EE Light & Image Formation
|
|
|
- Jasper Jenkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EE Light & Electric Electronic Engineering Bogazici University January 29, 2018 EE Light &
2 EE Light &
3 The image of a three-dimensional object depends on: 1. Shape 2. Reflectance properties 3. Distribution of light sources EE Light &
4 Reflectance Model Outline Reflectance model - A mathematical formulation of how light energy incident on an object is transferred from the object to the camera sensor. EE Light &
5 Radiance & Irradiance EE Light &
6 Figure: SolidEE angle Light & Outline Solid angle subtended by a patch Proportional to its area A and the cos of the angle of inclination θ Inversely proportional to the distance R as Ω = Acosθ R 2.
7 Radiance & Irradiance Radiance: The amount of light emitted from a surface as measured by power per unit unit area per unit solid angle. (Wm 2 sr 1 watts per square meter per steradian) Irradiance: The amount of light falling on a surface as measured by power per unit area (Wm 2 Watts per square meter) EE Light &
8 Relation btw Radiance & Irradiance EE Light &
9 Brightness Apparent area: Surface area multiplied by the cosine of the angle between the surface normal and the specified direction. Brightness - Amount of energy an imaging system receives per unit apparent area EE Light &
10 Optics Outline Rays passing through the center of the lens are not deflected. The solid angle of the cone of rays leading to the patch on the object = Solid angle of corresponding image patch. Solid angle of the object patch as seen from the lens center: δocosθ (z/cosα) 2 Solid angle subtended by the image patch: δicosα (f/cosα) 2 Equality δo δi = ( z f )2cosα cosθ EE Light &
11 Object Radiance Outline Amount of light emitted by the surface that makes its way through the lens is equal to Ω = (d 2 )2 πcosα (z/cosα) 2 Power of the light originating from the object patch and passing through the lens is δp = LδOΩcosθ = LδO (d 2 )2 πcosαcosθ (z/cosα) 2 EE Light &
12 Image Irradiance Outline The resulting image irradiance of the image patch: E = δp δi = L δo δi Ωcosθ = LδO(d 2 )2 πcosα (z/cosα) 2 = Lπ 4 (d f )2 cos 4 α EE Light &
13 Next Question Scene Radiance The amount of light falling on a surface E The fraction of light that is reflected as well as viewing angle L EE Light &
14 BRDF A measure on the observed brightness from a certain direction θ e when the light is incident in a different direction θ i : f(θ i,φ i,θ e,φ e ) = δl(θ e,φ e ) δe(θ i,φ i ) EE Light &
15 Bidirectional reflectance distribution function Figure: Left: Spherical coordinate system; Right: Bidirectional reflectance distribution function. EE Light &
16 BRDF Models Lambertian Equally bright from all directions Specular The surface luminance is highest when the observer is located at the perfect reflection direction, and falls off sharply. Phong A mixture of Lambertian and Specular EE Light &
17 Light Reflection from a Surface EE Light &
18 Lambertian Surfaces Apparent brightness of the surface to an observer - The same regardless of the observer s angle of view L = Eρcosθ ρ is the albedo EE Light &
19 Specular Reflection The surface luminance is highest when the observer is situated at the perfect reflection direction, and falls off sharply. Law of reflection The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. The incident, normal, and reflected directions coplanar. EE Light &
20 Phong Model Lambertian reflection is typically accompanied by specular reflection. L = E(acosθ +bcos n α) a Diffuse albedo b Specular albedo EE Light &
21 Phong Reflection Outline EE Light &
22 Surface Normals Outline EE Light &
23 Surface Normals (cont) Surface normal at each point on the surface Expressed as the directional slope in the X 1 and X 2 directions. f X1 f X2 1 = p q 1 EE Light &
24 Normalized Surface Normals p, q Gradient or gradient space representation for local surface orientation Normalized surface normal 1 1+p 2 +q 2 p q 1 EE Light &
25 Gradient Space The p q plane is called the gradient space and every point corresponds to a particular surface orientation. The point at the origin represents the orientation of all planes normal to the viewing direction A contour map Depict the reflectance map. EE Light &
26 Reflectance Map A viewer-centered representation of reflectance. Expresses the reflectance of a material directly in terms of viewer-centered representation of local surface orientation. Gives us the dependence of the scene radiance on the surface orientation. EE Light &
27 Reflectance Map Outline Figure: Reflectance map. EE Light &
28 Lambertian Reflectance Map Consider Lambertian surface where E = Lρcosθ 1+p s p +q s q cosθ = Lρ 1+p 2 s +qs 2 1+p 2 +q = R(p,q) 2 Grouping L and ρ as a constant, local surface orientations that produce equivalent intensities under the Lambertian reflectance map are quadratic conic section contours in gradient space. (1+p s p +q s q) 2 = c 2 (1+p 2 s +q 2 s)(1+p 2 +q 2 ) EE Light &
29 Reflectance map - Isobrightness Contours EE Light &
30 Reflectance map - Isobrightness Contours (cont.) EE Light &
31 Reflectance map with p s = q s = 0 EE Light &
32 Reflectance map with p s = 0.7 and q s = 0.3 Figure: Reflectance map with p s = 0.7 and q s = 0.3. EE Light &
33 Reflectance map with p s = 2 and q s = 1 EE Light &
34 Figure: Left: Surface normal map; Right: Reflectance EE Light &
35 Surface Description Outline Figure: Reflectance map. EE Light &
36 Surface Description (cont.) EE Light &
37 Surface Normal and Depth Depth Map can be determined from from Normal Map by integrating over gradients p,q across the image. Not all normal maps have a unique depth map. Integrable: A normal map that produces a unique depth map independent of image plane direction used to sum over gradients Integrability is enforced when the following condition holds: p = q X 2 X 1 EE Light &
38 Green s Theorem Outline Note that by using Green s Theorem, this integral is equivalent to a closed contour integral as follows: ( p q ) dx 1 dx2 = pdx 1 + qdx 2 X 2 X 1 EE Light &
39 Violation of Integrability EE Light &
Capturing light. Source: A. Efros
 Capturing light Source: A. Efros Review Pinhole projection models What are vanishing points and vanishing lines? What is orthographic projection? How can we approximate orthographic projection? Lenses
Capturing light Source: A. Efros Review Pinhole projection models What are vanishing points and vanishing lines? What is orthographic projection? How can we approximate orthographic projection? Lenses
Understanding Variability
 Understanding Variability Why so different? Light and Optics Pinhole camera model Perspective projection Thin lens model Fundamental equation Distortion: spherical & chromatic aberration, radial distortion
Understanding Variability Why so different? Light and Optics Pinhole camera model Perspective projection Thin lens model Fundamental equation Distortion: spherical & chromatic aberration, radial distortion
CENG 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics. Ray Tracing: Shading
 CENG 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Ray Tracing: Shading Last Week Until now we learned: How to create the primary rays from the given camera and image plane parameters How to intersect these rays
CENG 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Ray Tracing: Shading Last Week Until now we learned: How to create the primary rays from the given camera and image plane parameters How to intersect these rays
Photometric Stereo. Lighting and Photometric Stereo. Computer Vision I. Last lecture in a nutshell BRDF. CSE252A Lecture 7
 Lighting and Photometric Stereo Photometric Stereo HW will be on web later today CSE5A Lecture 7 Radiometry of thin lenses δa Last lecture in a nutshell δa δa'cosα δacos β δω = = ( z' / cosα ) ( z / cosα
Lighting and Photometric Stereo Photometric Stereo HW will be on web later today CSE5A Lecture 7 Radiometry of thin lenses δa Last lecture in a nutshell δa δa'cosα δacos β δω = = ( z' / cosα ) ( z / cosα
General Principles of 3D Image Analysis
 General Principles of 3D Image Analysis high-level interpretations objects scene elements Extraction of 3D information from an image (sequence) is important for - vision in general (= scene reconstruction)
General Principles of 3D Image Analysis high-level interpretations objects scene elements Extraction of 3D information from an image (sequence) is important for - vision in general (= scene reconstruction)
INFOGR Computer Graphics. J. Bikker - April-July Lecture 10: Shading Models. Welcome!
 INFOGR Computer Graphics J. Bikker - April-July 2016 - Lecture 10: Shading Models Welcome! Today s Agenda: Introduction Light Transport Materials Sensors Shading INFOGR Lecture 10 Shading Models 3 Introduction
INFOGR Computer Graphics J. Bikker - April-July 2016 - Lecture 10: Shading Models Welcome! Today s Agenda: Introduction Light Transport Materials Sensors Shading INFOGR Lecture 10 Shading Models 3 Introduction
Photometric Stereo.
 Photometric Stereo Photometric Stereo v.s.. Structure from Shading [1] Photometric stereo is a technique in computer vision for estimating the surface normals of objects by observing that object under
Photometric Stereo Photometric Stereo v.s.. Structure from Shading [1] Photometric stereo is a technique in computer vision for estimating the surface normals of objects by observing that object under
Reflectance & Lighting
 Reflectance & Lighting Computer Vision I CSE5A Lecture 6 Last lecture in a nutshell Need for lenses (blur from pinhole) Thin lens equation Distortion and aberrations Vignetting CS5A, Winter 007 Computer
Reflectance & Lighting Computer Vision I CSE5A Lecture 6 Last lecture in a nutshell Need for lenses (blur from pinhole) Thin lens equation Distortion and aberrations Vignetting CS5A, Winter 007 Computer
Illumination in Computer Graphics
 Illumination in Computer Graphics Ann McNamara Illumination in Computer Graphics Definition of light sources. Analysis of interaction between light and objects in a scene. Rendering images that are faithful
Illumination in Computer Graphics Ann McNamara Illumination in Computer Graphics Definition of light sources. Analysis of interaction between light and objects in a scene. Rendering images that are faithful
Image Processing 1 (IP1) Bildverarbeitung 1
 MIN-Fakultät Fachbereich Informatik Arbeitsbereich SAV/BV (KOGS) Image Processing 1 (IP1) Bildverarbeitung 1 Lecture 20: Shape from Shading Winter Semester 2015/16 Slides: Prof. Bernd Neumann Slightly
MIN-Fakultät Fachbereich Informatik Arbeitsbereich SAV/BV (KOGS) Image Processing 1 (IP1) Bildverarbeitung 1 Lecture 20: Shape from Shading Winter Semester 2015/16 Slides: Prof. Bernd Neumann Slightly
Radiometry. Radiometry. Measuring Angle. Solid Angle. Radiance
 Radiometry Radiometry Computer Vision I CSE5A ecture 5-Part II Read Chapter 4 of Ponce & Forsyth Solid Angle Irradiance Radiance BRDF ambertian/phong BRDF Measuring Angle Solid Angle By analogy with angle
Radiometry Radiometry Computer Vision I CSE5A ecture 5-Part II Read Chapter 4 of Ponce & Forsyth Solid Angle Irradiance Radiance BRDF ambertian/phong BRDF Measuring Angle Solid Angle By analogy with angle
Assignment #2. (Due date: 11/6/2012)
 Computer Vision I CSE 252a, Fall 2012 David Kriegman Assignment #2 (Due date: 11/6/2012) Name: Student ID: Email: Problem 1 [1 pts] Calculate the number of steradians contained in a spherical wedge with
Computer Vision I CSE 252a, Fall 2012 David Kriegman Assignment #2 (Due date: 11/6/2012) Name: Student ID: Email: Problem 1 [1 pts] Calculate the number of steradians contained in a spherical wedge with
Radiometry and reflectance
 Radiometry and reflectance http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2018, Lecture 16 Course announcements Homework 4 is still ongoing - Any questions?
Radiometry and reflectance http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2018, Lecture 16 Course announcements Homework 4 is still ongoing - Any questions?
Shape from shading. Surface brightness and Surface Orientation --> Reflectance map READING: Nalwa Chapter 5. BKP Horn, Chapter 10.
 Shape from shading Surface brightness and Surface Orientation --> Reflectance map READING: Nalwa Chapter 5. BKP Horn, Chapter 10. May 2004 SFS 1 Shading produces a compelling perception of 3-D shape. One
Shape from shading Surface brightness and Surface Orientation --> Reflectance map READING: Nalwa Chapter 5. BKP Horn, Chapter 10. May 2004 SFS 1 Shading produces a compelling perception of 3-D shape. One
The Light Field. Last lecture: Radiometry and photometry
 The Light Field Last lecture: Radiometry and photometry This lecture: Light field = radiance function on rays Conservation of radiance Measurement equation Throughput and counting rays Irradiance calculations
The Light Field Last lecture: Radiometry and photometry This lecture: Light field = radiance function on rays Conservation of radiance Measurement equation Throughput and counting rays Irradiance calculations
OPPA European Social Fund Prague & EU: We invest in your future.
 OPPA European Social Fund Prague & EU: We invest in your future. Image formation and its physical basis Václav Hlaváč Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Department
OPPA European Social Fund Prague & EU: We invest in your future. Image formation and its physical basis Václav Hlaváč Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Department
Radiometry. Reflectance & Lighting. Solid Angle. Radiance. Radiance Power is energy per unit time
 Radiometry Reflectance & Lighting Computer Vision I CSE5A Lecture 6 Read Chapter 4 of Ponce & Forsyth Homework 1 Assigned Outline Solid Angle Irradiance Radiance BRDF Lambertian/Phong BRDF By analogy with
Radiometry Reflectance & Lighting Computer Vision I CSE5A Lecture 6 Read Chapter 4 of Ponce & Forsyth Homework 1 Assigned Outline Solid Angle Irradiance Radiance BRDF Lambertian/Phong BRDF By analogy with
Overview. Radiometry and Photometry. Foundations of Computer Graphics (Spring 2012)
 Foundations of Computer Graphics (Spring 2012) CS 184, Lecture 21: Radiometry http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs184 Overview Lighting and shading key in computer graphics HW 2 etc. ad-hoc shading models,
Foundations of Computer Graphics (Spring 2012) CS 184, Lecture 21: Radiometry http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs184 Overview Lighting and shading key in computer graphics HW 2 etc. ad-hoc shading models,
dq dt I = Irradiance or Light Intensity is Flux Φ per area A (W/m 2 ) Φ =
 Radiometry (From Intro to Optics, Pedrotti -4) Radiometry is measurement of Emag radiation (light) Consider a small spherical source Total energy radiating from the body over some time is Q total Radiant
Radiometry (From Intro to Optics, Pedrotti -4) Radiometry is measurement of Emag radiation (light) Consider a small spherical source Total energy radiating from the body over some time is Q total Radiant
Paths, diffuse interreflections, caching and radiometry. D.A. Forsyth
 Paths, diffuse interreflections, caching and radiometry D.A. Forsyth How we got here We want to render diffuse interreflections strategy: compute approximation B-hat, then gather B = E +(ρk)e +(ρk)( ˆB
Paths, diffuse interreflections, caching and radiometry D.A. Forsyth How we got here We want to render diffuse interreflections strategy: compute approximation B-hat, then gather B = E +(ρk)e +(ρk)( ˆB
Introduction to Computer Vision. Introduction CMPSCI 591A/691A CMPSCI 570/670. Image Formation
 Introduction CMPSCI 591A/691A CMPSCI 570/670 Image Formation Lecture Outline Light and Optics Pinhole camera model Perspective projection Thin lens model Fundamental equation Distortion: spherical & chromatic
Introduction CMPSCI 591A/691A CMPSCI 570/670 Image Formation Lecture Outline Light and Optics Pinhole camera model Perspective projection Thin lens model Fundamental equation Distortion: spherical & chromatic
A question from Piazza
 Radiometry, Reflectance, Lights CSE 252A Lecture 6 A question from Piazza 1 Announcements HW1 posted HWO graded, will be returned today If anyone has any registration issues, talk to me. Appearance: lighting,
Radiometry, Reflectance, Lights CSE 252A Lecture 6 A question from Piazza 1 Announcements HW1 posted HWO graded, will be returned today If anyone has any registration issues, talk to me. Appearance: lighting,
Lighting and Reflectance COS 426
 ighting and Reflectance COS 426 Ray Casting R2mage *RayCast(R3Scene *scene, int width, int height) { R2mage *image = new R2mage(width, height); for (int i = 0; i < width; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < height;
ighting and Reflectance COS 426 Ray Casting R2mage *RayCast(R3Scene *scene, int width, int height) { R2mage *image = new R2mage(width, height); for (int i = 0; i < width; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < height;
Lecture 22: Basic Image Formation CAP 5415
 Lecture 22: Basic Image Formation CAP 5415 Today We've talked about the geometry of scenes and how that affects the image We haven't talked about light yet Today, we will talk about image formation and
Lecture 22: Basic Image Formation CAP 5415 Today We've talked about the geometry of scenes and how that affects the image We haven't talked about light yet Today, we will talk about image formation and
Image Formation: Light and Shading. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 3
 Image Formation: Light and Shading CSE 152 Lecture 3 Announcements Homework 1 is due Apr 11, 11:59 PM Homework 2 will be assigned on Apr 11 Reading: Chapter 2: Light and Shading Geometric image formation
Image Formation: Light and Shading CSE 152 Lecture 3 Announcements Homework 1 is due Apr 11, 11:59 PM Homework 2 will be assigned on Apr 11 Reading: Chapter 2: Light and Shading Geometric image formation
Global Illumination. CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller. Machiraju/Zhang/Möller
 Global Illumination CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Reading Foley, van Dam (better): Chapter 16.7-13 Angel: Chapter 5.11, 11.1-11.5 2 Limitation of local illumination A concrete
Global Illumination CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Reading Foley, van Dam (better): Chapter 16.7-13 Angel: Chapter 5.11, 11.1-11.5 2 Limitation of local illumination A concrete
Announcements. Image Formation: Light and Shading. Photometric image formation. Geometric image formation
 Announcements Image Formation: Light and Shading Homework 0 is due Oct 5, 11:59 PM Homework 1 will be assigned on Oct 5 Reading: Chapters 2: Light and Shading CSE 252A Lecture 3 Geometric image formation
Announcements Image Formation: Light and Shading Homework 0 is due Oct 5, 11:59 PM Homework 1 will be assigned on Oct 5 Reading: Chapters 2: Light and Shading CSE 252A Lecture 3 Geometric image formation
dq dt I = Irradiance or Light Intensity is Flux Φ per area A (W/m 2 ) Φ =
 Radiometry (From Intro to Optics, Pedrotti -4) Radiometry is measurement of Emag radiation (light) Consider a small spherical source Total energy radiating from the body over some time is Q total Radiant
Radiometry (From Intro to Optics, Pedrotti -4) Radiometry is measurement of Emag radiation (light) Consider a small spherical source Total energy radiating from the body over some time is Q total Radiant
Announcements. Radiometry and Sources, Shadows, and Shading
 Announcements Radiometry and Sources, Shadows, and Shading CSE 252A Lecture 6 Instructor office hours This week only: Thursday, 3:45 PM-4:45 PM Tuesdays 6:30 PM-7:30 PM Library (for now) Homework 1 is
Announcements Radiometry and Sources, Shadows, and Shading CSE 252A Lecture 6 Instructor office hours This week only: Thursday, 3:45 PM-4:45 PM Tuesdays 6:30 PM-7:30 PM Library (for now) Homework 1 is
Announcement. Lighting and Photometric Stereo. Computer Vision I. Surface Reflectance Models. Lambertian (Diffuse) Surface.
 Lighting and Photometric Stereo CSE252A Lecture 7 Announcement Read Chapter 2 of Forsyth & Ponce Might find section 12.1.3 of Forsyth & Ponce useful. HW Problem Emitted radiance in direction f r for incident
Lighting and Photometric Stereo CSE252A Lecture 7 Announcement Read Chapter 2 of Forsyth & Ponce Might find section 12.1.3 of Forsyth & Ponce useful. HW Problem Emitted radiance in direction f r for incident
Radiance. Radiance properties. Radiance properties. Computer Graphics (Fall 2008)
 Computer Graphics (Fall 2008) COMS 4160, Lecture 19: Illumination and Shading 2 http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~cs4160 Radiance Power per unit projected area perpendicular to the ray per unit solid angle in
Computer Graphics (Fall 2008) COMS 4160, Lecture 19: Illumination and Shading 2 http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~cs4160 Radiance Power per unit projected area perpendicular to the ray per unit solid angle in
Lights, Surfaces, and Cameras. Light sources emit photons Surfaces reflect & absorb photons Cameras measure photons
 Reflectance 1 Lights, Surfaces, and Cameras Light sources emit photons Surfaces reflect & absorb photons Cameras measure photons 2 Light at Surfaces Many effects when light strikes a surface -- could be:
Reflectance 1 Lights, Surfaces, and Cameras Light sources emit photons Surfaces reflect & absorb photons Cameras measure photons 2 Light at Surfaces Many effects when light strikes a surface -- could be:
Lecture 15: Shading-I. CITS3003 Graphics & Animation
 Lecture 15: Shading-I CITS3003 Graphics & Animation E. Angel and D. Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 6E Addison-Wesley 2012 Objectives Learn that with appropriate shading so objects appear as threedimensional
Lecture 15: Shading-I CITS3003 Graphics & Animation E. Angel and D. Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 6E Addison-Wesley 2012 Objectives Learn that with appropriate shading so objects appear as threedimensional
Shading. Why we need shading. Scattering. Shading. Objectives
 Shading Why we need shading Objectives Learn to shade objects so their images appear three-dimensional Suppose we build a model of a sphere using many polygons and color it with glcolor. We get something
Shading Why we need shading Objectives Learn to shade objects so their images appear three-dimensional Suppose we build a model of a sphere using many polygons and color it with glcolor. We get something
Radiometry & BRDFs CS295, Spring 2017 Shuang Zhao
 Radiometry & BRDFs CS295, Spring 2017 Shuang Zhao Computer Science Department University of California, Irvine CS295, Spring 2017 Shuang Zhao 1 Today s Lecture Radiometry Physics of light BRDFs How materials
Radiometry & BRDFs CS295, Spring 2017 Shuang Zhao Computer Science Department University of California, Irvine CS295, Spring 2017 Shuang Zhao 1 Today s Lecture Radiometry Physics of light BRDFs How materials
CMSC427 Shading Intro. Credit: slides from Dr. Zwicker
 CMSC427 Shading Intro Credit: slides from Dr. Zwicker 2 Today Shading Introduction Radiometry & BRDFs Local shading models Light sources Shading strategies Shading Compute interaction of light with surfaces
CMSC427 Shading Intro Credit: slides from Dr. Zwicker 2 Today Shading Introduction Radiometry & BRDFs Local shading models Light sources Shading strategies Shading Compute interaction of light with surfaces
Lighting affects appearance
 Lighting affects appearance 1 Source emits photons Light And then some reach the eye/camera. Photons travel in a straight line When they hit an object they: bounce off in a new direction or are absorbed
Lighting affects appearance 1 Source emits photons Light And then some reach the eye/camera. Photons travel in a straight line When they hit an object they: bounce off in a new direction or are absorbed
3D Motion Analysis Based on 2D Point Displacements
 3D Motion Analysis Based on 2D Point Displacements 2D displacements of points observed on an unknown moving rigid body may provide information about - the 3D structure of the points - the 3D motion parameters
3D Motion Analysis Based on 2D Point Displacements 2D displacements of points observed on an unknown moving rigid body may provide information about - the 3D structure of the points - the 3D motion parameters
Rays and Throughput. The Light Field. Page 1
 Page 1 The Light Field Rays and throughput Form factors Light field representations Hemispherical illumination Illumination from uniform area light sources Shadows: Blockers, umbras and penumbras Radiosity
Page 1 The Light Field Rays and throughput Form factors Light field representations Hemispherical illumination Illumination from uniform area light sources Shadows: Blockers, umbras and penumbras Radiosity
CS-184: Computer Graphics. Today. Lecture 22: Radiometry! James O Brien University of California, Berkeley! V2014-S
 CS-184: Computer Graphics Lecture 22: Radiometry James O Brien University of California, Berkeley V2014-S-15-1.0 Today Radiometry: measuring light Local Illumination and Raytracing were discussed in an
CS-184: Computer Graphics Lecture 22: Radiometry James O Brien University of California, Berkeley V2014-S-15-1.0 Today Radiometry: measuring light Local Illumination and Raytracing were discussed in an
WHY WE NEED SHADING. Suppose we build a model of a sphere using many polygons and color it with glcolor. We get something like.
 LIGHTING 1 OUTLINE Learn to light/shade objects so their images appear three-dimensional Introduce the types of light-material interactions Build a simple reflection model---the Phong model--- that can
LIGHTING 1 OUTLINE Learn to light/shade objects so their images appear three-dimensional Introduce the types of light-material interactions Build a simple reflection model---the Phong model--- that can
Light Field = Radiance(Ray)
 The Light Field Concepts Light field = radiance function on rays Conservation of radiance Throughput and counting rays Measurement equation Irradiance calculations From London and Upton Light Field = Radiance(Ray)
The Light Field Concepts Light field = radiance function on rays Conservation of radiance Throughput and counting rays Measurement equation Irradiance calculations From London and Upton Light Field = Radiance(Ray)
Lecture 7 - Path Tracing
 INFOMAGR Advanced Graphics Jacco Bikker - November 2016 - February 2017 Lecture 7 - I x, x = g(x, x ) ε x, x + S ρ x, x, x I x, x dx Welcome! Today s Agenda: Introduction Advanced Graphics 3 Introduction
INFOMAGR Advanced Graphics Jacco Bikker - November 2016 - February 2017 Lecture 7 - I x, x = g(x, x ) ε x, x + S ρ x, x, x I x, x dx Welcome! Today s Agenda: Introduction Advanced Graphics 3 Introduction
Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 16: Lighting, Shading and Materials (Part 1)
 Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 16: Lighting, Shading and Materials (Part 1) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Why do we need Lighting & shading? Sphere
Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 16: Lighting, Shading and Materials (Part 1) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Why do we need Lighting & shading? Sphere
And if that 120MP Camera was cool
 Reflectance, Lights and on to photometric stereo CSE 252A Lecture 7 And if that 120MP Camera was cool Large Synoptic Survey Telescope 3.2Gigapixel camera 189 CCD s, each with 16 megapixels Pixels are 10µm
Reflectance, Lights and on to photometric stereo CSE 252A Lecture 7 And if that 120MP Camera was cool Large Synoptic Survey Telescope 3.2Gigapixel camera 189 CCD s, each with 16 megapixels Pixels are 10µm
Lighting and Materials
 http://graphics.ucsd.edu/~henrik/images/global.html Lighting and Materials Introduction The goal of any graphics rendering app is to simulate light Trying to convince the viewer they are seeing the real
http://graphics.ucsd.edu/~henrik/images/global.html Lighting and Materials Introduction The goal of any graphics rendering app is to simulate light Trying to convince the viewer they are seeing the real
Engineered Diffusers Intensity vs Irradiance
 Engineered Diffusers Intensity vs Irradiance Engineered Diffusers are specified by their divergence angle and intensity profile. The divergence angle usually is given as the width of the intensity distribution
Engineered Diffusers Intensity vs Irradiance Engineered Diffusers are specified by their divergence angle and intensity profile. The divergence angle usually is given as the width of the intensity distribution
CS201 Computer Vision Lect 4 - Image Formation
 CS201 Computer Vision Lect 4 - Image Formation John Magee 9 September, 2014 Slides courtesy of Diane H. Theriault Question of the Day: Why is Computer Vision hard? Something to think about from our view
CS201 Computer Vision Lect 4 - Image Formation John Magee 9 September, 2014 Slides courtesy of Diane H. Theriault Question of the Day: Why is Computer Vision hard? Something to think about from our view
Global Illumination The Game of Light Transport. Jian Huang
 Global Illumination The Game of Light Transport Jian Huang Looking Back Ray-tracing and radiosity both computes global illumination Is there a more general methodology? It s a game of light transport.
Global Illumination The Game of Light Transport Jian Huang Looking Back Ray-tracing and radiosity both computes global illumination Is there a more general methodology? It s a game of light transport.
Lighting and Shading Computer Graphics I Lecture 7. Light Sources Phong Illumination Model Normal Vectors [Angel, Ch
 15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 7 Lighting and Shading February 12, 2002 Frank Pfenning Carnegie Mellon University http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~fp/courses/graphics/ Light Sources Phong Illumination Model
15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 7 Lighting and Shading February 12, 2002 Frank Pfenning Carnegie Mellon University http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~fp/courses/graphics/ Light Sources Phong Illumination Model
Illumination. Courtesy of Adam Finkelstein, Princeton University
 llumination Courtesy of Adam Finkelstein, Princeton University Ray Casting mage RayCast(Camera camera, Scene scene, int width, int height) { mage image = new mage(width, height); for (int i = 0; i < width;
llumination Courtesy of Adam Finkelstein, Princeton University Ray Casting mage RayCast(Camera camera, Scene scene, int width, int height) { mage image = new mage(width, height); for (int i = 0; i < width;
Illumination. Michael Kazhdan ( /657) HB Ch. 14.1, 14.2 FvDFH 16.1, 16.2
 Illumination Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) HB Ch. 14.1, 14.2 FvDFH 16.1, 16.2 Ray Casting Image RayCast(Camera camera, Scene scene, int width, int height) { Image image = new Image(width, height); for
Illumination Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) HB Ch. 14.1, 14.2 FvDFH 16.1, 16.2 Ray Casting Image RayCast(Camera camera, Scene scene, int width, int height) { Image image = new Image(width, height); for
Computer Graphics. Illumination and Shading
 () Illumination and Shading Dr. Ayman Eldeib Lighting So given a 3-D triangle and a 3-D viewpoint, we can set the right pixels But what color should those pixels be? If we re attempting to create a realistic
() Illumination and Shading Dr. Ayman Eldeib Lighting So given a 3-D triangle and a 3-D viewpoint, we can set the right pixels But what color should those pixels be? If we re attempting to create a realistic
Today. Global illumination. Shading. Interactive applications. Rendering pipeline. Computergrafik. Shading Introduction Local shading models
 Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2009 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation of physics Global
Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2009 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation of physics Global
CS184 LECTURE RADIOMETRY. Kevin Wu November 10, Material HEAVILY adapted from James O'Brien, Brandon Wang, Fu-Chung Huang, and Aayush Dawra
 CS184 LECTURE RADIOMETRY Kevin Wu November 10, 2014 Material HEAVILY adapted from James O'Brien, Brandon Wang, Fu-Chung Huang, and Aayush Dawra ADMINISTRATIVE STUFF Project! TODAY Radiometry (Abridged):
CS184 LECTURE RADIOMETRY Kevin Wu November 10, 2014 Material HEAVILY adapted from James O'Brien, Brandon Wang, Fu-Chung Huang, and Aayush Dawra ADMINISTRATIVE STUFF Project! TODAY Radiometry (Abridged):
Philpot & Philipson: Remote Sensing Fundamentals Interactions 3.1 W.D. Philpot, Cornell University, Fall 12
 Philpot & Philipson: Remote Sensing Fundamentals Interactions 3.1 W.D. Philpot, Cornell University, Fall 1 3. EM INTERACTIONS WITH MATERIALS In order for an object to be sensed, the object must reflect,
Philpot & Philipson: Remote Sensing Fundamentals Interactions 3.1 W.D. Philpot, Cornell University, Fall 1 3. EM INTERACTIONS WITH MATERIALS In order for an object to be sensed, the object must reflect,
Announcements. Lighting. Camera s sensor. HW1 has been posted See links on web page for readings on color. Intro Computer Vision.
 Announcements HW1 has been posted See links on web page for readings on color. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 6 Deviations from the lens model Deviations from this ideal are aberrations
Announcements HW1 has been posted See links on web page for readings on color. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 6 Deviations from the lens model Deviations from this ideal are aberrations
Shading I Computer Graphics I, Fall 2008
 Shading I 1 Objectives Learn to shade objects ==> images appear threedimensional Introduce types of light-material interactions Build simple reflection model Phong model Can be used with real time graphics
Shading I 1 Objectives Learn to shade objects ==> images appear threedimensional Introduce types of light-material interactions Build simple reflection model Phong model Can be used with real time graphics
Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics. Spring Shading
 Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2017 Shading Why we need shading Suppose we build a model of a sphere using many polygons and then color it using a fixed color. We get something like But we rather
Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2017 Shading Why we need shading Suppose we build a model of a sphere using many polygons and then color it using a fixed color. We get something like But we rather
Light Field = Radiance(Ray)
 Page 1 The Light Field Light field = radiance function on rays Surface and field radiance Conservation of radiance Measurement Irradiance from area sources Measuring rays Form factors and throughput Conservation
Page 1 The Light Field Light field = radiance function on rays Surface and field radiance Conservation of radiance Measurement Irradiance from area sources Measuring rays Form factors and throughput Conservation
Introduction to Computer Graphics. Farhana Bandukwala, PhD Lecture 14: Light Interacting with Surfaces
 Introduction to Computer Graphics Farhana Bandukwala, PhD Lecture 14: Light Interacting with Surfaces Outline Computational tools Reflection models Polygon shading Computation tools Surface normals Vector
Introduction to Computer Graphics Farhana Bandukwala, PhD Lecture 14: Light Interacting with Surfaces Outline Computational tools Reflection models Polygon shading Computation tools Surface normals Vector
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 7b: Intro to lighting, Shading and Materials + Phong Lighting Model
 Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 7b: Intro to lighting, Shading and Materials + Phong Lighting Model Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Why do we need Lighting
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 7b: Intro to lighting, Shading and Materials + Phong Lighting Model Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Why do we need Lighting
CS5620 Intro to Computer Graphics
 So Far wireframe hidden surfaces Next step 1 2 Light! Need to understand: How lighting works Types of lights Types of surfaces How shading works Shading algorithms What s Missing? Lighting vs. Shading
So Far wireframe hidden surfaces Next step 1 2 Light! Need to understand: How lighting works Types of lights Types of surfaces How shading works Shading algorithms What s Missing? Lighting vs. Shading
Other approaches to obtaining 3D structure
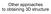 Other approaches to obtaining 3D structure Active stereo with structured light Project structured light patterns onto the object simplifies the correspondence problem Allows us to use only one camera camera
Other approaches to obtaining 3D structure Active stereo with structured light Project structured light patterns onto the object simplifies the correspondence problem Allows us to use only one camera camera
Computer Graphics and GPGPU Programming
 Computer Graphics and GPGPU Programming Donato D Ambrosio Department of Mathematics and Computer Science and Center of Excellence for High Performace Computing Cubo 22B, University of Calabria, Rende 87036,
Computer Graphics and GPGPU Programming Donato D Ambrosio Department of Mathematics and Computer Science and Center of Excellence for High Performace Computing Cubo 22B, University of Calabria, Rende 87036,
Local Reflection Models
 Local Reflection Models Illumination Thus Far Simple Illumination Models Ambient + Diffuse + Attenuation + Specular Additions Texture, Shadows, Used in global algs! (Ray tracing) Problem: Different materials
Local Reflection Models Illumination Thus Far Simple Illumination Models Ambient + Diffuse + Attenuation + Specular Additions Texture, Shadows, Used in global algs! (Ray tracing) Problem: Different materials
Illumination & Shading
 Illumination & Shading Goals Introduce the types of light-material interactions Build a simple reflection model---the Phong model--- that can be used with real time graphics hardware Why we need Illumination
Illumination & Shading Goals Introduce the types of light-material interactions Build a simple reflection model---the Phong model--- that can be used with real time graphics hardware Why we need Illumination
6. Illumination, Lighting
 Jorg s Graphics Lecture Notes 6. Illumination, Lighting 1 6. Illumination, Lighting No ray tracing in OpenGL! ray tracing: direct paths COP interreflection: soft shadows, color bleeding. umbra, penumbra,
Jorg s Graphics Lecture Notes 6. Illumination, Lighting 1 6. Illumination, Lighting No ray tracing in OpenGL! ray tracing: direct paths COP interreflection: soft shadows, color bleeding. umbra, penumbra,
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #6: Lights. Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2016
 CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #6: Lights Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2016 Announcements Thursday in class: midterm #1 Closed book Material
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #6: Lights Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2016 Announcements Thursday in class: midterm #1 Closed book Material
Perception of Shape from Shading
 1 Percetion of Shae from Shading Continuous image brightness variation due to shae variations is called shading Our ercetion of shae deends on shading Circular region on left is erceived as a flat disk
1 Percetion of Shae from Shading Continuous image brightness variation due to shae variations is called shading Our ercetion of shae deends on shading Circular region on left is erceived as a flat disk
Raytracing. COSC 4328/5327 Scott A. King
 Raytracing COSC 4328/5327 Scott A. King Basic Ray Casting Method pixels in screen Shoot ray p from the eye through the pixel. Find closest ray-object intersection. Get color at intersection Basic Ray Casting
Raytracing COSC 4328/5327 Scott A. King Basic Ray Casting Method pixels in screen Shoot ray p from the eye through the pixel. Find closest ray-object intersection. Get color at intersection Basic Ray Casting
COMPUTER GRAPHICS COURSE. LuxRender. Light Transport Foundations
 COMPUTER GRAPHICS COURSE LuxRender Light Transport Foundations Georgios Papaioannou - 2015 Light Transport Light is emitted at the light sources and scattered around a 3D environment in a practically infinite
COMPUTER GRAPHICS COURSE LuxRender Light Transport Foundations Georgios Papaioannou - 2015 Light Transport Light is emitted at the light sources and scattered around a 3D environment in a practically infinite
2/1/10. Outline. The Radiance Equation. Light: Flux Equilibrium. Light: Radiant Power. Light: Equation. Radiance. Jan Kautz
 Outline Jan Kautz Basic terms in radiometry Radiance Reflectance The operator form of the radiance equation Meaning of the operator form Approximations to the radiance equation 2005 Mel Slater, 2006 Céline
Outline Jan Kautz Basic terms in radiometry Radiance Reflectance The operator form of the radiance equation Meaning of the operator form Approximations to the radiance equation 2005 Mel Slater, 2006 Céline
rendering equation computer graphics rendering equation 2009 fabio pellacini 1
 rendering equation computer graphics rendering equation 2009 fabio pellacini 1 physically-based rendering synthesis algorithms that compute images by simulation the physical behavior of light computer
rendering equation computer graphics rendering equation 2009 fabio pellacini 1 physically-based rendering synthesis algorithms that compute images by simulation the physical behavior of light computer
Introduction to Computer Vision. Week 8, Fall 2010 Instructor: Prof. Ko Nishino
 Introduction to Computer Vision Week 8, Fall 2010 Instructor: Prof. Ko Nishino Midterm Project 2 without radial distortion correction with radial distortion correction Light Light Light! How do you recover
Introduction to Computer Vision Week 8, Fall 2010 Instructor: Prof. Ko Nishino Midterm Project 2 without radial distortion correction with radial distortion correction Light Light Light! How do you recover
Epipolar geometry contd.
 Epipolar geometry contd. Estimating F 8-point algorithm The fundamental matrix F is defined by x' T Fx = 0 for any pair of matches x and x in two images. Let x=(u,v,1) T and x =(u,v,1) T, each match gives
Epipolar geometry contd. Estimating F 8-point algorithm The fundamental matrix F is defined by x' T Fx = 0 for any pair of matches x and x in two images. Let x=(u,v,1) T and x =(u,v,1) T, each match gives
Introduction to Radiosity
 Introduction to Radiosity Produce photorealistic pictures using global illumination Mathematical basis from the theory of heat transfer Enables color bleeding Provides view independent representation Unfortunately,
Introduction to Radiosity Produce photorealistic pictures using global illumination Mathematical basis from the theory of heat transfer Enables color bleeding Provides view independent representation Unfortunately,
CS667 Lecture Notes: Radiometry
 CS667 Lecture Notes: Radiometry Steve Marschner Cornell University 23-28 August 2007 Radiometry is a system for describing the flow of radiant energy through space. It is essentially a geometric topic
CS667 Lecture Notes: Radiometry Steve Marschner Cornell University 23-28 August 2007 Radiometry is a system for describing the flow of radiant energy through space. It is essentially a geometric topic
CS6670: Computer Vision
 CS6670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 20: Light, reflectance and photometric stereo Light by Ted Adelson Readings Szeliski, 2.2, 2.3.2 Light by Ted Adelson Readings Szeliski, 2.2, 2.3.2 Properties
CS6670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 20: Light, reflectance and photometric stereo Light by Ted Adelson Readings Szeliski, 2.2, 2.3.2 Light by Ted Adelson Readings Szeliski, 2.2, 2.3.2 Properties
CSE 681 Illumination and Phong Shading
 CSE 681 Illumination and Phong Shading Physics tells us What is Light? We don t see objects, we see light reflected off of objects Light is a particle and a wave The frequency of light What is Color? Our
CSE 681 Illumination and Phong Shading Physics tells us What is Light? We don t see objects, we see light reflected off of objects Light is a particle and a wave The frequency of light What is Color? Our
Local vs. Global Illumination & Radiosity
 Last Time? Local vs. Global Illumination & Radiosity Ray Casting & Ray-Object Intersection Recursive Ray Tracing Distributed Ray Tracing An early application of radiative heat transfer in stables. Reading
Last Time? Local vs. Global Illumination & Radiosity Ray Casting & Ray-Object Intersection Recursive Ray Tracing Distributed Ray Tracing An early application of radiative heat transfer in stables. Reading
Cameras and Radiometry. Last lecture in a nutshell. Conversion Euclidean -> Homogenous -> Euclidean. Affine Camera Model. Simplified Camera Models
 Cameras and Radiometry Last lecture in a nutshell CSE 252A Lecture 5 Conversion Euclidean -> Homogenous -> Euclidean In 2-D Euclidean -> Homogenous: (x, y) -> k (x,y,1) Homogenous -> Euclidean: (x, y,
Cameras and Radiometry Last lecture in a nutshell CSE 252A Lecture 5 Conversion Euclidean -> Homogenous -> Euclidean In 2-D Euclidean -> Homogenous: (x, y) -> k (x,y,1) Homogenous -> Euclidean: (x, y,
3D model reconstruction using photoconsistency
 3D model reconstruction using photoconsistency Kirk Michael Joubert Submitted to the Department of Electrical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering and the Built Environment, University of Cape Town in fulfillment
3D model reconstruction using photoconsistency Kirk Michael Joubert Submitted to the Department of Electrical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering and the Built Environment, University of Cape Town in fulfillment
Ghost and Stray Light Analysis using TracePro. February 2012 Webinar
 Ghost and Stray Light Analysis using TracePro February 2012 Webinar Moderator: Andy Knight Technical Sales Manager Lambda Research Corporation Presenter: Michael Gauvin Vice President of Sales Lambda Research
Ghost and Stray Light Analysis using TracePro February 2012 Webinar Moderator: Andy Knight Technical Sales Manager Lambda Research Corporation Presenter: Michael Gauvin Vice President of Sales Lambda Research
Mosaics, Plenoptic Function, and Light Field Rendering. Last Lecture
 Mosaics, Plenoptic Function, and Light Field Rendering Topics in Image-ased Modeling and Rendering CSE291 J00 Lecture 3 Last Lecture Camera Models Pinhole perspective Affine/Orthographic models Homogeneous
Mosaics, Plenoptic Function, and Light Field Rendering Topics in Image-ased Modeling and Rendering CSE291 J00 Lecture 3 Last Lecture Camera Models Pinhole perspective Affine/Orthographic models Homogeneous
surface: reflectance transparency, opacity, translucency orientation illumination: location intensity wavelength point-source, diffuse source
 walters@buffalo.edu CSE 480/580 Lecture 18 Slide 1 Illumination and Shading Light reflected from nonluminous objects depends on: surface: reflectance transparency, opacity, translucency orientation illumination:
walters@buffalo.edu CSE 480/580 Lecture 18 Slide 1 Illumination and Shading Light reflected from nonluminous objects depends on: surface: reflectance transparency, opacity, translucency orientation illumination:
Visualisatie BMT. Rendering. Arjan Kok
 Visualisatie BMT Rendering Arjan Kok a.j.f.kok@tue.nl 1 Lecture overview Color Rendering Illumination 2 Visualization pipeline Raw Data Data Enrichment/Enhancement Derived Data Visualization Mapping Abstract
Visualisatie BMT Rendering Arjan Kok a.j.f.kok@tue.nl 1 Lecture overview Color Rendering Illumination 2 Visualization pipeline Raw Data Data Enrichment/Enhancement Derived Data Visualization Mapping Abstract
Objectives. Shading II. Distance Terms. The Phong Reflection Model
 Shading II Objectives Introduce distance terms to the shading model. More details about the Phong model (lightmaterial interaction). Introduce the Blinn lighting model (also known as the modified Phong
Shading II Objectives Introduce distance terms to the shading model. More details about the Phong model (lightmaterial interaction). Introduce the Blinn lighting model (also known as the modified Phong
x ~ Hemispheric Lighting
 Irradiance and Incoming Radiance Imagine a sensor which is a small, flat plane centered at a point ~ x in space and oriented so that its normal points in the direction n. This sensor can compute the total
Irradiance and Incoming Radiance Imagine a sensor which is a small, flat plane centered at a point ~ x in space and oriented so that its normal points in the direction n. This sensor can compute the total
Illumination Models & Shading
 Illumination Models & Shading Lighting vs. Shading Lighting Interaction between materials and light sources Physics Shading Determining the color of a pixel Computer Graphics ZBuffer(Scene) PutColor(x,y,Col(P));
Illumination Models & Shading Lighting vs. Shading Lighting Interaction between materials and light sources Physics Shading Determining the color of a pixel Computer Graphics ZBuffer(Scene) PutColor(x,y,Col(P));
rendering equation computer graphics rendering equation 2009 fabio pellacini 1
 rendering equation computer graphics rendering equation 2009 fabio pellacini 1 phsicall-based rendering snthesis algorithms that compute images b simulation the phsical behavior of light computer graphics
rendering equation computer graphics rendering equation 2009 fabio pellacini 1 phsicall-based rendering snthesis algorithms that compute images b simulation the phsical behavior of light computer graphics
Ambien Occlusion. Lighting: Ambient Light Sources. Lighting: Ambient Light Sources. Summary
 Summary Ambien Occlusion Kadi Bouatouch IRISA Email: kadi@irisa.fr 1. Lighting 2. Definition 3. Computing the ambient occlusion 4. Ambient occlusion fields 5. Dynamic ambient occlusion 1 2 Lighting: Ambient
Summary Ambien Occlusion Kadi Bouatouch IRISA Email: kadi@irisa.fr 1. Lighting 2. Definition 3. Computing the ambient occlusion 4. Ambient occlusion fields 5. Dynamic ambient occlusion 1 2 Lighting: Ambient
Objectives. Introduce Phong model Introduce modified Phong model Consider computation of required vectors Discuss polygonal shading.
 Shading II 1 Objectives Introduce Phong model Introduce modified Phong model Consider computation of required vectors Discuss polygonal shading Flat Smooth Gouraud 2 Phong Lighting Model A simple model
Shading II 1 Objectives Introduce Phong model Introduce modified Phong model Consider computation of required vectors Discuss polygonal shading Flat Smooth Gouraud 2 Phong Lighting Model A simple model
CS6670: Computer Vision
 CS6670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 21: Light, reflectance and photometric stereo Announcements Final projects Midterm reports due November 24 (next Tuesday) by 11:59pm (upload to CMS) State the
CS6670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 21: Light, reflectance and photometric stereo Announcements Final projects Midterm reports due November 24 (next Tuesday) by 11:59pm (upload to CMS) State the
Specular Reflection. Lecture 19. Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Oct 4, 2017
 Specular Reflection Lecture 19 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 4, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, 2017 1 / 22 Outline 1 Specular Reflection
Specular Reflection Lecture 19 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Oct 4, 2017 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Specular Reflection Wed, Oct 4, 2017 1 / 22 Outline 1 Specular Reflection
The Rendering Equation. Computer Graphics CMU /15-662
 The Rendering Equation Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662 Review: What is radiance? Radiance at point p in direction N is radiant energy ( #hits ) per unit time, per solid angle, per unit area perpendicular
The Rendering Equation Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662 Review: What is radiance? Radiance at point p in direction N is radiant energy ( #hits ) per unit time, per solid angle, per unit area perpendicular
Raytracing CS148 AS3. Due :59pm PDT
 Raytracing CS148 AS3 Due 2010-07-25 11:59pm PDT We start our exploration of Rendering - the process of converting a high-level object-based description of scene into an image. We will do this by building
Raytracing CS148 AS3 Due 2010-07-25 11:59pm PDT We start our exploration of Rendering - the process of converting a high-level object-based description of scene into an image. We will do this by building
Local Illumination. CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller. Machiraju/Zhang/Möller
 Local Illumination CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Graphics Pipeline Hardware Modelling Transform Visibility Illumination + Shading Perception, Interaction Color Texture/ Realism
Local Illumination CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Graphics Pipeline Hardware Modelling Transform Visibility Illumination + Shading Perception, Interaction Color Texture/ Realism
Lighting. Camera s sensor. Lambertian Surface BRDF
 Lighting Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 6 Special light sources Point sources Distant point sources Strip sources Area sources Common to think of lighting at infinity (a function on the
Lighting Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 6 Special light sources Point sources Distant point sources Strip sources Area sources Common to think of lighting at infinity (a function on the
Lighting affects appearance
 Lighting affects appearance 1 Source emits photons Light And then some reach the eye/camera. Photons travel in a straight line When they hit an object they: bounce off in a new direction or are absorbed
Lighting affects appearance 1 Source emits photons Light And then some reach the eye/camera. Photons travel in a straight line When they hit an object they: bounce off in a new direction or are absorbed
