Using Pulsar as an upgrade for L2 decision crate Ted Liu, FNAL (for CDF Pulsar group)
|
|
|
- Ashlee Wilkinson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Using Pulsar as an upgrade for 2 decision crate ed iu, FNA (for CDF Pulsar group) For more information about Pulsar board:
2 Back to Basic: What does Global 2 really do? racks Jets make decisions based on objects already found upstream 1 trk svt clist Iso reces mu umet,met electron photon muon aus Met umet physics object examples Combines/matches trigger objects into e, muon, jets Count physics objects above thresholds, or, Cut on kinematics quantities echnical requirement: need a FA way to collect many data inputs Global 2 2
3 Current 2 Global Crate: echnical requirement: need a FA way to collect many data inputs With the technology available back then, had to design custom backplane (magicbus) and processor data is either pushed(via DMA) or pulled (via Programed IO) to ease the bandwidth demands In addition, one has to deal with the fact that each data input was implemented in a different way 6 different type of custom interface boards Magic bus 1 eces x 4 a(s) X P V Only one MB crate C I I O M U O N largest data size Global 2 3
4 Basic idea on possible new approach using modern technology: Convert/merge different data inputs into a standard link interface with commodity PC(s) high bandwidth, commercially available link to PCI interface cards: CEN -INK is designed just for this purpose for HC and other experiments. eal question: can we design an universal interface board s s (and the rest are all commercial products)? Concept Pulsar is designed to be able to do more than this. ss s s s PCI link to PCI mem CPU 4
5 INK format example: INK interface mezzanine card AA INK data format 5
6 Pulsar design P1 9U VME (VME and CDF ctrl signals are visible to all three FPGAs) K 3 Altera APEX 20K400_652 (BGA) FPGAs 502 user IO pins each Data IO Mezz card connectors P2 INK signal lines Control/ Merger AM 128K x 36 bits P3 spare lines 1 K Data IO AM 3 APEX20K400 FPGAs on board = 3 Million system gates/80kb AM per board K x 36 pipelined AMs with No Bus atency: 1 MB AM (~5ns access time)
7 Front-panel (double width) VD connectors Mezzanine cards 1 1 Mezzanine Card Hotlink/ axi/ -INK PUA design Each mezzanine card can have up to 4 (hotlink/axi) fiber channels IO VME Ctrl optional user defined signal connection from P2/P3 Optional V input V V IO INK spares -INK x or x -INK x or x hree FPGAs: Atlera APEX20K400 component side he mezzanine card connectors can be used either for user I/O or INK cards o/from Pulsar or 7 a PC
8 Pulsar Design methodology A major fraction of the design effort was dedicated to core firmware development and extensive design verifications by using state-of-the-art CAD tools: eonardo pectrum for VHD synthesis; Quartus II for place and route, and FPGA level simulation; developed core firmware (VHD) first to guide and optimize the board design Quickim for board and multi-board level simulation; used to carefully verify board schematics Interconnect ynthesis tool for trace and cross talk analysis; I_MultiBoard tool for signal integrity checks between motherboard and mezzanine cards; used to carefully verify board layout All details can be found at: 8
9 Performed multi-board simulation to verify the design 9
10 Board design work started Nov Pulsar prototypes received: ept 19 th, Initial VME access to all three FPGAs are successful: ept. 21th,
11 11
12 Hotlink mezzanine card prototypes have been tested in July, Hotlink x mezzanine card prototype (for muon and cluster data paths) Hotlink x mezzanine card prototype 12
13 Pulsar with AUX card INK Mezzanine card 13
14 Pulsar approach: Goal: only build one type of custom interface board and the rest are all commercial products. Use mezzanine cards to take care optical data paths (Cluster,Isolation, Muon and eces) P1 P2 INK P3 Pulsar design I Control/ Merger 1 K K Optical IO Optical IO Mezz card connectors Extra features: 1 trigger bits and trk/svt input are visible to all three FPGAs 14 for flexibility
15 racks Jets electron photon muon aus Met umet 1 trk svt clist Iso reces mu umet,met P1 What does evel 2 really do? Combine/matches trigger objects into e,muon Count objects above thresholds, or, Cut on kinematics quantities K Data IO Mezz card connectors Most trigger objects need 1 and track/svt trigger information, this is reflected in Pulsar design: for flexibility INK I/O P2 P3 user ctrl spare lines Control/ Merger 1 K Data IO 15
16 One possible simple configuration: link to PCI CPU PCI to link or use V_PCI_ Global Processor Controller 1 2 decision V eces/trk 160MB/s INK INK Cluster/trk INK Muon/trk ume,me (can plug into one of other boards) All 8 motherboards are physically identical 4 eces eces Pre-processor Pre-processor + 1 merger X 3 Cluster Pre-processor Muon Pre-processor eces: 12 x4 =48 taxi fibers Cluster: 6 hotlink fibers Iso: 7 taxi fibers Muon: 16 hotlink fibers XP 16 1 bits
17 Possible New 2 Decision Crate O C A C E All 8 motherboards are physically identical M U O N C U E E C E Muon/trk E C E E C E M E G E Cluster/trk eces/trk umet,met Each Pulsar board take two slots (due to mezzanine cards) otal: 8 pulsar boards = 16 slots Baseline design: use pre-processor Pulsars to simply suppress/organize data, use Processor Controller Pulsar to simply pass data to CPU via link to PCI and also handshake with. All trigger algorithm will be handled by CPU. E C E 160MB/s P O C C 160MB/s link to PCI PCI to link/v/ GHz PC or mem CPU 17 VME processor
18 New 32-bit INK to 64 bit PCI interface card: 32PCI64 highly autonomous data reception 32-bit INK, 64-bit PCI bus 33MHz and 66 MHz PCI clock speed up to 520MByte/s raw bandwidth CEN -INK to to PCI-64 interface I II N I N K N K K to 32 to to 64 to 64 map 64 map INPU INPU BUFFE BUFFE FIFO FIFO (1024 (1024 x x 64-bit) x 64-bit) PCI PCI BU PCI BU FIFO FIFO 128x 128x 64-bit 128x 64-bit DMA DMA ENGINE ENGINE High-speed follow up of the imple INK to PCI interface card BACKEND BACKEND CONO CONO OGIC OGIC EQUE EQUE FIFO FIFO (address, (address, length) length) ACKNOWEDGE ACKNOWEDGE FIFO FIFO (ctl FIFO (ctl words, (ctl words, length) words, length) length) CONO, CONO, AU AU & & INEUP & INEUP EGIE EGIE 64-BI 64-BI PCI PCI PCI COE COE 18 33/66 33/66 MHz 33/66 MHz 32/64-bit MH 32/64-bit PCI PCI PCI Erik Erik van van der der Bij Bij division division EP EP AE/DQ AE/DQ
19 New 32-bit INK to 64 bit PCI interface card: 32PCI64 highly autonomous data reception 32-bit INK, 64-bit PCI bus 33MHz and 66 MHz PCI clock speed up to 520MByte/s raw bandwidth High-speed follow up of the imple INK to PCI interface card 19
20 2 decision from CPU: how to handshake with rigger upervisor? here could be a few ways to achieve this: (1) could use PCI to INK card: send a INK message back to Pulsar Processor Controller, then Pulsar handshakes with ; (2) Or use V_PCI_ daughter card built by Pisa group. V in V out I link to PCI PCI to link/v/ mem CPU 20
21 PCI daughter card: V-PCI- which can be plugged into Altera PCI board he time to send a decision from CPU to Pulsar/ can be short: ~ 1us measured value 21
22 Baseline Design (with the simple configuration) could be: PreProcessor/Interface versions of the board gather data from each subsystem and package the data. his can include sparsification based on 1 trigger bits, tracking, or the data itself. Processor controller/merger version of the board merges data from interface boards and packages the data for transfer to a CPU. he data can be further sparsified at this stage. his board also provide the interface between 2 and the rigger upervisor. Both types of PreProcesor board can be used to readout data he default operation would have the final decisions made in code in the CPU. Pulsar is designed to be able to do more if necessary. Designed to be quite flexible board level and system level Pulsar flexibility 22
23 P1 P2 P3 Control/ Merger Pulsar as Muon Pre-processor (interface board) Can create physics objects (i.e., muons) at this stage (optional) INK signals spare lines A muon data available with rack info: muons 1 K Data IO Info available: 1, XP, Muon matchbox data (0-240 degree) DataIO Info available: 1, XP, Muon matchbox, Pre-matchbox AM AM data from Matchbox (16 hotlink fibers) degree degree degree data from pre-match box (4 hotlink fibers) Board level flexibility 23
24 Pulsar as eces data PreProcessor (merger) P1 P2 P3 Could use AM as U to match XP and eces info to create electrons (optional) Control/ Merger INK signal lines spare lines A Info for XP and eces available: electrons 1 K Data IO Info available: 1, XP, eces electrons DataIO Info available: 1, XP, eces electrons Assume 4 Pulsars upstream AM AM East wegdes 1-12 West wedges 1-12 East wedges West wedges Board level flexibility 24
25 P1 P2 P3 Control/ Merger Pulsar as Processor Controller Pulsar design is driven by physics needs possible to combine trigger objects here (optional) INK signal lines spare lines A Info available for 2 decisions, 1 V Data IO Info available: 1, V, XP, eces, Cluster, Iso racks, Jets, e, photon,tau etc DataIO Info available: 1, V,XP, Muon,Met, umet racks, muon, Met,umEt etc AM AM eces/trk Cluster/Iso Muon/trk Met/umEt Board evel Flexibility 25
26 One possible configuration one PC use two PCI slots to receive INK data: One receives normal trigger data, the other is dedicated for V data (arrives late). CPU can start working on the early arrival data first -INK Pulsar Custom Mezzanine cards Pulsar -INK -INK Pulsar -INK Normal data V data V Pulsar 2 decision link to PCI link to PCI PCI to link/v/ ystem level flexibility mem CPU Pulsar 26
27 Another possible configuration using four PCs: Each PC(i) gets its own event(say buffer i), each works on a different event. ay PC 0 is working on buffer 0, PC 2 is working on buffer 1 etc. his way one long tail event would not prevent other three events to be processed. -INK Pulsar Custom Mezzanine cards -INK Pulsar -INK Buffer 0,2 events -INK Pulsar PC 0 PC 2 Pulsar Pulsar -INK PC 1 PC 3 -INK Buffer 1,3 events Pulsar ystem level flexibility 27
28 Current firmware status: we have written firmware to record data into a PC for the teststand. Work applicable to upgrade needs. Pulsar can convert any user data (via custom mezzanine cards) into INK format then transfer the data into a PC K Optical IO Mezzanine card connectors CDF ctrl Merger data PC INK to PCI INK 1 K Optical IO ctrl Pulsar in (general purpose) recorder mode (directly into a PC) 28
29 1A Buffer# Firmware for Pulsar in recorder mode(into a PC): 1A(x4) queue 1A egister 1 trigger bits mezzanine cards inputs FIFO FIFO 32-bit FIFO 32-bit 1 egister (pulls one event worth of data at a time) Output FIFO *Checks data consistence merges and stamp data INK Formatter 32-bit his formatter is based on existing code from CEN tate machine 29
30 Firmware design is similar in all three FPGA s on all versions of the Pulsar DataIO FPGA 1A 1 Control/merger FPGA DataIO FPGA P3 Data package (per 1A) in INK format sent 30
31 In ummary Pulsar design is powerful, modular and universal Distributed processing motivated by physics ufficient safety margin in raw bandwidth and flexibility at both board- and system-level to handle unexpected un II B challenges Can be used as a test-stand as well as an upgrade path uitable to develop and tune an upgrade in stand-alone mode educes impact on running experiment during commissioning phase Pulsar is useful for un II A maintenance and any 2 upgrade Built-in maintenance capability ystem relies heavily on commercial resources Only one custom board Firmware design is similar in all FPGA s on all incarnations of the Pulsar Easier long-term maintenance he rest is commercially available Easily upgradeable CPU, PCI boards Widely used link well documented HC standard Knowledge transferable to and from HC community 31
CDF Pulsar Board. PULSAR: PULSer And Recorder
 CDF Pulsar Board PUA: PUer And ecorder People involved in this project A few words about CDF trigger (evel 2): why building this board? Pulsar design: (1) as 2 teststand tool; (2) as a prototype for possible
CDF Pulsar Board PUA: PUer And ecorder People involved in this project A few words about CDF trigger (evel 2): why building this board? Pulsar design: (1) as 2 teststand tool; (2) as a prototype for possible
Design of Pulsar Board. Mircea Bogdan (for Pulsar group) Level 2 Pulsar Mini-Review Wednesday, July 24, 2002
 Design of Pulsar Board Mircea Bogdan (for Pulsar group) Level 2 Pulsar Mini-Review Wednesday, July 24, 2002 1 Level 2 Pulsar Hardware Requirements Hotlink IO Taxi IO SVT/XTRP Level 1 TS IO S-LINK IO PULSAR
Design of Pulsar Board Mircea Bogdan (for Pulsar group) Level 2 Pulsar Mini-Review Wednesday, July 24, 2002 1 Level 2 Pulsar Hardware Requirements Hotlink IO Taxi IO SVT/XTRP Level 1 TS IO S-LINK IO PULSAR
Mezzanine card specifications for Level-2 Calorimeter Trigger Upgrade
 CDF/DOC/TRIGGER/CDFR/8533 Mezzanine card specifications for Level-2 Calorimeter Trigger Upgrade L. Sartori 1, A. Bhatti 2, A. Canepa 3, M. Casarsa 4, M. Covery 2, G. Cortiana 5, M. Dell Orso 1, G. Flanagan
CDF/DOC/TRIGGER/CDFR/8533 Mezzanine card specifications for Level-2 Calorimeter Trigger Upgrade L. Sartori 1, A. Bhatti 2, A. Canepa 3, M. Casarsa 4, M. Covery 2, G. Cortiana 5, M. Dell Orso 1, G. Flanagan
DTTF muon sorting: Wedge Sorter and Barrel Sorter
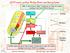 DTTF muon sorting: Wedge Sorter and Barrel Sorter 1 BS, it sorts the 4 best tracks out of max 24 tracks coming from the 12 WS of barrel Vienna Bologna PHTF 72 x Vienna Bologna Padova 12 WS, each one sorts
DTTF muon sorting: Wedge Sorter and Barrel Sorter 1 BS, it sorts the 4 best tracks out of max 24 tracks coming from the 12 WS of barrel Vienna Bologna PHTF 72 x Vienna Bologna Padova 12 WS, each one sorts
CMX (Common Merger extension module) Y. Ermoline for CMX collaboration Preliminary Design Review, Stockholm, 29 June 2011
 (Common Merger extension module) Y. Ermoline for collaboration Preliminary Design Review, Stockholm, 29 June 2011 Outline Current L1 Calorimeter trigger system Possible improvement to maintain trigger
(Common Merger extension module) Y. Ermoline for collaboration Preliminary Design Review, Stockholm, 29 June 2011 Outline Current L1 Calorimeter trigger system Possible improvement to maintain trigger
Module Performance Report. ATLAS Calorimeter Level-1 Trigger- Common Merger Module. Version February-2005
 Module Performance Report ATLAS Calorimeter Level-1 Trigger- Common Merger Module B. M. Barnett, I. P. Brawn, C N P Gee Version 1.0 23 February-2005 Table of Contents 1 Scope...3 2 Measured Performance...3
Module Performance Report ATLAS Calorimeter Level-1 Trigger- Common Merger Module B. M. Barnett, I. P. Brawn, C N P Gee Version 1.0 23 February-2005 Table of Contents 1 Scope...3 2 Measured Performance...3
FIC for L2 Inputs? With Updates and Decisions from Workshop
 FIC for L2 Inputs? With Updates and Decisions from Workshop James T. Linnemann Michigan State University UIC Workshop April 24, 1998 D0 / Michigan State University 4/30/98 1 Criteria for Decisions Meet
FIC for L2 Inputs? With Updates and Decisions from Workshop James T. Linnemann Michigan State University UIC Workshop April 24, 1998 D0 / Michigan State University 4/30/98 1 Criteria for Decisions Meet
Performance Study of GPUs in Real-Time Trigger Applications for HEP Experiments
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 37 (212 ) 1965 1972 TIPP 211 Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 211 Performance Study of GPUs in Real-Time Trigger Applications
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 37 (212 ) 1965 1972 TIPP 211 Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 211 Performance Study of GPUs in Real-Time Trigger Applications
FRC & L3 Buffering. H.Evans Columbia U. 1) Receive/Transmit Road Data from L1CTT 2) Interface to SCL (trigger) 3) Manage L3 Buffers for STT System
 D FRC & L3 ing H.Evans Columbia U. FRC asks: 1) Receive/ransmit Road Data from L1C 2) Interface to SCL (trigger) 3) Manage L3 s for S System wo Stages to FRC Design 1) Exact Spec s of Control Functions
D FRC & L3 ing H.Evans Columbia U. FRC asks: 1) Receive/ransmit Road Data from L1C 2) Interface to SCL (trigger) 3) Manage L3 s for S System wo Stages to FRC Design 1) Exact Spec s of Control Functions
Track-Finder Test Results and VME Backplane R&D. D.Acosta University of Florida
 Track-Finder Test Results and VME Backplane R&D D.Acosta University of Florida 1 Technical Design Report Trigger TDR is completed! A large amount effort went not only into the 630 pages, but into CSC Track-Finder
Track-Finder Test Results and VME Backplane R&D D.Acosta University of Florida 1 Technical Design Report Trigger TDR is completed! A large amount effort went not only into the 630 pages, but into CSC Track-Finder
DTTF muon sorting: Wedge Sorter and Barrel Sorter
 DTTF muon sorting: Wedge Sorter and Barrel Sorter 1 BS, it sorts the 4 best tracks out of max 24 tracks coming from the 12 WS of barrel Vienna Bologna PHTF 72 x Vienna Bologna Padova 12 WS, each one sorts
DTTF muon sorting: Wedge Sorter and Barrel Sorter 1 BS, it sorts the 4 best tracks out of max 24 tracks coming from the 12 WS of barrel Vienna Bologna PHTF 72 x Vienna Bologna Padova 12 WS, each one sorts
6 February 1999 R. D. Martin, Level 2 Review 2
 Robert D. Martin University of Illinois at Chicago 6 February 1999 Fast CPU Event processing within 100 µs VME Interface Communication with TCC Upload of Events to L3 via VBD VME interrupts enabled MBus
Robert D. Martin University of Illinois at Chicago 6 February 1999 Fast CPU Event processing within 100 µs VME Interface Communication with TCC Upload of Events to L3 via VBD VME interrupts enabled MBus
Prototyping NGC. First Light. PICNIC Array Image of ESO Messenger Front Page
 Prototyping NGC First Light PICNIC Array Image of ESO Messenger Front Page Introduction and Key Points Constructed is a modular system with : A Back-End as 64 Bit PCI Master/Slave Interface A basic Front-end
Prototyping NGC First Light PICNIC Array Image of ESO Messenger Front Page Introduction and Key Points Constructed is a modular system with : A Back-End as 64 Bit PCI Master/Slave Interface A basic Front-end
ATLAS TDAQ RoI Builder and the Level 2 Supervisor system
 ATLAS TDAQ RoI Builder and the Level 2 Supervisor system R. E. Blair 1, J. Dawson 1, G. Drake 1, W. Haberichter 1, J. Schlereth 1, M. Abolins 2, Y. Ermoline 2, B. G. Pope 2 1 Argonne National Laboratory,
ATLAS TDAQ RoI Builder and the Level 2 Supervisor system R. E. Blair 1, J. Dawson 1, G. Drake 1, W. Haberichter 1, J. Schlereth 1, M. Abolins 2, Y. Ermoline 2, B. G. Pope 2 1 Argonne National Laboratory,
System-on-a-Programmable-Chip (SOPC) Development Board
 System-on-a-Programmable-Chip (SOPC) Development Board Solution Brief 47 March 2000, ver. 1 Target Applications: Embedded microprocessor-based solutions Family: APEX TM 20K Ordering Code: SOPC-BOARD/A4E
System-on-a-Programmable-Chip (SOPC) Development Board Solution Brief 47 March 2000, ver. 1 Target Applications: Embedded microprocessor-based solutions Family: APEX TM 20K Ordering Code: SOPC-BOARD/A4E
S-LINK: A Prototype of the ATLAS Read-out Link
 : A Prototype of the ATLAS Read-out Link Erik van der Bij, Robert McLaren, Zoltán Meggyesi EP-Division CERN, CH-1211 Geneva 23 Abstract The ATLAS data acquisition system needs over 1500 read-out links
: A Prototype of the ATLAS Read-out Link Erik van der Bij, Robert McLaren, Zoltán Meggyesi EP-Division CERN, CH-1211 Geneva 23 Abstract The ATLAS data acquisition system needs over 1500 read-out links
CMX Hardware Status. Chip Brock, Dan Edmunds, Philippe Yuri Ermoline, Duc Bao Wojciech UBC
 Hardware Status Chip Brock, Dan Edmunds, Philippe Laurens@MSU Yuri Ermoline, Duc Bao Ta @CERN Wojciech Fedorko @ UBC Michigan State University 25-Oct-2013 Outline Review of hardware project (Some) hardware
Hardware Status Chip Brock, Dan Edmunds, Philippe Laurens@MSU Yuri Ermoline, Duc Bao Ta @CERN Wojciech Fedorko @ UBC Michigan State University 25-Oct-2013 Outline Review of hardware project (Some) hardware
RPC Trigger Overview
 RPC Trigger Overview presented by Maciek Kudla, Warsaw University RPC Trigger ESR Warsaw, July 8th, 2003 RPC Trigger Task The task of RPC Muon Trigger electronics is to deliver 4 highest momentum muons
RPC Trigger Overview presented by Maciek Kudla, Warsaw University RPC Trigger ESR Warsaw, July 8th, 2003 RPC Trigger Task The task of RPC Muon Trigger electronics is to deliver 4 highest momentum muons
Comments from the Review committee:
 Comments from the Review committee: 10/27/2003 Page 1 Frank Chlebana, Eric James, and Jonathan Lewis Summer 2005 should be the target to have all updates complete. We thought that the DAQ simulation should
Comments from the Review committee: 10/27/2003 Page 1 Frank Chlebana, Eric James, and Jonathan Lewis Summer 2005 should be the target to have all updates complete. We thought that the DAQ simulation should
The MROD. The MDT Precision Chambers ROD. Adriaan König University of Nijmegen. 5 October nd ATLAS ROD Workshop 1
 The MROD The MDT Precision Chambers ROD Adriaan König University of Nijmegen 5 October 2000 2nd ATLAS ROD Workshop 1 Contents System Overview MROD-0 Prototype MROD-1 Prototype Performance Study FE Parameter
The MROD The MDT Precision Chambers ROD Adriaan König University of Nijmegen 5 October 2000 2nd ATLAS ROD Workshop 1 Contents System Overview MROD-0 Prototype MROD-1 Prototype Performance Study FE Parameter
BES-III off-detector readout electronics for the GEM detector: an update
 BES-III off-detector readout electronics for the GEM detector: an update The CGEM off-detector collaboration ( INFN/Univ. FE, INFN LNF, Univ. Uppsala ) 1 Outline Reminder Update on development status Off-detector
BES-III off-detector readout electronics for the GEM detector: an update The CGEM off-detector collaboration ( INFN/Univ. FE, INFN LNF, Univ. Uppsala ) 1 Outline Reminder Update on development status Off-detector
Front End Electronics. Level 1 Trigger
 0. CMS HCAL rigger and Readout Electronics Project he overall technical coordination for the HCAL trigger and readout electronics (ri- DAS) project will be located in the Maryland HEP group, led by Drew
0. CMS HCAL rigger and Readout Electronics Project he overall technical coordination for the HCAL trigger and readout electronics (ri- DAS) project will be located in the Maryland HEP group, led by Drew
Alternative Ideas for the CALICE Back-End System
 Alternative Ideas for the CALICE Back-End System Matthew Warren and Gordon Crone University College London 5 February 2002 5 Feb 2002 Alternative Ideas for the CALICE Backend System 1 Concept Based on
Alternative Ideas for the CALICE Back-End System Matthew Warren and Gordon Crone University College London 5 February 2002 5 Feb 2002 Alternative Ideas for the CALICE Backend System 1 Concept Based on
Level 0 trigger decision unit for the LHCb experiment
 Level 0 trigger decision unit for the LHCb experiment J. Laubser, H. Chanal, R. Cornat, O. Deschamps, M. Magne, P. Perret for the LHCb Collaboration Laboratoire de Physique Corpusculaire (IN2P3/CNRS),
Level 0 trigger decision unit for the LHCb experiment J. Laubser, H. Chanal, R. Cornat, O. Deschamps, M. Magne, P. Perret for the LHCb Collaboration Laboratoire de Physique Corpusculaire (IN2P3/CNRS),
CMX Hardware Overview
 Hardware Overview Chip Brock, Dan Edmunds, Philippe Laurens@MSU Yuri Ermoline @CERN Wojciech Fedorko @UBC Michigan State University 12-May-2014 Common Merger extended module () 12-May-2014 2 Overall project
Hardware Overview Chip Brock, Dan Edmunds, Philippe Laurens@MSU Yuri Ermoline @CERN Wojciech Fedorko @UBC Michigan State University 12-May-2014 Common Merger extended module () 12-May-2014 2 Overall project
The CMS Event Builder
 The CMS Event Builder Frans Meijers CERN/EP-CMD CMD on behalf of the CMS-DAQ group CHEP03, La Jolla, USA, March 24-28 28 2003 1. Introduction 2. Selected Results from the Technical Design Report R&D programme
The CMS Event Builder Frans Meijers CERN/EP-CMD CMD on behalf of the CMS-DAQ group CHEP03, La Jolla, USA, March 24-28 28 2003 1. Introduction 2. Selected Results from the Technical Design Report R&D programme
HCAL DCC Technical Reference E. Hazen - Revised March 27, 2007 Note: Latest version of this document should be available at:
 HCAL DCC Technical Reference E. Hazen - Revised March 27, 2007 Note: Latest version of this document should be available at: http://cmsdoc.cern.ch/cms/hcal/document/countinghouse/dcc/dcctechref.pdf Table
HCAL DCC Technical Reference E. Hazen - Revised March 27, 2007 Note: Latest version of this document should be available at: http://cmsdoc.cern.ch/cms/hcal/document/countinghouse/dcc/dcctechref.pdf Table
Scenarios for a ROB system built with SHARC processors. Jos Vermeulen, 7 September 1999 Paper model results updated on 7 October 1999
 Scenarios for a ROB system built with processors Jos Vermeulen, 7 September 1999 Paper model results updated on 7 October 1999 1 Scenario I : 6 ROBIns on normal size VME card Configuration 1. 80 Mbyte/s
Scenarios for a ROB system built with processors Jos Vermeulen, 7 September 1999 Paper model results updated on 7 October 1999 1 Scenario I : 6 ROBIns on normal size VME card Configuration 1. 80 Mbyte/s
USCMS HCAL FERU: Front End Readout Unit. Drew Baden University of Maryland February 2000
 USCMS HCAL FERU: Front End Readout Unit Drew Baden University of Maryland February 2000 HCAL Front-End Readout Unit Joint effort between: University of Maryland Drew Baden (Level 3 Manager) Boston University
USCMS HCAL FERU: Front End Readout Unit Drew Baden University of Maryland February 2000 HCAL Front-End Readout Unit Joint effort between: University of Maryland Drew Baden (Level 3 Manager) Boston University
Read-out of High Speed S-LINK Data Via a Buffered PCI Card
 Read-out of High Speed S-LINK Data Via a Buffered PCI Card A. Guirao Talk for the 4 th PCaPAC International Workshop - This is the paper copy version of the presentation- Slide 9th is repeated due to an
Read-out of High Speed S-LINK Data Via a Buffered PCI Card A. Guirao Talk for the 4 th PCaPAC International Workshop - This is the paper copy version of the presentation- Slide 9th is repeated due to an
Lecture 23. Finish-up buses Storage
 Lecture 23 Finish-up buses Storage 1 Example Bus Problems, cont. 2) Assume the following system: A CPU and memory share a 32-bit bus running at 100MHz. The memory needs 50ns to access a 64-bit value from
Lecture 23 Finish-up buses Storage 1 Example Bus Problems, cont. 2) Assume the following system: A CPU and memory share a 32-bit bus running at 100MHz. The memory needs 50ns to access a 64-bit value from
Flexible Architecture Research Machine (FARM)
 Flexible Architecture Research Machine (FARM) RAMP Retreat June 25, 2009 Jared Casper, Tayo Oguntebi, Sungpack Hong, Nathan Bronson Christos Kozyrakis, Kunle Olukotun Motivation Why CPUs + FPGAs make sense
Flexible Architecture Research Machine (FARM) RAMP Retreat June 25, 2009 Jared Casper, Tayo Oguntebi, Sungpack Hong, Nathan Bronson Christos Kozyrakis, Kunle Olukotun Motivation Why CPUs + FPGAs make sense
Nios Embedded Processor Development Board
 Nios Embedded Processor Development Board July 2003, ver. 2.2 Data Sheet Introduction Development Board Features Functional Overview This data sheet describes the features and functionality of the Nios
Nios Embedded Processor Development Board July 2003, ver. 2.2 Data Sheet Introduction Development Board Features Functional Overview This data sheet describes the features and functionality of the Nios
Status and planning of the CMX. Wojtek Fedorko for the MSU group TDAQ Week, CERN April 23-27, 2012
 Status and planning of the Wojtek Fedorko for the MSU group TDAQ Week, CERN April 23-27, 2012 : CMM upgrade Will replace CMM: Backplane rate 40 160Mbs Crate to system rate (LVDS) 40 160Mbs Cluster information
Status and planning of the Wojtek Fedorko for the MSU group TDAQ Week, CERN April 23-27, 2012 : CMM upgrade Will replace CMM: Backplane rate 40 160Mbs Crate to system rate (LVDS) 40 160Mbs Cluster information
Trigger and Data Acquisition at the Large Hadron Collider
 Trigger and Data Acquisition at the Large Hadron Collider Acknowledgments (again) This overview talk would not exist without the help of many colleagues and all the material available online I wish to
Trigger and Data Acquisition at the Large Hadron Collider Acknowledgments (again) This overview talk would not exist without the help of many colleagues and all the material available online I wish to
Data Acquisition in Particle Physics Experiments. Ing. Giuseppe De Robertis INFN Sez. Di Bari
 Data Acquisition in Particle Physics Experiments Ing. Giuseppe De Robertis INFN Sez. Di Bari Outline DAQ systems Theory of operation Case of a large experiment (CMS) Example of readout GEM detectors for
Data Acquisition in Particle Physics Experiments Ing. Giuseppe De Robertis INFN Sez. Di Bari Outline DAQ systems Theory of operation Case of a large experiment (CMS) Example of readout GEM detectors for
Detector Data Acquisition Hardware Designs and Features of NGC (New General Detector Controller)
 Detector Data Acquisition Hardware Designs and Features of NGC (New General Detector Controller) Manfred Meyer, Gert Finger European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere, Karl-Schwarzschild-Str.
Detector Data Acquisition Hardware Designs and Features of NGC (New General Detector Controller) Manfred Meyer, Gert Finger European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere, Karl-Schwarzschild-Str.
ROB-IN Functional demonstrator of the ATLAS Trigger / DAQ Read-Out Buffer O.Gachelin, M.Huet, P.Le Dû, M.Mur C.E.A.
 1 ROB-IN Functional demonstrator of the ATLAS Trigger / DAQ Read-Out Buffer O.Gachelin, M.Huet, P.Le Dû, M.Mur C.E.A. Saclay - DAPNIA 2 Basic principles Data flow : output < input including L2 and L3 according
1 ROB-IN Functional demonstrator of the ATLAS Trigger / DAQ Read-Out Buffer O.Gachelin, M.Huet, P.Le Dû, M.Mur C.E.A. Saclay - DAPNIA 2 Basic principles Data flow : output < input including L2 and L3 according
Trigger Layout and Responsibilities
 CMS EMU TRIGGER ELECTRONICS B. Paul Padley Rice University February 1999 Trigger Layout and Responsibilities Basic Requirements z Latency: < 3.2 us z Fully pipelined synchronous architecture, dead time
CMS EMU TRIGGER ELECTRONICS B. Paul Padley Rice University February 1999 Trigger Layout and Responsibilities Basic Requirements z Latency: < 3.2 us z Fully pipelined synchronous architecture, dead time
Frontend Control Electronics for the LHCb upgrade Hardware realization and test
 First Prototype of the muon Frontend Control Electronics for the LHCb upgrade Hardware realization and test V. Bocci, G. Chiodi, P. Fresch et al. International Conference on Technology and Instrumentation
First Prototype of the muon Frontend Control Electronics for the LHCb upgrade Hardware realization and test V. Bocci, G. Chiodi, P. Fresch et al. International Conference on Technology and Instrumentation
SONICS, INC. Sonics SOC Integration Architecture. Drew Wingard. (Systems-ON-ICS)
 Sonics SOC Integration Architecture Drew Wingard 2440 West El Camino Real, Suite 620 Mountain View, California 94040 650-938-2500 Fax 650-938-2577 http://www.sonicsinc.com (Systems-ON-ICS) Overview 10
Sonics SOC Integration Architecture Drew Wingard 2440 West El Camino Real, Suite 620 Mountain View, California 94040 650-938-2500 Fax 650-938-2577 http://www.sonicsinc.com (Systems-ON-ICS) Overview 10
WBS Trigger. Wesley H. Smith, U. Wisconsin CMS Trigger Project Manager. DOE/NSF Status Review November 20, 2003
 WBS 3.1 - Trigger Wesley H. Smith, U. Wisconsin CMS Trigger Project Manager DOE/NSF Status Review November 20, 2003 This talk is available on: http://hep.wisc.edu/wsmith/cms/trig_lehman_nov03.pdf US CMS
WBS 3.1 - Trigger Wesley H. Smith, U. Wisconsin CMS Trigger Project Manager DOE/NSF Status Review November 20, 2003 This talk is available on: http://hep.wisc.edu/wsmith/cms/trig_lehman_nov03.pdf US CMS
Velo readout board RB3. Common L1 board (ROB)
 Velo readout board RB3 Testing... Common L1 board (ROB) Specifying Federica Legger 10 February 2003 1 Summary LHCb Detectors Online (Trigger, DAQ) VELO (detector and Readout chain) L1 electronics for VELO
Velo readout board RB3 Testing... Common L1 board (ROB) Specifying Federica Legger 10 February 2003 1 Summary LHCb Detectors Online (Trigger, DAQ) VELO (detector and Readout chain) L1 electronics for VELO
BLM and BWS installation examples
 BLM and BWS installation examples Front Back LHC BLM system: 4 crates connected through P2 connector (with the combiner card) for HV control, crate interconnections, beam permit and beam energy distribution.
BLM and BWS installation examples Front Back LHC BLM system: 4 crates connected through P2 connector (with the combiner card) for HV control, crate interconnections, beam permit and beam energy distribution.
WBS Trigger. Wesley H. Smith, U. Wisconsin CMS Trigger Project Manager. DOE/NSF Review June 5, 2002
 WBS 3.1 - Trigger Wesley H. Smith, U. Wisconsin CMS Trigger Project Manager DOE/NSF Review June 5, 2002 This talk is available on: http://hep.wisc.edu/wsmith/cms/trig_lehman_plen02.pdf W. Smith, U. Wisconsin,
WBS 3.1 - Trigger Wesley H. Smith, U. Wisconsin CMS Trigger Project Manager DOE/NSF Review June 5, 2002 This talk is available on: http://hep.wisc.edu/wsmith/cms/trig_lehman_plen02.pdf W. Smith, U. Wisconsin,
Overview of SVT DAQ Upgrades. Per Hansson Ryan Herbst Benjamin Reese
 Overview of SVT DAQ Upgrades Per Hansson Ryan Herbst Benjamin Reese 1 SVT DAQ Requirements and Constraints Basic requirements for the SVT DAQ Continuous readout of 23 040 channels Low noise (S/N>20 to
Overview of SVT DAQ Upgrades Per Hansson Ryan Herbst Benjamin Reese 1 SVT DAQ Requirements and Constraints Basic requirements for the SVT DAQ Continuous readout of 23 040 channels Low noise (S/N>20 to
System Debugging Tools Overview
 9 QII53027 Subscribe About Altera System Debugging Tools The Altera system debugging tools help you verify your FPGA designs. As your product requirements continue to increase in complexity, the time you
9 QII53027 Subscribe About Altera System Debugging Tools The Altera system debugging tools help you verify your FPGA designs. As your product requirements continue to increase in complexity, the time you
ROBIN Functional demonstrator of the ATLAS Trigger / DAQ Read-Out Buffer O.Gachelin, M.Huet, P.Le Dû, M.Mur C.E.A. Saclay - DAPNIA
 1 ROBIN Functional demonstrator of the ATLAS Trigger / DAQ Read-Out Buffer O.Gachelin, M.Huet, P.Le Dû, M.Mur C.E.A. Saclay - DAPNIA 2 Basic principles Data flow : output < input including L2 and L3 according
1 ROBIN Functional demonstrator of the ATLAS Trigger / DAQ Read-Out Buffer O.Gachelin, M.Huet, P.Le Dû, M.Mur C.E.A. Saclay - DAPNIA 2 Basic principles Data flow : output < input including L2 and L3 according
2008 JINST 3 S Online System. Chapter System decomposition and architecture. 8.2 Data Acquisition System
 Chapter 8 Online System The task of the Online system is to ensure the transfer of data from the front-end electronics to permanent storage under known and controlled conditions. This includes not only
Chapter 8 Online System The task of the Online system is to ensure the transfer of data from the front-end electronics to permanent storage under known and controlled conditions. This includes not only
Nuclear Physics Division Data Acquisition Group
 Nuclear Physics Division Data Acquisition Group FANIO, TI to CAEN_TDC interface board J. William Gu (jgu@jlab.org) Oct. 12, 2012 Table of Contents Section Title Page 1 Introduction 3 2 Purpose of FanioDC
Nuclear Physics Division Data Acquisition Group FANIO, TI to CAEN_TDC interface board J. William Gu (jgu@jlab.org) Oct. 12, 2012 Table of Contents Section Title Page 1 Introduction 3 2 Purpose of FanioDC
Why a new kit Introduction to OH OH products Gateware architecture New tools Future work & conclusions. CERN s FMC kit
 , Evangelia Gousiou, Javier Serrano, Erik van der Bij, Tomasz Włostowski CERN, Geneva, Switzerland ICALEPCS 2013, San Francisco, 9 October 2013 Outline 1 Why a new kit 2 Introduction to Open Hardware 3
, Evangelia Gousiou, Javier Serrano, Erik van der Bij, Tomasz Włostowski CERN, Geneva, Switzerland ICALEPCS 2013, San Francisco, 9 October 2013 Outline 1 Why a new kit 2 Introduction to Open Hardware 3
Design and Implementation of the Global Calorimeter Trigger for CMS
 Design and Implementation of the Global Calorimeter Trigger for CMS J. J. Brooke, D. G. Cussans, R. Frazier, G. P. Heath, D. M. Newbold Department of Physics, University of Bristol, BS8 1TL, UK dave.newbold@cern.ch
Design and Implementation of the Global Calorimeter Trigger for CMS J. J. Brooke, D. G. Cussans, R. Frazier, G. P. Heath, D. M. Newbold Department of Physics, University of Bristol, BS8 1TL, UK dave.newbold@cern.ch
Solving the Data Transfer Bottleneck in Digitizers
 Solving the Data Transfer Bottleneck in Digitizers With most modern PC based digitizers and data acquisition systems a common problem is caused by the fact that the ADC technology usually runs in advance
Solving the Data Transfer Bottleneck in Digitizers With most modern PC based digitizers and data acquisition systems a common problem is caused by the fact that the ADC technology usually runs in advance
Employing Multi-FPGA Debug Techniques
 Employing Multi-FPGA Debug Techniques White Paper Traditional FPGA Debugging Methods Debugging in FPGAs has been difficult since day one. Unlike simulation where designers can see any signal at any time,
Employing Multi-FPGA Debug Techniques White Paper Traditional FPGA Debugging Methods Debugging in FPGAs has been difficult since day one. Unlike simulation where designers can see any signal at any time,
CPCI-HPDI32ALT High-speed 64 Bit Parallel Digital I/O PCI Board 100 to 400 Mbytes/s Cable I/O with PCI-DMA engine
 CPCI-HPDI32ALT High-speed 64 Bit Parallel Digital I/O PCI Board 100 to 400 Mbytes/s Cable I/O with PCI-DMA engine Features Include: 200 Mbytes per second (max) input transfer rate via the front panel connector
CPCI-HPDI32ALT High-speed 64 Bit Parallel Digital I/O PCI Board 100 to 400 Mbytes/s Cable I/O with PCI-DMA engine Features Include: 200 Mbytes per second (max) input transfer rate via the front panel connector
The MROD. The Read Out Driver for the ATLAS MDT Muon Precision Chambers
 The MROD The Read Out Driver for the ATLAS MDT Muon Precision Chambers Design Review Report Overview Marcello Barisonzi, Henk Boterenbrood, Rutger van der Eijk, Peter Jansweijer, Gerard Kieft, Jos Vermeulen
The MROD The Read Out Driver for the ATLAS MDT Muon Precision Chambers Design Review Report Overview Marcello Barisonzi, Henk Boterenbrood, Rutger van der Eijk, Peter Jansweijer, Gerard Kieft, Jos Vermeulen
Transient Buffer Wideband (TBW) Preliminary Design Ver. 0.1
 Transient Buffer Wideband (TBW) Preliminary Design Ver. 0.1 Steve Ellingson November 11, 2007 Contents 1 Summary 2 2 Design Concept 2 3 FPGA Implementation 3 4 Extending Capture Length 3 5 Issues to Address
Transient Buffer Wideband (TBW) Preliminary Design Ver. 0.1 Steve Ellingson November 11, 2007 Contents 1 Summary 2 2 Design Concept 2 3 FPGA Implementation 3 4 Extending Capture Length 3 5 Issues to Address
IBM Network Processor, Development Environment and LHCb Software
 IBM Network Processor, Development Environment and LHCb Software LHCb Readout Unit Internal Review July 24 th 2001 Niko Neufeld, CERN 1 Outline IBM NP4GS3 Architecture A Readout Unit based on the NP4GS3
IBM Network Processor, Development Environment and LHCb Software LHCb Readout Unit Internal Review July 24 th 2001 Niko Neufeld, CERN 1 Outline IBM NP4GS3 Architecture A Readout Unit based on the NP4GS3
MicroTCA / AMC Solutions for Real-Time Data Acquisition
 THE MAGAZINE OF RECORD FOR THE EMBEDDED COMPUTING INDUSTRY May 2013 TECHNOLOGY IN SYSTEMS MicroTCA / AMC Solutions for Real-Time Data Acquisition MicroTCA has evolved out of the world of ATCA to become
THE MAGAZINE OF RECORD FOR THE EMBEDDED COMPUTING INDUSTRY May 2013 TECHNOLOGY IN SYSTEMS MicroTCA / AMC Solutions for Real-Time Data Acquisition MicroTCA has evolved out of the world of ATCA to become
Development of a PCI Based Data Acquisition Platform for High Intensity Accelerator Experiments
 Development of a PCI Based Data Acquisition Platform for High Intensity Accelerator Experiments T. Higuchi, H. Fujii, M. Ikeno, Y. Igarashi, E. Inoue, R. Itoh, H. Kodama, T. Murakami, M. Nakao, K. Nakayoshi,
Development of a PCI Based Data Acquisition Platform for High Intensity Accelerator Experiments T. Higuchi, H. Fujii, M. Ikeno, Y. Igarashi, E. Inoue, R. Itoh, H. Kodama, T. Murakami, M. Nakao, K. Nakayoshi,
Scintillator-strip Plane Electronics
 Scintillator-strip Plane Electronics Mani Tripathi Britt Holbrook (Engineer) Juan Lizarazo (Grad student) Peter Marleau (Grad student) Tiffany Landry (Junior Specialist) Cherie Williams (Undergrad student)
Scintillator-strip Plane Electronics Mani Tripathi Britt Holbrook (Engineer) Juan Lizarazo (Grad student) Peter Marleau (Grad student) Tiffany Landry (Junior Specialist) Cherie Williams (Undergrad student)
Dominique Gigi CMS/DAQ. Siena 4th October 2006
 . CMS/DAQ overview. Environment. FRL-Slink (Front-End Readout Link) - Boards - Features - Protocol with NIC & results - Production.FMM (Fast Monitoring Module) -Requirements -Implementation -Features -Production.Conclusions
. CMS/DAQ overview. Environment. FRL-Slink (Front-End Readout Link) - Boards - Features - Protocol with NIC & results - Production.FMM (Fast Monitoring Module) -Requirements -Implementation -Features -Production.Conclusions
LHCb Online System BEAUTY-2002
 BEAUTY-2002 8th International Conference on B-Physics at Hadron machines June 17-21 2002 antiago de Compostela, Galicia (pain ) Niko Neufeld, CERN EP (for the LHCb Online Team) 1 Mission The LHCb Online
BEAUTY-2002 8th International Conference on B-Physics at Hadron machines June 17-21 2002 antiago de Compostela, Galicia (pain ) Niko Neufeld, CERN EP (for the LHCb Online Team) 1 Mission The LHCb Online
The PXI Modular Instrumentation Architecture
 The PXI Modular Instrumentation Architecture Overview The PXI (PCI extensions for Instrumentation) specification defines a rugged PC platform for measurement and automation. PXI modular instrumentation
The PXI Modular Instrumentation Architecture Overview The PXI (PCI extensions for Instrumentation) specification defines a rugged PC platform for measurement and automation. PXI modular instrumentation
The Nios II Family of Configurable Soft-core Processors
 The Nios II Family of Configurable Soft-core Processors James Ball August 16, 2005 2005 Altera Corporation Agenda Nios II Introduction Configuring your CPU FPGA vs. ASIC CPU Design Instruction Set Architecture
The Nios II Family of Configurable Soft-core Processors James Ball August 16, 2005 2005 Altera Corporation Agenda Nios II Introduction Configuring your CPU FPGA vs. ASIC CPU Design Instruction Set Architecture
Decision Node Kristian Hahn
 Decision Node Kristian Hahn, Paul Keener, Joe Kroll, Chris Neu, Fritz Stabenau, Rick Van Berg, Daniel Whiteson, Peter Wittich System & Context Run2b L2 Trigger Data Data Loading Data Decision Node Decisions
Decision Node Kristian Hahn, Paul Keener, Joe Kroll, Chris Neu, Fritz Stabenau, Rick Van Berg, Daniel Whiteson, Peter Wittich System & Context Run2b L2 Trigger Data Data Loading Data Decision Node Decisions
L2 Overview II, and Summary
 L2 Overview II, and Summary James T. Linnemann Michigan State University Level 2 Review Feb 6, 1999 Michigan State University 2/4/99 32 L2 Maximum Event Sizes (FIFO size choice) Length = 16B(min) 4KB (max)
L2 Overview II, and Summary James T. Linnemann Michigan State University Level 2 Review Feb 6, 1999 Michigan State University 2/4/99 32 L2 Maximum Event Sizes (FIFO size choice) Length = 16B(min) 4KB (max)
EMU FED. --- Crate and Electronics. ESR, CERN, November B. Bylsma, S. Durkin, Jason Gilmore, Jianhui Gu, T.Y. Ling. The Ohio State University
 EMU FED --- Crate and Electronics B. Bylsma, S. Durkin, Jason Gilmore, Jianhui Gu, T.Y. Ling The Ohio State University ESR, CERN, November 2004 EMU FED Design EMU FED: Outline FED Crate & Custom Backplane
EMU FED --- Crate and Electronics B. Bylsma, S. Durkin, Jason Gilmore, Jianhui Gu, T.Y. Ling The Ohio State University ESR, CERN, November 2004 EMU FED Design EMU FED: Outline FED Crate & Custom Backplane
CMS Trigger/DAQ HCAL FERU System
 CMS Trigger/DAQ HCAL FERU System Drew Baden University of Maryland October 2000 http://macdrew.physics.umd.edu/cms/ Honest assessment: About 3 months behind schedule. TRIDAS Overall Project Timelines Expected
CMS Trigger/DAQ HCAL FERU System Drew Baden University of Maryland October 2000 http://macdrew.physics.umd.edu/cms/ Honest assessment: About 3 months behind schedule. TRIDAS Overall Project Timelines Expected
The ALICE TPC Readout Control Unit 10th Workshop on Electronics for LHC and future Experiments September 2004, BOSTON, USA
 Carmen González Gutierrez (CERN PH/ED) The ALICE TPC Readout Control Unit 10th Workshop on Electronics for LHC and future Experiments 13 17 September 2004, BOSTON, USA Outline: 9 System overview 9 Readout
Carmen González Gutierrez (CERN PH/ED) The ALICE TPC Readout Control Unit 10th Workshop on Electronics for LHC and future Experiments 13 17 September 2004, BOSTON, USA Outline: 9 System overview 9 Readout
The ATLAS Level-1 Muon to Central Trigger Processor Interface
 The ATLAS Level-1 Muon to Central Processor D. Berge a, N. Ellis a, P. Farthouat a, S. Haas a, P. Klofver a, A. Krasznahorkay a,b, A. Messina a, T. Pauly a, G. Schuler a, R. Spiwoks a, T. Wengler a,c a
The ATLAS Level-1 Muon to Central Processor D. Berge a, N. Ellis a, P. Farthouat a, S. Haas a, P. Klofver a, A. Krasznahorkay a,b, A. Messina a, T. Pauly a, G. Schuler a, R. Spiwoks a, T. Wengler a,c a
The ATLAS High Level Trigger Region of Interest Builder
 Preprint typeset in JINST style - PAPER VERSION ATL-DAQ-PUB-2007-001 The ATLAS High Level Trigger Region of Interest Builder Robert Blair, John Dawson, Gary Drake, William Haberichter, James Schlereth,
Preprint typeset in JINST style - PAPER VERSION ATL-DAQ-PUB-2007-001 The ATLAS High Level Trigger Region of Interest Builder Robert Blair, John Dawson, Gary Drake, William Haberichter, James Schlereth,
FPGA Solutions: Modular Architecture for Peak Performance
 FPGA Solutions: Modular Architecture for Peak Performance Real Time & Embedded Computing Conference Houston, TX June 17, 2004 Andy Reddig President & CTO andyr@tekmicro.com Agenda Company Overview FPGA
FPGA Solutions: Modular Architecture for Peak Performance Real Time & Embedded Computing Conference Houston, TX June 17, 2004 Andy Reddig President & CTO andyr@tekmicro.com Agenda Company Overview FPGA
A Reconfigurable Crossbar Switch with Adaptive Bandwidth Control for Networks-on
 A Reconfigurable Crossbar Switch with Adaptive Bandwidth Control for Networks-on on-chip Donghyun Kim, Kangmin Lee, Se-joong Lee and Hoi-Jun Yoo Semiconductor System Laboratory, Dept. of EECS, Korea Advanced
A Reconfigurable Crossbar Switch with Adaptive Bandwidth Control for Networks-on on-chip Donghyun Kim, Kangmin Lee, Se-joong Lee and Hoi-Jun Yoo Semiconductor System Laboratory, Dept. of EECS, Korea Advanced
ATLANTIS - a modular, hybrid FPGA/CPU processor for the ATLAS. University of Mannheim, B6, 26, Mannheim, Germany
 ATLANTIS - a modular, hybrid FPGA/CPU processor for the ATLAS Readout Systems A. Kugel, Ch. Hinkelbein, R. Manner, M. Muller, H. Singpiel University of Mannheim, B6, 26, 68131 Mannheim, Germany fkugel,
ATLANTIS - a modular, hybrid FPGA/CPU processor for the ATLAS Readout Systems A. Kugel, Ch. Hinkelbein, R. Manner, M. Muller, H. Singpiel University of Mannheim, B6, 26, 68131 Mannheim, Germany fkugel,
PXIe FPGA board SMT G Parker
 Form : QCF51 Date : 6 July 2006 PXIe FPGA board SMT700 1.5 20 th November 2009 G Parker Sundance Multiprocessor Technology Ltd, Chiltern House, Waterside, Chesham, Bucks. HP5 1PS. This document is the
Form : QCF51 Date : 6 July 2006 PXIe FPGA board SMT700 1.5 20 th November 2009 G Parker Sundance Multiprocessor Technology Ltd, Chiltern House, Waterside, Chesham, Bucks. HP5 1PS. This document is the
Muon Port Card Upgrade Status May 2013
 CSC Endcap Muon Port Card and Muon Sorter Upgrade Status May 2013 MPC Upgrade Requirements Be able to deliver all 18 trigger primitives from the EMU peripheral crate to the upgraded Sector Processor Preserve
CSC Endcap Muon Port Card and Muon Sorter Upgrade Status May 2013 MPC Upgrade Requirements Be able to deliver all 18 trigger primitives from the EMU peripheral crate to the upgraded Sector Processor Preserve
Readout-Nodes. Master-Node S-LINK. Crate Controller VME ROD. Read out data (PipelineBus) VME. PipelineBus Controller PPM VME. To DAQ (S-Link) PPM
 THE READOUT BU OF THE ATLA LEVEL- CALORIMETER TRIGGER PRE-PROCEOR C. chumacher Institut fur Hochenergiephysik, Heidelberg, Germany (e-mail: schumacher@asic.uni-heidelberg.de) representing the ATLA level-
THE READOUT BU OF THE ATLA LEVEL- CALORIMETER TRIGGER PRE-PROCEOR C. chumacher Institut fur Hochenergiephysik, Heidelberg, Germany (e-mail: schumacher@asic.uni-heidelberg.de) representing the ATLA level-
LUPO TimeStamp Module (Ver. 1.2) Hidetada Baba
 LUPO TimeStamp Module (Ver. 1.2) Hidetada Baba November 28, 2009 1 1 General 1 General 1.1 Function This module is a CAMAC/VME LUPO module which including the functions of Time stamp, Output register and
LUPO TimeStamp Module (Ver. 1.2) Hidetada Baba November 28, 2009 1 1 General 1 General 1.1 Function This module is a CAMAC/VME LUPO module which including the functions of Time stamp, Output register and
300 MBPS CCSDS PROCESSING USING FPGA s
 300 MBPS CCSDS PROCESSING USING FPGA s Thad J. Genrich ABSTRACT This paper describes a 300 Mega Bit Per Second (MBPS) Front End Processor (FEP) prototype completed in early 1993. The FEP implements a patent
300 MBPS CCSDS PROCESSING USING FPGA s Thad J. Genrich ABSTRACT This paper describes a 300 Mega Bit Per Second (MBPS) Front End Processor (FEP) prototype completed in early 1993. The FEP implements a patent
Vertex Detector Electronics: ODE to ECS Interface
 Vertex Detector Electronics: ODE to ECS Interface LHCb Technical Note Issue: 1 Revision: 0 Reference: LHCb 2000-012 VELO Created: 1 February 2000 Last modified: 20 March 2000 Prepared By: Yuri Ermoline
Vertex Detector Electronics: ODE to ECS Interface LHCb Technical Note Issue: 1 Revision: 0 Reference: LHCb 2000-012 VELO Created: 1 February 2000 Last modified: 20 March 2000 Prepared By: Yuri Ermoline
Using the FADC250 Module (V1C - 5/5/14)
 Using the FADC250 Module (V1C - 5/5/14) 1.1 Controlling the Module Communication with the module is by standard VME bus protocols. All registers and memory locations are defined to be 4-byte entities.
Using the FADC250 Module (V1C - 5/5/14) 1.1 Controlling the Module Communication with the module is by standard VME bus protocols. All registers and memory locations are defined to be 4-byte entities.
JMR ELECTRONICS INC. WHITE PAPER
 THE NEED FOR SPEED: USING PCI EXPRESS ATTACHED STORAGE FOREWORD The highest performance, expandable, directly attached storage can be achieved at low cost by moving the server or work station s PCI bus
THE NEED FOR SPEED: USING PCI EXPRESS ATTACHED STORAGE FOREWORD The highest performance, expandable, directly attached storage can be achieved at low cost by moving the server or work station s PCI bus
System overview Production status. MPD firmware upgrade. Front Tracker boards SID equipment Back Tracker (UVa) FIR blocks Optical interface
 1 GEM Readout and DAQ System overview Production status Front Tracker boards SID equipment Back Tracker (UVa) MPD firmware upgrade FIR blocks Optical interface Paolo Musico and Evaristo Cisbani 2 APV25
1 GEM Readout and DAQ System overview Production status Front Tracker boards SID equipment Back Tracker (UVa) MPD firmware upgrade FIR blocks Optical interface Paolo Musico and Evaristo Cisbani 2 APV25
Performance Optimization for an ARM Cortex-A53 System Using Software Workloads and Cycle Accurate Models. Jason Andrews
 Performance Optimization for an ARM Cortex-A53 System Using Software Workloads and Cycle Accurate Models Jason Andrews Agenda System Performance Analysis IP Configuration System Creation Methodology: Create,
Performance Optimization for an ARM Cortex-A53 System Using Software Workloads and Cycle Accurate Models Jason Andrews Agenda System Performance Analysis IP Configuration System Creation Methodology: Create,
Field Program mable Gate Arrays
 Field Program mable Gate Arrays M andakini Patil E H E P g r o u p D H E P T I F R SERC school NISER, Bhubaneshwar Nov 7-27 2017 Outline Digital electronics Short history of programmable logic devices
Field Program mable Gate Arrays M andakini Patil E H E P g r o u p D H E P T I F R SERC school NISER, Bhubaneshwar Nov 7-27 2017 Outline Digital electronics Short history of programmable logic devices
High Performance Embedded Applications. Raja Pillai Applications Engineering Specialist
 High Performance Embedded Applications Raja Pillai Applications Engineering Specialist Agenda What is High Performance Embedded? NI s History in HPE FlexRIO Overview System architecture Adapter modules
High Performance Embedded Applications Raja Pillai Applications Engineering Specialist Agenda What is High Performance Embedded? NI s History in HPE FlexRIO Overview System architecture Adapter modules
CompuScope bit, 100 MHz digital input card for the PCI bus
 CompuScope 3200 32 bit, 100 MHz digital input card for the PCI bus Fast and versatile digital capture card with logic analyzer characteristics for electronic test applications. FEATURES Capture 32 bits
CompuScope 3200 32 bit, 100 MHz digital input card for the PCI bus Fast and versatile digital capture card with logic analyzer characteristics for electronic test applications. FEATURES Capture 32 bits
HCAL Trigger Readout
 HCAL Trigger Readout HTR Status and Clocking Issues D. Baden, T. Grassi http://www.physics.umd.edu/hep/esr_dec_2002.pdf 1 FE/DAQ Electronics S-Link: 64 bits @ 25 MHz Trigger Primitives READ-OUT Crate CAL
HCAL Trigger Readout HTR Status and Clocking Issues D. Baden, T. Grassi http://www.physics.umd.edu/hep/esr_dec_2002.pdf 1 FE/DAQ Electronics S-Link: 64 bits @ 25 MHz Trigger Primitives READ-OUT Crate CAL
APENet: LQCD clusters a la APE
 Overview Hardware/Software Benchmarks Conclusions APENet: LQCD clusters a la APE Concept, Development and Use Roberto Ammendola Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare, Sezione Roma Tor Vergata Centro Ricerce
Overview Hardware/Software Benchmarks Conclusions APENet: LQCD clusters a la APE Concept, Development and Use Roberto Ammendola Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare, Sezione Roma Tor Vergata Centro Ricerce
Jumping Hurdles. High Expectations in a Low Power Environment. Christopher Fadeley Software Engineering Manager EIZO Rugged Solutions
 Jumping Hurdles High Expectations in a Low Power Environment Christopher Fadeley Software Engineering Manager EIZO Rugged Solutions Biggest Challenges Embedded/Rugged Environment High performance expectations
Jumping Hurdles High Expectations in a Low Power Environment Christopher Fadeley Software Engineering Manager EIZO Rugged Solutions Biggest Challenges Embedded/Rugged Environment High performance expectations
PCI to SH-3 AN Hitachi SH3 to PCI bus
 PCI to SH-3 AN Hitachi SH3 to PCI bus Version 1.0 Application Note FEATURES GENERAL DESCRIPTION Complete Application Note for designing a PCI adapter or embedded system based on the Hitachi SH-3 including:
PCI to SH-3 AN Hitachi SH3 to PCI bus Version 1.0 Application Note FEATURES GENERAL DESCRIPTION Complete Application Note for designing a PCI adapter or embedded system based on the Hitachi SH-3 including:
High Bandwidth Electronics
 DOE BES Neutron & Photon Detectors Workshop, August 1-3, 2012 Ryan Herbst System Overview What are the standard components in a detector system? Detector/Amplifier & ADC Digital front end - Configure and
DOE BES Neutron & Photon Detectors Workshop, August 1-3, 2012 Ryan Herbst System Overview What are the standard components in a detector system? Detector/Amplifier & ADC Digital front end - Configure and
APPLICATION NOTE. Application note about SMT702_SMT712 System: 2-Ghz Platform. SMT702 and SMT712 SUNDANCE MULTIPROCESSOR TECHNOLOGY LTD.
 Application note about SMT702_SMT712 System: 2-Ghz Platform SMT702 and SMT712 SUNDANCE MULTIPROCESSOR TECHNOLOGY LTD. Date Comments / Changes Author Revision 12/03/10 Original Document completed PhSR 1
Application note about SMT702_SMT712 System: 2-Ghz Platform SMT702 and SMT712 SUNDANCE MULTIPROCESSOR TECHNOLOGY LTD. Date Comments / Changes Author Revision 12/03/10 Original Document completed PhSR 1
CompuScope 3200C. 32 bit, 100 MHz digital input card for the CompactPCI/PXI bus. Features. We offer the widest range
 We offer the widest range of high-speed digitizers and instrumentation cards CompuScope 3200C 32 bit, 100 MHz digital input card for the CompactPCI/PXI bus available on the market today. Our powerful PC-based
We offer the widest range of high-speed digitizers and instrumentation cards CompuScope 3200C 32 bit, 100 MHz digital input card for the CompactPCI/PXI bus available on the market today. Our powerful PC-based
APV-25 based readout electronics for the SBS front GEM Tracker
 APV-25 based readout electronics for the SBS front GEM Tracker Authors: Evaristo Cisbani, Paolo Musico Date: 26/June/2014 Version: 1.0 APV-25 based readout electronics for the SBS front GEM Tracker...
APV-25 based readout electronics for the SBS front GEM Tracker Authors: Evaristo Cisbani, Paolo Musico Date: 26/June/2014 Version: 1.0 APV-25 based readout electronics for the SBS front GEM Tracker...
SCL init. July Q. An, H.G. Evans, G. Steinbrück
 SCL init July 26 2000 Q. An, H.G. Evans, G. Steinbrück In the first part of this document, we describe under which conditions and how the STT requests an SCL initialize. In the second part we describe
SCL init July 26 2000 Q. An, H.G. Evans, G. Steinbrück In the first part of this document, we describe under which conditions and how the STT requests an SCL initialize. In the second part we describe
A synchronous architecture for the L0 muon trigger
 CPPM, IN2P3 CNRS et Université d Aix Marseille II A synchronous architecture for the L0 muon trigger LHCb Technical Note Issue: 1 Revision: 1 Reference: LHCb 2001 010 Created: January 23, 2001 Last modified:
CPPM, IN2P3 CNRS et Université d Aix Marseille II A synchronous architecture for the L0 muon trigger LHCb Technical Note Issue: 1 Revision: 1 Reference: LHCb 2001 010 Created: January 23, 2001 Last modified:
Heavy Photon Search Data Acquisition
 Heavy Photon Search Data Acquisition Presented by Ryan Herbst PPA Engineering 5/25/2011 1 Overview Data Output & Control 1GigE Read Out Board Ethernet Switch Processor Blade Trigger Board ATCA Crate RTM
Heavy Photon Search Data Acquisition Presented by Ryan Herbst PPA Engineering 5/25/2011 1 Overview Data Output & Control 1GigE Read Out Board Ethernet Switch Processor Blade Trigger Board ATCA Crate RTM
CSC Trigger Motherboard
 CSC Trigger Motherboard Functions of TMB Tests: Performance at summer 2003 test beam Radiation, magnetic fields, etc. Plans for TMB production and testing 1 Cathode LCT CSC Trigger Requirements Identify
CSC Trigger Motherboard Functions of TMB Tests: Performance at summer 2003 test beam Radiation, magnetic fields, etc. Plans for TMB production and testing 1 Cathode LCT CSC Trigger Requirements Identify
