PHY120 LAB 4 Maps, Landforms, and Google Earth
|
|
|
- Daniel Norton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PHY120 LAB 4 Maps, Landforms, and Google Earth Sources: en.wikipedia.org Holcombe_conv_and_meas.pdf mrdata.usgs.gov/geology/state/ Lisle, R. J., 2004, Geological Structures and Maps, A Practical Guide, Third edition
2 LANDFORMS MAPS MAP ELEMENTS MAP SCALES TOPOGRAPHY and HYPSOGRAPHY TOPOGRAPHY and DEMS GIS POINTS, LINES, and POLYGONS GIS TINS DEMS and HYPSOGRAPHY GEOLOGICAL PLANES and LINES GEOLOGIC POINTS USING GOOGLE EARTH
3 LANDFORMS Landform elements include seascape and oceanic water-body interface features such as bays, peninsulas, seas and so forth, including sub-aqueous terrain features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great ocean basins. Topography -The expression of landscape forms and locations as part of a terrain
4 MAPS 1482 printed map depicting Ptolemy's description of the Oecumene, Johannes Schnitzer, engraver Cartography (Greekchartes= map and graphein= to write)is the study and practice of making maps Maps in the traditional sense are depictions of the Earths terrain and associated objects represented on flat media. They combine science, technique, and cartographic elements in order to communicate spatial information effectively. Attempts are made to eliminate distortion in one or several aspects of the map. The map maker must choose which distortions are less important than the others. Rider Structural Geology GCHERMAN
5 MAPS They may choose to allow a little distortion in all four of the following aspects to produce the right type of map: Conformality-the shapes of places are accurate Distance-measured distances are accurate Area/Equivalence-the areas represented on the map are proportional to their area on the Earth (Scale) Direction-angles of direction are portrayed accurately Modern cartography is closely integrated with geographic information science and constitutes many theoretical and practical foundations of geographic information systems (GIS).
6 MAPS Basic map elements that should be included in all maps: 1) Distance or Scale 2) Direction 3) Legend or explanation of map symbols 4) Sources of information More information USGS Google 1:24,000 Earth aerial scale photographic topographic maps image are of commonly TCNJ campus. used as base for geological maps in many parts of the US.
7 MAP ELEMENTS Context-sensitive: Title Projection Cartographer Date of production Effective communication: Neatlines Locator maps Inset maps Index maps Component and color balance
8 MAP SCALES 13-color Topographic Map Monochromatic Bit-map image (one- color and no color)
9 MAP SCALES A scale of 1:24,000 means 1 inch = 24,000 inches or 2000 ft. This is a convenient scale when using feet and inches, and provides a basis for other scales that are useful for measuring distances: IMPERIAL UNITS SCALE 1 inch = 1:63,360 1 mile 1:24, ft 1:12, ft 1:6, ft 1:4, ft 1:2, ft 1:1, ft 1: ft 1: ft Converion to metric is underway, with 1:100,000 scale and 1:50,000 scale maps being the modern standard. 1:250,000 scale means 1 cm = 250,000 cm on the map, or METRIC UNITS SCALE 1 cm = 1:250, km 1:100,000 1 km 1:50, m 1:20, m 1:5, m 1:2, m 1: m 1:500 5m 1:100 1m
10 TOPOGRAPHY & HYPSOGRAPHY Each brown line on a colored topographic map (right) represents the intersection trace between a horizontal planeat a certain elevation and the land surface. The 2D lines tracing topography are called hypsography and represent a horizontal plane of specific elevation that intersects landforms relative to a datum, like sea level (0 feet (ft) or meters (m). Hypsographic lines are graduated (e.g. 2 or 20 ft or/m).
11 TOPOGRAPHY & and Digital Elevation Models (DEMS or DEM)
12 DEMS and HYPSOGRAPHY value 0 value 1 10m = 32.8 contour line Hypsographyconsists of many polylines, sets of individual line segments connected end-to-end by vertices. Digital-elevation-models (DEMs) are raster data, equivalent to a screen having equi-dimensional cells, each coded with an unique elevation value. value 60 value 8 10m = 32.8 contour line Detail of a DEM with 100-ft cells overlain by hypsography lines with one showing its vertices.
13 GIS POINTS, LINES, and POLYGONS CARTESIAN COORDINATE SYSTEM uses X, Y, and Z coordinates 0,0,0 POINT(X n Y n Z n ) 2,3,0 6,3,0 SIMPLE LINE(X 1 Y 1 Z 0, X 2 Y 2 Z 0 ) 2,3,0 6,3,0 POLYLINE(X 1 Y 1 Z 0, X 2 Y 2 Z 0, X 3 Y 3 Z 0,X n Y n Z n ) 3,2,0 Z Y 4,2,2 2,3,0 6,3,0 4,2,0 POLYLINEZ(X 1 Y 1 Z 0, X 2 Y 2 Z 0, X 3 Y 3 Z 0,X 4 Y 4 Z 1,X n Y n Z n ) X 2,3,0 6,3,0 3,2,0 POLYGON(X 1 Y 1 Z 0, X 2 Y 2 Z 0, X 3 Y 3 Z 3,X n Y n Z n ) 2,3,0 4,2,2 6,3,0 POLYGONZ(X 1 Y 1 Z 0, X 2 Y 2 Z 0, X 3 Y 3 Z 1,X n Y n Z n ) 3,2,0
14 GIS TINS (Triangulated Integrated Networks) Detail of a DEM with 100-ft cells overlain by a TIN showing it s components, points (vertices), lines, and polygons P1 P2 P3 P4 P6 P5 POLYGONZ(X 1 Y 1 Z 1, X 2 Y 2 Z 2, X 3 Y 3 Z 3 ) + POLYGONZ(X 2 Y 2 Z 2, X 3 Y 3 Z 3, X 4 Y 4 Z 4 ) + POLYGONZ(X 3 Y 3 Z 3, X 4 Y 4 Z 4, X 5 Y 5 Z 5 ) + POLYGONZ(X 4 Y 4 Z 4, X 5 Y 5 Z 5, X 5 Y 5 Z 5 ) + POLYGONZ(X n Y n Z n, X n+1 Y n+1 Z n+1, X n+2 Y n+ Z n+2 ) TIN SURFACE WITH ELEVATION RANGES
15 GEOLOGICAL PLANES and LINES TOPOGRAPHY AND INCLINED PLANES The dark, irregular line on the geological map (fig. 2.9A) separates two rock formations even though the contact between the formations is a planar surface (fig. 2.9B). The lighter lines are hypsography. It is important to realize that this polyline represents the formational boundary produced by the 3D intersection of two surfaces; 1) the planar, inclined geological surface, and 2) the irregular the surface of the ground, or the topographic surface. Unlike the geological surface, the topographic surface is not planar but has features such as hills, valleys and ridges. It is these topographic irregularities which produce the sinuous trace of geological contacts we observe on maps. Geologic map with variable topography Block diagrams If, for example, the ground surface were planar (fig. 2.9D), the contacts would run as straight lines on the map (fig. 2.9C). Geologic map with uniform topography Adapted from Richard J Lisle, Geological Structures and Maps, A practical Guide.
16 GEOLOGICAL PLANES and LINES The word azimuthstems from an Arabic word meaning "direction, and means an angular measurement in a spherical coordinate system. Brunton Pocket Transit In geology, we primarily deal with land navigation and directional readings on two-dimensional maps of the Earth surface, and azimuth commonly refers to incremental measures in a circular (0-360 ) and horizontal reference frame relative to land surface.
17 GEOLOGICAL PLANES and LINES Plane Dip - Bedding and other geological layers and planes that are not horizontal are said to dip. There are two aspects to the dip of a plane: (a) the direction of dip, or dip azimuth) which is the compass direction towards which the plane slopes; and (b) the dip angle, which is the angle that the plane makes with a horizontal plane (right). The angle of dip = 0 for a horizontal plane, and 90 for the vertical plane. To record the dip of a plane all that is needed are two numbers; the dip angle followed by the dip azimuth, e.g. 74/138 is a plane which dips 74 in the direction 138. horizontal Dip = d o d o The direction of dip can be visualized as the direction in which water would flow if poured onto the plane.
18 GEOLOGICAL PLANES and LINES Linear Plunge and Trend Any dipping plane can be thought of as containing a large number of lines of varying plunge(fig. 2.4). The strikeline is a non-plunging, horizontal line within a dipping plane (e.g. line 5 is a strike line; it is not the only one but the other strike lines are all parallel to it.) Think of the sloping roof of a house as a dipping plane, the line along the roof ridge is a strike line Plungedescribes the tilt of lines, and the word dipbeing reserved for planes. Trend The plunge fully expresses the 3D orientation of a line and has two parts: (a) the plunge angle, and (b) the plunge azimuth or trend. 30 Consider the plunging line on the dipping plane to the right and an imaginary vertical plane containing the plunging line. The trendis the azimuth in which this vertical plane runs, and the direction towards which the line is tilted. The plunge is the amount the line is tilted with respect to the horizontal. The angle of plunge of a horizontal line is 0 and the angle of plunge of a vertical line is 90.
19 WELCOME TO GOOGLE EARTH
20 GOOGLE EARTH SPEAK KMLstands for Keyhole Markup Language (KML), an XML notation for expressing geographic annotation and visualization within Internet-based, two dimensional maps and three-dimensional Earth browsers (Wikipedia, 2012). KML is an international standard of the Open Geospatial Consortium. XML (Extensible Markup Language) is a markup language that defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both humanreadable and machine-readable (Wikipedia, 2012). KMZis a compiledkml file, meaning that it has been encrypted in machine language and is not readily open or read in ordinary language or ASCII text editors. You can <File><Save> or <File Save As> from going to KMZ to a KML or vice versa. But if you want to manually edit the GE file, <Save As> a KML, then <Open> it using Microsoft (MS) Notepad or Wordpad, common ASCII-text editing files for PCs.
21 Go to and download Google_Earth_1.kmz file (~4 MB) Double click on it to Start Google Earth, or In Google Earth <File><Open >, navigate to the downloads folder and <Open>. The file will load into the Temporary folder. After it loads the legend on the left should reside in the file into the Temporary Places folder: Before doing anything else, <right click> on the TCNJ PHY120 GE Labs.kmz then<save Place As >.A pop-up menu will prompt you for a location to save the file. Point it to your flashdriveor hard drive and <Save>
22 L4-TCNJ_Google_Earth_1.kmz (16.0MB) GE Legend controls 100% opaque Expand the folder Turn on/off layers Object folder Compiled KMZ file of objects DO NOT TURN ON ALL LAYERS BY CLICKING ON THE BUTTON FIRST INSTEAD, CLICK ON THE BUTTON TO EXPAND THE TREE TO SEE WHAT LAYERS ARE CURRENTLY ACTIVE (CHECKED) 50% opaque
23 Default view of TCNJ PHY120 GE Labs.kmz
24 First, the folder expands to show: Clicking next to TCNJ Labs expands to: basalt diabase The two active themes include the USGS 7-1/2 quadrangles covering New Jersey (NJ) and the trap rock (diabase and basalt) formations in Pennsylvania and NJ mrdata.usgs.gov/geology/state/
25 Clicking on will result in this view basalt diabase
26 Hopewell Fault objects Flemington Fault objects
27 GEOLOGICAL POINTS Now let s consider two geological traverses conducted by the NJGS and a Rider U. field trip down two streams that cross two normal fault in the Mesozoic Newark Basin, NJ
28 GEOLOGICAL POINTS
29 GEOLOGICAL POINTS Each traverse has a set of point-based field station where stratigraphic, structural, GPS locations, and multimedia have been collected during 4 or 5 different visits. Jd Hopewell fault traverses along A-A Lambertville 7-1/2 quadrangle (quad) Flemington Fault traverses along B-B Flemington, NJ 7-1/2 quad Jd Jo Jd
30 GEOLOGICAL POINTS in KML format <Placemark> <name>57061</name> <description>57061</description> <styleurl>#msn_placemark_circle0</styleurl> <Point><coordinates> , ,0</coordinates></Point> </Placemark> <Placemark> <name>58186</name> <description>58186</description> <styleurl>#msn_placemark_circle0</styleurl> <Point><coordinates> , ,0</coordinates></Point> </Placemark> <Placemark> <name>58188</name> <description>58188</description> <styleurl>#msn_placemark_circle0</styleurl> <Point><coordinates> , ,0</coordinates></Point> </Placemark>
31 GE and middle mouse button interoperability A key GE viewing tool is to use the mouse for interactive viewing by <Pressing><Holding> the middle button of your mouse after the cursor is positioned over the feature or area of interest, then moving the mouse while the middle button is depressed: Depressing and holding the middle mouse button while moving the cursor allows you tilt and rotate the view simultaneously
32 GE and Vertical topographic exaggeration The command <Tools><Options > take you to the following menu: The elevation exaggeration will multiply the height of the topography by the factor entered (up to a maximum 3X) This function should be used in areas of muted topographic relief, and not for mountain ranges or areas of drastic relief.
33 3X Elevation exaggeration and oblique view of the Moore s, Station Trap Rock Quarry, Lambertville, NJ 3X Elevation exaggeration and oblique view of the Moore s, Station Trap Rock Quarry, Lambertville, NJ with part of the Lambertville, NJ- Pa USGS 7-1/ topographic quadrangle draped and set at 75% transparency (25% opaque)
34
35 TCNJ PHY GCHERMAN
Engineering Geology. Engineering Geology is backbone of civil engineering. Topographic Maps. Eng. Iqbal Marie
 Engineering Geology Engineering Geology is backbone of civil engineering Topographic Maps Eng. Iqbal Marie Maps: are a two dimensional representation, of an area or region. There are many types of maps,
Engineering Geology Engineering Geology is backbone of civil engineering Topographic Maps Eng. Iqbal Marie Maps: are a two dimensional representation, of an area or region. There are many types of maps,
Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL. Lecture-7 Chapters 13 and 14
 Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL Lecture-7 Chapters 13 and 14 Data for Terrain Mapping and Analysis DEM (digital elevation model) and TIN (triangulated irregular network) are two
Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL Lecture-7 Chapters 13 and 14 Data for Terrain Mapping and Analysis DEM (digital elevation model) and TIN (triangulated irregular network) are two
What is a Topographic Map?
 Topographic Maps Topography From Greek topos, place and grapho, write the study of surface shape and features of the Earth and other planetary bodies. Depiction in maps. Person whom makes maps is called
Topographic Maps Topography From Greek topos, place and grapho, write the study of surface shape and features of the Earth and other planetary bodies. Depiction in maps. Person whom makes maps is called
Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2)
 GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2) Today: Digital Elevation Models (DEMs), Topographic functions (surface analysis): slope, aspect hillshade, viewshed,
GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2) Today: Digital Elevation Models (DEMs), Topographic functions (surface analysis): slope, aspect hillshade, viewshed,
Contents of Lecture. Surface (Terrain) Data Models. Terrain Surface Representation. Sampling in Surface Model DEM
 Lecture 13: Advanced Data Models: Terrain mapping and Analysis Contents of Lecture Surface Data Models DEM GRID Model TIN Model Visibility Analysis Geography 373 Spring, 2006 Changjoo Kim 11/29/2006 1
Lecture 13: Advanced Data Models: Terrain mapping and Analysis Contents of Lecture Surface Data Models DEM GRID Model TIN Model Visibility Analysis Geography 373 Spring, 2006 Changjoo Kim 11/29/2006 1
2. AREAL PHOTOGRAPHS, SATELLITE IMAGES, & TOPOGRAPHIC MAPS
 LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: 2. AREAL PHOTOGRAPHS, SATELLITE IMAGES, & TOPOGRAPHIC MAPS Instructions: Refer to Exercise 3 in your Lab Manual on pages 47-64 to answer the questions in this work
LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: 2. AREAL PHOTOGRAPHS, SATELLITE IMAGES, & TOPOGRAPHIC MAPS Instructions: Refer to Exercise 3 in your Lab Manual on pages 47-64 to answer the questions in this work
Making Topographic Maps
 T O P O Applications N Making Topographic Maps M A P S Making Topographic Maps with TNTmips page 1 Before Getting Started TNTmips provides a variety of tools for working with map data and making topographic
T O P O Applications N Making Topographic Maps M A P S Making Topographic Maps with TNTmips page 1 Before Getting Started TNTmips provides a variety of tools for working with map data and making topographic
Using Google Earth. Middlebury College Library and Information Services
 Using Google Earth Middlebury College Introduction: While Google Earth can be a fun tool for simply looking at the surface of the earth, there are many other more sophisticated features to explore. Google
Using Google Earth Middlebury College Introduction: While Google Earth can be a fun tool for simply looking at the surface of the earth, there are many other more sophisticated features to explore. Google
START>PROGRAMS>ARCGIS>
 Department of Urban Studies and Planning Spring 2006 Department of Architecture Site and Urban Systems Planning 11.304J / 4.255J GIS EXERCISE 2 Objectives: To generate the following maps using ArcGIS Software:
Department of Urban Studies and Planning Spring 2006 Department of Architecture Site and Urban Systems Planning 11.304J / 4.255J GIS EXERCISE 2 Objectives: To generate the following maps using ArcGIS Software:
Final project: Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2) GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I
 GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2) Talk about class project (copy follow_along_data\ch8a_class_ex into U:\ArcGIS\ if needed) Catch up with lecture 20
GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2) Talk about class project (copy follow_along_data\ch8a_class_ex into U:\ArcGIS\ if needed) Catch up with lecture 20
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 13. TERRAIN MAPPING AND ANALYSIS 13.1 Data for Terrain Mapping and Analysis 13.1.1 DEM 13.1.2 TIN Box 13.1 Terrain Data Format 13.2 Terrain Mapping 13.2.1 Contouring 13.2.2 Vertical Profiling 13.2.3
Chapter 13. TERRAIN MAPPING AND ANALYSIS 13.1 Data for Terrain Mapping and Analysis 13.1.1 DEM 13.1.2 TIN Box 13.1 Terrain Data Format 13.2 Terrain Mapping 13.2.1 Contouring 13.2.2 Vertical Profiling 13.2.3
CSTools Guide (for ArcGIS version 10.2 and 10.3)
 CSTools Guide (for ArcGIS version 10.2 and 10.3) 1. Why to use Orientation Analysis and Cross section tools (CSTools) in ArcGIS? 2 2. Data format 2 2.1 Coordinate Systems 2 3. How to get the tools into
CSTools Guide (for ArcGIS version 10.2 and 10.3) 1. Why to use Orientation Analysis and Cross section tools (CSTools) in ArcGIS? 2 2. Data format 2 2.1 Coordinate Systems 2 3. How to get the tools into
LAB #7 Creating TIN and 3D scenes (ArcScene) GISC, UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA BERKELEY
 LAB #7 Creating TIN and 3D scenes (ArcScene) GISC, UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA BERKELEY The purpose of this laboratory is to introduce and explore surface data analysis using a vector data model: TIN. We
LAB #7 Creating TIN and 3D scenes (ArcScene) GISC, UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA BERKELEY The purpose of this laboratory is to introduce and explore surface data analysis using a vector data model: TIN. We
Purpose: To explore the raster grid and vector map element concepts in GIS.
 GIS INTRODUCTION TO RASTER GRIDS AND VECTOR MAP ELEMENTS c:wou:nssi:vecrasex.wpd Purpose: To explore the raster grid and vector map element concepts in GIS. PART A. RASTER GRID NETWORKS Task A- Examine
GIS INTRODUCTION TO RASTER GRIDS AND VECTOR MAP ELEMENTS c:wou:nssi:vecrasex.wpd Purpose: To explore the raster grid and vector map element concepts in GIS. PART A. RASTER GRID NETWORKS Task A- Examine
Terrain Analysis. Using QGIS and SAGA
 Terrain Analysis Using QGIS and SAGA Tutorial ID: IGET_RS_010 This tutorial has been developed by BVIEER as part of the IGET web portal intended to provide easy access to geospatial education. This tutorial
Terrain Analysis Using QGIS and SAGA Tutorial ID: IGET_RS_010 This tutorial has been developed by BVIEER as part of the IGET web portal intended to provide easy access to geospatial education. This tutorial
DOWN PLUNGE CROSS SECTIONS
 GG303 Lab 7 10/6/10 1 DOWN PLUNGE CROSS SECTIONS I Main Topics A Cylindrical folds B Downplunge cross-section views C Apparent dip II Cylindrical folds A Surface of a cylindrical fold is parallel to a
GG303 Lab 7 10/6/10 1 DOWN PLUNGE CROSS SECTIONS I Main Topics A Cylindrical folds B Downplunge cross-section views C Apparent dip II Cylindrical folds A Surface of a cylindrical fold is parallel to a
AUTOMATIC EXTRACTION OF TERRAIN SKELETON LINES FROM DIGITAL ELEVATION MODELS
 AUTOMATIC EXTRACTION OF TERRAIN SKELETON LINES FROM DIGITAL ELEVATION MODELS F. Gülgen, T. Gökgöz Yildiz Technical University, Department of Geodetic and Photogrammetric Engineering, 34349 Besiktas Istanbul,
AUTOMATIC EXTRACTION OF TERRAIN SKELETON LINES FROM DIGITAL ELEVATION MODELS F. Gülgen, T. Gökgöz Yildiz Technical University, Department of Geodetic and Photogrammetric Engineering, 34349 Besiktas Istanbul,
Geological mapping using open
 Geological mapping using open source QGIS MOHSEN ALSHAGHDARI -2017- Abstract Geological mapping is very important to display your field work in a map for geologist and others, many geologists face problems
Geological mapping using open source QGIS MOHSEN ALSHAGHDARI -2017- Abstract Geological mapping is very important to display your field work in a map for geologist and others, many geologists face problems
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Introduction to 3D Data: Modeling with ArcGIS 3D Analyst and Google Earth CHAPTER 1
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction to 3D Data: Modeling with ArcGIS 3D Analyst and Google Earth Introduction to 3D Data is a self - study tutorial workbook that teaches you how to create data and maps with ESRI s
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to 3D Data: Modeling with ArcGIS 3D Analyst and Google Earth Introduction to 3D Data is a self - study tutorial workbook that teaches you how to create data and maps with ESRI s
I CALCULATIONS WITHIN AN ATTRIBUTE TABLE
 Geology & Geophysics REU GPS/GIS 1-day workshop handout #4: Working with data in ArcGIS You will create a raster DEM by interpolating contour data, create a shaded relief image, and pull data out of the
Geology & Geophysics REU GPS/GIS 1-day workshop handout #4: Working with data in ArcGIS You will create a raster DEM by interpolating contour data, create a shaded relief image, and pull data out of the
N.J.P.L.S. An Introduction to LiDAR Concepts and Applications
 N.J.P.L.S. An Introduction to LiDAR Concepts and Applications Presentation Outline LIDAR Data Capture Advantages of Lidar Technology Basics Intensity and Multiple Returns Lidar Accuracy Airborne Laser
N.J.P.L.S. An Introduction to LiDAR Concepts and Applications Presentation Outline LIDAR Data Capture Advantages of Lidar Technology Basics Intensity and Multiple Returns Lidar Accuracy Airborne Laser
WHERE THEORY MEETS PRACTICE
 world from others, leica geosystems WHERE THEORY MEETS PRACTICE A NEW BULLETIN COLUMN BY CHARLES GHILANI ON PRACTICAL ASPECTS OF SURVEYING WITH A THEORETICAL SLANT february 2012 ² ACSM BULLETIN ² 27 USGS
world from others, leica geosystems WHERE THEORY MEETS PRACTICE A NEW BULLETIN COLUMN BY CHARLES GHILANI ON PRACTICAL ASPECTS OF SURVEYING WITH A THEORETICAL SLANT february 2012 ² ACSM BULLETIN ² 27 USGS
Import, view, edit, convert, and digitize triangulated irregular networks
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Import, view, edit, convert, and digitize triangulated irregular networks Objectives Import survey data in an XYZ format. Digitize elevation points using contour imagery. Edit
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Import, view, edit, convert, and digitize triangulated irregular networks Objectives Import survey data in an XYZ format. Digitize elevation points using contour imagery. Edit
I. An Intro to ArcMap Version 9.3 and 10. 1) Arc Map is basically a build your own Google map
 I. An Intro to ArcMap Version 9.3 and 10 What is Arc Map? 1) Arc Map is basically a build your own Google map a. Display and manage geo-spatial data (maps, images, points that have a geographic location)
I. An Intro to ArcMap Version 9.3 and 10 What is Arc Map? 1) Arc Map is basically a build your own Google map a. Display and manage geo-spatial data (maps, images, points that have a geographic location)
COMPARISON OF TWO METHODS FOR DERIVING SKELETON LINES OF TERRAIN
 COMPARISON OF TWO METHODS FOR DERIVING SKELETON LINES OF TERRAIN T. Gökgöz, F. Gülgen Yildiz Technical University, Dept. of Geodesy and Photogrammetry Engineering, 34349 Besiktas Istanbul, Turkey (gokgoz,
COMPARISON OF TWO METHODS FOR DERIVING SKELETON LINES OF TERRAIN T. Gökgöz, F. Gülgen Yildiz Technical University, Dept. of Geodesy and Photogrammetry Engineering, 34349 Besiktas Istanbul, Turkey (gokgoz,
Geographic Surfaces. David Tenenbaum EEOS 383 UMass Boston
 Geographic Surfaces Up to this point, we have talked about spatial data models that operate in two dimensions How about the rd dimension? Surface the continuous variation in space of a third dimension
Geographic Surfaces Up to this point, we have talked about spatial data models that operate in two dimensions How about the rd dimension? Surface the continuous variation in space of a third dimension
A Google Earth User Manual for Earth Science Teachers
 A Google Earth User Manual for Earth Science Teachers Eric J. Fermann Eastchester High School Eric J. Fermann, 2006 TABLE OF CONTENTS Table of Contents... 1 Introduction... 2 Getting and Installing Google
A Google Earth User Manual for Earth Science Teachers Eric J. Fermann Eastchester High School Eric J. Fermann, 2006 TABLE OF CONTENTS Table of Contents... 1 Introduction... 2 Getting and Installing Google
Class #2. Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures
 Class #2 Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures Role of a Data Model Levels of Data Model Abstraction GIS as Digital
Class #2 Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures Role of a Data Model Levels of Data Model Abstraction GIS as Digital
Digital Elevation Models (DEMs)
 Digital Elevation Models (DEM) - Terrain Models (DTM) How has relief depiction on maps and online changed with digital mapping/ GIS?.. Perhaps more than the other map elements / layers Digital Elevation
Digital Elevation Models (DEM) - Terrain Models (DTM) How has relief depiction on maps and online changed with digital mapping/ GIS?.. Perhaps more than the other map elements / layers Digital Elevation
Lab 7: Bedrock rivers and the relief structure of mountain ranges
 Lab 7: Bedrock rivers and the relief structure of mountain ranges Objectives In this lab, you will analyze the relief structure of the San Gabriel Mountains in southern California and how it relates to
Lab 7: Bedrock rivers and the relief structure of mountain ranges Objectives In this lab, you will analyze the relief structure of the San Gabriel Mountains in southern California and how it relates to
DATA MODELS IN GIS. Prachi Misra Sahoo I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi
 DATA MODELS IN GIS Prachi Misra Sahoo I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi -110012 1. Introduction GIS depicts the real world through models involving geometry, attributes, relations, and data quality. Here the realization
DATA MODELS IN GIS Prachi Misra Sahoo I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi -110012 1. Introduction GIS depicts the real world through models involving geometry, attributes, relations, and data quality. Here the realization
GEO/GY461 Applied GIS: Environmental Geology of the Cheaha Mountain, AL, 7.5' Quadrangle Project
 Figure 1: Reference points spreadsheet for Cheaha Mt. 7.5' quadrangle (LatLongCalc_24k.xls). Page -1- Figure 2: RMS statistic from the Cheaha Mountain field map georeference. Page -2- Figure 3: Appearance
Figure 1: Reference points spreadsheet for Cheaha Mt. 7.5' quadrangle (LatLongCalc_24k.xls). Page -1- Figure 2: RMS statistic from the Cheaha Mountain field map georeference. Page -2- Figure 3: Appearance
Digital Elevation Models (DEM)
 Digital Elevation Models (DEM) Digital representation of the terrain surface also referred to as Digital Terrain Models (DTM) Digital Elevation Models (DEM) How has relief depiction changed with digital
Digital Elevation Models (DEM) Digital representation of the terrain surface also referred to as Digital Terrain Models (DTM) Digital Elevation Models (DEM) How has relief depiction changed with digital
Tutorial 1: Downloading elevation data
 Tutorial 1: Downloading elevation data Objectives In this exercise you will learn how to acquire elevation data from the website OpenTopography.org, project the dataset into a UTM coordinate system, and
Tutorial 1: Downloading elevation data Objectives In this exercise you will learn how to acquire elevation data from the website OpenTopography.org, project the dataset into a UTM coordinate system, and
Data Visualization Techniques with Google Earth
 Data Visualization Techniques with Google Earth E-Learning for the GIS Professional Any Time, Any Place! geospatialtraining.com Course Outline Module 1: Google Earth Pro Fundamentals Module 2: Adding Features
Data Visualization Techniques with Google Earth E-Learning for the GIS Professional Any Time, Any Place! geospatialtraining.com Course Outline Module 1: Google Earth Pro Fundamentals Module 2: Adding Features
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 25: 3D Analyst
 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 25: 3D Analyst 3D Analyst - 3D Analyst is an ArcGIS extension designed to work with TIN data (triangulated irregular network) - many of the tools in 3D Analyst also
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 25: 3D Analyst 3D Analyst - 3D Analyst is an ArcGIS extension designed to work with TIN data (triangulated irregular network) - many of the tools in 3D Analyst also
The 3D Analyst extension extends ArcGIS to support surface modeling and 3- dimensional visualization. 3D Shape Files
 NRM 435 Spring 2016 ArcGIS 3D Analyst Page#1 of 9 0B3D Analyst Extension The 3D Analyst extension extends ArcGIS to support surface modeling and 3- dimensional visualization. 3D Shape Files Analogous to
NRM 435 Spring 2016 ArcGIS 3D Analyst Page#1 of 9 0B3D Analyst Extension The 3D Analyst extension extends ArcGIS to support surface modeling and 3- dimensional visualization. 3D Shape Files Analogous to
Analyzing Terrain and Surfaces
 T E R R A I N Tutorial Analyzing Terrain and Surfaces A N A L Y S I S Analyzing Terrain and Surfaces with TNTmips page 1 Before Getting Started Topography profoundly influences many physical and biological
T E R R A I N Tutorial Analyzing Terrain and Surfaces A N A L Y S I S Analyzing Terrain and Surfaces with TNTmips page 1 Before Getting Started Topography profoundly influences many physical and biological
v Introduction to WMS WMS 11.0 Tutorial Become familiar with the WMS interface Prerequisite Tutorials None Required Components Data Map
 s v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Become familiar with the WMS interface Objectives Import files into WMS and change modules and display options to become familiar with the WMS interface. Prerequisite Tutorials
s v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Become familiar with the WMS interface Objectives Import files into WMS and change modules and display options to become familiar with the WMS interface. Prerequisite Tutorials
Digital Elevation Models
 Digital Elevation Models National Elevation Dataset 1 Data Sets US DEM series 7.5, 30, 1 o for conterminous US 7.5, 15 for Alaska US National Elevation Data (NED) GTOPO30 Global Land One-kilometer Base
Digital Elevation Models National Elevation Dataset 1 Data Sets US DEM series 7.5, 30, 1 o for conterminous US 7.5, 15 for Alaska US National Elevation Data (NED) GTOPO30 Global Land One-kilometer Base
Lecture 06. Raster and Vector Data Models. Part (1) Common Data Models. Raster. Vector. Points. Points. ( x,y ) Area. Area Line.
 Lecture 06 Raster and Vector Data Models Part (1) 1 Common Data Models Vector Raster Y Points Points ( x,y ) Line Area Line Area 2 X 1 3 Raster uses a grid cell structure Vector is more like a drawn map
Lecture 06 Raster and Vector Data Models Part (1) 1 Common Data Models Vector Raster Y Points Points ( x,y ) Line Area Line Area 2 X 1 3 Raster uses a grid cell structure Vector is more like a drawn map
Follow-Up on the Nueces River Groundwater Problem Uvalde Co. TX
 Follow-Up on the Nueces River Groundwater Problem Uvalde Co. TX Analysis by Ryan Kraft 12/4/2014 1 Problem Formulation A reduction in discharge was detected at a gauging station along a portion of the
Follow-Up on the Nueces River Groundwater Problem Uvalde Co. TX Analysis by Ryan Kraft 12/4/2014 1 Problem Formulation A reduction in discharge was detected at a gauging station along a portion of the
Converting AutoCAD Map 2002 Projects to ArcGIS
 Introduction This document outlines the procedures necessary for converting an AutoCAD Map drawing containing topologies to ArcGIS version 9.x and higher. This includes the export of polygon and network
Introduction This document outlines the procedures necessary for converting an AutoCAD Map drawing containing topologies to ArcGIS version 9.x and higher. This includes the export of polygon and network
Using Google Earth Pro
 Using Google Earth Pro (v7.3.2) University of Toronto Mississauga Library Hazel McCallion Academic Learning Centre October 2018 FURTHER ASSISTANCE If you have questions or need assistance contact Tanya
Using Google Earth Pro (v7.3.2) University of Toronto Mississauga Library Hazel McCallion Academic Learning Centre October 2018 FURTHER ASSISTANCE If you have questions or need assistance contact Tanya
Lab 1: Introduction to ArcGIS
 Lab 1: Introduction to ArcGIS Objectives In this lab you will: 1) Learn the basics of the software package we will be using for the remainder of the semester, and 2) Discover the role that climate and
Lab 1: Introduction to ArcGIS Objectives In this lab you will: 1) Learn the basics of the software package we will be using for the remainder of the semester, and 2) Discover the role that climate and
Vector Data Analysis Working with Topographic Data. Vector data analysis working with topographic data.
 Vector Data Analysis Working with Topographic Data Vector data analysis working with topographic data. 1 Triangulated Irregular Network Triangulated Irregular Network 2 Triangulated Irregular Networks
Vector Data Analysis Working with Topographic Data Vector data analysis working with topographic data. 1 Triangulated Irregular Network Triangulated Irregular Network 2 Triangulated Irregular Networks
MODULE 1 BASIC LIDAR TECHNIQUES
 MODULE SCENARIO One of the first tasks a geographic information systems (GIS) department using lidar data should perform is to check the quality of the data delivered by the data provider. The department
MODULE SCENARIO One of the first tasks a geographic information systems (GIS) department using lidar data should perform is to check the quality of the data delivered by the data provider. The department
3 Dimensional modeling of shelf margin clinoforms of the southwest Karoo Basin, South Africa.
 3 Dimensional modeling of shelf margin clinoforms of the southwest Karoo Basin, South Africa. Joshua F Dixon A. Introduction The Karoo Basin of South Africa contains some of the best exposed shelf margin
3 Dimensional modeling of shelf margin clinoforms of the southwest Karoo Basin, South Africa. Joshua F Dixon A. Introduction The Karoo Basin of South Africa contains some of the best exposed shelf margin
Terrain Modeling with ArcView GIS from ArcUser magazine
 Lesson 6: DEM-Based Terrain Modeling Lesson Goal: Lean how to output a grid theme that can be used to generate a thematic two-dimensional map, compute an attractive hillshaded map, and create a contour
Lesson 6: DEM-Based Terrain Modeling Lesson Goal: Lean how to output a grid theme that can be used to generate a thematic two-dimensional map, compute an attractive hillshaded map, and create a contour
Representing Geography
 Data models and axioms Chapters 3 and 7 Representing Geography Road map Representing the real world Conceptual models: objects vs fields Implementation models: vector vs raster Vector topological model
Data models and axioms Chapters 3 and 7 Representing Geography Road map Representing the real world Conceptual models: objects vs fields Implementation models: vector vs raster Vector topological model
Lecture 7 Digitizing. Dr. Zhang Spring, 2017
 Lecture 7 Digitizing Dr. Zhang Spring, 2017 Model of the course Using and making maps Navigating GIS maps Map design Working with spatial data Geoprocessing Spatial data infrastructure Digitizing File
Lecture 7 Digitizing Dr. Zhang Spring, 2017 Model of the course Using and making maps Navigating GIS maps Map design Working with spatial data Geoprocessing Spatial data infrastructure Digitizing File
Creating advanced shadedrelief maps and layer blending with Global Mapper software
 Creating advanced shadedrelief maps and layer blending with Global Mapper software J. Buck Ehler GIS Analyst/Cartographer Utah Geological Survey buckehler@utah.gov (801) 537-3343 SLUG Meeting August 11,
Creating advanced shadedrelief maps and layer blending with Global Mapper software J. Buck Ehler GIS Analyst/Cartographer Utah Geological Survey buckehler@utah.gov (801) 537-3343 SLUG Meeting August 11,
Using Google Earth in the Classroom (Tours)
 Eric J. Fermann 2006 Eastchester High School Using Google Earth in the Classroom (Tours) Since its release in the summer of 2005, Google Earth has provided an uncomplicated means of combining satellite
Eric J. Fermann 2006 Eastchester High School Using Google Earth in the Classroom (Tours) Since its release in the summer of 2005, Google Earth has provided an uncomplicated means of combining satellite
GeoPlanes. Interactive Analysis of Virtual Geological Outcrops. Alpha Version January 2016
 GeoPlanes Interactive Analysis of Virtual Geological Outcrops Alpha Version January 2016 1. Introduction Geoplanes is an application for interactive structural interpretation and annotation of 3D texture
GeoPlanes Interactive Analysis of Virtual Geological Outcrops Alpha Version January 2016 1. Introduction Geoplanes is an application for interactive structural interpretation and annotation of 3D texture
Measure the Perimeter of Polygons Over a Surface. Operations. What Do I Need?
 Measure the Perimeter of Polygons Over a Surface Operations What Do I Need? Incremental Frontage Score To measure the perimeter of polygons over a surface you need to have two input map layers. The first
Measure the Perimeter of Polygons Over a Surface Operations What Do I Need? Incremental Frontage Score To measure the perimeter of polygons over a surface you need to have two input map layers. The first
Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis. GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University
 Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University 1 Spatial Data It can be most simply defined as information that describes the distribution
Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University 1 Spatial Data It can be most simply defined as information that describes the distribution
Learn how to delineate a watershed using the hydrologic modeling wizard
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to delineate a watershed using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives Import a digital elevation model, compute flow directions, and delineate a watershed and sub-basins
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Learn how to delineate a watershed using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives Import a digital elevation model, compute flow directions, and delineate a watershed and sub-basins
Ilham Marsudi Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta Yogyakarta, Indonesia
 1st International Conference on Technology and Vocational Teachers (ICTVT 2017) Making a Digital Contour Map Ilham Marsudi Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta Yogyakarta, Indonesia ilham@uny.ac.id Abstract---
1st International Conference on Technology and Vocational Teachers (ICTVT 2017) Making a Digital Contour Map Ilham Marsudi Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta Yogyakarta, Indonesia ilham@uny.ac.id Abstract---
GIS LAB 8. Raster Data Applications Watershed Delineation
 GIS LAB 8 Raster Data Applications Watershed Delineation This lab will require you to further your familiarity with raster data structures and the Spatial Analyst. The data for this lab are drawn from
GIS LAB 8 Raster Data Applications Watershed Delineation This lab will require you to further your familiarity with raster data structures and the Spatial Analyst. The data for this lab are drawn from
GY461 GIS 1: Environmental Campus Topography Project with ArcGIS 9.x
 I. Introduction GY461 GIS 1: Environmental In this project you will use data from a topographic survey of the USA campus to generate 2 separate maps: 1. A color-coded 2-dimensional topographic contour
I. Introduction GY461 GIS 1: Environmental In this project you will use data from a topographic survey of the USA campus to generate 2 separate maps: 1. A color-coded 2-dimensional topographic contour
Maps as Numbers: Data Models
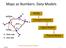 Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices E Reality S E S arcs S E Conceptual Models nodes E Logical Models S Start node E End node S Physical Models 1 The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can
Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices E Reality S E S arcs S E Conceptual Models nodes E Logical Models S Start node E End node S Physical Models 1 The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can
v TUFLOW-2D Hydrodynamics SMS Tutorials Time minutes Prerequisites Overview Tutorial
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial TUFLOW-2D Hydrodynamics Objectives This tutorial describes the generation of a TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. This project utilizes only the two dimensional flow calculation
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial TUFLOW-2D Hydrodynamics Objectives This tutorial describes the generation of a TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. This project utilizes only the two dimensional flow calculation
GIS IN ECOLOGY: VISUALIZING IN 3D
 GIS IN ECOLOGY: VISUALIZING IN 3D Contents Introduction... 2 3D Analyst and ArcScene... 2 3D Data... 2 Course Data Sources... 3 Instructions for Copying the Course Dataset... 4 Tasks... 4 Visualizing and
GIS IN ECOLOGY: VISUALIZING IN 3D Contents Introduction... 2 3D Analyst and ArcScene... 2 3D Data... 2 Course Data Sources... 3 Instructions for Copying the Course Dataset... 4 Tasks... 4 Visualizing and
1. NJDEP Landscape 3.3 Viewer Interface
 Using the Landscape Project through NJDEP Landscape 3.3 Viewer Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox are recommended for the use of this app. Navigate to the NJDEP-DFW s Landscape Project web page at www.njfishandwildlife.com/ensp/landscape/
Using the Landscape Project through NJDEP Landscape 3.3 Viewer Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox are recommended for the use of this app. Navigate to the NJDEP-DFW s Landscape Project web page at www.njfishandwildlife.com/ensp/landscape/
16) After contour layer is chosen, on column height_field, choose Elevation, and on tag_field column, choose <None>. Click OK button.
 16) After contour layer is chosen, on column height_field, choose Elevation, and on tag_field column, choose . Click OK button. 17) The process of TIN making will take some time. Various process
16) After contour layer is chosen, on column height_field, choose Elevation, and on tag_field column, choose . Click OK button. 17) The process of TIN making will take some time. Various process
Understanding Geospatial Data Models
 Understanding Geospatial Data Models 1 A geospatial data model is a formal means of representing spatially referenced information. It is a simplified view of physical entities and a conceptualization of
Understanding Geospatial Data Models 1 A geospatial data model is a formal means of representing spatially referenced information. It is a simplified view of physical entities and a conceptualization of
BASE FLOOD ELEVATION DETERMINATION MODULE
 BASE FLOOD ELEVATION DETERMINATION MODULE FEDERAL EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT AGENCY PREPARED BY: NOLTE ASSOCIATES, INC. June, 2003 ABSTRACT The FEMA Base Flood Elevation Determination Module is a Visual Basic
BASE FLOOD ELEVATION DETERMINATION MODULE FEDERAL EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT AGENCY PREPARED BY: NOLTE ASSOCIATES, INC. June, 2003 ABSTRACT The FEMA Base Flood Elevation Determination Module is a Visual Basic
Google Earth an introduction
 Luana Valentini InternetGIS course - 2011 Google Earth an introduction Google Earth combines the power of Google Search with satellite imagery, maps, terrain and 3D buildings to put the world's geographic
Luana Valentini InternetGIS course - 2011 Google Earth an introduction Google Earth combines the power of Google Search with satellite imagery, maps, terrain and 3D buildings to put the world's geographic
Accuracy: Irrigation Design Software and Google Earth
 Accuracy: Irrigation Design Software and Google Earth Ben van den Heever. B Ing. (Civil) Abstract. In the past, an irrigation designer was reliant on the surveyors data to provide an accurate digital terrain
Accuracy: Irrigation Design Software and Google Earth Ben van den Heever. B Ing. (Civil) Abstract. In the past, an irrigation designer was reliant on the surveyors data to provide an accurate digital terrain
GEO 465/565 - Lab 7 Working with GTOPO30 Data in ArcGIS 9
 GEO 465/565 - Lab 7 Working with GTOPO30 Data in ArcGIS 9 This lab explains how work with a Global 30-Arc-Second (GTOPO30) digital elevation model (DEM) from the U.S. Geological Survey. This dataset can
GEO 465/565 - Lab 7 Working with GTOPO30 Data in ArcGIS 9 This lab explains how work with a Global 30-Arc-Second (GTOPO30) digital elevation model (DEM) from the U.S. Geological Survey. This dataset can
NEXTMap World 10 Digital Elevation Model
 NEXTMap Digital Elevation Model Intermap Technologies, Inc. 8310 South Valley Highway, Suite 400 Englewood, CO 80112 10012015 NEXTMap (top) provides an improvement in vertical accuracy and brings out greater
NEXTMap Digital Elevation Model Intermap Technologies, Inc. 8310 South Valley Highway, Suite 400 Englewood, CO 80112 10012015 NEXTMap (top) provides an improvement in vertical accuracy and brings out greater
Keywords: 3D modeling, multimedia, dynamic handling threads, OpenGL, landscape generation, detail.
 67 Combined methods for virtual surface treatment of relief Shardakov V. 1[0000-0001-6151-6236] and Parfenov D. 1[0000-0002-1146-1270] 1 Orenburg State University, Ave. Pobedy 13, Russia Abstract. This
67 Combined methods for virtual surface treatment of relief Shardakov V. 1[0000-0001-6151-6236] and Parfenov D. 1[0000-0002-1146-1270] 1 Orenburg State University, Ave. Pobedy 13, Russia Abstract. This
UNDERSTAND HOW TO SET UP AND RUN A HYDRAULIC MODEL IN HEC-RAS CREATE A FLOOD INUNDATION MAP IN ARCGIS.
 CE 412/512, Spring 2017 HW9: Introduction to HEC-RAS and Floodplain Mapping Due: end of class, print and hand in. HEC-RAS is a Hydrologic Modeling System that is designed to describe the physical properties
CE 412/512, Spring 2017 HW9: Introduction to HEC-RAS and Floodplain Mapping Due: end of class, print and hand in. HEC-RAS is a Hydrologic Modeling System that is designed to describe the physical properties
Computation of Slope
 Computation of Slope Prepared by David R. Maidment and David Tarboton GIS in Water Resources Class University of Texas at Austin September 2011, Revised December 2011 There are various ways in which slope
Computation of Slope Prepared by David R. Maidment and David Tarboton GIS in Water Resources Class University of Texas at Austin September 2011, Revised December 2011 There are various ways in which slope
Introduction to Google Earth
 Introduction to Google Earth Assignment: The goal of this assignment is for you to become familiar with Google Earth. You may work alone or with a partner but you must turn in your own individual work.
Introduction to Google Earth Assignment: The goal of this assignment is for you to become familiar with Google Earth. You may work alone or with a partner but you must turn in your own individual work.
Review of Cartographic Data Types and Data Models
 Review of Cartographic Data Types and Data Models GIS Data Models Raster Versus Vector in GIS Analysis Fundamental element used to represent spatial features: Raster: pixel or grid cell. Vector: x,y coordinate
Review of Cartographic Data Types and Data Models GIS Data Models Raster Versus Vector in GIS Analysis Fundamental element used to represent spatial features: Raster: pixel or grid cell. Vector: x,y coordinate
Improved Applications with SAMB Derived 3 meter DTMs
 Improved Applications with SAMB Derived 3 meter DTMs Evan J Fedorko West Virginia GIS Technical Center 20 April 2005 This report sums up the processes used to create several products from the Lorado 7
Improved Applications with SAMB Derived 3 meter DTMs Evan J Fedorko West Virginia GIS Technical Center 20 April 2005 This report sums up the processes used to create several products from the Lorado 7
Make a TOPOGRAPHIC MAP
 How can you make a topographic map, and what information can you get from it? Activity Overview To build the Panama Canal, engineers dammed the Chagres River. In the process, new lakes were formed, a valley
How can you make a topographic map, and what information can you get from it? Activity Overview To build the Panama Canal, engineers dammed the Chagres River. In the process, new lakes were formed, a valley
Objectives for Terrain Week
 The Terrain Correction Chuck Connor, Laura Connor Potential Fields Geophysics: Terrain Week for Terrain Week Learn about the terrain correction The inner terrain correction Learn about The outer terrain
The Terrain Correction Chuck Connor, Laura Connor Potential Fields Geophysics: Terrain Week for Terrain Week Learn about the terrain correction The inner terrain correction Learn about The outer terrain
SPATIAL DATA MODELS Introduction to GIS Winter 2015
 SPATIAL DATA MODELS Introduction to GIS Winter 2015 GIS Data Organization The basics Data can be organized in a variety of ways Spatial location, content (attributes), frequency of use Come up with a system
SPATIAL DATA MODELS Introduction to GIS Winter 2015 GIS Data Organization The basics Data can be organized in a variety of ways Spatial location, content (attributes), frequency of use Come up with a system
GIS IN ECOLOGY: VISUALIZING IN 3D
 GIS IN ECOLOGY: VISUALIZING IN 3D Contents Introduction... 2 3D Analyst and ArcScene... 2 3D Data... 3 Course Data Sources... 4 Copying the Course Dataset... 5 Tasks... 5 Creating/Converting 3D Data...
GIS IN ECOLOGY: VISUALIZING IN 3D Contents Introduction... 2 3D Analyst and ArcScene... 2 3D Data... 3 Course Data Sources... 4 Copying the Course Dataset... 5 Tasks... 5 Creating/Converting 3D Data...
Surface Analysis. Data for Surface Analysis. What are Surfaces 4/22/2010
 Surface Analysis Cornell University Data for Surface Analysis Vector Triangulated Irregular Networks (TIN) a surface layer where space is partitioned into a set of non-overlapping triangles Attribute and
Surface Analysis Cornell University Data for Surface Analysis Vector Triangulated Irregular Networks (TIN) a surface layer where space is partitioned into a set of non-overlapping triangles Attribute and
Contour Simplification with Defined Spatial Accuracy
 Contour Simplification with Defined Spatial Accuracy Bulent Cetinkaya, Serdar Aslan, Yavuz Selim Sengun, O. Nuri Cobankaya, Dursun Er Ilgin General Command of Mapping, 06100 Cebeci, Ankara, Turkey bulent.cetinkaya@hgk.mil.tr
Contour Simplification with Defined Spatial Accuracy Bulent Cetinkaya, Serdar Aslan, Yavuz Selim Sengun, O. Nuri Cobankaya, Dursun Er Ilgin General Command of Mapping, 06100 Cebeci, Ankara, Turkey bulent.cetinkaya@hgk.mil.tr
GIS Data Collection. This chapter reviews the main methods of GIS data capture and transfer and introduces key practical management issues.
 9 GIS Data Collection OVERVIEW This chapter reviews the main methods of GIS data capture and transfer and introduces key practical management issues. It distinguishes between primary (direct measurement)
9 GIS Data Collection OVERVIEW This chapter reviews the main methods of GIS data capture and transfer and introduces key practical management issues. It distinguishes between primary (direct measurement)
Mapping Photoperiod as a Variable in Vegetation Distribution Analysis. Photoperiod is defined as the duration of time for which an organism receives
 Paul Southard December 7 th, 2017 Mapping Photoperiod as a Variable in Vegetation Distribution Analysis Introduction Photoperiod is defined as the duration of time for which an organism receives illumination.
Paul Southard December 7 th, 2017 Mapping Photoperiod as a Variable in Vegetation Distribution Analysis Introduction Photoperiod is defined as the duration of time for which an organism receives illumination.
Geomorphology Lab 6: GPS Surveying
 Introduction In this lab you will use hand-held GPS receiver units to map a running trail on campus. In addition, you will take waypoints for the benchmarks used for the Total Station project. You will
Introduction In this lab you will use hand-held GPS receiver units to map a running trail on campus. In addition, you will take waypoints for the benchmarks used for the Total Station project. You will
Statistical surfaces and interpolation. This is lecture ten
 Statistical surfaces and interpolation This is lecture ten Data models for representation of surfaces So far have considered field and object data models (represented by raster and vector data structures).
Statistical surfaces and interpolation This is lecture ten Data models for representation of surfaces So far have considered field and object data models (represented by raster and vector data structures).
Lab 18c: Spatial Analysis III: Clip a raster file using a Polygon Shapefile
 Environmental GIS Prepared by Dr. Zhi Wang, CSUF EES Department Lab 18c: Spatial Analysis III: Clip a raster file using a Polygon Shapefile These instructions enable you to clip a raster layer in ArcMap
Environmental GIS Prepared by Dr. Zhi Wang, CSUF EES Department Lab 18c: Spatial Analysis III: Clip a raster file using a Polygon Shapefile These instructions enable you to clip a raster layer in ArcMap
The Extraction of Lineaments Using Slope Image Derived from Digital Elevation Model: Case Study of Sungai Lembing Maran area, Malaysia.
 Journal of Applied Sciences Research, 6(11): 1745-1751, 2010 2010, INSInet Publication The Extraction of Lineaments Using Slope Image Derived from Digital Elevation Model: Case Study of Sungai Lembing
Journal of Applied Sciences Research, 6(11): 1745-1751, 2010 2010, INSInet Publication The Extraction of Lineaments Using Slope Image Derived from Digital Elevation Model: Case Study of Sungai Lembing
Report: Comparison of Methods to Produce Digital Terrain Models
 Report: Comparison of Methods to Produce Digital Terrain Models Evan J Fedorko West Virginia GIS Technical Center 27 April 2005 Introduction This report compares Digital Terrain Models (DTM) created through
Report: Comparison of Methods to Produce Digital Terrain Models Evan J Fedorko West Virginia GIS Technical Center 27 April 2005 Introduction This report compares Digital Terrain Models (DTM) created through
Chapter 3: Maps as Numbers
 Chapter 3: Maps as Numbers 3. Representing Maps as Numbers 3.2 Structuring Attributes 3.3 Structuring Maps 3.4 Why Topology Matters 3.5 Formats for GIS Data 3.6 Exchanging Data David Tenenbaum EEOS 265
Chapter 3: Maps as Numbers 3. Representing Maps as Numbers 3.2 Structuring Attributes 3.3 Structuring Maps 3.4 Why Topology Matters 3.5 Formats for GIS Data 3.6 Exchanging Data David Tenenbaum EEOS 265
Creating an Event Theme from X, Y Data
 Creating an Event Theme from X, Y Data In Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) Coordinates Eastings (measured in meters) typically have 6 digits left of the decimal. Northings (also in meters) typically
Creating an Event Theme from X, Y Data In Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) Coordinates Eastings (measured in meters) typically have 6 digits left of the decimal. Northings (also in meters) typically
MARS v Release Notes Revised: May 23, 2018 (Builds and )
 MARS v2018.0 Release Notes Revised: May 23, 2018 (Builds 8302.01 8302.18 and 8350.00 8352.00) Contents New Features:... 2 Enhancements:... 6 List of Bug Fixes... 13 1 New Features: LAS Up-Conversion prompts
MARS v2018.0 Release Notes Revised: May 23, 2018 (Builds 8302.01 8302.18 and 8350.00 8352.00) Contents New Features:... 2 Enhancements:... 6 List of Bug Fixes... 13 1 New Features: LAS Up-Conversion prompts
TcpMDT Version 7.0 Summary of Differences with Version 6.5
 Sumatra, 9 E-29190 Málaga (Spain) www.aplitop.com Tel.: +34 95 2439771 Fax: +34 95 2431371 TcpMDT Version 7.0 Summary of Differences with Version 6.5 CAD Versions supported TcpMDT 7 works with several
Sumatra, 9 E-29190 Málaga (Spain) www.aplitop.com Tel.: +34 95 2439771 Fax: +34 95 2431371 TcpMDT Version 7.0 Summary of Differences with Version 6.5 CAD Versions supported TcpMDT 7 works with several
GIS Visualization, 3D Visualization and Animation. Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University
 GIS Visualization, 3D Visualization and Animation Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Definitions 3D Visualization: Presenting or observing spatial,
GIS Visualization, 3D Visualization and Animation Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Definitions 3D Visualization: Presenting or observing spatial,
A Method to Create a Single Photon LiDAR based Hydro-flattened DEM
 A Method to Create a Single Photon LiDAR based Hydro-flattened DEM Sagar Deshpande 1 and Alper Yilmaz 2 1 Surveying Engineering, Ferris State University 2 Department of Civil, Environmental, and Geodetic
A Method to Create a Single Photon LiDAR based Hydro-flattened DEM Sagar Deshpande 1 and Alper Yilmaz 2 1 Surveying Engineering, Ferris State University 2 Department of Civil, Environmental, and Geodetic
I.1. Digitize landslide region and micro-topography using satellite image
 I. Data Preparation At this part, it will be shown the stages of process on preparing all types of data which required in making of landslide potential and banjir bandang hazard map. I.1. Digitize landslide
I. Data Preparation At this part, it will be shown the stages of process on preparing all types of data which required in making of landslide potential and banjir bandang hazard map. I.1. Digitize landslide
ENVI Classic Tutorial: 3D SurfaceView and Fly- Through
 ENVI Classic Tutorial: 3D SurfaceView and Fly- Through 3D SurfaceView and Fly-Through 2 Files Used in this Tutorial 2 3D Visualization in ENVI Classic 2 Load a 3D SurfaceView 3 Open and Display Landsat
ENVI Classic Tutorial: 3D SurfaceView and Fly- Through 3D SurfaceView and Fly-Through 2 Files Used in this Tutorial 2 3D Visualization in ENVI Classic 2 Load a 3D SurfaceView 3 Open and Display Landsat
WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA WMS Basics Watershed Delineation using DEMs and 2D Grid Generation Delineate a watershed and create a GSSHA model from a DEM
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA WMS Basics Watershed Delineation using DEMs and 2D Grid Generation Delineate a watershed and create a GSSHA model from a DEM Objectives Learn how to delineate a watershed
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA WMS Basics Watershed Delineation using DEMs and 2D Grid Generation Delineate a watershed and create a GSSHA model from a DEM Objectives Learn how to delineate a watershed
Displaying Strike and Dip Measurements on Your Map in Surfer
 Displaying Strike and Dip Measurements on Your Map in Surfer Measuring strike and dip is a fundamental part of geological mapping, and displaying strike and dip information on a map is an effective way
Displaying Strike and Dip Measurements on Your Map in Surfer Measuring strike and dip is a fundamental part of geological mapping, and displaying strike and dip information on a map is an effective way
