Considerations Regarding Light. Introduction and Theory. Basics of Architectural Visualization. Light in the Real World
|
|
|
- Morgan Freeman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Basics of Architectural Visualization The primary purpose of every picture is to impart an idea, concept, or draft. Sketches and templates for image formation are not necessarily required but can be very helpful. In architectural visualizations, photorealistic pictures are not in great demand. Instead, abstracted renderings are sought after in order to elaborate the idea and eliminate unimportant elements. Good communication with your client is therefore very important: you have to be speaking the same language, so to speak. It is also helpful to have a certain amount of background knowledge about your client s trade. More concrete basics are a three-dimensional, digital model, reference photos of the surroundings, and materials or even mood pictures. You should build a well-structured database of fixtures and fittings, textures, background images, and other accessories. This database will grow rather large over time, so it needs to be properly arranged. We do not want to comment in great detail on technical equipment, as it constantly needs to be updated. We recommend that you have at least two computers. One should be a workstation with an up-to-date, powerful processor; a lot of RAM; a good graphics card; and two monitors. Ideally, one monitor should be at least 24 inches (diagonally) to allow comfortable working. You are going to be working on this computer, while the other one calculates your pictures. The second computer does not require a powerful graphics card or monitors. If possible, you should use processors of the same type. In addition to your knowledge and your equipment, you will need a lot of patience and of course a great deal of inspiration for creative computer work. Considerations Regarding Light In this section, we are going to approach the topic of light from three angles: its observation in real life, its translation within computer graphics, and its significance in architecture. Light in the Real World Perception and Mood First, it must be said that the topic of light is far too complex for us to sufficiently explore here. We are going to comment on only a few aspects regarding atmosphere and phenomenology. In everyday life, we rarely think about light in the real world, although it is present everywhere. But we are so used to the conditions of reality that we notice immediately if something is not real. Consequently, we would 3
2 Architectural Rendering with 3ds Max and V-Ray almost always notice a difference between a computer-generated picture and a photograph. This is mainly due to differences or errors in computer-generated presentations of light. Almost anyone can notice that these diverge from reality, but only a trained eye can actually specify the differences. Light has a subconscious influence on our feelings; it can stimulate emotions and create atmosphere. For example, when we are watching a sunset, we might feel romantic. Depending on its color, light can have a calming effect or make us feel uncomfortable. Think of the difference between warm candlelight and a corridor with the cold light from fluorescent tubes. Creating moods therefore requires conscious and deliberate observation of our surroundings. In the real world, there are three lighting scenarios. The first one is natural light, which means sunlight shining directly or indirectly onto Earth, such as moonlight or through a layer of clouds. Natural and weather phenomena provide an exception for example, lightning and fire. The second scenario is artificial light: any light that is not of natural origin, but manmade. This includes electric light, but also candlelight. The third and most common scenario is a simultaneous occurrence of both natural and artificial light. One of the first discussions you should therefore have with your client is determining which of these scenarios is present in the picture you are going to create. Some units of measurement in dealing with light: Luminous flux (lumen): Describes the radiated output of a light source per second Luminous intensity (candela): Describes the luminous flux which is emitted in a certain direction Illuminance (lux): Describes the luminous flux which arrives at a certain surface Luminance (candelas per square meter): Describes the luminous flux which is emitted from a certain surface Illuminance Light is subject to a series of rules. Three of these are of great importance in computer graphics. The first rule is that the illuminance decreases with the square of the distance from the light source. This means that a surface of one meter square that is one meter away from the light source is illuminated with the full assumed luminous intensity of the light source. If you increase the distance by another meter so that it is now two meters, the illuminance is only a quarter of the luminous intensity. At a distance of three meters, the illuminance is only a ninth of the luminous intensity. The luminous intensity always remains constant. The two other important qualities are the reflection and refraction of light. If light hits a surface, a certain amount of it is absorbed and the 4
3 FIG 1.1 Light Source without Decrease in Illuminance. FIG 1.2 Light Source with Natural Decrease in Illuminance. FIG 1.3 The Blue Floor Makes the Entire Scene Look Blue. FIG 1.4 The Multicolored Floor Affects the Coloration of the Surrounding Objects, Depending on its Surface Color. rest reflected. The reflected part is the determining factor that enables us to perceive objects. An object that absorbs 100 percent of light appears completely black to us. White surfaces reflect most of the light. The darker and rougher the surface, the less light it will reflect and the more it will absorb. An object always reflects light in its object color, which can lead to what is called color bleeding, or the bleeding or overlapping of colors onto other objects. 5
4 Architectural Rendering with 3ds Max and V-Ray The refraction of light occurs if light travels through a translucent medium with a different density than that of the medium in which the light was before. Again, the light will take on the color of the material. Light travels at the speed of light, which is measured inside a vacuum. If the light s speed is decelerated by a change in density, there will be refraction. The refractive index or index of refraction (IOR) can be determined for each material. It measures how much the speed of light is reduced when passing from air into the medium. FIG 1.5 Refraction; Glass Cuboids with Varying IOR. The following table contains some examples. TABLE 1.1 Overview of Refractive Indices Medium IOR Medium IOR Medium IOR vacuum 1 quartz 1.46 flint glass air (near the ground) 1 Plexiglas 1.49 glass plasma 0 1 crown glass lead crystal Up to 1.93 ice 1.31 polycarbonate 1.59 zircon 1.92 water 1.33 epoxy diamond The Color Temperature of Light The color temperature of light has been measured in Kelvins since William Thompson Kelvin realized that carbon emits different colors depending on its temperature. In blue light, the red and green components of the light source are lower or nonexistent. Under these circumstances, all red and green objects would appear black. When using colored light sources, you therefore need to make sure to always mix a certain proportion of all colors to avoid black objects.
5 FIG 1.6 Cuboids with the Three Primary Colors and their Combinations, White Light. FIG 1.7 The Same Cuboids, Red Light (R:255; G:0; B:0). FIG 1.8 Cuboids, Green Light (R:0; G:255; B:0); Here You Can See Clearly that the Green Portion is the LargestinOurColorSpectrum. 7
6 Architectural Rendering with 3ds Max and V-Ray FIG 1.9 The Same Scene, Blue Light (R:0; G:0; G:255). The following table contains an overview of several color temperatures. TABLE 1.2 Overview of Color Temperatures Type of light Kelvin Type of light Kelvin Type of light Kelvin Candle light up to 1900 Neutral white 5000 Cloudy north sky 6500 Warm white Up to 3300 Sun at noon Daylight white (summer) Light bulbs Cloudy sky Blue sky at noon (January) (December) Fluorescent tubes Over 3900 Xenon lamp 6500 Color Temperature and Its Effect Colored light is very important, for example, to express the time of day. The color of the light in the morning has a different proportion of red than the light of the setting sun. The color of daylight also depends on the place, the time of year, and the weather conditions while you observe it. 8 Shadow The shadow being cast is not really a property of the light, but rather a property of illuminated objects. A shadow in itself is the absence of direct light and mostly refers to a diffusely illuminated area. Shadows always appear behind objects that are positioned in front of a light source. The shadow area does not necessarily have to be darker than the directly illuminated area. Transparent objects, for example, also cast a shadow and can even produce lighter shadows, due to a concentration of rays of light or caustics. Shadows play a very important role: they indicate the position and type of the light source. Without shadow, a picture cannot have any spatial depth.
7 An object that does not cast a shadow appears unrealistic, as if it were always floating. Parallel shadows do not occur in nature; they can be created only by artificial light. Light in Computer Graphics Unlike in the real world, the light in computer graphics is not subject to any restrictions. You therefore have many options and great freedom, but it becomes more difficult to produce realistic illuminated scenes. A watchful eye is required to achieve a rendering that appears realistic. Sometimes one light source is not enough and you have to resort to tricks in order to achieve a result that appears realistic or expresses the desired idea. Consider possible scenarios of illumination: Location of scene, time of year, and time of day Indoors, artificial light, sunshine with clear sky Indoors, artificial light, cloudy sky Indoors, only artificial light Exterior view of a building, sunset, artificial light inside Ask yourself which atmosphere you want to convey: Do I want to create a calm atmosphere or a romantic one? Do I want to draw to attention to something in particular? Is there a reference that I need to integrate my rendering into? Get an overview of the light sources and their qualities: Standard light sources Point light, spot light, parallel light Create even illumination Are not subject to physical laws Photometrical light sources Point light, plane light Are essential for physically correct illumination Can be expanded with IES profiles Are based on physical units Daylight systems Even, diffuse lighting (sky) and direct illumination (sun) Light-emitting materials For representing luminescent, such as neon tubes or monitors Render-engine-specific light sources Dependent on the render engine used (V-Ray, Mental Ray, Maxwell, Brazil) These are some tips when working with light: Try to work with surrounding light that corresponds to natural light from the sky to light the scene diffusely. The main light should always be clearly noticeable. 9
8 Architectural Rendering with 3ds Max and V-Ray Pay more attention to convincing light setup than physical correctness. The shadows are as important as the light. Become familiar with materials in reality and their physical properties. Hardly any material has a completely smooth surface; the irregularities affect the light distribution on the surface. Highlights help the viewer to determine the quality and nature of a material, but not all materials have hard highlights. No two materials are the same; the differences in surface appearance create a more realistic effect. Light in Architecture Light has always played a decisive role in architecture. Light creates atmosphere, can make rooms appear bigger or smaller, and can emphasize details or hide them. The first great buildings that specifically employed light were religious buildings. Initially, they did not let much natural light in, in order to emphasize the few existing windows. The windows seemed to shine, creating a mystical effect. Light and architecture are closely linked; light presents good architecture favorably, but can also show mistakes. During the day, the light wanders across the façade, constantly giving it a different appearance. Architects have always used this medium, from the old master builders of temples and churches to famous architects of today, such as Tadao Ando, Jean Nouvell, or Louis I. Kahn. Light can also be used as an effect in architecture, such as the Empire State Building, with its varying illumination for different occasions. The use of artificial light is of particular importance in exhibition architecture, whereas daylight plays an important role when constructing domestic buildings. V-Ray Let s now turn our attention to the render engine V-Ray. We will begin with some product specifications that convinced us to work with this product; then we will comment on the methods for light calculation and introduce some features specific to V-Ray. Last, we will discuss linear workflow. 10 Why V-Ray? Here is a list of the product features that we particularly appreciate during our daily production tasks: V-Ray is platform-independent and available for many 3D programs. The parameters are the same for the different applications. The product is relatively cheap.
9 The quality of the pictures is in good proportion to the render time. V-Ray is constantly being updated. There is a large worldwide community. V-Ray is used widely, also in the film and advertising industry. It has excellent displacement. It supports IES data, an important factor for architectural visualizations. Version 3 and later also support Mental Ray materials. V-Ray is very well integrated into the 3D programs. Indirect Illumination The calculation of indirect illumination in V-Ray is divided into two processes, which can be combined in different ways: Primary bounces The light is emitted from the light source onto the scene until it hits an object. The first complex calculation takes place here, and the light is scattered, absorbed, refracted and reflected. FIG 1.10 Rendering without Global Illumination. FIG 1.11 Rendering with Global Illumination. 11
10 Architectural Rendering with 3ds Max and V-Ray Secondary bounces Starting from the point where the primary bounce hits the geometry, the light is spread around the scene once more in this calculation process, achieving diffuse illumination of the scene. If you did not activate the calculation of global illumination, only the process of primary bounces is applied automatically. In the following section, we will introduce the various render algorithms with their advantages and disadvantages. Brute Force The BRUTE FORCE algorithm calculates the GI (global illumination) for each pixel in the picture. Advantages: Few setting options Very consistent results Reveals even small details Only little flickering in animations Disadvantages: Very high render times, especially in complex scenes Renderings are partly affected by severe noise, especially in darker image areas, which can be remedied only by higher render settings and therefore very long render times. 12 Irradiance Map The IRRADIANCE MAP algorithm calculates the GI depending on the complexity of the scene with different accuracy. Interpolation takes place between the calculated areas. A multitude of setting options is available and can be managed well with a selection of presets. Advantages: In comparison with the brute force algorithm, this produces shorter rendering times for the same complexity of scene. No noise in darker image areas. The irradiance map the result of the calculation can be saved and reused, which can drastically reduce the render time for animations. Disadvantages: Due to interpolation, fine shadows can be lost in detailed areas. Animations can be affected by flickering, which can be remedied by saving the irradiance map as a multiframe incremental map (i.e., provided that the output frame sizes are equal). Requires a lot of RAM.
11 Very complex setting options. The light solution is dependent on the location only the visible portion of the scene is calculated. Photon Map For the PHOTON MAP algorithm, photons are emitted from all light sources in the scene and then bounced around between objects until their energy is used up. Only true light sources are taken into consideration, not surrounding illumination or luminous materials. The algorithm is useful for interior scenes with many light sources and achieves good results with short rendering times when used in combination with irradiance map. Advantages: Very fast algorithm. Location-independent. The photon map can be saved, but changes in material, light, and position of objects are not possible. Disadvantages: Very imprecise calculation; usage under primary bounces is not recommended. High memory requirements. Restrictions in selecting light sources. Light Cache This algorithm functions in a similar way to the photon map, but the photons are emitted into the scene from the camera and the algorithm can be used for any kind of scene. Advantages: Simple setup. Very quick calculation. Very fast, good results in combination with the irradiance map. Very precise calculation of contact shadow and shadows in corners. Preview during calculation process; therefore, serious mistakes can be spotted quickly. Disadvantages: Location-dependent; has to be recalculated every time. Problems in calculating bump maps, but this has no effects when used for secondary bounces. Finally, we would like to offer you some guidance by comparing the most sensible combinations for an interior scene and an outdoor scene. For the first comparison, we refer only to the quality of the result; for the second 13
12 Architectural Rendering with 3ds Max and V-Ray comparison, we relate the quality to the rendering time. We are analyzing only stationary images these comparisons are not necessarily applicable to animations. Interior Scene Criteria: Quality The best quality is produced by a combination of the algorithms BRUTE FORCE (primary bounces) and LIGHT CACHE (secondary bounces). Hardly any artifacts occur, and even in detailed image areas, the accuracy remains high. A clear disadvantage, however, is the long rendering time. Criteria: Time invested in relation to quality In this case, we recommend a combination of IRRADIANCE MAP (PRIMARY BOUNCES) and LIGHT CACHE (SECONDARY BOUNCES). The calculation is very quick and exact, even in detailed image areas. Possible errors can usually be fixed by selecting a better preset. This combination is the better choice for everyday work. Exterior Scene For the exterior scene, the same applies as for the interior scene. The calculation can potentially take even longer in this case, as the scene has a higher number of polygons due to trees, bushes, and lawn, and therefore more detailed areas. We can therefore conclude that the combination of IRRADIANCE MAP and LIGHT CACHE is the most appropriate. As there is an exception to every rule and sometimes the rendering time is irrelevant, you should not completely disregard the other algorithms. 14 Ambient Occlusion In areas where two or more objects are touching, there is insufficient light, and these areas appear darker in comparison to the surroundings. These darker areas are called contact shadows (ambient occlusion or AO). Ambient occlusion is always calculated without direct light, and with only a diffuse surrounding light. In V-Ray, there are several options for calculating the ambient occlusion. For example, you can output it as a separate rendering channel, resulting in a grayscale image. In an image editing program, you can multiply this image with the actual rendering. Only certain image areas are darkened, as the image consists of color values between one and zero. In this book, we use a VRAYDIRT material for objects that are to have a contact shadow. In this case, the ambient occlusion is already saved in the output image. As you can adapt the parameters for each material, you have good control over the contact shadow.
13 FIG 1.12 Ambient Occlusion Channel. FIG 1.13 Diffuse Channel, Rendered without a Light Source. FIG 1.14 Result of Overlaying Both Channels. 15
THEA RENDER ADAPTIVE BSD ENGINE
 THEA RENDER ADAPTIVE BSD ENGINE ADAPTIVE (BSD) ENGINE Adaptive (BSD) is the name of the biased engine inside Thea Render. This engine is a biased one (this is why we use the abbreviation "BSD") as it uses
THEA RENDER ADAPTIVE BSD ENGINE ADAPTIVE (BSD) ENGINE Adaptive (BSD) is the name of the biased engine inside Thea Render. This engine is a biased one (this is why we use the abbreviation "BSD") as it uses
Lighting & 3D Graphics. Images from 3D Creative Magazine
 Lighting & 3D Graphics Images from 3D Creative Magazine Contents Introduction Definitions 3D Lighting Basics 3D Light Sources Lighting Controls & Effects Brightness & Colour Shadows Hotspot And Falloff
Lighting & 3D Graphics Images from 3D Creative Magazine Contents Introduction Definitions 3D Lighting Basics 3D Light Sources Lighting Controls & Effects Brightness & Colour Shadows Hotspot And Falloff
AECOsim Building Designer Quick Start Guide
 AECOsim Building Designer Quick Start Guide Chapter A17 Rendering 2012 Bentley Systems, Incorporated www.bentley.com/aecosim Table of Contents Rendering...3 The Camera... 3 Materials... 5 Material Palettes...
AECOsim Building Designer Quick Start Guide Chapter A17 Rendering 2012 Bentley Systems, Incorporated www.bentley.com/aecosim Table of Contents Rendering...3 The Camera... 3 Materials... 5 Material Palettes...
Ambient Occlusion Pass
 Ambient Occlusion Pass (Soft Shadows in the Nooks and Crannies to Replicate Photorealistic Lighting) In this tutorial we are going to go over some advanced lighting techniques for an Ambient Occlusion
Ambient Occlusion Pass (Soft Shadows in the Nooks and Crannies to Replicate Photorealistic Lighting) In this tutorial we are going to go over some advanced lighting techniques for an Ambient Occlusion
Consider a partially transparent object that is illuminated with two lights, one visible from each side of the object. Start with a ray from the eye
 Ray Tracing What was the rendering equation? Motivate & list the terms. Relate the rendering equation to forward ray tracing. Why is forward ray tracing not good for image formation? What is the difference
Ray Tracing What was the rendering equation? Motivate & list the terms. Relate the rendering equation to forward ray tracing. Why is forward ray tracing not good for image formation? What is the difference
Chapter 11. Caustics and Global Illumination
 11 and Global Illumination Chapter 11 Direct illumination occurs when a light source directly illuminates an object or objects in a scene. Indirect illumination occurs if light illuminates objects by reflection
11 and Global Illumination Chapter 11 Direct illumination occurs when a light source directly illuminates an object or objects in a scene. Indirect illumination occurs if light illuminates objects by reflection
MITOCW MIT6_172_F10_lec18_300k-mp4
 MITOCW MIT6_172_F10_lec18_300k-mp4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for
MITOCW MIT6_172_F10_lec18_300k-mp4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for
Corona Sky Corona Sun Corona Light Create Camera About
 Plugin menu Corona Sky creates Sky object with attached Corona Sky tag Corona Sun creates Corona Sun object Corona Light creates Corona Light object Create Camera creates Camera with attached Corona Camera
Plugin menu Corona Sky creates Sky object with attached Corona Sky tag Corona Sun creates Corona Sun object Corona Light creates Corona Light object Create Camera creates Camera with attached Corona Camera
Photo-realism Fundamentals
 1-(800) 877-2745 www.ashlar-vellum.com Photo-realism Fundamentals Using Cobalt, Xenon, Argon Copyright 2008 Ashlar Incorporated. All rights reserved. Photo-realism Fundamentals Photo-realistic rendering
1-(800) 877-2745 www.ashlar-vellum.com Photo-realism Fundamentals Using Cobalt, Xenon, Argon Copyright 2008 Ashlar Incorporated. All rights reserved. Photo-realism Fundamentals Photo-realistic rendering
Caustics - Mental Ray
 Caustics - Mental Ray (Working with real caustic generation) In this tutorial we are going to go over some advanced lighting techniques for creating realistic caustic effects. Caustics are the bent reflections
Caustics - Mental Ray (Working with real caustic generation) In this tutorial we are going to go over some advanced lighting techniques for creating realistic caustic effects. Caustics are the bent reflections
Advanced Distant Light for DAZ Studio
 Contents Advanced Distant Light for DAZ Studio Introduction Important Concepts Quick Start Quick Tips Parameter Settings Light Group Shadow Group Lighting Control Group Known Issues Introduction The Advanced
Contents Advanced Distant Light for DAZ Studio Introduction Important Concepts Quick Start Quick Tips Parameter Settings Light Group Shadow Group Lighting Control Group Known Issues Introduction The Advanced
Rendering Engines - Specific tools may depend on "Rendering Engine"
 Week 5 3DS Max, Cameras, Lighting and Materials Rendering - Process of turning geometry into pixels Rendering Engines - Specific tools may depend on "Rendering Engine" 1. Internal (3DS MAX) ART (Autodesk
Week 5 3DS Max, Cameras, Lighting and Materials Rendering - Process of turning geometry into pixels Rendering Engines - Specific tools may depend on "Rendering Engine" 1. Internal (3DS MAX) ART (Autodesk
Point based global illumination is now a standard tool for film quality renderers. Since it started out as a real time technique it is only natural
 1 Point based global illumination is now a standard tool for film quality renderers. Since it started out as a real time technique it is only natural to consider using it in video games too. 2 I hope that
1 Point based global illumination is now a standard tool for film quality renderers. Since it started out as a real time technique it is only natural to consider using it in video games too. 2 I hope that
Texture Mapping. Images from 3D Creative Magazine
 Texture Mapping Images from 3D Creative Magazine Contents Introduction Definitions Light And Colour Surface Attributes Surface Attributes: Colour Surface Attributes: Shininess Surface Attributes: Specularity
Texture Mapping Images from 3D Creative Magazine Contents Introduction Definitions Light And Colour Surface Attributes Surface Attributes: Colour Surface Attributes: Shininess Surface Attributes: Specularity
CS 325 Computer Graphics
 CS 325 Computer Graphics 04 / 02 / 2012 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Illumination modelling Ambient, Diffuse, Specular Reflection Surface Rendering / Shading models Flat
CS 325 Computer Graphics 04 / 02 / 2012 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Illumination modelling Ambient, Diffuse, Specular Reflection Surface Rendering / Shading models Flat
Light Energy and Matter
 Light Energy and Matter UNIT 9 Student Reader E5 Student Reader v. 9 Unit 9 Page 1 2017 KnowAtom TM Front Cover: The front cover shows a photograph of a library s bookshelves that are illuminated by a
Light Energy and Matter UNIT 9 Student Reader E5 Student Reader v. 9 Unit 9 Page 1 2017 KnowAtom TM Front Cover: The front cover shows a photograph of a library s bookshelves that are illuminated by a
03. 3ds Max Design & Mental Ray
 Design + Computing 03. 3ds Max Design & Mental Ray 9/23/2015 CAD & Graphics II HOM2027 Fall 2014 Every Wednesday 2:00 pm 5:50 pm Jin Kook Lee, PhD. 02-2220-2645 designit@hanyang.ac.kr Assistant Professor,
Design + Computing 03. 3ds Max Design & Mental Ray 9/23/2015 CAD & Graphics II HOM2027 Fall 2014 Every Wednesday 2:00 pm 5:50 pm Jin Kook Lee, PhD. 02-2220-2645 designit@hanyang.ac.kr Assistant Professor,
Chapter 17: The Truth about Normals
 Chapter 17: The Truth about Normals What are Normals? When I first started with Blender I read about normals everywhere, but all I knew about them was: If there are weird black spots on your object, go
Chapter 17: The Truth about Normals What are Normals? When I first started with Blender I read about normals everywhere, but all I knew about them was: If there are weird black spots on your object, go
SAMPLING AND NOISE. Increasing the number of samples per pixel gives an anti-aliased image which better represents the actual scene.
 SAMPLING AND NOISE When generating an image, Mantra must determine a color value for each pixel by examining the scene behind the image plane. Mantra achieves this by sending out a number of rays from
SAMPLING AND NOISE When generating an image, Mantra must determine a color value for each pixel by examining the scene behind the image plane. Mantra achieves this by sending out a number of rays from
Photo Studio Optimizer
 CATIA V5 Training Foils Photo Studio Optimizer Version 5 Release 19 September 008 EDU_CAT_EN_PSO_FF_V5R19 Photo Studio Optimizer Objectives of the course Upon completion of this course you will be able
CATIA V5 Training Foils Photo Studio Optimizer Version 5 Release 19 September 008 EDU_CAT_EN_PSO_FF_V5R19 Photo Studio Optimizer Objectives of the course Upon completion of this course you will be able
TUTORIAL 7: Global Illumination & Ambient Occlusion
 TUTORIAL 7: Global Illumination & Ambient Occlusion The goal of this short tutorial is to introduce a few select aspects of mental ray so that you may consider incorporating them in your projects if appropriate.
TUTORIAL 7: Global Illumination & Ambient Occlusion The goal of this short tutorial is to introduce a few select aspects of mental ray so that you may consider incorporating them in your projects if appropriate.
Ray Tracing: Special Topics CSCI 4239/5239 Advanced Computer Graphics Spring 2018
 Ray Tracing: Special Topics CSCI 4239/5239 Advanced Computer Graphics Spring 2018 Theoretical foundations Ray Tracing from the Ground Up Chapters 13-15 Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function BRDF
Ray Tracing: Special Topics CSCI 4239/5239 Advanced Computer Graphics Spring 2018 Theoretical foundations Ray Tracing from the Ground Up Chapters 13-15 Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function BRDF
Advanced Graphics. Path Tracing and Photon Mapping Part 2. Path Tracing and Photon Mapping
 Advanced Graphics Path Tracing and Photon Mapping Part 2 Path Tracing and Photon Mapping Importance Sampling Combine importance sampling techniques Reflectance function (diffuse + specular) Light source
Advanced Graphics Path Tracing and Photon Mapping Part 2 Path Tracing and Photon Mapping Importance Sampling Combine importance sampling techniques Reflectance function (diffuse + specular) Light source
LEVEL 1 ANIMATION ACADEMY2010
 1 Textures add more realism to an environment and characters. There are many 2D painting programs that can be used to create textures, such as Adobe Photoshop and Corel Painter. Many artists use photographs
1 Textures add more realism to an environment and characters. There are many 2D painting programs that can be used to create textures, such as Adobe Photoshop and Corel Painter. Many artists use photographs
LIGHTING - 1. Note. Lights. Ambient occlusion
 Note LIGHTING - 1 The creation and use of lights varies greatly between the default Blender renderer and the Cycles renderer. This section refers only to simple lighting in the default renderer. Lights
Note LIGHTING - 1 The creation and use of lights varies greatly between the default Blender renderer and the Cycles renderer. This section refers only to simple lighting in the default renderer. Lights
Think about film & lighting
 Quiz 3: Textures Camera and Lighting for Animation Hand back Quiz 2 Amy Gooch CS 395: Intro to Animation Summer 2004 Think about film & lighting Reality! Cameras & Viewpoint Lighting in animation Same
Quiz 3: Textures Camera and Lighting for Animation Hand back Quiz 2 Amy Gooch CS 395: Intro to Animation Summer 2004 Think about film & lighting Reality! Cameras & Viewpoint Lighting in animation Same
Ok, so to get started we will take a look at the settings in the Render setup. If we were to take a render right now this is what we would see...
 Caustics - V-Ray In this tutorial we are going to go over some advanced lighting techniques for creating realistic caustic effects using the V-Ray renderer. Caustics function in V-Ray much like they function
Caustics - V-Ray In this tutorial we are going to go over some advanced lighting techniques for creating realistic caustic effects using the V-Ray renderer. Caustics function in V-Ray much like they function
Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction Units of Chapter 32 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formation by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Mirrors Index of Refraction Refraction:
Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction Units of Chapter 32 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formation by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Mirrors Index of Refraction Refraction:
Interior space in daylight Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Interior space in daylight Bonus Chapter 1 Day Lighting an Interior Space 1.1 Introduction In this chapter, you will learn about lighting an interior scene while you work on the lighting for the living
Interior space in daylight Bonus Chapter 1 Day Lighting an Interior Space 1.1 Introduction In this chapter, you will learn about lighting an interior scene while you work on the lighting for the living
Shadow Casting in World Builder. A step to step tutorial on how to reach decent results on the creation of shadows
 Shadow Casting in World Builder A step to step tutorial on how to reach decent results on the creation of shadows Tutorial on shadow casting in World Builder 3.* Introduction Creating decent shadows in
Shadow Casting in World Builder A step to step tutorial on how to reach decent results on the creation of shadows Tutorial on shadow casting in World Builder 3.* Introduction Creating decent shadows in
UNIT C: LIGHT AND OPTICAL SYSTEMS
 1 UNIT C: LIGHT AND OPTICAL SYSTEMS Science 8 2 LIGHT BEHAVES IN PREDICTABLE WAYS. Section 2.0 1 3 LIGHT TRAVELS IN RAYS AND INTERACTS WITH MATERIALS Topic 2.1 RAY DIAGRAMS Scientists use ray diagrams
1 UNIT C: LIGHT AND OPTICAL SYSTEMS Science 8 2 LIGHT BEHAVES IN PREDICTABLE WAYS. Section 2.0 1 3 LIGHT TRAVELS IN RAYS AND INTERACTS WITH MATERIALS Topic 2.1 RAY DIAGRAMS Scientists use ray diagrams
The V-Ray installer will automatically remove any previous installations. This will allow you to seamlessly upgrade from previous versions.
 Overview This guide is to serve as a reference for installing V-Ray for 3ds Max and 3ds Max Design. Please refer to the Glossary page for specific terms used in this document. If you experience any problems,
Overview This guide is to serve as a reference for installing V-Ray for 3ds Max and 3ds Max Design. Please refer to the Glossary page for specific terms used in this document. If you experience any problems,
Advanced Rendering CHAPTER. Render Window. Learning Objectives. Image Pane
 CHAPTER Advanced Rendering Learning Objectives After completing this chapter, you will be able to: Make advanced rendering settings. Set the resolution for a rendering. Save a rendering to an image file.
CHAPTER Advanced Rendering Learning Objectives After completing this chapter, you will be able to: Make advanced rendering settings. Set the resolution for a rendering. Save a rendering to an image file.
Exam Review: Geometric Optics 1. Know the meaning of the following terms and be able to apply or recognize them:
 Exam Review: Geometric Optics 1. Know the meaning of the following terms and be able to apply or recognize them: physics transparent convex mirror real image optics translucent refraction virtual image
Exam Review: Geometric Optics 1. Know the meaning of the following terms and be able to apply or recognize them: physics transparent convex mirror real image optics translucent refraction virtual image
Glass Gambit: Chess set and shader presets for DAZ Studio
 Glass Gambit: Chess set and shader presets for DAZ Studio This product includes a beautiful glass chess set, 70 faceted glass shader presets and a 360 degree prop with 5 material files. Some people find
Glass Gambit: Chess set and shader presets for DAZ Studio This product includes a beautiful glass chess set, 70 faceted glass shader presets and a 360 degree prop with 5 material files. Some people find
Introduction. Chapter Computer Graphics
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1. Computer Graphics Computer graphics has grown at an astounding rate over the last three decades. In the 1970s, frame-buffers capable of displaying digital images were rare and
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1. Computer Graphics Computer graphics has grown at an astounding rate over the last three decades. In the 1970s, frame-buffers capable of displaying digital images were rare and
Lights and Colour in VR. Cecília Sik Lányi University of Pannonia Veszprém
 Lights and Colour in VR Cecília Sik Lányi University of Pannonia Veszprém lanyi@almos.uni-pannon.hu Content First part Definitions (virtual reality, light ) Light types in VR Some examples of these lights
Lights and Colour in VR Cecília Sik Lányi University of Pannonia Veszprém lanyi@almos.uni-pannon.hu Content First part Definitions (virtual reality, light ) Light types in VR Some examples of these lights
Optics Test Science What are some devices that you use in everyday life that require optics?
 Optics Test Science 8 Introduction to Optics 1. What are some devices that you use in everyday life that require optics? Light Energy and Its Sources 308-8 identify and describe properties of visible light
Optics Test Science 8 Introduction to Optics 1. What are some devices that you use in everyday life that require optics? Light Energy and Its Sources 308-8 identify and describe properties of visible light
Lighting for Photorealistic Renderings
 11/28/2005-8:00 am - 9:30 am Room:N. Hemispheres (Salon A4) (Dolphin) Walt Disney World Swan and Dolphin Resort Orlando, Florida Alexander Bicalho - Autodesk DV11-2 If you ever created a 3D model, applied
11/28/2005-8:00 am - 9:30 am Room:N. Hemispheres (Salon A4) (Dolphin) Walt Disney World Swan and Dolphin Resort Orlando, Florida Alexander Bicalho - Autodesk DV11-2 If you ever created a 3D model, applied
ART 268 3D Computer Graphics Texture Mapping and Rendering. Texture Mapping
 ART 268 3D Computer Graphics Texture Mapping and Rendering Texture Mapping Is the way in which a material is wrapped around an object. The default method is UVW mapping (see below). When you drag a material
ART 268 3D Computer Graphics Texture Mapping and Rendering Texture Mapping Is the way in which a material is wrapped around an object. The default method is UVW mapping (see below). When you drag a material
CS130 : Computer Graphics Lecture 8: Lighting and Shading. Tamar Shinar Computer Science & Engineering UC Riverside
 CS130 : Computer Graphics Lecture 8: Lighting and Shading Tamar Shinar Computer Science & Engineering UC Riverside Why we need shading Suppose we build a model of a sphere using many polygons and color
CS130 : Computer Graphics Lecture 8: Lighting and Shading Tamar Shinar Computer Science & Engineering UC Riverside Why we need shading Suppose we build a model of a sphere using many polygons and color
: CASE STUDY: USING MAYA AND MENTAL RAY FOR PHOTOREALISTIC INTERIOR LIGHTING
 2006-1795: CASE STUDY: USING MAYA AND MENTAL RAY FOR PHOTOREALISTIC INTERIOR LIGHTING Marty Fitzgerald, East Tennessee State University American Society for Engineering Education, 2006 Page 11.312.1 Case
2006-1795: CASE STUDY: USING MAYA AND MENTAL RAY FOR PHOTOREALISTIC INTERIOR LIGHTING Marty Fitzgerald, East Tennessee State University American Society for Engineering Education, 2006 Page 11.312.1 Case
Introduction: The Nature of Light
 O1 Introduction: The Nature of Light Introduction Optical elements and systems Basic properties O1.1 Overview Generally Geometrical Optics is considered a less abstract subject than Waves or Physical Optics
O1 Introduction: The Nature of Light Introduction Optical elements and systems Basic properties O1.1 Overview Generally Geometrical Optics is considered a less abstract subject than Waves or Physical Optics
The Animation Process. Lighting: Illusions of Illumination
 The Animation Process Lighting: Illusions of Illumination Lighting = realism Although real people versus real clay/plastic is up to textures Realistic lighting = render time Some properties of lights Colour
The Animation Process Lighting: Illusions of Illumination Lighting = realism Although real people versus real clay/plastic is up to textures Realistic lighting = render time Some properties of lights Colour
Computer visualizations of architectural building illumination
 Lighting in Engineering, Architecture and the Environment 95 Computer visualizations of architectural building illumination S. Mroczkowska Poznan University of Technology, Institute of Electrical Engineering
Lighting in Engineering, Architecture and the Environment 95 Computer visualizations of architectural building illumination S. Mroczkowska Poznan University of Technology, Institute of Electrical Engineering
Caustics - Mental Ray
 Caustics - Mental Ray In this tutorial we are going to go over some advanced lighting techniques for creating realistic caustic effects. Caustics are the focused patterns of light which form after light
Caustics - Mental Ray In this tutorial we are going to go over some advanced lighting techniques for creating realistic caustic effects. Caustics are the focused patterns of light which form after light
Introduction to 3D Concepts
 PART I Introduction to 3D Concepts Chapter 1 Scene... 3 Chapter 2 Rendering: OpenGL (OGL) and Adobe Ray Tracer (ART)...19 1 CHAPTER 1 Scene s0010 1.1. The 3D Scene p0010 A typical 3D scene has several
PART I Introduction to 3D Concepts Chapter 1 Scene... 3 Chapter 2 Rendering: OpenGL (OGL) and Adobe Ray Tracer (ART)...19 1 CHAPTER 1 Scene s0010 1.1. The 3D Scene p0010 A typical 3D scene has several
Light and Sound. Wave Behavior and Interactions
 Light and Sound Wave Behavior and Interactions How do light/sound waves interact with matter? WORD Definition Example Picture REFLECTED REFRACTED is the change in direction of a wave when it changes speed
Light and Sound Wave Behavior and Interactions How do light/sound waves interact with matter? WORD Definition Example Picture REFLECTED REFRACTED is the change in direction of a wave when it changes speed
Table of Contents. What are Ghost Lights? What is Two-sided? What is Kcdm2?
 Page 1 Table of Contents What are Ghost Lights?...1 What is Two-sided?...1 What is Kcdm2?...1 What is Kelvin?...2 Included Props...2 Utility Props...2 Ghost Setup Material...2 GLK Materials...3 How to
Page 1 Table of Contents What are Ghost Lights?...1 What is Two-sided?...1 What is Kcdm2?...1 What is Kelvin?...2 Included Props...2 Utility Props...2 Ghost Setup Material...2 GLK Materials...3 How to
Rules for Deviation of Light Rays During Refraction
 REFLECTION OF LIGHT Refraction of light is the phenomenon due to which a ray of light deviates from its path, at the surface of separation of two media, when the ray of light is travelling from one optical
REFLECTION OF LIGHT Refraction of light is the phenomenon due to which a ray of light deviates from its path, at the surface of separation of two media, when the ray of light is travelling from one optical
AV Using Autodesk 3ds Max Design, Autodesk Revit, and iray to Render Compelling Photographic Scenes
 AV4672 - Using Autodesk 3ds Max Design, Autodesk Revit, and iray to Render Compelling Photographic Scenes Steven Schain Autodesk Certified Instructor AV4672 This virtual class introduces designers to the
AV4672 - Using Autodesk 3ds Max Design, Autodesk Revit, and iray to Render Compelling Photographic Scenes Steven Schain Autodesk Certified Instructor AV4672 This virtual class introduces designers to the
Lecture 7 Notes: 07 / 11. Reflection and refraction
 Lecture 7 Notes: 07 / 11 Reflection and refraction When an electromagnetic wave, such as light, encounters the surface of a medium, some of it is reflected off the surface, while some crosses the boundary
Lecture 7 Notes: 07 / 11 Reflection and refraction When an electromagnetic wave, such as light, encounters the surface of a medium, some of it is reflected off the surface, while some crosses the boundary
Lighting and Shadows. Lecture #11. Thanks to Langer-Zucker, Henrik Wann Jensen, Ravi Ramamoorthi, Hanrahan, Preetham
 Lighting and Shadows Lecture #11 Thanks to Langer-Zucker, Henrik Wann Jensen, Ravi Ramamoorthi, Hanrahan, Preetham Appearance of An Outdoor Scene Illumination Spectrum Reflectance (BRDF, BTF) Illumination
Lighting and Shadows Lecture #11 Thanks to Langer-Zucker, Henrik Wann Jensen, Ravi Ramamoorthi, Hanrahan, Preetham Appearance of An Outdoor Scene Illumination Spectrum Reflectance (BRDF, BTF) Illumination
How does light energy travel? transparent transmit mediums media medium
 Have you ever observed a solar eclipse like the one in this photograph? During a solar eclipse, it can become very dark in the middle of a sunny day. This may seem amazing to us, but it was terrifying
Have you ever observed a solar eclipse like the one in this photograph? During a solar eclipse, it can become very dark in the middle of a sunny day. This may seem amazing to us, but it was terrifying
Science 8 Chapter 5 Section 1
 Science 8 Chapter 5 Section 1 The Ray Model of Light (pp. 172-187) Models of Light wave model of light: a model in which light is a type of wave that travels through space and transfers energy from one
Science 8 Chapter 5 Section 1 The Ray Model of Light (pp. 172-187) Models of Light wave model of light: a model in which light is a type of wave that travels through space and transfers energy from one
Shadows in the graphics pipeline
 Shadows in the graphics pipeline Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 19 February There are a number of visual cues that help let the viewer know about the 3D relationships between objects
Shadows in the graphics pipeline Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 19 February There are a number of visual cues that help let the viewer know about the 3D relationships between objects
2/26/2016. Chapter 23 Ray Optics. Chapter 23 Preview. Chapter 23 Preview
 Chapter 23 Ray Optics Chapter Goal: To understand and apply the ray model of light. Slide 23-2 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-3 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-4 1 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-5 Chapter 23 Preview
Chapter 23 Ray Optics Chapter Goal: To understand and apply the ray model of light. Slide 23-2 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-3 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-4 1 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-5 Chapter 23 Preview
Rendering with mental ray and 3ds Max
 Rendering with mental ray and 3ds Max Rendering with mental ray and 3ds Max Second Edition Joep van der Steen Ted Boardman AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO
Rendering with mental ray and 3ds Max Rendering with mental ray and 3ds Max Second Edition Joep van der Steen Ted Boardman AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO
COMP environment mapping Mar. 12, r = 2n(n v) v
 Rendering mirror surfaces The next texture mapping method assumes we have a mirror surface, or at least a reflectance function that contains a mirror component. Examples might be a car window or hood,
Rendering mirror surfaces The next texture mapping method assumes we have a mirror surface, or at least a reflectance function that contains a mirror component. Examples might be a car window or hood,
w Foley, Section16.1 Reading
 Shading w Foley, Section16.1 Reading Introduction So far, we ve talked exclusively about geometry. w What is the shape of an object? w How do I place it in a virtual 3D space? w How do I know which pixels
Shading w Foley, Section16.1 Reading Introduction So far, we ve talked exclusively about geometry. w What is the shape of an object? w How do I place it in a virtual 3D space? w How do I know which pixels
COM337 COMPUTER GRAPHICS Other Topics
 COM337 COMPUTER GRAPHICS Other Topics Animation, Surface Details, Global Illumination Kurtuluş Küllü based on the book by Hearn, Baker, and Carithers There are some other important issues and topics that
COM337 COMPUTER GRAPHICS Other Topics Animation, Surface Details, Global Illumination Kurtuluş Küllü based on the book by Hearn, Baker, and Carithers There are some other important issues and topics that
Lighting affects appearance
 Lighting affects appearance 1 Source emits photons Light And then some reach the eye/camera. Photons travel in a straight line When they hit an object they: bounce off in a new direction or are absorbed
Lighting affects appearance 1 Source emits photons Light And then some reach the eye/camera. Photons travel in a straight line When they hit an object they: bounce off in a new direction or are absorbed
What is Light? What is Electromagnetic Radiation?
 What is Light? Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that can be seen by the eye. What is Electromagnetic Radiation? Electromagnetic radiation is a term used to describe waves that are created by
What is Light? Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that can be seen by the eye. What is Electromagnetic Radiation? Electromagnetic radiation is a term used to describe waves that are created by
OpenGl Pipeline. triangles, lines, points, images. Per-vertex ops. Primitive assembly. Texturing. Rasterization. Per-fragment ops.
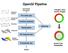 OpenGl Pipeline Individual Vertices Transformed Vertices Commands Processor Per-vertex ops Primitive assembly triangles, lines, points, images Primitives Fragments Rasterization Texturing Per-fragment
OpenGl Pipeline Individual Vertices Transformed Vertices Commands Processor Per-vertex ops Primitive assembly triangles, lines, points, images Primitives Fragments Rasterization Texturing Per-fragment
All forms of EM waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum = 3.00 x 10 8 m/s This speed is constant in air as well
 Pre AP Physics Light & Optics Chapters 14-16 Light is an electromagnetic wave Electromagnetic waves: Oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to the direction the wave moves Difference
Pre AP Physics Light & Optics Chapters 14-16 Light is an electromagnetic wave Electromagnetic waves: Oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to the direction the wave moves Difference
What is it? How does it work? How do we use it?
 What is it? How does it work? How do we use it? Dual Nature http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dfpeprq7ogc o Electromagnetic Waves display wave behavior o Created by oscillating electric and magnetic fields
What is it? How does it work? How do we use it? Dual Nature http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dfpeprq7ogc o Electromagnetic Waves display wave behavior o Created by oscillating electric and magnetic fields
Visualization Insider A Little Background Information
 Visualization Insider A Little Background Information Visualization Insider 2 Creating Backgrounds for 3D Scenes Backgrounds are a critical part of just about every type of 3D scene. Although they are
Visualization Insider A Little Background Information Visualization Insider 2 Creating Backgrounds for 3D Scenes Backgrounds are a critical part of just about every type of 3D scene. Although they are
Chapter 35. The Nature of Light and the Laws of Geometric Optics
 Chapter 35 The Nature of Light and the Laws of Geometric Optics Introduction to Light Light is basic to almost all life on Earth. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation. Light represents energy transfer
Chapter 35 The Nature of Light and the Laws of Geometric Optics Introduction to Light Light is basic to almost all life on Earth. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation. Light represents energy transfer
Soft shadows. Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 21 February
 Soft shadows Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 21 February Soft shadows are what we normally see in the real world. If you are near a bare halogen bulb, a stage spotlight, or other
Soft shadows Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 21 February Soft shadows are what we normally see in the real world. If you are near a bare halogen bulb, a stage spotlight, or other
SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT. Key Concepts. X-planation. Physical Sciences Grade In this session we:
 SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT Key Concepts In this session we: Explain what light is, where light comes from and why it is important Identify what happens when light strikes the surface of different objects
SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT Key Concepts In this session we: Explain what light is, where light comes from and why it is important Identify what happens when light strikes the surface of different objects
Daylighting. Note: Daylight is typically defined as diffuse light and is very different from sunlight (direct solar radiation).
 systems can significantly reduce both lighting consumption and cooling-energy consumption by reducing the electric-lighting heat gain in the building. However, daylighting can also cause increased heating-energy
systems can significantly reduce both lighting consumption and cooling-energy consumption by reducing the electric-lighting heat gain in the building. However, daylighting can also cause increased heating-energy
Computer Graphics. Lecture 13. Global Illumination 1: Ray Tracing and Radiosity. Taku Komura
 Computer Graphics Lecture 13 Global Illumination 1: Ray Tracing and Radiosity Taku Komura 1 Rendering techniques Can be classified as Local Illumination techniques Global Illumination techniques Local
Computer Graphics Lecture 13 Global Illumination 1: Ray Tracing and Radiosity Taku Komura 1 Rendering techniques Can be classified as Local Illumination techniques Global Illumination techniques Local
Computer Graphics. Illumination and Shading
 () Illumination and Shading Dr. Ayman Eldeib Lighting So given a 3-D triangle and a 3-D viewpoint, we can set the right pixels But what color should those pixels be? If we re attempting to create a realistic
() Illumination and Shading Dr. Ayman Eldeib Lighting So given a 3-D triangle and a 3-D viewpoint, we can set the right pixels But what color should those pixels be? If we re attempting to create a realistic
Computer graphics Labs: Blender (2/3) LuxRender: Interior Scene Rendering
 Computer graphics Labs: Blender (2/3) LuxRender: Interior Scene Rendering University of Liège Department of Aerospace and Mechanical engineering Designed with Blender 2.76b LuxRender During the first tutorial
Computer graphics Labs: Blender (2/3) LuxRender: Interior Scene Rendering University of Liège Department of Aerospace and Mechanical engineering Designed with Blender 2.76b LuxRender During the first tutorial
CENG 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics. Ray Tracing: Shading
 CENG 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Ray Tracing: Shading Last Week Until now we learned: How to create the primary rays from the given camera and image plane parameters How to intersect these rays
CENG 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Ray Tracing: Shading Last Week Until now we learned: How to create the primary rays from the given camera and image plane parameters How to intersect these rays
CSCI 4972/6963 Advanced Computer Graphics Quiz 2 Tuesday April 17, 2007 noon-1:30pm
 CSCI 4972/6963 Advanced Computer Graphics Quiz 2 Tuesday April 17, 2007 noon-1:30pm Name: RCS username: This quiz is closed book & closed notes except for one 8.5x11 (double-sided) sheet of notes. Please
CSCI 4972/6963 Advanced Computer Graphics Quiz 2 Tuesday April 17, 2007 noon-1:30pm Name: RCS username: This quiz is closed book & closed notes except for one 8.5x11 (double-sided) sheet of notes. Please
Physics 1230: Light and Color
 Physics 1230: Light and Color Chuck Rogers, Charles.Rogers@colorado.edu Ryan Henley, Valyria McFarland, Peter Siegfried physicscourses.colorado.edu/phys1230 Congratulations on completing Exam 1. Great
Physics 1230: Light and Color Chuck Rogers, Charles.Rogers@colorado.edu Ryan Henley, Valyria McFarland, Peter Siegfried physicscourses.colorado.edu/phys1230 Congratulations on completing Exam 1. Great
SNC2D PHYSICS 4/27/2013. LIGHT & GEOMETRIC OPTICS L Light Rays & Reflection (P ) Light Rays & Reflection. The Ray Model of Light
 SNC2D PHYSICS LIGHT & GEOMETRIC OPTICS L Light Rays & Reflection (P.402-409) Light Rays & Reflection A driver adjusts her rearview mirror. The mirror allows her to see the cars behind her. Mirrors help
SNC2D PHYSICS LIGHT & GEOMETRIC OPTICS L Light Rays & Reflection (P.402-409) Light Rays & Reflection A driver adjusts her rearview mirror. The mirror allows her to see the cars behind her. Mirrors help
MODELING LED LIGHTING COLOR EFFECTS IN MODERN OPTICAL ANALYSIS SOFTWARE LED Professional Magazine Webinar 10/27/2015
 MODELING LED LIGHTING COLOR EFFECTS IN MODERN OPTICAL ANALYSIS SOFTWARE LED Professional Magazine Webinar 10/27/2015 Presenter Dave Jacobsen Senior Application Engineer at Lambda Research Corporation for
MODELING LED LIGHTING COLOR EFFECTS IN MODERN OPTICAL ANALYSIS SOFTWARE LED Professional Magazine Webinar 10/27/2015 Presenter Dave Jacobsen Senior Application Engineer at Lambda Research Corporation for
critical theory Computer Science
 Art/Science Shading, Materials, Collaboration Textures Example title Artists In the recommend real world, two the main following: factors determine the appearance of a surface: basic understanding what
Art/Science Shading, Materials, Collaboration Textures Example title Artists In the recommend real world, two the main following: factors determine the appearance of a surface: basic understanding what
At the interface between two materials, where light can be reflected or refracted. Within a material, where the light can be scattered or absorbed.
 At the interface between two materials, where light can be reflected or refracted. Within a material, where the light can be scattered or absorbed. The eye sees by focusing a diverging bundle of rays from
At the interface between two materials, where light can be reflected or refracted. Within a material, where the light can be scattered or absorbed. The eye sees by focusing a diverging bundle of rays from
There are many kinds of surface shaders, from those that affect basic surface color, to ones that apply bitmap textures and displacement.
 mental ray Overview Mental ray is a powerful renderer which is based on a scene description language. You can use it as a standalone renderer, or even better, integrated with 3D applications. In 3D applications,
mental ray Overview Mental ray is a powerful renderer which is based on a scene description language. You can use it as a standalone renderer, or even better, integrated with 3D applications. In 3D applications,
COMP371 COMPUTER GRAPHICS
 COMP371 COMPUTER GRAPHICS SESSION 15 RAY TRACING 1 Announcements Programming Assignment 3 out today - overview @ end of the class Ray Tracing 2 Lecture Overview Review of last class Ray Tracing 3 Local
COMP371 COMPUTER GRAPHICS SESSION 15 RAY TRACING 1 Announcements Programming Assignment 3 out today - overview @ end of the class Ray Tracing 2 Lecture Overview Review of last class Ray Tracing 3 Local
Local Illumination. CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller. Machiraju/Zhang/Möller
 Local Illumination CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Graphics Pipeline Hardware Modelling Transform Visibility Illumination + Shading Perception, Interaction Color Texture/ Realism
Local Illumination CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Graphics Pipeline Hardware Modelling Transform Visibility Illumination + Shading Perception, Interaction Color Texture/ Realism
Lighting Simulation Tools in the process of design. Laleh Amany Autumn 2017
 Lighting Simulation Tools in the process of design Laleh Amany Autumn 2017 Lighting simulation is important for architectural projects from multiple p e r s p e c t i v e f o r c o n c e p t i o n a n
Lighting Simulation Tools in the process of design Laleh Amany Autumn 2017 Lighting simulation is important for architectural projects from multiple p e r s p e c t i v e f o r c o n c e p t i o n a n
3D Space is one of the most rewarding areas
 Lesson 8 206 3D Space Add a new dimension to your animations. In This Lesson 207 enabling layers for 3D 208 moving and rotating layers in 3D space 210 multiplaning effects 212 3D motion paths 213 multiple
Lesson 8 206 3D Space Add a new dimension to your animations. In This Lesson 207 enabling layers for 3D 208 moving and rotating layers in 3D space 210 multiplaning effects 212 3D motion paths 213 multiple
Topics and things to know about them:
 Practice Final CMSC 427 Distributed Tuesday, December 11, 2007 Review Session, Monday, December 17, 5:00pm, 4424 AV Williams Final: 10:30 AM Wednesday, December 19, 2007 General Guidelines: The final will
Practice Final CMSC 427 Distributed Tuesday, December 11, 2007 Review Session, Monday, December 17, 5:00pm, 4424 AV Williams Final: 10:30 AM Wednesday, December 19, 2007 General Guidelines: The final will
CS5670: Computer Vision
 CS5670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Light & Perception Announcements Quiz on Tuesday Project 3 code due Monday, April 17, by 11:59pm artifact due Wednesday, April 19, by 11:59pm Can we determine shape
CS5670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Light & Perception Announcements Quiz on Tuesday Project 3 code due Monday, April 17, by 11:59pm artifact due Wednesday, April 19, by 11:59pm Can we determine shape
Lecture 18: Primer on Ray Tracing Techniques
 Lecture 18: Primer on Ray Tracing Techniques 6.172: Performance Engineering of Software Systems Joshua Slocum November 16, 2010 A Little Background Image rendering technique Simulate rays of light - ray
Lecture 18: Primer on Ray Tracing Techniques 6.172: Performance Engineering of Software Systems Joshua Slocum November 16, 2010 A Little Background Image rendering technique Simulate rays of light - ray
Light and all its colours
 Light and all its colours Hold a CD to the light You can see all the colours of the rainbow The CD is a non-luminous body It is reflecting white light from the sun Where do the colours come from? Truth
Light and all its colours Hold a CD to the light You can see all the colours of the rainbow The CD is a non-luminous body It is reflecting white light from the sun Where do the colours come from? Truth
3 Interactions of Light Waves
 CHAPTER 22 3 Interactions of Light Waves SECTION The Nature of Light BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How does reflection affect the way we see
CHAPTER 22 3 Interactions of Light Waves SECTION The Nature of Light BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How does reflection affect the way we see
Module 5: Video Modeling Lecture 28: Illumination model. The Lecture Contains: Diffuse and Specular Reflection. Objectives_template
 The Lecture Contains: Diffuse and Specular Reflection file:///d /...0(Ganesh%20Rana)/MY%20COURSE_Ganesh%20Rana/Prof.%20Sumana%20Gupta/FINAL%20DVSP/lecture%2028/28_1.htm[12/30/2015 4:22:29 PM] Diffuse and
The Lecture Contains: Diffuse and Specular Reflection file:///d /...0(Ganesh%20Rana)/MY%20COURSE_Ganesh%20Rana/Prof.%20Sumana%20Gupta/FINAL%20DVSP/lecture%2028/28_1.htm[12/30/2015 4:22:29 PM] Diffuse and
Unit 5.A Properties of Light Essential Fundamentals of Light 1. Electromagnetic radiation has oscillating magnetic and electric components.
 Unit 5.A Properties of Light Essential Fundamentals of Light 1. Electromagnetic radiation has oscillating magnetic and electric components. Early Booklet E.C.: + 1 Unit 5.A Hwk. Pts.: / 18 Unit 5.A Lab
Unit 5.A Properties of Light Essential Fundamentals of Light 1. Electromagnetic radiation has oscillating magnetic and electric components. Early Booklet E.C.: + 1 Unit 5.A Hwk. Pts.: / 18 Unit 5.A Lab
Today. Global illumination. Shading. Interactive applications. Rendering pipeline. Computergrafik. Shading Introduction Local shading models
 Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2009 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation of physics Global
Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2009 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation of physics Global
Autodesk Fusion 360: Render. Overview
 Overview Rendering is the process of generating an image by combining geometry, camera, texture, lighting and shading (also called materials) information using a computer program. Before an image can be
Overview Rendering is the process of generating an image by combining geometry, camera, texture, lighting and shading (also called materials) information using a computer program. Before an image can be
Problem Set 4 Part 1 CMSC 427 Distributed: Thursday, November 1, 2007 Due: Tuesday, November 20, 2007
 Problem Set 4 Part 1 CMSC 427 Distributed: Thursday, November 1, 2007 Due: Tuesday, November 20, 2007 Programming For this assignment you will write a simple ray tracer. It will be written in C++ without
Problem Set 4 Part 1 CMSC 427 Distributed: Thursday, November 1, 2007 Due: Tuesday, November 20, 2007 Programming For this assignment you will write a simple ray tracer. It will be written in C++ without
Lecture 15: Shading-I. CITS3003 Graphics & Animation
 Lecture 15: Shading-I CITS3003 Graphics & Animation E. Angel and D. Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 6E Addison-Wesley 2012 Objectives Learn that with appropriate shading so objects appear as threedimensional
Lecture 15: Shading-I CITS3003 Graphics & Animation E. Angel and D. Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 6E Addison-Wesley 2012 Objectives Learn that with appropriate shading so objects appear as threedimensional
4. A bulb has a luminous flux of 2400 lm. What is the luminous intensity of the bulb?
 1. Match the physical quantities (first column) with the units (second column). 4. A bulb has a luminous flux of 2400 lm. What is the luminous intensity of the bulb? (π=3.) Luminous flux A. candela Radiant
1. Match the physical quantities (first column) with the units (second column). 4. A bulb has a luminous flux of 2400 lm. What is the luminous intensity of the bulb? (π=3.) Luminous flux A. candela Radiant
Light and Optics Learning Goals Review
 SNC2D Light and Optics Learning Goals Review Different types of light be familiar with the different types of light i.e. direct and indirect, natural and artificial and be able to describe the different
SNC2D Light and Optics Learning Goals Review Different types of light be familiar with the different types of light i.e. direct and indirect, natural and artificial and be able to describe the different
diffuse diffuse reflection refraction diffuse mapping diffuse reflection reflection filter mapping mapping reflection
 Matières 1 2 3 mapping diffuse reflection diffuse transparency reflection refraction diffuse mapping diffuse reflection diffuse reflection filter mapping bump mapping mapping mapping diffuse reflection
Matières 1 2 3 mapping diffuse reflection diffuse transparency reflection refraction diffuse mapping diffuse reflection diffuse reflection filter mapping bump mapping mapping mapping diffuse reflection
