Lab 1: FPGA Physical Layout
|
|
|
- Darcy Potter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lab 1: FPGA Physical Layout University of California, Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS150 Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems John Wawrzynek, James Parker, Daiwei Li Due February 6 th, 2PM Table of Contents 0 Introduction Prelab CAD Tools Synthesis Translate & Map Placement Routing Lab Procedure Setting up Modifying the Design Deploying to hardware Testing Extending the Design The Build System Synthesizing your code Verification Circuit Analysis Checkoff
2 0 Introduction In the previous lab, you learned how to manipulate inputs and outputs on the FPGA using Verilog code. In this lab, you will see how the Verilog code you wrote in the previous lab maps to resources on the FPGA. Throughout the rest of the semester you will be focusing on more abstract methods of describing circuits, and the tools that are used to transform that description into actual hardware. As you will see, being able to represent hardware in a more abstract way increases productivity and design flexibility, but also hides some of the details of the FPGA platform. Completing this lab will help to establish the underlying architecture of the FPGA in your mind, as well as help you to make optimal design decisions in the future. 1 Prelab To help you become familiar with the FPGA that you will be working with through the semester, please read Chapter 5: Configurable Logic Blocks (page 171) of the Virtex-5 User Guide and answer the following questions: 1. How many SLICEs are in a single CLB? 2. How many inputs do each of the LUTs on a Virtex-5 LX110T FPGA have? 3. How many of LUTs does the LX110T have? 4. How do you implement logic functions of 7 inputs in a single SLICEL? How about 8? 5. What is the difference between a SLICEL and a SLICEM? 2 CAD Tools Before we dive into the lab, let us familiarize ourselves with the CAD (Computer Aided Design) tools that translate HDL into a working circuit on the FPGA. These tools will pass your design through several stages, each one bringing it closer to a concrete implementation. Brief descriptions of these stages follow: 2.1 Synthesis The synthesis tool (in the case of this lab, Xilinx Synthesis Tool (xst)) is the first program that processes your design. Among other tasks, it is responsible for the process of transforming the primitive gates and flip-flops that you wrote in Verilog into LUTs and other primitive FPGA elements. For example, if you described a circuit composed of many gates, but ultimately of 6 inputs and 1 output, xst will map your circuit down to a single 6-LUT. Likewise, if you described a flip-flop it will be mapped to a specific type of flip-flop which actually exists on the FPGA. The final product of the design partitioning phase is a netlist file, a text file that contains a list of all the instances of primitive components in the translated circuit and a description of how they are connected. 2.2 Translate & Map The translate & map stages are responsible for taking the generic netlist produced by the synthesis stage and translating each component to an equivalent on the specific Xilinx xc5vlx110t FPGAs we have in the lab. 2.3 Placement Placement takes a mapped design and determines the specific location of each component in the design on the FPGA. For example, each slice in the mapped designed is assigned to a specific site. 2
3 2.4 Routing Once placement is done, all of the connections specified in the netlist must be made. In general, routing is one of the most time-consuming parts of computer-aided circuit design. Optimizing placement can help speed up the process. 3 Lab Procedure In this lab, you will use a tool called FPGA Editor to manipulate logic and nets in the design that you wrote in Verilog in the last lab. In practice, you would not want to design your logic in FPGA editor, as it is much slower and extensible than writing Verilog code. However, this exercise is useful for visualizing the hardware and understanding the underlying processes. 3.1 Setting up If you would like to be able to copy paste commands from this lab guide, first type the following command so that the % prompt in front of each command is ignored: alias %='' Grab the resources for this lab; we will be using them later in the lab. % wget % tar -xvzf lab1.tar.gz Build the project from last week s lab0 (if you haven t done so already; you only need to make if there isn t already a build directory in lab0). You will need the build files in order to complete the first part of the lab. % cd ~/lab0 % make Open your design with FPGA editor. The.ncd file is the final result of the CAD tools design flow discussed above. The.pcf includes physical constraints; in our case, it tells us where the I/O pins are actually located on the board. By opening these files in FPGA editor, you can visualize how your design will actually be mapped to the FPGA. % cd ~/lab0/build/ml505top % fpga_editor ml505top.ncd ml505top.pcf 3
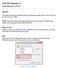
4 The image above shows the main view for FPGA editor. It is split up into the following windows: 1. Array Window - shows a schematic of the FPGA and highlights the part of the FPGA that are currently utilized, as well as the connections between these components 2. List Window - lists the components and nets that are used in your design. Double-clicking items here will zoom in on them in the Array Window 3. World Window - this shows you where you are currently focused in the Array Window 4. Console Output - prints messages that often contains useful diagnostic information 5. Toolbar - contains useful buttons for manipulating the windows; mouse over the buttons to reveal what it does 6. Button Bar - contains other useful buttons for modifying the design 3.2 Modifying the Design Now let s explore the design and look for the modules that you wrote in the previous lab. If you scroll down in the List Window, you will find that the Type of the last few items is SLICEL. Recall from the prelab reading that SLICEL s contain the look-up tables (LUTs) that actually implement the logic you want. Double-clicking on the SLICEL named GPIO_LED_0BUF will take you to the corresponding SLICEL in your Array Window. Double-click on the red rectangle (the SLICEL) to bring up the following Block Window: 4
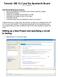
5 Click the F= button to reveal the function of the LUT. You should see that it corresponds to an AND gate. You can deduce from this that this LUT corresponds to the following Verilog code: and (GPIO_LED[0], GPIO_DIP[0], GPIO_DIP[1]); We can verify that this is the case by looking at where the nets connected to the slice are going by zooming in and single clicking on the triangles attached to the slice. The screenshot below shows that the output is going to the net GPIO_LED_0_0BUF, which corresponds to GPIO_LED[0] from the Verilog code. 5
6 You can change the logic function of the LUT through FPGA editor. To do so: 1. Click the following menus: File->Main Properties..., set the Edit Mode field to Read Write, click Apply and click Close. 2. Go back to the Block Window, and click on the Begin Editing (the pencil icon), and F= again. 3. Now you may change the logic function of the LUT. Change the function of the C6LUT such that it performs an OR rather than an AND. You can do this by changing the * to a + in the function definition for C6LUT. 4. Click Apply (button with the down arrow), then save your changes and close the window (second button from the right). 5. Save your design and close FPGA editor. 3.3 Deploying to hardware We will now deploy your edited design onto the hardware. Run the following command. If you need to, overwrite any conflicting files in order to generate the new.bit file. You may need to use w to specify overwriting the file. % bitgen ml505top.ncd ml505top.bit ml505top.pcf This converts your design into a bitstream that can be used to program the FPGA. The last step is to invoke Impact to program the FPGA. Unfortunately the command line interface to Impact is a little clunky, and since you will ever only use Impact to program the LX110T chip on the XUPv5, the staff provides a simple wrapper script that contains all of the functionality you should need this semester. Simply execute the following: % ezimpact ml505top.bit Once the message '5': Programmed successfully is displayed, the FPGA has been configured with your.bit file Testing Locate the DIP switches in the lower right corner, and the LEDs in the lower center of the XUPv5, your board should now be showing the results of a logical OR between switch 1 and switch 2 on LED 0. Change the positions of the two switches and note the change in LED Extending the Design In the previous lab we built up a ripple adder in the Adder.v file. For this next part, copy over your Adder.v file into the Adder.v in your /lab1 directory. We will experiment with the width of the adder to see how it will affect the resource usage for different adder widths. 3.5 The Build System After you ve copied over your Adder, you will want to synthesize the code into a netlist, to see how the amount of resources it takes up. The following introduces the build system that we will use for this lab and for the rest of the course. 6
7 The lab distribution contains a Makefile that lets you easily build and debug your designs. For those unfamiliar with make, you use it by invoking the program make with a target passed in as an argument. For instance, make synth will run the tool chain up to synthesis. Several important targets will be described later in the lab. The Makefile has several variables defined at the very top of the file that let you control the behavior of the build system. TOP := FPGA_TOP_ML505 UCF := src/$(top).ucf PART := xc5vlx110t-ff SRCS := $(wildcard src/*.v) The most important one for this lab will be the definition of TOP. You use it to change the top level module for hardware synthesis. You can change it either by editing the Makefile (and remembering to change it back afterwards) or by invoking make like this: % make TOP=<your top module here> The first thing you want to do after writing new Verilog modules (like Adder.v) is check that it at least makes basic sense. The synth make target is very useful for this purpose. Run it like this: % cd ~/lab1 % make synth Synthesizing your code The Xilinx tools that this target invokes generate a huge amount of output. Sometimes warnings and errors are obvious, sometimes they are not. The target make report launches a program that makes it much easier to view the output of the synthesis tool. Do this now, and select the Synthesis Messages item on the left to see what messages the synthesizer generated. Errors must be addressed before continuing. Ask your TA if you are unsure if you should be worried about a warning you see at this stage. Once you have cleared all errors from the synthesis stage, you know your Verilog is at least syntactically correct. Unfortunately this doesn't mean much because Verilog compilers are often very willing to accept complete nonsense (and give you complete nonsense in return). Another useful step to take is checking a diagram of the generated circuit. There is another make target for this: schematic. This will launch the ISE project navigator. Once inside ISE, go to File -> Open and select ml505top.ngr. Choose Start with a schematic of the top-level block in the dialog that pops up. This will give you a fairly straight-forward hierarchical block-level view of your design. You will find your circuit by drilling down in the following modules: ml505top, Adder, FA. Check to see that your Adder module is hooked up properly and looks sane. It's ok if the wires aren't connected, just hover your mouse over the endpoints on the schematic and ensure that the connections are as you expect Verification Once your circuit looks correct, it is time to verify it using it by pushing the design onto the board. The ml505top module has instantiated copies of both the Adder you wrote and a BehavioralAdder, an alternative version of the adder written in behavioral Verilog. It simply says Out = A+B and lets the tools 7
8 interpret this statement. You will learn more about behavioral Verilog in later labs; for now, you just need to know that is a higher level way to describe your circuit. The top module compares the outputs of these two adders for all the possible inputs, and signals an error if there is a difference. In later labs, you will see other methods of testing your circuits. To push this design to the board, start by issuing a make command in your lab directory. This should build your entire design all the way through to the bitfile. At this point you can issue the make impact command to program the board. Once the board has been programmed, either LED 0 or LED 1 will light up. The test harness uses LED 0 to indicate success and LED 1 indicates failure. If LED 1 lights up, you can check: a) That you wrote your generate statement correctly b) By changing the test harness to add the same 2 constant numbers and wire the result to the unused LEDs. Please ask a TA if you need assistance. 3.6 Circuit Analysis Now that your circuit is fully functional, we will perform a resource analysis. This will give you a better idea of what hardware the tools inferred from your HDL. For the Adder circuit, note down the following values for Width = 16 and 32. You can change the width in the Verilog file: module Adder #( parameter Width = 16 Change this number ) Number of occupied SLICEs. Number of SLICE LUTs Maximum Delay Path (look in Post-PAR Static Timing Report and write down approximately the biggest number in the Delay column) You will be able to find these numbers by running make report after mapping your design. Here we actually also place and route the design so that you can visually inspect it in fpga_editor: % make TOP=Adder % make TOP=Adder report Additionally, open up the placed and routed adder using fpga_editor and note down the logic function of any of the LUTs (doesn t matter what width). As a reminder, to open up fpga_editor, do the following: % cd ~/lab1/build/adder % fpga_editor Adder.ncd Adder.pcf Now do the same thing for the BehavioralAdder. Note the differences in the hardware generated and the resources used by the Adder and the BehavioralAdder. 8
9 Now we will purposely make use of some of the dedicated hardware blocks on the FPGA. Recall from the FPGA introduction lecture that the Virtex5 has DSP48E slices that are can be used for efficient implementation of multiply, add, bit-wise logical operations. However, the tools will not infer DSP48E slices for addition by default. You will need to change the synthesis options located in cfg/xst.batch. Open this file and change the line: use_dsp48 auto to: use_dsp48 yes You will not need to make any modifications to BehavioralAdder.v other than to change the width. Now run make again for width=16 and 32 note down the maximum delay path for each. Note that no LUTs or SLICELs will be used since we are using a DSP48E block for our addition operation. 4 Checkoff For checkoff, show a TA the items that you were asked to record in 3.6 Circuit Analysis. Please also answer the following checkoff questions: 1. Was the number of LUTs used for the Adder you wrote the same as how many you expected it to use? Why or why not? 2. What hardware did the BehavioralAdder (without changing the use_dsp48 flag) map to? 3. Why does the BehavioralAdder map to less LUTs than the structural Adder you wrote? 4. Why do you think the tools didn t choose to use the DSP48E block to perform addition by default? 9
Lab 0: Introduction to the FPGA Development Board
 Lab 0: Introduction to the FPGA Development Board University of California, Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS150 Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems
Lab 0: Introduction to the FPGA Development Board University of California, Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS150 Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems
EECS150: Lab 1, FPGA Editor
 EECS150: Lab 1, FPGA Editor UC Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 1 Time Table ASSIGNED DUE Friday, January 23 rd Week 3: February 1 st 7 th, 10 minutes
EECS150: Lab 1, FPGA Editor UC Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 1 Time Table ASSIGNED DUE Friday, January 23 rd Week 3: February 1 st 7 th, 10 minutes
Don t expect to be able to write and debug your code during the lab session.
 EECS150 Spring 2002 Lab 4 Verilog Simulation Mapping UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Lab 4 Verilog Simulation Mapping
EECS150 Spring 2002 Lab 4 Verilog Simulation Mapping UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Lab 4 Verilog Simulation Mapping
Lab 3 Verilog Simulation Mapping
 University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences 1. Motivation Lab 3 Verilog Simulation Mapping In this lab you will learn how to use
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences 1. Motivation Lab 3 Verilog Simulation Mapping In this lab you will learn how to use
EECS150: Lab 1, FPGA Editor
 EECS150: Lab 1, FPGA Editor UC Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 1 Time Table ASSIGNED DUE Friday, August 27 nd Week 3: August 7 th 8 th, during
EECS150: Lab 1, FPGA Editor UC Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 1 Time Table ASSIGNED DUE Friday, August 27 nd Week 3: August 7 th 8 th, during
Verilog Simulation Mapping
 1 Motivation UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Lab 4 Verilog Simulation Mapping In this lab you will learn how to use
1 Motivation UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Lab 4 Verilog Simulation Mapping In this lab you will learn how to use
EECS150: Lab 2, Mapping Circuit Elements to FPGAs
 EECS150: Lab 2, Mapping Circuit Elements to FPGAs UC Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science February 4, 2009 1 Time Table ASSIGNED DUE Friday, January
EECS150: Lab 2, Mapping Circuit Elements to FPGAs UC Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science February 4, 2009 1 Time Table ASSIGNED DUE Friday, January
Lab 0: Introduction to the FPGA Development Board
 Lab 0: Introduction to the FPGA Development Board University of California, Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS150 Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems
Lab 0: Introduction to the FPGA Development Board University of California, Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS150 Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems
EECS 151/251A FPGA Lab Lab 2: Introduction to FPGA Development + Creating a Tone Generator
 EECS 151/251A FPGA Lab Lab 2: Introduction to FPGA Development + Creating a Tone Generator Prof. John Wawrzynek, Nicholas Weaver TAs: Arya Reais-Parsi, Taehwan Kim Department of Electrical Engineering
EECS 151/251A FPGA Lab Lab 2: Introduction to FPGA Development + Creating a Tone Generator Prof. John Wawrzynek, Nicholas Weaver TAs: Arya Reais-Parsi, Taehwan Kim Department of Electrical Engineering
PlanAhead Release Notes
 PlanAhead Release Notes What s New in the 11.1 Release UG656(v 11.1.0) April 27, 2009 PlanAhead 11.1 Release Notes Page 1 Table of Contents What s New in the PlanAhead 11.1 Release... 4 Device Support...
PlanAhead Release Notes What s New in the 11.1 Release UG656(v 11.1.0) April 27, 2009 PlanAhead 11.1 Release Notes Page 1 Table of Contents What s New in the PlanAhead 11.1 Release... 4 Device Support...
RTL and Technology Schematic Viewers Tutorial. UG685 (v13.1) March 1, 2011
 RTL and Technology Schematic Viewers Tutorial The information disclosed to you hereunder (the Information ) is provided AS-IS with no warranty of any kind, express or implied. Xilinx does not assume any
RTL and Technology Schematic Viewers Tutorial The information disclosed to you hereunder (the Information ) is provided AS-IS with no warranty of any kind, express or implied. Xilinx does not assume any
University of California, Davis Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. EEC180B DIGITAL SYSTEMS Spring Quarter 2018
 University of California, Davis Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EEC180B DIGITAL SYSTEMS Spring Quarter 2018 LAB 2: FPGA Synthesis and Combinational Logic Design Objective: This lab covers
University of California, Davis Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EEC180B DIGITAL SYSTEMS Spring Quarter 2018 LAB 2: FPGA Synthesis and Combinational Logic Design Objective: This lab covers
Lab 4: List Processor and Chipscope
 Lab 4: List Processor and Chipscope University of California, Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS150 Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems John Wawrzynek,
Lab 4: List Processor and Chipscope University of California, Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS150 Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems John Wawrzynek,
EE183 LAB TUTORIAL. Introduction. Projects. Design Entry
 EE183 LAB TUTORIAL Introduction You will be using several CAD tools to implement your designs in EE183. The purpose of this lab tutorial is to introduce you to the tools that you will be using, Xilinx
EE183 LAB TUTORIAL Introduction You will be using several CAD tools to implement your designs in EE183. The purpose of this lab tutorial is to introduce you to the tools that you will be using, Xilinx
Revision: February 27, E Main Suite D Pullman, WA (509) Voice and Fax
 Xilinx ISE WebPACK Schematic Capture Tutorial Revision: February 27, 2010 215 E Main Suite D Pullman, WA 99163 (509) 334 6306 Voice and Fax Overview This tutorial provides instruction for using the Xilinx
Xilinx ISE WebPACK Schematic Capture Tutorial Revision: February 27, 2010 215 E Main Suite D Pullman, WA 99163 (509) 334 6306 Voice and Fax Overview This tutorial provides instruction for using the Xilinx
Xilinx ChipScope ICON/VIO/ILA Tutorial
 Xilinx ChipScope ICON/VIO/ILA Tutorial The Xilinx ChipScope tools package has several modules that you can add to your Verilog design to capture input and output directly from the FPGA hardware. These
Xilinx ChipScope ICON/VIO/ILA Tutorial The Xilinx ChipScope tools package has several modules that you can add to your Verilog design to capture input and output directly from the FPGA hardware. These
EECS150: Lab 3, Verilog Synthesis & FSMs
 EECS150: Lab 3, Verilog Synthesis & FSMs UC Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science February 11, 2009 1 Time Table ASSIGNED DUE Friday, Febuary 6 th Week
EECS150: Lab 3, Verilog Synthesis & FSMs UC Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science February 11, 2009 1 Time Table ASSIGNED DUE Friday, Febuary 6 th Week
Tutorial: Working with the Xilinx tools 14.4
 Tutorial: Working with the Xilinx tools 14.4 This tutorial will show you how to: Part I: Set up a new project in ISE Part II: Implement a function using Schematics Part III: Implement a function using
Tutorial: Working with the Xilinx tools 14.4 This tutorial will show you how to: Part I: Set up a new project in ISE Part II: Implement a function using Schematics Part III: Implement a function using
and 32 bit for 32 bit. If you don t pay attention to this, there will be unexpected behavior in the ISE software and thing may not work properly!
 This tutorial will show you how to: Part I: Set up a new project in ISE 14.7 Part II: Implement a function using Schematics Part III: Simulate the schematic circuit using ISim Part IV: Constraint, Synthesize,
This tutorial will show you how to: Part I: Set up a new project in ISE 14.7 Part II: Implement a function using Schematics Part III: Simulate the schematic circuit using ISim Part IV: Constraint, Synthesize,
EECS150: Lab 3, Verilog Synthesis & FSMs
 EECS5: Lab 3, Verilog Synthesis & FSMs UC Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science September 3, 2 Time Table ASSIGNED DUE Friday, September th September
EECS5: Lab 3, Verilog Synthesis & FSMs UC Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science September 3, 2 Time Table ASSIGNED DUE Friday, September th September
Lab 6 Debugging. Objective. Introduction. Prelab
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Lab 6 Debugging Objective You will explore several techniques for debugging a digital
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Lab 6 Debugging Objective You will explore several techniques for debugging a digital
Tutorial on FPGA Design Flow based on Aldec Active HDL. Ver 1.5
 Tutorial on FPGA Design Flow based on Aldec Active HDL Ver 1.5 1 Prepared by Ekawat (Ice) Homsirikamol, Marcin Rogawski, Jeremy Kelly, John Pham, and Dr. Kris Gaj This tutorial assumes that you have basic
Tutorial on FPGA Design Flow based on Aldec Active HDL Ver 1.5 1 Prepared by Ekawat (Ice) Homsirikamol, Marcin Rogawski, Jeremy Kelly, John Pham, and Dr. Kris Gaj This tutorial assumes that you have basic
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science EECS 150 Fall 2000 Original Lab By: J.Wawrzynek and N. Weaver Edited by B. Choi, R.
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science EECS 150 Fall 2000 Original Lab By: J.Wawrzynek and N. Weaver Edited by B. Choi, R.
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science. EECS 150 Spring 2000
 University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science EECS 150 Spring 2000 Lab 1 Introduction to Xilinx Design Software 1 Objectives In this
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science EECS 150 Spring 2000 Lab 1 Introduction to Xilinx Design Software 1 Objectives In this
EECS150 Lab Lecture 0
 EECS150 Lab Lecture 0 Kris Pister, Vincent Lee, Ian Juch, Albert Magyar Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley 8/24/2012 EECS150-Fa12-Lab0 1 What is lab lecture?
EECS150 Lab Lecture 0 Kris Pister, Vincent Lee, Ian Juch, Albert Magyar Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley 8/24/2012 EECS150-Fa12-Lab0 1 What is lab lecture?
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs)
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) September 12, 2002 John Wawrzynek Fall 2002 EECS150 - Lec06-FPGA Page 1 Outline What are FPGAs? Why use FPGAs (a short history
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) September 12, 2002 John Wawrzynek Fall 2002 EECS150 - Lec06-FPGA Page 1 Outline What are FPGAs? Why use FPGAs (a short history
Outline. EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) FPGA Overview. Why FPGAs?
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) September 12, 2002 John Wawrzynek Outline What are FPGAs? Why use FPGAs (a short history lesson). FPGA variations Internal logic
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) September 12, 2002 John Wawrzynek Outline What are FPGAs? Why use FPGAs (a short history lesson). FPGA variations Internal logic
What is Xilinx Design Language?
 Bill Jason P. Tomas University of Nevada Las Vegas Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering What is Xilinx Design Language? XDL is a human readable ASCII format compatible with the more widely used
Bill Jason P. Tomas University of Nevada Las Vegas Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering What is Xilinx Design Language? XDL is a human readable ASCII format compatible with the more widely used
FPGA Design Flow 1. All About FPGA
 FPGA Design Flow 1 In this part of tutorial we are going to have a short intro on FPGA design flow. A simplified version of FPGA design flow is given in the flowing diagram. FPGA Design Flow 2 FPGA_Design_FLOW
FPGA Design Flow 1 In this part of tutorial we are going to have a short intro on FPGA design flow. A simplified version of FPGA design flow is given in the flowing diagram. FPGA Design Flow 2 FPGA_Design_FLOW
Verilog Design Entry, Synthesis, and Behavioral Simulation
 ------------------------------------------------------------- PURPOSE - This lab will present a brief overview of a typical design flow and then will start to walk you through some typical tasks and familiarize
------------------------------------------------------------- PURPOSE - This lab will present a brief overview of a typical design flow and then will start to walk you through some typical tasks and familiarize
1. Introduction EE108A. Lab 1: Combinational Logic: Extension of the Tic Tac Toe Game
 EE108A Lab 1: Combinational Logic: Extension of the Tic Tac Toe Game 1. Introduction Objective This lab is designed to familiarize you with the process of designing, verifying, and implementing a combinational
EE108A Lab 1: Combinational Logic: Extension of the Tic Tac Toe Game 1. Introduction Objective This lab is designed to familiarize you with the process of designing, verifying, and implementing a combinational
EE 367 Logic Design Lab #1 Introduction to Xilinx ISE and the ML40X Eval Board Date: 1/21/09 Due: 1/28/09
 EE 367 Logic Design Lab #1 Introduction to Xilinx ISE and the ML40X Eval Board Date: 1/21/09 Due: 1/28/09 Lab Description Today s lab will introduce you to the Xilinx Integrated Software Environment (ISE)
EE 367 Logic Design Lab #1 Introduction to Xilinx ISE and the ML40X Eval Board Date: 1/21/09 Due: 1/28/09 Lab Description Today s lab will introduce you to the Xilinx Integrated Software Environment (ISE)
Quartus II Tutorial. September 10, 2014 Quartus II Version 14.0
 Quartus II Tutorial September 10, 2014 Quartus II Version 14.0 This tutorial will walk you through the process of developing circuit designs within Quartus II, simulating with Modelsim, and downloading
Quartus II Tutorial September 10, 2014 Quartus II Version 14.0 This tutorial will walk you through the process of developing circuit designs within Quartus II, simulating with Modelsim, and downloading
CS152 FPGA CAD Tool Flow University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences
 CS152 FPGA CAD Tool Flow University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Compiled: 4/3/2003 for CS152 Spring 03, Prof. John Kubiatowicz
CS152 FPGA CAD Tool Flow University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Compiled: 4/3/2003 for CS152 Spring 03, Prof. John Kubiatowicz
FPGA Design Tutorial
 ECE 554 Digital Engineering Laboratory FPGA Design Tutorial Version 5.0 Fall 2006 Updated Tutorial: Jake Adriaens Original Tutorial: Matt King, Surin Kittitornkun and Charles R. Kime Table of Contents
ECE 554 Digital Engineering Laboratory FPGA Design Tutorial Version 5.0 Fall 2006 Updated Tutorial: Jake Adriaens Original Tutorial: Matt King, Surin Kittitornkun and Charles R. Kime Table of Contents
TLL5000 Electronic System Design Base Module. Getting Started Guide, Ver 3.4
 TLL5000 Electronic System Design Base Module Getting Started Guide, Ver 3.4 COPYRIGHT NOTICE The Learning Labs, Inc. ( TLL ) All rights reserved, 2008 Reproduction in any form without permission is prohibited.
TLL5000 Electronic System Design Base Module Getting Started Guide, Ver 3.4 COPYRIGHT NOTICE The Learning Labs, Inc. ( TLL ) All rights reserved, 2008 Reproduction in any form without permission is prohibited.
EE 1315 DIGITAL LOGIC LAB EE Dept, UMD
 EE 1315 DIGITAL LOGIC LAB EE Dept, UMD EXPERIMENT # 1: Logic building blocks The main objective of this experiment is to let you familiarize with the lab equipment and learn about the operation of the
EE 1315 DIGITAL LOGIC LAB EE Dept, UMD EXPERIMENT # 1: Logic building blocks The main objective of this experiment is to let you familiarize with the lab equipment and learn about the operation of the
Introduction. About this tutorial. How to use this tutorial
 Basic Entry & not About this tutorial This tutorial consists of an introduction to creating simple circuits on an FPGA using a variety of methods. There are two ways to create the circuit: using or by
Basic Entry & not About this tutorial This tutorial consists of an introduction to creating simple circuits on an FPGA using a variety of methods. There are two ways to create the circuit: using or by
Lab 1 FPGA CAD Tools
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Lab 1 FPGA CAD Tools ASSIGNED: Week of 1/21 DUE: Week of 1/28, 10 minutes after start
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Lab 1 FPGA CAD Tools ASSIGNED: Week of 1/21 DUE: Week of 1/28, 10 minutes after start
PlanAhead Software Tutorial
 PlanAhead Software Tutorial RTL Design and IP Generation The information disclosed to you hereunder (the Information ) is provided AS-IS with no warranty of any kind, express or implied. Xilinx does not
PlanAhead Software Tutorial RTL Design and IP Generation The information disclosed to you hereunder (the Information ) is provided AS-IS with no warranty of any kind, express or implied. Xilinx does not
TLL5000 Electronic System Design Base Module
 TLL5000 Electronic System Design Base Module The Learning Labs, Inc. Copyright 2007 Manual Revision 2007.12.28 1 Copyright 2007 The Learning Labs, Inc. Copyright Notice The Learning Labs, Inc. ( TLL )
TLL5000 Electronic System Design Base Module The Learning Labs, Inc. Copyright 2007 Manual Revision 2007.12.28 1 Copyright 2007 The Learning Labs, Inc. Copyright Notice The Learning Labs, Inc. ( TLL )
Quick Front-to-Back Overview Tutorial
 Quick Front-to-Back Overview Tutorial PlanAhead Design Tool This tutorial document was last validated using the following software version: ISE Design Suite 14.5 If using a later software version, there
Quick Front-to-Back Overview Tutorial PlanAhead Design Tool This tutorial document was last validated using the following software version: ISE Design Suite 14.5 If using a later software version, there
Xilinx Tutorial Basic Walk-through
 Introduction to Digital Logic Design with FPGA s: Digital logic circuits form the basis of all digital electronic devices. FPGAs (Field Programmable Gate Array) are large programmable digital electronic
Introduction to Digital Logic Design with FPGA s: Digital logic circuits form the basis of all digital electronic devices. FPGAs (Field Programmable Gate Array) are large programmable digital electronic
2IN35 VLSI Programming Lab Work Assignment 1: Hardware design using Verilog
 2IN35 VLSI Programming Lab Work Assignment 1: Hardware design using Verilog Hrishikesh Salunkhe, h.l.salunkhe@tue.nl, Alok Lele, a.lele@tue.nl April 28, 2015 1 Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Hardware design
2IN35 VLSI Programming Lab Work Assignment 1: Hardware design using Verilog Hrishikesh Salunkhe, h.l.salunkhe@tue.nl, Alok Lele, a.lele@tue.nl April 28, 2015 1 Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Hardware design
ECE 491 Laboratory 1 Introducing FPGA Design with Verilog September 6, 2004
 Goals ECE 491 Laboratory 1 Introducing FPGA Design with Verilog September 6, 2004 1. To review the use of Verilog for combinational logic design. 2. To become familiar with using the Xilinx ISE software
Goals ECE 491 Laboratory 1 Introducing FPGA Design with Verilog September 6, 2004 1. To review the use of Verilog for combinational logic design. 2. To become familiar with using the Xilinx ISE software
Quartus II Version 14.0 Tutorial Created September 10, 2014; Last Updated January 9, 2017
 Quartus II Version 14.0 Tutorial Created September 10, 2014; Last Updated January 9, 2017 This tutorial will walk you through the process of developing circuit designs within Quartus II, simulating with
Quartus II Version 14.0 Tutorial Created September 10, 2014; Last Updated January 9, 2017 This tutorial will walk you through the process of developing circuit designs within Quartus II, simulating with
Lab 2 Verilog Synthesis & Logic Optimization
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Lab 2 Verilog Synthesis & Logic Optimization 1.0 Motivation The goals of this lab are
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Lab 2 Verilog Synthesis & Logic Optimization 1.0 Motivation The goals of this lab are
EEC 116 Fall 2011 Lab #3: Digital Simulation Tutorial
 EEC 116 Fall 2011 Lab #3: Digital Simulation Tutorial Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, Davis Issued: October 10, 2011 Due: October 19, 2011, 4PM Reading: Rabaey Insert
EEC 116 Fall 2011 Lab #3: Digital Simulation Tutorial Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, Davis Issued: October 10, 2011 Due: October 19, 2011, 4PM Reading: Rabaey Insert
Xilinx Schematic Entry Tutorial
 Overview Xilinx Schematic Entry Tutorial Xilinx ISE Schematic Entry & Modelsim Simulation What is circuit simulation and why is it important? Complex designs, short design cycle Simultaneous system design
Overview Xilinx Schematic Entry Tutorial Xilinx ISE Schematic Entry & Modelsim Simulation What is circuit simulation and why is it important? Complex designs, short design cycle Simultaneous system design
EECS150: Lab 1, FPGA CAD Tools
 EECS150: Lab 1, FPGA CAD Tools UC Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 1 Time Table ASSIGNED DUE Friday, August 29 th Week 3: September 7 th 13 th,
EECS150: Lab 1, FPGA CAD Tools UC Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 1 Time Table ASSIGNED DUE Friday, August 29 th Week 3: September 7 th 13 th,
Tutorial: Working with Verilog and the Xilinx FPGA in ISE 9.2i
 Tutorial: Working with Verilog and the Xilinx FPGA in ISE 9.2i This tutorial will show you how to: Use Verilog to specify a design Simulate that Verilog design Define pin constraints for the FPGA (.ucf
Tutorial: Working with Verilog and the Xilinx FPGA in ISE 9.2i This tutorial will show you how to: Use Verilog to specify a design Simulate that Verilog design Define pin constraints for the FPGA (.ucf
Xilinx ISE/WebPack: Introduction to Schematic Capture and Simulation
 Xilinx ISE/WebPack: Introduction to Schematic Capture and Simulation Revision: February 7, 2003 Overview This document is intended to assist new entry-level users of the Xilinx ISE/WebPack software. It
Xilinx ISE/WebPack: Introduction to Schematic Capture and Simulation Revision: February 7, 2003 Overview This document is intended to assist new entry-level users of the Xilinx ISE/WebPack software. It
ECSE-323 Digital System Design. Lab #1 Using the Altera Quartus II Software Fall 2008
 1 ECSE-323 Digital System Design Lab #1 Using the Altera Quartus II Software Fall 2008 2 Introduction. In this lab you will learn the basics of the Altera Quartus II FPGA design software through following
1 ECSE-323 Digital System Design Lab #1 Using the Altera Quartus II Software Fall 2008 2 Introduction. In this lab you will learn the basics of the Altera Quartus II FPGA design software through following
Lab 6 : Introduction to Verilog
 Lab 6 : Introduction to Verilog Name: Sign the following statement: On my honor, as an Aggie, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this academic work 1 Objective The main objective of
Lab 6 : Introduction to Verilog Name: Sign the following statement: On my honor, as an Aggie, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this academic work 1 Objective The main objective of
Lab 1: Introduction to Verilog HDL and the Xilinx ISE
 EE 231-1 - Fall 2016 Lab 1: Introduction to Verilog HDL and the Xilinx ISE Introduction In this lab simple circuits will be designed by programming the field-programmable gate array (FPGA). At the end
EE 231-1 - Fall 2016 Lab 1: Introduction to Verilog HDL and the Xilinx ISE Introduction In this lab simple circuits will be designed by programming the field-programmable gate array (FPGA). At the end
Lab 3: Simulation and Testing
 Lab 3: Simulation and Testing University of California, Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS150 Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Ronald Fearing,
Lab 3: Simulation and Testing University of California, Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS150 Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Ronald Fearing,
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science EECS 150 Spring 2002 Original Lab By: J.Wawrzynek and N. Weaver Later revisions by
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science EECS 150 Spring 2002 Original Lab By: J.Wawrzynek and N. Weaver Later revisions by
DESIGN STRATEGIES & TOOLS UTILIZED
 CHAPTER 7 DESIGN STRATEGIES & TOOLS UTILIZED 7-1. Field Programmable Gate Array The internal architecture of an FPGA consist of several uncommitted logic blocks in which the design is to be encoded. The
CHAPTER 7 DESIGN STRATEGIES & TOOLS UTILIZED 7-1. Field Programmable Gate Array The internal architecture of an FPGA consist of several uncommitted logic blocks in which the design is to be encoded. The
EE 101 Lab 5 Fast Adders
 EE 0 Lab 5 Fast Adders Introduction In this lab you will compare the performance of a 6-bit ripple-carry adder (RCA) with a 6-bit carry-lookahead adder (CLA). The 6-bit CLA will be implemented hierarchically
EE 0 Lab 5 Fast Adders Introduction In this lab you will compare the performance of a 6-bit ripple-carry adder (RCA) with a 6-bit carry-lookahead adder (CLA). The 6-bit CLA will be implemented hierarchically
NOTE: This tutorial contains many large illustrations. Page breaks have been added to keep images on the same page as the step that they represent.
 CSE 352 Tutorial # 4 Synthesizing onto an FPGA Objectives This tutorial will walk you through the steps of implementing a design made in Active-HDL onto the Altera Cyclone II FPGA NOTE: This tutorial contains
CSE 352 Tutorial # 4 Synthesizing onto an FPGA Objectives This tutorial will walk you through the steps of implementing a design made in Active-HDL onto the Altera Cyclone II FPGA NOTE: This tutorial contains
Lab 1 Modular Design and Testbench Simulation ENGIN 341 Advanced Digital Design University of Massachusetts Boston
 Lab 1 Modular Design and Testbench Simulation ENGIN 341 Advanced Digital Design University of Massachusetts Boston Introduction This lab introduces the concept of modular design by guiding you through
Lab 1 Modular Design and Testbench Simulation ENGIN 341 Advanced Digital Design University of Massachusetts Boston Introduction This lab introduces the concept of modular design by guiding you through
Partial Reconfiguration Tutorial. PlanAhead Design Tool
 Partial Reconfiguration Tutorial PlanAhead Design Tool Xilinx is disclosing this user guide, manual, release note, and/or specification (the Documentation ) to you solely for use in the development of
Partial Reconfiguration Tutorial PlanAhead Design Tool Xilinx is disclosing this user guide, manual, release note, and/or specification (the Documentation ) to you solely for use in the development of
RTL Design and IP Generation Tutorial. PlanAhead Design Tool
 RTL Design and IP Generation Tutorial PlanAhead Design Tool Notice of Disclaimer The information disclosed to you hereunder (the "Materials") is provided solely for the selection and use of Xilinx products.
RTL Design and IP Generation Tutorial PlanAhead Design Tool Notice of Disclaimer The information disclosed to you hereunder (the "Materials") is provided solely for the selection and use of Xilinx products.
Design Analysis and Floorplanning Tutorial. PlanAhead Design Tool
 Design Analysis and Floorplanning Tutorial PlanAhead Design Tool Xilinx is disclosing this user guide, manual, release note, and/or specification (the Documentation ) to you solely for use in the development
Design Analysis and Floorplanning Tutorial PlanAhead Design Tool Xilinx is disclosing this user guide, manual, release note, and/or specification (the Documentation ) to you solely for use in the development
Laboratory 6. - Using Encounter for Automatic Place and Route. By Mulong Li, 2013
 CME 342 (VLSI Circuit Design) Laboratory 6 - Using Encounter for Automatic Place and Route By Mulong Li, 2013 Reference: Digital VLSI Chip Design with Cadence and Synopsys CAD Tools, Erik Brunvand Background
CME 342 (VLSI Circuit Design) Laboratory 6 - Using Encounter for Automatic Place and Route By Mulong Li, 2013 Reference: Digital VLSI Chip Design with Cadence and Synopsys CAD Tools, Erik Brunvand Background
Xilinx Project Navigator Reference Guide
 31 July 2003 Author: David M. Sendek Xilinx Project Navigator Reference Guide Background: This guide provides you with step-by-step procedures in using the Xilinx Project Navigator to perform the following:
31 July 2003 Author: David M. Sendek Xilinx Project Navigator Reference Guide Background: This guide provides you with step-by-step procedures in using the Xilinx Project Navigator to perform the following:
Chapter 9: Integration of Full ASIP and its FPGA Implementation
 Chapter 9: Integration of Full ASIP and its FPGA Implementation 9.1 Introduction A top-level module has been created for the ASIP in VHDL in which all the blocks have been instantiated at the Register
Chapter 9: Integration of Full ASIP and its FPGA Implementation 9.1 Introduction A top-level module has been created for the ASIP in VHDL in which all the blocks have been instantiated at the Register
ELEC 4200 Lab#0 Tutorial
 1 ELEC 4200 Lab#0 Tutorial Objectives(1) In this Lab exercise, we will design and implement a 2-to-1 multiplexer (MUX), using Xilinx Vivado tools to create a VHDL model of the design, verify the model,
1 ELEC 4200 Lab#0 Tutorial Objectives(1) In this Lab exercise, we will design and implement a 2-to-1 multiplexer (MUX), using Xilinx Vivado tools to create a VHDL model of the design, verify the model,
Actel Libero TM Integrated Design Environment v2.3 Structural Schematic Flow Design Tutorial
 Actel Libero TM Integrated Design Environment v2.3 Structural Schematic Flow Design Tutorial 1 Table of Contents Design Flow in Libero TM IDE v2.3 Step 1 - Design Creation 3 Step 2 - Design Verification
Actel Libero TM Integrated Design Environment v2.3 Structural Schematic Flow Design Tutorial 1 Table of Contents Design Flow in Libero TM IDE v2.3 Step 1 - Design Creation 3 Step 2 - Design Verification
Xilinx ISE Synthesis Tutorial
 Xilinx ISE Synthesis Tutorial The following tutorial provides a basic description of how to use Xilinx ISE to create a simple 2-input AND gate and synthesize the design onto the Spartan-3E Starter Board
Xilinx ISE Synthesis Tutorial The following tutorial provides a basic description of how to use Xilinx ISE to create a simple 2-input AND gate and synthesize the design onto the Spartan-3E Starter Board
Digital Circuit Design Using Xilinx ISE Tools
 Digital Circuit Design Using Xilinx ISE Tools Poras T. Balsara and Prashant Vallur Table of Contents 1. Introduction 2. Programmable logic devices: FPGA and CPLD 3. Creating a new project in Xilinx Foundation
Digital Circuit Design Using Xilinx ISE Tools Poras T. Balsara and Prashant Vallur Table of Contents 1. Introduction 2. Programmable logic devices: FPGA and CPLD 3. Creating a new project in Xilinx Foundation
Graduate Institute of Electronics Engineering, NTU FPGA Design with Xilinx ISE
 FPGA Design with Xilinx ISE Presenter: Shu-yen Lin Advisor: Prof. An-Yeu Wu 2005/6/6 ACCESS IC LAB Outline Concepts of Xilinx FPGA Xilinx FPGA Architecture Introduction to ISE Code Generator Constraints
FPGA Design with Xilinx ISE Presenter: Shu-yen Lin Advisor: Prof. An-Yeu Wu 2005/6/6 ACCESS IC LAB Outline Concepts of Xilinx FPGA Xilinx FPGA Architecture Introduction to ISE Code Generator Constraints
Engineering 1630 Fall Simulating XC9572XL s on the ENGN1630 CPLD-II Board
 Engineering 1630 Fall 2016 Simulating XC9572XL s on the ENGN1630 CPLD-II Board You will use the Aldec Active-HDL software for the required timing simulation of the XC9572XL CPLD programmable logic chips
Engineering 1630 Fall 2016 Simulating XC9572XL s on the ENGN1630 CPLD-II Board You will use the Aldec Active-HDL software for the required timing simulation of the XC9572XL CPLD programmable logic chips
University of Florida EEL 3701 Dr. Eric M. Schwartz Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Revision 0 12-Jun-16
 Page 1/14 Quartus Tutorial with Basic Graphical Gate Entry and Simulation Example Problem Given the logic equation Y = A*/B + /C, implement this equation using a two input AND gate, a two input OR gate
Page 1/14 Quartus Tutorial with Basic Graphical Gate Entry and Simulation Example Problem Given the logic equation Y = A*/B + /C, implement this equation using a two input AND gate, a two input OR gate
Building Combinatorial Circuit Using Behavioral Modeling Lab
 Building Combinatorial Circuit Using Behavioral Modeling Lab Overview: In this lab you will learn how to model a combinatorial circuit using behavioral modeling style of Verilog HDL. You will model a combinatorial
Building Combinatorial Circuit Using Behavioral Modeling Lab Overview: In this lab you will learn how to model a combinatorial circuit using behavioral modeling style of Verilog HDL. You will model a combinatorial
RTL Coding General Concepts
 RTL Coding General Concepts Typical Digital System 2 Components of a Digital System Printed circuit board (PCB) Embedded d software microprocessor microcontroller digital signal processor (DSP) ASIC Programmable
RTL Coding General Concepts Typical Digital System 2 Components of a Digital System Printed circuit board (PCB) Embedded d software microprocessor microcontroller digital signal processor (DSP) ASIC Programmable
Getting started with the Xilinx Project Navigator and the Digilent BASYS 2 board.
 Getting started with the Xilinx Project Navigator and the Digilent BASYS 2 board. This lab is based on: Xilinx Project Navigator, Release Version 14.6 Digilent Adept System Rev 2.7, Runtime Rev 2.16 Digilent
Getting started with the Xilinx Project Navigator and the Digilent BASYS 2 board. This lab is based on: Xilinx Project Navigator, Release Version 14.6 Digilent Adept System Rev 2.7, Runtime Rev 2.16 Digilent
EEC 118 Spring 2011 Lab #5 Manchester Carry-Chain Adder
 EEC 118 Spring 2011 Lab #5 Manchester Carry-Chain Adder Rajeevan Amirtharajah Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, Davis Issued: May 9, 2011 Due: May 20, 2011, 5 PM in
EEC 118 Spring 2011 Lab #5 Manchester Carry-Chain Adder Rajeevan Amirtharajah Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, Davis Issued: May 9, 2011 Due: May 20, 2011, 5 PM in
To practice combinational logic on Logisim and Xilinx ISE tools. ...
 ENGG1203: Introduction to Electrical and Electronic Engineering Second Semester, 2017 18 Lab 1 Objective: To practice combinational logic on Logisim and Xilinx ISE tools. 1 Find your lab partner You will
ENGG1203: Introduction to Electrical and Electronic Engineering Second Semester, 2017 18 Lab 1 Objective: To practice combinational logic on Logisim and Xilinx ISE tools. 1 Find your lab partner You will
PlanAhead Software Tutorial
 PlanAhead Software Tutorial Overview of the Partial Reconfiguration Flow The information disclosed to you hereunder (the Information ) is provided AS-IS with no warranty of any kind, express or implied.
PlanAhead Software Tutorial Overview of the Partial Reconfiguration Flow The information disclosed to you hereunder (the Information ) is provided AS-IS with no warranty of any kind, express or implied.
VLSI Lab Tutorial 1. Cadence Virtuoso Schematic Composer Introduction
 VLSI Lab Tutorial 1 Cadence Virtuoso Schematic Composer Introduction 1.0 Introduction The purpose of the first lab tutorial is to help you become familiar with the schematic editor, Virtuoso Schematic
VLSI Lab Tutorial 1 Cadence Virtuoso Schematic Composer Introduction 1.0 Introduction The purpose of the first lab tutorial is to help you become familiar with the schematic editor, Virtuoso Schematic
EECS150 Lab Lecture 2 Design Verification
 EECS150 Lab Lecture 2 Design Verification Vincent Lee Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley 9/7/2012 EECS150-Fa12-lab1 1 Lab Logistics T minus three weeks-ish
EECS150 Lab Lecture 2 Design Verification Vincent Lee Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley 9/7/2012 EECS150-Fa12-lab1 1 Lab Logistics T minus three weeks-ish
PINE TRAINING ACADEMY
 PINE TRAINING ACADEMY Course Module A d d r e s s D - 5 5 7, G o v i n d p u r a m, G h a z i a b a d, U. P., 2 0 1 0 1 3, I n d i a Digital Logic System Design using Gates/Verilog or VHDL and Implementation
PINE TRAINING ACADEMY Course Module A d d r e s s D - 5 5 7, G o v i n d p u r a m, G h a z i a b a d, U. P., 2 0 1 0 1 3, I n d i a Digital Logic System Design using Gates/Verilog or VHDL and Implementation
Circuit Design and Simulation with VHDL 2nd edition Volnei A. Pedroni MIT Press, 2010 Book web:
 Circuit Design and Simulation with VHDL 2nd edition Volnei A. Pedroni MIT Press, 2010 Book web: www.vhdl.us Appendix C Xilinx ISE Tutorial (ISE 11.1) This tutorial is based on ISE 11.1 WebPack (free at
Circuit Design and Simulation with VHDL 2nd edition Volnei A. Pedroni MIT Press, 2010 Book web: www.vhdl.us Appendix C Xilinx ISE Tutorial (ISE 11.1) This tutorial is based on ISE 11.1 WebPack (free at
Introduction to WebPACK 5.2 for FPGAs. Using Xilinx WebPACK Software to Create FPGA Designs for the XSB-300E Board
 Introduction to WebPACK 5.2 for FPGAs Using Xilinx WebPACK Software to Create FPGA Designs for the XSB-300E Board Release date: 10/27/2003 All XS-prefix product designations are trademarks of XESS Corp.
Introduction to WebPACK 5.2 for FPGAs Using Xilinx WebPACK Software to Create FPGA Designs for the XSB-300E Board Release date: 10/27/2003 All XS-prefix product designations are trademarks of XESS Corp.
CCE 3202 Advanced Digital System Design
 CCE 3202 Advanced Digital System Design Lab Exercise #2 Introduction You will use Xilinx Webpack v9.1 to allow the synthesis and creation of VHDLbased designs. This lab will outline the steps necessary
CCE 3202 Advanced Digital System Design Lab Exercise #2 Introduction You will use Xilinx Webpack v9.1 to allow the synthesis and creation of VHDLbased designs. This lab will outline the steps necessary
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, DAVIS Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. EEC180A DIGITAL SYSTEMS I Winter 2015
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, DAVIS Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EEC180A DIGITAL SYSTEMS I Winter 2015 LAB 1: Introduction to Quartus II Schematic Capture and ModelSim Simulation This
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, DAVIS Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EEC180A DIGITAL SYSTEMS I Winter 2015 LAB 1: Introduction to Quartus II Schematic Capture and ModelSim Simulation This
ELEC 204 Digital System Design LABORATORY MANUAL
 ELEC 204 Digital System Design LABORATORY MANUAL : Introductory Tutorial For Xilinx ISE Foundation v10.1 & Implementing XOR Gate College of Engineering Koç University Important Note: In order to effectively
ELEC 204 Digital System Design LABORATORY MANUAL : Introductory Tutorial For Xilinx ISE Foundation v10.1 & Implementing XOR Gate College of Engineering Koç University Important Note: In order to effectively
Step 1: Downloading the source files
 Introduction: In this lab and in the remainder of the ELEC 2607 labs, you will be using the Xilinx ISE to enter and simulate the designs for your circuits. In labs 3 and 4, you will use ISE to compile
Introduction: In this lab and in the remainder of the ELEC 2607 labs, you will be using the Xilinx ISE to enter and simulate the designs for your circuits. In labs 3 and 4, you will use ISE to compile
Physics 364, Fall 2014, reading due your answers to by 11pm on Sunday
 Physics 364, Fall 2014, reading due 2014-11-23. Email your answers to ashmansk@hep.upenn.edu by 11pm on Sunday Course materials and schedule are at positron.hep.upenn.edu/p364 Assignment: (a) First read
Physics 364, Fall 2014, reading due 2014-11-23. Email your answers to ashmansk@hep.upenn.edu by 11pm on Sunday Course materials and schedule are at positron.hep.upenn.edu/p364 Assignment: (a) First read
Design Analysis and Floorplanning Tutorial. PlanAhead Design Tool
 Design Analysis and Floorplanning Tutorial PlanAhead Design Tool This tutorial document was last validated using the following software version: ISE Design Suite 14.1 If using a later software version,
Design Analysis and Floorplanning Tutorial PlanAhead Design Tool This tutorial document was last validated using the following software version: ISE Design Suite 14.1 If using a later software version,
Tutorial: ISE 12.2 and the Spartan3e Board v August 2010
 Tutorial: ISE 12.2 and the Spartan3e Board v12.2.1 August 2010 This tutorial will show you how to: Use a combination of schematics and Verilog to specify a design Simulate that design Define pin constraints
Tutorial: ISE 12.2 and the Spartan3e Board v12.2.1 August 2010 This tutorial will show you how to: Use a combination of schematics and Verilog to specify a design Simulate that design Define pin constraints
Chapter 2 Getting Hands on Altera Quartus II Software
 Chapter 2 Getting Hands on Altera Quartus II Software Contents 2.1 Installation of Software... 20 2.2 Setting Up of License... 21 2.3 Creation of First Embedded System Project... 22 2.4 Project Building
Chapter 2 Getting Hands on Altera Quartus II Software Contents 2.1 Installation of Software... 20 2.2 Setting Up of License... 21 2.3 Creation of First Embedded System Project... 22 2.4 Project Building
Vivado Design Suite User Guide
 Vivado Design Suite User Guide Design Flows Overview Notice of Disclaimer The information disclosed to you hereunder (the Materials ) is provided solely for the selection and use of Xilinx products. To
Vivado Design Suite User Guide Design Flows Overview Notice of Disclaimer The information disclosed to you hereunder (the Materials ) is provided solely for the selection and use of Xilinx products. To
PlanAhead Software Tutorial
 PlanAhead Software Tutorial Team Design NOTICE OF DISCLAIMER: The information disclosed to you hereunder (the Information ) is provided AS-IS with no warranty of any kind, express or implied. Xilinx does
PlanAhead Software Tutorial Team Design NOTICE OF DISCLAIMER: The information disclosed to you hereunder (the Information ) is provided AS-IS with no warranty of any kind, express or implied. Xilinx does
Circuit design with configurable devices (FPGA)
 1 Material Circuit design with configurable devices (FPGA) Computer with Xilinx's ISE software installed. Digilent's Basys2 prototype board and documentation. Sample design files (lab kit). Files and documents
1 Material Circuit design with configurable devices (FPGA) Computer with Xilinx's ISE software installed. Digilent's Basys2 prototype board and documentation. Sample design files (lab kit). Files and documents
Vivado Tutorial. Introduction. Objectives. Procedure. Lab Workbook. Vivado Tutorial
 Lab Workbook Introduction This tutorial guides you through the design flow using Xilinx Vivado software to create a simple digital circuit using Verilog HDL. A typical design flow consists of creating
Lab Workbook Introduction This tutorial guides you through the design flow using Xilinx Vivado software to create a simple digital circuit using Verilog HDL. A typical design flow consists of creating
Tutorial for Altera DE1 and Quartus II
 Tutorial for Altera DE1 and Quartus II Qin-Zhong Ye December, 2013 This tutorial teaches you the basic steps to use Quartus II version 13.0 to program Altera s FPGA, Cyclone II EP2C20 on the Development
Tutorial for Altera DE1 and Quartus II Qin-Zhong Ye December, 2013 This tutorial teaches you the basic steps to use Quartus II version 13.0 to program Altera s FPGA, Cyclone II EP2C20 on the Development
Physics 364, Fall 2012, reading due your answers to before the end of Wednesday s lab.
 Physics 364, Fall 2012, reading due 2012-11-28. Email your answers to ashmansk@hep.upenn.edu before the end of Wednesday s lab. Course materials and schedule are at http://positron.hep.upenn.edu/p364 Assignment:
Physics 364, Fall 2012, reading due 2012-11-28. Email your answers to ashmansk@hep.upenn.edu before the end of Wednesday s lab. Course materials and schedule are at http://positron.hep.upenn.edu/p364 Assignment:
Introduction to WebPACK 4.1 for FPGAs. Using Xilinx WebPACK Software to Create FPGA Designs for the XSA Board
 Introduction to WebPACK 4.1 for FPGAs Using Xilinx WebPACK Software to Create FPGA Designs for the XSA Board Release date: 10/29/2001 All XS-prefix product designations are trademarks of XESS Corp. All
Introduction to WebPACK 4.1 for FPGAs Using Xilinx WebPACK Software to Create FPGA Designs for the XSA Board Release date: 10/29/2001 All XS-prefix product designations are trademarks of XESS Corp. All
