Welcome to Solid Edge University 2015
|
|
|
- Sybil Lucas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 #SEU15 Welcome to Solid Edge University 2015 Realize innovation.
2 Surfacing: A Hands-on Experience Solid Edge isn t just a great tool for typical machinery design; it s also very powerful when it comes to creating complex shapes, like those found in consumer products. To show you Solid Edge s capabilities we re going to redesign the rear panel of an Actifry deep fryer from one of our French customers, Groupe SEB. I m sure you ve heard of their brands Rowenta, Moulinex, Krups, and Tefal. An industrial designer has come up with an aesthetically pleasing and functional design modification to the rear panel and we will use those sketches to redesign the panel using Solid Edge s powerful surfacing capabilities. Page 2
3 SEB Surfacing enhancement in SOLID EDGE ST6 have enabled us to create some models 40% faster compared to other CAD systems Olivier Pellerin IT Innovation Manager Page 3
4 Surface Modeling Surface based features Edges Rule Curves a major part of model definition. Highlight lines Silhouette edges, flow lines But surface shape is still important Edges and faces are mainly Bspline based. Typically start with a wire frame and add surfaces. Aesthetics is primary concern, function is secondary. Page 4
5 Surface Modeling A Surfacing Approach Exact edge control. Edges are NOT just the result of extrudes and cuts. Edges are developed through character curves. Page 5
6 Surface Modeling Character Curves Hard Edges Actual edges used to help define the flow of a surface. Typically curves are of importance for aesthetic definition. Soft Edges Horizon edges are typically visible from front, top, and end views. Important in defining the overall shape of the model. Soft Edges Hard Edges Page 6
7 Creating Curves 2D Curve Bspline Curve created on a sketch plane. Creating by clicking 3 or more points adds edit points and control vertices. Click and drag to define a freehand curve adds only control vertices. Keep it simple! Less edit points make the curve easier to adjust into smooth shapes. Page 7
8 Creating Curves Curves can also be defined by: Cross Curves which are created by projecting 2 curves and determining their intersection for a resulting curve Intersecting surfaces Projected sketches onto a surface Contour curves Sketching a curve directly onto a surface Page 8
9 Curvature: Solid Modeling vs.- Surface Modeling With traditional solid modeling, designers typically use sketch elements like lines and arcs to define extrusions and cuts in a solid model. Sketched fillets and rounds are tangent to lines and other arcs. You can t define curvature in the sketch element unless using Bspline curves. Page 9
10 Curvature: Solid Modeling vs.- Surface Modeling The result is reflections that have abrupt changes and it is clear to see where the curvature changes from one patch to the next. Page 10
11 Curvature: Solid Modeling vs.- Surface Modeling If this model was created using surface modeling techniques with curvature continuous 2D and 3D curves, the result is much more appealing! Page 11
12 Typical Workflows Use 3D curves to develop surfaces. Some additional 3D curves are obtained from surfaces. It is common to use Strip Surfaces to ensure continuous curvature across the mid-line on symmetric parts. Over-Building surfaces is also common to extend, trim and intersect surfaces to get the final design. Strip Surfaces Page 12
13 Techniques It is very difficult to model 100% accurately to the exact numbers for the curves at intersecting surfaces. It is typical, and more reliable, to overbuild surfaces and trim them back to each other, rather than determine the exact curve at the intersection and build surfaces from there. A surface that is too small is difficult to work with, but a surface that is too large, once trimmed, is never a problem. Making a surface larger than it needs to be helps to prevent extra edges from showing up in the model. One thing that gives surface modelers the most problems is building smooth transitions between faces and across edges. The best way to eliminate this difficulty is to eliminate the edges as much as possible. Page 13
14 Workflow REMEMBER - Every surface coming from an Industrial Design is not necessarily critical to the overall design. A tiny blend in this example has been modeled with many curves. There are some basic practices that are used for most surface model designs. Break the model up into as few surface patches as possible. Never surface model fillets, rounds and non-critical small blends. Let the software do what it is good at: Let Parasolid handle these once you have a solid model. Page 14
15 Techniques Surface modeling is a lot more work than solid modeling. Surface modeling forces you to work face, by face, by face, and faces must be manually fit together. These actions are all performed automatically in solid modeling. Where surfacing techniques become beneficial is in situations where solid modeling becomes clumsy or inefficient, or when a given modeling task is simply impossible with solids. Leave out detail that can be modeled later using solid modeling features. This is easier and with far less features in the solid. LETS GET STARTED! Page 15
16 Surfacing Open PJ857 ACTIFRY 1,5yp.asm from the Actifry folder Change the config to 01-Interior Components. Rotate to the back to see the Fan assembly. Change the config to 00-All. Note the new fan design is protruding through the back panel. Page 16
17 Surfacing Change the config to 02-Industrial Design Sketches. Note: The Industrial Designer has come up with an ergonomic solution for the interference problem. Cycle through the Front and Top views using the view cube to see the sketches. Page 17
18 Surfacing Select the rear panel and Edit-in-place ( d.par). If not displayed, CTRL+Q to show the ID sketches. Create a Sketch on the Top plane. CTRL+H to orient to a sketch plane view Zoom and pan to the part where we will add the feature to remove the interference. Page 18
19 Surfacing Start a 2D curve at about the center plane. Click and hold + drag a curve to match the top ID sketch. Holding the left mouse button down as you drag the curve prevents adding keypoints which can affect editing it to match the ID sketch correctly. Connect the endpoint to the Front plane. Page 19
20 Surfacing Increase the Degree of the curve to 5 Add a horiz/vert relationship to the first control vertex. Tweak the control vertices to match the curve. Exit the sketch. Page 20
21 Surfacing Rotate the model Show the Upper and Lower sketches at the bottom of the feature list. These were created parallel to the Top plane and relative to the top and bottom of the new feature in the industrial design sketch. Right click on the last Sketch feature in PathFinder and select Multi-Color Sketch Display Page 21
22 Surfacing Start a new Sketch on the Front Plane. CTL+H to transition to the sketch plane Zoom and pan to the part where we will add the feature to remove the interference. Select the Curve command from the radial menu. Holding down the ALT key through the entire process, left click and drag a curve matching the ID sketch. The ALT key keeps it from attaching to points as you are creating it. Page 22
23 Surfacing Connect the top and bottom endpoints to the Upper and Lower Sketches that you displayed earlier. Tweak the control vertices to best match the ID sketch. Exit the sketch. Page 23
24 Surfacing Right click on the last Sketch feature in PathFinder and select Multi-Color Sketch Display CTRL+Q to hide the Industrial Design sketches. Use BlueDot to connect the endpoint of the top view sketch and the one you just created. NOTE that BlueDot connects the sketches and is not dependent on creation order. Page 24
25 Surfacing Create an Extruded surface using the Front profile sketch curve. This is a strip surface used for construction. Hide the last sketch and All BlueDots. Page 25
26 Surfacing Create a BlueSurf between the Upper sketch, middle sketch and the Lower sketch. Use the edge of the strip surface as a guide curve. Change the tangency option to Tangent Continuous with the strip surface. If this is not available you had missed the step to hide the first 2D curve. Hide all sketches, curves and the extruded strip surface. Page 26
27 Surfacing From the Inspect tab turn on the Reflective Plane. Show the Rear Profile Sketch. Project this sketch onto the BlueSurf. Hide sketches. Turn off the reflective plane Page 27
28 Surfacing Trim the BlueSurf with the Projected curve. Select the face to remove. Hide curves. Page 28
29 Surfacing Mirror the surface about the Front plane. Stitch the surfaces together. Use default settings and dismiss the dialog. Page 29
30 Surfacing Use the Ruled surface command to generate a ruled surface around the perimeter of the surface body. Use the Taper to plane option. Select the Right plane to taper to. Set the length to mm and the taper angle to Page 30
31 Surfacing Hide all Ref. Planes Create a Surface Blend with a Constant Width between the ruled surface and the stitched surface mm radius. Point the arrows toward the inside of the part. 2x Page 31
32 Surfacing Create a Bounded surface to cap the ruled surface. Stitch the surfaces together. This creates a construction solid. Page 32
33 Surfacing Run the Emboss command. Select the part as the target to emboss. Select the construction solid as the tool body. Flip the side for the embossed feature. Accept the default thickness of 2.50 mm. Page 33
34 Surfacing Run the Round command. Press CTRL+Shift+D to disable dynamic preview as you select edges to round. Add a 5.00 mm round to convex side of the embossed feature (4 edges). Preview and finish but stay in the round command. Page 34
35 Surfacing Rotate the model and add a 7.00 mm round to the edges of the convex side of the feature. Dynamic preview is still disabled (5 edges). Finish the command. Save the model and Close and Return to the top level Assembly Page 35
36 Surfacing Change the display configuration to 03-No Lid Page 36
37 Surfacing Pan and zoom to the handle shroud ( A.par). Select the shroud and Edit in place. Note the broken up individual faces. Increase the sharpness to 4 or 5 Page 37
38 Surfacing From the inspect tab, display the Zebra striping to show the C1 edges Abrupt changes in direction. Run the Redefine surface command and select 6 individual top surfaces. Enable Replace faces on solid body. Change the common tangency option to Tangent Continuous and note the smooth transitions on edges and internal to the selection. Page 38
39 Surfacing Turn off the Zebra striping Change the sharpness to 3. This will speed up display as you return to the assembly as it would attempt to sharpen every curve in the assembly. Close and return to the top level assembly. Save and close the Assembly Page 39
40 Surfacing Free Styling! Let s Get Creative! We have the design of a simple ballpoint pen cap. The Goal: Use Surface Modeling to create an aesthetically pleasing and functional transitional housing from the basic Pen Cap for a Micro USB Drive. Page 40
41 Surfacing Free Styling! Open USB-PEN_Design.par from the Pen Cap Exercise folder. Show the Construction body (USB Drive) and the sketch by checking their display option in the PathFinder. Page 41
42 Surfacing Free Styling! The Plan: We will create planer sketches in the Front and Right views to define what the transition should look like. The existing sketch represents the rectangular size/shape we will transition to. Show the Front and right Reference Planes from the PathFinder. Page 42
43 Surfacing Free Styling! Because surfaces are driven and reliant on sketches and curves, surface modeling is done in the Ordered mode to preserve the history of these elements. Right mouse click in space and select Transition to Ordered Start a sketch. Create an offset Parallel Plane from the Right reference plane. Offset about 25 mm Page 43
44 Surfacing Free Styling! Transition to a sketch plane view by pressing CTRL+H. Select the Curve command from the Draw Group on the Home tab. Start the curve by clicking the endpoint of the top sketch and then click-and-drag a curve down to the inside of the pen body. When picking the ending point, stop short of the centerline and do not connect to the centerline. Press and holding the ALT key prevents connecting to any background geometry inadvertently. Page 44
45 Surfacing Free Styling! By using the click-and-drag curve creation method we end up with about 4 control vertices. Let s increase the control by increasing the degree of the curve from 3 to 4. Using the Horizontal/Vertical relationship, create a vertical relationship between the starting endpoint and the first control vertex. This guarantees the start of the curve to be perpendicular to the plane of the rectangular sketch. Page 45
46 Surfacing Free Styling! Adjust the curve by dragging the control vertices around. If you want more control you can always go back and increase the degree of the curve incrementally to add another control vertex to adjust. Select the curve and mirror about the center plane. Close out of the sketch. Page 46
47 Surfacing Free Styling! Next we will repeat this process to define the shape we want from the Front view. Create a new Sketch and define a Parallel plane from the Front reference plane. Offset about 25 mm. Transition to a sketch plane view by pressing CTRL+H. Page 47
48 Surfacing Free Styling! Just like before, select the Curve command from the Draw Group on the Home tab. Start the curve by clicking the endpoint of the top sketch and then click-and-drag a curve down to the inside of the pen body. Finish the curve roughly close to alignment with the first curves Page 48
49 Surfacing Free Styling! Like before, increase the degree of the curve to at least 4 to add more control. Create the vertical alignment between the starting endpoint nd the first control vertex. Tweak the curve to you liking. Page 49
50 Surfacing Free Styling! Once again, mirror the final curve about the center plane. Finish the sketch. Hide the reference planes. You now have profiles of what you would like the new area to look like from the front and right views Page 50
51 Surfacing Free Styling! The next step is to find the resulting 3D Cross curves from the intersections of the these 2D curves. Basically think of it as projecting a surface from each curve and the intersection of these surfaces would be the resulting cross curve. Page 51
52 Surfacing Free Styling! From the surfacing tab, click on the Cross curve command. Select one curve from each profile to get the resulting curve. Repeat this process until you have all 4 Cross curves generated. Page 52
53 Surfacing Free Styling! Hide the 2D curve sketches. Next we will create surfaces (4) between the curves using the BlueSurf command. Hide all sketches and curves. Page 53
54 Surfacing Free Styling! Create a Bounded surface on the top using the edges of the surfaces. Set selection option to Single. Stitch the 5 surfaces together. Add a 2.00 mm round to each corner Page 54
55 Surfacing Free Styling! If you rotate the model and look inside the cap, you will see that the surfaces extend through the cap. In order to successfully add this geometry, it will need to be trimmed. Copy the inside surface of the cap. From the right click context menu, Hide the Design Body. Page 55
56 Surfacing Free Styling! Using the Intersect command, select the 2 surface bodies. Select the area inside the copied cap surface to remove. Select the extending copied surface to trip it back to the stitched surface. Stitch the surfaces together to form a new construction solid. Page 56
57 Surfacing Free Styling! Now lets turn on the 2D Sketches and tweak the shape of this design. Show the 2 sketches under the Ordered header. Select a sketch and click Dynamic Edit. Tweak the curves using the control vertices and the watch the solid dynamically update to the changes. Caution: Avoid making extreme radical tweaks as it will slow down recalculation and may fail if surfaces overlap. Page 57
58 Surfacing Free Styling! Rename the new construction solid to USB Housing. Toggle the Construction Body to a Design Body. Double click to make it the Activate body. Check the box to show the Pen Cap body also. SAVE the part file Page 58
59 Surfacing Free Styling! You may also wish to change the size of the top rectangle. Show the Synchronous sketch. Edit the length dimension and/or width dimensions and again the solid will react. Hide the sketches Page 59
60 Surfacing Free Styling! Let s add a lip to the top face. Extrude and offset profile from the edge of the top face. Use Project to Sketch with the Offset option in the profile. Use Single Face to pick the outer edges and offset to the outside 1.00 mm. Extend up 2.00 mm. Page 60
61 Surfacing Free Styling! Add 1.00 mm rounds to the edges of the extrusion. After that, add another 1.00 mm round where those intersect the main body. Page 61
62 Surfacing Free Styling! Now let s subtract the USB Drive body from the housing. Select the Housing as the Target. Select the USB Drive as the Tool. Making the Pen Cap the Active body shows how the parts fit together. Select the Move Faces command to increase the size of the pocket for the PCB components on the Micro USB Drive. Page 62
63 Surfacing Free Styling! Finally let s unite the Pen Cap body with the USB Housing body to make them one. Select the Pen Cap as the Target. Select the USB housing as the Tool Add a 1.00 mm round to the intersecting edge. Use Edge/Corner option and fence select the edge. Make the round larger: mm Change to Shaded view to see how it will really look. Page 63
64 Surfacing Free Styling! Toggle the USB Drive to a Design Body. Save the Part file again. Now lets Publish the 2 Design Bodies into an Assembly of the Pen Cap and the Micro USB Drive. Select Multi-body Publish command and make sure the option is chacked to build the assembly, The Path and filenames leave as default. Click Save Files Page 64
65 Surfacing Free Styling! From the publish dialog box, double click the assembly at the bottom to open it in Solid Edge and see the final product. CONGRATULATIONS! Your design is complete! Page 65
66 Contact Doug Stainbrook Global Technical Business Development Mainstream Engineering/ Inc. Digital Factory Division 675 Discovery Drive Huntsville, AL United States Tel. :+1 (256) Fax :+1 (256) Mobile :+1 (256) Realize innovation. Page 66
Constructing treatment features
 Constructing treatment features Publication Number spse01530 Constructing treatment features Publication Number spse01530 Proprietary and restricted rights notice This software and related documentation
Constructing treatment features Publication Number spse01530 Constructing treatment features Publication Number spse01530 Proprietary and restricted rights notice This software and related documentation
Solid Edge Surfacing
 Solid Edge Surfacing Publication Number MT01418 160 Proprietary and Restricted Rights Notices Copyright 2004 UGS Corp. All Rights Reserved. This software and related documentation are proprietary to UGS
Solid Edge Surfacing Publication Number MT01418 160 Proprietary and Restricted Rights Notices Copyright 2004 UGS Corp. All Rights Reserved. This software and related documentation are proprietary to UGS
Proprietary and restricted rights notice
 Proprietary and restricted rights notice This software and related documentation are proprietary to Siemens Product Lifecycle Management Software Inc. 2012 Siemens Product Lifecycle Management Software
Proprietary and restricted rights notice This software and related documentation are proprietary to Siemens Product Lifecycle Management Software Inc. 2012 Siemens Product Lifecycle Management Software
Autodesk Inventor Design Exercise 2: F1 Team Challenge Car Developed by Tim Varner Synergis Technologies
 Autodesk Inventor Design Exercise 2: F1 Team Challenge Car Developed by Tim Varner Synergis Technologies Tim Varner - 2004 The Inventor User Interface Command Panel Lists the commands that are currently
Autodesk Inventor Design Exercise 2: F1 Team Challenge Car Developed by Tim Varner Synergis Technologies Tim Varner - 2004 The Inventor User Interface Command Panel Lists the commands that are currently
Inventor 201. Work Planes, Features & Constraints: Advanced part features and constraints
 Work Planes, Features & Constraints: 1. Select the Work Plane feature tool, move the cursor to the rim of the base so that inside and outside edges are highlighted and click once on the bottom rim of the
Work Planes, Features & Constraints: 1. Select the Work Plane feature tool, move the cursor to the rim of the base so that inside and outside edges are highlighted and click once on the bottom rim of the
Create the Through Curves surface
 Create the Through Curves surface 1. Open ffm4_mc_fender. 2. Select all three strings, and then on the Analyze Shape toolbar, click Show End Points. Notice there are two curves in the strings on the left
Create the Through Curves surface 1. Open ffm4_mc_fender. 2. Select all three strings, and then on the Analyze Shape toolbar, click Show End Points. Notice there are two curves in the strings on the left
3 AXIS STANDARD CAD. BobCAD-CAM Version 28 Training Workbook 3 Axis Standard CAD
 3 AXIS STANDARD CAD This tutorial explains how to create the CAD model for the Mill 3 Axis Standard demonstration file. The design process includes using the Shape Library and other wireframe functions
3 AXIS STANDARD CAD This tutorial explains how to create the CAD model for the Mill 3 Axis Standard demonstration file. The design process includes using the Shape Library and other wireframe functions
Autodesk Fusion 360: Model. Overview. Modeling techniques in Fusion 360
 Overview Modeling techniques in Fusion 360 Modeling in Fusion 360 is quite a different experience from how you would model in conventional history-based CAD software. Some users have expressed that it
Overview Modeling techniques in Fusion 360 Modeling in Fusion 360 is quite a different experience from how you would model in conventional history-based CAD software. Some users have expressed that it
#SEU Welcome! Solid Edge University 2016
 #SEU 2016 Welcome! Solid Edge University 2016 Realize innovation. Surface Modeling in Solid Edge Basic Curve and Surface Generation Realize innovation. Surface Modeling in Solid Edge Basic Curve and Surface
#SEU 2016 Welcome! Solid Edge University 2016 Realize innovation. Surface Modeling in Solid Edge Basic Curve and Surface Generation Realize innovation. Surface Modeling in Solid Edge Basic Curve and Surface
Skateboard. Hanger. in the Feature Manager and click Sketch on the Context toolbar, Fig. 1. Fig. 2
 Chapter 3 Skateboard Hanger A. Sketch1 Lines. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part Metric and OK. Step 2. Click Right Plane in the Feature Manager and click Sketch on the Context toolbar, Fig. 1.
Chapter 3 Skateboard Hanger A. Sketch1 Lines. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part Metric and OK. Step 2. Click Right Plane in the Feature Manager and click Sketch on the Context toolbar, Fig. 1.
CATIA V5 Parametric Surface Modeling
 CATIA V5 Parametric Surface Modeling Version 5 Release 16 A- 1 Toolbars in A B A. Wireframe: Create 3D curves / lines/ points/ plane B. Surfaces: Create surfaces C. Operations: Join surfaces, Split & Trim
CATIA V5 Parametric Surface Modeling Version 5 Release 16 A- 1 Toolbars in A B A. Wireframe: Create 3D curves / lines/ points/ plane B. Surfaces: Create surfaces C. Operations: Join surfaces, Split & Trim
Introduction to Synchronous Modeling
 #SEU15 Introduction to Synchronous Modeling Craig Ruchti Global Technical Business Development Applications Engineer Realize innovation. Introduction to Synchronous Technology Agenda Introduction Synchronous
#SEU15 Introduction to Synchronous Modeling Craig Ruchti Global Technical Business Development Applications Engineer Realize innovation. Introduction to Synchronous Technology Agenda Introduction Synchronous
422 - Getting the Most out of Surfacing
 4 th Generation VLC courtesy of Edison2 422 - Getting the Most out of Surfacing Dan Vinson, Part Product Manager, 19930 #SEU13 Agenda: 422 - Getting the Most out of Surfacing Who am I? What you will learn
4 th Generation VLC courtesy of Edison2 422 - Getting the Most out of Surfacing Dan Vinson, Part Product Manager, 19930 #SEU13 Agenda: 422 - Getting the Most out of Surfacing Who am I? What you will learn
Autodesk Fusion 360 Training: The Future of Making Things Attendee Guide
 Autodesk Fusion 360 Training: The Future of Making Things Attendee Guide Abstract After completing this workshop, you will have a basic understanding of editing 3D models using Autodesk Fusion 360 TM to
Autodesk Fusion 360 Training: The Future of Making Things Attendee Guide Abstract After completing this workshop, you will have a basic understanding of editing 3D models using Autodesk Fusion 360 TM to
Autodesk Inventor 6 Essentials Instructor Guide Chapter Four: Creating Placed Features Chapter Outline This chapter provides instruction on the follow
 Chapter Four: Creating Placed Features Chapter Outline This chapter provides instruction on the following topics and provides exercises for students to practice their skills. Day Two Topic: How to create
Chapter Four: Creating Placed Features Chapter Outline This chapter provides instruction on the following topics and provides exercises for students to practice their skills. Day Two Topic: How to create
Solidworks 2006 Surface-modeling
 Solidworks 2006 Surface-modeling (Tutorial 2-Mouse) Surface-modeling Solid-modeling A- 1 Assembly Design Design with a Master Model Surface-modeling Tutorial 2A Import 2D outline drawing into Solidworks2006
Solidworks 2006 Surface-modeling (Tutorial 2-Mouse) Surface-modeling Solid-modeling A- 1 Assembly Design Design with a Master Model Surface-modeling Tutorial 2A Import 2D outline drawing into Solidworks2006
Adjust model for 3D Printing. Direct modeling tools 13,0600,1489,1616(SP6)
 Adjust model for 3D Printing Direct modeling tools 13,0600,1489,1616(SP6) Sometimes, the model needs to be prepared or adapted for printing. Adding material, change of a draft angles are an example. In
Adjust model for 3D Printing Direct modeling tools 13,0600,1489,1616(SP6) Sometimes, the model needs to be prepared or adapted for printing. Adding material, change of a draft angles are an example. In
Lesson 1: Creating T- Spline Forms. In Samples section of your Data Panel, browse to: Fusion 101 Training > 03 Sculpt > 03_Sculpting_Introduction.
 3.1: Sculpting Sculpting in Fusion 360 allows for the intuitive freeform creation of organic solid bodies and surfaces by leveraging the T- Splines technology. In the Sculpt Workspace, you can rapidly
3.1: Sculpting Sculpting in Fusion 360 allows for the intuitive freeform creation of organic solid bodies and surfaces by leveraging the T- Splines technology. In the Sculpt Workspace, you can rapidly
Module 1: Basics of Solids Modeling with SolidWorks
 Module 1: Basics of Solids Modeling with SolidWorks Introduction SolidWorks is the state of the art in computer-aided design (CAD). SolidWorks represents an object in a virtual environment just as it exists
Module 1: Basics of Solids Modeling with SolidWorks Introduction SolidWorks is the state of the art in computer-aided design (CAD). SolidWorks represents an object in a virtual environment just as it exists
Exercise Guide. Published: August MecSoft Corpotation
 VisualCAD Exercise Guide Published: August 2018 MecSoft Corpotation Copyright 1998-2018 VisualCAD 2018 Exercise Guide by Mecsoft Corporation User Notes: Contents 2 Table of Contents About this Guide 4
VisualCAD Exercise Guide Published: August 2018 MecSoft Corpotation Copyright 1998-2018 VisualCAD 2018 Exercise Guide by Mecsoft Corporation User Notes: Contents 2 Table of Contents About this Guide 4
CO 2 Shell Car. Body. in the Feature Manager and click Sketch from the context toolbar, Fig. 1. on the Standard Views toolbar.
 CO 2 Shell Car Chapter 2 Body A. Save as "BODY". Step 1. If necessary, open your BLANK file. Step 2. Click File Menu > Save As. Step 3. Key-in BODY for the filename and press ENTER. B. FRONT Wheel Shell.
CO 2 Shell Car Chapter 2 Body A. Save as "BODY". Step 1. If necessary, open your BLANK file. Step 2. Click File Menu > Save As. Step 3. Key-in BODY for the filename and press ENTER. B. FRONT Wheel Shell.
3D Design with 123D Design
 3D Design with 123D Design Introduction: 3D Design involves thinking and creating in 3 dimensions. x, y and z axis Working with 123D Design 123D Design is a 3D design software package from Autodesk. A
3D Design with 123D Design Introduction: 3D Design involves thinking and creating in 3 dimensions. x, y and z axis Working with 123D Design 123D Design is a 3D design software package from Autodesk. A
CATIA Surface Design
 CATIA V5 Training Exercises CATIA Surface Design Version 5 Release 19 September 2008 EDU_CAT_EN_GS1_FX_V5R19 Table of Contents (1/2) Creating Wireframe Geometry: Recap Exercises 4 Creating Wireframe Geometry:
CATIA V5 Training Exercises CATIA Surface Design Version 5 Release 19 September 2008 EDU_CAT_EN_GS1_FX_V5R19 Table of Contents (1/2) Creating Wireframe Geometry: Recap Exercises 4 Creating Wireframe Geometry:
Feature-Based Modeling and Optional Advanced Modeling. ENGR 1182 SolidWorks 05
 Feature-Based Modeling and Optional Advanced Modeling ENGR 1182 SolidWorks 05 Today s Objectives Feature-Based Modeling (comprised of 2 sections as shown below) 1. Breaking it down into features Creating
Feature-Based Modeling and Optional Advanced Modeling ENGR 1182 SolidWorks 05 Today s Objectives Feature-Based Modeling (comprised of 2 sections as shown below) 1. Breaking it down into features Creating
SOLIDWORKS 2016: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate Users
 SOLIDWORKS 2016: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate Users The premium provider of learning products and solutions www.cadartifex.com Table of Contents Dedication... 3 Preface... 15 Part 1. Introducing
SOLIDWORKS 2016: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate Users The premium provider of learning products and solutions www.cadartifex.com Table of Contents Dedication... 3 Preface... 15 Part 1. Introducing
Input CAD Solid Model Assemblies - Split into separate Part Files. DXF, IGES WMF, EMF STL, VDA, Rhino Parasolid, ACIS
 General NC File Output List NC Code Post Processor Selection Printer/Plotter Output Insert Existing Drawing File Input NC Code as Geometry or Tool Paths Input Raster Image Files Report Creator and Designer
General NC File Output List NC Code Post Processor Selection Printer/Plotter Output Insert Existing Drawing File Input NC Code as Geometry or Tool Paths Input Raster Image Files Report Creator and Designer
SOLIDWORKS: Lesson III Patterns & Mirrors. UCF Engineering
 SOLIDWORKS: Lesson III Patterns & Mirrors UCF Engineering Solidworks Review Last lesson we discussed several more features that can be added to models in order to increase their complexity. We are now
SOLIDWORKS: Lesson III Patterns & Mirrors UCF Engineering Solidworks Review Last lesson we discussed several more features that can be added to models in order to increase their complexity. We are now
Skateboard. Hanger. in the Feature Manager and click Sketch. (S) on the Sketch. Line
 Chapter 3 Skateboard Hanger A. Sketch 1. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part Metric and OK. Step 2. Click Right Plane from the Content toolbar, Fig. 1. in the Feature Manager and click Sketch Step
Chapter 3 Skateboard Hanger A. Sketch 1. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part Metric and OK. Step 2. Click Right Plane from the Content toolbar, Fig. 1. in the Feature Manager and click Sketch Step
Obtaining Meshable Surfaces
 Chapter 2 Obtaining Meshable Surfaces Exercise 2a: Importing and Repairing CAD Geometry Overview of Exercise Strategy: Import CAD geometry and organize your model using the Assembly Hierarchy. Evaluate
Chapter 2 Obtaining Meshable Surfaces Exercise 2a: Importing and Repairing CAD Geometry Overview of Exercise Strategy: Import CAD geometry and organize your model using the Assembly Hierarchy. Evaluate
Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals
 2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Extruded Solid Models Understand the Basic Parametric Modeling Procedure Create 2-D Sketches Understand the Shape before Size Approach Use the
2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Extruded Solid Models Understand the Basic Parametric Modeling Procedure Create 2-D Sketches Understand the Shape before Size Approach Use the
Module 4B: Creating Sheet Metal Parts Enclosing The 3D Space of Right and Oblique Pyramids With The Work Surface of Derived Parts
 Inventor (5) Module 4B: 4B- 1 Module 4B: Creating Sheet Metal Parts Enclosing The 3D Space of Right and Oblique Pyramids With The Work Surface of Derived Parts In Module 4B, we will learn how to create
Inventor (5) Module 4B: 4B- 1 Module 4B: Creating Sheet Metal Parts Enclosing The 3D Space of Right and Oblique Pyramids With The Work Surface of Derived Parts In Module 4B, we will learn how to create
Technique or Feature Where Introduced
 Part 6: Keypad 4 Mirrored features Patterned features First extrusion Rounded corners In the earpiece part, you defined a radial pattern, one that created new instances of a feature at intervals around
Part 6: Keypad 4 Mirrored features Patterned features First extrusion Rounded corners In the earpiece part, you defined a radial pattern, one that created new instances of a feature at intervals around
A Comprehensive Introduction to SolidWorks 2011
 A Comprehensive Introduction to SolidWorks 2011 Godfrey Onwubolu, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation Chapter 2 Geometric Construction Tools Objectives: When
A Comprehensive Introduction to SolidWorks 2011 Godfrey Onwubolu, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation Chapter 2 Geometric Construction Tools Objectives: When
Google SketchUp. and SketchUp Pro 7. The book you need to succeed! CD-ROM Included! Kelly L. Murdock. Master SketchUp Pro 7 s tools and features
 CD-ROM Included! Free version of Google SketchUp 7 Trial version of Google SketchUp Pro 7 Chapter example files from the book Kelly L. Murdock Google SketchUp and SketchUp Pro 7 Master SketchUp Pro 7 s
CD-ROM Included! Free version of Google SketchUp 7 Trial version of Google SketchUp Pro 7 Chapter example files from the book Kelly L. Murdock Google SketchUp and SketchUp Pro 7 Master SketchUp Pro 7 s
ME009 Engineering Graphics and Design CAD 1. 1 Create a new part. Click. New Bar. 2 Click the Tutorial tab. 3 Select the Part icon. 4 Click OK.
 PART A Reference: SolidWorks CAD Student Guide 2014 2 Lesson 2: Basic Functionality Active Learning Exercises Creating a Basic Part Use SolidWorks to create the box shown at the right. The step-by-step
PART A Reference: SolidWorks CAD Student Guide 2014 2 Lesson 2: Basic Functionality Active Learning Exercises Creating a Basic Part Use SolidWorks to create the box shown at the right. The step-by-step
Modeling a Gear Standard Tools, Surface Tools Solid Tool View, Trackball, Show-Hide Snaps Window 1-1
 Modeling a Gear This tutorial describes how to create a toothed gear. It combines using wireframe, solid, and surface modeling together to create a part. The model was created in standard units. To begin,
Modeling a Gear This tutorial describes how to create a toothed gear. It combines using wireframe, solid, and surface modeling together to create a part. The model was created in standard units. To begin,
H Stab and V Stab. Chapter 6. Glider. A. Open and Save as "H STAB". Step 1. Open your STABILIZER BLANK file.
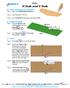 Chapter 6 Glider H Stab and V Stab A. Open and Save as "H STAB". Step 1. Open your STABILIZER BLANK file. Step 2. Click File Menu > Save As. Step 3. Key-in H STAB for the filename and press ENTER. B. Sketch
Chapter 6 Glider H Stab and V Stab A. Open and Save as "H STAB". Step 1. Open your STABILIZER BLANK file. Step 2. Click File Menu > Save As. Step 3. Key-in H STAB for the filename and press ENTER. B. Sketch
Module 4A: Creating the 3D Model of Right and Oblique Pyramids
 Inventor (5) Module 4A: 4A- 1 Module 4A: Creating the 3D Model of Right and Oblique Pyramids In Module 4A, we will learn how to create 3D solid models of right-axis and oblique-axis pyramid (regular or
Inventor (5) Module 4A: 4A- 1 Module 4A: Creating the 3D Model of Right and Oblique Pyramids In Module 4A, we will learn how to create 3D solid models of right-axis and oblique-axis pyramid (regular or
The Rectangular Problem
 C h a p t e r 2 The Rectangular Problem In this chapter, you will cover the following to World Class standards: The tools for simple 2D Computer Aided Drafting (CAD) The Command Line and the Tray The Line
C h a p t e r 2 The Rectangular Problem In this chapter, you will cover the following to World Class standards: The tools for simple 2D Computer Aided Drafting (CAD) The Command Line and the Tray The Line
Module 5: Creating Sheet Metal Transition Piece Between a Square Tube and a Rectangular Tube with Triangulation
 1 Module 5: Creating Sheet Metal Transition Piece Between a Square Tube and a Rectangular Tube with Triangulation In Module 5, we will learn how to create a 3D folded model of a sheet metal transition
1 Module 5: Creating Sheet Metal Transition Piece Between a Square Tube and a Rectangular Tube with Triangulation In Module 5, we will learn how to create a 3D folded model of a sheet metal transition
ECE 480: Design Team #9 Application Note Designing Box with AutoCAD
 ECE 480: Design Team #9 Application Note Designing Box with AutoCAD By: Radhika Somayya Due Date: Friday, March 28, 2014 1 S o m a y y a Table of Contents Executive Summary... 3 Keywords... 3 Introduction...
ECE 480: Design Team #9 Application Note Designing Box with AutoCAD By: Radhika Somayya Due Date: Friday, March 28, 2014 1 S o m a y y a Table of Contents Executive Summary... 3 Keywords... 3 Introduction...
Publication Number spse01695
 XpresRoute (tubing) Publication Number spse01695 XpresRoute (tubing) Publication Number spse01695 Proprietary and restricted rights notice This software and related documentation are proprietary to Siemens
XpresRoute (tubing) Publication Number spse01695 XpresRoute (tubing) Publication Number spse01695 Proprietary and restricted rights notice This software and related documentation are proprietary to Siemens
SketchUp + Google Earth LEARNING GUIDE by Jordan Martin. Source (images): Architecture
 SketchUp + Google Earth LEARNING GUIDE by Jordan Martin Source (images): www.sketchup.com Part 1: Getting Started with SketchUp GETTING STARTED: Throughout this manual users will learn different tools
SketchUp + Google Earth LEARNING GUIDE by Jordan Martin Source (images): www.sketchup.com Part 1: Getting Started with SketchUp GETTING STARTED: Throughout this manual users will learn different tools
Lesson 4: Surface Re-limitation and Connection
 Lesson 4: Surface Re-limitation and Connection In this lesson you will learn how to limit the surfaces and form connection between the surfaces. Lesson contents: Case Study: Surface Re-limitation and Connection
Lesson 4: Surface Re-limitation and Connection In this lesson you will learn how to limit the surfaces and form connection between the surfaces. Lesson contents: Case Study: Surface Re-limitation and Connection
Assembly Design: A Hands-On Experience
 Mark Thompson Sr. Application Engineer Assembly Design: A Hands-On Experience Solid Edge University 2014 May 12-14, Atlanta, GA, USA SOLID EDGE UNIVERSITY 2014 Re-imagine What s Possible #SEU14 Agenda
Mark Thompson Sr. Application Engineer Assembly Design: A Hands-On Experience Solid Edge University 2014 May 12-14, Atlanta, GA, USA SOLID EDGE UNIVERSITY 2014 Re-imagine What s Possible #SEU14 Agenda
3D Modeling and Design Glossary - Beginner
 3D Modeling and Design Glossary - Beginner Align: to place or arrange (things) in a straight line. To use the Align tool, select at least two objects by Shift left-clicking on them or by dragging a box
3D Modeling and Design Glossary - Beginner Align: to place or arrange (things) in a straight line. To use the Align tool, select at least two objects by Shift left-clicking on them or by dragging a box
Solid Edge ST3. for Engineers and Designers. CADCIM Technologies 525 St. Andrews Drive Schererville, IN 46375, USA (
 Solid Edge ST3 for Engineers and Designers CADCIM Technologies 525 St. Andrews Drive Schererville, IN 46375, USA (www.cadcim.com) Contributing Author Sham Tickoo Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering
Solid Edge ST3 for Engineers and Designers CADCIM Technologies 525 St. Andrews Drive Schererville, IN 46375, USA (www.cadcim.com) Contributing Author Sham Tickoo Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering
Publication Number spse01695
 XpresRoute (tubing) Publication Number spse01695 XpresRoute (tubing) Publication Number spse01695 Proprietary and restricted rights notice This software and related documentation are proprietary to Siemens
XpresRoute (tubing) Publication Number spse01695 XpresRoute (tubing) Publication Number spse01695 Proprietary and restricted rights notice This software and related documentation are proprietary to Siemens
Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals
 2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Extruded Solid Models Understand the Basic Parametric Modeling Procedure Create 2-D Sketches Understand the "Shape before Size" Approach Use
2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Extruded Solid Models Understand the Basic Parametric Modeling Procedure Create 2-D Sketches Understand the "Shape before Size" Approach Use
Licom Systems Ltd., Training Course Notes. 3D Surface Creation
 , Training Course Notes Work Volume and Work Planes...........................1 Overview..........................................1 Work Volume....................................1 Work Plane......................................1
, Training Course Notes Work Volume and Work Planes...........................1 Overview..........................................1 Work Volume....................................1 Work Plane......................................1
3ds Max Cottage Step 1. Always start out by setting up units: We re going with this setup as we will round everything off to one inch.
 3ds Max Cottage Step 1 Always start out by setting up units: We re going with this setup as we will round everything off to one inch. File/Import the CAD drawing Be sure Files of Type is set to all formats
3ds Max Cottage Step 1 Always start out by setting up units: We re going with this setup as we will round everything off to one inch. File/Import the CAD drawing Be sure Files of Type is set to all formats
4) Finish the spline here. To complete the spline, double click the last point or select the spline tool again.
 1) Select the line tool 3) Move the cursor along the X direction (be careful to stay on the X axis alignment so that the line is perpendicular) and click for the second point of the line. Type 0.5 for
1) Select the line tool 3) Move the cursor along the X direction (be careful to stay on the X axis alignment so that the line is perpendicular) and click for the second point of the line. Type 0.5 for
LAB # 2 3D Modeling, Properties Commands & Attributes
 COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Electrical Engineering Department (Islamabad Campus) LAB # 2 3D Modeling, Properties Commands & Attributes Designed by Syed Muzahir Abbas 1 1. Overview of the
COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Electrical Engineering Department (Islamabad Campus) LAB # 2 3D Modeling, Properties Commands & Attributes Designed by Syed Muzahir Abbas 1 1. Overview of the
Speedway. Body. (S) on the Sketch toolbar. Fig. 1
 Chapter 1 A. New Part. Step 1. Click File Menu > New. Speedway Body Step 2. Click Part from the list and click OK, Fig. 1. B. Sketch Construction Rectangle. Step 1. Click Right Plane in the Feature Manager
Chapter 1 A. New Part. Step 1. Click File Menu > New. Speedway Body Step 2. Click Part from the list and click OK, Fig. 1. B. Sketch Construction Rectangle. Step 1. Click Right Plane in the Feature Manager
Lesson 1 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals
 1-1 Lesson 1 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Parametric Models. Understand the Basic Parametric Modeling Process. Create and Profile Rough Sketches. Understand the "Shape before size" approach.
1-1 Lesson 1 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Parametric Models. Understand the Basic Parametric Modeling Process. Create and Profile Rough Sketches. Understand the "Shape before size" approach.
Proprietary and restricted rights notice
 Proprietary and restricted rights notice This software and related documentation are proprietary to Siemens Product Lifecycle Management Software Inc. 2012 Siemens Product Lifecycle Management Software
Proprietary and restricted rights notice This software and related documentation are proprietary to Siemens Product Lifecycle Management Software Inc. 2012 Siemens Product Lifecycle Management Software
Memo Block. This lesson includes the commands Sketch, Extruded Boss/Base, Extruded Cut, Shell, Polygon and Fillet.
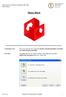 Commands Used New Part This lesson includes the commands Sketch, Extruded Boss/Base, Extruded Cut, Shell, Polygon and Fillet. Click File, New on the standard toolbar. Select Part from the New SolidWorks
Commands Used New Part This lesson includes the commands Sketch, Extruded Boss/Base, Extruded Cut, Shell, Polygon and Fillet. Click File, New on the standard toolbar. Select Part from the New SolidWorks
Complex Shapes Creation with Hybrid Modelling
 Complex Shapes Creation with Hybrid Modelling Peter De Strijker Technical Sales Executive MFG - Benelux Our Customer s Industries Discrete product manufacture Agenda Quality Analyses of sketches and surfaces
Complex Shapes Creation with Hybrid Modelling Peter De Strijker Technical Sales Executive MFG - Benelux Our Customer s Industries Discrete product manufacture Agenda Quality Analyses of sketches and surfaces
VERO UK TRAINING MATERIAL
 VERO UK TRAINING MATERIAL VISI Basic 2-D Modelling course (V-16) VISI Modelling 2D Design Introduction Many component designs follow a similar route, beginning with a 2D design, part modelled using solids
VERO UK TRAINING MATERIAL VISI Basic 2-D Modelling course (V-16) VISI Modelling 2D Design Introduction Many component designs follow a similar route, beginning with a 2D design, part modelled using solids
Images from 3D Creative Magazine. 3D Modelling Systems
 Images from 3D Creative Magazine 3D Modelling Systems Contents Reference & Accuracy 3D Primitives Transforms Move (Translate) Rotate Scale Mirror Align 3D Booleans Deforms Bend Taper Skew Twist Squash
Images from 3D Creative Magazine 3D Modelling Systems Contents Reference & Accuracy 3D Primitives Transforms Move (Translate) Rotate Scale Mirror Align 3D Booleans Deforms Bend Taper Skew Twist Squash
Brief Introduction to MasterCAM X4
 Brief Introduction to MasterCAM X4 Fall 2013 Meung J Kim, Ph.D., Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering College of Engineering and Engineering Technology Northern Illinois University DeKalb, IL
Brief Introduction to MasterCAM X4 Fall 2013 Meung J Kim, Ph.D., Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering College of Engineering and Engineering Technology Northern Illinois University DeKalb, IL
Parametric Modeling with UGS NX 4
 Parametric Modeling with UGS NX 4 Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com 2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling
Parametric Modeling with UGS NX 4 Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com 2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling
Version 2011 R1 - Router
 GENERAL NC File Output List NC Code Post Processor Selection Printer/Plotter Output Insert Existing Drawing File Input NC Code as Geometry or Tool Paths Input Raster Image Files Convert Raster to Vector
GENERAL NC File Output List NC Code Post Processor Selection Printer/Plotter Output Insert Existing Drawing File Input NC Code as Geometry or Tool Paths Input Raster Image Files Convert Raster to Vector
SWITCHING FROM SKETCHUP TO VECTORWORKS
 SWITCHING FROM SKETCHUP TO VECTORWORKS INTRODUCTION There are a lot of 3D modeling software programs to choose from and each has its own strengths and weaknesses. For architects, flexibility and ease of
SWITCHING FROM SKETCHUP TO VECTORWORKS INTRODUCTION There are a lot of 3D modeling software programs to choose from and each has its own strengths and weaknesses. For architects, flexibility and ease of
Delta Dart. Socket. (L) on the Sketch toolbar. Fig. 1. (S) on the Sketch toolbar. on the Sketch toolbar. on the Standard Views toolbar.
 Chapter 6 Delta Dart Socket A. Sketch. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part Metric and OK. Step 2. Click Front Plane in the Feature Manager and click Sketch from the Content toolbar, Fig. 1. Step
Chapter 6 Delta Dart Socket A. Sketch. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part Metric and OK. Step 2. Click Front Plane in the Feature Manager and click Sketch from the Content toolbar, Fig. 1. Step
Surface Modeling Tutorial
 Surface Modeling Tutorial Complex Surfacing in SolidWorks By Matthew Perez By Matthew Perez Who is this tutorial for? This tutorial assumes that you have prior surfacing knowledge as well as a general
Surface Modeling Tutorial Complex Surfacing in SolidWorks By Matthew Perez By Matthew Perez Who is this tutorial for? This tutorial assumes that you have prior surfacing knowledge as well as a general
Battery Holder 2 x AA
 Chapter 22 JSS Battery Holder 2 x AA A. Front Extrude. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part Metric and OK. Step 2. Click Front Plane in the Feature Manager and click Sketch from the Context toolbar,
Chapter 22 JSS Battery Holder 2 x AA A. Front Extrude. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part Metric and OK. Step 2. Click Front Plane in the Feature Manager and click Sketch from the Context toolbar,
Battery Holder. Chapter 9. Boat. A. Front Extrude. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part and OK. SolidWorks 10 BATTERY HOLDER AA BOAT Page 9-1
 Chapter 9 Boat Battery Holder A. Front Extrude. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part and OK. AA Step 2. Click Front (plane) in the Feature Manager and click Sketch from the Content toolbar, Fig. 1.
Chapter 9 Boat Battery Holder A. Front Extrude. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part and OK. AA Step 2. Click Front (plane) in the Feature Manager and click Sketch from the Content toolbar, Fig. 1.
Fuselage and Sharks Tooth
 Chapter 4 Glider Fuselage and Sharks Tooth A. Save as "FUSELAGE". Step 1. Open your FUSELAGE BLANK file. Step 2. Click File Menu > Save As. Step 3. Key-in FUSELAGE for the filename and press ENTER. B.
Chapter 4 Glider Fuselage and Sharks Tooth A. Save as "FUSELAGE". Step 1. Open your FUSELAGE BLANK file. Step 2. Click File Menu > Save As. Step 3. Key-in FUSELAGE for the filename and press ENTER. B.
Solid Problem Ten. In this chapter, you will learn the following to World Class standards:
 C h a p t e r 11 Solid Problem Ten In this chapter, you will learn the following to World Class standards: 1. Sketch of Solid Problem Ten 2. Starting a 3D Part Drawing 3. Modifying How the UCS Icon is
C h a p t e r 11 Solid Problem Ten In this chapter, you will learn the following to World Class standards: 1. Sketch of Solid Problem Ten 2. Starting a 3D Part Drawing 3. Modifying How the UCS Icon is
It is a good idea to practice View Control tools for 5 minutes at the start of every 3D session, before doing any other work.
 3D View Control Module Overview All the 2D view controls, such as Fit View, Zoom In and Out, Window Area, and Pan, can be used in 3D. As in 2D, elements to the left, right, above, or below can be excluded
3D View Control Module Overview All the 2D view controls, such as Fit View, Zoom In and Out, Window Area, and Pan, can be used in 3D. As in 2D, elements to the left, right, above, or below can be excluded
AUTODESK FUSION 360 Designing a RC Car Body
 AUTODESK FUSION 360 Designing a RC Car Body Abstract This project explores how to use the sculpting tools available in Autodesk Fusion 360 Ultimate to design the body of a RC car. John Helfen john.helfen@autodesk.com
AUTODESK FUSION 360 Designing a RC Car Body Abstract This project explores how to use the sculpting tools available in Autodesk Fusion 360 Ultimate to design the body of a RC car. John Helfen john.helfen@autodesk.com
Chapter 4 Feature Design Tree
 4-1 Chapter 4 Feature Design Tree Understand Feature Interactions Use the FeatureManager Design Tree Modify and Update Feature Dimensions Perform History-Based Part Modifications Change the Names of Created
4-1 Chapter 4 Feature Design Tree Understand Feature Interactions Use the FeatureManager Design Tree Modify and Update Feature Dimensions Perform History-Based Part Modifications Change the Names of Created
CHAPTER 6 THE SUITES VECTOR DRAWING SUITE
 CHAPTER 6 THE SUITES There are two additional tool bar suites for Project Designer sold separately as add-on modules. These are the Vector Drawing Suite, and the Pattern Modeling Suite. This section will
CHAPTER 6 THE SUITES There are two additional tool bar suites for Project Designer sold separately as add-on modules. These are the Vector Drawing Suite, and the Pattern Modeling Suite. This section will
Parametric Modeling with SOLIDWORKS 2017
 Parametric Modeling with SOLIDWORKS 2017 NEW Contains a new chapter on 3D printing Covers material found on the CSWA exam Randy H. Shih Paul J. Schilling SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices.
Parametric Modeling with SOLIDWORKS 2017 NEW Contains a new chapter on 3D printing Covers material found on the CSWA exam Randy H. Shih Paul J. Schilling SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices.
Getting started with Solid Edge with Synchronous Technology
 Getting started with Solid Edge with Synchronous Technology Publication Number MU29000-ENG-1000 Proprietary and Restricted Rights Notice This software and related documentation are proprietary to Siemens
Getting started with Solid Edge with Synchronous Technology Publication Number MU29000-ENG-1000 Proprietary and Restricted Rights Notice This software and related documentation are proprietary to Siemens
ARCHITECTURE & GAMES. A is for Architect Simple Mass Modeling FORM & SPACE. Industry Careers Framework. Applied. Getting Started.
 A is for Architect Simple Mass Modeling One of the first introductions to form and space usually comes at a very early age. As an infant, you might have played with building blocks to help hone your motor
A is for Architect Simple Mass Modeling One of the first introductions to form and space usually comes at a very early age. As an infant, you might have played with building blocks to help hone your motor
Swept Blend Creates a quilt using swept blend geometry.
 Swept Blend Creates a quilt using swept blend geometry. 1 A surface can be defined by a set of cross-sections located at various points along a controlling Spine Curve. In Pro/SURFACE, this is known as
Swept Blend Creates a quilt using swept blend geometry. 1 A surface can be defined by a set of cross-sections located at various points along a controlling Spine Curve. In Pro/SURFACE, this is known as
Learning. Modeling, Assembly and Analysis SOLIDWORKS Randy H. Shih SDC. Better Textbooks. Lower Prices.
 Learning SOLIDWORKS 2016 Modeling, Assembly and Analysis Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites
Learning SOLIDWORKS 2016 Modeling, Assembly and Analysis Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites
Rhinoceros Car Modeling Tutorial
 Rhinoceros Car Modeling Tutorial This tutorial will guide you to car nurbs modeling process using Rhinoceros 3.0. To start a car modeling you will need some car images (or sketches) to get an idea of the
Rhinoceros Car Modeling Tutorial This tutorial will guide you to car nurbs modeling process using Rhinoceros 3.0. To start a car modeling you will need some car images (or sketches) to get an idea of the
Solid Modeling: Part 1
 Solid Modeling: Part 1 Basics of Revolving, Extruding, and Boolean Operations Revolving Exercise: Stepped Shaft Start AutoCAD and use the solid.dwt template file to create a new drawing. Create the top
Solid Modeling: Part 1 Basics of Revolving, Extruding, and Boolean Operations Revolving Exercise: Stepped Shaft Start AutoCAD and use the solid.dwt template file to create a new drawing. Create the top
Equipment Support Structures
 Equipment Support Structures Overview Conventions What's New? Getting Started Setting Up Your Session Creating a Simple Structural Frame Creating Non-uniform Columns Creating Plates with Openings Bracing
Equipment Support Structures Overview Conventions What's New? Getting Started Setting Up Your Session Creating a Simple Structural Frame Creating Non-uniform Columns Creating Plates with Openings Bracing
1st Point. 2nd Point. hold shift & drag along Y. Splines
 Splines STEP 1: open 3DS Max _ from the Command Panel under the Create tab click on Shapes (note: shapes are really Splines) _ under Object Type click on Ellipse STEP 2: Expand the Keyboard Entry tab type
Splines STEP 1: open 3DS Max _ from the Command Panel under the Create tab click on Shapes (note: shapes are really Splines) _ under Object Type click on Ellipse STEP 2: Expand the Keyboard Entry tab type
SOLIDWORKS Parametric Modeling with SDC. Covers material found on the CSWA exam. Randy H. Shih Paul J. Schilling
 Parametric Modeling with SOLIDWORKS 2015 Covers material found on the CSWA exam Randy H. Shih Paul J. Schilling SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF
Parametric Modeling with SOLIDWORKS 2015 Covers material found on the CSWA exam Randy H. Shih Paul J. Schilling SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF
Parametric Modeling. With. Autodesk Inventor. Randy H. Shih. Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS
 Parametric Modeling With Autodesk Inventor R10 Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com 2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric
Parametric Modeling With Autodesk Inventor R10 Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com 2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric
Boat. Battery Holder AA
 Chapter 9 Boat Battery Holder AA A. Front Extrude. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part and OK. Step 2. Click Front Plane in the Feature Manager and click Sketch context toolbar, Fig. 1. Step 3. Click
Chapter 9 Boat Battery Holder AA A. Front Extrude. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part and OK. Step 2. Click Front Plane in the Feature Manager and click Sketch context toolbar, Fig. 1. Step 3. Click
Tutorial Second Level
 AutoCAD 2018 Tutorial Second Level 3D Modeling Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites to learn
AutoCAD 2018 Tutorial Second Level 3D Modeling Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites to learn
Jewelry Box Lid. A. Sketch Lid Circle. Step 1. If necessary start a new Mastercam file, click FILE Menu > New. Fig. 3
 Mastercam X9 Chapter 39 Jewelry Box Lid A. Sketch Lid Circle. Step 1. If necessary start a new Mastercam file, click FILE Menu > New. Step 2. Click CREATE Menu > Arc > Circle Center Point. Step 3. Key-in
Mastercam X9 Chapter 39 Jewelry Box Lid A. Sketch Lid Circle. Step 1. If necessary start a new Mastercam file, click FILE Menu > New. Step 2. Click CREATE Menu > Arc > Circle Center Point. Step 3. Key-in
Parametric Modeling Design and Modeling 2011 Project Lead The Way, Inc.
 Parametric Modeling Design and Modeling 2011 Project Lead The Way, Inc. 3D Modeling Steps - Sketch Step 1 Sketch Geometry Sketch Geometry Line Sketch Tool 3D Modeling Steps - Constrain Step 1 Sketch Geometry
Parametric Modeling Design and Modeling 2011 Project Lead The Way, Inc. 3D Modeling Steps - Sketch Step 1 Sketch Geometry Sketch Geometry Line Sketch Tool 3D Modeling Steps - Constrain Step 1 Sketch Geometry
Quick Crash Scene Tutorial
 Quick Crash Scene Tutorial With Crash Zone or Crime Zone, even new users can create a quick crash scene diagram in less than 10 minutes! In this tutorial we ll show how to use Crash Zone s unique features
Quick Crash Scene Tutorial With Crash Zone or Crime Zone, even new users can create a quick crash scene diagram in less than 10 minutes! In this tutorial we ll show how to use Crash Zone s unique features
1.1: Introduction to Fusion 360
 .: Introduction to Fusion 360 Fusion 360 is a cloud- based CAD/CAM tool for collaborative product development. The tools in Fusion enable exploration and iteration on product ideas and collaboration within
.: Introduction to Fusion 360 Fusion 360 is a cloud- based CAD/CAM tool for collaborative product development. The tools in Fusion enable exploration and iteration on product ideas and collaboration within
Create Complex Surfaces
 Create Complex Surfaces In this lesson, you will be introduced to the functionalities available in the Generative Surface Design workbench. Lesson content: Case Study: Surface Design Design Intent Stages
Create Complex Surfaces In this lesson, you will be introduced to the functionalities available in the Generative Surface Design workbench. Lesson content: Case Study: Surface Design Design Intent Stages
Delta Dart. Propeller. in the Feature Manager and click Sketch from the Content toolbar, Fig. 1. on the Sketch toolbar.
 Chapter 8 Delta Dart Propeller A. Base for Blade. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part Metric and OK. Step 2. Click Top Plane in the Feature Manager and click Sketch from the Content toolbar, Fig.
Chapter 8 Delta Dart Propeller A. Base for Blade. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part Metric and OK. Step 2. Click Top Plane in the Feature Manager and click Sketch from the Content toolbar, Fig.
3D ModelingChapter1: Chapter. Objectives
 Chapter 1 3D ModelingChapter1: The lessons covered in this chapter familiarize you with 3D modeling and how you view your designs as you create them. You also learn the coordinate system and how you can
Chapter 1 3D ModelingChapter1: The lessons covered in this chapter familiarize you with 3D modeling and how you view your designs as you create them. You also learn the coordinate system and how you can
Revit Architecture 2015 Basics
 Revit Architecture 2015 Basics From the Ground Up Elise Moss Authorized Author SDC P U B L I C AT I O N S Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit
Revit Architecture 2015 Basics From the Ground Up Elise Moss Authorized Author SDC P U B L I C AT I O N S Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit
Glider. Wing. Top face click Sketch. on the Standard Views. (S) on the Sketch toolbar.
 Chapter 5 Glider Wing 4 Panel Tip A. Open and Save As "WING 4 PANEL". Step 1. Open your WING BLANK file. Step 2. Click File Menu > Save As. Step 3. Key-in WING 4 PANEL for the filename and press ENTER.
Chapter 5 Glider Wing 4 Panel Tip A. Open and Save As "WING 4 PANEL". Step 1. Open your WING BLANK file. Step 2. Click File Menu > Save As. Step 3. Key-in WING 4 PANEL for the filename and press ENTER.
REVIT ARCHITECTURE 2016
 Page 1 of 6 REVIT ARCHITECTURE 2016 Revit Architecture 2016: CREATE A CHAMFERED COLUMN COMPONENT About creating a chamfered column family typical to the Victorian cottage style. Add the column to your
Page 1 of 6 REVIT ARCHITECTURE 2016 Revit Architecture 2016: CREATE A CHAMFERED COLUMN COMPONENT About creating a chamfered column family typical to the Victorian cottage style. Add the column to your
TRAINING GUIDE LATHE-LESSON-1 FACE, ROUGH, FINISH AND CUTOFF
 TRAINING GUIDE LATHE-LESSON-1 FACE, ROUGH, FINISH AND CUTOFF Mastercam Training Guide Objectives You will create the geometry for Lathe-Lesson-1, and then generate a toolpath to machine the part on a CNC
TRAINING GUIDE LATHE-LESSON-1 FACE, ROUGH, FINISH AND CUTOFF Mastercam Training Guide Objectives You will create the geometry for Lathe-Lesson-1, and then generate a toolpath to machine the part on a CNC
Creating T-Spline Forms
 1 / 28 Goals 1. Create a T-Spline Primitive Form 2. Create a T-Spline Revolve Form 3. Create a T-Spline Sweep Form 4. Create a T-Spline Loft Form 2 / 28 Instructions Step 1: Go to the Sculpt workspace
1 / 28 Goals 1. Create a T-Spline Primitive Form 2. Create a T-Spline Revolve Form 3. Create a T-Spline Sweep Form 4. Create a T-Spline Loft Form 2 / 28 Instructions Step 1: Go to the Sculpt workspace
Solid Bodies and Disjointed Bodies
 Solid Bodies and Disjointed Bodies Generally speaking when modelling in Solid Works each Part file will contain single solid object. As you are modelling, each feature is merged or joined to the previous
Solid Bodies and Disjointed Bodies Generally speaking when modelling in Solid Works each Part file will contain single solid object. As you are modelling, each feature is merged or joined to the previous
