Travel Time and Time of Concentration
|
|
|
- Bethanie Morgan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Methods in Stormwater Management Using HydroCAD ravel ime and ime of Concentration H05 ravel ime.pdf 1
2 opics 1. ime of Concentration Definition 2. Segmental Flow 3. Sheet Flow 4. Concentrated Flow 5. Channel and Pipe Flow 6. ravel ime Equations 7. Example: Echo Valley Watershed 2
3 Outcomes 1. Understand the concept of time of concentration. 2. Understand the differences between sheet flow, shallow concentrated flow and channel/pipe flow. 3. Be familiar with the NRCS and other travel time methods. 4. Be able to apply travel time equations in a segmental manner in order to compute a watershed time of concentration. 3
4 ime of Concentration Hydrograph analysis definition time from end of rainfall excess to point of inflection on receding limb of graph Flow (cfs) rainfall excess c 400 Lag inflection point ime (hours) 4
5 ime of Concentration Flow path analysis definition time required for runoff to travel from the most hydraulically remote point in the watershed to the design point of interest. sheet POI sheet In-channel concentrated sheet 5
6 Segmental Calculation of c Segmental Method Break the flow path into distinctly different flow types Select appropriate equation for each segment Compute travel time, t, for each segment Sum the travel times to get time of concentration, c 6
7 Segmental Flow ypes Overland Flow Sheet Concentrated (natural swale) In-channel Flow Designed swale Designed channel Natural stream Pipe (gravity flow) Different flow types require different mathematical models 7
8 Overland Sheet Flow Very shallow overland flow Surface resistance dominates flow Uniform depth across a plane surface Path lengths typically short Impervious surfaces: approx ft Pervious surfaces: approx ft Depth same order of magnitude as surface roughness 8
9 Overland Sheet Flow Paved sheet flow Grassed sheet flow Sheet transitioning to concentrated Depth and roughness similar 9
10 Shallow Concentrated Flow Overland flow with visible depth Depth not uniform but shallow compared to flow path width More dynamic flow than kinematic flow Depth significantly larger than surface roughness dimension Also known as swale flow Can be ditch flow if depth is shallow 10
11 Shallow Concentrated Flow Impervious (gutter) flow Pervious (grass) flow 11
12 In-channel Flow Flow in a well defined channel Flow depth significant Dynamic forces dominate flow Pipe flow or channel flow Manning s equation is typical default model 12
13 In-channel Flow Pipe flow storm sewers Vegetated channel Rip-rap channel 13
14 Equations and Methods Equation types can be categorized as Sheet flow Shallow concentrated flow Combined sheet and shallow concentrated flow In-channel flow Lumped flow Most methods developed for very specific situations Most methods cannot be verified directly Choose best method to match flow path situation (regime/type) to get reasonable results 14
15 Izzard (1946) sheet flow on roadway and turf surfaces iterative solution with i and (two unknowns) i S i C L 0.33 = time in minutes i = rainfall intensity (in/hr) C = retardance coefficient L = length of flow path (ft) S = slope of flow path (ft/ft) 15
16 Morgali and Linsley (1965) sheet flow kinematic wave on paved surfaces iterative solution (two unknowns) 0.94L 0.4 i S n 0.6 L = length of overland flow (ft) n = Manning roughness coefficient i = rainfall intensity (in/hr) S = average overland slope (ft/ft) 16
17 NRCS Sheet Flow Equation (1986) t 0.42 nl P S 0.8 P 2 = 2-yr, 24-hr rainfall depth (in) n = Manning s sheet flow roughness L = length of overland flow path (ft) S = average overland slope (ft/ft) t = travel time (minutes). 17
18 NRCS Sheet Flow Equation Roughness Coefficients Surface description n 1 Smooth surface (concrete, asphalt, gravel or bare soil) Fallow (no residue) 0.05 Cultivated soils: Residue cover < 20% Residue cover > 20% Grass: Short-grass prairie Dense grasses 2 Bermuda grass Range (natural) 0.13 Woods: 3 Light underbrush Dense underbrush NOES: 1. he Manning s equation n values are composite of information compiled by Engman (1986). 2. Includes species such as weeping love grass, bluegrass, buffalo grass, blue grama grass and native grass mixtures. 3. When selecting n consider cover to a height of about 0.1 ft. his is the only part of the plant cover that will obstruct sheet flow. 18
19 NRCS Sheet Flow Maximum Path Lengths (1995) l 100 S n l = maximum length of flow (ft) n = Manning s sheet flow roughness S = average overland slope (ft/ft) Cover ype n values Slope (ft/ft) Length (ft) Grass Woods Grass Woods Grass Woods
20 Kirpich (1940) overland sheet and concentrated flow agricultural basins in PA and N 3% to 10% slopes, 1.25 to 112 acre watershed K L S K = surface roughness adjustment factor L = length of flow path from headwater to outlet (ft) S = average slope of the flow path (ft/ft) 20
21 Kerby-Hathaway (1959) overland sheet and concentrated flow sheet flow dominated the flow path 1% or less slopes, 10 acre and smaller watersheds 0.83 nl 0.5 S 0.47 L = length of overland flow (ft) n = Manning roughness coefficient S = average overland slope (ft/ft) 21
22 FAA (1970) overland sheet and concentrated flow developed from airfield drainage data frequently used for overland flow in urban watersheds C S L 0.5 C = Rational method runoff coefficient L = length of flow path (ft) S = average overland slope (%) 22
23 NRCS Average Velocity Method (1975, 2010) shallow concentrated flow velocity as a function of slope and surface cover reduced to two curves (paved and unpaved) by SCS when R was issued re-introduced by NRCS in May 2010 L 60V L = length of flow path (ft) S = watershed slope in percent V = average velocity 23
24 NRCS Concentrated Overland Flow (2010) V KS 0.5 t L 60V V = velocity (ft/s) K = surface coefficient S = watershed slope (ft/ft) L = length of path (ft) t = travel time (minutes). 24
25 L 1220S pavememt 0.5 L 968S grassed waterway 0.5 woodlands 0.5 nearly bare untilled L S L 526S cultivated row crops 0.5 L 418 S L 302S short-grass pasture 0.5 forest w/heavy ground litter and hay meadows 0.5 NRCS Shallow Concentrated Flow Equations L 151S L = length of path (ft) S = watershed slope (ft/ft) t = travel time (minutes). 25
26 NRCS R-55 (1986) Concentrated Flow L 1220S paved 0.5 L 968S unpaved 0.5 L = length of path (ft) S = watershed slope (ft/ft) t = travel time (minutes). 26
27 Manning s Equation (1890) in-channel flow compute velocity as a function of n, R h, and S V R S n h + t L 60V V = average channel velocity (ft/s) n = roughness coefficient R h = hydraulic radius (ft) = A/P A = flow area (ft 2 ) P = wetted perimeter of flow area (ft) S = average channel or pipe slope (ft/ft) t = travel time (minutes). L = length of flow path (ft) t 89.2 R nl h S 27
28 NRCS Lag Equation (1975) lumped watershed flow for upper reaches of the watershed adjust for channel improvements and impervious area L CN S 0.7 L = hydraulic length of watershed ; longest flow path (ft) CN = runoff curve number S = average watershed slope (ft/ft) 28
29 NRCS Segmental Method (2010) hree flow types sheet kinematic wave concentrated velocity method (Fig NEH 630 Ch. 15) in-channel Manning s equation 1. Sheet 0.42 nl P S Concentrated 3. In-channel nl 89.2 R h S 29
30 Exercise 1. Compute time of concentration for the Echo Valley watershed with the data provided on the following pages. 30
31 Echo Valley Watershed five flow segments 1. Sheet 2. Concentrated #1 3. Pipe 4. Concentrated #2 5. Channel 31
32 Echo Valley Watershed 1. Sheet Flow Segment L = 30 ft S = ft/ft Dense grass 2P 24 = 2.73 in (Atlas 14) 0.42 nl P S n = 0.24 (able 3.1 R-55) t = 6.0 minutes 32
33 Echo Valley Watershed 2. Concentrated Flow #1 L = 1080 ft S = ft/ft Wooded L 302 S woodland 0.5 t = 11.1 minutes 33
34 Echo Valley Watershed 3. Pipe Flow L = 520 ft S = ft/ft 18 Concrete Pipe (n = 0.013) Manning s channel flow nl 89.2 R h S nl 35.4 D circ. pipe S t = 1.1 minutes 34
35 Echo Valley Watershed 4. Concentrated Flow #2 L = 790 ft S = ft/ft Grass waterway L 968S grassed waterway 0.5 t = 5.8 minutes 35
36 Echo Valley Watershed 5. Channel Flow A = 3.0 ft 2 WP = 5.0 ft S = ft/ft n = L = 2500 ft 89.2 nl R S t = 5.4 minutes 36
37 NRCS Segmental Method Echo Valley Watershed c = c = c = 29.4 minutes 37
38 NRCS NEH Ch. 15 ime of Concentration Contains the latest time of concentration methodologies recommended by the NRCS. (May 2010) 38
39 Example: ime of Concentration for Echo Valley WS 39
40 Echo Valley WS travel time flow segments 1. Sheet Flow Segment L = 30 ft, S = ft/ft Dense grass, 2 P 24 = 2.68 in 2. Concentrated Flow #1 L = 1080 ft, S = ft/ft Wooded 3. Pipe Flow L = 520 ft, S = ft/ft 18 Concrete Pipe (n = 0.013) 4. Concentrated Flow #2 L = 790 ft, S = ft/ft Grass waterway 5. Channel Flow A = 3.0 ft 2, WP = 5.0 ft S = ft/ft, n = L = 2500 ft 40
41 ime of Concentration in HydroCAD for Echo Valley 1. Highlight WS Node 2. Under Nodes tab 3. Select Edit 4. Under c tab 5. Double Click on first row 6. Choose Sheet Flow. 7. Enter appropriate data 8. Click OK 9. Double click second row 10.Choose Shallow Concentrated Flow 11.Enter data, click OK 12.Repeat for other segments. 41
42 Summary opics 1. ime of Concentration Definition 2. Segmental Flow 3. Sheet Flow 4. Concentrated Flow 5. Channel and Pipe Flow 6. ravel ime Equations 7. Example: Echo Valley Watershed Outcomes 1. Understand the concept of time of concentration. 2. Understand the differences between sheet flow, shallow concentrated flow and channel/pipe flow. 3. Be familiar with the NRCS and other travel time methods. 4. Be able to apply travel time equations in a segmental manner in order to compute a watershed time of concentration. 42
Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Rational Design
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to design storm drain inlets, pipes, and other components of a storm drain system using FHWA's HY-12 storm drain analysis software and the WMS interface Objectives Define
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to design storm drain inlets, pipes, and other components of a storm drain system using FHWA's HY-12 storm drain analysis software and the WMS interface Objectives Define
VOLUME & FLOW RATE CALCULATIONS
 A.2 FLOW RATE AND VOLUME CALCULATION EXAMPLE PROJECT NAME Industrial Site Example A-8 NOMENCLATURE A I = Impervious Area (acres) A P = Pervious Area (acres) A U = Contributing Undeveloped Upstream Area
A.2 FLOW RATE AND VOLUME CALCULATION EXAMPLE PROJECT NAME Industrial Site Example A-8 NOMENCLATURE A I = Impervious Area (acres) A P = Pervious Area (acres) A U = Contributing Undeveloped Upstream Area
Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Modeling with the Hydraulic Toolbox
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Modeling with the Hydraulic Toolbox Learn how to design inlet grates, detention basins, channels, and riprap using the FHWA Hydraulic Toolbox
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Modeling with the Hydraulic Toolbox Learn how to design inlet grates, detention basins, channels, and riprap using the FHWA Hydraulic Toolbox
Evaluating Multiple Stormwater Analysis and Design Alternatives with StormCAD
 Evaluating Multiple Stormwater Analysis and Design Alternatives with StormCAD Workshop Overview In this workshop you will use StormCAD to analyze an existing storm sewer system. You will add a parking
Evaluating Multiple Stormwater Analysis and Design Alternatives with StormCAD Workshop Overview In this workshop you will use StormCAD to analyze an existing storm sewer system. You will add a parking
Watershed Modeling Rational Method Interface. Learn how to model urban areas using WMS' rational method interface
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to model urban areas using WMS' rational method interface Objectives Learn how to model urban areas using the Rational method, including how to compute rainfall intensity,
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to model urban areas using WMS' rational method interface Objectives Learn how to model urban areas using the Rational method, including how to compute rainfall intensity,
Documentation for Velocity Method Segment Generator Glenn E. Moglen February 2005 (Revised March 2005)
 Documentation for Velocity Method Segment Generator Glenn E. Moglen February 2005 (Revised March 2005) The purpose of this document is to provide guidance on the use of a new dialog box recently added
Documentation for Velocity Method Segment Generator Glenn E. Moglen February 2005 (Revised March 2005) The purpose of this document is to provide guidance on the use of a new dialog box recently added
Appendix E-1. Hydrology Analysis
 Appendix E-1 Hydrology Analysis July 2016 HYDROLOGY ANALYSIS For Tentative Tract 20049 City of Chino Hills County of San Bernardino Prepared For: 450 Newport Center Drive, Suite 300 Newport Beach, CA 92660
Appendix E-1 Hydrology Analysis July 2016 HYDROLOGY ANALYSIS For Tentative Tract 20049 City of Chino Hills County of San Bernardino Prepared For: 450 Newport Center Drive, Suite 300 Newport Beach, CA 92660
Objectives This tutorial shows you how to define data for and run a rational method model for a watershed in Orange County.
 v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial Modeling Orange County Rational Method GIS Learn how to define a rational method hydrologic model for Orange County (California) from GIS data Objectives This tutorial shows you
v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial Modeling Orange County Rational Method GIS Learn how to define a rational method hydrologic model for Orange County (California) from GIS data Objectives This tutorial shows you
v Modeling Orange County Rational Method GIS Learn how to define a rational method hydrologic model for Orange County (California) from GIS data
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Modeling Orange County Rational Method GIS Learn how to define a rational method hydrologic model for Orange County (California) from GIS data Objectives This tutorial shows how
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Modeling Orange County Rational Method GIS Learn how to define a rational method hydrologic model for Orange County (California) from GIS data Objectives This tutorial shows how
Harris County Flood Control District HEC-RAS 2D Modeling Guidelines (Standardizing HEC-RAS 2D Models for Submittal Within Harris County)
 Harris County Flood Control District HEC-RAS 2D Modeling Guidelines (Standardizing HEC-RAS 2D Models for Submittal Within Harris County) Presented by: April 27, 2017 Matthew Zeve, P.E., CFM Harris County
Harris County Flood Control District HEC-RAS 2D Modeling Guidelines (Standardizing HEC-RAS 2D Models for Submittal Within Harris County) Presented by: April 27, 2017 Matthew Zeve, P.E., CFM Harris County
Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network
Watershed Modeling HEC-HMS Interface
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to set up a basic HEC-HMS model using WMS Objectives Build a basic HEC-HMS model from scratch using a DEM, land use, and soil data. Compute the geometric and hydrologic
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to set up a basic HEC-HMS model using WMS Objectives Build a basic HEC-HMS model from scratch using a DEM, land use, and soil data. Compute the geometric and hydrologic
DESIGN MANUAL CHAPTER 5: Open Channel Hydraulics
 DESIGN MANUAL CHAPTER 5: Open Channel Hydraulics 5.0 OPEN CHANNEL HYDRAULICS...5-1 5.1 SYMBOLS AND DEFINITIONS...5-1 5.2 DESIGN CRITERIA...5-2 5.2.1 GENERAL CRITERIA...5-2 5.2.2 VELOCITY LIMITATIONS...5-3
DESIGN MANUAL CHAPTER 5: Open Channel Hydraulics 5.0 OPEN CHANNEL HYDRAULICS...5-1 5.1 SYMBOLS AND DEFINITIONS...5-1 5.2 DESIGN CRITERIA...5-2 5.2.1 GENERAL CRITERIA...5-2 5.2.2 VELOCITY LIMITATIONS...5-3
Objectives Divide a single watershed into multiple sub-basins, and define routing between sub-basins.
 v. 11.0 HEC-HMS WMS 11.0 Tutorial HEC-HMS Learn how to create multiple sub-basins using HEC-HMS Objectives Divide a single watershed into multiple sub-basins, and define routing between sub-basins. Prerequisite
v. 11.0 HEC-HMS WMS 11.0 Tutorial HEC-HMS Learn how to create multiple sub-basins using HEC-HMS Objectives Divide a single watershed into multiple sub-basins, and define routing between sub-basins. Prerequisite
WMS 10.0 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling SWMM Modeling Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network
H y d r o C A D. Owner's Manual
 H y d r o C A D Stormwater Modeling System Version 8 Owner's Manual Copyright 2006 HydroCAD Software Solutions LLC. All rights reserved. HydroCAD is a registered trademark of HydroCAD Software Solutions
H y d r o C A D Stormwater Modeling System Version 8 Owner's Manual Copyright 2006 HydroCAD Software Solutions LLC. All rights reserved. HydroCAD is a registered trademark of HydroCAD Software Solutions
WMS 9.1 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling SWMM Modeling Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network information
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to link a hydrologic model to the SWMM storm drain model Objectives Build a rational method hydrologic model and compute sub-basin flows. Import storm drain network information
WMS 8.4 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface (GISbased) Delineate a watershed and build a MODRAT model
 v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface (GISbased) Delineate a watershed and build a MODRAT model Objectives Delineate a watershed from a DEM and derive many of the MODRAT input parameters
v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface (GISbased) Delineate a watershed and build a MODRAT model Objectives Delineate a watershed from a DEM and derive many of the MODRAT input parameters
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling HEC-1 Interface Learn how to setup a basic HEC-1 model using WMS
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to setup a basic HEC-1 model using WMS Objectives Build a basic HEC-1 model from scratch using a DEM, land use, and soil data. Compute the geometric and hydrologic parameters
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to setup a basic HEC-1 model using WMS Objectives Build a basic HEC-1 model from scratch using a DEM, land use, and soil data. Compute the geometric and hydrologic parameters
v Prerequisite Tutorials GSSHA Modeling Basics Stream Flow GSSHA WMS Basics Creating Feature Objects and Mapping their Attributes to the 2D Grid
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Developing a GSSHA Model Using the Hydrologic Modeling Wizard in WMS Learn how to setup a basic GSSHA model using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Developing a GSSHA Model Using the Hydrologic Modeling Wizard in WMS Learn how to setup a basic GSSHA model using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives
Multi-Stage Outlet Structures
 Methods in Stormwater Management Using HydroCAD Multi-Stage Outlet Structures H09 Multi-Stage Outlet Structures.pdf 1 Topics 1. Multi-State Outlet Structures Definition 2. Orifice and Weir Equations 3.
Methods in Stormwater Management Using HydroCAD Multi-Stage Outlet Structures H09 Multi-Stage Outlet Structures.pdf 1 Topics 1. Multi-State Outlet Structures Definition 2. Orifice and Weir Equations 3.
Linear Routing: Floodrouting. HEC-RAS Introduction. Brays Bayou. Uniform Open Channel Flow. v = 1 n R2/3. S S.I. units
 Linear Routing: Floodrouting HEC-RAS Introduction Shirley Clark Penn State Harrisburg Robert Pitt University of Alabama April 26, 2004 Two (2) types of floodrouting of a hydrograph Linear Muskingum Reservoir
Linear Routing: Floodrouting HEC-RAS Introduction Shirley Clark Penn State Harrisburg Robert Pitt University of Alabama April 26, 2004 Two (2) types of floodrouting of a hydrograph Linear Muskingum Reservoir
WMS 10.0 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface Schematic Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface Schematic Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic Objectives This tutorial shows users how to define a basic MODRAT model using
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface Schematic Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic Objectives This tutorial shows users how to define a basic MODRAT model using
WMS 8.4 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface Schematic Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic
 v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface Schematic Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic Objectives This tutorial shows you how to define a basic MODRAT model using
v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface Schematic Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic Objectives This tutorial shows you how to define a basic MODRAT model using
25 Using Numerical Methods, GIS & Remote Sensing 1
 Module 6 (L22 L26): Use of Modern Techniques es in Watershed Management Applications of Geographical Information System and Remote Sensing in Watershed Management, Role of Decision Support System in Watershed
Module 6 (L22 L26): Use of Modern Techniques es in Watershed Management Applications of Geographical Information System and Remote Sensing in Watershed Management, Role of Decision Support System in Watershed
Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic
 v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic Objectives Learn how to define a basic MODRAT model using the hydrologic schematic tree in WMS by building a tree and defining
v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Build a MODRAT model by defining a hydrologic schematic Objectives Learn how to define a basic MODRAT model using the hydrologic schematic tree in WMS by building a tree and defining
PCSWMM 2002 RUNOFF Block PAT AVENUE Storm Drainage Design
 PCSWMM 2002 RUNOFF Block PAT AVENUE Storm Drainage Design A Hello World Example Prepared by Robert Pitt and Alex Maestre, Department of Civil Engineering, University of Alabama April 10, 2002 Introduction
PCSWMM 2002 RUNOFF Block PAT AVENUE Storm Drainage Design A Hello World Example Prepared by Robert Pitt and Alex Maestre, Department of Civil Engineering, University of Alabama April 10, 2002 Introduction
Modeling Detention Ponds Malaysian Example (v2009)
 Modeling Detention Ponds Malaysian Example (v2009) This tutorial demonstrates the usability of xpswmm and xpstorm for simulating detention basins in urban areas. This fictitious example includes the use
Modeling Detention Ponds Malaysian Example (v2009) This tutorial demonstrates the usability of xpswmm and xpstorm for simulating detention basins in urban areas. This fictitious example includes the use
Introduction to Bentley PondPack
 Introduction to Bentley PondPack CE 365K Hydraulic Engineering Design Prepared by Cassandra Fagan and David Maidment Spring 2015 Contents Goals of the Tutorial... 1 Procedure... 1 (1) Opening Bentley PondPack...
Introduction to Bentley PondPack CE 365K Hydraulic Engineering Design Prepared by Cassandra Fagan and David Maidment Spring 2015 Contents Goals of the Tutorial... 1 Procedure... 1 (1) Opening Bentley PondPack...
Appendix A - Design Charts and Nomographs
 Appendix A - Design Charts and Nomographs 4-22 Horry County Manual This Page Intentionally Left Blank Horry County Manual 4-23 4-24 Horry County Manual Horry County Manual 4-25 4-26 Horry County Manual
Appendix A - Design Charts and Nomographs 4-22 Horry County Manual This Page Intentionally Left Blank Horry County Manual 4-23 4-24 Horry County Manual Horry County Manual 4-25 4-26 Horry County Manual
OPEN CHANNEL HYDROLOGY AND DESIGN...
 SPALDING COUNTY, GEORGIA CHAPTER 5 5.0 OPEN CHANNEL HYDROLOGY AND DESIGN... 5-1 5.1 OVERVIEW... 5-1 5.1.1 INTRODUCTION... 5-1 5.1.2 OPEN CHANNEL TYPES... 5-1 5.2 SYMBOLS AND DEFINITIONS... 5-2 5.3 DESIGN
SPALDING COUNTY, GEORGIA CHAPTER 5 5.0 OPEN CHANNEL HYDROLOGY AND DESIGN... 5-1 5.1 OVERVIEW... 5-1 5.1.1 INTRODUCTION... 5-1 5.1.2 OPEN CHANNEL TYPES... 5-1 5.2 SYMBOLS AND DEFINITIONS... 5-2 5.3 DESIGN
Watershed Modeling Using Arc Hydro Tools. Geo HMS, and HEC-HMS
 South Dakota State University Open PRAIRIE: Open Public Research Access Institutional Repository and Information Exchange Civil and Environmental Engineering Faculty Publications Department of Civil and
South Dakota State University Open PRAIRIE: Open Public Research Access Institutional Repository and Information Exchange Civil and Environmental Engineering Faculty Publications Department of Civil and
Appendix H Drainage Ditch Design - Lab TABLE OF CONTENTS APPENDIX H... 2
 Appendix H Drainage Ditch Design - Lab TABLE OF CONTENTS APPENDIX H... 2 H.1 Ditch Design... 2 H.1.1 Introduction... 2 H.1.2 Link/Ditch Configuration... 2 H.2 Lab 19: Ditch Design... 3 H.2.1 Introduction...
Appendix H Drainage Ditch Design - Lab TABLE OF CONTENTS APPENDIX H... 2 H.1 Ditch Design... 2 H.1.1 Introduction... 2 H.1.2 Link/Ditch Configuration... 2 H.2 Lab 19: Ditch Design... 3 H.2.1 Introduction...
Volume 4. Carlson Hydrology 2007 Carlson Natural Regrade Carlson Software Inc.
 Carlson Software 2007 Volume 4 Carlson Hydrology 2007 Carlson Natural Regrade 2007 Carlson Software Inc. User s manual August 8, 2006 Contents Chapter 1. Hydrology Module 1 Surface Menu....................................
Carlson Software 2007 Volume 4 Carlson Hydrology 2007 Carlson Natural Regrade 2007 Carlson Software Inc. User s manual August 8, 2006 Contents Chapter 1. Hydrology Module 1 Surface Menu....................................
Culvert Studio User's Guide
 Culvert Studio User's Guide 2 Culvert Studio Table of Contents Foreword 0 Part I Introduction 5 1 Installing... and Activating 6 2 Getting... Updates 7 3 About... This Guide 7 Part II Overview 9 1 The
Culvert Studio User's Guide 2 Culvert Studio Table of Contents Foreword 0 Part I Introduction 5 1 Installing... and Activating 6 2 Getting... Updates 7 3 About... This Guide 7 Part II Overview 9 1 The
v. 8.4 Prerequisite Tutorials Watershed Modeling Advanced DEM Delineation Techniques Time minutes
 v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Modeling Orange County Rational Method GIS Learn how to define a rational method hydrologic model for Orange County (California) from GIS data Objectives This tutorial shows you
v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Modeling Orange County Rational Method GIS Learn how to define a rational method hydrologic model for Orange County (California) from GIS data Objectives This tutorial shows you
WinSLAMM v 10.2 User s Guide
 WinSLAMM v 10.2 User s Guide Batch Editor, Cost Analysis, pre Development Runoff Volume Calculation lationandand Creating a Model File from a Data File Batch Editor Running a Set of Files Batch Editor
WinSLAMM v 10.2 User s Guide Batch Editor, Cost Analysis, pre Development Runoff Volume Calculation lationandand Creating a Model File from a Data File Batch Editor Running a Set of Files Batch Editor
CHAPTER 7 FLOOD HYDRAULICS & HYDROLOGIC VIVEK VERMA
 CHAPTER 7 FLOOD HYDRAULICS & HYDROLOGIC VIVEK VERMA CONTENTS 1. Flow Classification 2. Chezy s and Manning Equation 3. Specific Energy 4. Surface Water Profiles 5. Hydraulic Jump 6. HEC-RAS 7. HEC-HMS
CHAPTER 7 FLOOD HYDRAULICS & HYDROLOGIC VIVEK VERMA CONTENTS 1. Flow Classification 2. Chezy s and Manning Equation 3. Specific Energy 4. Surface Water Profiles 5. Hydraulic Jump 6. HEC-RAS 7. HEC-HMS
Surveys and Maps for Drainage Design
 Surveys and Maps for Drainage Design SURVEY TYPES BENCH LEVEL Survey Used to determine the elevation of a point (1-D) PROFILE Survey Used to determine the elevations of a line (2-D) TOPOGRAPHIC Survey
Surveys and Maps for Drainage Design SURVEY TYPES BENCH LEVEL Survey Used to determine the elevation of a point (1-D) PROFILE Survey Used to determine the elevations of a line (2-D) TOPOGRAPHIC Survey
Volume 4 Carlson Hydrology 2007 Carlson Natural Regrade Carlson Software Inc.
 Carlson Software 2007 Volume 4 Carlson Hydrology 2007 Carlson Natural Regrade 2007 Carlson Software Inc. User s manual August 8, 2006 Contents Chapter 1. Hydrology Module 1 Surface Menu... 2 Overview...
Carlson Software 2007 Volume 4 Carlson Hydrology 2007 Carlson Natural Regrade 2007 Carlson Software Inc. User s manual August 8, 2006 Contents Chapter 1. Hydrology Module 1 Surface Menu... 2 Overview...
ENV3104 Hydraulics II 2017 Assignment 1. Gradually Varied Flow Profiles and Numerical Solution of the Kinematic Equations:
 ENV3104 Hydraulics II 2017 Assignment 1 Assignment 1 Gradually Varied Flow Profiles and Numerical Solution of the Kinematic Equations: Examiner: Jahangir Alam Due Date: 27 Apr 2017 Weighting: 1% Objectives
ENV3104 Hydraulics II 2017 Assignment 1 Assignment 1 Gradually Varied Flow Profiles and Numerical Solution of the Kinematic Equations: Examiner: Jahangir Alam Due Date: 27 Apr 2017 Weighting: 1% Objectives
This loads a preset standard set of data appropriate for Malaysian modeling projects.
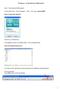 XP Software On-Site Detention (OSD) Example Step 1 Open xpswmm2010 program Or from Start menu select Programs XPS - then select xpswmm2010 Select Create From Template Save file, e.g. Filename.xp The program
XP Software On-Site Detention (OSD) Example Step 1 Open xpswmm2010 program Or from Start menu select Programs XPS - then select xpswmm2010 Select Create From Template Save file, e.g. Filename.xp The program
v Modeling Orange County Unit Hydrograph GIS Learn how to define a unit hydrograph model for Orange County (California) from GIS data
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Modeling Orange County Unit Hydrograph GIS Learn how to define a unit hydrograph model for Orange County (California) from GIS data Objectives This tutorial shows how to define
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Modeling Orange County Unit Hydrograph GIS Learn how to define a unit hydrograph model for Orange County (California) from GIS data Objectives This tutorial shows how to define
WMS 10.0 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HY-8 Modeling Wizard Learn how to model a culvert using HY-8 and WMS
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HY-8 Modeling Wizard Learn how to model a culvert using HY-8 and WMS Objectives Define a conceptual schematic of the roadway, invert, and downstream
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling HY-8 Modeling Wizard Learn how to model a culvert using HY-8 and WMS Objectives Define a conceptual schematic of the roadway, invert, and downstream
Watershed Modeling Advanced DEM Delineation
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Advanced DEM Delineation Techniques Model manmade and natural drainage features Objectives Learn to manipulate the default watershed boundaries by assigning
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Advanced DEM Delineation Techniques Model manmade and natural drainage features Objectives Learn to manipulate the default watershed boundaries by assigning
Background to Rock Roughness Equation
 Background to Rock Roughness Equation WATERWAY MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Photo 1 Rock-lined fish ramp Photo 2 Added culvert bed roughness Introduction Formulas such as the Strickler Equation have been commonly
Background to Rock Roughness Equation WATERWAY MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Photo 1 Rock-lined fish ramp Photo 2 Added culvert bed roughness Introduction Formulas such as the Strickler Equation have been commonly
Watershed Modeling Orange County Hydrology Using GIS Data
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Orange County Hydrology Using GIS Data Learn how to delineate sub-basins and compute soil losses for Orange County (California) hydrologic modeling Objectives
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Orange County Hydrology Using GIS Data Learn how to delineate sub-basins and compute soil losses for Orange County (California) hydrologic modeling Objectives
Hydrologic Modeling using HEC-HMS
 Hydrologic Modeling using HEC-HMS CE 412/512 Spring 2017 Introduction The intent of this exercise is to introduce you to the structure and some of the functions of the HEC-Hydrologic Modeling System (HEC-HMS),
Hydrologic Modeling using HEC-HMS CE 412/512 Spring 2017 Introduction The intent of this exercise is to introduce you to the structure and some of the functions of the HEC-Hydrologic Modeling System (HEC-HMS),
PACIFIC CENTER Anaheim, California
 HYDROLOGY REPORT PACIFIC CENTER Anaheim, California Prepared for Hines Company 4000 MacArthur Blvd. Suite 110 Newport Beach, CA 92660 949.313.2230 Prepared by Fuscoe Engineering, Inc. 16795 Von Karman,
HYDROLOGY REPORT PACIFIC CENTER Anaheim, California Prepared for Hines Company 4000 MacArthur Blvd. Suite 110 Newport Beach, CA 92660 949.313.2230 Prepared by Fuscoe Engineering, Inc. 16795 Von Karman,
Spatial Hydrologic Modeling HEC-HMS Distributed Parameter Modeling with the MODClark Transform
 v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial Spatial Hydrologic Modeling HEC-HMS Distributed Parameter Modeling with the MODClark Transform Setup a basic distributed MODClark model using the WMS interface Objectives In this
v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial Spatial Hydrologic Modeling HEC-HMS Distributed Parameter Modeling with the MODClark Transform Setup a basic distributed MODClark model using the WMS interface Objectives In this
Watershed Modeling Using Online Spatial Data to Create an HEC-HMS Model
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Using Online Spatial Data to Create an HEC-HMS Model Learn how to setup an HEC-HMS model using WMS online spatial data Objectives This tutorial shows how to
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Using Online Spatial Data to Create an HEC-HMS Model Learn how to setup an HEC-HMS model using WMS online spatial data Objectives This tutorial shows how to
Module 9. Lecture 3: Major hydrologic models-hspf, HEC and MIKE
 Lecture 3: Major hydrologic models-hspf, HEC and MIKE Major Hydrologic Models HSPF (SWM) HEC MIKE Hydrological Simulation Program-Fortran (HSPF) Commercial successor of the Stanford Watershed Model (SWM-IV)
Lecture 3: Major hydrologic models-hspf, HEC and MIKE Major Hydrologic Models HSPF (SWM) HEC MIKE Hydrological Simulation Program-Fortran (HSPF) Commercial successor of the Stanford Watershed Model (SWM-IV)
Appendix C.6. Best Management Practices for Construction Activities
 Appendix C.6 Best Management Practices for Construction Activities In accordance with Section F.2 of San Diego Regional Water Quality Control Board (RWQCB) Order 2001-01 (Permit), the City of La Mesa has
Appendix C.6 Best Management Practices for Construction Activities In accordance with Section F.2 of San Diego Regional Water Quality Control Board (RWQCB) Order 2001-01 (Permit), the City of La Mesa has
VDOT GEOPAK Drainage Training Manual
 VDOT GEOPAK Drainage Training Manual Training Manual 2004 Edition TRN007630-1/0002 Trademarks AccuDraw, Bentley, the B Bentley logo, MDL, MicroStation and SmartLine are registered trademarks; PopSet and
VDOT GEOPAK Drainage Training Manual Training Manual 2004 Edition TRN007630-1/0002 Trademarks AccuDraw, Bentley, the B Bentley logo, MDL, MicroStation and SmartLine are registered trademarks; PopSet and
WMS 9.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Stream Flow Integrate stream flow with your GSSHA overland flow model
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Integrate stream flow with your GSSHA overland flow model Objectives Learn how to add hydraulic channel routing to your GSSHA model and how to define channel properties. Learn how
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Integrate stream flow with your GSSHA overland flow model Objectives Learn how to add hydraulic channel routing to your GSSHA model and how to define channel properties. Learn how
Soil Map Adams County Area, Parts of Adams and Denver Counties, Colorado ' 39''
 Soil Map Adams County Area, Parts of Adams and Denver Counties, Colorado 4411660 4411670 4411680 4411690 4411700 4411710 4411720 4411730 104 58' 39'' W 4411660 4411670 4411680 4411690 4411700 4411710 4411720
Soil Map Adams County Area, Parts of Adams and Denver Counties, Colorado 4411660 4411670 4411680 4411690 4411700 4411710 4411720 4411730 104 58' 39'' W 4411660 4411670 4411680 4411690 4411700 4411710 4411720
DESCRIPTION SITE SUITABILITY. Advantages. Disadvantages. Alternative Names: Fiber Roll Barriers, Sediment Log, Coir Roll and Coir Log
 4.5-q FIBER ROLL Alternative Names: Fiber Roll Barriers, Sediment Log, Coir Roll and Coir Log DESCRIPTION Fiber rolls are sediment control devices made from fibrous organic material, such as rice or coconut
4.5-q FIBER ROLL Alternative Names: Fiber Roll Barriers, Sediment Log, Coir Roll and Coir Log DESCRIPTION Fiber rolls are sediment control devices made from fibrous organic material, such as rice or coconut
MODRET VERSION 6.0 FOR WINDOWS 95. Setup Hydrograph Infiltration Routing Graphic Windows ReadMe
 MODRET VERSION 6.0 FOR WINDOWS 95 EXPLANATIONS FOR MENU COMMAND OPTIONS FIRST SCREEN PROMPT Setup Hydrograph Infiltration Routing Graphic Windows ReadMe Select one of these options using the mouse and
MODRET VERSION 6.0 FOR WINDOWS 95 EXPLANATIONS FOR MENU COMMAND OPTIONS FIRST SCREEN PROMPT Setup Hydrograph Infiltration Routing Graphic Windows ReadMe Select one of these options using the mouse and
Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Pump Station
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Pump Station Analysis Setup a simple HY-12 pump station storm drain model in the WMS interface with pump and pipe information Objectives Using the HY-12
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Pump Station Analysis Setup a simple HY-12 pump station storm drain model in the WMS interface with pump and pipe information Objectives Using the HY-12
Automatic Discretization and Parameterization of Watersheds using a Digital Elevation Model
 Automatic Discretization and Parameterization of Watersheds using a Digital Elevation Model Ellen Hachborn, Karen Finney, Rob James, Nandana Perera, Tiehong Xiao WaterTech 2017 Computational Hydraulics
Automatic Discretization and Parameterization of Watersheds using a Digital Elevation Model Ellen Hachborn, Karen Finney, Rob James, Nandana Perera, Tiehong Xiao WaterTech 2017 Computational Hydraulics
Gavin Fields Senior Water Resources Engineer XP Solutions
 Hydraulics 101 Gavin Fields Senior Water Resources Engineer XP Solutions Hydraulics 101 Introduction Structures Hydraulic Model Building Q&A XP Solutions Software for modeling wastewater, stormwater, and
Hydraulics 101 Gavin Fields Senior Water Resources Engineer XP Solutions Hydraulics 101 Introduction Structures Hydraulic Model Building Q&A XP Solutions Software for modeling wastewater, stormwater, and
Bentley OpenRoads Workshop 2017 FLUG Fall Training Event
 Bentley OpenRoads Workshop 2017 FLUG Fall Training Event F-1P - Designing with a Pond Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com Practice Workbook This workbook is
Bentley OpenRoads Workshop 2017 FLUG Fall Training Event F-1P - Designing with a Pond Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com Practice Workbook This workbook is
SurvCADD Hydrology Module
 SurvCADD Hydrology Module Overview The Hydrology Module consists of several routines that work together in sequence. This manual only explains the operation of the commands and not hydrology concepts.
SurvCADD Hydrology Module Overview The Hydrology Module consists of several routines that work together in sequence. This manual only explains the operation of the commands and not hydrology concepts.
Questions and Answers
 Autodesk Storm and Sanitary Analysis Extension 2011 Questions and Answers Design stormwater and wastewater systems more effectively with integrated analysis. Contents 1. GENERAL PRODUCT INFORMATION...
Autodesk Storm and Sanitary Analysis Extension 2011 Questions and Answers Design stormwater and wastewater systems more effectively with integrated analysis. Contents 1. GENERAL PRODUCT INFORMATION...
Watershed Modeling Maricopa County: Master Plan Creating a Predictive HEC-1 Model
 v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Maricopa County: Master Plan Creating a Predictive HEC-1 Model Build a watershed model to predict hydrologic reactions based on land use development in Maricopa
v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Maricopa County: Master Plan Creating a Predictive HEC-1 Model Build a watershed model to predict hydrologic reactions based on land use development in Maricopa
Hysteresis in River Discharge Rating Curves. Histerésis en las curvas de gasto en ríos (caudal/calado) Madrid, March 25, 2013
 Hysteresis in River Discharge Rating Curves Histerésis en las curvas de gasto en ríos (caudal/calado) Madrid, March 25, 2013 Marian Muste and Kyutae Lee IIHR Hydroscience & Engineering The University of
Hysteresis in River Discharge Rating Curves Histerésis en las curvas de gasto en ríos (caudal/calado) Madrid, March 25, 2013 Marian Muste and Kyutae Lee IIHR Hydroscience & Engineering The University of
Flood Routing for Continuous Simulation Models
 Improving Life through Science and Technology Flood Routing for Continuous Simulation Models J. Williams, W. Merkel, J. Arnold, J. Jeong 11 International SWAT Conference, Toledo, Spain, June 15-17, 11
Improving Life through Science and Technology Flood Routing for Continuous Simulation Models J. Williams, W. Merkel, J. Arnold, J. Jeong 11 International SWAT Conference, Toledo, Spain, June 15-17, 11
Watershed Modeling Maricopa Predictive HEC-1 Model. Watershed Modeling Maricopa County: Master Plan Creating a Predictive HEC-1 Model
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Maricopa County: Master Plan Creating a Predictive HEC-1 Model Build a watershed model to predict hydrologic reactions based on land use development in Maricopa
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Maricopa County: Master Plan Creating a Predictive HEC-1 Model Build a watershed model to predict hydrologic reactions based on land use development in Maricopa
Spatial Hydrologic Modeling Using NEXRAD Rainfall Data in an HEC-HMS (MODClark) Model
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Spatial Hydrologic Modeling Using NEXRAD Rainfall Data in an HEC-HMS (MODClark) Model Learn how to setup a MODClark model using distributed rainfall data Objectives Read an existing
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Spatial Hydrologic Modeling Using NEXRAD Rainfall Data in an HEC-HMS (MODClark) Model Learn how to setup a MODClark model using distributed rainfall data Objectives Read an existing
Peak Stormwater Engineering, LLC MEMORANDUM
 Peak Stormwater Engineering, LLC 922 Cypress Lane, Louisville, CO 80027 Tel: (720) 239-1151 Fax: (720) 239-1191 Email: drapp@peakstormwater.com MEMORANDUM Date: To: Holly Piza, UDFCD Ken MacKenzie, UDFCD
Peak Stormwater Engineering, LLC 922 Cypress Lane, Louisville, CO 80027 Tel: (720) 239-1151 Fax: (720) 239-1191 Email: drapp@peakstormwater.com MEMORANDUM Date: To: Holly Piza, UDFCD Ken MacKenzie, UDFCD
2D Large Scale Automated Engineering for FEMA Floodplain Development in South Dakota. Eli Gruber, PE Brooke Conner, PE
 2D Large Scale Automated Engineering for FEMA Floodplain Development in South Dakota Eli Gruber, PE Brooke Conner, PE Project Acknowledgments FEMA Region 8 Staff: Brooke Conner, PE Casey Zuzak, GISP Ryan
2D Large Scale Automated Engineering for FEMA Floodplain Development in South Dakota Eli Gruber, PE Brooke Conner, PE Project Acknowledgments FEMA Region 8 Staff: Brooke Conner, PE Casey Zuzak, GISP Ryan
Required: 486DX-33, 8MB RAM, HDD w. 20 MB free, VGA, Win95. Recommended: Pentium 60, 16 MB RAM, SVGA, Win95 or NT
 Evaluation Form Evaluator Information Name: Jeff Hagan Date: Feb. 17, 2000 Software Information Title of Software: Purpose: Publisher: CulvertMaster Culvert Hydraulic Design Haestad Methods, Inc. Version:
Evaluation Form Evaluator Information Name: Jeff Hagan Date: Feb. 17, 2000 Software Information Title of Software: Purpose: Publisher: CulvertMaster Culvert Hydraulic Design Haestad Methods, Inc. Version:
Tutorial 6 - Subdivision - Pre Development
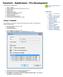 Tutorial 6 - Subdivision - Pre Development In this tutorial, you will learn about: 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 2. Using a Template Adding a Background Image and Using the Zoom Tool Creating Nodes Creating
Tutorial 6 - Subdivision - Pre Development In this tutorial, you will learn about: 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 2. Using a Template Adding a Background Image and Using the Zoom Tool Creating Nodes Creating
Lesson 7: Gathering Stand-Level Information
 Lesson 7: Gathering Stand-Level Information Review and Introduction In previous lessons, you learned how to establish and take measurements in sample plots. Now we will begin to transition toward using
Lesson 7: Gathering Stand-Level Information Review and Introduction In previous lessons, you learned how to establish and take measurements in sample plots. Now we will begin to transition toward using
On Automatic Calibration of the SWMM Model
 On Automatic Calibration of the SWMM Model Van-Thanh-Van Nguyen, Hamed Javaheri and Shie-Yui Liong Conceptual urban runoff (CUR) models, such as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Storm Water Management
On Automatic Calibration of the SWMM Model Van-Thanh-Van Nguyen, Hamed Javaheri and Shie-Yui Liong Conceptual urban runoff (CUR) models, such as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Storm Water Management
WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Post-Processing and Visualization of GSSHA Model Results Learn how to visualize GSSHA model results
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Post-Processing and Visualization of GSSHA Model Results Learn how to visualize GSSHA model results Objectives This tutorial demonstrates different ways
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Post-Processing and Visualization of GSSHA Model Results Learn how to visualize GSSHA model results Objectives This tutorial demonstrates different ways
URBAN & RURAL RUNOFF ROUTING APPLICATION GETTING STARTED MANUAL
 URBAN & RURAL RUNOFF ROUTING APPLICATION GETTING STARTED MANUAL Copyright 2013 XP Solutions. All right reserved. No part of this publication maybe reproduced in any form by any means without the written
URBAN & RURAL RUNOFF ROUTING APPLICATION GETTING STARTED MANUAL Copyright 2013 XP Solutions. All right reserved. No part of this publication maybe reproduced in any form by any means without the written
Benefits of 2D Modeling for Urban Stormwater Master Planning Niles, Illinois
 Benefits of 2D Modeling for Urban Stormwater Master Planning Niles, Illinois Patrick Lach, P.E., CFM, Hey and Associates, Inc. Steve Vinezeano, ICMA CM, LEED AP Assistant Village Manager Three Geographic
Benefits of 2D Modeling for Urban Stormwater Master Planning Niles, Illinois Patrick Lach, P.E., CFM, Hey and Associates, Inc. Steve Vinezeano, ICMA CM, LEED AP Assistant Village Manager Three Geographic
EFH2 Computer Program Estimating Runoff and Peak Discharge. User s Manual August Photo credit NRCSIA99447
 EFH2 Computer Program Estimating Runoff and Peak Discharge User s Manual Photo credit NRCSIA99447 The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) prohibits discrimination in all its programs and activities on
EFH2 Computer Program Estimating Runoff and Peak Discharge User s Manual Photo credit NRCSIA99447 The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) prohibits discrimination in all its programs and activities on
HEC-22 Inlets in INFOSWMM and H2OMAP SWMM v12
 HEC-22 Inlets in INFOSWMM and H2OMAP SWMM v12 Table of Contents How the Inlet and Overland Junctions are Defined 3 Why Would You Use the HEC-22 Inlets Option? 4 Types of Inlets 5 Nodes in InfoSWMM and
HEC-22 Inlets in INFOSWMM and H2OMAP SWMM v12 Table of Contents How the Inlet and Overland Junctions are Defined 3 Why Would You Use the HEC-22 Inlets Option? 4 Types of Inlets 5 Nodes in InfoSWMM and
HECRAS 2D: Are you ready for the revolution in the world of hydraulic modeling?
 HECRAS 2D: Are you ready for the revolution in the world of hydraulic modeling? Rishab Mahajan, Emily Campbell and Matt Bardol March 8, 2017 Outline Reasons for hydraulic modeling 1D Modeling 2D Modeling-
HECRAS 2D: Are you ready for the revolution in the world of hydraulic modeling? Rishab Mahajan, Emily Campbell and Matt Bardol March 8, 2017 Outline Reasons for hydraulic modeling 1D Modeling 2D Modeling-
Prof. B.S. Thandaveswara. The computation of a flood wave resulting from a dam break basically involves two
 41.4 Routing The computation of a flood wave resulting from a dam break basically involves two problems, which may be considered jointly or seperately: 1. Determination of the outflow hydrograph from the
41.4 Routing The computation of a flood wave resulting from a dam break basically involves two problems, which may be considered jointly or seperately: 1. Determination of the outflow hydrograph from the
PCSWMM 2002 EXTRAN Block PAT AVENUE Storm Drainage Design
 PCSWMM 2002 EXTRAN Block PAT AVENUE Storm Drainage Design A Hello World Example Prepared by Dr. Robert Pitt and Jason Kirby, Department of Civil Engineering, University of Alabama August 20, 2002 Introduction
PCSWMM 2002 EXTRAN Block PAT AVENUE Storm Drainage Design A Hello World Example Prepared by Dr. Robert Pitt and Jason Kirby, Department of Civil Engineering, University of Alabama August 20, 2002 Introduction
George Mason University Department of Civil, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering
 George Mason University Department of Civil, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering Dr. Celso Ferreira Prepared by Lora Baumgartner December 2015 Revised by Brian Ross July 2016 Exercise Topic: Getting
George Mason University Department of Civil, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering Dr. Celso Ferreira Prepared by Lora Baumgartner December 2015 Revised by Brian Ross July 2016 Exercise Topic: Getting
INPUT DATA PROCEDURES
 79 SECTION 7 INPUT DATA PROCEDURES This section describes the forms and message boxes used to enter input data for an RSRAP optimization problem. These forms and message boxes implement Steps 1 through
79 SECTION 7 INPUT DATA PROCEDURES This section describes the forms and message boxes used to enter input data for an RSRAP optimization problem. These forms and message boxes implement Steps 1 through
WMS 9.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Post-Processing and Visualization of GSSHA Model Results Learn how to visualize GSSHA model results
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Post-Processing and Visualization of GSSHA Model Results Learn how to visualize GSSHA model results Objectives This tutorial demonstrates different ways of
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Post-Processing and Visualization of GSSHA Model Results Learn how to visualize GSSHA model results Objectives This tutorial demonstrates different ways of
Introduction to Compound Channel Flow Analysis for Floodplains
 Introduction to Compound Channel Flow Analysis for Floodplains by Kelly McAtee, P.E., LEED A.P. Course Summary Natural and restored waterways do not usually posses the typical cross-sectional areas undergraduate
Introduction to Compound Channel Flow Analysis for Floodplains by Kelly McAtee, P.E., LEED A.P. Course Summary Natural and restored waterways do not usually posses the typical cross-sectional areas undergraduate
Automated Calibration of the GSSHA Watershed Model: A Look at Accuracy and Viability for Routine Hydrologic Modeling
 Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2009-11-23 Automated Calibration of the GSSHA Watershed Model: A Look at Accuracy and Viability for Routine Hydrologic Modeling
Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2009-11-23 Automated Calibration of the GSSHA Watershed Model: A Look at Accuracy and Viability for Routine Hydrologic Modeling
Introduction to GISHydroNXT. GIS Based Hydrologic Analysis in Maryland gishydro.eng.umd.edu
 Introduction to GISHydroNXT GIS Based Hydrologic Analysis in Maryland gishydro.eng.umd.edu Training Manual 4th Edition August 2018 Dr. Kaye L. Brubaker Associate Professor Department of Civil and Environmental
Introduction to GISHydroNXT GIS Based Hydrologic Analysis in Maryland gishydro.eng.umd.edu Training Manual 4th Edition August 2018 Dr. Kaye L. Brubaker Associate Professor Department of Civil and Environmental
Objectives Read a delineated watershed and setup and run an HSPF model for the watershed.
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Setup a basic HSPF model Objectives Read a delineated watershed and setup and run an HSPF model for the watershed. Prerequisite Tutorials Watershed Modeling DEM Delineation Watershed
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Setup a basic HSPF model Objectives Read a delineated watershed and setup and run an HSPF model for the watershed. Prerequisite Tutorials Watershed Modeling DEM Delineation Watershed
Faculty of Engineering. Irrigation & Hydraulics Department Excel Tutorial (1)
 Problem Statement: Excel Tutorial (1) Create an Excel spread sheet that can calculate the flow area A, wetted perimeter P, hydraulic radius R, top water surface width B, and hydraulic depth D for the following
Problem Statement: Excel Tutorial (1) Create an Excel spread sheet that can calculate the flow area A, wetted perimeter P, hydraulic radius R, top water surface width B, and hydraulic depth D for the following
2-D Hydraulic Modeling Theory & Practice
 2-D Hydraulic Modeling Theory & Practice Author: Maged A. Aboelata, PhD, PE, CFM Presenter: Heather Zhao, PE, CFM October 2017 Presentation Outline * 1-D vs. 2-D modeling * Theory of 2-D simulation * Commonly
2-D Hydraulic Modeling Theory & Practice Author: Maged A. Aboelata, PhD, PE, CFM Presenter: Heather Zhao, PE, CFM October 2017 Presentation Outline * 1-D vs. 2-D modeling * Theory of 2-D simulation * Commonly
AutoCAD Civil 3D 2010 Education Curriculum Instructor Guide Unit 4: Environmental Design
 AutoCAD Civil 3D 2010 Education Curriculum Instructor Guide Unit 4: Environmental Design Lesson 2 Watershed Analysis Overview In this lesson, you learn about how AutoCAD Civil 3D software is used to analyze
AutoCAD Civil 3D 2010 Education Curriculum Instructor Guide Unit 4: Environmental Design Lesson 2 Watershed Analysis Overview In this lesson, you learn about how AutoCAD Civil 3D software is used to analyze
SiphoniTec. User s Guide
 SiphoniTec A Siphonic Roof Drainage Design Utility The Level Approach to Roof Drainage User s Guide Release 2.0 RAINWATER MANAGEMENT SOLUTIONS 1260 West Riverside Drive Salem, Virginia 24153 Telephone:
SiphoniTec A Siphonic Roof Drainage Design Utility The Level Approach to Roof Drainage User s Guide Release 2.0 RAINWATER MANAGEMENT SOLUTIONS 1260 West Riverside Drive Salem, Virginia 24153 Telephone:
Bentleyuser.dk Årsmøde 2009 Nordic Civil 2009
 Bentleyuser.dk Årsmøde 2009 Nordic Civil 2009 9.-11. November 2009, Munkebjerg Hotel, Vejle Workshop - X3 Using InRoads Storm & Sanitary V8i Presenter: Robert Nice, Solutions Engineer, Bentley Systems
Bentleyuser.dk Årsmøde 2009 Nordic Civil 2009 9.-11. November 2009, Munkebjerg Hotel, Vejle Workshop - X3 Using InRoads Storm & Sanitary V8i Presenter: Robert Nice, Solutions Engineer, Bentley Systems
Cloud-Computing Based Real-Time Flood Simulation (RealFlood Engine)
 Cloud-Computing Based Real-Time Flood Simulation (RealFlood Engine) Jennifer G Duan, PhD., PE Principal, KKC Engineering (UA Tech Launch) Associate Professor Delbert R. Lewis Distinguished Professor Civil
Cloud-Computing Based Real-Time Flood Simulation (RealFlood Engine) Jennifer G Duan, PhD., PE Principal, KKC Engineering (UA Tech Launch) Associate Professor Delbert R. Lewis Distinguished Professor Civil
2D Model Implementation for Complex Floodplain Studies. Sam Crampton, P.E., CFM Dewberry
 2D Model Implementation for Complex Floodplain Studies Sam Crampton, P.E., CFM Dewberry 2D Case Studies Case Study 1 Rain-on-Grid 2D floodplain simulation for unconfined flat topography in coastal plain
2D Model Implementation for Complex Floodplain Studies Sam Crampton, P.E., CFM Dewberry 2D Case Studies Case Study 1 Rain-on-Grid 2D floodplain simulation for unconfined flat topography in coastal plain
JCE 4600 Fundamentals of Traffic Engineering. Horizontal and Vertical Curves
 JCE 4600 Fundamentals of Traffic Engineering Horizontal and Vertical Curves Agenda Horizontal Curves Vertical Curves Passing Sight Distance 1 Roadway Design Motivations Vehicle performance Acceleration
JCE 4600 Fundamentals of Traffic Engineering Horizontal and Vertical Curves Agenda Horizontal Curves Vertical Curves Passing Sight Distance 1 Roadway Design Motivations Vehicle performance Acceleration
Precalculus 2 Section 10.6 Parametric Equations
 Precalculus 2 Section 10.6 Parametric Equations Parametric Equations Write parametric equations. Graph parametric equations. Determine an equivalent rectangular equation for parametric equations. Determine
Precalculus 2 Section 10.6 Parametric Equations Parametric Equations Write parametric equations. Graph parametric equations. Determine an equivalent rectangular equation for parametric equations. Determine
Applicant Type (Conditional Use Permit, Variance, Tract Map, etc.): Applicant: Address: Phone(s): Fax:
 ENVIRONMENTAL QUESTIONNAIRE City of Twentynine Palms Community Development Department 6136 Adobe Road Twentynine Palms, CA 92277 (760) 367-6799 Fax (760) 367-5400 29palms.org : Please complete each statement
ENVIRONMENTAL QUESTIONNAIRE City of Twentynine Palms Community Development Department 6136 Adobe Road Twentynine Palms, CA 92277 (760) 367-6799 Fax (760) 367-5400 29palms.org : Please complete each statement
