The portable Finnish Geodetic Institute Field Goniospectrometer. Maria Gritsevich, Jouni Peltoniemi, Teemu Hakala and Juha Suomalainen
|
|
|
- Kevin Matthews
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The portable Finnish Geodetic Institute Field Goniospectrometer Maria Gritsevich, Jouni Peltoniemi, Teemu Hakala and Juha Suomalainen
2 Finnish Geodetic Institute Governmental research institute scientific basis for Finnish maps and geospatial information research on methods for the measurements, data acquisition, processing and exploiting of geospatial information Departments: Geodesy and Geodynamics, Remote Sensing and Photogrammetry, Geoinformatics and Cartography, Navigation and Positioning 2
3 Dep. Remote Sensing and Photogrammetry Spectrophotogrammetry Photogrammetry, BRF, spectrometry, test fields, optical UAV systems ActiveSensing Lidar and SAR, physics and their integration, map updating, environmental applications Mobile Mapping Mobile mapping HW, Sensor technology, methods, virtual reality, intelligent environment, precision forestry
4 Measurement and Analysis of Bidirectional Reflectances
5 Reflectance factor Radiance from target divided by radiance from white matte (Lambertian) surface 0 for black surface 1 for white diffuse surface (Lambertian) The most typical reference material is Spectralon
6 Lambertian surfaces 600 nm An ideal surface that is perfectly matte scatters same amount of light to all view directions is not affected by illumination direction Do not exist in real life All surfaces are more or less anisotropic scatterers Not even Spectralon is Lambertian.. Sandmeier et al., RSE, 64, (1998)
7 Bidirectional Reflectance Factor Anisotropy of reflectance is described with concept Bidirectional Reflectance Factor (BRF) Bidirectional geometry is defined by illumination and view directions zenith angle azimuth angle
8 EXAMPLES OF BRF/HDRF
9 Snow (Sodankylä) Melting snow with wet surface layer Forward scatterer Nadir Reflectance Wavelength / nm
10 Dwarf birch (Abisko) A thick layer at the top of a mountain Concave shaped HDRF Nadir Reflectance Wavelength / nm
11 Lichen 550 nm 850 nm
12 MEASURING BIDIRECTIONAL REFLECTANCE FACTOR
13 How to measure BRF? All reflectance factors have some illumination and view geometry Thus we need to measure reflectance from multiple directions while registering of illumination and view geometry Goniometer devices have been built to solve this task
14 Some large scale goniometers A.EGO B.FIGOS C.MUFSPEM D.Sandmeier Field Goniometer E.PARABOLA III
15 FGI goniometer model III
16 Model III goniometer A fine instrument, but Heavy limited only to road access sites Large needed a trailer, not suitable for rough ground Manual use slow prone for human errors Laboursome 3 busy operators
17 FIGIFIGO FGI s Field Goniospectrometer Primary targets: Vegetation and snow Extra Applications: Planetary science (e.g. meteorite measurements and their matches with asteroids)
18 The active optics system is located horizontally at the top of the measuring arm, and is looking down to the target through a mirror. FIGIFIGO consists of the following main components: casing, measurement arm, rugged computer, and a sunphotometer on a tripod. The casing contains the main sensor ASD FieldSpec Pro FR optical fiber spectroradiometer ( nm), most of the electronics, and batteries. 18
19 Left: Newport Rotation stage with the polarizing optics. Right: Spectralon reference panel 19
20 FIGIFIGO Key features Automated zenith turn Manual azimuth turn ASD FieldSpec Pro FR nm Changeable optics Field of view 5-25 cm Option: Computer turned linearly polarizing optics
21 Portability Battery powered Quick to assemble 30 kg Fits inside an estate car A rugged control computer
22 The optical construct of the old polarizing optics The leftmost is the surface of the optical fiber, next is depolarizer, polarizer and f 75 mm D 25.4 mm lens. The units of the axis are in millimetres. Different colored lines represent beams hitting different areas of the fiber optic bundle 22
23 The optical construct of the new polarizing optics The leftmost is the optical fiber, next is f 15 mm D 12.7 mm lens, depolarizer, polarizer and f 60 mm D 25.4 mm lens. The units of the axis are in millimeters. Different colored lines represent beams hitting different areas of the fiber optic bundle. 23
24 Attenuation of light intensity for old and new polarizing optics The graph is the signal measured through each optics set divided by the signal from bare fiber. The signal is dropping around 2200 nm because the Glan Thompson polarizer has transmission range of only nm. The signal to noise ratio of the detector is poor at the very ends of the measurement range, and thus the data there is mostly noise. The clearly visible steps at sensor borders might be because of the different locations of the fibers in the fiber bundle leading to different sensors
25 The laboratory lighting setup The light source and the off axis parabolic mirror are mounted in same frame to keep the geometry constant. A large flat mirror is placed on a heavy tripod, and is used to reflect the light to the sample
26 The laboratory lighting setup 26
27 Problem: Non-constant illumination The intensity and the spectrum of the incident irradiance varies over time A hemisphere of BRF measurements may take up to 20 minutes In that time sun has moved ~5 degrees Even thin, practically invisible, clouds affect the irradiance
28 Answer: Record the changes in your data Work only on clear sky days Measure white reference often Measure white reference before and after the target and interpolate Use a sun photometer to record illumination and scale each spectrum with that Use a second spectrometer if possible
29 Problem: How to determine view direction? In sunlight measurements it is necessary to determine goniometer orientation An electronic compass is a plausible solution, but accuracy is at best 2 and it is vulnerable to magnetic disturbances Dual-antenna GPS would be an ideal solution, but currently they are large and expensive
30 Answer: A hemispherical sky camera All the measurements are taken in direct sunlight Sun position can be calculated using GPS data A hemispherical sky camera is mounted on the goniometer body Sun is detected from the image and with assistance from an inclinometer the orientation is calculated + we get automated cloud/sky images
31 Problem: spectrometer footprint position On heterogenous surfaces, the spectrometer footprint should be held constant in order to produce consistent BRF Two major error sources Rotation of a goniometer Elevation of the sample
32 Answer: laser pointer & active optics Spectrometer optics have laser pointers to show the footprint position Sample elevation is entered and a servo controlled mirror adjusts the footprint according to tilt
33 Problem: Representativeness of the sampling The BRF measurement is usually taken from a small area, ~15cm in diameter It is too slow to repeat measurements in tens of spots
34 Answer: Use traditional field spectroscopy for support Take a spectrometer and measure tens of reflectances around the area Scale the BRF with mean reflectance spectrum Repeat principal plane BRF measurement in a few places Most distinct BRF effect are seen on principal plane
35 Tips for succesfull measurements Always take tea/coffee/candy/sandwiches with you Hungry/cold/bored operators produce low quality results Wear sunglasses You need to watch for clouds and stare at the Sun Take your time to observe the target Natural samples always have more details and properties than you might imagine
36 BRF retrieval accuracy The general accuracy of FIGIFIGO BRF measurement is between 1-5% for a well defined sample Accuracy depends especially on wavelength, sample reflectance factor, and solar zenith angle Spectrometer noise causes error that is proportional to reflected radiance Levelling of Spectralon panel
37 Level your Spectralon! If a Spectralon panel is tilted even slightly towards the Sun, the panel will receive and reflect significantly more light and spoil the reference E.g. at 60 solar zenith angle the panel is tilted only 1, the reflectance factor will have an error of 3% A panel held on hand can easily be tilted 5 degrees, one must use a bubble level
38 FGI reflectance library Currently the library contains BRF/HDRF measurements of over 150 samples A pdf datasheet is produced from each library file Shows contents of the file Describes the reflectance properties of the sample The library files can be opened using e.g. Matlab or IDL tools A toolbox is available: FGI Reflectance toolbox for Matlab
39 Conclusions / Take home messages Polarised Multiangular Reflectance Measurements Using FGI's Goniospectrometer are possible Reflectance factor is a function of both view and illumination angle BRF/HDRF effects are source of errors if ignored, but also a valuable source of information If you want to have accurate measurement results Take Spectralon reflectance in to account Always level your Spectralon panel with a bubble level
40 THANK YOU 40
41 The field of view test results for nonpolarizing optics The x and y axes display the displacement of each axes in degrees from the center. Z axis represents the normalized intensity values in that direction. The plot is for each individual sensor and total is the combination of all of the sensors.
Radiance, Irradiance and Reflectance
 CEE 6100 Remote Sensing Fundamentals 1 Radiance, Irradiance and Reflectance When making field optical measurements we are generally interested in reflectance, a relative measurement. At a minimum, measurements
CEE 6100 Remote Sensing Fundamentals 1 Radiance, Irradiance and Reflectance When making field optical measurements we are generally interested in reflectance, a relative measurement. At a minimum, measurements
Class 11 Introduction to Surface BRDF and Atmospheric Scattering. Class 12/13 - Measurements of Surface BRDF and Atmospheric Scattering
 University of Maryland Baltimore County - UMBC Phys650 - Special Topics in Experimental Atmospheric Physics (Spring 2009) J. V. Martins and M. H. Tabacniks http://userpages.umbc.edu/~martins/phys650/ Class
University of Maryland Baltimore County - UMBC Phys650 - Special Topics in Experimental Atmospheric Physics (Spring 2009) J. V. Martins and M. H. Tabacniks http://userpages.umbc.edu/~martins/phys650/ Class
Scattering measurements. Guidelines for measurements service
 Scattering measurements Guidelines for measurements service 1 Content Introduction Light Tec Presentation Instruments availalable. Scattering measurements Refelctors Diffusers Colors issuses Volume Scattering
Scattering measurements Guidelines for measurements service 1 Content Introduction Light Tec Presentation Instruments availalable. Scattering measurements Refelctors Diffusers Colors issuses Volume Scattering
ENY-C2005 Geoinformation in Environmental Modeling Lecture 4b: Laser scanning
 1 ENY-C2005 Geoinformation in Environmental Modeling Lecture 4b: Laser scanning Petri Rönnholm Aalto University 2 Learning objectives To recognize applications of laser scanning To understand principles
1 ENY-C2005 Geoinformation in Environmental Modeling Lecture 4b: Laser scanning Petri Rönnholm Aalto University 2 Learning objectives To recognize applications of laser scanning To understand principles
Snow cover change detection with laser scanning range and brightness measurements
 Snow cover change detection with laser scanning range and brightness measurements Sanna Kaasalainen, Harri Kaartinen, Antero Kukko, Henri Niittymäki Department of Remote Sensing and Photogrammetry 5th
Snow cover change detection with laser scanning range and brightness measurements Sanna Kaasalainen, Harri Kaartinen, Antero Kukko, Henri Niittymäki Department of Remote Sensing and Photogrammetry 5th
DUAL FIELD-OF-VIEW GONIOMETER SYSTEM FIGOS
 DUAL FIELD-OF-VIEW GONIOMETER SYSTEM FIGOS J.T. Schopfer*, S. Dangel, M. Kneubühler, K.I. Itten Remote Sensing Laboratories (RSL), Departement of Geography, University of Zurich, Winterthurerstrasse 190,
DUAL FIELD-OF-VIEW GONIOMETER SYSTEM FIGOS J.T. Schopfer*, S. Dangel, M. Kneubühler, K.I. Itten Remote Sensing Laboratories (RSL), Departement of Geography, University of Zurich, Winterthurerstrasse 190,
Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction Units of Chapter 32 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formation by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Mirrors Index of Refraction Refraction:
Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction Units of Chapter 32 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formation by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Mirrors Index of Refraction Refraction:
Philpot & Philipson: Remote Sensing Fundamentals Interactions 3.1 W.D. Philpot, Cornell University, Fall 12
 Philpot & Philipson: Remote Sensing Fundamentals Interactions 3.1 W.D. Philpot, Cornell University, Fall 1 3. EM INTERACTIONS WITH MATERIALS In order for an object to be sensed, the object must reflect,
Philpot & Philipson: Remote Sensing Fundamentals Interactions 3.1 W.D. Philpot, Cornell University, Fall 1 3. EM INTERACTIONS WITH MATERIALS In order for an object to be sensed, the object must reflect,
Light Tec Scattering measurements guideline
 Light Tec Scattering measurements guideline 1 Our Laboratory Light Tec is equipped with a Photometric Laboratory (a dark room) including: Goniophotometers: REFLET 180S. High specular bench (10 meters),
Light Tec Scattering measurements guideline 1 Our Laboratory Light Tec is equipped with a Photometric Laboratory (a dark room) including: Goniophotometers: REFLET 180S. High specular bench (10 meters),
Acuity. Acuity Sensors and Scanners. Product Brochure
 Acuity Acuity Sensors and Scanners Product Brochure CCS PRIMA The CCS Prima series of confocal displacement sensors are amongst the most precise measuring instruments in the world. Using a confocal chromatic
Acuity Acuity Sensors and Scanners Product Brochure CCS PRIMA The CCS Prima series of confocal displacement sensors are amongst the most precise measuring instruments in the world. Using a confocal chromatic
Experiment 8 Wave Optics
 Physics 263 Experiment 8 Wave Optics In this laboratory, we will perform two experiments on wave optics. 1 Double Slit Interference In two-slit interference, light falls on an opaque screen with two closely
Physics 263 Experiment 8 Wave Optics In this laboratory, we will perform two experiments on wave optics. 1 Double Slit Interference In two-slit interference, light falls on an opaque screen with two closely
All forms of EM waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum = 3.00 x 10 8 m/s This speed is constant in air as well
 Pre AP Physics Light & Optics Chapters 14-16 Light is an electromagnetic wave Electromagnetic waves: Oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to the direction the wave moves Difference
Pre AP Physics Light & Optics Chapters 14-16 Light is an electromagnetic wave Electromagnetic waves: Oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to the direction the wave moves Difference
Light Tec Scattering measurements guideline
 Light Tec Scattering measurements guideline 1 Our Laboratory Light Tec is equipped with a Photometric Laboratory (a dark room) including: Goniophotometers: REFLET180s. High specular bench (10 meters),
Light Tec Scattering measurements guideline 1 Our Laboratory Light Tec is equipped with a Photometric Laboratory (a dark room) including: Goniophotometers: REFLET180s. High specular bench (10 meters),
Remote Sensing ISSN
 Remote Sens. 21, 2, 1892-1917; doi:1.339/rs281892 Article OPEN ACCESS Remote Sensing ISSN 272-4292 www.mdpi.com/journal/remotesensing Analysis of Properties of Reflectance Reference Targets for Permanent
Remote Sens. 21, 2, 1892-1917; doi:1.339/rs281892 Article OPEN ACCESS Remote Sensing ISSN 272-4292 www.mdpi.com/journal/remotesensing Analysis of Properties of Reflectance Reference Targets for Permanent
Light Tec Scattering measurements guideline
 Light Tec Scattering measurements guideline 1 2 Light Tec Locations REFLET assembling plant, Aix-en-Provence, France Light Tec GmbH, Munich, Germany German office Light Tec Sarl, Hyères, France Main office
Light Tec Scattering measurements guideline 1 2 Light Tec Locations REFLET assembling plant, Aix-en-Provence, France Light Tec GmbH, Munich, Germany German office Light Tec Sarl, Hyères, France Main office
Light: Geometric Optics
 Light: Geometric Optics The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but
Light: Geometric Optics The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but
Assignment 8 Due November 29, Problems
 Assignment 8 Due November 29, 2011 Text readings Fresnel equations, chapter 4.6 Polarization, chapter 8, sections 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, and 8. Problems Problem 1 Polarization by Reflection: Given a polarizer
Assignment 8 Due November 29, 2011 Text readings Fresnel equations, chapter 4.6 Polarization, chapter 8, sections 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, and 8. Problems Problem 1 Polarization by Reflection: Given a polarizer
IAC ETH Goniospectrometer: A Tool for Hyperspectral HDRF Measurements
 APRIL 2006 B O U R G E O I S E T A L. 573 IAC ETH Goniospectrometer: A Tool for Hyperspectral HDRF Measurements C. SASKIA BOURGEOIS, ATSUMU OHMURA, KARL SCHROFF, HANS-JÖRG FREI, AND PIERLUIGI CALANCA Institute
APRIL 2006 B O U R G E O I S E T A L. 573 IAC ETH Goniospectrometer: A Tool for Hyperspectral HDRF Measurements C. SASKIA BOURGEOIS, ATSUMU OHMURA, KARL SCHROFF, HANS-JÖRG FREI, AND PIERLUIGI CALANCA Institute
Laboratory 6: Light and the Laser
 Laboratory 6: Light and the Laser WARNING NEVER LOOK DIRECTLY AT LASER LIGHT Index of Refraction: Snell's Law 1. Read the section on physical optics in some introductory physics text. 2. Set the semicircular
Laboratory 6: Light and the Laser WARNING NEVER LOOK DIRECTLY AT LASER LIGHT Index of Refraction: Snell's Law 1. Read the section on physical optics in some introductory physics text. 2. Set the semicircular
Light Tec Scattering measurements guideline
 Light Tec Scattering measurements guideline 1 Our Laboratory Light Tec is equipped with a Photometric Laboratory (a dark room) including: Goniophotometers: REFLET 180S. High specular bench (10 meters),
Light Tec Scattering measurements guideline 1 Our Laboratory Light Tec is equipped with a Photometric Laboratory (a dark room) including: Goniophotometers: REFLET 180S. High specular bench (10 meters),
Reflective Illumination for DMS 803 / 505
 APPLICATION NOTE // Dr. Michael E. Becker Reflective Illumination for DMS 803 / 505 DHS, SDR, VADIS, PID & PLS The instruments of the DMS 803 / 505 series are precision goniometers for directional scanning
APPLICATION NOTE // Dr. Michael E. Becker Reflective Illumination for DMS 803 / 505 DHS, SDR, VADIS, PID & PLS The instruments of the DMS 803 / 505 series are precision goniometers for directional scanning
Engineered Diffusers Intensity vs Irradiance
 Engineered Diffusers Intensity vs Irradiance Engineered Diffusers are specified by their divergence angle and intensity profile. The divergence angle usually is given as the width of the intensity distribution
Engineered Diffusers Intensity vs Irradiance Engineered Diffusers are specified by their divergence angle and intensity profile. The divergence angle usually is given as the width of the intensity distribution
Optics Vac Work MT 2008
 Optics Vac Work MT 2008 1. Explain what is meant by the Fraunhofer condition for diffraction. [4] An aperture lies in the plane z = 0 and has amplitude transmission function T(y) independent of x. It is
Optics Vac Work MT 2008 1. Explain what is meant by the Fraunhofer condition for diffraction. [4] An aperture lies in the plane z = 0 and has amplitude transmission function T(y) independent of x. It is
UHD 185 FAQs. Optical System
 UHD 185 FAQs System Setup How is a typical setup of the UHD 185? Is a wireless control during flight possible? How do I trigger the image acquisition? What is the power consumption? What are the specs
UHD 185 FAQs System Setup How is a typical setup of the UHD 185? Is a wireless control during flight possible? How do I trigger the image acquisition? What is the power consumption? What are the specs
dq dt I = Irradiance or Light Intensity is Flux Φ per area A (W/m 2 ) Φ =
 Radiometry (From Intro to Optics, Pedrotti -4) Radiometry is measurement of Emag radiation (light) Consider a small spherical source Total energy radiating from the body over some time is Q total Radiant
Radiometry (From Intro to Optics, Pedrotti -4) Radiometry is measurement of Emag radiation (light) Consider a small spherical source Total energy radiating from the body over some time is Q total Radiant
Validation of the Gonioreflectometer
 Validation of the Gonioreflectometer Hongsong Li Kenneth E. Torrance PCG-03-2 May 21, 2003 i Abstract This report describes a series of experiments conducted in the Light Measurement Laboratory of the
Validation of the Gonioreflectometer Hongsong Li Kenneth E. Torrance PCG-03-2 May 21, 2003 i Abstract This report describes a series of experiments conducted in the Light Measurement Laboratory of the
Field Spectroscopy, and its role in Earth Observation
 Field Spectroscopy, and its role in Earth Observation Ted Milton University of Southampton, UK e.j.milton@soton.ac.uk Paul Cezanne, Mont Sainte-Victoire, seen from the road to Le Tholonet, 1896-98 Vincent
Field Spectroscopy, and its role in Earth Observation Ted Milton University of Southampton, UK e.j.milton@soton.ac.uk Paul Cezanne, Mont Sainte-Victoire, seen from the road to Le Tholonet, 1896-98 Vincent
Cary Fiber Optic Probes
 Cary Fiber Optic Probes Fiber Optic Probes Use With Cary 50/60 Wavelength range 200-1100 nm Cary 100/300 Cary 50/60/100/300 Cary 4000/5000/6000i Fiber optic dip probe stainless steel body only Requires
Cary Fiber Optic Probes Fiber Optic Probes Use With Cary 50/60 Wavelength range 200-1100 nm Cary 100/300 Cary 50/60/100/300 Cary 4000/5000/6000i Fiber optic dip probe stainless steel body only Requires
GEOG 4110/5100 Advanced Remote Sensing Lecture 2
 GEOG 4110/5100 Advanced Remote Sensing Lecture 2 Data Quality Radiometric Distortion Radiometric Error Correction Relevant reading: Richards, sections 2.1 2.8; 2.10.1 2.10.3 Data Quality/Resolution Spatial
GEOG 4110/5100 Advanced Remote Sensing Lecture 2 Data Quality Radiometric Distortion Radiometric Error Correction Relevant reading: Richards, sections 2.1 2.8; 2.10.1 2.10.3 Data Quality/Resolution Spatial
Airborne Laser Scanning: Remote Sensing with LiDAR
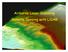 Airborne Laser Scanning: Remote Sensing with LiDAR ALS / LIDAR OUTLINE Laser remote sensing background Basic components of an ALS/LIDAR system Two distinct families of ALS systems Waveform Discrete Return
Airborne Laser Scanning: Remote Sensing with LiDAR ALS / LIDAR OUTLINE Laser remote sensing background Basic components of an ALS/LIDAR system Two distinct families of ALS systems Waveform Discrete Return
2011 Optical Science & Engineering PhD Qualifying Examination Optical Sciences Track: Advanced Optics Time allowed: 90 minutes
 2011 Optical Science & Engineering PhD Qualifying Examination Optical Sciences Track: Advanced Optics Time allowed: 90 minutes Answer all four questions. All questions count equally. 3(a) A linearly polarized
2011 Optical Science & Engineering PhD Qualifying Examination Optical Sciences Track: Advanced Optics Time allowed: 90 minutes Answer all four questions. All questions count equally. 3(a) A linearly polarized
Spectral signature databases and their application/misapplication to modeling and exploitation of multispectral/hyperspectral data
 Spectral signature databases and their application/misapplication to modeling and exploitation of multispectral/hyperspectral data Carl Salvaggio 1, Lon E. Smith 1, and Emily J. Antoine 2 Rochester Institute
Spectral signature databases and their application/misapplication to modeling and exploitation of multispectral/hyperspectral data Carl Salvaggio 1, Lon E. Smith 1, and Emily J. Antoine 2 Rochester Institute
Nanoparticle Optics: Light Scattering Size Determination of Polystryene Nanospheres by Light Scattering and Mie Theory
 Nanoparticle Optics: Light Scattering Size Determination of Polystryene Nanospheres by Light Scattering and Mie Theory OUTLINE OF THE PROCEDURE A) Observe Rayleigh scattering from silica nanoparticles.
Nanoparticle Optics: Light Scattering Size Determination of Polystryene Nanospheres by Light Scattering and Mie Theory OUTLINE OF THE PROCEDURE A) Observe Rayleigh scattering from silica nanoparticles.
CORRECTION OF INTENSITY INCIDENCE ANGLE EFFECT IN TERRESTRIAL LASER SCANNING
 CORRECTION OF INTENSITY INCIDENCE ANGLE EFFECT IN TERRESTRIAL LASER SCANNING A. Krooks a, *, S. Kaasalainen a, T. Hakala a, O. Nevalainen a a Department of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, Finnish Geodetic
CORRECTION OF INTENSITY INCIDENCE ANGLE EFFECT IN TERRESTRIAL LASER SCANNING A. Krooks a, *, S. Kaasalainen a, T. Hakala a, O. Nevalainen a a Department of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, Finnish Geodetic
Mu lt i s p e c t r a l
 Viewing Angle Analyser Revolutionary system for full spectral and polarization measurement in the entire viewing angle EZContrastMS80 & EZContrastMS88 ADVANCED LIGHT ANALYSIS by Field iris Fourier plane
Viewing Angle Analyser Revolutionary system for full spectral and polarization measurement in the entire viewing angle EZContrastMS80 & EZContrastMS88 ADVANCED LIGHT ANALYSIS by Field iris Fourier plane
LAS extrabytes implementation in RIEGL software WHITEPAPER
 in RIEGL software WHITEPAPER _ Author: RIEGL Laser Measurement Systems GmbH Date: May 25, 2012 Status: Release Pages: 13 All rights are reserved in the event of the grant or the registration of a utility
in RIEGL software WHITEPAPER _ Author: RIEGL Laser Measurement Systems GmbH Date: May 25, 2012 Status: Release Pages: 13 All rights are reserved in the event of the grant or the registration of a utility
Instrument to measure the bidirectional reflectance distribution function of surfaces
 Instrument to measure the bidirectional reflectance distribution function of surfaces Kenneth J. Voss, Albert Chapin, Marco Monti, and Hao Zhang A new instrument to measure the in situ bidirectional reflectance
Instrument to measure the bidirectional reflectance distribution function of surfaces Kenneth J. Voss, Albert Chapin, Marco Monti, and Hao Zhang A new instrument to measure the in situ bidirectional reflectance
Dr. Larry J. Paxton Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory Laurel, MD (301) (301) fax
 Dr. Larry J. Paxton Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory Laurel, MD 20723 (301) 953-6871 (301) 953-6670 fax Understand the instrument. Be able to convert measured counts/pixel on-orbit into
Dr. Larry J. Paxton Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory Laurel, MD 20723 (301) 953-6871 (301) 953-6670 fax Understand the instrument. Be able to convert measured counts/pixel on-orbit into
Glare Spread Function (GSF) - 12 Source Angle
 Normalized Pixel Value POWERED BY OPTEST SOFTWARE Stray Light Measurement on LensCheck Lens Measurement Systems 1 Glare Spread Function (GSF) - 12 Source Angle 0.1 0.01 0.001 0.0001 0.00001 0.000001 1
Normalized Pixel Value POWERED BY OPTEST SOFTWARE Stray Light Measurement on LensCheck Lens Measurement Systems 1 Glare Spread Function (GSF) - 12 Source Angle 0.1 0.01 0.001 0.0001 0.00001 0.000001 1
Understanding Variability
 Understanding Variability Why so different? Light and Optics Pinhole camera model Perspective projection Thin lens model Fundamental equation Distortion: spherical & chromatic aberration, radial distortion
Understanding Variability Why so different? Light and Optics Pinhole camera model Perspective projection Thin lens model Fundamental equation Distortion: spherical & chromatic aberration, radial distortion
TOPOGRAPHIC NORMALIZATION INTRODUCTION
 TOPOGRAPHIC NORMALIZATION INTRODUCTION Use of remotely sensed data from mountainous regions generally requires additional preprocessing, including corrections for relief displacement and solar illumination
TOPOGRAPHIC NORMALIZATION INTRODUCTION Use of remotely sensed data from mountainous regions generally requires additional preprocessing, including corrections for relief displacement and solar illumination
Phys102 Lecture 21/22 Light: Reflection and Refraction
 Phys102 Lecture 21/22 Light: Reflection and Refraction Key Points The Ray Model of Light Reflection and Mirrors Refraction, Snell s Law Total internal Reflection References 23-1,2,3,4,5,6. The Ray Model
Phys102 Lecture 21/22 Light: Reflection and Refraction Key Points The Ray Model of Light Reflection and Mirrors Refraction, Snell s Law Total internal Reflection References 23-1,2,3,4,5,6. The Ray Model
Today. Global illumination. Shading. Interactive applications. Rendering pipeline. Computergrafik. Shading Introduction Local shading models
 Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2009 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation of physics Global
Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2009 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation of physics Global
Single-Axis Lasers for Flatness and Leveling Applications. Laser Systems for Flatness and Leveling L-730/L-740 Series
 Single-Axis Lasers for Flatness and Leveling Applications Laser Systems for Flatness and Leveling L-730/L-740 Series Why the L-730/L-740 Flatness Leveling Systems are Better Sooner or later everything
Single-Axis Lasers for Flatness and Leveling Applications Laser Systems for Flatness and Leveling L-730/L-740 Series Why the L-730/L-740 Flatness Leveling Systems are Better Sooner or later everything
dq dt I = Irradiance or Light Intensity is Flux Φ per area A (W/m 2 ) Φ =
 Radiometry (From Intro to Optics, Pedrotti -4) Radiometry is measurement of Emag radiation (light) Consider a small spherical source Total energy radiating from the body over some time is Q total Radiant
Radiometry (From Intro to Optics, Pedrotti -4) Radiometry is measurement of Emag radiation (light) Consider a small spherical source Total energy radiating from the body over some time is Q total Radiant
AP* Optics Free Response Questions
 AP* Optics Free Response Questions 1978 Q5 MIRRORS An object 6 centimeters high is placed 30 centimeters from a concave mirror of focal length 10 centimeters as shown above. (a) On the diagram above, locate
AP* Optics Free Response Questions 1978 Q5 MIRRORS An object 6 centimeters high is placed 30 centimeters from a concave mirror of focal length 10 centimeters as shown above. (a) On the diagram above, locate
Light: Geometric Optics (Chapter 23)
 Light: Geometric Optics (Chapter 23) Units of Chapter 23 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formed by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Index of Refraction Refraction: Snell s Law 1
Light: Geometric Optics (Chapter 23) Units of Chapter 23 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formed by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Index of Refraction Refraction: Snell s Law 1
Radiometry (From Intro to Optics, Pedrotti 1-4) Radiometry is measurement of Emag radiation (light) Consider a small spherical source Assume a black
 Radiometry (From Intro to Optics, Pedrotti -4) Radiometry is measurement of Emag radiation (light) Consider a small spherical source Assume a black body type emitter: uniform emission Total energy radiating
Radiometry (From Intro to Optics, Pedrotti -4) Radiometry is measurement of Emag radiation (light) Consider a small spherical source Assume a black body type emitter: uniform emission Total energy radiating
ENHANCEMENT OF DIFFUSERS BRDF ACCURACY
 ENHANCEMENT OF DIFFUSERS BRDF ACCURACY Grégory Bazalgette Courrèges-Lacoste (1), Hedser van Brug (1) and Gerard Otter (1) (1) TNO Science and Industry, Opto-Mechanical Instrumentation Space, P.O.Box 155,
ENHANCEMENT OF DIFFUSERS BRDF ACCURACY Grégory Bazalgette Courrèges-Lacoste (1), Hedser van Brug (1) and Gerard Otter (1) (1) TNO Science and Industry, Opto-Mechanical Instrumentation Space, P.O.Box 155,
CMSC427 Shading Intro. Credit: slides from Dr. Zwicker
 CMSC427 Shading Intro Credit: slides from Dr. Zwicker 2 Today Shading Introduction Radiometry & BRDFs Local shading models Light sources Shading strategies Shading Compute interaction of light with surfaces
CMSC427 Shading Intro Credit: slides from Dr. Zwicker 2 Today Shading Introduction Radiometry & BRDFs Local shading models Light sources Shading strategies Shading Compute interaction of light with surfaces
Light: Geometric Optics
 Light: Geometric Optics 23.1 The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization,
Light: Geometric Optics 23.1 The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization,
Nicholas J. Giordano. Chapter 24. Geometrical Optics. Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 24 Geometrical Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Optics The study of light is called optics Some highlights in the history
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 24 Geometrical Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Optics The study of light is called optics Some highlights in the history
Physical Optics. You can observe a lot just by watching. Yogi Berra ( )
 Physical Optics You can observe a lot just by watching. Yogi Berra (1925-2015) OBJECTIVES To observe some interference and diffraction phenomena with visible light. THEORY In a previous experiment you
Physical Optics You can observe a lot just by watching. Yogi Berra (1925-2015) OBJECTIVES To observe some interference and diffraction phenomena with visible light. THEORY In a previous experiment you
Imaging Sphere Measurement of Luminous Intensity, View Angle, and Scatter Distribution Functions
 Imaging Sphere Measurement of Luminous Intensity, View Angle, and Scatter Distribution Functions Hubert Kostal, Vice President of Sales and Marketing Radiant Imaging, Inc. 22908 NE Alder Crest Drive, Suite
Imaging Sphere Measurement of Luminous Intensity, View Angle, and Scatter Distribution Functions Hubert Kostal, Vice President of Sales and Marketing Radiant Imaging, Inc. 22908 NE Alder Crest Drive, Suite
EVALUATION OF DIURNAL HYPERSPECTRAL BRF DATA ACQUIRED WITH THE RSL FIELD GONIOMETER DURING THE DAISEX 99 CAMPAIGN
 EVALUATION OF DIURNAL HYPERSPECTRAL BRF DATA ACQUIRED WITH THE RSL FIELD GONIOMETER DURING THE DAISEX 99 CAMPAIGN G. Strub (1), U. Beisl (2), M. Schaepman (1), D. Schläpfer (1), C. Dickerhof (1), K. Itten
EVALUATION OF DIURNAL HYPERSPECTRAL BRF DATA ACQUIRED WITH THE RSL FIELD GONIOMETER DURING THE DAISEX 99 CAMPAIGN G. Strub (1), U. Beisl (2), M. Schaepman (1), D. Schläpfer (1), C. Dickerhof (1), K. Itten
Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition
 Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition Chapter 28: REFLECTION & REFRACTION This lecture will help you understand: Reflection Principle of Least Time Law of Reflection Refraction Cause of Refraction Dispersion
Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition Chapter 28: REFLECTION & REFRACTION This lecture will help you understand: Reflection Principle of Least Time Law of Reflection Refraction Cause of Refraction Dispersion
Suitability of the parametric model RPV to assess canopy structure and heterogeneity from multi-angular CHRIS-PROBA data
 Suitability of the parametric model RPV to assess canopy structure and heterogeneity from multi-angular CHRIS-PROBA data B. Koetz a*, J.-L. Widlowski b, F. Morsdorf a,, J. Verrelst c, M. Schaepman c and
Suitability of the parametric model RPV to assess canopy structure and heterogeneity from multi-angular CHRIS-PROBA data B. Koetz a*, J.-L. Widlowski b, F. Morsdorf a,, J. Verrelst c, M. Schaepman c and
DIGITAL SURFACE MODELS OF CITY AREAS BY VERY HIGH RESOLUTION SPACE IMAGERY
 DIGITAL SURFACE MODELS OF CITY AREAS BY VERY HIGH RESOLUTION SPACE IMAGERY Jacobsen, K. University of Hannover, Institute of Photogrammetry and Geoinformation, Nienburger Str.1, D30167 Hannover phone +49
DIGITAL SURFACE MODELS OF CITY AREAS BY VERY HIGH RESOLUTION SPACE IMAGERY Jacobsen, K. University of Hannover, Institute of Photogrammetry and Geoinformation, Nienburger Str.1, D30167 Hannover phone +49
New capabilities of diffuser calibration lab at GSFC NASA to support remote sensing instrumentation
 New capabilities of diffuser calibration lab at GSFC NASA to support remote sensing instrumentation Jinan Zeng1, Jim Butler2, and Jack Xiong2 1Fibertek Incorporation, 13605 Dulles Technology Dr., Herndon,
New capabilities of diffuser calibration lab at GSFC NASA to support remote sensing instrumentation Jinan Zeng1, Jim Butler2, and Jack Xiong2 1Fibertek Incorporation, 13605 Dulles Technology Dr., Herndon,
2/26/2016. Chapter 23 Ray Optics. Chapter 23 Preview. Chapter 23 Preview
 Chapter 23 Ray Optics Chapter Goal: To understand and apply the ray model of light. Slide 23-2 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-3 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-4 1 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-5 Chapter 23 Preview
Chapter 23 Ray Optics Chapter Goal: To understand and apply the ray model of light. Slide 23-2 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-3 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-4 1 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-5 Chapter 23 Preview
Evaluation of Satellite Ocean Color Data Using SIMBADA Radiometers
 Evaluation of Satellite Ocean Color Data Using SIMBADA Radiometers Robert Frouin Scripps Institution of Oceanography, la Jolla, California OCR-VC Workshop, 21 October 2010, Ispra, Italy The SIMBADA Project
Evaluation of Satellite Ocean Color Data Using SIMBADA Radiometers Robert Frouin Scripps Institution of Oceanography, la Jolla, California OCR-VC Workshop, 21 October 2010, Ispra, Italy The SIMBADA Project
Chapter 24 - The Wave Nature of Light
 Chapter 24 - The Wave Nature of Light Summary Four Consequences of the Wave nature of Light: Diffraction Dispersion Interference Polarization Huygens principle: every point on a wavefront is a source of
Chapter 24 - The Wave Nature of Light Summary Four Consequences of the Wave nature of Light: Diffraction Dispersion Interference Polarization Huygens principle: every point on a wavefront is a source of
Spectrographs. C. A. Griffith, Class Notes, PTYS 521, 2016 Not for distribution.
 Spectrographs C A Griffith, Class Notes, PTYS 521, 2016 Not for distribution 1 Spectrographs and their characteristics A spectrograph is an instrument that disperses light into a frequency spectrum, which
Spectrographs C A Griffith, Class Notes, PTYS 521, 2016 Not for distribution 1 Spectrographs and their characteristics A spectrograph is an instrument that disperses light into a frequency spectrum, which
CLASSIFICATION OF NONPHOTOGRAPHIC REMOTE SENSORS
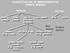 CLASSIFICATION OF NONPHOTOGRAPHIC REMOTE SENSORS PASSIVE ACTIVE DIGITAL CAMERA THERMAL (e.g. TIMS) VIDEO CAMERA MULTI- SPECTRAL SCANNERS VISIBLE & NIR MICROWAVE HYPERSPECTRAL (e.g. AVIRIS) SLAR Real Aperture
CLASSIFICATION OF NONPHOTOGRAPHIC REMOTE SENSORS PASSIVE ACTIVE DIGITAL CAMERA THERMAL (e.g. TIMS) VIDEO CAMERA MULTI- SPECTRAL SCANNERS VISIBLE & NIR MICROWAVE HYPERSPECTRAL (e.g. AVIRIS) SLAR Real Aperture
BLACKOUT FLEX BB TECHNICAL DATA SHEET » ARTICLE CODE» WIDTH» LENGTH» WEIGHT » COMPOSITION » FLAME RESISTANCE » AVAILABLE COLOURS.
 BLACKOUT FLEX BB TECHNICAL DATA SHEET March 2018 Blackout Flex BB is the perfect blackout fabric to combine with AV Drop or Print Frame Profiles by ShowTex. It s black backing prevents visible bracing
BLACKOUT FLEX BB TECHNICAL DATA SHEET March 2018 Blackout Flex BB is the perfect blackout fabric to combine with AV Drop or Print Frame Profiles by ShowTex. It s black backing prevents visible bracing
Fast, Easy and Highly Accurate Extruder Alignment. L-705 Laser Borescope Alignment System for Extruders
 Fast, Easy and Highly Accurate Extruder Alignment L-705 Laser Borescope Alignment System for Extruders L-705 Laser Borescope Alignment System for Extruders The Leader in Extruder Alignment Technology Hamar
Fast, Easy and Highly Accurate Extruder Alignment L-705 Laser Borescope Alignment System for Extruders L-705 Laser Borescope Alignment System for Extruders The Leader in Extruder Alignment Technology Hamar
CONTENTS. Quick Start Guide V1.0
 Quick Start Guide CONTENTS 1 Introduction... 2 2 What s in the box?... 3 3 Using your buzzard multispectral sensor... 4 3.1 Overview... 4 3.2 Connecting the power / remote trigger cable... 5 3.3 Attaching
Quick Start Guide CONTENTS 1 Introduction... 2 2 What s in the box?... 3 3 Using your buzzard multispectral sensor... 4 3.1 Overview... 4 3.2 Connecting the power / remote trigger cable... 5 3.3 Attaching
ASD FieldSpec Pro HandHeld Cookbook
 ASD FieldSpec Pro HandHeld Cookbook NLWRA ASD instrument system: setup and use Version 1.3: Hannalie Botha, Rebecca Edwards and Paul Daniel, CSIRO Land and Water, August 26, 2008. Version 1.4: Paul Daniel,
ASD FieldSpec Pro HandHeld Cookbook NLWRA ASD instrument system: setup and use Version 1.3: Hannalie Botha, Rebecca Edwards and Paul Daniel, CSIRO Land and Water, August 26, 2008. Version 1.4: Paul Daniel,
3D Laser Scanner VS1000 User Manual
 3D Laser Scanner VS1000 User Manual 1 VS1000 Introduction SMART MAX GEOSYSTEMS CO., LTD VS1000 3D Laser Scanner based on pulses ranging principle, could quick acquire massive point cloud data from the
3D Laser Scanner VS1000 User Manual 1 VS1000 Introduction SMART MAX GEOSYSTEMS CO., LTD VS1000 3D Laser Scanner based on pulses ranging principle, could quick acquire massive point cloud data from the
1.! Questions about reflected intensity. [Use the formulas on p. 8 of Light.] , no matter
![1.! Questions about reflected intensity. [Use the formulas on p. 8 of Light.] , no matter 1.! Questions about reflected intensity. [Use the formulas on p. 8 of Light.] , no matter](/thumbs/81/83191942.jpg) Reading: Light Key concepts: Huygens s principle; reflection; refraction; reflectivity; total reflection; Brewster angle; polarization by absorption, reflection and Rayleigh scattering. 1.! Questions about
Reading: Light Key concepts: Huygens s principle; reflection; refraction; reflectivity; total reflection; Brewster angle; polarization by absorption, reflection and Rayleigh scattering. 1.! Questions about
PHYSICS. Chapter 34 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 34 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 34 Ray Optics IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about and apply the ray model of light Slide 34-2
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 34 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 34 Ray Optics IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about and apply the ray model of light Slide 34-2
Council for Optical Radiation Measurements (CORM) 2016 Annual Technical Conference May 15 18, 2016, Gaithersburg, MD
 Council for Optical Radiation Measurements (CORM) 2016 Annual Technical Conference May 15 18, 2016, Gaithersburg, MD Multispectral measurements of emissive and reflective properties of displays: Application
Council for Optical Radiation Measurements (CORM) 2016 Annual Technical Conference May 15 18, 2016, Gaithersburg, MD Multispectral measurements of emissive and reflective properties of displays: Application
PHYSICS 213 PRACTICE EXAM 3*
 PHYSICS 213 PRACTICE EXAM 3* *The actual exam will contain EIGHT multiple choice quiz-type questions covering concepts from lecture (16 points), ONE essay-type question covering an important fundamental
PHYSICS 213 PRACTICE EXAM 3* *The actual exam will contain EIGHT multiple choice quiz-type questions covering concepts from lecture (16 points), ONE essay-type question covering an important fundamental
The Council for Optical Radiation Measurements (CORM), NIST July 30 - Aug 1, 2018
 Study of the optical properties of black materials at solar reflective wavelengths in support of instrument development and satellite sensor calibration 1Jinan Zeng, 2 Nathan Kelley, 3 James J. Butler,
Study of the optical properties of black materials at solar reflective wavelengths in support of instrument development and satellite sensor calibration 1Jinan Zeng, 2 Nathan Kelley, 3 James J. Butler,
OPSE FINAL EXAM Fall CLOSED BOOK. Two pages (front/back of both pages) of equations are allowed.
 CLOSED BOOK. Two pages (front/back of both pages) of equations are allowed. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED.
CLOSED BOOK. Two pages (front/back of both pages) of equations are allowed. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED.
SIMULATION AND VISUALIZATION IN THE EDUCATION OF COHERENT OPTICS
 SIMULATION AND VISUALIZATION IN THE EDUCATION OF COHERENT OPTICS J. KORNIS, P. PACHER Department of Physics Technical University of Budapest H-1111 Budafoki út 8., Hungary e-mail: kornis@phy.bme.hu, pacher@phy.bme.hu
SIMULATION AND VISUALIZATION IN THE EDUCATION OF COHERENT OPTICS J. KORNIS, P. PACHER Department of Physics Technical University of Budapest H-1111 Budafoki út 8., Hungary e-mail: kornis@phy.bme.hu, pacher@phy.bme.hu
TLS Parameters, Workflows and Field Methods
 TLS Parameters, Workflows and Field Methods Marianne Okal, UNAVCO GSA, October 20 th, 2017 How a Lidar instrument works (Recap) Transmits laser signals and measures the reflected light to create 3D point
TLS Parameters, Workflows and Field Methods Marianne Okal, UNAVCO GSA, October 20 th, 2017 How a Lidar instrument works (Recap) Transmits laser signals and measures the reflected light to create 3D point
Physical Optics. 1 st year physics laboratories. University of Ottawa.
 Physical Optics 1 st year physics laboratories University of Ottawa https://uottawa.brightspace.com/d2l/home INTRODUCTION Physical optics deals with light as a wave which can bend around obstacles (diffraction)
Physical Optics 1 st year physics laboratories University of Ottawa https://uottawa.brightspace.com/d2l/home INTRODUCTION Physical optics deals with light as a wave which can bend around obstacles (diffraction)
The goal of this lab is to give you a chance to align and use a Pockel s Cell.
 880 Quantum Electronics Lab Pockel s Cell Alignment And Use The goal of this lab is to give you a chance to align and use a Pockel s Cell. You may not take this lab unless you have read the laser safety
880 Quantum Electronics Lab Pockel s Cell Alignment And Use The goal of this lab is to give you a chance to align and use a Pockel s Cell. You may not take this lab unless you have read the laser safety
Gregory Walsh, Ph.D. San Ramon, CA January 25, 2011
 Leica ScanStation:: Calibration and QA Gregory Walsh, Ph.D. San Ramon, CA January 25, 2011 1. Summary Leica Geosystems, in creating the Leica Scanstation family of products, has designed and conducted
Leica ScanStation:: Calibration and QA Gregory Walsh, Ph.D. San Ramon, CA January 25, 2011 1. Summary Leica Geosystems, in creating the Leica Scanstation family of products, has designed and conducted
Chapter 23. Light Geometric Optics
 Chapter 23. Light Geometric Optics There are 3 basic ways to gather light and focus it to make an image. Pinhole - Simple geometry Mirror - Reflection Lens - Refraction Pinhole Camera Image Formation (the
Chapter 23. Light Geometric Optics There are 3 basic ways to gather light and focus it to make an image. Pinhole - Simple geometry Mirror - Reflection Lens - Refraction Pinhole Camera Image Formation (the
specular diffuse reflection.
 Lesson 8 Light and Optics The Nature of Light Properties of Light: Reflection Refraction Interference Diffraction Polarization Dispersion and Prisms Total Internal Reflection Huygens s Principle The Nature
Lesson 8 Light and Optics The Nature of Light Properties of Light: Reflection Refraction Interference Diffraction Polarization Dispersion and Prisms Total Internal Reflection Huygens s Principle The Nature
Textbook Reference: Physics (Wilson, Buffa, Lou): Chapter 24
 AP Physics-B Physical Optics Introduction: We have seen that the reflection and refraction of light can be understood in terms of both rays and wave fronts of light. Light rays are quite compatible with
AP Physics-B Physical Optics Introduction: We have seen that the reflection and refraction of light can be understood in terms of both rays and wave fronts of light. Light rays are quite compatible with
from P.R.Engineering Ltd Tel:
 Quick Start FRE-205 INSTRUCTIONS from P.R.Engineering Ltd www.laser-level.co.uk Tel: 01246 269 777 Thank you for purchasing the FRE-205 Auto Rotary laser level kit. These instructions are intended to explain
Quick Start FRE-205 INSTRUCTIONS from P.R.Engineering Ltd www.laser-level.co.uk Tel: 01246 269 777 Thank you for purchasing the FRE-205 Auto Rotary laser level kit. These instructions are intended to explain
Remote Sensing Introduction to the course
 Remote Sensing Introduction to the course Remote Sensing (Prof. L. Biagi) Exploitation of remotely assessed data for information retrieval Data: Digital images of the Earth, obtained by sensors recording
Remote Sensing Introduction to the course Remote Sensing (Prof. L. Biagi) Exploitation of remotely assessed data for information retrieval Data: Digital images of the Earth, obtained by sensors recording
Instruction manual for operating the Goniospectrometer in SSL Characterization
 Aalto University School of Electrical Engineering Metrology Research Institute Janne Askola Instruction manual for operating Version 1.0 16/08/2016 Page 2 (7) Table of contents 1. Definition... 3 1.1.
Aalto University School of Electrical Engineering Metrology Research Institute Janne Askola Instruction manual for operating Version 1.0 16/08/2016 Page 2 (7) Table of contents 1. Definition... 3 1.1.
Aligning Parallelism of Rolls Has Never Been Faster. L-732 Precision Dual-Scan Roll Alignment System
 Aligning Parallelism of Rolls Has Never Been Faster L-732 Precision Dual-Scan Roll Alignment System Why the L-732 Roll Alignment System is Better Roll parallelism accuracy of.00018 in/ft (0.015 mm/m) Up
Aligning Parallelism of Rolls Has Never Been Faster L-732 Precision Dual-Scan Roll Alignment System Why the L-732 Roll Alignment System is Better Roll parallelism accuracy of.00018 in/ft (0.015 mm/m) Up
Binoculars. with. Digital Compass. Instruction Manual. Model: Lit. #: /08-12
 Binoculars with Digital Compass Model: 137570 Instruction Manual Lit. #: 98-1192/08-12 Right Eyepiece Focus Compass Power Switch Battery Cover Left Eyepiece Focus Parts Reference Tripod Attachment Socket
Binoculars with Digital Compass Model: 137570 Instruction Manual Lit. #: 98-1192/08-12 Right Eyepiece Focus Compass Power Switch Battery Cover Left Eyepiece Focus Parts Reference Tripod Attachment Socket
ksa MOS Ultra-Scan Performance Test Data
 ksa MOS Ultra-Scan Performance Test Data Introduction: ksa MOS Ultra Scan 200mm Patterned Silicon Wafers The ksa MOS Ultra Scan is a flexible, highresolution scanning curvature and tilt-measurement system.
ksa MOS Ultra-Scan Performance Test Data Introduction: ksa MOS Ultra Scan 200mm Patterned Silicon Wafers The ksa MOS Ultra Scan is a flexible, highresolution scanning curvature and tilt-measurement system.
13. Brewster angle measurement
 13. Brewster angle measurement Brewster angle measurement Objective: 1. Verification of Malus law 2. Measurement of reflection coefficient of a glass plate for p- and s- polarizations 3. Determination
13. Brewster angle measurement Brewster angle measurement Objective: 1. Verification of Malus law 2. Measurement of reflection coefficient of a glass plate for p- and s- polarizations 3. Determination
Homework Set 3 Due Thursday, 07/14
 Homework Set 3 Due Thursday, 07/14 Problem 1 A room contains two parallel wall mirrors, on opposite walls 5 meters apart. The mirrors are 8 meters long. Suppose that one person stands in a doorway, in
Homework Set 3 Due Thursday, 07/14 Problem 1 A room contains two parallel wall mirrors, on opposite walls 5 meters apart. The mirrors are 8 meters long. Suppose that one person stands in a doorway, in
TLS Parameters, Workflows and Field Methods
 TLS Parameters, Workflows and Field Methods Marianne Okal, UNAVCO GSA, September 23 rd, 2016 How a Lidar instrument works (Recap) Transmits laser signals and measures the reflected light to create 3D point
TLS Parameters, Workflows and Field Methods Marianne Okal, UNAVCO GSA, September 23 rd, 2016 How a Lidar instrument works (Recap) Transmits laser signals and measures the reflected light to create 3D point
Basic Polarization Techniques and Devices 1998, 2003 Meadowlark Optics, Inc
 Basic Polarization Techniques and Devices 1998, 2003 Meadowlark Optics, Inc This application note briefly describes polarized light, retardation and a few of the tools used to manipulate the polarization
Basic Polarization Techniques and Devices 1998, 2003 Meadowlark Optics, Inc This application note briefly describes polarized light, retardation and a few of the tools used to manipulate the polarization
Conceptual Physics Fundamentals
 Conceptual Physics Fundamentals Chapter 14: PROPERTIES OF LIGHT This lecture will help you understand: Reflection Refraction Dispersion Total Internal Reflection Lenses Polarization Properties of Light
Conceptual Physics Fundamentals Chapter 14: PROPERTIES OF LIGHT This lecture will help you understand: Reflection Refraction Dispersion Total Internal Reflection Lenses Polarization Properties of Light
Discussion Question 13A P212, Week 13 Electromagnetic Waves
 Discussion Question 13A P1, Week 13 Electromagnetic Waves This problem is a continuation of discussion question 1B from last week. Please refer to your work from last week as necessary. A laser beam travels
Discussion Question 13A P1, Week 13 Electromagnetic Waves This problem is a continuation of discussion question 1B from last week. Please refer to your work from last week as necessary. A laser beam travels
POL-001 Fiber-Optic In-Line Polarizer. Operation Manual
 POL-001 Fiber-Optic In-Line Polarizer Operation Manual Feb. 18, 2002 General Photonics Corp. Ph: (909) 590-5473 5228 Edison Ave. Fax: (909) 902-5536 Chino, CA 91710 USA www.generalphotonics.com Document
POL-001 Fiber-Optic In-Line Polarizer Operation Manual Feb. 18, 2002 General Photonics Corp. Ph: (909) 590-5473 5228 Edison Ave. Fax: (909) 902-5536 Chino, CA 91710 USA www.generalphotonics.com Document
Downloaded from UNIT 06 Optics
 1 Mark UNIT 06 Optics Q1: A partially plane polarised beam of light is passed through a polaroid. Show graphically the variation of the transmitted light intensity with angle of rotation of the Polaroid.
1 Mark UNIT 06 Optics Q1: A partially plane polarised beam of light is passed through a polaroid. Show graphically the variation of the transmitted light intensity with angle of rotation of the Polaroid.
Chapter 24. Wave Optics. Wave Optics. The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena
 Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
Chapter 36. Image Formation
 Chapter 36 Image Formation Apr 22, 2012 Light from distant things We learn about a distant thing from the light it generates or redirects. The lenses in our eyes create images of objects our brains can
Chapter 36 Image Formation Apr 22, 2012 Light from distant things We learn about a distant thing from the light it generates or redirects. The lenses in our eyes create images of objects our brains can
OPTICS MIRRORS AND LENSES
 Downloaded from OPTICS MIRRORS AND LENSES 1. An object AB is kept in front of a concave mirror as shown in the figure. (i)complete the ray diagram showing the image formation of the object. (ii) How will
Downloaded from OPTICS MIRRORS AND LENSES 1. An object AB is kept in front of a concave mirror as shown in the figure. (i)complete the ray diagram showing the image formation of the object. (ii) How will
