Fitting D.A. Forsyth, CS 543
|
|
|
- Letitia Stafford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fitting D.A. Forsyth, CS 543
2 Fitting Choose a parametric object/some objects to represent a set of tokens Most interesting case is when criterion is not local can t tell whether a set of points lies on a line by looking only at each point and the next. Three main questions: what object represents this set of tokens best? which of several objects gets which token? how many objects are there? (you could read line for object here, or circle, or ellipse or...)
3 Scenes as stages Hedau et al, in review
4 The stage Hedau et al, in review
5 The players Hedau et al, in review
6 Hedau et al, in review
7 Stage and Players
8 Now, what can we do... Free space estimate using standard SFM construction for camera given manhattan world couple appearance model of objects to approximate geometric models? Hedau et al, in review
9 Fitting and the Hough Transform Purports to answer all three questions We do for lines only in practice, answer isn t usually all that much help A line is the set of points (x, y) such that Different choices of θ, d>0 give different lines ( sinθ)x + ( cosθ)y + d = 0 For any (x, y) there is a one parameter family of lines through this point, given by ( sinθ)x + ( cosθ)y + d = 0 Each point gets to vote for each line in the family; if there is a line that has lots of votes, that should be the line passing through the points
10 tokens votes
11 Mechanics of the Hough transform Construct an array representing θ, d For each point, render the curve (θ, d) into this array, adding one at each cell Difficulties how big should the cells be? (too big, and we cannot distinguish between quite different lines; too small, and noise causes lines to be missed) How many lines? count the peaks in the Hough array Who belongs to which line? tag the votes Hardly ever satisfactory in practice, because problems with noise and cell size defeat it
12 tokens votes
13
14
15
16 Line fitting can be max. likelihood - but choice of model is important
17 Who came from which line? Assume we know how many lines there are - but which lines are they? easy, if we know who came from which line Three strategies Incremental line fitting K-means Probabilistic (later!)
18
19
20 Robustness As we have seen, squared error can be a source of bias in the presence of noise points Another is an M-estimator One fix is EM - we ll do this shortly Square nearby, threshold far away A third is RANSAC Search for good points
21
22
23
24
25 RANSAC Algorithm Choose a small subset uniformly at random Fit to that Anything that is close to result is signal; all others are noise Refit Do this many times and choose the best Issues How many times? Often enough that we are likely to have a good line How big a subset? Smallest possible What does close mean? Depends on the problem What is a good line? The number of nearby points is so big it is unlikely to be all outliers
26
27 Fitting curves other than lines In principle, an easy generalisation The probability of obtaining a point, given a curve, is given by a negative exponential of distance squared In practice, rather hard It is generally difficult to compute the distance between a point and a curve
28 Missing variable problems In many vision problems, if some variables were known the maximum likelihood inference problem would be easy fitting; if we knew which line each token came from, it would be easy to determine line parameters segmentation; if we knew the segment each pixel came from, it would be easy to determine the segment parameters etc. fundamental matrix estimation; if we knew which feature corresponded to which, it would be easy to determine the fundamental matrix This sort of thing happens in statistics, too
29 Missing variable problems Strategy eg estimate appropriate values for the missing variables plug these in, now estimate parameters re-estimate appropriate values for missing variables, continue guess which line gets which point now fit the lines now reallocate points to lines, using our knowledge of the lines now refit, etc. We ve seen this line of thought before (k means)
30 Missing variables - strategy We have a problem with parameters, missing variables This suggests: Iterate until convergence replace missing variable with expected values, given fixed values of parameters fix missing variables, choose parameters to maximise likelihood given fixed values of missing variable e.g., iterate till convergence allocate each point to a line with a weight, which is the probability of the point given the line refit lines to the weighted set of points Converges to local extremum Somewhat more general form is available
31 Lines and robustness We have one line, and n points This is a mixture model: Some come from the line, some from noise ( ) = P point line P point line and noise params We wish to determine line parameters p(comes from line) ( )P( comes from line) + P( point noise)p( comes from noise) = P( point line)λ + P( point noise)(1 λ)
32 Complete data Introduce a set of hidden variables, δ, one for each point. They are one when the point is on the line, and zero when off. If these were known, we would have: log P (x i, y i, δ i φ, c) = [[ δ i x i cos φ + y i sin φ + c 2σ 2 + (1 δ i )k n ] ] + K + log P (δ i )
33 The complete data log-likelihood Log-likelihood if delta s were known quite easy to work with θ = (φ, c, P (δ i = 1)) = (φ, c, π) L(θ; x, δ) = i = i log P (x i, y i, δ i φ, c) [[ δ i x i cos φ + y i sin φ + c 2σ 2 ] + (1 δ i )k n + K + log P (δ i )
34 But we don t know delta Solution: Iterate estimate delta s with fixed parameters estimate parameters with new estimates of delta Formally obtain a starting theta now at each step, maximize Q(θ; θ (n) ) = L(θ; x, δ)p (δ x, θ (n) )dδ
35 Substituting for delta Notice: points close to current line means P(delta=1 x, theta) will be big far -> small like k-means but now we are averaging sometimes called soft assignment P (δ i = 1 x, θ (n) ) = P (δ i = 1 x i, θ (n) ) = P (x i, δ i = 1 θ (n) ) P (x i θ (n) ) = P (x i, δ i = 1, θ (n) )P (δ i = 1) P (x i δ i = 1, θ (n) )P (δ i = 1) + P (x i δ i = 0, θ (n) )P (δ i = 0
36 Algorithm for line fitting Obtain some start point ( ) = φ ( 0 ),c ( 0),λ 0 θ 0 ( ( ) ) Now compute δ s using formula above Now compute maximum likelihood estimate of φ, c come from fitting to weighted points λ comes by counting Iterate to convergence θ ( 1)
37
38 The expected values of the deltas at the maximum (notice the one value close to zero).
39 Closeup of the fit
40 Choosing parameters What about the noise parameter, and the sigma for the line? several methods from first principles knowledge of the problem (seldom really possible) play around with a few examples and choose (usually quite effective, as precise choice doesn t matter much) notice that if kn is large, this says that points very seldom come from noise, however far from the line they lie usually biases the fit, by pushing outliers into the line rule of thumb; its better to fit to the better fitting points, within reason; if this is hard to do, then the model could be a problem
41 Issues with EM Local maxima can be a serious nuisance in some problems Starting k means to cluster the points is often a good idea no guarantee that we have reached the right maximum
42 Local maximum
43 which is an excellent fit to some points
44 and the deltas for this maximum
45 A dataset that is well fitted by four lines
46 Result of EM fitting, with one line (or at least, one available local maximum).
47 Result of EM fitting, with two lines (or at least, one available local maximum).
48 Seven lines can produce a rather logical answer
49 Motion segmentation with EM Model image pair (or video sequence) as consisting of regions of parametric motion affine motion is popular Now we need to Likelihood assume v x v y = a c determine which pixels belong to which region estimate parameters I( x, y,t) = I( x + v x, y + v y,t +1) +noise b d x y + t x t y Straightforward missing variable problem, rest is calculation
50 Sequence
51 Three frames from the MPEG flower garden sequence Figure from Representing Images with layers,, by J. Wang and E.H. Adelson, IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1994, c 1994, IEEE
52 Grey level shows region no. with highest probability Segments and motion fields associated with them Figure from Representing Images with layers,, by J. Wang and E.H. Adelson, IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1994, c 1994, IEEE
53 Segments
54 Alignment (motion compensation) For each segment in each frame, know a motion model We could add a motion to all pixels in the frame that stabilizes the segment
55 Compensation
56 Compensation
57 Compensation
58
59 Segment appearance
60 Segment appearance
61 Reassembling segments
62 If we use multiple frames to estimate the appearance of a segment, we can fill in occlusions; so we can re-render the sequence with some segments removed. Figure from Representing Images with layers,, by J. Wang and E.H. Adelson, IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1994, c 1994, IEEE
63 Reassemble w/o tree
Fitting. Choose a parametric object/some objects to represent a set of tokens Most interesting case is when criterion is not local
 Fitting Choose a parametric object/some objects to represent a set of tokens Most interesting case is when criterion is not local can t tell whether a set of points lies on a line by looking only at each
Fitting Choose a parametric object/some objects to represent a set of tokens Most interesting case is when criterion is not local can t tell whether a set of points lies on a line by looking only at each
Missing variable problems
 Missing variable problems In many vision problems, if some variables were known the maximum likelihood inference problem would be easy fitting; if we knew which line each token came from, it would be easy
Missing variable problems In many vision problems, if some variables were known the maximum likelihood inference problem would be easy fitting; if we knew which line each token came from, it would be easy
6.801/866. Segmentation and Line Fitting. T. Darrell
 6.801/866 Segmentation and Line Fitting T. Darrell Segmentation and Line Fitting Gestalt grouping Background subtraction K-Means Graph cuts Hough transform Iterative fitting (Next time: Probabilistic segmentation)
6.801/866 Segmentation and Line Fitting T. Darrell Segmentation and Line Fitting Gestalt grouping Background subtraction K-Means Graph cuts Hough transform Iterative fitting (Next time: Probabilistic segmentation)
CS443: Digital Imaging and Multimedia Perceptual Grouping Detecting Lines and Simple Curves
 CS443: Digital Imaging and Multimedia Perceptual Grouping Detecting Lines and Simple Curves Spring 2008 Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines Perceptual Grouping and Segmentation
CS443: Digital Imaging and Multimedia Perceptual Grouping Detecting Lines and Simple Curves Spring 2008 Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines Perceptual Grouping and Segmentation
Computer Vision 6 Segmentation by Fitting
 Computer Vision 6 Segmentation by Fitting MAP-I Doctoral Programme Miguel Tavares Coimbra Outline The Hough Transform Fitting Lines Fitting Curves Fitting as a Probabilistic Inference Problem Acknowledgements:
Computer Vision 6 Segmentation by Fitting MAP-I Doctoral Programme Miguel Tavares Coimbra Outline The Hough Transform Fitting Lines Fitting Curves Fitting as a Probabilistic Inference Problem Acknowledgements:
Fitting. Lecture 8. Cristian Sminchisescu. Slide credits: K. Grauman, S. Seitz, S. Lazebnik, D. Forsyth, J. Ponce
 Fitting Lecture 8 Cristian Sminchisescu Slide credits: K. Grauman, S. Seitz, S. Lazebnik, D. Forsyth, J. Ponce Fitting We want to associate a model with observed features [Fig from Marszalek & Schmid,
Fitting Lecture 8 Cristian Sminchisescu Slide credits: K. Grauman, S. Seitz, S. Lazebnik, D. Forsyth, J. Ponce Fitting We want to associate a model with observed features [Fig from Marszalek & Schmid,
Segmentation and low-level grouping.
 Segmentation and low-level grouping. Bill Freeman, MIT 6.869 April 14, 2005 Readings: Mean shift paper and background segmentation paper. Mean shift IEEE PAMI paper by Comanici and Meer, http://www.caip.rutgers.edu/~comanici/papers/msrobustapproach.pdf
Segmentation and low-level grouping. Bill Freeman, MIT 6.869 April 14, 2005 Readings: Mean shift paper and background segmentation paper. Mean shift IEEE PAMI paper by Comanici and Meer, http://www.caip.rutgers.edu/~comanici/papers/msrobustapproach.pdf
Feature Detectors and Descriptors: Corners, Lines, etc.
 Feature Detectors and Descriptors: Corners, Lines, etc. Edges vs. Corners Edges = maxima in intensity gradient Edges vs. Corners Corners = lots of variation in direction of gradient in a small neighborhood
Feature Detectors and Descriptors: Corners, Lines, etc. Edges vs. Corners Edges = maxima in intensity gradient Edges vs. Corners Corners = lots of variation in direction of gradient in a small neighborhood
Mixture Models and EM
 Mixture Models and EM Goal: Introduction to probabilistic mixture models and the expectationmaximization (EM) algorithm. Motivation: simultaneous fitting of multiple model instances unsupervised clustering
Mixture Models and EM Goal: Introduction to probabilistic mixture models and the expectationmaximization (EM) algorithm. Motivation: simultaneous fitting of multiple model instances unsupervised clustering
HOUGH TRANSFORM CS 6350 C V
 HOUGH TRANSFORM CS 6350 C V HOUGH TRANSFORM The problem: Given a set of points in 2-D, find if a sub-set of these points, fall on a LINE. Hough Transform One powerful global method for detecting edges
HOUGH TRANSFORM CS 6350 C V HOUGH TRANSFORM The problem: Given a set of points in 2-D, find if a sub-set of these points, fall on a LINE. Hough Transform One powerful global method for detecting edges
Fitting. Fitting. Slides S. Lazebnik Harris Corners Pkwy, Charlotte, NC
 Fitting We ve learned how to detect edges, corners, blobs. Now what? We would like to form a higher-level, more compact representation of the features in the image by grouping multiple features according
Fitting We ve learned how to detect edges, corners, blobs. Now what? We would like to form a higher-level, more compact representation of the features in the image by grouping multiple features according
Multiple Model Estimation : The EM Algorithm & Applications
 Multiple Model Estimation : The EM Algorithm & Applications Princeton University COS 429 Lecture Dec. 4, 2008 Harpreet S. Sawhney hsawhney@sarnoff.com Plan IBR / Rendering applications of motion / pose
Multiple Model Estimation : The EM Algorithm & Applications Princeton University COS 429 Lecture Dec. 4, 2008 Harpreet S. Sawhney hsawhney@sarnoff.com Plan IBR / Rendering applications of motion / pose
Segmentation: Clustering, Graph Cut and EM
 Segmentation: Clustering, Graph Cut and EM Ying Wu Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Northwestern University, Evanston, IL 60208 yingwu@northwestern.edu http://www.eecs.northwestern.edu/~yingwu
Segmentation: Clustering, Graph Cut and EM Ying Wu Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Northwestern University, Evanston, IL 60208 yingwu@northwestern.edu http://www.eecs.northwestern.edu/~yingwu
CS 534: Computer Vision Segmentation and Perceptual Grouping
 CS 534: Computer Vision Segmentation and Perceptual Grouping Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science CS 534 Segmentation - 1 Outlines Mid-level vision What is segmentation Perceptual Grouping Segmentation
CS 534: Computer Vision Segmentation and Perceptual Grouping Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science CS 534 Segmentation - 1 Outlines Mid-level vision What is segmentation Perceptual Grouping Segmentation
INFO0948 Fitting and Shape Matching
 INFO0948 Fitting and Shape Matching Renaud Detry University of Liège, Belgium Updated March 31, 2015 1 / 33 These slides are based on the following book: D. Forsyth and J. Ponce. Computer vision: a modern
INFO0948 Fitting and Shape Matching Renaud Detry University of Liège, Belgium Updated March 31, 2015 1 / 33 These slides are based on the following book: D. Forsyth and J. Ponce. Computer vision: a modern
human vision: grouping k-means clustering graph-theoretic clustering Hough transform line fitting RANSAC
 COS 429: COMPUTER VISON Segmentation human vision: grouping k-means clustering graph-theoretic clustering Hough transform line fitting RANSAC Reading: Chapters 14, 15 Some of the slides are credited to:
COS 429: COMPUTER VISON Segmentation human vision: grouping k-means clustering graph-theoretic clustering Hough transform line fitting RANSAC Reading: Chapters 14, 15 Some of the slides are credited to:
Here are some of the more basic curves that we ll need to know how to do as well as limits on the parameter if they are required.
 1 of 10 23/07/2016 05:15 Paul's Online Math Notes Calculus III (Notes) / Line Integrals / Line Integrals - Part I Problems] [Notes] [Practice Problems] [Assignment Calculus III - Notes Line Integrals Part
1 of 10 23/07/2016 05:15 Paul's Online Math Notes Calculus III (Notes) / Line Integrals / Line Integrals - Part I Problems] [Notes] [Practice Problems] [Assignment Calculus III - Notes Line Integrals Part
SEGMENTATION AND FITTING USING PROBABILISTIC METHODS
 Chapter 8 SEGMENTATION AND FITTING USING PROBABILISTIC METHODS All the segmentation algorithms we described in the previous chapter involve essentially local models of similarity. Even though some algorithms
Chapter 8 SEGMENTATION AND FITTING USING PROBABILISTIC METHODS All the segmentation algorithms we described in the previous chapter involve essentially local models of similarity. Even though some algorithms
CS787: Assignment 3, Robust and Mixture Models for Optic Flow Due: 3:30pm, Mon. Mar. 12, 2007.
 CS787: Assignment 3, Robust and Mixture Models for Optic Flow Due: 3:30pm, Mon. Mar. 12, 2007. Many image features, such as image lines, curves, local image velocity, and local stereo disparity, can be
CS787: Assignment 3, Robust and Mixture Models for Optic Flow Due: 3:30pm, Mon. Mar. 12, 2007. Many image features, such as image lines, curves, local image velocity, and local stereo disparity, can be
CS 534: Computer Vision Segmentation and Perceptual Grouping
 CS 534: Computer Vision Segmentation and Perceptual Grouping Spring 2005 Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science CS 534 Segmentation - 1 Where are we? Image Formation Human vision Cameras Geometric Camera
CS 534: Computer Vision Segmentation and Perceptual Grouping Spring 2005 Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science CS 534 Segmentation - 1 Where are we? Image Formation Human vision Cameras Geometric Camera
Lecture 11: E-M and MeanShift. CAP 5415 Fall 2007
 Lecture 11: E-M and MeanShift CAP 5415 Fall 2007 Review on Segmentation by Clustering Each Pixel Data Vector Example (From Comanciu and Meer) Review of k-means Let's find three clusters in this data These
Lecture 11: E-M and MeanShift CAP 5415 Fall 2007 Review on Segmentation by Clustering Each Pixel Data Vector Example (From Comanciu and Meer) Review of k-means Let's find three clusters in this data These
Note Set 4: Finite Mixture Models and the EM Algorithm
 Note Set 4: Finite Mixture Models and the EM Algorithm Padhraic Smyth, Department of Computer Science University of California, Irvine Finite Mixture Models A finite mixture model with K components, for
Note Set 4: Finite Mixture Models and the EM Algorithm Padhraic Smyth, Department of Computer Science University of California, Irvine Finite Mixture Models A finite mixture model with K components, for
Lecture 8: Fitting. Tuesday, Sept 25
 Lecture 8: Fitting Tuesday, Sept 25 Announcements, schedule Grad student extensions Due end of term Data sets, suggestions Reminder: Midterm Tuesday 10/9 Problem set 2 out Thursday, due 10/11 Outline Review
Lecture 8: Fitting Tuesday, Sept 25 Announcements, schedule Grad student extensions Due end of term Data sets, suggestions Reminder: Midterm Tuesday 10/9 Problem set 2 out Thursday, due 10/11 Outline Review
Template Matching Rigid Motion
 Template Matching Rigid Motion Find transformation to align two images. Focus on geometric features (not so much interesting with intensity images) Emphasis on tricks to make this efficient. Problem Definition
Template Matching Rigid Motion Find transformation to align two images. Focus on geometric features (not so much interesting with intensity images) Emphasis on tricks to make this efficient. Problem Definition
Lecture 9: Hough Transform and Thresholding base Segmentation
 #1 Lecture 9: Hough Transform and Thresholding base Segmentation Saad Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Hough Transform Robust method to find a shape in an image Shape can be described in parametric form A voting
#1 Lecture 9: Hough Transform and Thresholding base Segmentation Saad Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Hough Transform Robust method to find a shape in an image Shape can be described in parametric form A voting
Multiple Model Estimation : The EM Algorithm & Applications
 Multiple Model Estimation : The EM Algorithm & Applications Princeton University COS 429 Lecture Nov. 13, 2007 Harpreet S. Sawhney hsawhney@sarnoff.com Recapitulation Problem of motion estimation Parametric
Multiple Model Estimation : The EM Algorithm & Applications Princeton University COS 429 Lecture Nov. 13, 2007 Harpreet S. Sawhney hsawhney@sarnoff.com Recapitulation Problem of motion estimation Parametric
Announcements. Edges. Last Lecture. Gradients: Numerical Derivatives f(x) Edge Detection, Lines. Intro Computer Vision. CSE 152 Lecture 10
 Announcements Assignment 2 due Tuesday, May 4. Edge Detection, Lines Midterm: Thursday, May 6. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 10 Edges Last Lecture 1. Object boundaries 2. Surface normal
Announcements Assignment 2 due Tuesday, May 4. Edge Detection, Lines Midterm: Thursday, May 6. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 10 Edges Last Lecture 1. Object boundaries 2. Surface normal
Fitting. Instructor: Jason Corso (jjcorso)! web.eecs.umich.edu/~jjcorso/t/598f14!! EECS Fall 2014! Foundations of Computer Vision!
 Fitting EECS 598-08 Fall 2014! Foundations of Computer Vision!! Instructor: Jason Corso (jjcorso)! web.eecs.umich.edu/~jjcorso/t/598f14!! Readings: FP 10; SZ 4.3, 5.1! Date: 10/8/14!! Materials on these
Fitting EECS 598-08 Fall 2014! Foundations of Computer Vision!! Instructor: Jason Corso (jjcorso)! web.eecs.umich.edu/~jjcorso/t/598f14!! Readings: FP 10; SZ 4.3, 5.1! Date: 10/8/14!! Materials on these
Template Matching Rigid Motion. Find transformation to align two images. Focus on geometric features
 Template Matching Rigid Motion Find transformation to align two images. Focus on geometric features (not so much interesting with intensity images) Emphasis on tricks to make this efficient. Problem Definition
Template Matching Rigid Motion Find transformation to align two images. Focus on geometric features (not so much interesting with intensity images) Emphasis on tricks to make this efficient. Problem Definition
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems
 EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 10 130221 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Canny Edge Detector Hough Transform Feature-Based
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 10 130221 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Canny Edge Detector Hough Transform Feature-Based
Homography estimation
 RANSAC continued Homography estimation x w? ~x img H~x w Homography estimation? x img ~x w = H 1 ~x img Homography estimation (0,0) (1,0) (6.4,2.8) (8.0,2.9) (5.6, 4.0) (7.8, 4.2) (0,1) (1,1) Ah =0s.tkhk
RANSAC continued Homography estimation x w? ~x img H~x w Homography estimation? x img ~x w = H 1 ~x img Homography estimation (0,0) (1,0) (6.4,2.8) (8.0,2.9) (5.6, 4.0) (7.8, 4.2) (0,1) (1,1) Ah =0s.tkhk
Perception IV: Place Recognition, Line Extraction
 Perception IV: Place Recognition, Line Extraction Davide Scaramuzza University of Zurich Margarita Chli, Paul Furgale, Marco Hutter, Roland Siegwart 1 Outline of Today s lecture Place recognition using
Perception IV: Place Recognition, Line Extraction Davide Scaramuzza University of Zurich Margarita Chli, Paul Furgale, Marco Hutter, Roland Siegwart 1 Outline of Today s lecture Place recognition using
Model Fitting, RANSAC. Jana Kosecka
 Model Fitting, RANSAC Jana Kosecka Fitting: Overview If we know which points belong to the line, how do we find the optimal line parameters? Least squares What if there are outliers? Robust fitting, RANSAC
Model Fitting, RANSAC Jana Kosecka Fitting: Overview If we know which points belong to the line, how do we find the optimal line parameters? Least squares What if there are outliers? Robust fitting, RANSAC
CS 229 Midterm Review
 CS 229 Midterm Review Course Staff Fall 2018 11/2/2018 Outline Today: SVMs Kernels Tree Ensembles EM Algorithm / Mixture Models [ Focus on building intuition, less so on solving specific problems. Ask
CS 229 Midterm Review Course Staff Fall 2018 11/2/2018 Outline Today: SVMs Kernels Tree Ensembles EM Algorithm / Mixture Models [ Focus on building intuition, less so on solving specific problems. Ask
Model Fitting: The Hough transform I
 Model Fitting: The Hough transform I Guido Gerig, CS6640 Image Processing, Utah Credit: Svetlana Lazebnik (Computer Vision UNC Chapel Hill, 2008) Fitting Parametric Models: Beyond Lines Choose a parametric
Model Fitting: The Hough transform I Guido Gerig, CS6640 Image Processing, Utah Credit: Svetlana Lazebnik (Computer Vision UNC Chapel Hill, 2008) Fitting Parametric Models: Beyond Lines Choose a parametric
Discovering Visual Hierarchy through Unsupervised Learning Haider Razvi
 Discovering Visual Hierarchy through Unsupervised Learning Haider Razvi hrazvi@stanford.edu 1 Introduction: We present a method for discovering visual hierarchy in a set of images. Automatically grouping
Discovering Visual Hierarchy through Unsupervised Learning Haider Razvi hrazvi@stanford.edu 1 Introduction: We present a method for discovering visual hierarchy in a set of images. Automatically grouping
Uncertainties: Representation and Propagation & Line Extraction from Range data
 41 Uncertainties: Representation and Propagation & Line Extraction from Range data 42 Uncertainty Representation Section 4.1.3 of the book Sensing in the real world is always uncertain How can uncertainty
41 Uncertainties: Representation and Propagation & Line Extraction from Range data 42 Uncertainty Representation Section 4.1.3 of the book Sensing in the real world is always uncertain How can uncertainty
Lecture 8 Fitting and Matching
 Lecture 8 Fitting and Matching Problem formulation Least square methods RANSAC Hough transforms Multi-model fitting Fitting helps matching! Reading: [HZ] Chapter: 4 Estimation 2D projective transformation
Lecture 8 Fitting and Matching Problem formulation Least square methods RANSAC Hough transforms Multi-model fitting Fitting helps matching! Reading: [HZ] Chapter: 4 Estimation 2D projective transformation
Feature Matching and Robust Fitting
 Feature Matching and Robust Fitting Computer Vision CS 143, Brown Read Szeliski 4.1 James Hays Acknowledgment: Many slides from Derek Hoiem and Grauman&Leibe 2008 AAAI Tutorial Project 2 questions? This
Feature Matching and Robust Fitting Computer Vision CS 143, Brown Read Szeliski 4.1 James Hays Acknowledgment: Many slides from Derek Hoiem and Grauman&Leibe 2008 AAAI Tutorial Project 2 questions? This
Finding 2D Shapes and the Hough Transform
 CS 4495 Computer Vision Finding 2D Shapes and the Aaron Bobick School of Interactive Computing Administrivia Today: Modeling Lines and Finding them CS4495: Problem set 1 is still posted. Please read the
CS 4495 Computer Vision Finding 2D Shapes and the Aaron Bobick School of Interactive Computing Administrivia Today: Modeling Lines and Finding them CS4495: Problem set 1 is still posted. Please read the
Clustering: Classic Methods and Modern Views
 Clustering: Classic Methods and Modern Views Marina Meilă University of Washington mmp@stat.washington.edu June 22, 2015 Lorentz Center Workshop on Clusters, Games and Axioms Outline Paradigms for clustering
Clustering: Classic Methods and Modern Views Marina Meilă University of Washington mmp@stat.washington.edu June 22, 2015 Lorentz Center Workshop on Clusters, Games and Axioms Outline Paradigms for clustering
Bayesian Methods in Vision: MAP Estimation, MRFs, Optimization
 Bayesian Methods in Vision: MAP Estimation, MRFs, Optimization CS 650: Computer Vision Bryan S. Morse Optimization Approaches to Vision / Image Processing Recurring theme: Cast vision problem as an optimization
Bayesian Methods in Vision: MAP Estimation, MRFs, Optimization CS 650: Computer Vision Bryan S. Morse Optimization Approaches to Vision / Image Processing Recurring theme: Cast vision problem as an optimization
CS664 Lecture #19: Layers, RANSAC, panoramas, epipolar geometry
 CS664 Lecture #19: Layers, RANSAC, panoramas, epipolar geometry Some material taken from: David Lowe, UBC Jiri Matas, CMP Prague http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/~matas/papers/presentations/matas_beyondransac_cvprac05.ppt
CS664 Lecture #19: Layers, RANSAC, panoramas, epipolar geometry Some material taken from: David Lowe, UBC Jiri Matas, CMP Prague http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/~matas/papers/presentations/matas_beyondransac_cvprac05.ppt
CS231A Midterm Review. Friday 5/6/2016
 CS231A Midterm Review Friday 5/6/2016 Outline General Logistics Camera Models Non-perspective cameras Calibration Single View Metrology Epipolar Geometry Structure from Motion Active Stereo and Volumetric
CS231A Midterm Review Friday 5/6/2016 Outline General Logistics Camera Models Non-perspective cameras Calibration Single View Metrology Epipolar Geometry Structure from Motion Active Stereo and Volumetric
Lecture 9 Fitting and Matching
 Lecture 9 Fitting and Matching Problem formulation Least square methods RANSAC Hough transforms Multi- model fitting Fitting helps matching! Reading: [HZ] Chapter: 4 Estimation 2D projective transformation
Lecture 9 Fitting and Matching Problem formulation Least square methods RANSAC Hough transforms Multi- model fitting Fitting helps matching! Reading: [HZ] Chapter: 4 Estimation 2D projective transformation
DATA MINING LECTURE 7. Hierarchical Clustering, DBSCAN The EM Algorithm
 DATA MINING LECTURE 7 Hierarchical Clustering, DBSCAN The EM Algorithm CLUSTERING What is a Clustering? In general a grouping of objects such that the objects in a group (cluster) are similar (or related)
DATA MINING LECTURE 7 Hierarchical Clustering, DBSCAN The EM Algorithm CLUSTERING What is a Clustering? In general a grouping of objects such that the objects in a group (cluster) are similar (or related)
Expectation Maximization (EM) and Gaussian Mixture Models
 Expectation Maximization (EM) and Gaussian Mixture Models Reference: The Elements of Statistical Learning, by T. Hastie, R. Tibshirani, J. Friedman, Springer 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Unsupervised Learning Motivation
Expectation Maximization (EM) and Gaussian Mixture Models Reference: The Elements of Statistical Learning, by T. Hastie, R. Tibshirani, J. Friedman, Springer 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Unsupervised Learning Motivation
Issues with Curve Detection Grouping (e.g., the Canny hysteresis thresholding procedure) Model tting They can be performed sequentially or simultaneou
 an edge image, nd line or curve segments present Given the image. in Line and Curves Detection 1 Issues with Curve Detection Grouping (e.g., the Canny hysteresis thresholding procedure) Model tting They
an edge image, nd line or curve segments present Given the image. in Line and Curves Detection 1 Issues with Curve Detection Grouping (e.g., the Canny hysteresis thresholding procedure) Model tting They
SUMMARY: DISTINCTIVE IMAGE FEATURES FROM SCALE- INVARIANT KEYPOINTS
 SUMMARY: DISTINCTIVE IMAGE FEATURES FROM SCALE- INVARIANT KEYPOINTS Cognitive Robotics Original: David G. Lowe, 004 Summary: Coen van Leeuwen, s1460919 Abstract: This article presents a method to extract
SUMMARY: DISTINCTIVE IMAGE FEATURES FROM SCALE- INVARIANT KEYPOINTS Cognitive Robotics Original: David G. Lowe, 004 Summary: Coen van Leeuwen, s1460919 Abstract: This article presents a method to extract
Representing Moving Images with Layers. J. Y. Wang and E. H. Adelson MIT Media Lab
 Representing Moving Images with Layers J. Y. Wang and E. H. Adelson MIT Media Lab Goal Represent moving images with sets of overlapping layers Layers are ordered in depth and occlude each other Velocity
Representing Moving Images with Layers J. Y. Wang and E. H. Adelson MIT Media Lab Goal Represent moving images with sets of overlapping layers Layers are ordered in depth and occlude each other Velocity
Computer Vision Grouping and Segmentation. Grouping and Segmentation
 Computer Vision Grouping and Segmentation Professor Hager http://www.cs.jhu.edu/~hager Grouping and Segmentation G&S appear to be one of the early processes in human vision They are a way of *organizing*
Computer Vision Grouping and Segmentation Professor Hager http://www.cs.jhu.edu/~hager Grouping and Segmentation G&S appear to be one of the early processes in human vision They are a way of *organizing*
Introduction. Chapter Overview
 Chapter 1 Introduction The Hough Transform is an algorithm presented by Paul Hough in 1962 for the detection of features of a particular shape like lines or circles in digitalized images. In its classical
Chapter 1 Introduction The Hough Transform is an algorithm presented by Paul Hough in 1962 for the detection of features of a particular shape like lines or circles in digitalized images. In its classical
Final Exam Assigned: 11/21/02 Due: 12/05/02 at 2:30pm
 6.801/6.866 Machine Vision Final Exam Assigned: 11/21/02 Due: 12/05/02 at 2:30pm Problem 1 Line Fitting through Segmentation (Matlab) a) Write a Matlab function to generate noisy line segment data with
6.801/6.866 Machine Vision Final Exam Assigned: 11/21/02 Due: 12/05/02 at 2:30pm Problem 1 Line Fitting through Segmentation (Matlab) a) Write a Matlab function to generate noisy line segment data with
Lecture on Modeling Tools for Clustering & Regression
 Lecture on Modeling Tools for Clustering & Regression CS 590.21 Analysis and Modeling of Brain Networks Department of Computer Science University of Crete Data Clustering Overview Organizing data into
Lecture on Modeling Tools for Clustering & Regression CS 590.21 Analysis and Modeling of Brain Networks Department of Computer Science University of Crete Data Clustering Overview Organizing data into
Image Segmentation. Selim Aksoy. Bilkent University
 Image Segmentation Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr Examples of grouping in vision [http://poseidon.csd.auth.gr/lab_research/latest/imgs/s peakdepvidindex_img2.jpg]
Image Segmentation Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr Examples of grouping in vision [http://poseidon.csd.auth.gr/lab_research/latest/imgs/s peakdepvidindex_img2.jpg]
MultiDimensional Signal Processing Master Degree in Ingegneria delle Telecomunicazioni A.A
 MultiDimensional Signal Processing Master Degree in Ingegneria delle Telecomunicazioni A.A. 205-206 Pietro Guccione, PhD DEI - DIPARTIMENTO DI INGEGNERIA ELETTRICA E DELL INFORMAZIONE POLITECNICO DI BARI
MultiDimensional Signal Processing Master Degree in Ingegneria delle Telecomunicazioni A.A. 205-206 Pietro Guccione, PhD DEI - DIPARTIMENTO DI INGEGNERIA ELETTRICA E DELL INFORMAZIONE POLITECNICO DI BARI
Image Segmentation. Selim Aksoy. Bilkent University
 Image Segmentation Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr Examples of grouping in vision [http://poseidon.csd.auth.gr/lab_research/latest/imgs/s peakdepvidindex_img2.jpg]
Image Segmentation Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr Examples of grouping in vision [http://poseidon.csd.auth.gr/lab_research/latest/imgs/s peakdepvidindex_img2.jpg]
Mixture Models and the EM Algorithm
 Mixture Models and the EM Algorithm Padhraic Smyth, Department of Computer Science University of California, Irvine c 2017 1 Finite Mixture Models Say we have a data set D = {x 1,..., x N } where x i is
Mixture Models and the EM Algorithm Padhraic Smyth, Department of Computer Science University of California, Irvine c 2017 1 Finite Mixture Models Say we have a data set D = {x 1,..., x N } where x i is
EECS 442 Computer vision. Fitting methods
 EECS 442 Computer vision Fitting methods - Problem formulation - Least square methods - RANSAC - Hough transforms - Multi-model fitting - Fitting helps matching! Reading: [HZ] Chapters: 4, 11 [FP] Chapters:
EECS 442 Computer vision Fitting methods - Problem formulation - Least square methods - RANSAC - Hough transforms - Multi-model fitting - Fitting helps matching! Reading: [HZ] Chapters: 4, 11 [FP] Chapters:
CS839: Probabilistic Graphical Models. Lecture 10: Learning with Partially Observed Data. Theo Rekatsinas
 CS839: Probabilistic Graphical Models Lecture 10: Learning with Partially Observed Data Theo Rekatsinas 1 Partially Observed GMs Speech recognition 2 Partially Observed GMs Evolution 3 Partially Observed
CS839: Probabilistic Graphical Models Lecture 10: Learning with Partially Observed Data Theo Rekatsinas 1 Partially Observed GMs Speech recognition 2 Partially Observed GMs Evolution 3 Partially Observed
Computer Vision Lecture 6
 Course Outline Computer Vision Lecture 6 Segmentation Image Processing Basics Structure Extraction Segmentation Segmentation as Clustering Graph-theoretic Segmentation 12.11.2015 Recognition Global Representations
Course Outline Computer Vision Lecture 6 Segmentation Image Processing Basics Structure Extraction Segmentation Segmentation as Clustering Graph-theoretic Segmentation 12.11.2015 Recognition Global Representations
Hough Transform and RANSAC
 CS4501: Introduction to Computer Vision Hough Transform and RANSAC Various slides from previous courses by: D.A. Forsyth (Berkeley / UIUC), I. Kokkinos (Ecole Centrale / UCL). S. Lazebnik (UNC / UIUC),
CS4501: Introduction to Computer Vision Hough Transform and RANSAC Various slides from previous courses by: D.A. Forsyth (Berkeley / UIUC), I. Kokkinos (Ecole Centrale / UCL). S. Lazebnik (UNC / UIUC),
Straight Lines and Hough
 09/30/11 Straight Lines and Hough Computer Vision CS 143, Brown James Hays Many slides from Derek Hoiem, Lana Lazebnik, Steve Seitz, David Forsyth, David Lowe, Fei-Fei Li Project 1 A few project highlights
09/30/11 Straight Lines and Hough Computer Vision CS 143, Brown James Hays Many slides from Derek Hoiem, Lana Lazebnik, Steve Seitz, David Forsyth, David Lowe, Fei-Fei Li Project 1 A few project highlights
CS 664 Image Matching and Robust Fitting. Daniel Huttenlocher
 CS 664 Image Matching and Robust Fitting Daniel Huttenlocher Matching and Fitting Recognition and matching are closely related to fitting problems Parametric fitting can serve as more restricted domain
CS 664 Image Matching and Robust Fitting Daniel Huttenlocher Matching and Fitting Recognition and matching are closely related to fitting problems Parametric fitting can serve as more restricted domain
Object Recognition with Invariant Features
 Object Recognition with Invariant Features Definition: Identify objects or scenes and determine their pose and model parameters Applications Industrial automation and inspection Mobile robots, toys, user
Object Recognition with Invariant Features Definition: Identify objects or scenes and determine their pose and model parameters Applications Industrial automation and inspection Mobile robots, toys, user
17.1 TheHough Transform
 Chapter 17 FITTING There are a variety of segmentation criteria that involve models at a larger scale. Typically, one wants to decompose an image or a set of tokens which could be pixels, isolated points,
Chapter 17 FITTING There are a variety of segmentation criteria that involve models at a larger scale. Typically, one wants to decompose an image or a set of tokens which could be pixels, isolated points,
Machine Learning and Data Mining. Clustering (1): Basics. Kalev Kask
 Machine Learning and Data Mining Clustering (1): Basics Kalev Kask Unsupervised learning Supervised learning Predict target value ( y ) given features ( x ) Unsupervised learning Understand patterns of
Machine Learning and Data Mining Clustering (1): Basics Kalev Kask Unsupervised learning Supervised learning Predict target value ( y ) given features ( x ) Unsupervised learning Understand patterns of
CS Introduction to Data Mining Instructor: Abdullah Mueen
 CS 591.03 Introduction to Data Mining Instructor: Abdullah Mueen LECTURE 8: ADVANCED CLUSTERING (FUZZY AND CO -CLUSTERING) Review: Basic Cluster Analysis Methods (Chap. 10) Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts
CS 591.03 Introduction to Data Mining Instructor: Abdullah Mueen LECTURE 8: ADVANCED CLUSTERING (FUZZY AND CO -CLUSTERING) Review: Basic Cluster Analysis Methods (Chap. 10) Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts
Feature Based Registration - Image Alignment
 Feature Based Registration - Image Alignment Image Registration Image registration is the process of estimating an optimal transformation between two or more images. Many slides from Alexei Efros http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463/2007_fall/463.html
Feature Based Registration - Image Alignment Image Registration Image registration is the process of estimating an optimal transformation between two or more images. Many slides from Alexei Efros http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463/2007_fall/463.html
Introduction to Mobile Robotics
 Introduction to Mobile Robotics Clustering Wolfram Burgard Cyrill Stachniss Giorgio Grisetti Maren Bennewitz Christian Plagemann Clustering (1) Common technique for statistical data analysis (machine learning,
Introduction to Mobile Robotics Clustering Wolfram Burgard Cyrill Stachniss Giorgio Grisetti Maren Bennewitz Christian Plagemann Clustering (1) Common technique for statistical data analysis (machine learning,
Lecture 8: The EM algorithm
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2017 Lecture 8: The EM algorithm Lecturer: Manuela M. Veloso, Eric P. Xing Scribes: Huiting Liu, Yifan Yang 1 Introduction Previous lecture discusses
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2017 Lecture 8: The EM algorithm Lecturer: Manuela M. Veloso, Eric P. Xing Scribes: Huiting Liu, Yifan Yang 1 Introduction Previous lecture discusses
Harder case. Image matching. Even harder case. Harder still? by Diva Sian. by swashford
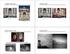 Image matching Harder case by Diva Sian by Diva Sian by scgbt by swashford Even harder case Harder still? How the Afghan Girl was Identified by Her Iris Patterns Read the story NASA Mars Rover images Answer
Image matching Harder case by Diva Sian by Diva Sian by scgbt by swashford Even harder case Harder still? How the Afghan Girl was Identified by Her Iris Patterns Read the story NASA Mars Rover images Answer
Lecture 7: Segmentation. Thursday, Sept 20
 Lecture 7: Segmentation Thursday, Sept 20 Outline Why segmentation? Gestalt properties, fun illusions and/or revealing examples Clustering Hierarchical K-means Mean Shift Graph-theoretic Normalized cuts
Lecture 7: Segmentation Thursday, Sept 20 Outline Why segmentation? Gestalt properties, fun illusions and/or revealing examples Clustering Hierarchical K-means Mean Shift Graph-theoretic Normalized cuts
Edge detection. Convert a 2D image into a set of curves. Extracts salient features of the scene More compact than pixels
 Edge Detection Edge detection Convert a 2D image into a set of curves Extracts salient features of the scene More compact than pixels Origin of Edges surface normal discontinuity depth discontinuity surface
Edge Detection Edge detection Convert a 2D image into a set of curves Extracts salient features of the scene More compact than pixels Origin of Edges surface normal discontinuity depth discontinuity surface
Lecture 15: Segmentation (Edge Based, Hough Transform)
 Lecture 15: Segmentation (Edge Based, Hough Transform) c Bryan S. Morse, Brigham Young University, 1998 000 Last modified on February 3, 000 at :00 PM Contents 15.1 Introduction..............................................
Lecture 15: Segmentation (Edge Based, Hough Transform) c Bryan S. Morse, Brigham Young University, 1998 000 Last modified on February 3, 000 at :00 PM Contents 15.1 Introduction..............................................
Model Fitting. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 11
 Model Fitting CSE 152 Lecture 11 Announcements Homework 3 is due May 9, 11:59 PM Reading: Chapter 10: Grouping and Model Fitting What to do with edges? Segment linked edge chains into curve features (e.g.,
Model Fitting CSE 152 Lecture 11 Announcements Homework 3 is due May 9, 11:59 PM Reading: Chapter 10: Grouping and Model Fitting What to do with edges? Segment linked edge chains into curve features (e.g.,
Bioimage Informatics
 Bioimage Informatics Lecture 12, Spring 2012 Bioimage Data Analysis (III): Line/Curve Detection Bioimage Data Analysis (IV) Image Segmentation (part 1) Lecture 12 February 27, 2012 1 Outline Review: Line/curve
Bioimage Informatics Lecture 12, Spring 2012 Bioimage Data Analysis (III): Line/Curve Detection Bioimage Data Analysis (IV) Image Segmentation (part 1) Lecture 12 February 27, 2012 1 Outline Review: Line/curve
Clustering Lecture 5: Mixture Model
 Clustering Lecture 5: Mixture Model Jing Gao SUNY Buffalo 1 Outline Basics Motivation, definition, evaluation Methods Partitional Hierarchical Density-based Mixture model Spectral methods Advanced topics
Clustering Lecture 5: Mixture Model Jing Gao SUNY Buffalo 1 Outline Basics Motivation, definition, evaluation Methods Partitional Hierarchical Density-based Mixture model Spectral methods Advanced topics
Final Exam Study Guide
 Final Exam Study Guide Exam Window: 28th April, 12:00am EST to 30th April, 11:59pm EST Description As indicated in class the goal of the exam is to encourage you to review the material from the course.
Final Exam Study Guide Exam Window: 28th April, 12:00am EST to 30th April, 11:59pm EST Description As indicated in class the goal of the exam is to encourage you to review the material from the course.
Introduction to Computer Vision
 Introduction to Computer Vision Michael J. Black Nov 2009 Perspective projection and affine motion Goals Today Perspective projection 3D motion Wed Projects Friday Regularization and robust statistics
Introduction to Computer Vision Michael J. Black Nov 2009 Perspective projection and affine motion Goals Today Perspective projection 3D motion Wed Projects Friday Regularization and robust statistics
Today. Lecture 4: Last time. The EM algorithm. We examine clustering in a little more detail; we went over it a somewhat quickly last time
 Today Lecture 4: We examine clustering in a little more detail; we went over it a somewhat quickly last time The CAD data will return and give us an opportunity to work with curves (!) We then examine
Today Lecture 4: We examine clustering in a little more detail; we went over it a somewhat quickly last time The CAD data will return and give us an opportunity to work with curves (!) We then examine
CS 534: Computer Vision Segmentation II Graph Cuts and Image Segmentation
 CS 534: Computer Vision Segmentation II Graph Cuts and Image Segmentation Spring 2005 Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science CS 534 Segmentation II - 1 Outlines What is Graph cuts Graph-based clustering
CS 534: Computer Vision Segmentation II Graph Cuts and Image Segmentation Spring 2005 Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science CS 534 Segmentation II - 1 Outlines What is Graph cuts Graph-based clustering
A System of Image Matching and 3D Reconstruction
 A System of Image Matching and 3D Reconstruction CS231A Project Report 1. Introduction Xianfeng Rui Given thousands of unordered images of photos with a variety of scenes in your gallery, you will find
A System of Image Matching and 3D Reconstruction CS231A Project Report 1. Introduction Xianfeng Rui Given thousands of unordered images of photos with a variety of scenes in your gallery, you will find
Lecture 3: Linear Classification
 Lecture 3: Linear Classification Roger Grosse 1 Introduction Last week, we saw an example of a learning task called regression. There, the goal was to predict a scalar-valued target from a set of features.
Lecture 3: Linear Classification Roger Grosse 1 Introduction Last week, we saw an example of a learning task called regression. There, the goal was to predict a scalar-valued target from a set of features.
Announcements. Image Segmentation. From images to objects. Extracting objects. Status reports next Thursday ~5min presentations in class
 Image Segmentation Announcements Status reports next Thursday ~5min presentations in class Project voting From Sandlot Science Today s Readings Forsyth & Ponce, Chapter 1 (plus lots of optional references
Image Segmentation Announcements Status reports next Thursday ~5min presentations in class Project voting From Sandlot Science Today s Readings Forsyth & Ponce, Chapter 1 (plus lots of optional references
Unsupervised learning in Vision
 Chapter 7 Unsupervised learning in Vision The fields of Computer Vision and Machine Learning complement each other in a very natural way: the aim of the former is to extract useful information from visual
Chapter 7 Unsupervised learning in Vision The fields of Computer Vision and Machine Learning complement each other in a very natural way: the aim of the former is to extract useful information from visual
CAP 5415 Computer Vision Fall 2012
 CAP 5415 Computer Vision Fall 2012 Hough Transform Lecture-18 Sections 4.2, 4.3 Fundamentals of Computer Vision Image Feature Extraction Edges (edge pixels) Sobel, Roberts, Prewit Laplacian of Gaussian
CAP 5415 Computer Vision Fall 2012 Hough Transform Lecture-18 Sections 4.2, 4.3 Fundamentals of Computer Vision Image Feature Extraction Edges (edge pixels) Sobel, Roberts, Prewit Laplacian of Gaussian
Unsupervised Learning: Clustering
 Unsupervised Learning: Clustering Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas Slides adapted from Carlos Guestrin, Dan Klein & Luke Zettlemoyer Machine Learning Supervised Learning Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised Learning: Clustering Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas Slides adapted from Carlos Guestrin, Dan Klein & Luke Zettlemoyer Machine Learning Supervised Learning Unsupervised Learning
CS 223B Computer Vision Problem Set 3
 CS 223B Computer Vision Problem Set 3 Due: Feb. 22 nd, 2011 1 Probabilistic Recursion for Tracking In this problem you will derive a method for tracking a point of interest through a sequence of images.
CS 223B Computer Vision Problem Set 3 Due: Feb. 22 nd, 2011 1 Probabilistic Recursion for Tracking In this problem you will derive a method for tracking a point of interest through a sequence of images.
Kernels and Clustering
 Kernels and Clustering Robert Platt Northeastern University All slides in this file are adapted from CS188 UC Berkeley Case-Based Learning Non-Separable Data Case-Based Reasoning Classification from similarity
Kernels and Clustering Robert Platt Northeastern University All slides in this file are adapted from CS188 UC Berkeley Case-Based Learning Non-Separable Data Case-Based Reasoning Classification from similarity
CS 231A Computer Vision (Fall 2012) Problem Set 3
 CS 231A Computer Vision (Fall 2012) Problem Set 3 Due: Nov. 13 th, 2012 (2:15pm) 1 Probabilistic Recursion for Tracking (20 points) In this problem you will derive a method for tracking a point of interest
CS 231A Computer Vision (Fall 2012) Problem Set 3 Due: Nov. 13 th, 2012 (2:15pm) 1 Probabilistic Recursion for Tracking (20 points) In this problem you will derive a method for tracking a point of interest
Vision par ordinateur
 Epipolar geometry π Vision par ordinateur Underlying structure in set of matches for rigid scenes l T 1 l 2 C1 m1 l1 e1 M L2 L1 e2 Géométrie épipolaire Fundamental matrix (x rank 2 matrix) m2 C2 l2 Frédéric
Epipolar geometry π Vision par ordinateur Underlying structure in set of matches for rigid scenes l T 1 l 2 C1 m1 l1 e1 M L2 L1 e2 Géométrie épipolaire Fundamental matrix (x rank 2 matrix) m2 C2 l2 Frédéric
Clustering Color/Intensity. Group together pixels of similar color/intensity.
 Clustering Color/Intensity Group together pixels of similar color/intensity. Agglomerative Clustering Cluster = connected pixels with similar color. Optimal decomposition may be hard. For example, find
Clustering Color/Intensity Group together pixels of similar color/intensity. Agglomerative Clustering Cluster = connected pixels with similar color. Optimal decomposition may be hard. For example, find
Tracking. Establish where an object is, other aspects of state, using time sequence Biggest problem -- Data Association
 Tracking Establish where an object is, other aspects of state, using time sequence Biggest problem -- Data Association Key ideas Tracking by detection Tracking through flow Track by detection (simple form)
Tracking Establish where an object is, other aspects of state, using time sequence Biggest problem -- Data Association Key ideas Tracking by detection Tracking through flow Track by detection (simple form)
Prof. Noah Snavely CS Administrivia. A4 due on Friday (please sign up for demo slots)
 Robust fitting Prof. Noah Snavely CS111 http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs111 Administrivia A due on Friday (please sign up for demo slots) A5 will be out soon Prelim is coming up, Tuesday, / Roadmap
Robust fitting Prof. Noah Snavely CS111 http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs111 Administrivia A due on Friday (please sign up for demo slots) A5 will be out soon Prelim is coming up, Tuesday, / Roadmap
2D/3D Geometric Transformations and Scene Graphs
 2D/3D Geometric Transformations and Scene Graphs Week 4 Acknowledgement: The course slides are adapted from the slides prepared by Steve Marschner of Cornell University 1 A little quick math background
2D/3D Geometric Transformations and Scene Graphs Week 4 Acknowledgement: The course slides are adapted from the slides prepared by Steve Marschner of Cornell University 1 A little quick math background
10/03/11. Model Fitting. Computer Vision CS 143, Brown. James Hays. Slides from Silvio Savarese, Svetlana Lazebnik, and Derek Hoiem
 10/03/11 Model Fitting Computer Vision CS 143, Brown James Hays Slides from Silvio Savarese, Svetlana Lazebnik, and Derek Hoiem Fitting: find the parameters of a model that best fit the data Alignment:
10/03/11 Model Fitting Computer Vision CS 143, Brown James Hays Slides from Silvio Savarese, Svetlana Lazebnik, and Derek Hoiem Fitting: find the parameters of a model that best fit the data Alignment:
What is Computer Vision?
 Perceptual Grouping in Computer Vision Gérard Medioni University of Southern California What is Computer Vision? Computer Vision Attempt to emulate Human Visual System Perceive visual stimuli with cameras
Perceptual Grouping in Computer Vision Gérard Medioni University of Southern California What is Computer Vision? Computer Vision Attempt to emulate Human Visual System Perceive visual stimuli with cameras
CPSC 425: Computer Vision
 1 / 45 CPSC 425: Computer Vision Instructor: Fred Tung ftung@cs.ubc.ca Department of Computer Science University of British Columbia Lecture Notes 2015/2016 Term 2 2 / 45 Menu March 3, 2016 Topics: Hough
1 / 45 CPSC 425: Computer Vision Instructor: Fred Tung ftung@cs.ubc.ca Department of Computer Science University of British Columbia Lecture Notes 2015/2016 Term 2 2 / 45 Menu March 3, 2016 Topics: Hough
CSE 527: Introduction to Computer Vision
 CSE 527: Introduction to Computer Vision Week 5 - Class 1: Matching, Stitching, Registration September 26th, 2017 ??? Recap Today Feature Matching Image Alignment Panoramas HW2! Feature Matches Feature
CSE 527: Introduction to Computer Vision Week 5 - Class 1: Matching, Stitching, Registration September 26th, 2017 ??? Recap Today Feature Matching Image Alignment Panoramas HW2! Feature Matches Feature
