILDING CONTOURS SURFACE(S) ANALYSIS G) CONVERTING 2D TO 3D SURFACE ANALYSIS H) CALCULATING AREA AND VOLUME OF SURFACE(S) ) GIS MISALLIANCE TOOLS A) CONVERTING AUTOCAD FILES TO GIS SHAPE FILES B) CONVERTING GIS SHAPE FILES TO AUTOCAD FILES C) SYNCHRONIZE GOOGLE EARTH WITH LON LAT GEOGRAPHIC MAPS ) TRAINING ( BUILDING A GIS PROJECT ) A) DETERMINE A SPECIFIC SMALL WORKING AREA OR CITY B) DOWNLOADING SATELLITE IMAGES OF THE WORKING AREA C) BUILDING ROADS AND BUILDING SHAPE FILES LAYERS D) DIGITIZING THE WORKING AREA ROADS AND BUILDING LAYERS E) ENTERING THE AVAILABLE ATTRIBUTE DATA OF THE DIGITIZED LAYERS F) SPATIAL AND ATTRIBUTE DATA ANALYSIS OF THE DIGITIZED LAYERS G) DOWNLOADING ASTER DEM NASA HEIGHT FILE OF THE WORKING AREA H) SURFACE ANALYSIS OF THE WORKING AREA I) CONVERTING DIGITIZED GIS LAYERS TO AUTOCAD J) SAVE IMAGES OF THE PRODUCED MAP (PROJECT GALLERY) Page 3 of 36
4 1) Introduction A) Q. What is a Geographic Information System? A. Geographic Information System (GIS) is a computer program for storing, retrieving, analyzing, and displaying cartographic data. Vector Spatial Location Data = X, Y, Z Attribute Data Base = Data Information B) The Difference between Raster and Vector Maps Maps in Geographic Information Systems are represented thematically. A standard topographic map will show roads, rivers, contour elevations, vegetation, human settlement patterns and other features on a single map sheet. In a GIS these features are categorized separately and stored in different map themes or overlays. For example, roads will be stored in a separate overlay. Likewise, rivers and streams will each be stored as a separate theme. This way of organizing data in the GIS makes maps much more flexible to use since these themes can be combined in any manner that is useful. The following illustration shows conceptually how maps are stored as themes in a GIS. Each different theme is stored on a separate overlay. The overlays on the left represent a vector based GIS, where the information is stored as a series of points, lines and polygons. The overlays on the right represent a raster based GIS, where the information is stored as a series of discrete units called cells. Page 4 of 36
5 C) The Relation between Vector Spatial Location and Attribute Data Base Each Spatial Layer is consist of many Spatial features Each Spatial Feature consist of many vertexes (x, y, z) Each Spatial Layer is related to one Attribute Data Base Table Each Spatial Feature is related to one Attribute Data Base Record Each Record consist of many fields (up to 255) D) GIS Shape File types 2D & 3D (Point Polyline Polygon) Shp file contain spatial Location data of each feature Which are:- o Type 2D & 3D (Point Polyline Polygon) o Number of Parts o Number of Vertexes o X,Y, and Z of each vertex Dbf file contain Attribute Data o Each Attribute Data table consist of many records o Each record consist of many fields (up to 255) Shx file is a relation file between the Shp file and Dbf fie Point Layer consist of one vertex per Feature(x, y, z) Polyline Layer consist of many vertexes per Feature Polygon Layer consist of many vertexes per Feature and closed Page 5 of 36
6 2) Coordinates Systems A) Lon and Lat Geographic Coordinate System The geographic latitude (abbreviation: Lat., or phi) of a point on the Earth's surface is the angle between the equatorial plane and a line that passes through that point The North Pole is 90 N; the south pole is 90 S. The 0 parallel of latitude is designated the equator, the fundamental plane of all geographic coordinate systems. The equator divides the globe into Northern and Southern Hemispheres. The Longitude (abbreviation: Long., or lambda) of a point on the Earth's surface is the angle east or west from a reference meridian to another meridian that passes through that point. All meridians are halves of great ellipses (often improperly called great circles), which converge at the north and south poles. B) Universal Transverse Mercator Coordinate System UTM The UTM system divides the surface of Earth between 80 S and 84 N latitude into 60 zones, each 6 of longitude in width and centered over a meridian of longitude. Zone 1 is bounded by longitude 180 to 174 W and is centered on the 177th West meridian. Zone numbering increases in an easterly direction. Each of the 60 longitude zones in the UTM system is based on a transverse Mercator projection, which is capable of mapping a region of large north-south extent with a low amount of distortion. By using narrow zones of 6 (up to 800 km) in width, and reducing the scale factor along the central meridian by only to (a reduction of 1:2500), the amount of distortion is held below 1 part in 1,000 inside each zone. Distortion of scale increases to at the outer zone boundaries along the equator. C) Converting Coordinates Between Lon Lat and UTM Converting Coordinates System Calculator Page 6 of 36
7 D) UTM Map Projection AA Airy 1930 AN Australian National BR Bessel 1841 Ethiopia Indonesia Japan Korea BN Bessel 1841 Nambia CC Clarke 1866 (NAD 1927) CD Clarke 1880 EB Everest Brunei & E. Malasia (Sabah & Sarawak) EA Everest India 1830 EC Everest India 1956 EF Everest Pakistan EE Everest W. Malasia and Singapore 1948 ED Everest W. Malasia 1969 RF Geodetic Reference System 1980 (NAD 1983) HE Helmert 1906 HO Hough 1960 ID Indonesian 1974 IN International 1924 KA Krassovsky 1940 AM Modified Airy FA Modified Fischer 1960 (South Asia) SA South American 1969 WD World Geodetic System 1972 (WGS 72) WE World Geodetic System 1984 (WGS 84) Page 7 of 36
8 3) Spatial Digitizing and Editing A) Building New Shape File Spatial and Data Structure Menu Layers New Layer Select Layer type Building New Spatial Shape File Move up, Moves the selected layer up Move Down, moves the selected layer down Show all Layers Hide all Layers New Layer, Build a new Layer Add Layer, add an existing layer on the map viewer Save Layer Save Layer as, save the layer with different name Rectify Image (2 points) Un Rectify Image Validate Layer boundaries Go to Layer in Google Earth Remove layer Remove deleted features Import structure from Reload Layer Set Layer Data Source Data Table Layer Properties Zoom to Layer Page 8 of 36
9 B) Digitizing Spatial Shape File ( Feature Part Vertex ) Buttons Add New Feature Start Digitizing Digitizing Spatial Shape file Finish Drawing Start Drawing Circle in Active Layer Add New Vertex in Editing Part Add New Part in Editing Feature Full extend Zoom in Zoom out Center Pan move Start Pan mode Map Scale Map Projection and Unit Zoom Previous Zoom Next Refresh map Copy Map to Clipboard Page 9 of 36
10 C) Editing Shape File ( Feature Part Vertex ) Editing Spatial Shape file Buttons Edit Feature Click cursor on the Feature Right Click Undo Drawing Map Redo Drawing Map Insert Vertex Delete Vertex Delete Part Delete Feature Divide Feature Combine Feature Edit Feature Data Move Distance Move to X, Y Move Settings Set Pivot Point Rotate Scale Rotate Scale menu Go to Feature in Google Earth Bring Part to Front Send Part to Back Invert part Direction Add New Vertex in Editing Part Add New Part in Editing Feature Length Area Stop Edit Page 10 of 36
11 D) Move Settings Editing Spatial Shape file Menu Layers Move Settings Press Ctrl while moving or Rotating or Scaling to apply movement on This Vertex This Part This Feature All Selected Features in Editing Layer All Features in Editing Layer All Selected Features in All Visible Layers (None Image) All Features in All Visible Layers (None Images) Press Shift while Moving to Snap or Press Alt while Moving to Right Angle E) Map View Menu View Page 11 of 36
12 F) Converting between Shape File types 2D & 3D (Point Polyline Polygon) Menu Tools Convert Shape Type and Grouping Converting Shape Type and Grouping Select Destination Layer Select Criteria (All Feature or Inside Selected Features or Outside Selected Features) Select Output Shape File Select Output Shape File Type Select Group By or Not Select Summing Numerical Fields or Not Select Group By Field Page 12 of 36
13 G) Layer Properties Menu Layers Layer Properties General Layer Properties General Option Select Visible or not Select on which Layers, your selection will be applied Select Show Vertex or Not Select Vertex Width Select Always show to view the layer all the time Select Show When Scale between Min Scale and Max Scale Menu Layers Layer Properties Color Layer Properties Color Option Select Draw Fore Color and Draw Fill Color Select Draw Mode Select Draw Style Select Draw Width Select Draw Fill Style Select Thematic Field and add Values and select each Value Colors, Mode, Style Select Apply Color Ramp to change colors of all added values Page 13 of 36
14 Menu Layers Layer Properties Color Add Layer Properties Color Option : Add Thematic Value Layer Properties Color Option : Apply Color Ramp on Added Value Menu Layers Layer Properties Color Apply Color Ramp Page 14 of 36
15 Menu Layers Layer Properties Selection Layer Properties Selection Option Select Selection Fore Color Select Selection Fill Color Select Selection Mode Select Selection Style Select Selection Width Select Selection Fill Style Select Selectable ( Snap to ) or Not Menu Layers Layer Properties Edit Layer Properties Edit Option Select Edit Fore Color Select Edit Fill Color Select Edit Mode Select Edit Style Select Edit Width Select Edit Fill Style Select Editable ( Snap From ) or Not Select Edit Vertex Width ( Snap Area ) Page 15 of 36
16 Menu Layers Layer Properties Label Layer Properties Label Option Select Show Label or Not Select Label Field Name Select Label Font Select Label Fore Color Select Always show to view the layer all the time Select Show When Scale between Min Scale and Max Scale Select Refer Label Font Size to this Map Scale Select Force Label Size to Fit Polyline length and polygon width Menu Layers Layer Properties Label Layer Properties Hyperlink Option Select Identify Hyperlink or Not Select Hyperlink Field Name Select Open URL in Internet Explorer Select Open Using another Software (Please Select) Page 16 of 36
17 4) Attribute Data Table A) Modifying Dbf File Data Structure Layer Properties Fields Option Menu Layers Layer Properties Fields Press Append Button to add new field at end of fields list Press Insert Button to add new field above of the selected Field Press Delete Button to delete the selected field Press Up Button to move Selected Field Up Press Down Button to move Selected field Down In the Field Name Columns, type a Unique Field Name In the Type Columns, Select ( Character or Date or Logic or Numeric ) In the length Columns, Enter the field Length In the Decimal Count Columns, Enter the number of Decimal digits Press Modify Structure Button to apply the Field Modification Page 17 of 36
18 B) Editing Data Table Editing Data Table Menu Layers Data Table Undo Data Edit Redo Data Edit Select Features Unselect Features Delete Features Undelete Features Edit Feature Data Cut Cells Copy Cells Past Cells Fill Past Fill Series Clear Cells Sort Rows Ascending Sort Rows Descending Page 18 of 36
19 C) Running VB script in Data Table Fields Menu Layers Layer Properties VB Script Layer Properties VB Script Option Select Fields for Fields Name List Select Number for VB Number Functions List Select String for VB String Functions List Select Date for VB Date Functions List Select Conversion for VB Conversion Functions List Select Logic for VB Logic Functions List Select GIS Funcs for GIS Functions List Select GIS Subs for GIS Procedures List Press Apply & Run in All records Note that "ARB" Prefix is Reserved Select Run VB Script from File (to Load and Run External VB Script file) D) Editing One Feature (Record) Edit Feature Menu Edit Edit Feature Data Page 19 of 36
20 5) GIS Analysis and Selection A) Spatial Location Analysis and Selection Selection Find and Data Transfer By Location (Query Builder) Menu Selection Find and Data Transfer By Location (Query Builder) Select Layer Name Select Criteria (All Feature or Inside Selected Features or Outside Selected Features) Select Method (New Selection or Add to Selection or Clear from Selection) Select Relation Select Relation to Layer Select Apply Tolerance or not Select Tolerance value Select Apply Data Transfer for Similar Fields Name or not Select Data Transfer Fields Names Press Find to Start Searching Page 20 of 36
21 B) Attribute Data Base Analysis and Selection Menu Selection Find By Data (Query Builder) Selection Find By Data (Query Builder) Select Layer Name Select Criteria (All Feature or Inside Selected Features or Outside Selected Features) Select Method (New Selection or Add to Selection or Clear from Selection) Select Field from the Fields List Select Relation from the Relation List Press Update Unique Value to get all available values Select Value from the List or write it Select Match Case or not Select Map Scale for viewing result Press Find to Start Searching the selected value Page 21 of 36
22 C) Nested Attribute Data Base Analysis and Selection Nested Selection Find By Data (Query Builder) Menu Selection Nested Find By Data (Query Builder) Select Layer Name Select Criteria (All Feature or Inside Selected Features or Outside Selected Features) Select Method (New Selection or Add to Selection or Clear from Selection) Select Fields from the Fields Lists Select Values Select Map Scale for viewing result Press Find to Start Searching the selected values D) Spatial Features Snapping and Dividing Network Snap Vertexes to Menu Network Snap Vertexes to Menu Network Divide Polylines or Polygon on Select Layer Name Select Criteria (All Feature or Inside Selected Features or Outside Selected Features) Select Vertexes (All, OR (Begin & End) ) Select Relation Select Relation to Layer Select Apply Tolerance or not Select Tolerance value Page 22 of 36
23 E) Shortest Path Analysis Menu Network Build Shortest Path Network Building Shortest Path Network Menu Network Shortest Path Network Shortest Path Network Select Layer Name Select Field Name Press From Button Select on the map where to start Press To Button Select on the Map where to Go Press Run Page 23 of 36
24 6) Satellites Images A) Google Earth Settings Open Google Earth 4.3 or Later Versions ( It must be installed in your Computer ) Inside Google Earth, do the following Settings Tools Options : Turn Off Terrain Be Sure that North Arrow is completely very up by o View Show Navigation Always o Press Double Click on North Be Sure that Google Earth is very Flat by: o Pressing keyboard Shift and keyboard Up Arrow. o Pressing Keyboard Ctrl and keyboard down arrow Close Google Earth Page 24 of 36
25 B) Download From Google Earth Download From Google Earth Menu Tools Download Form Google Earth In GIS Software Press Login Google Earth 4.3 or Later Versions ( It must be installed in your Computer ) Press Refresh Cords Button in GIS Software to get Google Earth Position Enter Your Lon & Lat Cords' and Scale Zoom Press Go to Press Import Rectified Image (Will Capture B&W Google Earth Map) In Google Earth Software Press Save Image to overwrite the B&W Image File In GIS Software Reload Layer from Layers Menu to get colored rectified Image. Use Up, Down, Right, Left Buttons to navigate Press "Go to Layer in Google" in Layers Menu (to find layer area in Google) Press "Go to Feature in Google" in Edit Manu (to find your area in Google) Check Shift Maps, If your Google version is 5 or later Page 25 of 36
26 C) Save Images Save Images Setup Menu Files Save Images This Function will produce Bit map image BMP with Edges Coordinates BPW World File format for BMP Image JGW World file format For JPG image Page 26 of 36
27 7) Surface Analysis A) Downloading (ASTER and SRTM) NASA Geo DEM Height Files Open your Internet browser and go to the following URL to Download ASTER Geo DEM Open your Internet browser and go to the following URL to Download SRTM height files B) Convert (ASTER and SRTM) NASA Geo DEM Height Files to Tin Shape File Convert (ASTER & SRTM) DEM to Tin Shape file Menu Tools Convert (ASTER & SRTM) DEM to Tin Shape file Download Tiff DEM file from Select and Enter Clip values of your Area Left Top point and Right Bottom point Press Convert Page 27 of 36
28 C) Convert ASTER NASA Geo DEM to Color value bmp File Convert ASTER Geo DEM to Color Value bmp file Menu Layers Add Layer Files of Type TIFF Open Menu Layers Save Layer as Change the File extension to BMP Save Open Aster Geo DEM Tiff file Save Layer as bmp file Press Identify at any point in image to get Elevation value D) Building Contours from ASTER NASA Geo DEM Menu Surface Building Contours Surface(s) Analysis Page 28 of 36
29 E) Building Tin Surface Analysis Menu Surface Building Tin Surface(s) Analysis Select Height Layer Name Select Height Criteria (All Feature or Inside Selected Features or Outside Selected Features) Select Height Field Select Output Tin Surface Shape file name Select Build Surface by Delaunay, if elevation points have unequal distances among them. Select Build Surface by Matrix, if elevation points have equal distances among them. Press Build Page 29 of 36
30 F) Building Contours Surface(s) Analysis Building Contours Surface(s) Analysis Menu Surface Building Contours Surface(s) Analysis Check Use Height Layer as Tin Surface or Not Select Height Layer Name Select Height Criteria (All Feature or Inside Selected Features or Outside Selected Features) Select Height Field Select Contour Interval Select Base Contour Select Output Contour Shape file name Select Build Surface by Delaunay, if elevation points have unequal distances among them. Select Build Surface by Matrix, if elevation points have equal distances among them. Select Do not build Surface, if Height layer is a Tin Surface Press Build Page 30 of 36
31 Page 31 of 36
32 G) Converting 2D to 3D Surface Analysis Converting 2D to 3D Surface Analysis Menu Surface Converting 2D to 3D Surface Analysis Check Use Height Layer as Tin Surface or Not Select Height Layer Name Select Height Criteria (All Feature or Inside Selected Features or Outside Selected Features) Select Height Field Select Destination 2D GIS Shape File Select Criteria of the Destination 2D GIS Shape File Select Output 3D Shape file name Select Build Surface by Delaunay, if elevation points have unequal distances among them. Select Build Surface by Matrix, if elevation points have equal distances among them. Select Do not build Surface, if Height layer is a Tin Surface Press Convert Page 32 of 36
33 H) Calculating Area and Volume of Surface(s) Calculate Area and Volume of Surface(s) Menu Surface Calculate Area and Volume of Surface(s) Check Use Height Layer as Tin Surface or Not Select Height Layer Name Select Height Criteria (All Feature or Inside Selected Features or Outside Selected Features) Select Height Field Select Height of the Calculating Plane Select above Plane or Below Plane Select Build Surface by Delaunay, if elevation points have unequal distances among them. Select Build Surface by Matrix, if elevation points have equal distances among them. Select Do not build Surface, if Height layer is a Tin Surface Press Calculate Page 33 of 36
34 8) GIS Misalliance Tools A) Converting AutoCAD files to GIS Shape Files Converting AutoCAD file to Shape Files Menu Tools Converting AutoCAD file to Shape File B) Converting GIS Shape Files to AutoCAD files Converting Shape File to AutoCAD file Menu Tools Converting Shape File to AutoCAD file Page 34 of 36
35 C) Synchronize Google Earth with Lon Lat Geographic maps Synchronize Google Earth with Lon Lat Geographic Maps Menu Tools Synchronize Google Earth with Lon Lat Geographic Maps Settings Open Google Earth 4.3 or Later Versions ( It must be installed in your Computer ) Inside Google Earth, do the following Settings Tools Options : Turn Off Terrain Be Sure that North Arrow is completely very up by o View Show Navigation Always o Press Double Click on North Be Sure that Google Earth is very Flat by: o Pressing keyboard Shift and keyboard Up Arrow. o Pressing Keyboard Ctrl and keyboard down arrow Close Google Earth Open GIS Software Set Map Projection to Decimal Degree Be Sure Google Earth Software is NOT maximized and is NOT Full Screen Page 35 of 36
36 9) Training ( Building A GIS project ) A) Determine a Specific Small Working Area or City B) Downloading Satellite Images of the Working Area C) Building Roads and Building shape Files Layers D) Digitizing the Working Area Roads and Building layers E) Entering the Available Attribute Data of the Digitized Layers F) Spatial and Attribute Data Analysis of the Digitized Layers G) Downloading ASTER DEM NASA Height File of the Working Area H) Surface Analysis of the Working Area I) Converting Digitized GIS Layers to AutoCAD. J) Save Images of the Produced Map (Project Gallery) Done Page 36 of 36
Navigation coordinate systems
 Lecture 3 Navigation coordinate systems Topic items: 1. Basic Coordinate Systems. 2. Plane Cartesian Coordinate Systems. 3. Polar Coordinate Systems. 4. Earth-Based Locational Reference Systems. 5. Reference
Lecture 3 Navigation coordinate systems Topic items: 1. Basic Coordinate Systems. 2. Plane Cartesian Coordinate Systems. 3. Polar Coordinate Systems. 4. Earth-Based Locational Reference Systems. 5. Reference
3. Map Overlay and Digitizing
 3. Map Overlay and Digitizing 3.1 Opening Map Files NavviewW/SprayView supports digital map files in ShapeFile format from ArcView, DXF format from AutoCAD, MRK format from AG-NAV, Bitmap and JPEG formats
3. Map Overlay and Digitizing 3.1 Opening Map Files NavviewW/SprayView supports digital map files in ShapeFile format from ArcView, DXF format from AutoCAD, MRK format from AG-NAV, Bitmap and JPEG formats
Review of Cartographic Data Types and Data Models
 Review of Cartographic Data Types and Data Models GIS Data Models Raster Versus Vector in GIS Analysis Fundamental element used to represent spatial features: Raster: pixel or grid cell. Vector: x,y coordinate
Review of Cartographic Data Types and Data Models GIS Data Models Raster Versus Vector in GIS Analysis Fundamental element used to represent spatial features: Raster: pixel or grid cell. Vector: x,y coordinate
I. An Intro to ArcMap Version 9.3 and 10. 1) Arc Map is basically a build your own Google map
 I. An Intro to ArcMap Version 9.3 and 10 What is Arc Map? 1) Arc Map is basically a build your own Google map a. Display and manage geo-spatial data (maps, images, points that have a geographic location)
I. An Intro to ArcMap Version 9.3 and 10 What is Arc Map? 1) Arc Map is basically a build your own Google map a. Display and manage geo-spatial data (maps, images, points that have a geographic location)
Import, view, edit, convert, and digitize triangulated irregular networks
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Import, view, edit, convert, and digitize triangulated irregular networks Objectives Import survey data in an XYZ format. Digitize elevation points using contour imagery. Edit
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Import, view, edit, convert, and digitize triangulated irregular networks Objectives Import survey data in an XYZ format. Digitize elevation points using contour imagery. Edit
Creating and editing vector maps
 Software PHOTOMOD Module PHOTOMOD VectOr Creating and editing vector maps Racurs, Moscow, 2009 PHOTOMOD CONTENTS 1. GENERAL PURPOSE OF VECTOR MAP EDITOR... 3 2. VECTOR MAP EDITOR MANAGING.... 3 3. ADDING
Software PHOTOMOD Module PHOTOMOD VectOr Creating and editing vector maps Racurs, Moscow, 2009 PHOTOMOD CONTENTS 1. GENERAL PURPOSE OF VECTOR MAP EDITOR... 3 2. VECTOR MAP EDITOR MANAGING.... 3 3. ADDING
Technical Specifications
 1 Contents INTRODUCTION...3 ABOUT THIS LAB...3 IMPORTANCE OF THIS MODULE...3 EXPORTING AND IMPORTING DATA...4 VIEWING PROJECTION INFORMATION...5...6 Assigning Projection...6 Reprojecting Data...7 CLIPPING/SUBSETTING...7
1 Contents INTRODUCTION...3 ABOUT THIS LAB...3 IMPORTANCE OF THIS MODULE...3 EXPORTING AND IMPORTING DATA...4 VIEWING PROJECTION INFORMATION...5...6 Assigning Projection...6 Reprojecting Data...7 CLIPPING/SUBSETTING...7
Introduction to GIS 2011
 Introduction to GIS 2011 Digital Elevation Models CREATING A TIN SURFACE FROM CONTOUR LINES 1. Start ArcCatalog from either Desktop or Start Menu. 2. In ArcCatalog, create a new folder dem under your c:\introgis_2011
Introduction to GIS 2011 Digital Elevation Models CREATING A TIN SURFACE FROM CONTOUR LINES 1. Start ArcCatalog from either Desktop or Start Menu. 2. In ArcCatalog, create a new folder dem under your c:\introgis_2011
3.1 Units. Angle Unit. Direction Reference
 Various settings allow the user to configure the software to function to his/her preference. It is important to review all the settings prior to using the software to ensure they are set to produce the
Various settings allow the user to configure the software to function to his/her preference. It is important to review all the settings prior to using the software to ensure they are set to produce the
D2M2 - GIS USER'S MANUAL
 D2M2 - GIS USER'S MANUAL USACE ERDC, July 2012 1 Content Overview of D2M2... 3 User Interface... 4 Menus... 4 File Menu... 4 Edit Menu... 5 View Menu... 5 Layer Menu... 6 Analysis Menu... 6 Tools Menu...
D2M2 - GIS USER'S MANUAL USACE ERDC, July 2012 1 Content Overview of D2M2... 3 User Interface... 4 Menus... 4 File Menu... 4 Edit Menu... 5 View Menu... 5 Layer Menu... 6 Analysis Menu... 6 Tools Menu...
ArcView QuickStart Guide. Contents. The ArcView Screen. Elements of an ArcView Project. Creating an ArcView Project. Adding Themes to Views
 ArcView QuickStart Guide Page 1 ArcView QuickStart Guide Contents The ArcView Screen Elements of an ArcView Project Creating an ArcView Project Adding Themes to Views Zoom and Pan Tools Querying Themes
ArcView QuickStart Guide Page 1 ArcView QuickStart Guide Contents The ArcView Screen Elements of an ArcView Project Creating an ArcView Project Adding Themes to Views Zoom and Pan Tools Querying Themes
An Introduction to Geographic Information Systems (GIS) using ArcGIS 9.2
 An Introduction to Geographic Information Systems (GIS) using ArcGIS 9.2 by Marcel Fortin, GIS and Map Librarian, University of Toronto Libraries, 2009 gis.maps@utoronto.ca http://www.library.utoronto.ca/maplib/
An Introduction to Geographic Information Systems (GIS) using ArcGIS 9.2 by Marcel Fortin, GIS and Map Librarian, University of Toronto Libraries, 2009 gis.maps@utoronto.ca http://www.library.utoronto.ca/maplib/
Yandex.Maps API Background theory
 8.02.2018 .. Version 1.0 Document build date: 8.02.2018. This volume is a part of Yandex technical documentation. Yandex helpdesk site: http://help.yandex.ru 2008 2018 Yandex LLC. All rights reserved.
8.02.2018 .. Version 1.0 Document build date: 8.02.2018. This volume is a part of Yandex technical documentation. Yandex helpdesk site: http://help.yandex.ru 2008 2018 Yandex LLC. All rights reserved.
INTRODUCTION TO GIS WORKSHOP EXERCISE
 111 Mulford Hall, College of Natural Resources, UC Berkeley (510) 643-4539 INTRODUCTION TO GIS WORKSHOP EXERCISE This exercise is a survey of some GIS and spatial analysis tools for ecological and natural
111 Mulford Hall, College of Natural Resources, UC Berkeley (510) 643-4539 INTRODUCTION TO GIS WORKSHOP EXERCISE This exercise is a survey of some GIS and spatial analysis tools for ecological and natural
Biodiversity GIS (BGIS) Internet Mapping User Guide
 Biodiversity GIS (BGIS) Internet Mapping User Guide http://bgis.sanbi.org Contents 1 Basic Introduction to BGIS Website (http://bgis.sanbi.org)... 6 1.1 LUDS... 6 1.2 Projects... 6 1.3 Services... 6 1.4
Biodiversity GIS (BGIS) Internet Mapping User Guide http://bgis.sanbi.org Contents 1 Basic Introduction to BGIS Website (http://bgis.sanbi.org)... 6 1.1 LUDS... 6 1.2 Projects... 6 1.3 Services... 6 1.4
All data is in Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) Zone 6 projection, and WGS 84 datum.
 111 Mulford Hall, College of Natural Resources, UC Berkeley (510) 643-4539 EXPLORING MOOREA DATA WITH QUANTUM GIS In this exercise, you will be using an open-source FREE GIS software, called Quantum GIS,
111 Mulford Hall, College of Natural Resources, UC Berkeley (510) 643-4539 EXPLORING MOOREA DATA WITH QUANTUM GIS In this exercise, you will be using an open-source FREE GIS software, called Quantum GIS,
RAPIDMAP Geocortex HTML5 Viewer Manual
 RAPIDMAP Geocortex HTML5 Viewer Manual This site was developed using the evolving HTML5 web standard and should work in most modern browsers including IE, Safari, Chrome and Firefox. Even though it was
RAPIDMAP Geocortex HTML5 Viewer Manual This site was developed using the evolving HTML5 web standard and should work in most modern browsers including IE, Safari, Chrome and Firefox. Even though it was
LECTURE TWO Representations, Projections and Coordinates
 LECTURE TWO Representations, Projections and Coordinates GEOGRAPHIC COORDINATE SYSTEMS Why project? What is the difference between a Geographic and Projected coordinate system? PROJECTED COORDINATE SYSTEMS
LECTURE TWO Representations, Projections and Coordinates GEOGRAPHIC COORDINATE SYSTEMS Why project? What is the difference between a Geographic and Projected coordinate system? PROJECTED COORDINATE SYSTEMS
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 25: 3D Analyst
 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 25: 3D Analyst 3D Analyst - 3D Analyst is an ArcGIS extension designed to work with TIN data (triangulated irregular network) - many of the tools in 3D Analyst also
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 25: 3D Analyst 3D Analyst - 3D Analyst is an ArcGIS extension designed to work with TIN data (triangulated irregular network) - many of the tools in 3D Analyst also
2 CARTALINX OPERATION MANUAL
 2 CARTALINX OPERATION MANUAL 2-1 Final Report (Volume IV) Usefulness of CartaLinx GeoConcept is an GIS software that is useful with good operability in mapping data processing, but it is not so strong
2 CARTALINX OPERATION MANUAL 2-1 Final Report (Volume IV) Usefulness of CartaLinx GeoConcept is an GIS software that is useful with good operability in mapping data processing, but it is not so strong
Geographical Information Systems Institute. Center for Geographic Analysis, Harvard University. LAB EXERCISE 1: Basic Mapping in ArcMap
 Harvard University Introduction to ArcMap Geographical Information Systems Institute Center for Geographic Analysis, Harvard University LAB EXERCISE 1: Basic Mapping in ArcMap Individual files (lab instructions,
Harvard University Introduction to ArcMap Geographical Information Systems Institute Center for Geographic Analysis, Harvard University LAB EXERCISE 1: Basic Mapping in ArcMap Individual files (lab instructions,
Lab#6: Editing Shapefiles With ArcMap. create a point layer from a text file, then join a table to your point attribute table
 NRM338 Fall 2018 Lab#6 Page#1 of 17 In this lab, you will Lab#6: Editing Shapefiles With ArcMap create a point layer from a text file, then join a table to your point attribute table create hyperlinks
NRM338 Fall 2018 Lab#6 Page#1 of 17 In this lab, you will Lab#6: Editing Shapefiles With ArcMap create a point layer from a text file, then join a table to your point attribute table create hyperlinks
Undo Button Clicking this tool will undo the last action. Clicking on this tool multiple times will undo all subsequent changes that were made.
 SMS Featured Icons: Editor Window This document includes a brief description of the tools in the SMS Desktop Software Editor windows, as well as showing you the toolbar shortcuts to easily access these
SMS Featured Icons: Editor Window This document includes a brief description of the tools in the SMS Desktop Software Editor windows, as well as showing you the toolbar shortcuts to easily access these
+ Make it from the satellite images in sale, (Easier & Faster, but not always available) (It does cost much. An astronomical number!
 BaseMap: + Look for it among the existent digital maps, (Easiest & Fastest because no processing required) (Therefore, the most desirable, but not always available) (It can cost much) + Make it from the
BaseMap: + Look for it among the existent digital maps, (Easiest & Fastest because no processing required) (Therefore, the most desirable, but not always available) (It can cost much) + Make it from the
Guide to Mapping Website (Public) December 2016 GC_236594
 Guide to Mapping Website (Public) December 2016 GC_236594 Table of Contents Guide to Mapping Website (Public)... 1 December 2016... 1 Quick Start... 3 Map Layers... 4 How do I?... 5 Draw on the Map...
Guide to Mapping Website (Public) December 2016 GC_236594 Table of Contents Guide to Mapping Website (Public)... 1 December 2016... 1 Quick Start... 3 Map Layers... 4 How do I?... 5 Draw on the Map...
Purpose: To explore the raster grid and vector map element concepts in GIS.
 GIS INTRODUCTION TO RASTER GRIDS AND VECTOR MAP ELEMENTS c:wou:nssi:vecrasex.wpd Purpose: To explore the raster grid and vector map element concepts in GIS. PART A. RASTER GRID NETWORKS Task A- Examine
GIS INTRODUCTION TO RASTER GRIDS AND VECTOR MAP ELEMENTS c:wou:nssi:vecrasex.wpd Purpose: To explore the raster grid and vector map element concepts in GIS. PART A. RASTER GRID NETWORKS Task A- Examine
Welcome to the Surface Water Data Viewer!
 1 Welcome to the Surface Water Data Viewer! The Surface Water Data Viewer is a mapping tool for the State of Wisconsin. It provides interactive web mapping tools for a variety of datasets, including chemistry,
1 Welcome to the Surface Water Data Viewer! The Surface Water Data Viewer is a mapping tool for the State of Wisconsin. It provides interactive web mapping tools for a variety of datasets, including chemistry,
GSSHA WMS Basics Loading DEMs, Contour Options, Images, and Projection Systems
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial GSSHA WMS Basics Loading DEMs, Contour Options, Images, and Projection Systems Learn how to work with DEMs and images and to convert between projection systems in the WMS interface
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial GSSHA WMS Basics Loading DEMs, Contour Options, Images, and Projection Systems Learn how to work with DEMs and images and to convert between projection systems in the WMS interface
Equipping Municipalities with GIS Software
 Equipping Municipalities with GIS Software Tutorial for QGIS 2.2 Prepared by Aylo Engineering s.a.r.l. 25/05/2014 www.ayloengineering.com Overview Welcome to the wonderful world of Geographical Information
Equipping Municipalities with GIS Software Tutorial for QGIS 2.2 Prepared by Aylo Engineering s.a.r.l. 25/05/2014 www.ayloengineering.com Overview Welcome to the wonderful world of Geographical Information
To the GeoView System Overview Online Training Course
 Welcome! To the GeoView System Overview Online Training Course The Alberta Department of Energy provides GeoView as a mapping system to enable users to find geographic information in Alberta. GeoView retrieves
Welcome! To the GeoView System Overview Online Training Course The Alberta Department of Energy provides GeoView as a mapping system to enable users to find geographic information in Alberta. GeoView retrieves
COGCC GIS Online Map Tools-Intranet Site July 12, 2011
 COGCC GIS Online Map Tools-Intranet Site July 12, 2011 Table of Contents Page Section Page Section 1 Introduction 7 Clear Selection 2 Double Click 7 Buffer 2 Arrow Tip Information 8 Select within 3 Busy
COGCC GIS Online Map Tools-Intranet Site July 12, 2011 Table of Contents Page Section Page Section 1 Introduction 7 Clear Selection 2 Double Click 7 Buffer 2 Arrow Tip Information 8 Select within 3 Busy
UTM Geo Map APP Quick Start (Version 1.2)
 UTM Geo Map APP Quick Start (Version 1.2) Measure Points (Marker) You can measure points of coordinate base on GPS or position on the Maps and save marker into database for unlimited number using Real-time
UTM Geo Map APP Quick Start (Version 1.2) Measure Points (Marker) You can measure points of coordinate base on GPS or position on the Maps and save marker into database for unlimited number using Real-time
City of La Crosse Online Mapping Website Help Document
 City of La Crosse Online Mapping Website Help Document This document was created to assist in using the new City of La Crosse online mapping sites. When the website is first opened, a map showing the City
City of La Crosse Online Mapping Website Help Document This document was created to assist in using the new City of La Crosse online mapping sites. When the website is first opened, a map showing the City
Maps as Numbers: Data Models
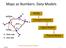 Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices E Reality S E S arcs S E Conceptual Models nodes E Logical Models S Start node E End node S Physical Models 1 The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can
Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices E Reality S E S arcs S E Conceptual Models nodes E Logical Models S Start node E End node S Physical Models 1 The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can
v Introduction to WMS WMS 11.0 Tutorial Become familiar with the WMS interface Prerequisite Tutorials None Required Components Data Map
 s v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Become familiar with the WMS interface Objectives Import files into WMS and change modules and display options to become familiar with the WMS interface. Prerequisite Tutorials
s v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Become familiar with the WMS interface Objectives Import files into WMS and change modules and display options to become familiar with the WMS interface. Prerequisite Tutorials
Map Viewer User Guide. January 2018
 January 2018 Revision History Map Viewer 3.0.1 Revision Date Author / Reviewer Description of Changes 1 April 6, 2017 RWE Addition of Known Issues, format changes. 2 April 11, 2017 RWE Revision for PROD
January 2018 Revision History Map Viewer 3.0.1 Revision Date Author / Reviewer Description of Changes 1 April 6, 2017 RWE Addition of Known Issues, format changes. 2 April 11, 2017 RWE Revision for PROD
User Manual Mobile client User Interface Version 5.0. Powered by
 User Manual Mobile client User Interface Version 5.0 Powered by Cartographic browser Gomap 4 1 Access control 5 1.1 Public access 5 1.2 Secured access 5 1.3 Multiple applications 5 2 Organisation 6 3 Parameters
User Manual Mobile client User Interface Version 5.0 Powered by Cartographic browser Gomap 4 1 Access control 5 1.1 Public access 5 1.2 Secured access 5 1.3 Multiple applications 5 2 Organisation 6 3 Parameters
Establishing a Geospatial EnvironmentChapter1:
 Chapter 1 Establishing a Geospatial EnvironmentChapter1: The lessons in this chapter describe working with the SDF format, and feature sources such as raster and ODBC points. Feature sources can be both
Chapter 1 Establishing a Geospatial EnvironmentChapter1: The lessons in this chapter describe working with the SDF format, and feature sources such as raster and ODBC points. Feature sources can be both
WHERE THEORY MEETS PRACTICE
 world from others, leica geosystems WHERE THEORY MEETS PRACTICE A NEW BULLETIN COLUMN BY CHARLES GHILANI ON PRACTICAL ASPECTS OF SURVEYING WITH A THEORETICAL SLANT february 2012 ² ACSM BULLETIN ² 27 USGS
world from others, leica geosystems WHERE THEORY MEETS PRACTICE A NEW BULLETIN COLUMN BY CHARLES GHILANI ON PRACTICAL ASPECTS OF SURVEYING WITH A THEORETICAL SLANT february 2012 ² ACSM BULLETIN ² 27 USGS
Contents of Lecture. Surface (Terrain) Data Models. Terrain Surface Representation. Sampling in Surface Model DEM
 Lecture 13: Advanced Data Models: Terrain mapping and Analysis Contents of Lecture Surface Data Models DEM GRID Model TIN Model Visibility Analysis Geography 373 Spring, 2006 Changjoo Kim 11/29/2006 1
Lecture 13: Advanced Data Models: Terrain mapping and Analysis Contents of Lecture Surface Data Models DEM GRID Model TIN Model Visibility Analysis Geography 373 Spring, 2006 Changjoo Kim 11/29/2006 1
v SMS Tutorials Working with Rasters Prerequisites Requirements Time Objectives
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Objectives Learn how to import a Raster, view elevations at individual points, change display options for multiple views of the data, show the 2D profile plots, and interpolate
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Objectives Learn how to import a Raster, view elevations at individual points, change display options for multiple views of the data, show the 2D profile plots, and interpolate
Real Geodetic Map (Map without Projection) Abstract Keywords: 1. Introduction
 Real ( without Projection) Ahmad Shaker 1 Abdullah Saad 1 Abdurrahman Arafa 2* 1.Surveying Dep., Shoubra Faculty of Engineering, Benha University, Egypt 2.Manager of Surveying Dep. in Horse Company. Egypt
Real ( without Projection) Ahmad Shaker 1 Abdullah Saad 1 Abdurrahman Arafa 2* 1.Surveying Dep., Shoubra Faculty of Engineering, Benha University, Egypt 2.Manager of Surveying Dep. in Horse Company. Egypt
Greater Bridgeport Regional Council Municipal GIS Viewer Training April 2015
 Greater Bridgeport Regional Council Municipal GIS Viewer Training April 2015 GBRC GIS Web Training Table of Contents Introduction........................................................... 3 Viewer Components.......................................................
Greater Bridgeport Regional Council Municipal GIS Viewer Training April 2015 GBRC GIS Web Training Table of Contents Introduction........................................................... 3 Viewer Components.......................................................
APPENDIX 13 TERRAIN NAVIGATOR PRO BASICS. Prepared by the Mapping and Marking Committee. Fifth Edition (Revised and Expanded) June 2014
 APPENDIX 13 TERRAIN NAVIGATOR PRO BASICS Prepared by the Mapping and Marking Committee Fifth Edition (Revised and Expanded) June 2014 Published by the Oregon-California Trails Association P.O. Box 1019
APPENDIX 13 TERRAIN NAVIGATOR PRO BASICS Prepared by the Mapping and Marking Committee Fifth Edition (Revised and Expanded) June 2014 Published by the Oregon-California Trails Association P.O. Box 1019
Downloading and importing DEM data from ASTER or SRTM (~30m resolution) into ArcMap
 Downloading and importing DEM data from ASTER or SRTM (~30m resolution) into ArcMap Step 1: ASTER or SRTM? There has been some concerns about the quality of ASTER data, nicely exemplified in the following
Downloading and importing DEM data from ASTER or SRTM (~30m resolution) into ArcMap Step 1: ASTER or SRTM? There has been some concerns about the quality of ASTER data, nicely exemplified in the following
State Plane Coordinates and Computations using them GISC Spring 2013
 State Plane Coordinates and Computations using them GISC-3325 - Spring 2013 Map Projections From UNAVCO site hosting.soonet.ca/eliris/gpsgis/lec2geodesy.html Taken from Ghilani, SPC State Plane Coordinate
State Plane Coordinates and Computations using them GISC-3325 - Spring 2013 Map Projections From UNAVCO site hosting.soonet.ca/eliris/gpsgis/lec2geodesy.html Taken from Ghilani, SPC State Plane Coordinate
Using GIS-GPS Devices with Thermo Scientific Niton XRF Analyzers. Standard Operating Procedure
 Using GIS-GPS Devices with Thermo Scientific Niton XRF Analyzers Standard Operating Procedure October 2011 TABLE OF CONTENTS Adding Niton XRF Applet to ArcPad.. 3 Bluetooth Connection of Thermo Scientific
Using GIS-GPS Devices with Thermo Scientific Niton XRF Analyzers Standard Operating Procedure October 2011 TABLE OF CONTENTS Adding Niton XRF Applet to ArcPad.. 3 Bluetooth Connection of Thermo Scientific
RIGTERSBLEEK - AALTEN 4 - B RB ENSCHEDE - THE NETHERLANDS
 RIGTERSBLEEK - AALTEN 4 - B17 7521 RB ENSCHEDE - THE NETHERLANDS Tel +31-53 4342001 - Fax +31 53 4302845 - Hot line +31 6 51363197 Email trackair@compuserve.com Internet http://www.trackair.com THE TRACKER
RIGTERSBLEEK - AALTEN 4 - B17 7521 RB ENSCHEDE - THE NETHERLANDS Tel +31-53 4342001 - Fax +31 53 4302845 - Hot line +31 6 51363197 Email trackair@compuserve.com Internet http://www.trackair.com THE TRACKER
User Manual. For Geographical Information System. Last Updated: 1-July-2013 Document No. : - 1 Document version: - 1
 User Manual For Geographical Information System Client: Department of Mines and GIS Government of Karnataka Last Updated: 1-July-2013 Document No. : - 1 Document version: - 1 (Geographical Information
User Manual For Geographical Information System Client: Department of Mines and GIS Government of Karnataka Last Updated: 1-July-2013 Document No. : - 1 Document version: - 1 (Geographical Information
BC Spatial Member Map Viewer. Version 2.0. User Guide. May 2015
 BC Spatial Member Map Viewer Version 2.0 User Guide May 2015 1 P a g e Revised: 16 June 2015 Contents Contents... 2 Introduction... 4 System Requirements... 5 BC Spatial Map Viewer... 6 I. Navigation Tools...
BC Spatial Member Map Viewer Version 2.0 User Guide May 2015 1 P a g e Revised: 16 June 2015 Contents Contents... 2 Introduction... 4 System Requirements... 5 BC Spatial Map Viewer... 6 I. Navigation Tools...
Spatial Hydrologic Modeling Using NEXRAD Rainfall Data in an HEC-HMS (MODClark) Model
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Spatial Hydrologic Modeling Using NEXRAD Rainfall Data in an HEC-HMS (MODClark) Model Learn how to setup a MODClark model using distributed rainfall data Objectives Read an existing
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Spatial Hydrologic Modeling Using NEXRAD Rainfall Data in an HEC-HMS (MODClark) Model Learn how to setup a MODClark model using distributed rainfall data Objectives Read an existing
MapInfo Professional Evolution!
 MapInfo Professional Evolution! A long history of improvement This presentation covers what is new in all of the MapInfo Pro releases since v9.0! MapInfo Pro Release History A feature release every year
MapInfo Professional Evolution! A long history of improvement This presentation covers what is new in all of the MapInfo Pro releases since v9.0! MapInfo Pro Release History A feature release every year
1. Preparing the base map. 2. Creating new shapefiles. Collecting Spatial Data by Digitizing
 Topics: 1. Preparing the base map 2. Creating new shapefiles 3. Digitizing Features 4. Modifying Existing Features 5. Adding Data Fields and editing Feature Attributes 6. Displaying and Labelling features
Topics: 1. Preparing the base map 2. Creating new shapefiles 3. Digitizing Features 4. Modifying Existing Features 5. Adding Data Fields and editing Feature Attributes 6. Displaying and Labelling features
10.1 Conversions. Grid to Geodetic
 10.1 Conversions Geodetic conversions work with the current geodetic settings. Convert grid coordinates to geodetic (Latitude/Longitude) or vice versa with any of the available projections. All results
10.1 Conversions Geodetic conversions work with the current geodetic settings. Convert grid coordinates to geodetic (Latitude/Longitude) or vice versa with any of the available projections. All results
MapInfo ProViewer 11.0 USER GUIDE
 MapInfo ProViewer 11.0 USER GUIDE Information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the part of the vendor or its representatives. No part of this
MapInfo ProViewer 11.0 USER GUIDE Information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the part of the vendor or its representatives. No part of this
Convert Local Coordinate Systems to Standard Coordinate Systems
 BENTLEY SYSTEMS, INC. Convert Local Coordinate Systems to Standard Coordinate Systems Using 2D Conformal Transformation in MicroStation V8i and Bentley Map V8i Jim McCoy P.E. and Alain Robert 4/18/2012
BENTLEY SYSTEMS, INC. Convert Local Coordinate Systems to Standard Coordinate Systems Using 2D Conformal Transformation in MicroStation V8i and Bentley Map V8i Jim McCoy P.E. and Alain Robert 4/18/2012
Excel Main Screen. Fundamental Concepts. General Keyboard Shortcuts Open a workbook Create New Save Preview and Print Close a Workbook
 Excel 2016 Main Screen Fundamental Concepts General Keyboard Shortcuts Open a workbook Create New Save Preview and Print Close a Ctrl + O Ctrl + N Ctrl + S Ctrl + P Ctrl + W Help Run Spell Check Calculate
Excel 2016 Main Screen Fundamental Concepts General Keyboard Shortcuts Open a workbook Create New Save Preview and Print Close a Ctrl + O Ctrl + N Ctrl + S Ctrl + P Ctrl + W Help Run Spell Check Calculate
v Working with Rasters SMS 12.1 Tutorial Requirements Raster Module Map Module Mesh Module Time minutes Prerequisites Overview Tutorial
 v. 12.1 SMS 12.1 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial teaches how to import a Raster, view elevations at individual points, change display options for multiple views of the data, show the 2D profile plots,
v. 12.1 SMS 12.1 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial teaches how to import a Raster, view elevations at individual points, change display options for multiple views of the data, show the 2D profile plots,
Using Syracuse Community Geography s MapSyracuse
 Using Syracuse Community Geography s MapSyracuse MapSyracuse allows the user to create custom maps with the data provided by Syracuse Community Geography. Starting with the basic template provided, you
Using Syracuse Community Geography s MapSyracuse MapSyracuse allows the user to create custom maps with the data provided by Syracuse Community Geography. Starting with the basic template provided, you
Getting Started with the new GIS Map Service Overview:
 Getting Started with the new GIS Map Service Overview: 1. Layer List Widget Shows all available layers. This widget will be open by default. 2. Legend Widget Gives symbology information for all visible
Getting Started with the new GIS Map Service Overview: 1. Layer List Widget Shows all available layers. This widget will be open by default. 2. Legend Widget Gives symbology information for all visible
Carlson GIS for Surveyors
 Professional Land Surveyors of Ohio 2016 Annual Conference -- Dayton Ohio Carlson GIS for Surveyors Presented by Who Is That CAD Girl? Jennifer DiBona is a long time CAD consultant and trainer doing business
Professional Land Surveyors of Ohio 2016 Annual Conference -- Dayton Ohio Carlson GIS for Surveyors Presented by Who Is That CAD Girl? Jennifer DiBona is a long time CAD consultant and trainer doing business
TerrainOnDemand ArcGIS
 TM TerrainOnDemand ArcGIS Connect to Intermap Technologies NEXTMap data within: ArcGIS Desktop 9.3.1 and Above AGDQS0312 TerrainOnDemand ArcGIS 2 TerrainOnDemand ArcGIS Table of Contents 1. Introduction...1
TM TerrainOnDemand ArcGIS Connect to Intermap Technologies NEXTMap data within: ArcGIS Desktop 9.3.1 and Above AGDQS0312 TerrainOnDemand ArcGIS 2 TerrainOnDemand ArcGIS Table of Contents 1. Introduction...1
Geographic Information Systems. using QGIS
 Geographic Information Systems using QGIS 1 - INTRODUCTION Generalities A GIS (Geographic Information System) consists of: -Computer hardware -Computer software - Digital Data Generalities GIS softwares
Geographic Information Systems using QGIS 1 - INTRODUCTION Generalities A GIS (Geographic Information System) consists of: -Computer hardware -Computer software - Digital Data Generalities GIS softwares
Raster Images Processing
 Software PHOTOMOD Module PHOTOMOD VectOr Raster Images Processing Racurs, Moscow, 2009 PHOTOMOD CONTENTS 1. Raster processing in PHOTOMOD VectOr...3 1.1. Raster map...3 1.2. Raster data conversion...4
Software PHOTOMOD Module PHOTOMOD VectOr Raster Images Processing Racurs, Moscow, 2009 PHOTOMOD CONTENTS 1. Raster processing in PHOTOMOD VectOr...3 1.1. Raster map...3 1.2. Raster data conversion...4
Terrain Analysis. Using QGIS and SAGA
 Terrain Analysis Using QGIS and SAGA Tutorial ID: IGET_RS_010 This tutorial has been developed by BVIEER as part of the IGET web portal intended to provide easy access to geospatial education. This tutorial
Terrain Analysis Using QGIS and SAGA Tutorial ID: IGET_RS_010 This tutorial has been developed by BVIEER as part of the IGET web portal intended to provide easy access to geospatial education. This tutorial
Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images
 Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images Airborne TerrestriaL Applications Sensor (ATLAS) Nine flight paths were recorded over the city of Providence. 1 True color ATLAS image (bands 4, 2, 1 in
Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images Airborne TerrestriaL Applications Sensor (ATLAS) Nine flight paths were recorded over the city of Providence. 1 True color ATLAS image (bands 4, 2, 1 in
Geometric Correction of Imagery
 Geometric Correction of Imagery Geometric Correction of Imagery Present by: Dr.Weerakaset Suanpaga D.Eng(RS&GIS) The intent is to compensate for the distortions introduced by a variety of factors, so that
Geometric Correction of Imagery Geometric Correction of Imagery Present by: Dr.Weerakaset Suanpaga D.Eng(RS&GIS) The intent is to compensate for the distortions introduced by a variety of factors, so that
Main concepts of ILWIS 3.0
 CHAPTER 2 Main concepts of ILWIS 3.0 In chapter one, Introduction to ILWIS, you started with ILWIS, and learned the basics of the user interface. This chapter presents some key concepts of ILWIS. In section
CHAPTER 2 Main concepts of ILWIS 3.0 In chapter one, Introduction to ILWIS, you started with ILWIS, and learned the basics of the user interface. This chapter presents some key concepts of ILWIS. In section
16) After contour layer is chosen, on column height_field, choose Elevation, and on tag_field column, choose <None>. Click OK button.
 16) After contour layer is chosen, on column height_field, choose Elevation, and on tag_field column, choose . Click OK button. 17) The process of TIN making will take some time. Various process
16) After contour layer is chosen, on column height_field, choose Elevation, and on tag_field column, choose . Click OK button. 17) The process of TIN making will take some time. Various process
THE FUTURE OF STATE PLANE COORDINATES AT ODOT
 THE FUTURE OF STATE PLANE COORDINATES AT ODOT BY: RAY FOOS P.S. AND BRIAN MEADE P.S. THE OHIO DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION WORKING WITH STATE PLANE COORDINATES OR HOW TO MAKE THE EARTH FLAT SURVEYORS AND
THE FUTURE OF STATE PLANE COORDINATES AT ODOT BY: RAY FOOS P.S. AND BRIAN MEADE P.S. THE OHIO DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION WORKING WITH STATE PLANE COORDINATES OR HOW TO MAKE THE EARTH FLAT SURVEYORS AND
The Raster Data Model
 The Raster Data Model 2 2 2 2 8 8 2 2 8 8 2 2 2 2 2 2 8 8 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 Llano River, Mason Co., TX 1 Rasters are: Regular square tessellations Matrices of values distributed among equal-sized, square
The Raster Data Model 2 2 2 2 8 8 2 2 8 8 2 2 2 2 2 2 8 8 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 Llano River, Mason Co., TX 1 Rasters are: Regular square tessellations Matrices of values distributed among equal-sized, square
Ortelia Space Builder User Manual
 Ortelia Space Builder User Manual http://ortelia.com 1 Table of Contents Introducing Ortelia Space Builder...2 System Requirements...3 1. Operating system:... 3 2. Hardware:... 3 Minimum Graphics card
Ortelia Space Builder User Manual http://ortelia.com 1 Table of Contents Introducing Ortelia Space Builder...2 System Requirements...3 1. Operating system:... 3 2. Hardware:... 3 Minimum Graphics card
1. NJDEP Landscape 3.3 Viewer Interface
 Using the Landscape Project through NJDEP Landscape 3.3 Viewer Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox are recommended for the use of this app. Navigate to the NJDEP-DFW s Landscape Project web page at www.njfishandwildlife.com/ensp/landscape/
Using the Landscape Project through NJDEP Landscape 3.3 Viewer Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox are recommended for the use of this app. Navigate to the NJDEP-DFW s Landscape Project web page at www.njfishandwildlife.com/ensp/landscape/
ESRI ArcPad 7.1 Quick Reference
 ESRI ArcPad 7.1 GPS POSITION WINDOW SATELLITE SKYPLOT Shows the almanac of which satellites should be available. Black: Available and used for calculating the GPS position Blue: Available but not used
ESRI ArcPad 7.1 GPS POSITION WINDOW SATELLITE SKYPLOT Shows the almanac of which satellites should be available. Black: Available and used for calculating the GPS position Blue: Available but not used
Steps for Modeling a Proposed New Reservoir in GIS
 Steps for Modeling a Proposed New Reservoir in GIS Requirements: ArcGIS ArcMap, ArcScene, Spatial Analyst, and 3D Analyst There s a new reservoir proposed for Right Hand Fork in Logan Canyon. I wanted
Steps for Modeling a Proposed New Reservoir in GIS Requirements: ArcGIS ArcMap, ArcScene, Spatial Analyst, and 3D Analyst There s a new reservoir proposed for Right Hand Fork in Logan Canyon. I wanted
The Functions of MapperWrapper
 The Functions of MapperWrapper Exercise 3 Step 1: Review the The MapPlace MapperWrapper Page Click Main Maps from the MapPlace home page. Select map MapperWrapper which is the fourth map from the top.
The Functions of MapperWrapper Exercise 3 Step 1: Review the The MapPlace MapperWrapper Page Click Main Maps from the MapPlace home page. Select map MapperWrapper which is the fourth map from the top.
GIS OPERATION MANUAL
 GIS OPERATION MANUAL 1. Computer System Description Hardware Make Compaq Presario 5004 CPU AMD Athlon 1.1 Ghz Main Memory 640MB CD-ROM 52 X CD-RW 8 X HD 57GB Monitor 19 inch Video Adapter 16 Mb Nvidia
GIS OPERATION MANUAL 1. Computer System Description Hardware Make Compaq Presario 5004 CPU AMD Athlon 1.1 Ghz Main Memory 640MB CD-ROM 52 X CD-RW 8 X HD 57GB Monitor 19 inch Video Adapter 16 Mb Nvidia
Juniata County, Pennsylvania
 GIS Parcel Viewer Web Mapping Application Functional Documentation June 21, 2017 Juniata County, Pennsylvania Presented by www.worldviewsolutions.com (804) 767-1870 (phone) (804) 545-0792 (fax) 115 South
GIS Parcel Viewer Web Mapping Application Functional Documentation June 21, 2017 Juniata County, Pennsylvania Presented by www.worldviewsolutions.com (804) 767-1870 (phone) (804) 545-0792 (fax) 115 South
v Getting Started An introduction to GMS GMS Tutorials Time minutes Prerequisite Tutorials None
 v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial An introduction to GMS Objectives This tutorial introduces GMS and covers the basic elements of the user interface. It is the first tutorial that new users should complete. Prerequisite
v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial An introduction to GMS Objectives This tutorial introduces GMS and covers the basic elements of the user interface. It is the first tutorial that new users should complete. Prerequisite
Rasters are: The Raster Data Model. Cell location specified by: Why squares? Raster Data Models 9/25/2014. GEO327G/386G, UT Austin 1
 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 2 2 5 5 2 2 2 2 2 2 8 8 2 2 5 5 5 5 5 5 2 2 2 2 5 5 5 5 5 2 2 2 5 5 5 5 The Raster Data Model Rasters are: Regular square tessellations Matrices of values distributed among equalsized,
5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 2 2 5 5 2 2 2 2 2 2 8 8 2 2 5 5 5 5 5 5 2 2 2 2 5 5 5 5 5 2 2 2 5 5 5 5 The Raster Data Model Rasters are: Regular square tessellations Matrices of values distributed among equalsized,
The Raster Data Model
 The Raster Data Model 2 2 2 2 8 8 2 2 8 8 2 2 2 2 2 2 8 8 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 Llano River, Mason Co., TX 9/24/201 GEO327G/386G, UT Austin 1 Rasters are: Regular square tessellations Matrices of values distributed
The Raster Data Model 2 2 2 2 8 8 2 2 8 8 2 2 2 2 2 2 8 8 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 Llano River, Mason Co., TX 9/24/201 GEO327G/386G, UT Austin 1 Rasters are: Regular square tessellations Matrices of values distributed
US Geo-Explorer User s Guide. Web:
 US Geo-Explorer User s Guide Web: http://usgeoexplorer.org Updated on October 26, 2016 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 3 1. System Interface... 5 2. Administrative Unit... 7 2.1 Region Selection... 7
US Geo-Explorer User s Guide Web: http://usgeoexplorer.org Updated on October 26, 2016 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 3 1. System Interface... 5 2. Administrative Unit... 7 2.1 Region Selection... 7
Raster Data Models 9/18/2018
 Raster Data Models The Raster Data Model Rasters are: Regular square tessellations Matrices of values distributed among equal-sized, square cells 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 2 2 5 5 5 5 5 5 2 2 2 2 5 5 5 5 5 2 2 2
Raster Data Models The Raster Data Model Rasters are: Regular square tessellations Matrices of values distributed among equal-sized, square cells 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 2 2 5 5 5 5 5 5 2 2 2 2 5 5 5 5 5 2 2 2
Map Library ArcView Version 1 02/20/03 Page 1 of 12. ArcView GIS
 Map Library ArcView Version 1 02/20/03 Page 1 of 12 1. Introduction 1 ArcView GIS ArcView is the most popular desktop GIS analysis and map presentation software package.. With ArcView GIS you can create
Map Library ArcView Version 1 02/20/03 Page 1 of 12 1. Introduction 1 ArcView GIS ArcView is the most popular desktop GIS analysis and map presentation software package.. With ArcView GIS you can create
A Practical Guide to Using QGIS
 A Practical Guide to Using QGIS 1.1 INTRODUCTION Quantum GIS (QGIS) is a useful mapping software that enables the compilation and displaying of spatial data in the form of a map. Gaining experience in
A Practical Guide to Using QGIS 1.1 INTRODUCTION Quantum GIS (QGIS) is a useful mapping software that enables the compilation and displaying of spatial data in the form of a map. Gaining experience in
Web Map Caching and Tiling. Overview David M. Horwood June 2011
 Web Map Caching and Tiling Overview David M. Horwood dhorwood@esricanada.com June 2011 Web Mapping Traditional Geographic projection Select / Refresh workflow Slow, non-interactive (refresh delay) http://www.geographynetwork.ca/website/obm/viewer.htm
Web Map Caching and Tiling Overview David M. Horwood dhorwood@esricanada.com June 2011 Web Mapping Traditional Geographic projection Select / Refresh workflow Slow, non-interactive (refresh delay) http://www.geographynetwork.ca/website/obm/viewer.htm
Google Earth an introduction
 Luana Valentini InternetGIS course - 2011 Google Earth an introduction Google Earth combines the power of Google Search with satellite imagery, maps, terrain and 3D buildings to put the world's geographic
Luana Valentini InternetGIS course - 2011 Google Earth an introduction Google Earth combines the power of Google Search with satellite imagery, maps, terrain and 3D buildings to put the world's geographic
User Guide. ExploreHRM ICT BIDS. 0 P a g e
 User Guide ICT BIDS 0 P a g e Contents Introduction... 2 Top Left Panel Navigation and Search Widgets... 3 Search... 3 Zoom In/Out... 3 Home... 3 Zoom Extent... 3 Right Panel Information and Print Widgets...
User Guide ICT BIDS 0 P a g e Contents Introduction... 2 Top Left Panel Navigation and Search Widgets... 3 Search... 3 Zoom In/Out... 3 Home... 3 Zoom Extent... 3 Right Panel Information and Print Widgets...
Vizit Pro User Manual
 Vizit Pro User Manual 1 Table of Contents Vizit Pro User Manual... 1 Using Vizit Pro... 3 The Vizit Pro User Interface... 3 Toolbars... 4 File Tab Toolbar... 4 Edit Tab Toolbar... 5 Annotations Tab Toolbar...
Vizit Pro User Manual 1 Table of Contents Vizit Pro User Manual... 1 Using Vizit Pro... 3 The Vizit Pro User Interface... 3 Toolbars... 4 File Tab Toolbar... 4 Edit Tab Toolbar... 5 Annotations Tab Toolbar...
Novel Real-Time Coordinate Transformations based on N-Dimensional Geo-Registration Parameters' Matrices
 FIG Working Week 009, Eilat, Israel, -8 May 009 Novel Real-Time Coordinate Transformations based on N-Dimensional Geo-Registration Parameters' Matrices Sagi Dalyot, Ariel Gershkovich, Yerach Doythser Mapping
FIG Working Week 009, Eilat, Israel, -8 May 009 Novel Real-Time Coordinate Transformations based on N-Dimensional Geo-Registration Parameters' Matrices Sagi Dalyot, Ariel Gershkovich, Yerach Doythser Mapping
COMMISSION OF TEXAS MAY
 GIS Viewer RAILROAD COMMISSION OF TEXAS MAY 2017 Table of Contents GIS Viewer Basics... 1 Basics... 1 Screen Overview... 2 Tools... 5 Visibility... 5 Measure Tool... 7 Identify Tool... 10 Coordinates Tool...
GIS Viewer RAILROAD COMMISSION OF TEXAS MAY 2017 Table of Contents GIS Viewer Basics... 1 Basics... 1 Screen Overview... 2 Tools... 5 Visibility... 5 Measure Tool... 7 Identify Tool... 10 Coordinates Tool...
GGR 375 QGIS Tutorial
 GGR 375 QGIS Tutorial With text taken from: Sherman, Gary E. Shuffling Quantum GIS into the Open Source GIS Stack. Free and Open Source Software for Geospatial (FOSS4G) Conference. 2007. Available online
GGR 375 QGIS Tutorial With text taken from: Sherman, Gary E. Shuffling Quantum GIS into the Open Source GIS Stack. Free and Open Source Software for Geospatial (FOSS4G) Conference. 2007. Available online
Basic Tasks in ArcGIS 10.3.x
 Basic Tasks in ArcGIS 10.3.x This guide provides instructions for performing a few basic tasks in ArcGIS 10.3.1, such as adding data to a map document, viewing and changing coordinate system information,
Basic Tasks in ArcGIS 10.3.x This guide provides instructions for performing a few basic tasks in ArcGIS 10.3.1, such as adding data to a map document, viewing and changing coordinate system information,
Guide to WB Annotations
 Guide to WB Annotations 04 May 2016 Annotations are a powerful new feature added to Workbench v1.2.0 (Released May 2016) for placing text and symbols within wb_view tabs and windows. They enable generation
Guide to WB Annotations 04 May 2016 Annotations are a powerful new feature added to Workbench v1.2.0 (Released May 2016) for placing text and symbols within wb_view tabs and windows. They enable generation
Objectives Learn how to work with projections in GMS, and how to combine data from different coordinate systems into the same GMS project.
 v. 10.2 GMS 10.2 Tutorial Working with map projections in GMS Objectives Learn how to work with projections in GMS, and how to combine data from different coordinate systems into the same GMS project.
v. 10.2 GMS 10.2 Tutorial Working with map projections in GMS Objectives Learn how to work with projections in GMS, and how to combine data from different coordinate systems into the same GMS project.
Using Google Earth. Middlebury College Library and Information Services
 Using Google Earth Middlebury College Introduction: While Google Earth can be a fun tool for simply looking at the surface of the earth, there are many other more sophisticated features to explore. Google
Using Google Earth Middlebury College Introduction: While Google Earth can be a fun tool for simply looking at the surface of the earth, there are many other more sophisticated features to explore. Google
Heads-up Digitizing from Scanned Hard-Copy Maps Part II - Vector Point, Segment and Polygon Editing 1
 Data conversion/entry (GIS, databases) February 18-25, 2007 Freetown, Sierra Leone Heads-up Digitizing from Scanned Hard-Copy Maps Part II - Vector Point, Segment and Polygon Editing 1 Objectives: Create
Data conversion/entry (GIS, databases) February 18-25, 2007 Freetown, Sierra Leone Heads-up Digitizing from Scanned Hard-Copy Maps Part II - Vector Point, Segment and Polygon Editing 1 Objectives: Create
SAS Report Viewer 8.3 Documentation
 SAS Report Viewer 8.3 Documentation About SAS Report Viewer Introduction to SAS Report Viewer SAS Report Viewer (the report viewer) enables users who are not report designers to view a report using a web
SAS Report Viewer 8.3 Documentation About SAS Report Viewer Introduction to SAS Report Viewer SAS Report Viewer (the report viewer) enables users who are not report designers to view a report using a web
SPECIFICATIONS FOR G.I.S. DATA/INFORMATION PROVIDED TO ONE-CALL
 SPECIFICATIONS FOR G.I.S. DATA/INFORMATION PROVIDED TO ONE-CALL Digital Mapping Files that we can accept: 1. G.I.S. dataset formats that we can accept: FORMAT AutoCad File Latest Releases ESRI Arc/Info
SPECIFICATIONS FOR G.I.S. DATA/INFORMATION PROVIDED TO ONE-CALL Digital Mapping Files that we can accept: 1. G.I.S. dataset formats that we can accept: FORMAT AutoCad File Latest Releases ESRI Arc/Info
Chapter 1 : Getting Started with Integrity... Chapter 2 : Interface Layout... Chapter 3 : Navigation... Chapter 4 : Printing...
 .0 User s Manual Table of Contents Chapter : Getting Started with Integrity... Chapter : Interface Layout... Chapter : Navigation... Chapter : Printing... Chapter : Quick Search and Results Pane... Results
.0 User s Manual Table of Contents Chapter : Getting Started with Integrity... Chapter : Interface Layout... Chapter : Navigation... Chapter : Printing... Chapter : Quick Search and Results Pane... Results
