This page will show you how to view and clean the data in Polyworks PIFEdit. Hint: You can click on any image to see a larger version.
|
|
|
- Dale Townsend
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
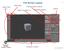
1 A Method Store for Advanced Survey and Modeling Technologies Mon, 01 Apr :29: en-us hourly Mon, 11 Feb :25: caitlin This page will show you how to view and clean the data in Polyworks PIFEdit. Hint: You can click on any image to see a larger version. POLYWORKS PIFEDIT Introducing Polyworks PIFEdit: PIFEdit is a data viewing and editing software available in the PolyWorks suite. It is used to clean scan data of unwanted data/points before importing the data into IMAlign. * Note: You have to have a full license of Polyworks (w/dongle) to be able to edit and save data out of PIFEdit (otherwise it functions only as a viewer. Basic Navigation: Upon opening the PIF file in PIF Edit, view the scan using the appropriate mouse buttons: Left Button: Rotates the scan Middle Button: Translates the scan Right Button: Zooms in and out on the scan Get accustomed to the use and feel of these buttons because they are used in all of the PolyWorks modules. VIEW DATA View the data from every angel to identify which data you want to keep and which data can be removed. In this un-cleaned data the trees and people, in this case ROTC soldiers, are
2 seen In the image above, a group of ROTC soldiers were included in the scan. Since the focus of the scan is the building, the scan data of the soldiers, the trees, and the ground in front of the building will all be removed. Notice how the trees and the soldiers (objects in the forefront) cause shadows or holes in the scan data of the structure (object in the rear). This can be remedied by simply acquiring another scan of the same area from another location if access and time permit another scan. SELECT UNWANTED DATA To remove the unwanted scan data, press the space bar. This activates the Selection dialog box. Hold down the Shift and Ctrl keys and use the middle mouse button to make your selection. Shift: Enables Volumetric Selection otherwise it is in Surface Selection mode which is only useful with polygon meshes Ctrl: Enables Polygonal Selection otherwise in Freeform Selection mode CONFIRM SELECTION & DELETE DATA Because you have to perform a volumetric selection in PIFEdit (aka it selects everything in the selection window), it is always good to double check the integrity of your selection before you delete any data. Once you have done so you can go ahead and delete the unwanted data points from the scan. Repeat this operation as many times as needed. The red indicates data that has been selected. On the left we view the data from above, on the right we view the same selected data in a perspective view When finished, go to File Save As save as name_cln.pf. Note: Our naming convention is to tack a cln onto the scan name or to put the cleaned data into a clean subfolder. As a rule of thumb never overwrite the original data. CONTINUE TO For further processing in the Polyworks Suite, continue on to Importing Data into IMAlign. ]]> 0
3 polyworks/creating-a-polygonal-mesh-using-immerge/ Mon, 24 Oct :53: Angie Continue reading ]]> This series will show you advanced modeling building modeling techniques using Leica s Cyclone. Hint: You can click on any image to see a larger version. As objects become more complex, using layers (Shift + L) becomes essential to organizing and controlling the model space. Once a point cloud data set has been properly aligned with overlap reduction, it is ready for meshing. IMMerge is the module in Polyworks that creates a mesh from an IMAlign project. Note Only IMAlign projects can be meshed. See below for specifics for IMMerge operations. BASIC SETTINGS In the Polyworks Workspace Manager, select the IMAlign project that you want to mesh and then select Create a Polygonal Model in the Workspace Manager. IMMerge Basic Settings Values Carried over from IMAlign Project (usually do not change) Max Distance: The maximum distance between two overlapping scans Surface Sampling Step: Average of interpolation step across scans; the resulting mesh density Standard Deviation: Approximate alignment error (In meters for Optech) Smoothing Level: Can be modified. It is generally recommended to have Low to Med level of smoothing. ADVANCED SETTINGS Advanced Settings Explained (usually do not change) Reduction Tolerance: - Compresses the mesh by reducing the number of triangles (without loosing definition) - Typical Reduction Tolerance = 1/5 * max standard deviation Smoothing Radius - Radius of the spherical filter used to smooth the resultant mesh. - The greater the smoothing radius, the more the mesh is smoothed. - Typical Smoothing Radius: 2-4 times the surface sampling step Smoothing Tolerance - Typical Smoothing Tolerance: 3 x s max standard deviation Common Error returned from IMMerge processing of very large datasets Error 1413: Block Size too small or Out of memory - Actually not a function of block size, so DO NOT increase block size. Recommended block size and compaction is 200 and 20, respectively. Instead, change the subdivision settings. Change the # of triangles per job to # of Merging jobs and where it says default, set a value. Start at 1000 then double if the operation still does not merge. If it does not merge in jobs or less, then the dataset is probably too
4 large. - If the dataset will not merge, split the IMAlign project into two pieces and mesh the two pieces separately. ]]> Mon, 24 Oct :18: Angie Continue reading ]]> This workflow will show you how to import Optech data into IMAlign, part of Polyworks V11 Hint: You can click on any image to see a larger version. As objects become more complex, using layers (Shift + L) becomes essential to organizing and controlling the model space. IMAlign INTIAL SETUP Figure 1: Set IMAlign options as suggested below prior to importing any data IMAlign is the Polyworks module that allows you to import and align scan data. When you first open IMAlign, it s good to define a couple of parameters. Before you import any data, open IMAlign options and change the Digitizer from Generic Close Range to Optech ILRIS 3D and change the working units to meters. Also, turn off the Interactive Mode Wizard and the Unknown Units Wizard. Also, under the Alignment section change Subsampling from 1/4 to 1/1 and under the Images section set Max Angle to 85 (see illustration below under Section 4). Next, go to Tools Save Configuration (to save the new settings). DISPLAY PARAMETERS Figure 2: The eye icon controls how objects are displayed in the scene Object color Mode Point or Default Default Static Display Drawing Type: Smooth or Flat Subsampling: 1/1
5 Default Dynamic Display (Recommended parameters bolded/italicized) Drawing Type: Point Subsampling: 1/16 or 1/64 IMPORTING OPTECH DATA Importing Optech Data (.pf format) 1. Go to File Import Images 3D Digitized Data Sets. Under Spherical Grids, choose Optech PIF. Next, navigate to the file, and select Open. Typically, you will not subsample the data set (choose 1/1), however if file size and/or memory become an issue, the only place to subsample or decimate a data set in IMAlign is upon import. The following is a basic description of the import parameters and additional guidance for modifying parameters. Note: Always hit the Reset button before adjusting any import parameters. Previous import settings are retained. When Optech data is imported into IMAlign, the data is automatically gridded or meshed. For spherical datasets like Optech data, IMAlign does this by subdividing the data by angle and range and then assigning a plane to each data section and then meshing that individual section. Therefore subdividing Optech data by both angle and range (or distance) is recommended. The smaller the angle, the more subscans created. A Subdivision Angle of 20 is generally recommended, however you might want to lower this value to 10 if there is a lot of ground/floor data in a scan. Figure 3: Interface for importing Optech data into IMAlign INTERPOLATION OPTIONS FOCUS Interpolation Options Focus Distance: The minimum distance, or the point at which data is first recorded. Typically leave as is. Step at Focus: The data resolution or point spacing at the focus distance (in meters) Max Angle: The angle from normal for which values are accepted for a scan. A value of is good for the Optech.
6 Figure 4: Graphic showing import parameters including the focus distance, number of ranges, and the minimum and maximum distances. INTERPOLATION OPTIONS MAX EDGE LENGTH Max Edge Length (Important): The distance at which points are connected or meshed. Typically 10 x s or lessthe step or point spacing. A value that is too large can erroneously connect points that should not be connected (Figure 5, left). Again, this value should be 10 s the Step or less. Decreasing will result in less data being imported (Figure 5, Right). Figure 5: Example of different max edge length values and the effect of these balues on data import INTERPOLATION OPTIONS NUMBER OF RANGES Number of Ranges: Self-Explanatory. Adjust as needed. Distance between ranges is based on the focus distance. Min Step: The smallest acceptable step value (typically do not change). Focus Distance/Ranges Interpolation Step MEL (FD) 10 meters.01 meter.1 (or less) (Rng 1) 20 meters.02 meters.2 (Rng 2) 40 meters.04 meters.4 (Rng 3) 80 meters.08 meters.8 For each range extending out from the scanner, the interpolation step and max edge length double. Remember to always hit the Reset button when importing a new scan. Most of the time, the default import values work well. Occasionally, the max angle or max edge length will need to be adjusted. Once imported, a scan is now comprised as a collection or group of sub scans or images. Note the scans now have surface information and are no longer point clouds. CONTINUE TO Continue to Registering Scans in Polyworks V11 IMAlign
7 ]]> Mon, 24 Oct :11: Angie Continue reading ]]> This document covers scan registration (alignment) and overlap reduction in Polyworks IMAlign. Hint: You can click on any image to see a larger version. As objects become more complex, using layers (Shift + L) becomes essential to organizing and controlling the model space. REGISTRATION 1 1. Import all scans into IMAlign. Lock (Ctrl + Shft + L or right click Edit Lock) the first scan in the table of contents (TOC). Note: To hide a scan s digitizer position, hit the plus next to the scan name in the table of contents, plus next to reference points, then middle click (to hide) the Digitizer Position. 2. Next select a scan in the TOC to align to the first scan and select the Split View Alignment icon to enter Local Mode. Note: The two scans have to have areas of overlap in order to be able to align them together. Also, you can only enter Split View Mode when the unlocked scan is selected. 3. Rotate both views so that they are oriented correctly with respect to one another (see Figure 1 below). This is important for identifying common points between the two scans. REGISTRATION 2 4. Select N Point Pairs Alignment. 5. Match at least 3 pairs of corresponding points between the two views (no more than 5 or so is necessary). Points should be across the entire scan (not concentrated in one area) and multi-planar. Right click when finished. Figure 1: Identifying common tie points between two scans 6. Next, run a best fit alignment between the scans. This is an iterative alignment that fine tunes the NtoN alignment. Subsampling should be 1/1; optionally you can choose to Show slipping color map. In the statistics tab, the Standard Deviation reflects the accuracy of the alignment. Ideally (though it doesn t always happen) you want the standard deviation to be less than the accuracy of the scanner. For the
8 Optech, this is approximately 1 centimeter (.01). For the Minolta VIVID 9i, this varies based on the lense that you use (tele = 200 microns (.2mm), mid = 400 microns (.4mm). If the best fit alignment is taking too long to run but the alignment is close enough (the standard deviation is less than or equal to the accuracy of the digitizer and the Convergence value and mean are very close to 0), then the alignment can be stopped. This accepts the best fit alignment computed up to that point. REGISTRATION 3 7. Once the best fit alignment is complete, lock the second scan. Select the next scan to align and repeat Steps Once all of the data has been aligned, compute one final Global or Best Fit Alignment. This adjusts the alignment across the entire dataset. To do this, select a single scan that has good coverage across the entire dataset and lock it then unlock all remaining scans. Run the Best Fit Alignment one final time. Once all alignments have been completed, save your IMAlign Project. A recommended naming convention is project_name_gr (GR = Global Registration. TIP: Scans can also be grouped together allowing you to hide, select and perform numerous operations on a group of scans at the same time. OVERLAP REDUCTION 1 Overlap reduction is performed to remove the overlapping or redundant data between scans. This is recommended prior to meshing and/or to reduce the size of the dataset. Make sure and save a copy of your dataset prior to overlap reduction. Next, select Image Reduce Overlap. The Overlap Reduction parameters are discussed more below: Max Distance: Determined by scanner Max # of overlapping images: Recommended 5 Number of overlap layers: Recommended 3 Best Data (Std) Default (when all scans are the same resolution) typically use this option Best Data (Extreme) Used when you have scans of multiple resolutions. This ensures that high resolution data will not be replaced by overlapping lower resolution data. Select all high resolution scans in TOC and then run operation. Suggested Setting: Best Data Standard OVERLAP REDUCTION 2 Data Quality: Viewing Angle: Accepts points that are orthogonal to the scan direction (directly in front of the scanner) rather than those that are more oblique. Point-to-Digitizer Distance: Accepts points that are closer to the scanner rather than those that are further away. Suggested Setting: Viewing Angle
9 Sometimes manual overlap reduction is required in addition to the automatic reduction in order to visually clean-up the data. The best way to go about this is by systematically selecting using the Select scan on Screen Tool and toggling scans (using the Hide and Keep commands) and deleting the redundant data. This is done primarily for visual purposes. Once overlap reduction is completed on your project, save your project with a different file name. A recommended naming convention is project_name_gre (GRE = Global Registration with additional edits/overlap reduction). It is best to save projects with different names at key processing steps, in case one wants to return to a specific processing point. For more on meshing, see Meshing using Polyworks IMMerge V11. ALIGNING MULTIPLE IMAlign PROJECTS Aligning Multiple IMAlign Projects Multiple IMAlign projects can also be aligned to one another. This allows for users to work on different sections of the site and then merge those sections together into one project. A global alignment and overlap reduction should be completed on each individual project before the projects are brought together. When an IMAlign project is imported to an existing project, the screen goes straight into a split view alignment. Align the 2 datasets using N Point pairs and then compute a Best Fit Alignment. Repeat for multiple projects. Multiple datasets can also be aligned in IMInspect if necessary. ]]> Tue, 10 May :54: Angie This document will introduce you to the inferface basics of Polyworks. Hint: You can click on any image to see a larger version. INTRODUCTION TO WORKSPACE MANAGER Polyworks is a modularized package that offers a centralized workspace for organizing component parts of 3D data processing from scan alignment to meshing to inspection. Users can access any of the main modules from the Polyworks Workspace Manager as well as individually from the Start Menu. The principal modules and their functionality are listed in Figure 1 below: Figure 1: Polyworks Workspace Manager showing principal software modules
10 The Polyworks Workspace is meant to house all processing components related to a project. Therefore it is best to create workspaces that are specific to a given project. For example with object scanning projects where multiple objects of a collection are scanned and process, a workspace should ideally be created for each individual object. When a Polyworks Workspace is saved, a.pwk file is created (sample.pwk) along with an associated workspace file structure (sample_files). The associated file structure (shown in Figure 2 below) manages all of the projects from the internal modules (IMAlign, IMEdit, etc ) as well as the data imported and exported from those modules. Figure 2: Polyworks Workspace file (PWK) and additional workspace files When moving files from one location to another, it is recommended to first zip a workspace to ensure that the workspace data structure and organization are retained. For more on the Polyworks Workspace Manager, please reference the Workspace Manger Basics.pdf from the Help menu in Polyworks. DESCRIPTION OF PRIMARY MODULES IMAlign IMAlign supports scan alignment of 3D digitized datasets. IMAlign offers direct interaction with a list of different digitizers as well as import support for a range of point cloud and mesh formats. Here users can align different datasets and prepare them for subsequent meshing. Figure 3: List of import formats for IMAlign IMMerge IMMerge is the meshing utility of Polyworks that produces a polygonal model directly from an IMAlign project. Note Only point clouds can be meshed in IMMerge. IMEdit IMEdit is the mesh editing module of Polyworks. Here a number of mesh cleanup operations are available including hole filling and smoothing. Curve Creation and NURBS Surfacing options are also available in IMEdit. IMInspect IMInspect offers product inspection, measurement, and comparison capabilities. Here users can import original 3D point clouds, polygonal meshes, and CAD datasets and perform a range of different measurements and comparisons. Primitive fitting as well as feature extraction is performed in IMInspect. DESCRIPTION OF LESSER MODULES
11 IMCompress IMCompress is a module completely dedicated to model reduction or decimation. The same capabilities are available from inside IMEdit. IMTexture (Add-On) IMTexture is an optional module available that generates texture maps from vertex colors for reduced models. It is currently available from Innovmetric for Academic pricing. IMView IMView is the free viewing software provided by Innovmetric. It is available in the main product sweet and also standalone from the Innovmetric website. IMKey IMKey is the licensing utility for the entire Polyworks suite. License borrowing capabilities are available here. MOUSE BUTTON FUNCTIONALITY Polyworks Mouse Button Functionality Left: Rotate Shift + Middle: Boxed Zoom In Middle: Pan Shift + Right: Rotate about Viewing Axis Right: Zoom In addition to the basic mouse functionality listed above, there are also options for single button controls available in each of the modules. These controls are shown below in Figure 4. Figure 4: Mouse Button Behavior Options in Polyworks modules SCENE DISPLAY OPTIONS Scene Display Options (all modules) The main display options in Polyworks are available by clicking on two highlighted icons in Figure 5. These icons are available in all of the main modules and may vary slightly between the different modules.
12 Figure 5: (Left) Polyworks Viewing Options and (Right) Scene Options as shown in IMAlign The object display options (shown bottom left in Figure 5 above) are covered here in more detail. Object color Mode Point: Displays image texture data Default: Displays all scans with default gray material Object: Displays each scan with unique color Image Subgroup: Displays each image subgroup with unique color Error Map: Displays error map from best fit alignment (if option is selected during alignment operation) Default Static Display Drawing Type Flat: Displays as mesh data set with flat shading (allows you to see individual facets) Point: Display as point cloud Smooth: Displays as mesh data set with smooth shading Wireframe: Displays wireframe of mesh Subsampling 1/1 1/4: One point is displayed for every 4 points 1/16 1/64 SELECTION TOOLS Selection Tools The user activates selection in Polyworks by tapping the space bar. Tapping the space bar again also deactivates selection and switches to view manipulation/scene navigation. To perform a selection the user must: (Hold) Shift: Allows Volumetric Selection necessary for selecting within point clouds (Optional Hold) Ctrl: Allows Polygonal Outline of Selection. No Ctrl: Freeform selection (Hold) Middle Mouse button- to trace the selection The Selection Menu shown in Figure 6 below is available in all PW modules. The default selection mode is set to toggle, therefore to append a selection or deselect the user must change the selection mode to mark or deselect respectively.
13 Figure 6: Selection Modes in Polyworks SHORTCUT KEYS Shortcut Keys Keys Ctrl + Shft + A Ctrl + Shft + D Ctrl + Shft + R Ctrl + Shft + E Ctrl + Shft + U Ctrl + Shft + K Ctrl + Shft + L Ctrl + Shft + O Function Select All Hide Scans Can also middle click on scan name in TOC Restore Scans Ignore Scans (ignored for most operations) Use Scans Keep Scan (Keeps selected scan hides all others) Lock Scan Unlock Scan IMALIGN BASICS IMAlign Basics (Getting Started) Figure 7: Remember to set IMAlign options as suggested below prior to importing any data IMAlign is the Polyworks module that allows you to import and align scan data. When you first open IMAlign, it s good to define a couple of parameters. Before you import any data, open IMAlign options and change the Digitizer from Generic Close Range to the scanner you are working with and change the working units to the digitizer units. Also, turn off the Interactive Mode Wizard and the Unknown Units Wizard. Also, under Alignment change Subsampling from 1/4 to 1/1 and under images, Max Angle choose 85. Next, go to Tools Save Configuration (to save the new settings).
14 Figure 8: The highlighted icon controls how the scan data will be displayed in the scene. RECOMMENDED VIEWING OPTIONS Below are the recommended settings for the Viewing Options Object color Mode Recommended parameters are bolded/italicized Point: Displays image texture data (Intensity (I) data for Optech; RGB data for Leica) Default: Displays all scans with default gray material Object: Displays each scan with unique color Image Subgroup: Displays each image subgroup with unique color Error Map: Displays error map from best fit alignment (if option is selected during alignment operation) Default Static Display Recommended parameters are bolded/italicized Drawing Type Flat: Displays as mesh data set with flat shading (allows you to see individual facets) Point: Display as point cloud Smooth: Displays as mesh data set with smooth shading Wireframe: Displays wireframe of mesh Subsampling 1/1 1/4 : One point is displayed for every 4 points 1/16 1/64 Default Dynamic Display (Recommended parameters bolded/italicized) Drawing Type Point Subsampling 1/16 or 1/64 You are now ready to begin importing scan data into your IMAlign Project! ]]> 0
RIGHT MIDDLE. Screen Plane Rotation. Zoom Window
 MOUSE OPERATIONS Use the mouse in the graphical window as shown below. LEFT MIDDLE RIGHT NONE Rotate Translate Zoom SHIFT Zoom Window Screen Plane Rotation FYI: To stay in dynamic mode, press and hold
MOUSE OPERATIONS Use the mouse in the graphical window as shown below. LEFT MIDDLE RIGHT NONE Rotate Translate Zoom SHIFT Zoom Window Screen Plane Rotation FYI: To stay in dynamic mode, press and hold
PolyWorks V10 Beginner s Guide
 PolyWorks V10 Beginner s Guide February 2007! IMAlign! IMEdit! IMInspect! IMMerge! IMView InnovMetric Software Inc. 2014 Cyrille-Duquet, Suite 310 Québec, Québec, Canada, G1N 4N6 Tel.: (418) 688-2061 Fax:
PolyWorks V10 Beginner s Guide February 2007! IMAlign! IMEdit! IMInspect! IMMerge! IMView InnovMetric Software Inc. 2014 Cyrille-Duquet, Suite 310 Québec, Québec, Canada, G1N 4N6 Tel.: (418) 688-2061 Fax:
Convergent Modeling and Reverse Engineering
 Convergent Modeling and Reverse Engineering 25 October 2017 Realize innovation. Tod Parrella NX Design Product Management Product Engineering Solutions tod.parrella@siemens.com Realize innovation. Siemens
Convergent Modeling and Reverse Engineering 25 October 2017 Realize innovation. Tod Parrella NX Design Product Management Product Engineering Solutions tod.parrella@siemens.com Realize innovation. Siemens
1 - Introduction Training Guide Objectives WorkXplore Environment Importing and Opening CAD Files 5
 Table Of Contents 1.1 - Training Guide Objectives Table Of Contents 1 - Introduction 3 1.1 - Training Guide Objectives... 3 1.2 - WorkXplore Environment... 3 2 - Importing and Opening CAD Files 5 2.1 -
Table Of Contents 1.1 - Training Guide Objectives Table Of Contents 1 - Introduction 3 1.1 - Training Guide Objectives... 3 1.2 - WorkXplore Environment... 3 2 - Importing and Opening CAD Files 5 2.1 -
CGS 3220 Lecture 13 Polygonal Character Modeling
 CGS 3220 Lecture 13 Polygonal Character Modeling Introduction to Computer Aided Modeling Instructor: Brent Rossen Overview Box modeling Polygon proxy Mirroring Polygonal components Topology editing Procedural
CGS 3220 Lecture 13 Polygonal Character Modeling Introduction to Computer Aided Modeling Instructor: Brent Rossen Overview Box modeling Polygon proxy Mirroring Polygonal components Topology editing Procedural
v Overview SMS Tutorials Prerequisites Requirements Time Objectives
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Overview Objectives This tutorial describes the major components of the SMS interface and gives a brief introduction to the different SMS modules. Ideally, this tutorial should
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Overview Objectives This tutorial describes the major components of the SMS interface and gives a brief introduction to the different SMS modules. Ideally, this tutorial should
Getting Started with ShowcaseChapter1:
 Chapter 1 Getting Started with ShowcaseChapter1: In this chapter, you learn the purpose of Autodesk Showcase, about its interface, and how to import geometry and adjust imported geometry. Objectives After
Chapter 1 Getting Started with ShowcaseChapter1: In this chapter, you learn the purpose of Autodesk Showcase, about its interface, and how to import geometry and adjust imported geometry. Objectives After
To familiarize of 3ds Max user interface and adapt a workflow based on preferences of navigating Autodesk 3D Max.
 Job No: 01 Duration: 8H Job Title: User interface overview Objective: To familiarize of 3ds Max user interface and adapt a workflow based on preferences of navigating Autodesk 3D Max. Students should be
Job No: 01 Duration: 8H Job Title: User interface overview Objective: To familiarize of 3ds Max user interface and adapt a workflow based on preferences of navigating Autodesk 3D Max. Students should be
Company overview. PolyWorks 3D metrology software helps oil field equipment manufacturer cut motor component inspection time in half
 Company overview PolyWorks 3D metrology software helps oil field equipment manufacturer cut motor component inspection time in half Weatherford International Ltd. (NYSE: WFT) is one of the world s largest
Company overview PolyWorks 3D metrology software helps oil field equipment manufacturer cut motor component inspection time in half Weatherford International Ltd. (NYSE: WFT) is one of the world s largest
Agisoft PhotoScan Tutorial
 Agisoft PhotoScan Tutorial Agisoft PhotoScan is a photogrammetry software that allows you to build 3D models from digital photographs. Photogrammetry requires a series of photographs of an object from
Agisoft PhotoScan Tutorial Agisoft PhotoScan is a photogrammetry software that allows you to build 3D models from digital photographs. Photogrammetry requires a series of photographs of an object from
Automatically search for holes and locate hole centers to offset measurement
 New Tools in PolyWorks 2018 InnovMetric Software Inc. All rights reserved. PolyWorks is a registered trademark of InnovMetric Software Inc. InnovMetric, PolyWorks Inspector, PolyWorks Modeler, PolyWorks
New Tools in PolyWorks 2018 InnovMetric Software Inc. All rights reserved. PolyWorks is a registered trademark of InnovMetric Software Inc. InnovMetric, PolyWorks Inspector, PolyWorks Modeler, PolyWorks
Pointfuse V3.4 Quick Start
 Pointfuse V3.4 Quick Start Pointfuse quickly and accurately converts point clouds into intelligent mesh models with selectable surfaces for classification. You can directly upload models to Autodesk BIM
Pointfuse V3.4 Quick Start Pointfuse quickly and accurately converts point clouds into intelligent mesh models with selectable surfaces for classification. You can directly upload models to Autodesk BIM
Full Screen Layout. Main Menu Property-specific Options. Object Tools ( t ) Outliner. Object Properties ( n ) Properties Buttons
 Object Tools ( t ) Full Screen Layout Main Menu Property-specific Options Object Properties ( n ) Properties Buttons Outliner 1 Animation Controls The Create and Add Menus 2 The Coordinate and Viewing
Object Tools ( t ) Full Screen Layout Main Menu Property-specific Options Object Properties ( n ) Properties Buttons Outliner 1 Animation Controls The Create and Add Menus 2 The Coordinate and Viewing
Laser scanning and CAD conversion accuracy correction of a highly curved engineering component using a precision tactile measuring system
 Laser scanning and CAD conversion accuracy correction of a highly curved engineering component using a precision tactile measuring system Athanasios Giannelis 1, Ioanna Symeonidou 2, Dimitrios Tzetzis
Laser scanning and CAD conversion accuracy correction of a highly curved engineering component using a precision tactile measuring system Athanasios Giannelis 1, Ioanna Symeonidou 2, Dimitrios Tzetzis
Lesson 1: Creating T- Spline Forms. In Samples section of your Data Panel, browse to: Fusion 101 Training > 03 Sculpt > 03_Sculpting_Introduction.
 3.1: Sculpting Sculpting in Fusion 360 allows for the intuitive freeform creation of organic solid bodies and surfaces by leveraging the T- Splines technology. In the Sculpt Workspace, you can rapidly
3.1: Sculpting Sculpting in Fusion 360 allows for the intuitive freeform creation of organic solid bodies and surfaces by leveraging the T- Splines technology. In the Sculpt Workspace, you can rapidly
4) Finish the spline here. To complete the spline, double click the last point or select the spline tool again.
 1) Select the line tool 3) Move the cursor along the X direction (be careful to stay on the X axis alignment so that the line is perpendicular) and click for the second point of the line. Type 0.5 for
1) Select the line tool 3) Move the cursor along the X direction (be careful to stay on the X axis alignment so that the line is perpendicular) and click for the second point of the line. Type 0.5 for
3 Polygonal Modeling. Getting Started with Maya 103
 3 Polygonal Modeling In Maya, modeling refers to the process of creating virtual 3D surfaces for the characters and objects in the Maya scene. Surfaces play an important role in the overall Maya workflow
3 Polygonal Modeling In Maya, modeling refers to the process of creating virtual 3D surfaces for the characters and objects in the Maya scene. Surfaces play an important role in the overall Maya workflow
An Introduction to Maya. Maya. Used in industrial design, CAD, computer games and motion picture effects. The ambition is what get
 An Introduction to Maya Gustav Taxén gustavt@nada.kth.se 2D1640 Grafik och Interaktionsprogrammering VT 2006 Maya Used in industrial design, CAD, computer games and motion picture effects Special focus
An Introduction to Maya Gustav Taxén gustavt@nada.kth.se 2D1640 Grafik och Interaktionsprogrammering VT 2006 Maya Used in industrial design, CAD, computer games and motion picture effects Special focus
Training Guide Getting Started with WorkXplore 3D
 Training Guide Getting Started with WorkXplore 3D Table of Contents Table of Contents 1 Training Guide Objectives 1-1 2 WorkXplore 3D Environment 2-1 3 Importing and Opening CAD Files 3-1 3.1 Importing
Training Guide Getting Started with WorkXplore 3D Table of Contents Table of Contents 1 Training Guide Objectives 1-1 2 WorkXplore 3D Environment 2-1 3 Importing and Opening CAD Files 3-1 3.1 Importing
Photogrammetry Guide to Creating Digital 3D Models
 Photogrammetry Guide to Creating Digital 3D Models By Emily Hauf (SUNY Geneseo) and the Paleontological Research Institution Guide Version 1.0 Part I - Photography Create studio setup with black cloth
Photogrammetry Guide to Creating Digital 3D Models By Emily Hauf (SUNY Geneseo) and the Paleontological Research Institution Guide Version 1.0 Part I - Photography Create studio setup with black cloth
3DReshaper Help DReshaper Beginner's Guide. Surveying
 3DReshaper Beginner's Guide Surveying 1 of 29 Cross sections Exercise: Tunnel analysis Surface analysis Exercise: Complete analysis of a concrete floor Surveying extraction Exercise: Automatic extraction
3DReshaper Beginner's Guide Surveying 1 of 29 Cross sections Exercise: Tunnel analysis Surface analysis Exercise: Complete analysis of a concrete floor Surveying extraction Exercise: Automatic extraction
Workshop 1: Basic Skills
 Workshop 1: Basic Skills 14.5 Release Introduction to ANSYS Fluent Meshing 2011 ANSYS, Inc. December 21, 2012 1 I Introduction Workshop Description: This workshop shows some of the clean up tools in Tgrid
Workshop 1: Basic Skills 14.5 Release Introduction to ANSYS Fluent Meshing 2011 ANSYS, Inc. December 21, 2012 1 I Introduction Workshop Description: This workshop shows some of the clean up tools in Tgrid
v SMS 11.1 Tutorial Overview Time minutes
 v. 11.1 SMS 11.1 Tutorial Overview Objectives This tutorial describes the major components of the SMS interface and gives a brief introduction to the different SMS modules. It is suggested that this tutorial
v. 11.1 SMS 11.1 Tutorial Overview Objectives This tutorial describes the major components of the SMS interface and gives a brief introduction to the different SMS modules. It is suggested that this tutorial
TRAINING SESSION Q2 2016
 There are 8 main topics in this training session which focus on the Sketch tools in IRONCAD. Content Sketch... 2 3D Scene Background Settings... 3 Creating a new empty Sketch... 4 Foam with cut out for
There are 8 main topics in this training session which focus on the Sketch tools in IRONCAD. Content Sketch... 2 3D Scene Background Settings... 3 Creating a new empty Sketch... 4 Foam with cut out for
1 - Introduction Training Guide Objectives WorkXplore Environment Importing and Opening CAD Files 5
 Table Of Contents 1.1 - Training Guide Objectives Table Of Contents 1 - Introduction 3 1.1 - Training Guide Objectives... 3 1.2 - WorkXplore Environment... 3 2 - Importing and Opening CAD Files 5 2.1 -
Table Of Contents 1.1 - Training Guide Objectives Table Of Contents 1 - Introduction 3 1.1 - Training Guide Objectives... 3 1.2 - WorkXplore Environment... 3 2 - Importing and Opening CAD Files 5 2.1 -
ORGANIZING YOUR ARTWORK WITH LAYERS
 9 ORGANIZING YOUR ARTWORK WITH LAYERS Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Work with the Layers panel. Create, rearrange, and lock layers and sublayers. Move objects between
9 ORGANIZING YOUR ARTWORK WITH LAYERS Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Work with the Layers panel. Create, rearrange, and lock layers and sublayers. Move objects between
STUDIO 12 MANUAL PROCESSING GUIDE
 STUDIO 12 MANUAL PROCESSING GUIDE www.artec3d.com Artec Studio offers Autopilot for automatic processing of scan data. While this works very well, sometimes manual processing may be desired or needed.
STUDIO 12 MANUAL PROCESSING GUIDE www.artec3d.com Artec Studio offers Autopilot for automatic processing of scan data. While this works very well, sometimes manual processing may be desired or needed.
Sliding and Rotating Objects. Appendix 1: Author s Notes
 AnimationWorks User Guide AnimationWORKS Introduction Camera Paths Cameras Moving Objects Moving Object Paths Sliding and Rotating Objects Light Objects Class Visibility Objects Transparency Objects Appendix
AnimationWorks User Guide AnimationWORKS Introduction Camera Paths Cameras Moving Objects Moving Object Paths Sliding and Rotating Objects Light Objects Class Visibility Objects Transparency Objects Appendix
SCENE FILE MANIPULATION SCENE FILE MANIPULATION GETTING STARTED MODELING ANIMATION MATERIALS + MAPPING RENDERING. Saving Files. Save.
 SCENE FILE MANIPULATION SCENE FILE MANIPULATION There are several things you can do with a scene file in 3ds Max. You can save a file, save a file temporarily and retrieve it, and combine scene files.
SCENE FILE MANIPULATION SCENE FILE MANIPULATION There are several things you can do with a scene file in 3ds Max. You can save a file, save a file temporarily and retrieve it, and combine scene files.
v SMS 11.2 Tutorial Overview Prerequisites Requirements Time Objectives
 v. 11.2 SMS 11.2 Tutorial Overview Objectives This tutorial describes the major components of the SMS interface and gives a brief introduction to the different SMS modules. Ideally, this tutorial should
v. 11.2 SMS 11.2 Tutorial Overview Objectives This tutorial describes the major components of the SMS interface and gives a brief introduction to the different SMS modules. Ideally, this tutorial should
ArcMap Editing Tips and Tricks. Sean Jones
 ArcMap Editing Tips and Tricks Sean Jones Overview Topics - Tuning your editing map - Creating features - Editing features and attributes - Aligning and editing coincident features - Addins Format - Software
ArcMap Editing Tips and Tricks Sean Jones Overview Topics - Tuning your editing map - Creating features - Editing features and attributes - Aligning and editing coincident features - Addins Format - Software
A Guide to Processing Photos into 3D Models Using Agisoft PhotoScan
 A Guide to Processing Photos into 3D Models Using Agisoft PhotoScan Samantha T. Porter University of Minnesota, Twin Cities Fall 2015 Index 1) Automatically masking a black background / Importing Images.
A Guide to Processing Photos into 3D Models Using Agisoft PhotoScan Samantha T. Porter University of Minnesota, Twin Cities Fall 2015 Index 1) Automatically masking a black background / Importing Images.
Guide for Geomagic Design X 3D Scan Data Cleanup and Editing. General Information
 Guide for Geomagic Design X 3D Scan Data Cleanup and Editing General Information Geomagic Design X (formerly Rapidform XOR) is an extremely powerful reverse engineering and 3D modeling software that combines
Guide for Geomagic Design X 3D Scan Data Cleanup and Editing General Information Geomagic Design X (formerly Rapidform XOR) is an extremely powerful reverse engineering and 3D modeling software that combines
OBJECT MANAGER PACKAGE USER S GUIDE
 OBJECT MANAGER PACKAGE USER S GUIDE 1 CONTENT I. Introduction... 3 II. Installation... 3 III. Using the plugins... 4 a- General... 4 b- Object properties manager... 4 c- Pipe manager... 6 d- Plane manager...
OBJECT MANAGER PACKAGE USER S GUIDE 1 CONTENT I. Introduction... 3 II. Installation... 3 III. Using the plugins... 4 a- General... 4 b- Object properties manager... 4 c- Pipe manager... 6 d- Plane manager...
Module 7 Defining Coordinate Systems
 Module 7 Defining Coordinate Systems Introduction Objectives Outline of Topics Covered The use of coordinate systems is very important in managing 3D spatial data including point clouds. In this module
Module 7 Defining Coordinate Systems Introduction Objectives Outline of Topics Covered The use of coordinate systems is very important in managing 3D spatial data including point clouds. In this module
Pointfuse V3.4 Quick Start
 Pointfuse V3.4 Quick Start Pointfuse quickly and accurately converts point clouds into intelligent mesh models with selectable surfaces for classification. You can directly upload models to Autodesk BIM
Pointfuse V3.4 Quick Start Pointfuse quickly and accurately converts point clouds into intelligent mesh models with selectable surfaces for classification. You can directly upload models to Autodesk BIM
Basic Blender Commands This is just a partial list of Blender commands. Please visit the Blender.org website for more details.
 Basic Key Commands Basic Blender Commands This is just a partial list of Blender commands. Please visit the Blender.org website for more details. TAB key- Toggles between edit mode (vertex editing) and
Basic Key Commands Basic Blender Commands This is just a partial list of Blender commands. Please visit the Blender.org website for more details. TAB key- Toggles between edit mode (vertex editing) and
Tutorial (Beginner level): Orthomosaic and DEM Generation with Agisoft PhotoScan Pro 1.3 (with Ground Control Points)
 Tutorial (Beginner level): Orthomosaic and DEM Generation with Agisoft PhotoScan Pro 1.3 (with Ground Control Points) Overview Agisoft PhotoScan Professional allows to generate georeferenced dense point
Tutorial (Beginner level): Orthomosaic and DEM Generation with Agisoft PhotoScan Pro 1.3 (with Ground Control Points) Overview Agisoft PhotoScan Professional allows to generate georeferenced dense point
Perceptron Scan Plugin 7.0
 Perceptron Scan Plugin 7.0 For compatibility with Geomagic products, see Release Notes for Geomagic Perceptron Plugin 7.0. Copyright 2004, Raindrop Geomagic, Inc. Plugins > Perceptron is the interface
Perceptron Scan Plugin 7.0 For compatibility with Geomagic products, see Release Notes for Geomagic Perceptron Plugin 7.0. Copyright 2004, Raindrop Geomagic, Inc. Plugins > Perceptron is the interface
Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM
 Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM Knowledge Worth Sharing Digitizing and Gridding Contours in Petrel SCM trainers and consultants use Petrel s contour digitizing and contour gridding tools on most projects.
Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM Knowledge Worth Sharing Digitizing and Gridding Contours in Petrel SCM trainers and consultants use Petrel s contour digitizing and contour gridding tools on most projects.
Google SketchUp INTRODUCTION WORKSHOPS
 INTRODUCTION WORKSHOPS Outcomes: -A basic understanding of SketchUp uses and outcomes -Why you would use it for project development -A basic understanding of workspace -Basic ability to use/ get satrted
INTRODUCTION WORKSHOPS Outcomes: -A basic understanding of SketchUp uses and outcomes -Why you would use it for project development -A basic understanding of workspace -Basic ability to use/ get satrted
Reconstruct Basics Patrick Parker Aug. 2017
 Reconstruct Basics Patrick Parker Aug. 2017 Trace Palette From the trace palette, you can select the color, name, and shape of the trace you want to make. Here s the Trace Palette: If the Trace Palette
Reconstruct Basics Patrick Parker Aug. 2017 Trace Palette From the trace palette, you can select the color, name, and shape of the trace you want to make. Here s the Trace Palette: If the Trace Palette
User Guide. for. JewelCAD Professional Version 2.0
 User Guide Page 1 of 121 User Guide for JewelCAD Professional Version 2.0-1 - User Guide Page 2 of 121 Table of Content 1. Introduction... 7 1.1. Purpose of this document... 7 2. Launch JewelCAD Professional
User Guide Page 1 of 121 User Guide for JewelCAD Professional Version 2.0-1 - User Guide Page 2 of 121 Table of Content 1. Introduction... 7 1.1. Purpose of this document... 7 2. Launch JewelCAD Professional
5 Subdivision Surfaces
 5 Subdivision Surfaces In Maya, subdivision surfaces possess characteristics of both polygon and NURBS surface types. This hybrid surface type offers some features not offered by the other surface types.
5 Subdivision Surfaces In Maya, subdivision surfaces possess characteristics of both polygon and NURBS surface types. This hybrid surface type offers some features not offered by the other surface types.
Maya Lesson 3 Temple Base & Columns
 Maya Lesson 3 Temple Base & Columns Make a new Folder inside your Computer Animation Folder and name it: Temple Save using Save As, and select Incremental Save, with 5 Saves. Name: Lesson3Temple YourName.ma
Maya Lesson 3 Temple Base & Columns Make a new Folder inside your Computer Animation Folder and name it: Temple Save using Save As, and select Incremental Save, with 5 Saves. Name: Lesson3Temple YourName.ma
3ds Max Cottage Step 1. Always start out by setting up units: We re going with this setup as we will round everything off to one inch.
 3ds Max Cottage Step 1 Always start out by setting up units: We re going with this setup as we will round everything off to one inch. File/Import the CAD drawing Be sure Files of Type is set to all formats
3ds Max Cottage Step 1 Always start out by setting up units: We re going with this setup as we will round everything off to one inch. File/Import the CAD drawing Be sure Files of Type is set to all formats
Section 8.3: Examining and Repairing the Input Geometry. Section 8.5: Examining the Cartesian Grid for Leakages
 Chapter 8. Wrapping Boundaries TGrid allows you to create a good quality boundary mesh using a bad quality surface mesh as input. This can be done using the wrapper utility in TGrid. The following sections
Chapter 8. Wrapping Boundaries TGrid allows you to create a good quality boundary mesh using a bad quality surface mesh as input. This can be done using the wrapper utility in TGrid. The following sections
COS 116 The Computational Universe Laboratory 10: Computer Graphics
 COS 116 The Computational Universe Laboratory 10: Computer Graphics As mentioned in lecture, computer graphics has four major parts: imaging, rendering, modeling, and animation. In this lab you will learn
COS 116 The Computational Universe Laboratory 10: Computer Graphics As mentioned in lecture, computer graphics has four major parts: imaging, rendering, modeling, and animation. In this lab you will learn
Tetra4D Reviewer. Version 5.1. User Guide. Details on how to use Tetra4D Reviewer.
 Tetra4D Reviewer Version 5.1 User Guide Details on how to use Tetra4D Reviewer. ii Contents Chapter 1: Work area... 7 Looking at the work area... 7 Toolbars and toolbar presets... 8 About toolbars and
Tetra4D Reviewer Version 5.1 User Guide Details on how to use Tetra4D Reviewer. ii Contents Chapter 1: Work area... 7 Looking at the work area... 7 Toolbars and toolbar presets... 8 About toolbars and
VCarve Pro. Vectric Ltd Unit 2B Dunstall Court Astwood Lane Feckenham B96 6QH UK.
 What's New In VCarve Pro Disclaimer All CNC machines (routing, engraving, and milling) are potentially dangerous and because Vectric Ltd has no control over how the software described in this manual might
What's New In VCarve Pro Disclaimer All CNC machines (routing, engraving, and milling) are potentially dangerous and because Vectric Ltd has no control over how the software described in this manual might
PAGE TITLE KEYBOARD SHORTCUTS
 PAGE TITLE KEYBOARD SHORTCUTS DEFAULT KEYBOARD SHORTCUTS MARKUP Align Bottom Ctrl + Alt + B Align Center Ctrl + Alt + E Align Left Ctrl + Alt + L Align Middle Ctrl + Alt + M Align Right Ctrl + Alt + R
PAGE TITLE KEYBOARD SHORTCUTS DEFAULT KEYBOARD SHORTCUTS MARKUP Align Bottom Ctrl + Alt + B Align Center Ctrl + Alt + E Align Left Ctrl + Alt + L Align Middle Ctrl + Alt + M Align Right Ctrl + Alt + R
Lecture 4, 5/27/2017, Rhino Interface an overview
 數字建築與城市设计 Spring 2017 Lecture 4, 5/27/2017, Rhino Interface an overview Copyright 2017, Chiu-Shui Chan. All Rights Reserved. This lecture concentrates on the use of tools, 3D solid modeling and editing
數字建築與城市设计 Spring 2017 Lecture 4, 5/27/2017, Rhino Interface an overview Copyright 2017, Chiu-Shui Chan. All Rights Reserved. This lecture concentrates on the use of tools, 3D solid modeling and editing
Introduction to Maya
 1 M CO PY RI GH TE D MA TE RI AL Introduction to Maya aya is a powerful 3D modeling, animation, effects, and rendering solution that has been used in everything from product design to feature films. In
1 M CO PY RI GH TE D MA TE RI AL Introduction to Maya aya is a powerful 3D modeling, animation, effects, and rendering solution that has been used in everything from product design to feature films. In
3DReshaper Help 2017 MR1. 3DReshaper Beginner's Guide. Tank
 3DReshaper Beginner's Guide Tank 1 of 20 1 Introduction The Tank module is dedicated to tank analysis. It is aimed to above ground tanks, with vertical cylinder design, single shell, with or without roof.
3DReshaper Beginner's Guide Tank 1 of 20 1 Introduction The Tank module is dedicated to tank analysis. It is aimed to above ground tanks, with vertical cylinder design, single shell, with or without roof.
Getting Started with Silo
 CHAPTER 1 Getting Started with Silo In this chapter, we discuss how to view, select, and manipulate models in Silo. If you are not familiar with Silo or polygon modeling, make sure to read the About Silo
CHAPTER 1 Getting Started with Silo In this chapter, we discuss how to view, select, and manipulate models in Silo. If you are not familiar with Silo or polygon modeling, make sure to read the About Silo
XPEL DAP SUPPORT. DAP Tool List & Overview DESCRIPTION ICON/TOOL (SHORTCUT)
 Pointer (S) Left-click on individual entities to add them to the current selection (selected entities will turn red). If the entity selected is a member of a group, the entire group will be added to the
Pointer (S) Left-click on individual entities to add them to the current selection (selected entities will turn red). If the entity selected is a member of a group, the entire group will be added to the
Dremel Digilab 3D Slicer Software
 Dremel Digilab 3D Slicer Software Dremel Digilab 3D Slicer prepares your model for 3D printing. For novices, it makes it easy to get great results. For experts, there are over 200 settings to adjust to
Dremel Digilab 3D Slicer Software Dremel Digilab 3D Slicer prepares your model for 3D printing. For novices, it makes it easy to get great results. For experts, there are over 200 settings to adjust to
Steinbichler T-Scan Plugin
 Steinbichler T-Scan Plugin For compatibility with Geomagic products, see Release Notes for Steinbichler T-Scan Plugin. Document version A. Copyright 2006, Geomagic, Inc. Plugins > T-Scan for Leica or Plugins
Steinbichler T-Scan Plugin For compatibility with Geomagic products, see Release Notes for Steinbichler T-Scan Plugin. Document version A. Copyright 2006, Geomagic, Inc. Plugins > T-Scan for Leica or Plugins
Chapter 3- Creating & Editing Objects
 Working with Basic Meshes Chapter 3- Creating & Editing Objects Now that we know how to move around in Blender, let s start doing some basic building and shaping. In this chapter we will talk about creating
Working with Basic Meshes Chapter 3- Creating & Editing Objects Now that we know how to move around in Blender, let s start doing some basic building and shaping. In this chapter we will talk about creating
RHINO; AN INTRODUCTION + FAKING TRABECULAE; EndOfLine.info;
 RHINO; AN INTRODUCTION + FAKING TRABECULAE; EndOfLine.info; Rhinoceros is a relatively simple program with an AUTOCAD based interface. The disadvantage of this type of interface is a series of terms need
RHINO; AN INTRODUCTION + FAKING TRABECULAE; EndOfLine.info; Rhinoceros is a relatively simple program with an AUTOCAD based interface. The disadvantage of this type of interface is a series of terms need
GUIDE TO POST-PROCESSING OF THE POINT CLOUD
 GUIDE TO POST-PROCESSING OF THE POINT CLOUD Contents Contents 3 Reconstructing the point cloud with MeshLab 16 Reconstructing the point cloud with CloudCompare 2 Reconstructing the point cloud with MeshLab
GUIDE TO POST-PROCESSING OF THE POINT CLOUD Contents Contents 3 Reconstructing the point cloud with MeshLab 16 Reconstructing the point cloud with CloudCompare 2 Reconstructing the point cloud with MeshLab
123D Catch - Tutorial
 123D Catch - Tutorial Autodesk s 123D Catch software (formerly Project Photofly) is based on photogrammetry. Photogrammetry is a process which derives geometric properties of an object from a series of
123D Catch - Tutorial Autodesk s 123D Catch software (formerly Project Photofly) is based on photogrammetry. Photogrammetry is a process which derives geometric properties of an object from a series of
Maya tutorial. 1 Camera calibration
 Maya tutorial In this tutorial we will augment a real scene with virtual objects. This tutorial assumes that you have downloaded the file Maya.zip from the course web page and extracted it somewhere. 1
Maya tutorial In this tutorial we will augment a real scene with virtual objects. This tutorial assumes that you have downloaded the file Maya.zip from the course web page and extracted it somewhere. 1
Spring 2011 Workshop ESSENTIALS OF 3D MODELING IN RHINOCEROS February 10 th 2011 S.R. Crown Hall Lower Core Computer Lab
 [1] Open Rhinoceros. PART 1 INTRODUCTION [4] Click and hold on the Boundary Lines in where they form a crossing and Drag from TOP RIGHT to BOTTOM LEFT to enable only the PERSPECTIVE VIEW. [2] When the
[1] Open Rhinoceros. PART 1 INTRODUCTION [4] Click and hold on the Boundary Lines in where they form a crossing and Drag from TOP RIGHT to BOTTOM LEFT to enable only the PERSPECTIVE VIEW. [2] When the
ARCHITECTURE & GAMES. A is for Architect Simple Mass Modeling FORM & SPACE. Industry Careers Framework. Applied. Getting Started.
 A is for Architect Simple Mass Modeling One of the first introductions to form and space usually comes at a very early age. As an infant, you might have played with building blocks to help hone your motor
A is for Architect Simple Mass Modeling One of the first introductions to form and space usually comes at a very early age. As an infant, you might have played with building blocks to help hone your motor
Getting Started. Extruding Features. Convert to feature class
 http://gmv.cast.uark.edu A Method Store for Advanced Survey and Modeling Technologies Mon, 01 Apr 2013 03:29:18 +0000 en-us hourly 1 http://wordpress.org/?v=3.5.1 http://gmv.cast.uark.edu/modeling/software-visualization/sketchup/workflow-sketchup/arcscene-tosketchup-to-arcscene/
http://gmv.cast.uark.edu A Method Store for Advanced Survey and Modeling Technologies Mon, 01 Apr 2013 03:29:18 +0000 en-us hourly 1 http://wordpress.org/?v=3.5.1 http://gmv.cast.uark.edu/modeling/software-visualization/sketchup/workflow-sketchup/arcscene-tosketchup-to-arcscene/
This lesson introduces Blender, covering the tools and concepts necessary to set up a minimal scene in virtual 3D space.
 3D Modeling with Blender: 01. Blender Basics Overview This lesson introduces Blender, covering the tools and concepts necessary to set up a minimal scene in virtual 3D space. Concepts Covered Blender s
3D Modeling with Blender: 01. Blender Basics Overview This lesson introduces Blender, covering the tools and concepts necessary to set up a minimal scene in virtual 3D space. Concepts Covered Blender s
Tutorial - Steering Wheel
 Tutorial - Steering Wheel (written by Jacob Tremmel, Student at Altair) This tutorial is about modeling (CAD) and rendering of a Steering Wheel with Altair s solidthinking Evolve 9.0. 1 Modeling 1. At
Tutorial - Steering Wheel (written by Jacob Tremmel, Student at Altair) This tutorial is about modeling (CAD) and rendering of a Steering Wheel with Altair s solidthinking Evolve 9.0. 1 Modeling 1. At
SolidWorks Implementation Guides. User Interface
 SolidWorks Implementation Guides User Interface Since most 2D CAD and SolidWorks are applications in the Microsoft Windows environment, tool buttons, toolbars, and the general appearance of the windows
SolidWorks Implementation Guides User Interface Since most 2D CAD and SolidWorks are applications in the Microsoft Windows environment, tool buttons, toolbars, and the general appearance of the windows
SEER-3D: An Introduction
 SEER-3D SEER-3D allows you to open and view part output from many widely-used Computer-Aided Design (CAD) applications, modify the associated data, and import it into SEER for Manufacturing for use in
SEER-3D SEER-3D allows you to open and view part output from many widely-used Computer-Aided Design (CAD) applications, modify the associated data, and import it into SEER for Manufacturing for use in
2010 by Microtek International, Inc. All rights reserved.
 2010 by Microtek International, Inc. All rights reserved. Microtek and DocWizard are trademarks of Microtek International, Inc. Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation. All other products
2010 by Microtek International, Inc. All rights reserved. Microtek and DocWizard are trademarks of Microtek International, Inc. Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation. All other products
Editing Parcel Fabrics Tutorial
 Editing Parcel Fabrics Tutorial Copyright 1995-2010 Esri All rights reserved. Table of Contents Tutorial: Getting started with parcel fabric editing...................... 3 Tutorial: Creating new parcels
Editing Parcel Fabrics Tutorial Copyright 1995-2010 Esri All rights reserved. Table of Contents Tutorial: Getting started with parcel fabric editing...................... 3 Tutorial: Creating new parcels
It is a good idea to practice View Control tools for 5 minutes at the start of every 3D session, before doing any other work.
 3D View Control Module Overview All the 2D view controls, such as Fit View, Zoom In and Out, Window Area, and Pan, can be used in 3D. As in 2D, elements to the left, right, above, or below can be excluded
3D View Control Module Overview All the 2D view controls, such as Fit View, Zoom In and Out, Window Area, and Pan, can be used in 3D. As in 2D, elements to the left, right, above, or below can be excluded
NURBS modeling for Windows. Training Manual Level 1
 NURBS modeling for Windows Training Manual Level 1 Rhino Level 1 Training 2nd Ed.doc Robert McNeel & Associates 1997-2000 All Rights Reserved. Printed in U.S.A. Copyright by Robert McNeel & Associates.
NURBS modeling for Windows Training Manual Level 1 Rhino Level 1 Training 2nd Ed.doc Robert McNeel & Associates 1997-2000 All Rights Reserved. Printed in U.S.A. Copyright by Robert McNeel & Associates.
Creating Digital Illustrations for Your Research Workshop III Basic Illustration Demo
 Creating Digital Illustrations for Your Research Workshop III Basic Illustration Demo Final Figure Size exclusion chromatography (SEC) is used primarily for the analysis of large molecules such as proteins
Creating Digital Illustrations for Your Research Workshop III Basic Illustration Demo Final Figure Size exclusion chromatography (SEC) is used primarily for the analysis of large molecules such as proteins
Autodesk Inventor Design Exercise 2: F1 Team Challenge Car Developed by Tim Varner Synergis Technologies
 Autodesk Inventor Design Exercise 2: F1 Team Challenge Car Developed by Tim Varner Synergis Technologies Tim Varner - 2004 The Inventor User Interface Command Panel Lists the commands that are currently
Autodesk Inventor Design Exercise 2: F1 Team Challenge Car Developed by Tim Varner Synergis Technologies Tim Varner - 2004 The Inventor User Interface Command Panel Lists the commands that are currently
LAB # 2 3D Modeling, Properties Commands & Attributes
 COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Electrical Engineering Department (Islamabad Campus) LAB # 2 3D Modeling, Properties Commands & Attributes Designed by Syed Muzahir Abbas 1 1. Overview of the
COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Electrical Engineering Department (Islamabad Campus) LAB # 2 3D Modeling, Properties Commands & Attributes Designed by Syed Muzahir Abbas 1 1. Overview of the
Modeling a Gear Standard Tools, Surface Tools Solid Tool View, Trackball, Show-Hide Snaps Window 1-1
 Modeling a Gear This tutorial describes how to create a toothed gear. It combines using wireframe, solid, and surface modeling together to create a part. The model was created in standard units. To begin,
Modeling a Gear This tutorial describes how to create a toothed gear. It combines using wireframe, solid, and surface modeling together to create a part. The model was created in standard units. To begin,
Lesson 11. Polygonal Spaceship
 11 Polygonal Spaceship In this lesson, you will build and texture map a polygonal spaceship. Starting with a polygonal cube, you will extrude facets until you have a completed ship. You will then be able
11 Polygonal Spaceship In this lesson, you will build and texture map a polygonal spaceship. Starting with a polygonal cube, you will extrude facets until you have a completed ship. You will then be able
SketchUp Tool Basics
 SketchUp Tool Basics Open SketchUp Click the Start Button Click All Programs Open SketchUp Scroll Down to the SketchUp 2013 folder Click on the folder to open. Click on SketchUp. Set Up SketchUp (look
SketchUp Tool Basics Open SketchUp Click the Start Button Click All Programs Open SketchUp Scroll Down to the SketchUp 2013 folder Click on the folder to open. Click on SketchUp. Set Up SketchUp (look
TLS Data Processing and Exploration Manual
 Katherine Shervais (UNAVCO), Marin Clark (University of Michigan) Collecting data in the field is only the first step in the complete TLS workflow. This manual will take you through the skills needed to
Katherine Shervais (UNAVCO), Marin Clark (University of Michigan) Collecting data in the field is only the first step in the complete TLS workflow. This manual will take you through the skills needed to
Autodesk Fusion 360 Training: The Future of Making Things Attendee Guide
 Autodesk Fusion 360 Training: The Future of Making Things Attendee Guide Abstract After completing this workshop, you will have a basic understanding of editing 3D models using Autodesk Fusion 360 TM to
Autodesk Fusion 360 Training: The Future of Making Things Attendee Guide Abstract After completing this workshop, you will have a basic understanding of editing 3D models using Autodesk Fusion 360 TM to
Max scene used to generate the image from the second pdf in this tutorial.
 Tutorial covers creating vector drawings from a 3ds max scene and methods for compositing these drawings back into a rendering. Rendering set up is based of the lighting set up from the mental ray/skylight/mr
Tutorial covers creating vector drawings from a 3ds max scene and methods for compositing these drawings back into a rendering. Rendering set up is based of the lighting set up from the mental ray/skylight/mr
solidthinking User Interface
 Lesson 1 solidthinking User Interface This lesson introduces you to the solidthinking interface. The functions described represent the tools necessary for effectively managing the modeling of a project.
Lesson 1 solidthinking User Interface This lesson introduces you to the solidthinking interface. The functions described represent the tools necessary for effectively managing the modeling of a project.
Cyclone Tips and Tricks. Hexagon Geosystems Track June 2012
 Cyclone Tips and Tricks Hexagon Geosystems Track June 2012 Built-in Hotkeys Enhanced Working Format Open GL Modes There are some very powerful built-in viewing hotkeys in Cyclone. Here are some of them:
Cyclone Tips and Tricks Hexagon Geosystems Track June 2012 Built-in Hotkeys Enhanced Working Format Open GL Modes There are some very powerful built-in viewing hotkeys in Cyclone. Here are some of them:
Character Modeling IAT 343 Lab 6. Lanz Singbeil
 Character Modeling IAT 343 Lab 6 Modeling Using Reference Sketches Start by creating a character sketch in a T-Pose (arms outstretched) Separate the sketch into 2 images with the same pixel height. Make
Character Modeling IAT 343 Lab 6 Modeling Using Reference Sketches Start by creating a character sketch in a T-Pose (arms outstretched) Separate the sketch into 2 images with the same pixel height. Make
Tutorial 4: Texture Mapping Techniques
 Tutorial 4: Texture Mapping Techniques Completion time 40 minutes In the previous tutorial we learned how to create materials, and how to assign texture maps to those materials. In this tutorial we will
Tutorial 4: Texture Mapping Techniques Completion time 40 minutes In the previous tutorial we learned how to create materials, and how to assign texture maps to those materials. In this tutorial we will
A QUICK TOUR OF ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR CC (2018 RELEASE)
 A QUICK TOUR OF ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR CC (2018 RELEASE) Lesson overview In this interactive demonstration of Adobe Illustrator CC (2018 release), you ll get an overview of the main features of the application.
A QUICK TOUR OF ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR CC (2018 RELEASE) Lesson overview In this interactive demonstration of Adobe Illustrator CC (2018 release), you ll get an overview of the main features of the application.
Introduction to ANSYS FLUENT Meshing
 Workshop 04 CAD Import and Meshing from Conformal Faceting Input 14.5 Release Introduction to ANSYS FLUENT Meshing 2011 ANSYS, Inc. December 21, 2012 1 I Introduction Workshop Description: CAD files will
Workshop 04 CAD Import and Meshing from Conformal Faceting Input 14.5 Release Introduction to ANSYS FLUENT Meshing 2011 ANSYS, Inc. December 21, 2012 1 I Introduction Workshop Description: CAD files will
Module 4A: Creating the 3D Model of Right and Oblique Pyramids
 Inventor (5) Module 4A: 4A- 1 Module 4A: Creating the 3D Model of Right and Oblique Pyramids In Module 4A, we will learn how to create 3D solid models of right-axis and oblique-axis pyramid (regular or
Inventor (5) Module 4A: 4A- 1 Module 4A: Creating the 3D Model of Right and Oblique Pyramids In Module 4A, we will learn how to create 3D solid models of right-axis and oblique-axis pyramid (regular or
Mosaic Tutorial: Advanced Workflow
 Mosaic Tutorial: Advanced Workflow This tutorial demonstrates how to mosaic two scenes with different color variations. You will learn how to: Reorder the display of the input scenes Achieve a consistent
Mosaic Tutorial: Advanced Workflow This tutorial demonstrates how to mosaic two scenes with different color variations. You will learn how to: Reorder the display of the input scenes Achieve a consistent
Tetra4D Reviewer. Version 2018 User Guide. Document version: V3.0. Tetra4D Reviewer 2018 Users Guide V3.0 1
 Tetra4D Reviewer Version 2018 User Guide Document version: V3.0 Tetra4D Reviewer 2018 Users Guide V3.0 1 Table of Contents Chapter 1: Tetra4D Reviewer overview... 4 Tetra4D Reviewer application... 4 Tetra4D
Tetra4D Reviewer Version 2018 User Guide Document version: V3.0 Tetra4D Reviewer 2018 Users Guide V3.0 1 Table of Contents Chapter 1: Tetra4D Reviewer overview... 4 Tetra4D Reviewer application... 4 Tetra4D
Rhinoceros NURBS modeling for Windows. Version 1.0 Training Manual Level 1
 Rhinoceros NURBS modeling for Windows Version 1.0 Training Manual Level 1 rhinolevel 1.doc Robert McNeel & Associates 1997. All Rights Reserved. Printed in U.S.A. Copyright by Robert McNeel & Associates.
Rhinoceros NURBS modeling for Windows Version 1.0 Training Manual Level 1 rhinolevel 1.doc Robert McNeel & Associates 1997. All Rights Reserved. Printed in U.S.A. Copyright by Robert McNeel & Associates.
Exercise Guide. Published: August MecSoft Corpotation
 VisualCAD Exercise Guide Published: August 2018 MecSoft Corpotation Copyright 1998-2018 VisualCAD 2018 Exercise Guide by Mecsoft Corporation User Notes: Contents 2 Table of Contents About this Guide 4
VisualCAD Exercise Guide Published: August 2018 MecSoft Corpotation Copyright 1998-2018 VisualCAD 2018 Exercise Guide by Mecsoft Corporation User Notes: Contents 2 Table of Contents About this Guide 4
POINT CLOUD PROCESSING
 POINT CLOUD PROCESSING August 19-20 Northern California Bentley Bash 2011 UC Berkeley Berkeley, CA Taught by: Mike Lazear Point Cloud Processing Point Cloud Processing N O R T H E R N C A L I F O R N I
POINT CLOUD PROCESSING August 19-20 Northern California Bentley Bash 2011 UC Berkeley Berkeley, CA Taught by: Mike Lazear Point Cloud Processing Point Cloud Processing N O R T H E R N C A L I F O R N I
Lesson 01 Polygon Basics 17. Lesson 02 Modeling a Body 27. Lesson 03 Modeling a Head 63. Lesson 04 Polygon Texturing 87. Lesson 05 NURBS Basics 117
 Table of Contents Project 01 Lesson 01 Polygon Basics 17 Lesson 02 Modeling a Body 27 Lesson 03 Modeling a Head 63 Lesson 04 Polygon Texturing 87 Project 02 Lesson 05 NURBS Basics 117 Lesson 06 Modeling
Table of Contents Project 01 Lesson 01 Polygon Basics 17 Lesson 02 Modeling a Body 27 Lesson 03 Modeling a Head 63 Lesson 04 Polygon Texturing 87 Project 02 Lesson 05 NURBS Basics 117 Lesson 06 Modeling
1.1: Introduction to Fusion 360
 .: Introduction to Fusion 360 Fusion 360 is a cloud- based CAD/CAM tool for collaborative product development. The tools in Fusion enable exploration and iteration on product ideas and collaboration within
.: Introduction to Fusion 360 Fusion 360 is a cloud- based CAD/CAM tool for collaborative product development. The tools in Fusion enable exploration and iteration on product ideas and collaboration within
A Study of Angles & Curves
 A Study of Angles & Curves Method 1: Cutting Quilt Shapes/Using the Shapes Tools Open BERNINA CutWork Software. Make sure that Create New is selected. Click Next. Place a dot in front of New Graphic. Select
A Study of Angles & Curves Method 1: Cutting Quilt Shapes/Using the Shapes Tools Open BERNINA CutWork Software. Make sure that Create New is selected. Click Next. Place a dot in front of New Graphic. Select
Advance Design. Tutorial
 TUTORIAL 2018 Advance Design Tutorial Table of Contents About this tutorial... 1 How to use this guide... 3 Lesson 1: Preparing and organizing your model... 4 Step 1: Start Advance Design... 5 Step 2:
TUTORIAL 2018 Advance Design Tutorial Table of Contents About this tutorial... 1 How to use this guide... 3 Lesson 1: Preparing and organizing your model... 4 Step 1: Start Advance Design... 5 Step 2:
Brief 3ds max Shaping Tutorial
 Brief 3ds max Shaping Tutorial Part1: Power Key Axe Shaft Written by Maestro 1. Creation: Go to top view, create a 6 sided cylinder, 0.1 radius this is the perfect shaft thickness to fit in the hand, so
Brief 3ds max Shaping Tutorial Part1: Power Key Axe Shaft Written by Maestro 1. Creation: Go to top view, create a 6 sided cylinder, 0.1 radius this is the perfect shaft thickness to fit in the hand, so
