CS 151 Midterm. Instructions: Student ID. (Last Name) (First Name) Signature
|
|
|
- Jonathan Wells
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CS 151 Midterm Name Student ID Signature :, (Last Name) (First Name) : : Instructions: 1. Please verify that your paper contains 11 pages including this cover. 2. Write down your Student-Id on the top of each page of this quiz. 3. This exam is closed book. No notes or other materials are permitted. 4. Total credits of this midterm are 70 points. 5. To receive credit you must show your work clearly. 6. For possible re-grade request make sure that your write clearly. 7. Calculators are NOT allowed. CS 151 Digital Logic Design, Spring Quarter 2007, Midterm Page 1
2 Q1: [ALU] [20 points] We are going to design a 4-bit Arithmetic Unit (AU) with the following functional table: M1 M0 Function Name F(A,B) 0 0 A + A multiplied by 8 times B A*(8*B)+A 0 1 If (A>B) subtract B from A; otherwise add A and B If (A>B) then A-B; else A+B 1 0 Decrement A A Add 1 to A+B A+B+1 A and B are two 4-bit binary numbers a3a2a1a0 and b3b2b1b0. M1, M0 are the control inputs to this AU. For doing this, the block labeled AL-Extender in the following block diagram should be designed. In this question you should design the logic inside AL-Extender using JUST Comparators and Multiplexers if needed. ALU a 3 a 2 a 1 a 0 b 3 b 2 b 1 b 0 M1 AL-Extender M0 IA IB Full Adder Cin IS s 3 s 2 s 1 s 0 CS 151 Digital Logic Design, Spring Quarter 2007, Midterm Page 2
3 <This page is intentionally left blank> A[3:0] B[3:0] Comparator B [3:0] B[3:0] a I1 A<=B 0 I0 A>B I1 C[3:0] I0 I1 I0 D b 0 X b 3 1 c 3 d b 2 1 c 2 0 b 1 1 c 1 0 b 0 0 c X 0 S0 I 0 I 1 I 2 I 3 S0 I 0 I 1 I 2 I 3 S0 I 0 I 1 I 2 I 3 S0 I 0 I 1 I 2 I 3 S0 I 0 I 1 I 2 I 3 IB 3 IB 2 IB 1 IB 0 Cin CS 151 Digital Logic Design, Spring Quarter 2007, Midterm Page 3
4 <This page is intentionally left blank> CS 151 Digital Logic Design, Spring Quarter 2007, Midterm Page 4
5 Q2: [High-Level State Machine Design] [15 points] Design the high-level state machine for a DVD player with the following functionality: Initially when we turn on the system it is in STOP mode and we can assume that there is a DVD already inserted in. The DVD player has four buttons: STOP, PLAY, FF (Fast Forward) and FB (Fast Backward). While in STOP mode if we hit STOP or FF or FB button we should stay at the same state. As well whenever we reach the STOP mode the value of the timer resets to ZERO. Once we hit PLAY button, the DVD player starts playing and every cycle the timer of the player is incremented by one unless it reaches the end of the DVD (time 200) when it goes to STOP mode automatically. While in play mode if we hit FF button and keep it depressed for just one clock cycle the timer is incremented by 50 and then we automatically go back to play mode. If we hit the FF button the next clock cycle the DVD player goes to Fast Forward mode and the timer is incremented by 5 for each cycle. The DVD player will remain at the same state unless: we hit the PLAY button or the FB button which takes us to the PLAY mode; or the end of the DVD is reached or we hit the STOP button which puts the player in STOP mode; The same thing happens if we push FB button with the difference that the timer is decremented by the same amount of FF mode. The player remains at FB mode unless: we hit the PLAY button or the FF button which takes the player to the PLAY mode; the beginning of the DVD is reached where the timer is set to ZERO and the player goes to the PLAY mode automatically; the STOP button is hit which puts the player in STOP mode; CS 151 Digital Logic Design, Spring Quarter 2007, Midterm Page 5
6 <This page is intentionally left blank> CS 151 Digital Logic Design, Spring Quarter 2007, Midterm Page 6
7 Q3: [RTL design] [35 points] Considering the following high-level state machine and assuming that X, Y, START and STOP are one bit control inputs and T is an 8-bit output of the circuit:!start T<30 X START Standby T=T+1 T>=30 & Y T<30 Y T>=30 STOP T=T+1 S2 START T>=30 STOP!START T=T+1 T>=60 STOP Z=1 T<60 CS 151 Digital Logic Design, Spring Quarter 2007, Midterm Page 7
8 3a. Design the data-path for this system. [15 points] 1 S T-sel T 1 T-ld T Reg Adder T S T Comp-Sel A Comparator T>=A T<A CS 151 Digital Logic Design, Spring Quarter 2007, Midterm Page 8
9 3b. Design the interface of the system and the interface between the controller and the datapath. [5 points] START STOP X Y T>=A T<A Controller T-Sel Data path T-ld Comp-Sel T[7:0] CS 151 Digital Logic Design, Spring Quarter 2007, Midterm Page 9
10 3c. Design the FSM of the controller. [15 points] HINT: There is no timing issue for this system so you do not have to consider timing issues in designing the controller s FSM.!START T<A Standby X START T-ld = 1 Comp_sel = 1 T>=A & Y T<A Y T-ld = 1 Comp_sel = 1 S2!START START T-ld = 1 Comp_sel = 0 T>=A STOP T>=A STOP T=1 T>=A STOP T<A In fact there is a timing issue in each of the states that increments T. To solve the timing issue we have to add a dummy state for each problematic state. This dummy state is just supposed to provide one more clock cycle for the register to load the value. All the incoming edges still enter to the original state. On the other hand all the outgoing edges exit the dummy state. For the sake of grading, the students do not have to be concerned about the timing issue as the problem had wanted them to ignore it. CS 151 Digital Logic Design, Spring Quarter 2007, Midterm Page 10
11 <This page is intentionally left blank> CS 151 Digital Logic Design, Spring Quarter 2007, Midterm Page 11
CS 151 Midterm. (Last Name) (First Name)
 CS 151 Midterm Name Student ID Signature :, (Last Name) (First Name) : : Instructions: 1. Please verify that your paper contains 13 pages including this cover. 2. Write down your Student-Id on the top
CS 151 Midterm Name Student ID Signature :, (Last Name) (First Name) : : Instructions: 1. Please verify that your paper contains 13 pages including this cover. 2. Write down your Student-Id on the top
CS 151 Quiz 4. Instructions: Student ID. (Last Name) (First Name) Signature
 CS 151 Quiz 4 Name Student ID Signature :, (Last Name) (First Name) : : Instructions: 1. Please verify that your paper contains 9 pages including this cover. 2. Write down your Student-Id on the top of
CS 151 Quiz 4 Name Student ID Signature :, (Last Name) (First Name) : : Instructions: 1. Please verify that your paper contains 9 pages including this cover. 2. Write down your Student-Id on the top of
CS 151 Final. Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q5 Total Credit Score. Instructions: Student ID. (Last Name) (First Name) Signature
 CS 151 Final Name Student ID Signature :, (Last Name) (First Name) : : Instructions: 1. Please verify that your paper contains 15 pages including this cover. 2. Write down your Student-Id on the top of
CS 151 Final Name Student ID Signature :, (Last Name) (First Name) : : Instructions: 1. Please verify that your paper contains 15 pages including this cover. 2. Write down your Student-Id on the top of
CS 151 Final. (Last Name) (First Name)
 CS 151 Final Name Student ID Signature :, (Last Name) (First Name) : : Instructions: 1. Please verify that your paper contains 20 pages including this cover. 2. Write down your Student-Id on the top of
CS 151 Final Name Student ID Signature :, (Last Name) (First Name) : : Instructions: 1. Please verify that your paper contains 20 pages including this cover. 2. Write down your Student-Id on the top of
CS 151 Midterm. Instructions: Student ID. (Last Name) (First Name) Signature
 CS 151 Midterm Name Student ID Signature :, (Last Name) (First Name) : : Instructions: 1. Please verify that your paper contains 11 pages including this cover. 2. Write down your Student-Id on the top
CS 151 Midterm Name Student ID Signature :, (Last Name) (First Name) : : Instructions: 1. Please verify that your paper contains 11 pages including this cover. 2. Write down your Student-Id on the top
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Introductory Digital Systems Lab (6.111) uiz - Spring 2004 Prof. Anantha Chandrakasan Student Name: Problem
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Introductory Digital Systems Lab (6.111) uiz - Spring 2004 Prof. Anantha Chandrakasan Student Name: Problem
Final Exam Solution Sunday, December 15, 10:05-12:05 PM
 Last (family) name: First (given) name: Student I.D. #: Circle section: Kim Hu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin - Madison ECE/CS 352 Digital System Fundamentals
Last (family) name: First (given) name: Student I.D. #: Circle section: Kim Hu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin - Madison ECE/CS 352 Digital System Fundamentals
Prerequisite Quiz January 23, 2007 CS252 Computer Architecture and Engineering
 University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Computer Science Division EECS Spring 2007 John Kubiatowicz Prerequisite Quiz January 23, 2007 CS252 Computer Architecture and Engineering This
University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Computer Science Division EECS Spring 2007 John Kubiatowicz Prerequisite Quiz January 23, 2007 CS252 Computer Architecture and Engineering This
Two hours - online EXAM PAPER MUST NOT BE REMOVED FROM THE EXAM ROOM UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE
 COMP 12111 Two hours - online This paper version is made available as a backup In this event, only MCQ answers written in the boxes on the exam paper will be marked. EXAM PAPER MUST NOT BE REMOVED FROM
COMP 12111 Two hours - online This paper version is made available as a backup In this event, only MCQ answers written in the boxes on the exam paper will be marked. EXAM PAPER MUST NOT BE REMOVED FROM
Computer Architecture and Engineering. CS152 Quiz #1. February 19th, Professor Krste Asanovic. Name:
 Computer Architecture and Engineering CS152 Quiz #1 February 19th, 2008 Professor Krste Asanovic Name: Notes: This is a closed book, closed notes exam. 80 Minutes 10 Pages Not all questions are of equal
Computer Architecture and Engineering CS152 Quiz #1 February 19th, 2008 Professor Krste Asanovic Name: Notes: This is a closed book, closed notes exam. 80 Minutes 10 Pages Not all questions are of equal
REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE
 REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE The operations executed on the data stored in the registers are called micro operations. Classifications of micro operations Register transfer micro operations Arithmetic micro
REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE The operations executed on the data stored in the registers are called micro operations. Classifications of micro operations Register transfer micro operations Arithmetic micro
QUIZ: What value is stored in a after this
 QUIZ: What value is stored in a after this statement is executed? Why? a = 23/7; QUIZ evaluates to 16. Lesson 4 Statements, Expressions, Operators Statement = complete instruction that directs the computer
QUIZ: What value is stored in a after this statement is executed? Why? a = 23/7; QUIZ evaluates to 16. Lesson 4 Statements, Expressions, Operators Statement = complete instruction that directs the computer
EKT 422/4 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE. MINI PROJECT : Design of an Arithmetic Logic Unit
 EKT 422/4 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE MINI PROJECT : Design of an Arithmetic Logic Unit Objective Students will design and build a customized Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU). It will perform 16 different operations
EKT 422/4 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE MINI PROJECT : Design of an Arithmetic Logic Unit Objective Students will design and build a customized Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU). It will perform 16 different operations
problem maximum score 1 8pts 2 6pts 3 10pts 4 15pts 5 12pts 6 10pts 7 24pts 8 16pts 9 19pts Total 120pts
 University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS150 J. Wawrzynek Spring 2010 3/31/09 Name: ID number: Midterm Exam This is a closed-book,
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS150 J. Wawrzynek Spring 2010 3/31/09 Name: ID number: Midterm Exam This is a closed-book,
Computer Organization
 Computer Organization! Computer design as an application of digital logic design procedures! Computer = processing unit + memory system! Processing unit = control + datapath! Control = finite state machine
Computer Organization! Computer design as an application of digital logic design procedures! Computer = processing unit + memory system! Processing unit = control + datapath! Control = finite state machine
CSE 140L Final Exam. Prof. Tajana Simunic Rosing. Spring 2008
 CSE 140L Final Exam Prof. Tajana Simunic Rosing Spring 2008 Do not start the exam until you are told to. Turn off any cell phones or pagers. Write your name and PID at the top of every page. Do not separate
CSE 140L Final Exam Prof. Tajana Simunic Rosing Spring 2008 Do not start the exam until you are told to. Turn off any cell phones or pagers. Write your name and PID at the top of every page. Do not separate
CSE 140L Final Exam. Prof. Tajana Simunic Rosing. Spring 2008
 CSE 140L Final Exam Prof. Tajana Simunic Rosing Spring 2008 NAME: ID#: Do not start the exam until you are told to. Turn off any cell phones or pagers. Write your name and PID at the top of every page.
CSE 140L Final Exam Prof. Tajana Simunic Rosing Spring 2008 NAME: ID#: Do not start the exam until you are told to. Turn off any cell phones or pagers. Write your name and PID at the top of every page.
Problem Set # 6 (Assigned 27 February, Due 9 March)
 University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science EECS 150 Spring 2007 R. H. Katz Problem Set # 6 (Assigned 27 February, Due 9 March)
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science EECS 150 Spring 2007 R. H. Katz Problem Set # 6 (Assigned 27 February, Due 9 March)
Introduction to Verilog
 Introduction to Verilog Structure of a Verilog Program A Verilog program is structured as a set of modules, which may represent anything from a collection of logic gates to a complete system. A module
Introduction to Verilog Structure of a Verilog Program A Verilog program is structured as a set of modules, which may represent anything from a collection of logic gates to a complete system. A module
EECS 151/251A: SRPING 2017 MIDTERM 1
 University of California College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences E. Alon Thursday, Mar 2 nd, 2017 7:00-8:30pm EECS 151/251A: SRPING 2017 MIDTERM 1 NAME Last First
University of California College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences E. Alon Thursday, Mar 2 nd, 2017 7:00-8:30pm EECS 151/251A: SRPING 2017 MIDTERM 1 NAME Last First
CSE 140L Spring 2010 Bonus Final
 CSE 140L Spring 2010 Bonus Final Logistics for Bonus Final: This final should be done in individually. Use Xilinx tools version 10.1. What is due: - Report: o Submit a single report in.pdf form via email
CSE 140L Spring 2010 Bonus Final Logistics for Bonus Final: This final should be done in individually. Use Xilinx tools version 10.1. What is due: - Report: o Submit a single report in.pdf form via email
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering. Complex Pipelines
 CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Complex Pipelines Assigned March 6 Problem Set #3 Due March 20 http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152/sp12 The problem sets are intended to help you learn the
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Complex Pipelines Assigned March 6 Problem Set #3 Due March 20 http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152/sp12 The problem sets are intended to help you learn the
Control and Datapath 8
 Control and Datapath 8 Engineering attempts to develop design methods that break a problem up into separate steps to simplify the design and increase the likelihood of a correct solution. Digital system
Control and Datapath 8 Engineering attempts to develop design methods that break a problem up into separate steps to simplify the design and increase the likelihood of a correct solution. Digital system
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO FACULTY OF APPLIED SCIENCE AN:p ENGINEERING. ECE241F - Digital Syst~ms Final Examination
 ~.. UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO FACULTY OF APPLIED SCIENCE AN:p ENGINEERING ECE241F - Digital Syst~ms Final Examination December 19, 2017, 2:00pm-4:30pm Duration: 2.5 hours Examiners: P. Anderson, P. Chow and
~.. UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO FACULTY OF APPLIED SCIENCE AN:p ENGINEERING ECE241F - Digital Syst~ms Final Examination December 19, 2017, 2:00pm-4:30pm Duration: 2.5 hours Examiners: P. Anderson, P. Chow and
Contents. Chapter 9 Datapaths Page 1 of 28
 Chapter 9 Datapaths Page of 2 Contents Contents... 9 Datapaths... 2 9. General Datapath... 3 9.2 Using a General Datapath... 5 9.3 Timing Issues... 7 9.4 A More Complex General Datapath... 9 9.5 VHDL for
Chapter 9 Datapaths Page of 2 Contents Contents... 9 Datapaths... 2 9. General Datapath... 3 9.2 Using a General Datapath... 5 9.3 Timing Issues... 7 9.4 A More Complex General Datapath... 9 9.5 VHDL for
COMP 303 Computer Architecture Lecture 6
 COMP 303 Computer Architecture Lecture 6 MULTIPLY (unsigned) Paper and pencil example (unsigned): Multiplicand 1000 = 8 Multiplier x 1001 = 9 1000 0000 0000 1000 Product 01001000 = 72 n bits x n bits =
COMP 303 Computer Architecture Lecture 6 MULTIPLY (unsigned) Paper and pencil example (unsigned): Multiplicand 1000 = 8 Multiplier x 1001 = 9 1000 0000 0000 1000 Product 01001000 = 72 n bits x n bits =
ECE 313 Computer Organization FINAL EXAM December 13, 2000
 This exam is open book and open notes. You have until 11:00AM. Credit for problems requiring calculation will be given only if you show your work. 1. Floating Point Representation / MIPS Assembly Language
This exam is open book and open notes. You have until 11:00AM. Credit for problems requiring calculation will be given only if you show your work. 1. Floating Point Representation / MIPS Assembly Language
TSEA 26 exam page 1 of Examination. Design of Embedded DSP Processors, TSEA26 Date 8-12, G34, G32, FOI hus G
 TSEA 26 exam page 1 of 10 20171019 Examination Design of Embedded DSP Processors, TSEA26 Date 8-12, 2017-10-19 Room G34, G32, FOI hus G Time 08-12AM Course code TSEA26 Exam code TEN1 Design of Embedded
TSEA 26 exam page 1 of 10 20171019 Examination Design of Embedded DSP Processors, TSEA26 Date 8-12, 2017-10-19 Room G34, G32, FOI hus G Time 08-12AM Course code TSEA26 Exam code TEN1 Design of Embedded
Good Evening! Welcome!
 University of Florida EEL 3701 Fall 2011 Dr Eric M Schwartz Page 1/11 Exam 2 Instructions: Turn off all cell phones, beepers and other noise making devices Show all work on the front of the test papers
University of Florida EEL 3701 Fall 2011 Dr Eric M Schwartz Page 1/11 Exam 2 Instructions: Turn off all cell phones, beepers and other noise making devices Show all work on the front of the test papers
Format. 10 multiple choice 8 points each. 1 short answer 20 points. Same basic principals as the midterm
 Final Review Format 10 multiple choice 8 points each Make sure to show your work Can write a description to the side as to why you think your answer is correct for possible partial credit 1 short answer
Final Review Format 10 multiple choice 8 points each Make sure to show your work Can write a description to the side as to why you think your answer is correct for possible partial credit 1 short answer
Computer Organization. Structure of a Computer. Registers. Register Transfer. Register Files. Memories
 Computer Organization Structure of a Computer Computer design as an application of digital logic design procedures Computer = processing unit + memory system Processing unit = control + Control = finite
Computer Organization Structure of a Computer Computer design as an application of digital logic design procedures Computer = processing unit + memory system Processing unit = control + Control = finite
Winter 2006 FINAL EXAMINATION Auxiliary Gymnasium Tuesday, April 18 7:00pm to 10:00pm
 University of Calgary Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ENCM 369: Computer Organization Lecture Instructor for L01 and L02: Dr. S. A. Norman Winter 2006 FINAL EXAMINATION Auxiliary Gymnasium
University of Calgary Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ENCM 369: Computer Organization Lecture Instructor for L01 and L02: Dr. S. A. Norman Winter 2006 FINAL EXAMINATION Auxiliary Gymnasium
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering March 13, 2008 Out of Order Execution and Branch Prediction Assigned March 13 Problem Set #4 Due March 25
 CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering March 13, 2008 Out of Order Execution and Branch Prediction Assigned March 13 Problem Set #4 Due March 25 http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152/sp08 The problem
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering March 13, 2008 Out of Order Execution and Branch Prediction Assigned March 13 Problem Set #4 Due March 25 http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152/sp08 The problem
CS303 LOGIC DESIGN FINAL EXAM
 JANUARY 2017. CS303 LOGIC DESIGN FINAL EXAM STUDENT NAME & ID: DATE: Instructions: Examination time: 100 min. Write your name and student number in the space provided above. This examination is closed
JANUARY 2017. CS303 LOGIC DESIGN FINAL EXAM STUDENT NAME & ID: DATE: Instructions: Examination time: 100 min. Write your name and student number in the space provided above. This examination is closed
Name: University of Michigan uniqname: (NOT your student ID number!)
 The University of Michigan - Department of EECS EECS370 Introduction to Computer Organization Midterm Exam 1 October 22, 2009 Name: University of Michigan uniqname: (NOT your student ID number!) Open book,
The University of Michigan - Department of EECS EECS370 Introduction to Computer Organization Midterm Exam 1 October 22, 2009 Name: University of Michigan uniqname: (NOT your student ID number!) Open book,
Midterm II CS164, Spring 2006
 Midterm II CS164, Spring 2006 April 11, 2006 Please read all instructions (including these) carefully. Write your name, login, SID, and circle the section time. There are 10 pages in this exam and 4 questions,
Midterm II CS164, Spring 2006 April 11, 2006 Please read all instructions (including these) carefully. Write your name, login, SID, and circle the section time. There are 10 pages in this exam and 4 questions,
Design of Embedded DSP Processors
 Design of Embedded DSP Processors Unit 3: Microarchitecture, Register file, and ALU 9/11/2017 Unit 3 of TSEA26-2017 H1 1 Contents 1. Microarchitecture and its design 2. Hardware design fundamentals 3.
Design of Embedded DSP Processors Unit 3: Microarchitecture, Register file, and ALU 9/11/2017 Unit 3 of TSEA26-2017 H1 1 Contents 1. Microarchitecture and its design 2. Hardware design fundamentals 3.
UW CSE 351, Winter 2013 Midterm Exam
 Full Name: Student ID: UW CSE 351, Winter 2013 Midterm Exam February 15, 2013 Instructions: Make sure that your exam is not missing any of the 9 pages, then write your full name and UW student ID on the
Full Name: Student ID: UW CSE 351, Winter 2013 Midterm Exam February 15, 2013 Instructions: Make sure that your exam is not missing any of the 9 pages, then write your full name and UW student ID on the
Digital Circuit Design and Language. Datapath Design. Chang, Ik Joon Kyunghee University
 Digital Circuit Design and Language Datapath Design Chang, Ik Joon Kyunghee University Typical Synchronous Design + Control Section : Finite State Machine + Data Section: Adder, Multiplier, Shift Register
Digital Circuit Design and Language Datapath Design Chang, Ik Joon Kyunghee University Typical Synchronous Design + Control Section : Finite State Machine + Data Section: Adder, Multiplier, Shift Register
Data paths and control logic
 Data paths and control logic! Building larger digital systems " Include data, not just control inputs! An example! Building up toward project - MasterMind Autumn 2014 CSE390C - IX - Data Paths and Control
Data paths and control logic! Building larger digital systems " Include data, not just control inputs! An example! Building up toward project - MasterMind Autumn 2014 CSE390C - IX - Data Paths and Control
Do not start the test until instructed to do so!
 CS 3204 Operating Systems Midterm (Abrams) Spring 2004 VIRG INIA POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE AND STATE U T PRO SI M UNI VERSI TY Instructions: Do not start the test until instructed to do so! Print your name
CS 3204 Operating Systems Midterm (Abrams) Spring 2004 VIRG INIA POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE AND STATE U T PRO SI M UNI VERSI TY Instructions: Do not start the test until instructed to do so! Print your name
CHAPTER 4: Register Transfer Language and Microoperations
 CS 224: Computer Organization S.KHABET CHAPTER 4: Register Transfer Language and Microoperations Outline Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus and Memory Transfers Arithmetic Microoperations
CS 224: Computer Organization S.KHABET CHAPTER 4: Register Transfer Language and Microoperations Outline Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus and Memory Transfers Arithmetic Microoperations
Programmable machines
 Page 1 of 9 Programmable machines indicates problems that have been selected for discussion in section, time permitting. Problem 1. Consider the following circuit: The heavy lines represent busses, which
Page 1 of 9 Programmable machines indicates problems that have been selected for discussion in section, time permitting. Problem 1. Consider the following circuit: The heavy lines represent busses, which
Block diagram view. Datapath = functional units + registers
 Computer design an application of digital logic design procedures Computer = processing unit + memory system Processing unit = control + datapath Control = finite state machine inputs = machine instruction,
Computer design an application of digital logic design procedures Computer = processing unit + memory system Processing unit = control + datapath Control = finite state machine inputs = machine instruction,
Register Transfer Level (RTL) Design
 CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Register Transfer Level (RTL) Design Instructor: Mohsen Imani Slides from Tajana Simunic Rosing CAPE CAPEs are out!!! https://cape.ucsd.edu/students/
CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Register Transfer Level (RTL) Design Instructor: Mohsen Imani Slides from Tajana Simunic Rosing CAPE CAPEs are out!!! https://cape.ucsd.edu/students/
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: S. Brown,
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: S. Brown,
Midterm I - Solution CS164, Spring 2014
 164sp14 Midterm 1 - Solution Midterm I - Solution CS164, Spring 2014 March 3, 2014 Please read all instructions (including these) carefully. This is a closed-book exam. You are allowed a one-page handwritten
164sp14 Midterm 1 - Solution Midterm I - Solution CS164, Spring 2014 March 3, 2014 Please read all instructions (including these) carefully. This is a closed-book exam. You are allowed a one-page handwritten
CS 265. Computer Architecture. Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng.
 CS 265 Computer Architecture Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng. CS 265 Midterm #1 Monday, Oct 18, 12:00pm-1:45pm, SCI 163 Questions on essential terms and concepts of Computer Architecture Mathematical questions on
CS 265 Computer Architecture Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng. CS 265 Midterm #1 Monday, Oct 18, 12:00pm-1:45pm, SCI 163 Questions on essential terms and concepts of Computer Architecture Mathematical questions on
CSE351 Spring 2018, Midterm Exam April 27, 2018
 CSE351 Spring 2018, Midterm Exam April 27, 2018 Please do not turn the page until 11:30. Last Name: First Name: Student ID Number: Name of person to your left: Name of person to your right: Signature indicating:
CSE351 Spring 2018, Midterm Exam April 27, 2018 Please do not turn the page until 11:30. Last Name: First Name: Student ID Number: Name of person to your left: Name of person to your right: Signature indicating:
EECS Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. Lec 20 RTL Design Optimization 11/6/2007
 EECS 5 - Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Lec 2 RTL Design Optimization /6/27 Shauki Elassaad Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Slides
EECS 5 - Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Lec 2 RTL Design Optimization /6/27 Shauki Elassaad Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Slides
10/21/2016. ECE 120: Introduction to Computing. Let s Extend Our Keyless Entry FSM. FSM Designs Also Allow Use of Abstraction
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 120: Introduction to Computing Extending Keyless Entry Combinational Logic Design Allows Use of Abstraction Recall
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 120: Introduction to Computing Extending Keyless Entry Combinational Logic Design Allows Use of Abstraction Recall
Truth Table! Review! Use this table and techniques we learned to transform from 1 to another! ! Gate Diagram! Today!
 CS61C L17 Combinational Logic Blocks and Intro to CPU Design (1)! inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 17 Combinational Logic Blocks and Intro to CPU Design 2010-07-20!!!Instructor
CS61C L17 Combinational Logic Blocks and Intro to CPU Design (1)! inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 17 Combinational Logic Blocks and Intro to CPU Design 2010-07-20!!!Instructor
Register Transfer Language and Microoperations (Part 2)
 Register Transfer Language and Microoperations (Part 2) Adapted by Dr. Adel Ammar Computer Organization 1 MICROOPERATIONS Computer system microoperations are of four types: Register transfer microoperations
Register Transfer Language and Microoperations (Part 2) Adapted by Dr. Adel Ammar Computer Organization 1 MICROOPERATIONS Computer system microoperations are of four types: Register transfer microoperations
ESE 150 Lab 07: Digital Logic
 LAB 07 In this lab we will do the following: 1. Investigate basic logic operations (AND, OR, INV, XOR) 2. Implement an ADDER on an FPGA 3. Implement a simple Finite- State Machine on an FPGA Background:
LAB 07 In this lab we will do the following: 1. Investigate basic logic operations (AND, OR, INV, XOR) 2. Implement an ADDER on an FPGA 3. Implement a simple Finite- State Machine on an FPGA Background:
The LC3's micro-coded controller ("useq") is nothing more than a finite-state machine (FSM). It has these inputs:
 midterm exam COSC-120, Computer Hardware Fundamentals, fall 2012 Computer Science Department Georgetown University NAME Open books, open notes (laptops included). Show and explain all your work. Answers
midterm exam COSC-120, Computer Hardware Fundamentals, fall 2012 Computer Science Department Georgetown University NAME Open books, open notes (laptops included). Show and explain all your work. Answers
Cpr E 281 FINAL PROJECT ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING IOWA STATE UNIVERSITY. FINAL Project. Objectives. Project Selection
 Objectives The main objective of the final project is to teach you how to put together all of the class material that you have learned so far in order to program the Altera DE2 board to carry out an independent
Objectives The main objective of the final project is to teach you how to put together all of the class material that you have learned so far in order to program the Altera DE2 board to carry out an independent
Student Number: UTORid: Question 0. [1 mark] Read and follow all instructions on this page, and fill in all fields.
![Student Number: UTORid: Question 0. [1 mark] Read and follow all instructions on this page, and fill in all fields. Student Number: UTORid: Question 0. [1 mark] Read and follow all instructions on this page, and fill in all fields.](/thumbs/86/93683386.jpg) CSC 258H1 Y 2016 Midterm Test Duration 1 hour and 50 minutes Aids allowed: none Student Number: UTORid: Last Name: First Name: Question 0. [1 mark] Read and follow all instructions on this page, and fill
CSC 258H1 Y 2016 Midterm Test Duration 1 hour and 50 minutes Aids allowed: none Student Number: UTORid: Last Name: First Name: Question 0. [1 mark] Read and follow all instructions on this page, and fill
ECE 341 Midterm Exam
 ECE 341 Midterm Exam Time allowed: 75 minutes Total Points: 75 Points Scored: Name: Problem No. 1 (8 points) For each of the following statements, indicate whether the statement is TRUE or FALSE: (a) A
ECE 341 Midterm Exam Time allowed: 75 minutes Total Points: 75 Points Scored: Name: Problem No. 1 (8 points) For each of the following statements, indicate whether the statement is TRUE or FALSE: (a) A
NAME: 1a. (10 pts.) Describe the characteristics of numbers for which this floating-point data type is well-suited. Give an example.
 MSU CSC 285 Spring, 2007 Exam 2 (5 pgs.) NAME: 1. Suppose that a eight-bit floating-point data type is defined with the eight bits divided into fields as follows, where the bits are numbered with zero
MSU CSC 285 Spring, 2007 Exam 2 (5 pgs.) NAME: 1. Suppose that a eight-bit floating-point data type is defined with the eight bits divided into fields as follows, where the bits are numbered with zero
EXPERIMENT NUMBER 11 REGISTERED ALU DESIGN
 11-1 EXPERIMENT NUMBER 11 REGISTERED ALU DESIGN Purpose Extend the design of the basic four bit adder to include other arithmetic and logic functions. References Wakerly: Section 5.1 Materials Required
11-1 EXPERIMENT NUMBER 11 REGISTERED ALU DESIGN Purpose Extend the design of the basic four bit adder to include other arithmetic and logic functions. References Wakerly: Section 5.1 Materials Required
DESIGN PROJECT TOY RPN CALCULATOR
 April 8, 1998 DESIGN PROJECT TOY RPN CALCULATOR ECE/Comp Sci 352 Digital System Fundamentals Semester II 1997-98 Due Tuesday, April 28, 1998; 10% of course grade. This project is to be submitted and will
April 8, 1998 DESIGN PROJECT TOY RPN CALCULATOR ECE/Comp Sci 352 Digital System Fundamentals Semester II 1997-98 Due Tuesday, April 28, 1998; 10% of course grade. This project is to be submitted and will
For Example: P: LOAD 5 R0. The command given here is used to load a data 5 to the register R0.
 Register Transfer Language Computers are the electronic devices which have several sets of digital hardware which are inter connected to exchange data. Digital hardware comprises of VLSI Chips which are
Register Transfer Language Computers are the electronic devices which have several sets of digital hardware which are inter connected to exchange data. Digital hardware comprises of VLSI Chips which are
MECH 1500 Quiz 4 Review
 Class: Date: MECH 1500 Quiz 4 Review True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. For the timer relay contact shown, when the relay coil is energized, there is a time delay before the
Class: Date: MECH 1500 Quiz 4 Review True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. For the timer relay contact shown, when the relay coil is energized, there is a time delay before the
ENEL 353: Digital Circuits Midterm Examination
 NAME: SECTION: L01: Norm Bartley, ST 143 L02: Steve Norman, ST 145 When you start the test, please repeat your name and section, and add your U of C ID number at the bottom of the last page. Instructions:
NAME: SECTION: L01: Norm Bartley, ST 143 L02: Steve Norman, ST 145 When you start the test, please repeat your name and section, and add your U of C ID number at the bottom of the last page. Instructions:
Midterm Exam ECE 448 Spring 2014 Monday, March 3 (15 points)
 ECE8 Midterm Midterm Exam ECE 8 Spring 2 Monday, March 3 (5 points) Instructions: Zip all your delierables into an archie .zip and submit it through lackboard no later than Monday, March 3,
ECE8 Midterm Midterm Exam ECE 8 Spring 2 Monday, March 3 (5 points) Instructions: Zip all your delierables into an archie .zip and submit it through lackboard no later than Monday, March 3,
Design of Digital Circuits ( L) ETH Zürich, Spring 2017
 Name: Student ID: Final Examination Design of Digital Circuits (252-0028-00L) ETH Zürich, Spring 2017 Professors Onur Mutlu and Srdjan Capkun Problem 1 (70 Points): Problem 2 (50 Points): Problem 3 (40
Name: Student ID: Final Examination Design of Digital Circuits (252-0028-00L) ETH Zürich, Spring 2017 Professors Onur Mutlu and Srdjan Capkun Problem 1 (70 Points): Problem 2 (50 Points): Problem 3 (40
CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems
 CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Tajana Simunic Rosing Announcements and Outline Check webct grades, make sure everything is there and is correct Pick up graded d homework at
CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Tajana Simunic Rosing Announcements and Outline Check webct grades, make sure everything is there and is correct Pick up graded d homework at
Arithmetic-logic units
 Arithmetic-logic units An arithmetic-logic unit, or ALU, performs many different arithmetic and logic operations. The ALU is the heart of a processor you could say that everything else in the CPU is there
Arithmetic-logic units An arithmetic-logic unit, or ALU, performs many different arithmetic and logic operations. The ALU is the heart of a processor you could say that everything else in the CPU is there
University of Toronto Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Midterm Examination. ECE 345 Algorithms and Data Structures Fall 2012
 1 University of Toronto Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Midterm Examination ECE 345 Algorithms and Data Structures Fall 2012 Print your name and ID number neatly in the space provided
1 University of Toronto Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Midterm Examination ECE 345 Algorithms and Data Structures Fall 2012 Print your name and ID number neatly in the space provided
Digital Systems. John SUM Institute of Technology Management National Chung Hsing University Taichung, ROC. December 6, 2012
 Digital Systems John SUM Institute of Technology Management National Chung Hsing University Taichung, ROC December 6, 2012 Contents 1 Logic Gates 3 1.1 Logic Gate............................. 3 1.2 Truth
Digital Systems John SUM Institute of Technology Management National Chung Hsing University Taichung, ROC December 6, 2012 Contents 1 Logic Gates 3 1.1 Logic Gate............................. 3 1.2 Truth
EECS150: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems
 EECS150: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems University of California Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Midterm 3 Fall 2004 Last name: First name Student ID: Login:
EECS150: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems University of California Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Midterm 3 Fall 2004 Last name: First name Student ID: Login:
The Need of Datapath or Register Transfer Logic. Number 1 Number 2 Number 3 Number 4. Numbers from 1 to million. Register
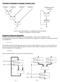 The Need of Datapath or Register Transfer Logic Number 1 Number 2 Number 3 Number 4 Numbers from 1 to million Register (a) (b) Circuits to add several numbers: (a) combinational circuit to add four numbers;
The Need of Datapath or Register Transfer Logic Number 1 Number 2 Number 3 Number 4 Numbers from 1 to million Register (a) (b) Circuits to add several numbers: (a) combinational circuit to add four numbers;
Digital System Design Verilog-Part III. Amir Masoud Gharehbaghi
 Digital System Design Verilog-Part III Amir Masoud Gharehbaghi amgh@mehr.sharif.edu Procedural Blocks initial block always block Place in module body Run concurrently with other module constructs Continuous
Digital System Design Verilog-Part III Amir Masoud Gharehbaghi amgh@mehr.sharif.edu Procedural Blocks initial block always block Place in module body Run concurrently with other module constructs Continuous
Good luck and have fun!
 Midterm Exam October 13, 2014 Name: Problem 1 2 3 4 total Points Exam rules: Time: 90 minutes. Individual test: No team work! Open book, open notes. No electronic devices, except an unprogrammed calculator.
Midterm Exam October 13, 2014 Name: Problem 1 2 3 4 total Points Exam rules: Time: 90 minutes. Individual test: No team work! Open book, open notes. No electronic devices, except an unprogrammed calculator.
EPC6055 Digital Integrated Circuits EXAM 1 Fall Semester 2013
 EPC6055 Digital Integrated Circuits EXAM 1 Fall Semester 2013 Print Here Student ID Signature This is a closed book exam. The exam is to be completed in one-hundred ten (110) minutes. Don t use scratch
EPC6055 Digital Integrated Circuits EXAM 1 Fall Semester 2013 Print Here Student ID Signature This is a closed book exam. The exam is to be completed in one-hundred ten (110) minutes. Don t use scratch
session 7. Datapath Design
 General Objective: Determine the hardware requirement of a digital computer based on its instruction set. Specific Objectives: Describe the general concepts in designing the data path of a digital computer
General Objective: Determine the hardware requirement of a digital computer based on its instruction set. Specific Objectives: Describe the general concepts in designing the data path of a digital computer
CSC 220: Computer Organization Unit 10 Arithmetic-logic units
 College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer Science CSC 220: Computer Organization Unit 10 Arithmetic-logic units 1 Remember: 2 Arithmetic-logic units An arithmetic-logic unit,
College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer Science CSC 220: Computer Organization Unit 10 Arithmetic-logic units 1 Remember: 2 Arithmetic-logic units An arithmetic-logic unit,
CS 170 Algorithms Spring 2009 David Wagner MT2
 CS 170 Algorithms Spring 2009 David Wagner MT2 PRINT your name:, (last) SIGN your name: (first) PRINT your Unix account login: Your TA s name: Discussion section time: Name of the person sitting to your
CS 170 Algorithms Spring 2009 David Wagner MT2 PRINT your name:, (last) SIGN your name: (first) PRINT your Unix account login: Your TA s name: Discussion section time: Name of the person sitting to your
Timing for Ripple Carry Adder
 Timing for Ripple Carry Adder 1 2 3 Look Ahead Method 5 6 7 8 9 Look-Ahead, bits wide 10 11 Multiplication Simple Gradeschool Algorithm for 32 Bits (6 Bit Result) Multiplier Multiplicand AND gates 32
Timing for Ripple Carry Adder 1 2 3 Look Ahead Method 5 6 7 8 9 Look-Ahead, bits wide 10 11 Multiplication Simple Gradeschool Algorithm for 32 Bits (6 Bit Result) Multiplier Multiplicand AND gates 32
One and a half hours. Section A is COMPULSORY UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE
 One and a half hours Section A is COMPULSORY UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE Fundamentals of Computer Engineering Date: Thursday 21st January 2016 Time: 14:00-15:30 Answer BOTH Questions
One and a half hours Section A is COMPULSORY UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE Fundamentals of Computer Engineering Date: Thursday 21st January 2016 Time: 14:00-15:30 Answer BOTH Questions
CS2100 COMPUTER ORGANISATION
 CS00 NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE CS00 COMPUTER ORGANISATION (Semester : AY07/8) Time Allowed: Hours INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES. This assessment paper consists of SEVEN (7) questions and comprises
CS00 NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE CS00 COMPUTER ORGANISATION (Semester : AY07/8) Time Allowed: Hours INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES. This assessment paper consists of SEVEN (7) questions and comprises
Computer Organization EE 3755 Midterm Examination
 Name Computer Organization EE 3755 Midterm Examination Wednesday, 30 October 2013, 8:30 9:20 CDT Alias Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem 4 Problem 5 Problem 6 Problem 7 Exam Total (21 pts) (15 pts)
Name Computer Organization EE 3755 Midterm Examination Wednesday, 30 October 2013, 8:30 9:20 CDT Alias Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem 4 Problem 5 Problem 6 Problem 7 Exam Total (21 pts) (15 pts)
CROWDMARK. Examination Midterm. Spring 2017 CS 350. Closed Book. Page 1 of 30. University of Waterloo CS350 Midterm Examination.
 Times: Thursday 2017-06-22 at 19:00 to 20:50 (7 to 8:50PM) Duration: 1 hour 50 minutes (110 minutes) Exam ID: 3520593 Please print in pen: Waterloo Student ID Number: WatIAM/Quest Login Userid: Sections:
Times: Thursday 2017-06-22 at 19:00 to 20:50 (7 to 8:50PM) Duration: 1 hour 50 minutes (110 minutes) Exam ID: 3520593 Please print in pen: Waterloo Student ID Number: WatIAM/Quest Login Userid: Sections:
University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering
 University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Spring 2016 Instructors: Vladimir Stojanovic, Nicholas Weaver 2016-04-04 L J After the
University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Spring 2016 Instructors: Vladimir Stojanovic, Nicholas Weaver 2016-04-04 L J After the
CS 351 Exam 2, Fall 2012
 CS 351 Exam 2, Fall 2012 Your name: Rules You may use one handwritten 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet (front and back). This is the only resource you may consult during this exam. Include explanations and comments
CS 351 Exam 2, Fall 2012 Your name: Rules You may use one handwritten 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet (front and back). This is the only resource you may consult during this exam. Include explanations and comments
URL: Offered by: Should already know how to design with logic. Will learn...
 00 1 EE 3755 Computer Organization 00 1 URL: http://www.ece.lsu.edu/ee3755 Offered by: David M. Koppelman Room 3191 P. Taylor Hall 578-5482, koppel@ece.lsu.edu, http://www.ece.lsu.edu/koppel Tentative
00 1 EE 3755 Computer Organization 00 1 URL: http://www.ece.lsu.edu/ee3755 Offered by: David M. Koppelman Room 3191 P. Taylor Hall 578-5482, koppel@ece.lsu.edu, http://www.ece.lsu.edu/koppel Tentative
University of Toronto Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Midterm Examination. ECE 345 Algorithms and Data Structures Fall 2010
 University of Toronto Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Midterm Examination ECE 345 Algorithms and Data Structures Fall 2010 Print your name and ID number neatly in the space provided below;
University of Toronto Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Midterm Examination ECE 345 Algorithms and Data Structures Fall 2010 Print your name and ID number neatly in the space provided below;
Two hours UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE
 COMP 22111 Two hours UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE Processor Microarchitecture Date: Wednesday 18th January 2017 Time: 14:00-16:00 Please answer any THREE Questions from the FOUR
COMP 22111 Two hours UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE Processor Microarchitecture Date: Wednesday 18th January 2017 Time: 14:00-16:00 Please answer any THREE Questions from the FOUR
REGISTER TRANSFER AND MICROOPERATIONS
 1 REGISTER TRANSFER AND MICROOPERATIONS Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus and Memory Transfers Arithmetic Microoperations Logic Microoperations Shift Microoperations Arithmetic Logic Shift
1 REGISTER TRANSFER AND MICROOPERATIONS Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus and Memory Transfers Arithmetic Microoperations Logic Microoperations Shift Microoperations Arithmetic Logic Shift
CSCI 111 First Midterm Exam Spring Solutions 09.05am 09.55am, Wednesday, March 14, 2018
 QUEENS COLLEGE Department of Computer Science CSCI 111 First Midterm Exam Spring 2018 03.14.18 Solutions 09.05am 09.55am, Wednesday, March 14, 2018 Problem 1 Write a complete C++ program that asks the
QUEENS COLLEGE Department of Computer Science CSCI 111 First Midterm Exam Spring 2018 03.14.18 Solutions 09.05am 09.55am, Wednesday, March 14, 2018 Problem 1 Write a complete C++ program that asks the
Fall 2016 Instructor: Gandhi Puvvada. Thursday, 9/22/2016 (A 2H 50M exam) 05:30 PM - 08:20 PM (170 min) in THH101. Student s Last Name:
 EE457 Quiz (~0%) Closed-book Closed-notes Exam; No cheat sheets; No cell phones or computers Calculators and Verilog Guides are not needed and hence not allowed. Fall 206 Instructor: Gandhi Puvvada Thursday,
EE457 Quiz (~0%) Closed-book Closed-notes Exam; No cheat sheets; No cell phones or computers Calculators and Verilog Guides are not needed and hence not allowed. Fall 206 Instructor: Gandhi Puvvada Thursday,
University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering
 University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Spring 2016 Instructors: Vladimir Stojanovic, Nicholas Weaver 2016-04-04 L J After the
University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Spring 2016 Instructors: Vladimir Stojanovic, Nicholas Weaver 2016-04-04 L J After the
Exp#8: Designing a Programmable Sequence Detector
 Exp#8: Designing a Programmable Sequence Detector Objectives Learning how to partition a system into data-path and control unit. Integrating Schematics and Verilog code together Overview In this lab you
Exp#8: Designing a Programmable Sequence Detector Objectives Learning how to partition a system into data-path and control unit. Integrating Schematics and Verilog code together Overview In this lab you
NAME: March 4. and ask me. To pace yourself, you should allow on more than 1 minute/point. For
 CS 241 Algorithms and Data Structures Spring Semester, 2004 Midterm Exam NAME: March 4 If you have any questions about a problem, quietly come to the front of the classroom and ask me. To pace yourself,
CS 241 Algorithms and Data Structures Spring Semester, 2004 Midterm Exam NAME: March 4 If you have any questions about a problem, quietly come to the front of the classroom and ask me. To pace yourself,
5 Arithmetic Logic Unit
 Arithmetic Logic Unit, Muxes 5 Arithmetic Logic Unit I Overview An Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) allows many pre-defined functions to be implemented on two binary inputs. We will look at a simple ALU that
Arithmetic Logic Unit, Muxes 5 Arithmetic Logic Unit I Overview An Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) allows many pre-defined functions to be implemented on two binary inputs. We will look at a simple ALU that
ECE 2300 Digital Logic & Computer Organization. More Finite State Machines
 ECE 2300 Digital Logic & Computer Organization Spring 2018 More Finite State Machines Lecture 9: 1 Announcements Prelab 3(B) due tomorrow Lab 4 to be released tonight You re not required to change partner(s)
ECE 2300 Digital Logic & Computer Organization Spring 2018 More Finite State Machines Lecture 9: 1 Announcements Prelab 3(B) due tomorrow Lab 4 to be released tonight You re not required to change partner(s)
CSE 351 Midterm - Winter 2015 Solutions
 CSE 351 Midterm - Winter 2015 Solutions February 09, 2015 Please read through the entire examination first! We designed this exam so that it can be completed in 50 minutes and, hopefully, this estimate
CSE 351 Midterm - Winter 2015 Solutions February 09, 2015 Please read through the entire examination first! We designed this exam so that it can be completed in 50 minutes and, hopefully, this estimate
CENG 3531 Computer Architecture Spring a. T / F A processor can have different CPIs for different programs.
 Exam 2 April 12, 2012 You have 80 minutes to complete the exam. Please write your answers clearly and legibly on this exam paper. GRADE: Name. Class ID. 1. (22 pts) Circle the selected answer for T/F and
Exam 2 April 12, 2012 You have 80 minutes to complete the exam. Please write your answers clearly and legibly on this exam paper. GRADE: Name. Class ID. 1. (22 pts) Circle the selected answer for T/F and
a, b sum module add32 sum vector bus sum[31:0] sum[0] sum[31]. sum[7:0] sum sum overflow module add32_carry assign
![a, b sum module add32 sum vector bus sum[31:0] sum[0] sum[31]. sum[7:0] sum sum overflow module add32_carry assign a, b sum module add32 sum vector bus sum[31:0] sum[0] sum[31]. sum[7:0] sum sum overflow module add32_carry assign](/thumbs/91/106466219.jpg) I hope you have completed Part 1 of the Experiment. This lecture leads you to Part 2 of the experiment and hopefully helps you with your progress to Part 2. It covers a number of topics: 1. How do we specify
I hope you have completed Part 1 of the Experiment. This lecture leads you to Part 2 of the experiment and hopefully helps you with your progress to Part 2. It covers a number of topics: 1. How do we specify
ELCT 501: Digital System Design
 ELCT 501: Digital System Lecture 4: CAD tools (Continued) Dr. Mohamed Abd El Ghany, Basic VHDL Concept Via an Example Problem: write VHDL code for 1-bit adder 4-bit adder 2 1-bit adder Inputs: A (1 bit)
ELCT 501: Digital System Lecture 4: CAD tools (Continued) Dr. Mohamed Abd El Ghany, Basic VHDL Concept Via an Example Problem: write VHDL code for 1-bit adder 4-bit adder 2 1-bit adder Inputs: A (1 bit)
