Métodos de fusão e co-registo de imagem
|
|
|
- Conrad Kelley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LICENCIATURA EM ENGENHARIA BIOMÉDICA Fundamentos de Imagem Diagnóstica e Terapeutica Métodos de fusão e co-registo de imagem Jorge Isidoro Sumário Introdução à imagem médica Registo de imagens Metodologia do registo de imagens Tipos de transformações Graus de liberdade Algoritmos de registo de imagem Comparação dos métodos de registo 1
2 Introduction Image registration is the process of aligning images so that corresponding features can easily be related. The images might be acquired with different sensors (e.g. sensitive to different parts or the electromagnetic spectrum) or the same sensor at different times. Introduction Image registration has applications in many fields, and the one that is addressed is medical imaging This encompasses a wide range of image usage, but the main emphasis is on radiological imaging 2
3 Introduction Medical images: In Xray Computed Tomography (CT) images are sensitive to tissue density, atomic composition and the X-ray attenuation coefficient In Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MR) they are related to proton density, relaxation times, flow and other parameters The introduction of contrast agents provides information on the patency and function of tubular structures such as blood vessels, the bile duct and the bowel, as well as the state of the blood brain barrier. Introduction Medical images: In nuclear medicine, radio-pharmaceuticals introduced into the body allow delineation of functioning tissue and measurement of metabolic and pathophysiological processes. Ultrasound detects subtle changes in acoustic impedance at tissue boundaries and diffraction patterns in different tissues providing discrimination of different tissue types. Doppler ultrasound provides images of flowing blood. Endoscopy and surgical microscopy provide images of visible surfaces deep within the body 3
4 Introduction Image Modalities Anatomical Depicting primarily morphology (MRI,CT,X-ray) Functional Depicting primarily information on the metabolism of the underlying anatomy (SPECT,PET) Introduction These and other imaging technologies now provide rich sources of data on the physical properties and biological function of tissues at spatial resolutions from: 5mm for nuclear medicine 1.0 or 0.5mm for MR and CT µm for optical systems. 4
5 Image Registration Since the mid 1980 s medical image registration has evolved from being perceived as a rather minor precursor to some medical imaging applications to a significant subdiscipline in itself. Image registration has also become one of the more successful areas of image processing with fully automated algorithms becoming available in a number of applications. Image Registration Why has registration become so important? Medical imaging is about establishing shape, structure, size, and spatial relationships of anatomical structures within the patient together with spatial information about function and any pathology or other abnormality Establishing the correspondence of spatial information in medical images and equivalent structures in the body is fundamental to medical image interpretation and analysis 5
6 Image Registration In many clinical scenarios images from several modalities may be acquired and the diagnostician s task is to draw useful clinical conclusions: This generally requires mental compensation for changes in subject position. Image registration aligns the images and so establishes correspondence between different features seen on different imaging modalities allows monitoring of subtle changes in size or intensity over time or across a population Image Registration Cont.: establishes correspondence between images and physical space in image guided interventions. Registration of an atlas or computer model aids in the delineation of anatomical and pathological structures in medical images and is an important precursor to detailed analysis. 6
7 Image Registration It is now common for patients to be imaged multiple times: either repeated imaging with a single modality, or imaging with different modalities to be imaged dynamically, that is to have sequences of images acquired, often at many frames per second The ever-increasing amount of image data acquired makes it more and more desirable to relate one image to another to assist in extracting relevant clinical information. Image Registration Image registration can help in: intermodality registration enables complementary information from different modalities to be combined intramodality registration enables accurate comparisons to be made between images from the same modality. 7
8 Image Registration Image registration can be used to align multiple images: from the same individual (intrasubject registration) from different subjects (intersubject registration) Image Registration All the images that we wish to register or manipulate must be available in digital form. For most medical images this means that they are made up of: rectangular array of small square or rectangular elements called pixels each pixel having an associated image intensity value 8
9 Image Registration 2D images are often stacked together to form a 3D volume: many images are now acquired directly as 3D volumes. each pixel will now correspond to a small volume element of tissue or voxel. The number stored in each voxel, the voxel image intensity, will be some average of a physical attribute measured over this volume Registration Methodology Image registration establishes spatial correspondence: which point on one image corresponds to a particular point on the other. by correspond we mean that these points represent a measurement localised to the same small element of tissue within the patient. yields the appropriate transformation between the co-ordinate systems of the two sets of scans 9
10 Registration Methodology No measurement is perfectly accurate and there will always be uncertainty, error or tolerance in this estimate of correspondence for many clinical applications it is important to know what this tolerance is so as not to over interpret the registered datasets. Registration Methodology Once correspondence is determined throughout the volume imaged by the two modalities then: one image can be transformed into the coordinate system of the other this calculation can itself lead to further approximations or errors typically there will be some blurring of the transformed image 10
11 Registration Methodology Finally we need to consider correspondence when combining images from multiple subjects or images between an individual and an atlas derived from one or more other individuals. Registration of images from different individuals requires the use of deformations that can accommodate biological variations Registration Methodology In many applications reported in the literature correspondence is implicitly defined as the points resulting from arbitrary transformations derived using algorithms that plausibly morph one image into another. There are an infinite number of possible transformations that can morph one image into another including those that lead to creation or destruction of complete structures. Medical imaging applications usually require deformations of the images that maintain correspondence (nose to nose, eye to eye etc.) 11
12 Registration Methodology Morphing Registration Methodology Finally we have the process of combining or fusing the information in the images in some useful or meaningful way: may be left entirely to the clinician in his/her mind s eye or simple visualisation effects may be used, including colour, or interactive fading in and out of one image s contribution overlaid on the other two cursors, so-called linked cursors, might be used to indicate corresponding points in the two images 12
13 Types of Transformation 2D to 2D If the geometry of image acquisition is tightly controlled, 2D images may be registered purely via a rotation and 2 orthogonal translations. It may also be necessary to correct for differences in scaling from the real object to each of the images. Types of Transformation 2D to 2D 13
14 Types of Transformation 3D to 3D The assumption is usually made that the internal anatomy of the patient has not distorted or changed in spatial relationships between organs so that the imaged part of the body behaves as a rigid body In this case 3 translations and 3 rotations will bring the images into registration Types of Transformation 3D to 3D Careful calibration of each scanning device is required to determine image scaling, i.e. the size of the voxels in each modality. 3D to 3D registration is the most well developed and widely used 14
15 Within-subject rigid registration - Example Full 3D Anatomic al Image Conventional Anatomical Image Within-subject rigid registration Example 15
16 Types of Transformation 2D to 3D 2D to 3D registration may be required when establishing correspondence between 3D volumes and projection images such as X-ray or optical images Time Another class of registration problem concerns registration of image sequences that follow some process that changes with time Degrees of freedom Degrees of freedom of the transformation: number of parameters needed to describe a registration transformation is referred to as the number of degrees of freedom depends on the dimensionality of the images and on the constraints of the imaged structures simplest transformation corresponds to the motion of a rigid body. 16
17 Degrees of freedom Degrees of freedom of the transformation For 2D to 2D registration there will be three degrees of freedom: 2 translations and 1 rotation Original Image Same after a rigid transformation Same after a linear affine transform Degrees of freedom For 3D to 3D registration: 3 translations and 3 rotations, giving six degrees of freedom. When we do not know the pixel or voxel sizes or the fields of view, the registration algorithm may need to determine these. This will lead to an extra: two degrees of freedom in 2D or three degrees of freedom in 3D equating to scaling in each direction 17
18 Degrees of freedom When images are coming from same subject only a rigid 6 parameter transformation has to be estimated: 3 translations (along X, Y and Z axis) 3 rotations (around X, Y and Z axis) Degrees of freedom affine transformation. In the affine transformation any straight line in one image will transform to a straight line in the other parallel lines are preserved allowing a combination of rigid body motion, scaling, and skew about any of the 3 axes has 12 degrees of freedom. non-rigid registration many more degrees of freedom are required (~2000!) 18
19 Image Registration Algorithms Corresponding landmark based registration Is based on identification of corresponding point landmarks or fiducial markers in the two images For a rigid structure, identification and location of three landmarks will be sufficient to establish the transformation between two 3D image volumes provided the fiducial points are not all in a straight line In practice it is usual to use more than three. The larger the number of points used the more any errors in marking the points are averaged out Image Registration Algorithms Corresponding landmark based registration It involves first computing the average or centroid of each set of points The difference between the centroids in 3D tells us the translation that must be applied to one set of points This point set is then rotated about its new centroid until the sum of the squared distances between each corresponding point pair is minimised The square root of the mean of this squared distance is also referred to as the Root Mean Square (RMS) error, residual error or Fiducial Registration Error (FRE) 19
20 Image Registration Algorithms Surface based registration The Head and Hat Algorithm the contours of the surface are drawn on a series of slices from one modality, the head a set of points that correspond to the same surface in the other modality are identified, the hat Image Registration Algorithms Surface based registration The Head and Hat Algorithm computer then attempts a series of trial fits of the hat points on the head contours At each iteration the sum of the squares of the distances between each hat point and the head is calculated and the process continues until this value is minimised tend to fail when the surfaces show symmetries to rotation and this is often the case for many anatomical structures. 20
21 Image Registration Algorithms The Head and Hat Algorithm Image Registration Algorithms Surface based registration The Iterative Closest Point Algorithm one surface is represented by a set of points while the other is represented by a surface made up of many triangular patches or facets. 21
22 Image Registration Algorithms Surface based registration The Iterative Closest Point Algorithm proceeds by finding the closest point on the appropriate triangular patch to each of the points in turn closest points form a set and these are registered using the corresponding landmark based registration and the residual error is calculated. the process is repeated until the residual error drops by less than a preset value. Image Registration Algorithms Registration Based on Voxel Intensities Alone Voxel Similarity Measures use the intensities in the two images alone without any requirement to segment or delineate corresponding structures a way of representing the image intensities of a pair of images that are to be registered is called the joint histogram or joint probability distribution these methods use all the data in each image and so tend to average out any errors caused by the noise or random fluctuations of image intensity 22
23 Image Registration Algorithms Image Registration Algorithms Registration Based on Voxel Intensities Alone Voxel Similarity Measures Registration of multiple images of the same patient acquired using the same imaging modality Because the images are acquired using the same modality, an approximately linear relationship will exist between the voxel intensities in one image and voxel intensities in the other In these cases the Correlation Coefficient is a good measure of alignment basically involves multiplication of corresponding image intensities One image is moved with respect to the other until the largest value of the correlation coefficient is found 23
24 Image Registration Algorithms Registration Based on Voxel Intensities Alone Voxel Similarity Measures Registration of multiple images of the same patient acquired using the same imaging modality Instead of multiplying corresponding intensities we may subtract them which leads to another measure, the sums of squared intensity differences (SSD) In this case alignment is adjusted until the smallest SSD is found Image Registration Algorithms Registration Based on Voxel Intensities Alone Voxel Similarity Measures Registration of multiple images of the same patient acquired using the same imaging modality If two images are very similar then their ratio will be most uniform at registration. This is the basis of Woods Ratio Image Uniformity (RIU) algorithm in which the variance of this ratio is calculated Alignment is adjusted until the smallest variance is found. 24
25 Image Registration Algorithms Registration Based on Voxel Intensities Alone Voxel Similarity Measures Registration of multiple images of the same patient acquired using the same imaging modality The most common technique for aligning these images is to find a rigid body transformation. Prior to carrying out the rigid body registration, it is advisable to correct for any scaling or intensity errors in the images and it may be necessary to carry out additional preprocessing such as segmentation Image Registration Algorithms Voxel similarity measures applied to images from different modalities - entropy as a measure of alignment. while images from different modalities exhibit complementary information there is usually also a high degree of shared information between images of the same structures 25
26 Image Registration Algorithms Voxel similarity measures applied to images from different modalities - entropy as a measure of alignment. Any algorithm that is being used to register images from two different modalities must be insensitive to modality specific differences in image intensity associated with the same tissue and also accommodate differences in relative intensity from tissue to tissue Image Registration Algorithms Voxel similarity measures applied to images from different modalities - entropy as a measure of alignment. generate a scatter plot of these image intensities, point by point. These are two-dimensional plots of image intensity of one image against corresponding image intensity of the other. The resulting plot is a type of two-dimensional histogram. when divided by the number of contributing pixels, is equal to the joint probability distribution. 26
27 Image Registration Algorithms aligned MR and 18FDG PET 2mm translation 5mm translation Image Registration Algorithms Voxel similarity measures applied to images from different modalities - entropy as a measure of alignment. the joint probability distribution provides a number that is equal to the probability that those intensities occur together at corresponding locations in the two images 27
28 Image Registration Algorithms Mutual Information: Entropies of images A,B: H(A), H(B) Joint entropy of A,B: H(A,B) If A and B independent H(A,B) = H(A)+H(B) Else difference is MI -> Minimize difference Problem: estimate pdfs for H(A), H(B), H(A,B) Registration Framework Components: 28
29 Comparison of registration methods West J, Fitzpatrick JM, Dawant BM, et al. AIR Headmounted fiducials serves as ``Gold standard'' coregistration between the modalities (MR/CT/PET). Coregistration parameters are kept for reference, and fiducials are removed from the datasets and replaced by artificial noise. Methods are tested ``blindly'' - no knowledge of the Gold standard answer. Method Mean(mm) Med.(mm) Max.(mm) Method Mean(mm) Med.(mm) Max.(mm) Pluim Rohlfing Woods Maintz Rohlfing Tanacs Rohlfing Luo Rohlfing corr Collignon Rohlfing corr Noz Harkness Ding Pelizzari Thevenaz Thevenaz Robb Arata Ashburner Hsu Malandain Rohlfing Nikou Woods Barillot Ren Thevenaz Hill Nikou Tanacs Ashburner Robb Capek SPM Bibliografia Medical Image Registration. Edited by Joseph Hajnal, David Hawkes and Derek Hill. CRC Press, 2001 Links: AIR - CISG - ImageJ - MIPAV - RView - MRIcro - XMedCon
Image Registration. Prof. Dr. Lucas Ferrari de Oliveira UFPR Informatics Department
 Image Registration Prof. Dr. Lucas Ferrari de Oliveira UFPR Informatics Department Introduction Visualize objects inside the human body Advances in CS methods to diagnosis, treatment planning and medical
Image Registration Prof. Dr. Lucas Ferrari de Oliveira UFPR Informatics Department Introduction Visualize objects inside the human body Advances in CS methods to diagnosis, treatment planning and medical
Mutual Information Based Methods to Localize Image Registration
 Mutual Information Based Methods to Localize Image Registration by Kathleen P. Wilkie A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfilment of the thesis requirement for the degree of Master of
Mutual Information Based Methods to Localize Image Registration by Kathleen P. Wilkie A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfilment of the thesis requirement for the degree of Master of
MEDICAL IMAGE ANALYSIS
 SECOND EDITION MEDICAL IMAGE ANALYSIS ATAM P. DHAWAN g, A B IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Sponsor IEEE Press Series in Biomedical Engineering Metin Akay, Series Editor +IEEE IEEE PRESS
SECOND EDITION MEDICAL IMAGE ANALYSIS ATAM P. DHAWAN g, A B IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Sponsor IEEE Press Series in Biomedical Engineering Metin Akay, Series Editor +IEEE IEEE PRESS
Overview of Proposed TG-132 Recommendations
 Overview of Proposed TG-132 Recommendations Kristy K Brock, Ph.D., DABR Associate Professor Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Michigan Chair, AAPM TG 132: Image Registration and Fusion Conflict
Overview of Proposed TG-132 Recommendations Kristy K Brock, Ph.D., DABR Associate Professor Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Michigan Chair, AAPM TG 132: Image Registration and Fusion Conflict
Chapter 3 Set Redundancy in Magnetic Resonance Brain Images
 16 Chapter 3 Set Redundancy in Magnetic Resonance Brain Images 3.1 MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) MRI is a technique of measuring physical structure within the human anatomy. Our proposed research focuses
16 Chapter 3 Set Redundancy in Magnetic Resonance Brain Images 3.1 MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) MRI is a technique of measuring physical structure within the human anatomy. Our proposed research focuses
Medical Image Registration
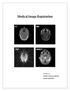 Medical Image Registration Submitted by NAREN BALRAJ SINGH SB ID# 105299299 Introduction Medical images are increasingly being used within healthcare for diagnosis, planning treatment, guiding treatment
Medical Image Registration Submitted by NAREN BALRAJ SINGH SB ID# 105299299 Introduction Medical images are increasingly being used within healthcare for diagnosis, planning treatment, guiding treatment
Medicale Image Analysis
 Medicale Image Analysis Registration Validation Prof. Dr. Philippe Cattin MIAC, University of Basel Prof. Dr. Philippe Cattin: Registration Validation Contents 1 Validation 1.1 Validation of Registration
Medicale Image Analysis Registration Validation Prof. Dr. Philippe Cattin MIAC, University of Basel Prof. Dr. Philippe Cattin: Registration Validation Contents 1 Validation 1.1 Validation of Registration
Spatio-Temporal Registration of Biomedical Images by Computational Methods
 Spatio-Temporal Registration of Biomedical Images by Computational Methods Francisco P. M. Oliveira, João Manuel R. S. Tavares tavares@fe.up.pt, www.fe.up.pt/~tavares Outline 1. Introduction 2. Spatial
Spatio-Temporal Registration of Biomedical Images by Computational Methods Francisco P. M. Oliveira, João Manuel R. S. Tavares tavares@fe.up.pt, www.fe.up.pt/~tavares Outline 1. Introduction 2. Spatial
Biomedical Imaging Registration Trends and Applications. Francisco P. M. Oliveira, João Manuel R. S. Tavares
 Biomedical Imaging Registration Trends and Applications Francisco P. M. Oliveira, João Manuel R. S. Tavares tavares@fe.up.pt, www.fe.up.pt/~tavares Outline 1. Introduction 2. Spatial Registration of (2D
Biomedical Imaging Registration Trends and Applications Francisco P. M. Oliveira, João Manuel R. S. Tavares tavares@fe.up.pt, www.fe.up.pt/~tavares Outline 1. Introduction 2. Spatial Registration of (2D
2D Rigid Registration of MR Scans using the 1d Binary Projections
 2D Rigid Registration of MR Scans using the 1d Binary Projections Panos D. Kotsas Abstract This paper presents the application of a signal intensity independent registration criterion for 2D rigid body
2D Rigid Registration of MR Scans using the 1d Binary Projections Panos D. Kotsas Abstract This paper presents the application of a signal intensity independent registration criterion for 2D rigid body
Whole Body MRI Intensity Standardization
 Whole Body MRI Intensity Standardization Florian Jäger 1, László Nyúl 1, Bernd Frericks 2, Frank Wacker 2 and Joachim Hornegger 1 1 Institute of Pattern Recognition, University of Erlangen, {jaeger,nyul,hornegger}@informatik.uni-erlangen.de
Whole Body MRI Intensity Standardization Florian Jäger 1, László Nyúl 1, Bernd Frericks 2, Frank Wacker 2 and Joachim Hornegger 1 1 Institute of Pattern Recognition, University of Erlangen, {jaeger,nyul,hornegger}@informatik.uni-erlangen.de
Medical Image Registration by Maximization of Mutual Information
 Medical Image Registration by Maximization of Mutual Information EE 591 Introduction to Information Theory Instructor Dr. Donald Adjeroh Submitted by Senthil.P.Ramamurthy Damodaraswamy, Umamaheswari Introduction
Medical Image Registration by Maximization of Mutual Information EE 591 Introduction to Information Theory Instructor Dr. Donald Adjeroh Submitted by Senthil.P.Ramamurthy Damodaraswamy, Umamaheswari Introduction
Medical Image Analysis
 Computer assisted Image Analysis VT04 29 april 2004 Medical Image Analysis Lecture 10 (part 1) Xavier Tizon Medical Image Processing Medical imaging modalities XRay,, CT Ultrasound MRI PET, SPECT Generic
Computer assisted Image Analysis VT04 29 april 2004 Medical Image Analysis Lecture 10 (part 1) Xavier Tizon Medical Image Processing Medical imaging modalities XRay,, CT Ultrasound MRI PET, SPECT Generic
Nonrigid Registration using Free-Form Deformations
 Nonrigid Registration using Free-Form Deformations Hongchang Peng April 20th Paper Presented: Rueckert et al., TMI 1999: Nonrigid registration using freeform deformations: Application to breast MR images
Nonrigid Registration using Free-Form Deformations Hongchang Peng April 20th Paper Presented: Rueckert et al., TMI 1999: Nonrigid registration using freeform deformations: Application to breast MR images
Lecture 6: Medical imaging and image-guided interventions
 ME 328: Medical Robotics Winter 2019 Lecture 6: Medical imaging and image-guided interventions Allison Okamura Stanford University Updates Assignment 3 Due this Thursday, Jan. 31 Note that this assignment
ME 328: Medical Robotics Winter 2019 Lecture 6: Medical imaging and image-guided interventions Allison Okamura Stanford University Updates Assignment 3 Due this Thursday, Jan. 31 Note that this assignment
Assessing Accuracy Factors in Deformable 2D/3D Medical Image Registration Using a Statistical Pelvis Model
 Assessing Accuracy Factors in Deformable 2D/3D Medical Image Registration Using a Statistical Pelvis Model Jianhua Yao National Institute of Health Bethesda, MD USA jyao@cc.nih.gov Russell Taylor The Johns
Assessing Accuracy Factors in Deformable 2D/3D Medical Image Registration Using a Statistical Pelvis Model Jianhua Yao National Institute of Health Bethesda, MD USA jyao@cc.nih.gov Russell Taylor The Johns
SIGMI Meeting ~Image Fusion~ Computer Graphics and Visualization Lab Image System Lab
 SIGMI Meeting ~Image Fusion~ Computer Graphics and Visualization Lab Image System Lab Introduction Medical Imaging and Application CGV 3D Organ Modeling Model-based Simulation Model-based Quantification
SIGMI Meeting ~Image Fusion~ Computer Graphics and Visualization Lab Image System Lab Introduction Medical Imaging and Application CGV 3D Organ Modeling Model-based Simulation Model-based Quantification
Biomedical Image Analysis based on Computational Registration Methods. João Manuel R. S. Tavares
 Biomedical Image Analysis based on Computational Registration Methods João Manuel R. S. Tavares tavares@fe.up.pt, www.fe.up.pt/~tavares Outline 1. Introduction 2. Methods a) Spatial Registration of (2D
Biomedical Image Analysis based on Computational Registration Methods João Manuel R. S. Tavares tavares@fe.up.pt, www.fe.up.pt/~tavares Outline 1. Introduction 2. Methods a) Spatial Registration of (2D
Image Registration I
 Image Registration I Comp 254 Spring 2002 Guido Gerig Image Registration: Motivation Motivation for Image Registration Combine images from different modalities (multi-modality registration), e.g. CT&MRI,
Image Registration I Comp 254 Spring 2002 Guido Gerig Image Registration: Motivation Motivation for Image Registration Combine images from different modalities (multi-modality registration), e.g. CT&MRI,
SPM Introduction. SPM : Overview. SPM: Preprocessing SPM! SPM: Preprocessing. Scott Peltier. FMRI Laboratory University of Michigan
 SPM Introduction Scott Peltier FMRI Laboratory University of Michigan! Slides adapted from T. Nichols SPM! SPM : Overview Library of MATLAB and C functions Graphical user interface Four main components:
SPM Introduction Scott Peltier FMRI Laboratory University of Michigan! Slides adapted from T. Nichols SPM! SPM : Overview Library of MATLAB and C functions Graphical user interface Four main components:
Computer-Aided Diagnosis in Abdominal and Cardiac Radiology Using Neural Networks
 Computer-Aided Diagnosis in Abdominal and Cardiac Radiology Using Neural Networks Du-Yih Tsai, Masaru Sekiya and Yongbum Lee Department of Radiological Technology, School of Health Sciences, Faculty of
Computer-Aided Diagnosis in Abdominal and Cardiac Radiology Using Neural Networks Du-Yih Tsai, Masaru Sekiya and Yongbum Lee Department of Radiological Technology, School of Health Sciences, Faculty of
Image Acquisition Systems
 Image Acquisition Systems Goals and Terminology Conventional Radiography Axial Tomography Computer Axial Tomography (CAT) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) PET, SPECT Ultrasound Microscopy Imaging ITCS
Image Acquisition Systems Goals and Terminology Conventional Radiography Axial Tomography Computer Axial Tomography (CAT) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) PET, SPECT Ultrasound Microscopy Imaging ITCS
SPM Introduction SPM! Scott Peltier. FMRI Laboratory University of Michigan. Software to perform computation, manipulation and display of imaging data
 SPM Introduction Scott Peltier FMRI Laboratory University of Michigan Slides adapted from T. Nichols SPM! Software to perform computation, manipulation and display of imaging data 1 1 SPM : Overview Library
SPM Introduction Scott Peltier FMRI Laboratory University of Michigan Slides adapted from T. Nichols SPM! Software to perform computation, manipulation and display of imaging data 1 1 SPM : Overview Library
Medical Images Analysis and Processing
 Medical Images Analysis and Processing - 25642 Emad Course Introduction Course Information: Type: Graduated Credits: 3 Prerequisites: Digital Image Processing Course Introduction Reference(s): Insight
Medical Images Analysis and Processing - 25642 Emad Course Introduction Course Information: Type: Graduated Credits: 3 Prerequisites: Digital Image Processing Course Introduction Reference(s): Insight
Introduction to Medical Image Processing
 Introduction to Medical Image Processing Δ Essential environments of a medical imaging system Subject Image Analysis Energy Imaging System Images Image Processing Feature Images Image processing may be
Introduction to Medical Image Processing Δ Essential environments of a medical imaging system Subject Image Analysis Energy Imaging System Images Image Processing Feature Images Image processing may be
Functional MRI in Clinical Research and Practice Preprocessing
 Functional MRI in Clinical Research and Practice Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization
Functional MRI in Clinical Research and Practice Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization
Non-rigid Image Registration
 Overview Non-rigid Image Registration Introduction to image registration - he goal of image registration - Motivation for medical image registration - Classification of image registration - Nonrigid registration
Overview Non-rigid Image Registration Introduction to image registration - he goal of image registration - Motivation for medical image registration - Classification of image registration - Nonrigid registration
White Pixel Artifact. Caused by a noise spike during acquisition Spike in K-space <--> sinusoid in image space
 White Pixel Artifact Caused by a noise spike during acquisition Spike in K-space sinusoid in image space Susceptibility Artifacts Off-resonance artifacts caused by adjacent regions with different
White Pixel Artifact Caused by a noise spike during acquisition Spike in K-space sinusoid in image space Susceptibility Artifacts Off-resonance artifacts caused by adjacent regions with different
SPM8 for Basic and Clinical Investigators. Preprocessing. fmri Preprocessing
 SPM8 for Basic and Clinical Investigators Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization Spatial
SPM8 for Basic and Clinical Investigators Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization Spatial
Using Probability Maps for Multi organ Automatic Segmentation
 Using Probability Maps for Multi organ Automatic Segmentation Ranveer Joyseeree 1,2, Óscar Jiménez del Toro1, and Henning Müller 1,3 1 University of Applied Sciences Western Switzerland (HES SO), Sierre,
Using Probability Maps for Multi organ Automatic Segmentation Ranveer Joyseeree 1,2, Óscar Jiménez del Toro1, and Henning Müller 1,3 1 University of Applied Sciences Western Switzerland (HES SO), Sierre,
Machine Learning for Medical Image Analysis. A. Criminisi
 Machine Learning for Medical Image Analysis A. Criminisi Overview Introduction to machine learning Decision forests Applications in medical image analysis Anatomy localization in CT Scans Spine Detection
Machine Learning for Medical Image Analysis A. Criminisi Overview Introduction to machine learning Decision forests Applications in medical image analysis Anatomy localization in CT Scans Spine Detection
A Study of Medical Image Analysis System
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 8(25), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2015/v8i25/80492, October 2015 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 A Study of Medical Image Analysis System Kim Tae-Eun
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 8(25), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2015/v8i25/80492, October 2015 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 A Study of Medical Image Analysis System Kim Tae-Eun
RADIOMICS: potential role in the clinics and challenges
 27 giugno 2018 Dipartimento di Fisica Università degli Studi di Milano RADIOMICS: potential role in the clinics and challenges Dr. Francesca Botta Medical Physicist Istituto Europeo di Oncologia (Milano)
27 giugno 2018 Dipartimento di Fisica Università degli Studi di Milano RADIOMICS: potential role in the clinics and challenges Dr. Francesca Botta Medical Physicist Istituto Europeo di Oncologia (Milano)
Utilizing Salient Region Features for 3D Multi-Modality Medical Image Registration
 Utilizing Salient Region Features for 3D Multi-Modality Medical Image Registration Dieter Hahn 1, Gabriele Wolz 2, Yiyong Sun 3, Frank Sauer 3, Joachim Hornegger 1, Torsten Kuwert 2 and Chenyang Xu 3 1
Utilizing Salient Region Features for 3D Multi-Modality Medical Image Registration Dieter Hahn 1, Gabriele Wolz 2, Yiyong Sun 3, Frank Sauer 3, Joachim Hornegger 1, Torsten Kuwert 2 and Chenyang Xu 3 1
Technical aspects of SPECT and SPECT-CT. John Buscombe
 Technical aspects of SPECT and SPECT-CT John Buscombe What does the clinician need to know? For SPECT What factors affect SPECT How those factors should be sought Looking for artefacts For SPECT-CT Issues
Technical aspects of SPECT and SPECT-CT John Buscombe What does the clinician need to know? For SPECT What factors affect SPECT How those factors should be sought Looking for artefacts For SPECT-CT Issues
Methods for data preprocessing
 Methods for data preprocessing John Ashburner Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging, 12 Queen Square, London, UK. Overview Voxel-Based Morphometry Morphometry in general Volumetrics VBM preprocessing
Methods for data preprocessing John Ashburner Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging, 12 Queen Square, London, UK. Overview Voxel-Based Morphometry Morphometry in general Volumetrics VBM preprocessing
Basic fmri Design and Analysis. Preprocessing
 Basic fmri Design and Analysis Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization Spatial filtering
Basic fmri Design and Analysis Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization Spatial filtering
EPI Data Are Acquired Serially. EPI Data Are Acquired Serially 10/23/2011. Functional Connectivity Preprocessing. fmri Preprocessing
 Functional Connectivity Preprocessing Geometric distortion Head motion Geometric distortion Head motion EPI Data Are Acquired Serially EPI Data Are Acquired Serially descending 1 EPI Data Are Acquired
Functional Connectivity Preprocessing Geometric distortion Head motion Geometric distortion Head motion EPI Data Are Acquired Serially EPI Data Are Acquired Serially descending 1 EPI Data Are Acquired
Parallelization of Mutual Information Registration
 Parallelization of Mutual Information Registration Krishna Sanka Simon Warfield William Wells Ron Kikinis May 5, 2000 Abstract Mutual information registration is an effective procedure that provides an
Parallelization of Mutual Information Registration Krishna Sanka Simon Warfield William Wells Ron Kikinis May 5, 2000 Abstract Mutual information registration is an effective procedure that provides an
The Anatomical Equivalence Class Formulation and its Application to Shape-based Computational Neuroanatomy
 The Anatomical Equivalence Class Formulation and its Application to Shape-based Computational Neuroanatomy Sokratis K. Makrogiannis, PhD From post-doctoral research at SBIA lab, Department of Radiology,
The Anatomical Equivalence Class Formulation and its Application to Shape-based Computational Neuroanatomy Sokratis K. Makrogiannis, PhD From post-doctoral research at SBIA lab, Department of Radiology,
Adaptive Local Multi-Atlas Segmentation: Application to Heart Segmentation in Chest CT Scans
 Adaptive Local Multi-Atlas Segmentation: Application to Heart Segmentation in Chest CT Scans Eva M. van Rikxoort, Ivana Isgum, Marius Staring, Stefan Klein and Bram van Ginneken Image Sciences Institute,
Adaptive Local Multi-Atlas Segmentation: Application to Heart Segmentation in Chest CT Scans Eva M. van Rikxoort, Ivana Isgum, Marius Staring, Stefan Klein and Bram van Ginneken Image Sciences Institute,
Computational Neuroanatomy
 Computational Neuroanatomy John Ashburner john@fil.ion.ucl.ac.uk Smoothing Motion Correction Between Modality Co-registration Spatial Normalisation Segmentation Morphometry Overview fmri time-series kernel
Computational Neuroanatomy John Ashburner john@fil.ion.ucl.ac.uk Smoothing Motion Correction Between Modality Co-registration Spatial Normalisation Segmentation Morphometry Overview fmri time-series kernel
SPM8 for Basic and Clinical Investigators. Preprocessing
 SPM8 for Basic and Clinical Investigators Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization Spatial
SPM8 for Basic and Clinical Investigators Preprocessing fmri Preprocessing Slice timing correction Geometric distortion correction Head motion correction Temporal filtering Intensity normalization Spatial
Deviceless respiratory motion correction in PET imaging exploring the potential of novel data driven strategies
 g Deviceless respiratory motion correction in PET imaging exploring the potential of novel data driven strategies Presented by Adam Kesner, Ph.D., DABR Assistant Professor, Division of Radiological Sciences,
g Deviceless respiratory motion correction in PET imaging exploring the potential of novel data driven strategies Presented by Adam Kesner, Ph.D., DABR Assistant Professor, Division of Radiological Sciences,
HST.582J / 6.555J / J Biomedical Signal and Image Processing Spring 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.582J / 6.555J / 16.456J Biomedical Signal and Image Processing Spring 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.582J / 6.555J / 16.456J Biomedical Signal and Image Processing Spring 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Non-Rigid Registration of Medical Images: Theory, Methods and Applications
 Non-Rigid Registration of Medical Images: Theory, Methods and Applications Daniel Rueckert Paul Aljabar Medical mage registration [1] plays an increasingly important role in many clinical applications
Non-Rigid Registration of Medical Images: Theory, Methods and Applications Daniel Rueckert Paul Aljabar Medical mage registration [1] plays an increasingly important role in many clinical applications
Introduction to Medical Image Registration
 Introduction to Medical Image Registration Sailesh Conjeti Computer Aided Medical Procedures (CAMP), Technische Universität München, Germany sailesh.conjeti@tum.de Partially adapted from slides by: 1.
Introduction to Medical Image Registration Sailesh Conjeti Computer Aided Medical Procedures (CAMP), Technische Universität München, Germany sailesh.conjeti@tum.de Partially adapted from slides by: 1.
Image Registration + Other Stuff
 Image Registration + Other Stuff John Ashburner Pre-processing Overview fmri time-series Motion Correct Anatomical MRI Coregister m11 m 21 m 31 m12 m13 m14 m 22 m 23 m 24 m 32 m 33 m 34 1 Template Estimate
Image Registration + Other Stuff John Ashburner Pre-processing Overview fmri time-series Motion Correct Anatomical MRI Coregister m11 m 21 m 31 m12 m13 m14 m 22 m 23 m 24 m 32 m 33 m 34 1 Template Estimate
Basic principles of MR image analysis. Basic principles of MR image analysis. Basic principles of MR image analysis
 Basic principles of MR image analysis Basic principles of MR image analysis Julien Milles Leiden University Medical Center Terminology of fmri Brain extraction Registration Linear registration Non-linear
Basic principles of MR image analysis Basic principles of MR image analysis Julien Milles Leiden University Medical Center Terminology of fmri Brain extraction Registration Linear registration Non-linear
Object Identification in Ultrasound Scans
 Object Identification in Ultrasound Scans Wits University Dec 05, 2012 Roadmap Introduction to the problem Motivation Related Work Our approach Expected Results Introduction Nowadays, imaging devices like
Object Identification in Ultrasound Scans Wits University Dec 05, 2012 Roadmap Introduction to the problem Motivation Related Work Our approach Expected Results Introduction Nowadays, imaging devices like
Digital Volume Correlation for Materials Characterization
 19 th World Conference on Non-Destructive Testing 2016 Digital Volume Correlation for Materials Characterization Enrico QUINTANA, Phillip REU, Edward JIMENEZ, Kyle THOMPSON, Sharlotte KRAMER Sandia National
19 th World Conference on Non-Destructive Testing 2016 Digital Volume Correlation for Materials Characterization Enrico QUINTANA, Phillip REU, Edward JIMENEZ, Kyle THOMPSON, Sharlotte KRAMER Sandia National
RT_Image v0.2β User s Guide
 RT_Image v0.2β User s Guide RT_Image is a three-dimensional image display and analysis suite developed in IDL (ITT, Boulder, CO). It offers a range of flexible tools for the visualization and quantitation
RT_Image v0.2β User s Guide RT_Image is a three-dimensional image display and analysis suite developed in IDL (ITT, Boulder, CO). It offers a range of flexible tools for the visualization and quantitation
Limitations of Projection Radiography. Stereoscopic Breast Imaging. Limitations of Projection Radiography. 3-D Breast Imaging Methods
 Stereoscopic Breast Imaging Andrew D. A. Maidment, Ph.D. Chief, Physics Section Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Limitations of Projection Radiography Mammography is a projection imaging
Stereoscopic Breast Imaging Andrew D. A. Maidment, Ph.D. Chief, Physics Section Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Limitations of Projection Radiography Mammography is a projection imaging
Deformable Registration Using Scale Space Keypoints
 Deformable Registration Using Scale Space Keypoints Mehdi Moradi a, Purang Abolmaesoumi a,b and Parvin Mousavi a a School of Computing, Queen s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada K7L 3N6; b Department
Deformable Registration Using Scale Space Keypoints Mehdi Moradi a, Purang Abolmaesoumi a,b and Parvin Mousavi a a School of Computing, Queen s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada K7L 3N6; b Department
Pathology Hinting as the Combination of Automatic Segmentation with a Statistical Shape Model
 Pathology Hinting as the Combination of Automatic Segmentation with a Statistical Shape Model Pascal A. Dufour 12,HannanAbdillahi 3, Lala Ceklic 3,Ute Wolf-Schnurrbusch 23,JensKowal 12 1 ARTORG Center
Pathology Hinting as the Combination of Automatic Segmentation with a Statistical Shape Model Pascal A. Dufour 12,HannanAbdillahi 3, Lala Ceklic 3,Ute Wolf-Schnurrbusch 23,JensKowal 12 1 ARTORG Center
3D Voxel-Based Volumetric Image Registration with Volume-View Guidance
 3D Voxel-Based Volumetric Image Registration with Volume-View Guidance Guang Li*, Huchen Xie, Holly Ning, Deborah Citrin, Jacek Copala, Barbara Arora, Norman Coleman, Kevin Camphausen, and Robert Miller
3D Voxel-Based Volumetric Image Registration with Volume-View Guidance Guang Li*, Huchen Xie, Holly Ning, Deborah Citrin, Jacek Copala, Barbara Arora, Norman Coleman, Kevin Camphausen, and Robert Miller
Computational Medical Imaging Analysis
 Computational Medical Imaging Analysis Chapter 1: Introduction to Imaging Science Jun Zhang Laboratory for Computational Medical Imaging & Data Analysis Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky
Computational Medical Imaging Analysis Chapter 1: Introduction to Imaging Science Jun Zhang Laboratory for Computational Medical Imaging & Data Analysis Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU)
 Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Physics Tutorial Physics Tutorial Purpose: Training: Assessments: This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum for
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Physics Tutorial Physics Tutorial Purpose: Training: Assessments: This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum for
Biomedical Image Processing
 Biomedical Image Processing Jason Thong Gabriel Grant 1 2 Motivation from the Medical Perspective MRI, CT and other biomedical imaging devices were designed to assist doctors in their diagnosis and treatment
Biomedical Image Processing Jason Thong Gabriel Grant 1 2 Motivation from the Medical Perspective MRI, CT and other biomedical imaging devices were designed to assist doctors in their diagnosis and treatment
Abstract. 1. Introduction
 A New Automated Method for Three- Dimensional Registration of Medical Images* P. Kotsas, M. Strintzis, D.W. Piraino Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Aristotelian University, 54006 Thessaloniki,
A New Automated Method for Three- Dimensional Registration of Medical Images* P. Kotsas, M. Strintzis, D.W. Piraino Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Aristotelian University, 54006 Thessaloniki,
Learning-based Neuroimage Registration
 Learning-based Neuroimage Registration Leonid Teverovskiy and Yanxi Liu 1 October 2004 CMU-CALD-04-108, CMU-RI-TR-04-59 School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213 Abstract
Learning-based Neuroimage Registration Leonid Teverovskiy and Yanxi Liu 1 October 2004 CMU-CALD-04-108, CMU-RI-TR-04-59 School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213 Abstract
CP Generalize Concepts in Abstract Multi-dimensional Image Model Component Semantics. David Clunie.
 CP-1390 - Generalize Concepts in Abstract Multi-dimensional Image Model Semantics Page 1 STATUS Date of Last Update Person Assigned Submitter Name Submission Date Assigned 2014/06/09 David Clunie mailto:dclunie@dclunie.com
CP-1390 - Generalize Concepts in Abstract Multi-dimensional Image Model Semantics Page 1 STATUS Date of Last Update Person Assigned Submitter Name Submission Date Assigned 2014/06/09 David Clunie mailto:dclunie@dclunie.com
The Insight Toolkit. Image Registration Algorithms & Frameworks
 The Insight Toolkit Image Registration Algorithms & Frameworks Registration in ITK Image Registration Framework Multi Resolution Registration Framework Components PDE Based Registration FEM Based Registration
The Insight Toolkit Image Registration Algorithms & Frameworks Registration in ITK Image Registration Framework Multi Resolution Registration Framework Components PDE Based Registration FEM Based Registration
Registration Techniques
 EMBO Practical Course on Light Sheet Microscopy Junior-Prof. Dr. Olaf Ronneberger Computer Science Department and BIOSS Centre for Biological Signalling Studies University of Freiburg Germany O. Ronneberger,
EMBO Practical Course on Light Sheet Microscopy Junior-Prof. Dr. Olaf Ronneberger Computer Science Department and BIOSS Centre for Biological Signalling Studies University of Freiburg Germany O. Ronneberger,
Image Co-Registration II: TG132 Quality Assurance for Image Registration. Image Co-Registration II: TG132 Quality Assurance for Image Registration
 Image Co-Registration II: TG132 Quality Assurance for Image Registration Preliminary Recommendations from TG 132* Kristy Brock, Sasa Mutic, Todd McNutt, Hua Li, and Marc Kessler *Recommendations are NOT
Image Co-Registration II: TG132 Quality Assurance for Image Registration Preliminary Recommendations from TG 132* Kristy Brock, Sasa Mutic, Todd McNutt, Hua Li, and Marc Kessler *Recommendations are NOT
Nonrigid Registration Using a Rigidity Constraint
 Nonrigid Registration Using a Rigidity Constraint Marius Staring, Stefan Klein and Josien P.W. Pluim Image Sciences Institute, University Medical Center Utrecht, P.O. Box 85500, 3508 GA, Room Q0S.459,
Nonrigid Registration Using a Rigidity Constraint Marius Staring, Stefan Klein and Josien P.W. Pluim Image Sciences Institute, University Medical Center Utrecht, P.O. Box 85500, 3508 GA, Room Q0S.459,
Methodological progress in image registration for ventilation estimation, segmentation propagation and multi-modal fusion
 Methodological progress in image registration for ventilation estimation, segmentation propagation and multi-modal fusion Mattias P. Heinrich Julia A. Schnabel, Mark Jenkinson, Sir Michael Brady 2 Clinical
Methodological progress in image registration for ventilation estimation, segmentation propagation and multi-modal fusion Mattias P. Heinrich Julia A. Schnabel, Mark Jenkinson, Sir Michael Brady 2 Clinical
Analysis of Functional MRI Timeseries Data Using Signal Processing Techniques
 Analysis of Functional MRI Timeseries Data Using Signal Processing Techniques Sea Chen Department of Biomedical Engineering Advisors: Dr. Charles A. Bouman and Dr. Mark J. Lowe S. Chen Final Exam October
Analysis of Functional MRI Timeseries Data Using Signal Processing Techniques Sea Chen Department of Biomedical Engineering Advisors: Dr. Charles A. Bouman and Dr. Mark J. Lowe S. Chen Final Exam October
A Radiometry Tolerant Method for Direct 3D/2D Registration of Computed Tomography Data to X-ray Images
 A Radiometry Tolerant Method for Direct 3D/2D Registration of Computed Tomography Data to X-ray Images Transfer Function Independent Registration Boris Peter Selby 1, Georgios Sakas 2, Stefan Walter 1,
A Radiometry Tolerant Method for Direct 3D/2D Registration of Computed Tomography Data to X-ray Images Transfer Function Independent Registration Boris Peter Selby 1, Georgios Sakas 2, Stefan Walter 1,
MR IMAGE SEGMENTATION
 MR IMAGE SEGMENTATION Prepared by : Monil Shah What is Segmentation? Partitioning a region or regions of interest in images such that each region corresponds to one or more anatomic structures Classification
MR IMAGE SEGMENTATION Prepared by : Monil Shah What is Segmentation? Partitioning a region or regions of interest in images such that each region corresponds to one or more anatomic structures Classification
Enhanced material contrast by dual-energy microct imaging
 Enhanced material contrast by dual-energy microct imaging Method note Page 1 of 12 2 Method note: Dual-energy microct analysis 1. Introduction 1.1. The basis for dual energy imaging Micro-computed tomography
Enhanced material contrast by dual-energy microct imaging Method note Page 1 of 12 2 Method note: Dual-energy microct analysis 1. Introduction 1.1. The basis for dual energy imaging Micro-computed tomography
Multi-modal Image Registration Using the Generalized Survival Exponential Entropy
 Multi-modal Image Registration Using the Generalized Survival Exponential Entropy Shu Liao and Albert C.S. Chung Lo Kwee-Seong Medical Image Analysis Laboratory, Department of Computer Science and Engineering,
Multi-modal Image Registration Using the Generalized Survival Exponential Entropy Shu Liao and Albert C.S. Chung Lo Kwee-Seong Medical Image Analysis Laboratory, Department of Computer Science and Engineering,
Visualisation : Lecture 1. So what is visualisation? Visualisation
 So what is visualisation? UG4 / M.Sc. Course 2006 toby.breckon@ed.ac.uk Computer Vision Lab. Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour Introducing 1 Application of interactive 3D computer graphics to
So what is visualisation? UG4 / M.Sc. Course 2006 toby.breckon@ed.ac.uk Computer Vision Lab. Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour Introducing 1 Application of interactive 3D computer graphics to
Non-Rigid Registration of Medical Images: Theory, Methods and Applications
 Non-Rigid Registration of Medical Images: Theory, Methods and Applications Daniel Rueckert Paul Aljabar Medical image registration [1] plays an increasingly important role in many clinical applications
Non-Rigid Registration of Medical Images: Theory, Methods and Applications Daniel Rueckert Paul Aljabar Medical image registration [1] plays an increasingly important role in many clinical applications
Image Processing for fmri John Ashburner. Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging, 12 Queen Square, London, UK.
 Iage Processing for fmri John Ashburner Wellcoe Trust Centre for Neuroiaging, 12 Queen Square, London, UK. Contents * Preliinaries * Rigid-Body and Affine Transforations * Optiisation and Objective Functions
Iage Processing for fmri John Ashburner Wellcoe Trust Centre for Neuroiaging, 12 Queen Square, London, UK. Contents * Preliinaries * Rigid-Body and Affine Transforations * Optiisation and Objective Functions
Functional MRI data preprocessing. Cyril Pernet, PhD
 Functional MRI data preprocessing Cyril Pernet, PhD Data have been acquired, what s s next? time No matter the design, multiple volumes (made from multiple slices) have been acquired in time. Before getting
Functional MRI data preprocessing Cyril Pernet, PhD Data have been acquired, what s s next? time No matter the design, multiple volumes (made from multiple slices) have been acquired in time. Before getting
Where are we now? Structural MRI processing and analysis
 Where are we now? Structural MRI processing and analysis Pierre-Louis Bazin bazin@cbs.mpg.de Leipzig, Germany Structural MRI processing: why bother? Just use the standards? SPM FreeSurfer FSL However:
Where are we now? Structural MRI processing and analysis Pierre-Louis Bazin bazin@cbs.mpg.de Leipzig, Germany Structural MRI processing: why bother? Just use the standards? SPM FreeSurfer FSL However:
CHAPTER 2. Morphometry on rodent brains. A.E.H. Scheenstra J. Dijkstra L. van der Weerd
 CHAPTER 2 Morphometry on rodent brains A.E.H. Scheenstra J. Dijkstra L. van der Weerd This chapter was adapted from: Volumetry and other quantitative measurements to assess the rodent brain, In vivo NMR
CHAPTER 2 Morphometry on rodent brains A.E.H. Scheenstra J. Dijkstra L. van der Weerd This chapter was adapted from: Volumetry and other quantitative measurements to assess the rodent brain, In vivo NMR
Modern Medical Image Analysis 8DC00 Exam
 Parts of answers are inside square brackets [... ]. These parts are optional. Answers can be written in Dutch or in English, as you prefer. You can use drawings and diagrams to support your textual answers.
Parts of answers are inside square brackets [... ]. These parts are optional. Answers can be written in Dutch or in English, as you prefer. You can use drawings and diagrams to support your textual answers.
Is deformable image registration a solved problem?
 Is deformable image registration a solved problem? Marcel van Herk On behalf of the imaging group of the RT department of NKI/AVL Amsterdam, the Netherlands DIR 1 Image registration Find translation.deformation
Is deformable image registration a solved problem? Marcel van Herk On behalf of the imaging group of the RT department of NKI/AVL Amsterdam, the Netherlands DIR 1 Image registration Find translation.deformation
Annales UMCS Informatica AI 1 (2003) UMCS. Registration of CT and MRI brain images. Karol Kuczyński, Paweł Mikołajczak
 Annales Informatica AI 1 (2003) 149-156 Registration of CT and MRI brain images Karol Kuczyński, Paweł Mikołajczak Annales Informatica Lublin-Polonia Sectio AI http://www.annales.umcs.lublin.pl/ Laboratory
Annales Informatica AI 1 (2003) 149-156 Registration of CT and MRI brain images Karol Kuczyński, Paweł Mikołajczak Annales Informatica Lublin-Polonia Sectio AI http://www.annales.umcs.lublin.pl/ Laboratory
Classification of Subject Motion for Improved Reconstruction of Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 1 CS 9 Final Project Classification of Subject Motion for Improved Reconstruction of Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging Feiyu Chen Department of Electrical Engineering ABSTRACT Subject motion is a significant
1 CS 9 Final Project Classification of Subject Motion for Improved Reconstruction of Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging Feiyu Chen Department of Electrical Engineering ABSTRACT Subject motion is a significant
RIGID IMAGE REGISTRATION
 RIGID IMAGE REGISTRATION Duygu Tosun-Turgut, Ph.D. Center for Imaging of Neurodegenerative Diseases Department of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging duygu.tosun@ucsf.edu What is registration? Image registration
RIGID IMAGE REGISTRATION Duygu Tosun-Turgut, Ph.D. Center for Imaging of Neurodegenerative Diseases Department of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging duygu.tosun@ucsf.edu What is registration? Image registration
Spatio-temporal Analysis of Biomedical Images based on Automated Methods of Image Registration
 Spatio-temporal Analysis of Biomedical Images based on Automated Methods of Image Registration João Manuel R. S. Tavares tavares@fe.up.pt, www.fe.up.pt/~tavares Outline 1. Introduction 2. Methods a) Spatial
Spatio-temporal Analysis of Biomedical Images based on Automated Methods of Image Registration João Manuel R. S. Tavares tavares@fe.up.pt, www.fe.up.pt/~tavares Outline 1. Introduction 2. Methods a) Spatial
Locating Motion Artifacts in Parametric fmri Analysis
 Tina Memo No. 200-002 Presented at MICCAI 999 Locating Motion Artifacts in Parametric fmri Analysis A.J.Lacey, N.A.Thacker, E. Burton, and A.Jackson Last updated 2 / 02 / 2002 Imaging Science and Biomedical
Tina Memo No. 200-002 Presented at MICCAI 999 Locating Motion Artifacts in Parametric fmri Analysis A.J.Lacey, N.A.Thacker, E. Burton, and A.Jackson Last updated 2 / 02 / 2002 Imaging Science and Biomedical
Atlas Based Segmentation of the prostate in MR images
 Atlas Based Segmentation of the prostate in MR images Albert Gubern-Merida and Robert Marti Universitat de Girona, Computer Vision and Robotics Group, Girona, Spain {agubern,marly}@eia.udg.edu Abstract.
Atlas Based Segmentation of the prostate in MR images Albert Gubern-Merida and Robert Marti Universitat de Girona, Computer Vision and Robotics Group, Girona, Spain {agubern,marly}@eia.udg.edu Abstract.
Advanced Visual Medicine: Techniques for Visual Exploration & Analysis
 Advanced Visual Medicine: Techniques for Visual Exploration & Analysis Interactive Visualization of Multimodal Volume Data for Neurosurgical Planning Felix Ritter, MeVis Research Bremen Multimodal Neurosurgical
Advanced Visual Medicine: Techniques for Visual Exploration & Analysis Interactive Visualization of Multimodal Volume Data for Neurosurgical Planning Felix Ritter, MeVis Research Bremen Multimodal Neurosurgical
INTRODUCTION TO MEDICAL IMAGING- 3D LOCALIZATION LAB MANUAL 1. Modifications for P551 Fall 2013 Medical Physics Laboratory
 INTRODUCTION TO MEDICAL IMAGING- 3D LOCALIZATION LAB MANUAL 1 Modifications for P551 Fall 2013 Medical Physics Laboratory Introduction Following the introductory lab 0, this lab exercise the student through
INTRODUCTION TO MEDICAL IMAGING- 3D LOCALIZATION LAB MANUAL 1 Modifications for P551 Fall 2013 Medical Physics Laboratory Introduction Following the introductory lab 0, this lab exercise the student through
Computational Medical Imaging Analysis Chapter 4: Image Visualization
 Computational Medical Imaging Analysis Chapter 4: Image Visualization Jun Zhang Laboratory for Computational Medical Imaging & Data Analysis Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky Lexington,
Computational Medical Imaging Analysis Chapter 4: Image Visualization Jun Zhang Laboratory for Computational Medical Imaging & Data Analysis Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky Lexington,
CP467 Image Processing and Pattern Recognition
 CP467 Image Processing and Pattern Recognition Instructor: Hongbing Fan Introduction About DIP & PR About this course Lecture 1: an overview of DIP DIP&PR show What is Digital Image? We use digital image
CP467 Image Processing and Pattern Recognition Instructor: Hongbing Fan Introduction About DIP & PR About this course Lecture 1: an overview of DIP DIP&PR show What is Digital Image? We use digital image
Constructing System Matrices for SPECT Simulations and Reconstructions
 Constructing System Matrices for SPECT Simulations and Reconstructions Nirantha Balagopal April 28th, 2017 M.S. Report The University of Arizona College of Optical Sciences 1 Acknowledgement I would like
Constructing System Matrices for SPECT Simulations and Reconstructions Nirantha Balagopal April 28th, 2017 M.S. Report The University of Arizona College of Optical Sciences 1 Acknowledgement I would like
TG 132: Use of Image Registration and Fusion in RT
 TG 132: Use of Image Registration and Fusion in RT Kristy K Brock, PhD, DABR, FAAPM Associate Professor Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Michigan Chair, AAPM TG 132: Image Registration and
TG 132: Use of Image Registration and Fusion in RT Kristy K Brock, PhD, DABR, FAAPM Associate Professor Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Michigan Chair, AAPM TG 132: Image Registration and
Pathology Hinting as the Combination of Automatic Segmentation with a Statistical Shape Model
 Pathology Hinting as the Combination of Automatic Segmentation with a Statistical Shape Model Pascal A. Dufour 1,2, Hannan Abdillahi 3, Lala Ceklic 3, Ute Wolf-Schnurrbusch 2,3, and Jens Kowal 1,2 1 ARTORG
Pathology Hinting as the Combination of Automatic Segmentation with a Statistical Shape Model Pascal A. Dufour 1,2, Hannan Abdillahi 3, Lala Ceklic 3, Ute Wolf-Schnurrbusch 2,3, and Jens Kowal 1,2 1 ARTORG
Preprocessing I: Within Subject John Ashburner
 Preprocessing I: Within Subject John Ashburner Pre-processing Overview Statistics or whatever fmri tie-series Anatoical MRI Teplate Soothed Estiate Spatial Nor Motion Correct Sooth Coregister 11 21 31
Preprocessing I: Within Subject John Ashburner Pre-processing Overview Statistics or whatever fmri tie-series Anatoical MRI Teplate Soothed Estiate Spatial Nor Motion Correct Sooth Coregister 11 21 31
Manual image registration in BrainVoyager QX Table of Contents
 Manual image registration in BrainVoyager QX Table of Contents Manual image registration in BrainVoyager QX......1 Performing manual alignment for functional to anatomical images......2 Step 1: preparation......2
Manual image registration in BrainVoyager QX Table of Contents Manual image registration in BrainVoyager QX......1 Performing manual alignment for functional to anatomical images......2 Step 1: preparation......2
VALIDATION OF DIR. Raj Varadhan, PhD, DABMP Minneapolis Radiation Oncology
 VALIDATION OF DIR Raj Varadhan, PhD, DABMP Minneapolis Radiation Oncology Overview Basics: Registration Framework, Theory Discuss Validation techniques Using Synthetic CT data & Phantoms What metrics to
VALIDATION OF DIR Raj Varadhan, PhD, DABMP Minneapolis Radiation Oncology Overview Basics: Registration Framework, Theory Discuss Validation techniques Using Synthetic CT data & Phantoms What metrics to
Introduction to fmri. Pre-processing
 Introduction to fmri Pre-processing Tibor Auer Department of Psychology Research Fellow in MRI Data Types Anatomical data: T 1 -weighted, 3D, 1/subject or session - (ME)MPRAGE/FLASH sequence, undistorted
Introduction to fmri Pre-processing Tibor Auer Department of Psychology Research Fellow in MRI Data Types Anatomical data: T 1 -weighted, 3D, 1/subject or session - (ME)MPRAGE/FLASH sequence, undistorted
A comparison of three methods of ultrasound to computed tomography registration
 A comparison of three methods of ultrasound to computed tomography registration by Neilson Mackay A thesis submitted to the School of Computing in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master
A comparison of three methods of ultrasound to computed tomography registration by Neilson Mackay A thesis submitted to the School of Computing in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master
Multi-Modal Volume Registration Using Joint Intensity Distributions
 Multi-Modal Volume Registration Using Joint Intensity Distributions Michael E. Leventon and W. Eric L. Grimson Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA leventon@ai.mit.edu
Multi-Modal Volume Registration Using Joint Intensity Distributions Michael E. Leventon and W. Eric L. Grimson Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA leventon@ai.mit.edu
PROSTATE CANCER DETECTION USING LABEL IMAGE CONSTRAINED MULTIATLAS SELECTION
 PROSTATE CANCER DETECTION USING LABEL IMAGE CONSTRAINED MULTIATLAS SELECTION Ms. Vaibhavi Nandkumar Jagtap 1, Mr. Santosh D. Kale 2 1 PG Scholar, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics and Telecommunication,
PROSTATE CANCER DETECTION USING LABEL IMAGE CONSTRAINED MULTIATLAS SELECTION Ms. Vaibhavi Nandkumar Jagtap 1, Mr. Santosh D. Kale 2 1 PG Scholar, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics and Telecommunication,
