Circuits. L3: Fabrication and Layout -1 ( ) B. Mazhari Dept. of EE, IIT Kanpur. B. Mazhari, IITK. G-Number
|
|
|
- Russell Jordan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EE60: CMOS Analog Circuits L: Fabrication and Layout - (8.8.0) B. Mazhari Dept. of EE, IIT Kanpur
2 Suppose we have a Silicon wafer which is P-type and we wish to create a region within it which is N-type as shown below: N + P-Silicon This can be done by carrying out diffusion/implantation of N-type dopant in the structure shown below. SiO The SiO acts a as a barrier P-Silicon and prevents diffusion of dopants through it. As a result the N-type region is created only in the region where Silicon is exposed
3 A window in SiO can be created by first covering the whole Silicon surface with oxide through the oxidation process. Next the Silicon surface is coated with an organic material which is sensitive to light called Photoresist. A positive photoresist undergoes changes upon exposure which makes it easier to dissolve in a developer solution We next need a Mask which specifies the location and dimension of N- region. It is basically a glass plate which has opaque and transparent regions. Wherever we want the photoresist to remain, that region is opaque and wherever we wish to remove the photoresist that region is made transparent. Light Mask P-Silicon The mask is placed either in contact or in close proximity to the resist coated Silicon wafer and exposed to light as illustrated below
4 After this step of Photolithography, the exposed photoresist is removed using a developer solution and we obtain the following structure: Photoresist P-Silicon SiO Next the whole wafer is dipped in HF acid to Etch the exposed oxide to obtain the following structure: Photoresist P-Silicon SiO SiO Next the photoresist is removed to obtain the structure required for carrying out diffusion. P-Silicon
5 Fabrication: simplified view SiO SiO Poly Poly P + N + N + N + P + P + N-well P-Silicon P-Silicon Transfer of pattern from mask to photoresist ----photolithography Transfer of pattern from photoresist to silicon Various processing steps.
6 S D D S B Active area Active area 6
7 The fabrication process begins with a Silicon substrate P-epilayer N A ~0 cm - Substrate thickness ~ 77µm for a 00mm wafer size Substrate - P-type 7
8 . AP-type Transistor requires creation of an N-well well. N-Well N-Well. Active areas are defined: Active Mask N-Well A A N A A 8
9 . Poly-Silicon Gate Definition Poly Mask N-Well. N diffusion - P-Select Mask N-Well 9
10 . P diffusion - N-Select Mask N-Well 6. Contacts : Contact cut Mask N-Well 0
11 7. Metal - Mask N-Well 8. Via Mask 9. Metal - Mask
12 Multi layers of Metal
13 Physicaly Design requires generation of geometrical Drawings for each one of the masks Design Rules are constraints that the design must obey in order to guarantee that the circuit can be fabricated without errors and with reasonable yield. These rules come about through interaction of electrical and reliability constraints with the capabilities of the fabrication technology.
14 Design Rules Design rules are specified as a set of layers and rules for patterns within layers (intra layer) and between objects on different layers. Some basic rules for a scalable SCMOS process are given below in terms of the parameter The minimum feature size is λ, so that if a technology is specified as m process, it implies thatt λ= 0. m.
15 Design Rules Same Potential Different Potential 9 0 Well or Polysilicon 6 0 Active Metal Contact or Via Hole Select
16 Design Rules o r s t n i a Tr rr ar r 6
17 Design Rules Via Metal to Metal to Poly Contact Active Contact 7
18 Design Rules Select Substrate Well 8
19 Example : spacing between diffusion wires has to be larger than a certain minimum value. Fabrication process is not perfect. -imperfections in Masking step, resist removal, oxide etching and diffusion cause the wire dimensions to from what they are specified on the mask. P-type 9
20 Design Rules : Origin N + N + P 0
21 CMOS Inverter/Amplifier : Layout V DD V DD V Bias V IN V OUT V OUT V IN GND GND CS amplifier with active PMOS Load relative placement and orientation of the transistors choice of interconnect and routing
22 CMOS Inverter : Layout. Make the NMOS D S. Make the contact between ground and source of NMOS GND
23 . Make the substrate contact for the NMOS GND
24 . The drain of NMOS has to be connected to drain of PMOS. SO we need a metal contact to the drain GND
25 . Next the PMOS transistor has to be drawn. The PMOS is fabricated in an N-well. The design rules dictate that the well boundary be away from all active regions by at least N-well Edge GND
26 6. P-type Tr. With Contacts VDD VDD 6 N-well Edge GND 6
27 7. Substrate contact is added VDD VDD 6 N-well Edge GND 7
28 8. Gates are connected VDD VDD 6 N-well Edge V IN V OUT V IN VOUT GND 8
29 Layout Analysis Area : x = 67. VDD Aspect ratio = Height / Width / NMOS: Drain Area = 9 ; Perimeter = PMOS: Drain Area = 0 ; V IN Perimeter = 6 6 N-well Edge V OUT poly area over field oxide ~ 80. Metal- area and perimeter at the output ~60, 6 GND 9
30 Capacitances : 0. µm technology VDD C OX (ff/ m ) C poly (ff/ m ) C M (ff/ m ) C 6 M (ff/ m) N-well Edge V IN V OUT -poly capacitance ~0.6fF -metal- capacitance ~0.fF (fringe component is x ) GND 0
31 Inverter : Net capacitance VDD VDD 6 6 C T N-well Edge N-well Edge C ( C C ) T gsn gdn V IN V V IN OUT V OUT ( C C ) gsp gdp ( C C ) dbn dbp GND GND C poly C metal C T ~.ff; ff; ffdue.ff to parasitic poly & M- capacitances delay about 9% higher with parasitic capacitances
32 Effect of Wire 00 m m The capacitance due to the metal interconnect is.ff, 7% of which is due to the fringe component. The wire capacitance is x.76 as large as the gate capacitance of inverter-! The wire capacitance is 7. x as large as the gate capacitance of inverter-! for 0.8µm technology Wire capacitance is the most significant capacitance sub-micron technologies. for deep
33 Identify the layout VDD GND GND M M V DD
34 Why multiple contacts to the source?
35 Design Rules : Design Reuse -rules are a simplified representation that have some advantages as well as disadvantages. Rules are easy to understand and remember making the design easier and less prone to error. Use of rules gives a design representation which is independent of technology.
36 Design reuse : Technology independent representation Technology is changing rapidly and circuit complexity is continuously increasing One of the ways of coping with this increased circuit complexity in an almost fixed design time is to employ the technique of Design Reuse A technology independent representation which can be easily technology-mapped or made technology specific facilitates design reuse. 6
37 Design reuse : Technology independent representation Specs. Specs. Design at higher abstraction level Tech. Info Design Design Intermediate Design (Tech. Ind.) Tech. Info Tech. Mapping Final Design 7
38 Design reuse : Technology independent representation Although rules make tech. mapping easy, they result in inferior design rules represent worst-case rules Technology Min. Min. Min. Feature size Feature size Feature size L L L m m 0 m m 0. m 0. m m m 8
39 Technology Min. Feature Min. Feature Min. Feature size L size L size L m m 0 m m 0. m 0. m m m Technology Min. Feature size L Min. Feature size L Min. Feature size L m 0. m m 0. m 8 9
40 Design reuse : Technology independent representation Technology Min. Feature Min. Feature Min. Feature size L size L size L m 0. m m 0. m 8 Common Design Rules : L : L : 0 L : 8 Rules very conservative Benefits of scaling to some extent lost 0
41 Need a better representation that can take full advantage of design rules Since rules pertain to actual widths, separations etc, the new representation would need to have no size or dimensional information. In other words, the layout representation would be a symbolic layout which includes all design information except for the dimensions. Stick Layout
42 Stick Layout VDD V DD X N-well Edge 6 i/p X X O/P X V IN V OUT X GND GND
43 Stick Layout: CMOS Inverter V DD X V DD V IN V OUT i/p X X X O/P GND X GND X V DD X X i/p X O/P X X X GND
FABRICATION OF CMOS INTEGRATED CIRCUITS. Dr. Mohammed M. Farag
 FABRICATION OF CMOS INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Dr. Mohammed M. Farag Outline Overview of CMOS Fabrication Processes The CMOS Fabrication Process Flow Design Rules EE 432 VLSI Modeling and Design 2 CMOS Fabrication
FABRICATION OF CMOS INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Dr. Mohammed M. Farag Outline Overview of CMOS Fabrication Processes The CMOS Fabrication Process Flow Design Rules EE 432 VLSI Modeling and Design 2 CMOS Fabrication
Composite Layout CS/EE N-type from the top. N-type Transistor. Diffusion Mask. Polysilicon Mask
 Composite Layout CS/EE 6710 Introduction to Layout Inverter Layout Example Layout Design Rules Drawing the mask layers that will be used by the fabrication folks to make the devices Very different from
Composite Layout CS/EE 6710 Introduction to Layout Inverter Layout Example Layout Design Rules Drawing the mask layers that will be used by the fabrication folks to make the devices Very different from
Digital Integrated CircuitDesign
 Digital Integrated CircuitDesign Lecture 8 Design Rules Adib Abrishamifar EE Department IUST Contents Design Rules CMOS Process Layers Intra-Layer Design Rules Via s and Contacts Select Layer Example Cell
Digital Integrated CircuitDesign Lecture 8 Design Rules Adib Abrishamifar EE Department IUST Contents Design Rules CMOS Process Layers Intra-Layer Design Rules Via s and Contacts Select Layer Example Cell
Lay ay ut Design g R ules
 HPTER 5: Layout esign Rules Introduction ny circuit physical mask layout must conform to a set of geometric constraints or rules called as Layout esign rules before it can be manufactured using particular
HPTER 5: Layout esign Rules Introduction ny circuit physical mask layout must conform to a set of geometric constraints or rules called as Layout esign rules before it can be manufactured using particular
TUTORIAL II ECE 555 / 755 Updated on September 11 th 2006 CADENCE LAYOUT AND PARASITIC EXTRACTION
 TUTORIAL II ECE 555 / 755 Updated on September 11 th 2006 CADENCE LAYOUT AND PARASITIC EXTRACTION After finishing a schematic of your design (Tutorial-I), the next step is creating masks which are for
TUTORIAL II ECE 555 / 755 Updated on September 11 th 2006 CADENCE LAYOUT AND PARASITIC EXTRACTION After finishing a schematic of your design (Tutorial-I), the next step is creating masks which are for
Lecture 4a. CMOS Fabrication, Layout and Simulation. R. Saleh Dept. of ECE University of British Columbia
 Lecture 4a CMOS Fabrication, Layout and Simulation R. Saleh Dept. of ECE University of British Columbia res@ece.ubc.ca 1 Fabrication Fabrication is the process used to create devices and wires. Transistors
Lecture 4a CMOS Fabrication, Layout and Simulation R. Saleh Dept. of ECE University of British Columbia res@ece.ubc.ca 1 Fabrication Fabrication is the process used to create devices and wires. Transistors
EE582 Physical Design Automation of VLSI Circuits and Systems
 EE582 Prof. Dae Hyun Kim School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Washington State University Preliminaries Table of Contents Semiconductor manufacturing Problems to solve Algorithm complexity
EE582 Prof. Dae Hyun Kim School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Washington State University Preliminaries Table of Contents Semiconductor manufacturing Problems to solve Algorithm complexity
VBIT COURSE MATERIAL VLSI DESIGN
 UNIT II VLSI CIRCUIT DESIGN PROCESSES: VLSI Design Flow, MOS Layers, Stick Diagrams, Design Rules and Layout, 2μm CMOS Design rules for wires, Contacts and Transistors Layout Diagrams for NMOS and CMOS
UNIT II VLSI CIRCUIT DESIGN PROCESSES: VLSI Design Flow, MOS Layers, Stick Diagrams, Design Rules and Layout, 2μm CMOS Design rules for wires, Contacts and Transistors Layout Diagrams for NMOS and CMOS
CMOS Process Flow. Layout CAD Tools
 CMOS Process Flow See supplementary power point file for animated CMOS process flow (see class ece410 website and/or* http://www.multimedia.vt.edu/ee5545/): This file should be viewed as a slide show It
CMOS Process Flow See supplementary power point file for animated CMOS process flow (see class ece410 website and/or* http://www.multimedia.vt.edu/ee5545/): This file should be viewed as a slide show It
Digital Integrated Circuits (83-313) Lecture 2: Technology and Standard Cell Layout
 Digital Integrated Circuits (83-313) Lecture 2: Technology and Standard Cell Layout Semester B, 2016-17 Lecturer: Dr. Adam Teman TAs: Itamar Levi, Robert Giterman 26 March 2017 Disclaimer: This course
Digital Integrated Circuits (83-313) Lecture 2: Technology and Standard Cell Layout Semester B, 2016-17 Lecturer: Dr. Adam Teman TAs: Itamar Levi, Robert Giterman 26 March 2017 Disclaimer: This course
ESE 570 Cadence Lab Assignment 2: Introduction to Spectre, Manual Layout Drawing and Post Layout Simulation (PLS)
 ESE 570 Cadence Lab Assignment 2: Introduction to Spectre, Manual Layout Drawing and Post Layout Simulation (PLS) Objective Part A: To become acquainted with Spectre (or HSpice) by simulating an inverter,
ESE 570 Cadence Lab Assignment 2: Introduction to Spectre, Manual Layout Drawing and Post Layout Simulation (PLS) Objective Part A: To become acquainted with Spectre (or HSpice) by simulating an inverter,
Integrated Circuits & Systems
 Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 23-1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br Semiconductor Memory Classification
Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 23-1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br Semiconductor Memory Classification
CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #1, Full Custom VLSI (inverter layout)
 CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #1, Full Custom VLSI (inverter layout) Joel Wilder, Aleksandar Milenkovic, ECE Dept., The University of Alabama in Huntsville Adapted from Virginia Tech, Dept.
CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #1, Full Custom VLSI (inverter layout) Joel Wilder, Aleksandar Milenkovic, ECE Dept., The University of Alabama in Huntsville Adapted from Virginia Tech, Dept.
CS310 Embedded Computer Systems. Maeng
 1 INTRODUCTION (PART II) Maeng Three key embedded system technologies 2 Technology A manner of accomplishing a task, especially using technical processes, methods, or knowledge Three key technologies for
1 INTRODUCTION (PART II) Maeng Three key embedded system technologies 2 Technology A manner of accomplishing a task, especially using technical processes, methods, or knowledge Three key technologies for
Process technology and introduction to physical
 Neuromorphic Engineering II Lab 3, Spring 2014 1 Lab 3 March 10, 2014 Process technology and introduction to physical layout Today you will start to learn to use the Virtuoso layout editor XL which is
Neuromorphic Engineering II Lab 3, Spring 2014 1 Lab 3 March 10, 2014 Process technology and introduction to physical layout Today you will start to learn to use the Virtuoso layout editor XL which is
VLSI Lab Tutorial 3. Virtuoso Layout Editing Introduction
 VLSI Lab Tutorial 3 Virtuoso Layout Editing Introduction 1.0 Introduction The purpose of this lab tutorial is to guide you through the design process in creating a custom IC layout for your CMOS inverter
VLSI Lab Tutorial 3 Virtuoso Layout Editing Introduction 1.0 Introduction The purpose of this lab tutorial is to guide you through the design process in creating a custom IC layout for your CMOS inverter
Spiral 2-8. Cell Layout
 2-8.1 Spiral 2-8 Cell Layout 2-8.2 Learning Outcomes I understand how a digital circuit is composed of layers of materials forming transistors and wires I understand how each layer is expressed as geometric
2-8.1 Spiral 2-8 Cell Layout 2-8.2 Learning Outcomes I understand how a digital circuit is composed of layers of materials forming transistors and wires I understand how each layer is expressed as geometric
Design rule illustrations for the AMI C5N process can be found at:
 Cadence Tutorial B: Layout, DRC, Extraction, and LVS Created for the MSU VLSI program by Professor A. Mason and the AMSaC lab group. Revised by C Young & Waqar A Qureshi -FS08 Document Contents Introduction
Cadence Tutorial B: Layout, DRC, Extraction, and LVS Created for the MSU VLSI program by Professor A. Mason and the AMSaC lab group. Revised by C Young & Waqar A Qureshi -FS08 Document Contents Introduction
10. Interconnects in CMOS Technology
 10. Interconnects in CMOS Technology 1 10. Interconnects in CMOS Technology Jacob Abraham Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin VLSI Design Fall 2017 October
10. Interconnects in CMOS Technology 1 10. Interconnects in CMOS Technology Jacob Abraham Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin VLSI Design Fall 2017 October
EE 330 Laboratory 3 Layout, DRC, and LVS Fall 2015
 EE 330 Laboratory 3 Layout, DRC, and LVS Fall 2015 Contents Objective:... 2 Part 1 Creating a layout... 2 1.1 Run DRC Early and Often... 2 1.2 Create N active and connect the transistors... 3 1.3 Vias...
EE 330 Laboratory 3 Layout, DRC, and LVS Fall 2015 Contents Objective:... 2 Part 1 Creating a layout... 2 1.1 Run DRC Early and Often... 2 1.2 Create N active and connect the transistors... 3 1.3 Vias...
Art of Layout Euler s path and stick diagram. Kunal Ghosh
 Art of Layout Euler s path and stick diagram Kunal Ghosh I wrote about Euler s path and stick diagram in two different blogs, but now is the time to show you how are they connected. It s simple and, seems,
Art of Layout Euler s path and stick diagram Kunal Ghosh I wrote about Euler s path and stick diagram in two different blogs, but now is the time to show you how are they connected. It s simple and, seems,
Virtuoso Layout Editor
 This tutorial will cover the basic steps involved in using the Cadence layout editor called Virtuoso, extracting layout, and running simulation on the layout. The inverter layout is used as an example
This tutorial will cover the basic steps involved in using the Cadence layout editor called Virtuoso, extracting layout, and running simulation on the layout. The inverter layout is used as an example
Schematic creation of MOS field effect transistor.
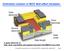 Schematic creation of MOS field effect transistor. Gate electrode Drain electrode Source electrode Gate length Gate oxide A good reference is http://jas2.eng.buffalo.edu/applets/education/fab/nmos/nmos.html
Schematic creation of MOS field effect transistor. Gate electrode Drain electrode Source electrode Gate length Gate oxide A good reference is http://jas2.eng.buffalo.edu/applets/education/fab/nmos/nmos.html
EE 330 Laboratory 3 Layout, DRC, and LVS
 EE 330 Laboratory 3 Layout, DRC, and LVS Spring 2018 Contents Objective:... 2 Part 1 creating a layout... 2 1.1 Run DRC... 2 1.2 Stick Diagram to Physical Layer... 3 1.3 Bulk Connections... 3 1.4 Pins...
EE 330 Laboratory 3 Layout, DRC, and LVS Spring 2018 Contents Objective:... 2 Part 1 creating a layout... 2 1.1 Run DRC... 2 1.2 Stick Diagram to Physical Layer... 3 1.3 Bulk Connections... 3 1.4 Pins...
UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO
 UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO UW ASIC DESIGN TEAM: Cadence Tutorial Description: Part I: Layout & DRC of a CMOS inverter. Part II: Extraction & LVS of a CMOS inverter. Part III: Post-Layout Simulation. The Cadence
UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO UW ASIC DESIGN TEAM: Cadence Tutorial Description: Part I: Layout & DRC of a CMOS inverter. Part II: Extraction & LVS of a CMOS inverter. Part III: Post-Layout Simulation. The Cadence
CMOS INVERTER LAYOUT TUTORIAL
 PRINCESS SUMAYA UNIVERSITY FOR TECHNOLOGY CMOS INVERTER LAYOUT TUTORIAL We will start the inverter by drawing a PMOS. The first step is to draw a poly layer. Click on draw a rectangle and choose the poly
PRINCESS SUMAYA UNIVERSITY FOR TECHNOLOGY CMOS INVERTER LAYOUT TUTORIAL We will start the inverter by drawing a PMOS. The first step is to draw a poly layer. Click on draw a rectangle and choose the poly
Professor Muller Fall 2016 Sameet Ramakrishnan Eric Chang Adapted from prior EE140 and EE141 labs. EE 140/240A Lab 0 Full IC Design Flow
 Professor Muller Fall 2016 Sameet Ramakrishnan Eric Chang Adapted from prior EE140 and EE141 labs EE 140/240A Lab 0 Full IC Design Flow In this lab, you will walk through the full process an analog designer
Professor Muller Fall 2016 Sameet Ramakrishnan Eric Chang Adapted from prior EE140 and EE141 labs EE 140/240A Lab 0 Full IC Design Flow In this lab, you will walk through the full process an analog designer
Computer-Based Project on VLSI Design Co 3/7
 Computer-Based Project on VLSI Design Co 3/7 IC Layout and Symbolic Representation This pamphlet introduces the topic of IC layout in integrated circuit design and discusses the role of Design Rules and
Computer-Based Project on VLSI Design Co 3/7 IC Layout and Symbolic Representation This pamphlet introduces the topic of IC layout in integrated circuit design and discusses the role of Design Rules and
EE 330 Spring 2018 Laboratory 2: Basic Boolean Circuits
 EE 330 Spring 2018 Laboratory 2: Basic Boolean Circuits Contents Objective:... 2 Part 1: Introduction... 2 Part 2 Simulation of a CMOS Inverter... 3 Part 2.1 Attaching technology information... 3 Part
EE 330 Spring 2018 Laboratory 2: Basic Boolean Circuits Contents Objective:... 2 Part 1: Introduction... 2 Part 2 Simulation of a CMOS Inverter... 3 Part 2.1 Attaching technology information... 3 Part
CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #2, Schematic Capture, DC Analysis, Transient Analysis (Inverter, NAND2)
 CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #2, Schematic Capture, DC Analysis, Transient Analysis (Inverter, NAND2) Joel Wilder, Aleksandar Milenkovic, ECE Dept., The University of Alabama in Huntsville
CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #2, Schematic Capture, DC Analysis, Transient Analysis (Inverter, NAND2) Joel Wilder, Aleksandar Milenkovic, ECE Dept., The University of Alabama in Huntsville
Virtuoso Schematic Composer
 is a schematic design tool from Cadence. In this tutorial you will learn how to put electrical components, make wire connections, insert pins and check for connection error. Start Cadence Custom IC Design
is a schematic design tool from Cadence. In this tutorial you will learn how to put electrical components, make wire connections, insert pins and check for connection error. Start Cadence Custom IC Design
ESE570 Spring University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and System Engineering Digital Integrated Cicruits AND VLSI Fundamentals
 University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and System Engineering Digital Integrated Cicruits AND VLSI Fundamentals ESE570, Spring 2019 HW5: Delay and Layout Sunday, February 17th Due: Friday,
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and System Engineering Digital Integrated Cicruits AND VLSI Fundamentals ESE570, Spring 2019 HW5: Delay and Layout Sunday, February 17th Due: Friday,
3. Implementing Logic in CMOS
 3. Implementing Logic in CMOS 3. Implementing Logic in CMOS Jacob Abraham Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin VLSI Design Fall 27 September, 27 ECE Department,
3. Implementing Logic in CMOS 3. Implementing Logic in CMOS Jacob Abraham Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin VLSI Design Fall 27 September, 27 ECE Department,
QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT OF ECE
 QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT OF ECE YEAR: III SEM: VI SUBJECTCODE:EC2354 SUBJECT NAME:VLSI DESIGN Prepared by V.GUNASUNDARI/AP 1.List the advantages of SOI CMOS process Denser transistor structures are possible.
QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT OF ECE YEAR: III SEM: VI SUBJECTCODE:EC2354 SUBJECT NAME:VLSI DESIGN Prepared by V.GUNASUNDARI/AP 1.List the advantages of SOI CMOS process Denser transistor structures are possible.
Cadence Virtuoso Schematic Design and Circuit Simulation Tutorial
 Cadence Virtuoso Schematic Design and Circuit Simulation Tutorial Introduction This tutorial is an introduction to schematic capture and circuit simulation for ENGN1600 using Cadence Virtuoso. These courses
Cadence Virtuoso Schematic Design and Circuit Simulation Tutorial Introduction This tutorial is an introduction to schematic capture and circuit simulation for ENGN1600 using Cadence Virtuoso. These courses
Lab 2. Standard Cell layout.
 Lab 2. Standard Cell layout. The purpose of this lab is to demonstrate CMOS-standard cell design. Use the lab instructions and the cadence manual (http://www.es.lth.se/ugradcourses/cadsys/cadence.html)
Lab 2. Standard Cell layout. The purpose of this lab is to demonstrate CMOS-standard cell design. Use the lab instructions and the cadence manual (http://www.es.lth.se/ugradcourses/cadsys/cadence.html)
Cadence Tutorial 2: Layout, DRC/LVS and Circuit Simulation with Extracted Parasitics
 Cadence Tutorial 2: Layout, DRC/LVS and Circuit Simulation with Extracted Parasitics Introduction This tutorial describes how to generate a mask layout in the Cadence Virtuoso Layout Editor. Use of DIVA
Cadence Tutorial 2: Layout, DRC/LVS and Circuit Simulation with Extracted Parasitics Introduction This tutorial describes how to generate a mask layout in the Cadence Virtuoso Layout Editor. Use of DIVA
Introduction to Layout design
 Introduction to Layout design Note: some figures are taken from Ref. B. Razavi, Design of Analog CMOS integrated circuits, Mc Graw-Hill, 001, and MOSIS web site: http://www.mosis.org/ 1 Introduction to
Introduction to Layout design Note: some figures are taken from Ref. B. Razavi, Design of Analog CMOS integrated circuits, Mc Graw-Hill, 001, and MOSIS web site: http://www.mosis.org/ 1 Introduction to
On-Chip Variation (OCV) Kunal Ghosh
 On-Chip Variation (OCV) Kunal Ghosh Ever thought what s an interviewer s favorite questions to rip you off all my previous ebooks. And On-Chip Variation (OCV) is one of them, specifically for Static Timing
On-Chip Variation (OCV) Kunal Ghosh Ever thought what s an interviewer s favorite questions to rip you off all my previous ebooks. And On-Chip Variation (OCV) is one of them, specifically for Static Timing
Memory Design I. Array-Structured Memory Architecture. Professor Chris H. Kim. Dept. of ECE.
 Memory Design I Professor Chris H. Kim University of Minnesota Dept. of ECE chriskim@ece.umn.edu Array-Structured Memory Architecture 2 1 Semiconductor Memory Classification Read-Write Wi Memory Non-Volatile
Memory Design I Professor Chris H. Kim University of Minnesota Dept. of ECE chriskim@ece.umn.edu Array-Structured Memory Architecture 2 1 Semiconductor Memory Classification Read-Write Wi Memory Non-Volatile
ENEE 359a Digital VLSI Design
 SLIDE 1 ENEE 359a Digital VLSI Design Course : Transistors to Systems Prof. blj@eng.umd.edu Credit where credit is due: Slides contain original artwork ( Jacob 2004) as well as material taken liberally
SLIDE 1 ENEE 359a Digital VLSI Design Course : Transistors to Systems Prof. blj@eng.umd.edu Credit where credit is due: Slides contain original artwork ( Jacob 2004) as well as material taken liberally
A Single Poly Flash Memory Intellectual Property for Low-Cost, Low-Density Embedded Nonvolatile Memory Applications
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 41, No. 6, December 2002, pp. 846 850 A Single Poly Flash Memory Intellectual Property for Low-Cost, Low-Density Embedded Nonvolatile Memory Applications Jai-Cheol
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 41, No. 6, December 2002, pp. 846 850 A Single Poly Flash Memory Intellectual Property for Low-Cost, Low-Density Embedded Nonvolatile Memory Applications Jai-Cheol
Amplifier Simulation Tutorial. Design Kit: Cadence 0.18μm CMOS PDK (gpdk180) (Cadence Version 6.1.5)
 Amplifier Simulation Tutorial Design Kit: Cadence 0.18μm CMOS PDK (gpdk180) (Cadence Version 6.1.5) Yongsuk Choi, Marvin Onabajo This tutorial provides a quick introduction to the use of Cadence tools
Amplifier Simulation Tutorial Design Kit: Cadence 0.18μm CMOS PDK (gpdk180) (Cadence Version 6.1.5) Yongsuk Choi, Marvin Onabajo This tutorial provides a quick introduction to the use of Cadence tools
EE586 VLSI Design. Partha Pande School of EECS Washington State University
 EE586 VLSI Design Partha Pande School of EECS Washington State University pande@eecs.wsu.edu Lecture 1 (Introduction) Why is designing digital ICs different today than it was before? Will it change in
EE586 VLSI Design Partha Pande School of EECS Washington State University pande@eecs.wsu.edu Lecture 1 (Introduction) Why is designing digital ICs different today than it was before? Will it change in
Full Custom Layout Optimization Using Minimum distance rule, Jogs and Depletion sharing
 Full Custom Layout Optimization Using Minimum distance rule, Jogs and Depletion sharing Umadevi.S #1, Vigneswaran.T #2 # Assistant Professor [Sr], School of Electronics Engineering, VIT University, Vandalur-
Full Custom Layout Optimization Using Minimum distance rule, Jogs and Depletion sharing Umadevi.S #1, Vigneswaran.T #2 # Assistant Professor [Sr], School of Electronics Engineering, VIT University, Vandalur-
Unit 7: Memory. Dynamic shift register: Circuit diagram: Refer to unit 4(ch 6.5.4)
 Unit 7: Memory Objectives: At the end of this unit we will be able to understand System timing consideration Storage / Memory Elements dynamic shift register 1T and 3T dynamic memory 4T dynamic and 6T
Unit 7: Memory Objectives: At the end of this unit we will be able to understand System timing consideration Storage / Memory Elements dynamic shift register 1T and 3T dynamic memory 4T dynamic and 6T
Latch-Up. Parasitic Bipolar Transistors
 Latch-Up LATCH-UP CIRCUIT Latch-up is caused by an SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier) circuit. Fabrication of CMOS integrated circuits with bulk silicon processing creates a parasitic SCR structure. The
Latch-Up LATCH-UP CIRCUIT Latch-up is caused by an SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier) circuit. Fabrication of CMOS integrated circuits with bulk silicon processing creates a parasitic SCR structure. The
Introduction 1. GENERAL TRENDS. 1. The technology scale down DEEP SUBMICRON CMOS DESIGN
 1 Introduction The evolution of integrated circuit (IC) fabrication techniques is a unique fact in the history of modern industry. The improvements in terms of speed, density and cost have kept constant
1 Introduction The evolution of integrated circuit (IC) fabrication techniques is a unique fact in the history of modern industry. The improvements in terms of speed, density and cost have kept constant
UNIT IV CMOS TESTING
 UNIT IV CMOS TESTING 1. Mention the levels at which testing of a chip can be done? At the wafer level At the packaged-chip level At the board level At the system level In the field 2. What is meant by
UNIT IV CMOS TESTING 1. Mention the levels at which testing of a chip can be done? At the wafer level At the packaged-chip level At the board level At the system level In the field 2. What is meant by
CMOS TECHNOLOGY- Chapter 2 in the Text
 CMOS TECHOLOGY- Chapter 2 in the Text CMOS Technology- Chapter 2 We will describe a modern CMOS process flow. In the simplest CMOS technologies, we need to realize simply MOS and MOS transistors for circuits
CMOS TECHOLOGY- Chapter 2 in the Text CMOS Technology- Chapter 2 We will describe a modern CMOS process flow. In the simplest CMOS technologies, we need to realize simply MOS and MOS transistors for circuits
TimeSPOT WP3 Workshop: Introduction to 28 nm CMOS
 TimeSPOT WP3 Workshop: Introduction to 28 nm CMOS Valentino Liberali INFN and Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Milano Via Celoria, 16 Milano valentino.liberali@mi.infn.it Milano, Jan. 2018 V. Liberali
TimeSPOT WP3 Workshop: Introduction to 28 nm CMOS Valentino Liberali INFN and Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Milano Via Celoria, 16 Milano valentino.liberali@mi.infn.it Milano, Jan. 2018 V. Liberali
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Lab #2: Layout and Simulation
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Lab #2: Layout and Simulation NTU IC541CA 1 Assumed Knowledge This lab assumes use of the Electric
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Lab #2: Layout and Simulation NTU IC541CA 1 Assumed Knowledge This lab assumes use of the Electric
Single-Strip Static CMOS Layout
 EE244: Design Technology for Integrated Circuits and Systems Outline Lecture 6.2 Regular Module Structures CMOS Synthetic Libraries Weinberger Arrays Gate Matrix Programmable Logic Array (PLA) Storage
EE244: Design Technology for Integrated Circuits and Systems Outline Lecture 6.2 Regular Module Structures CMOS Synthetic Libraries Weinberger Arrays Gate Matrix Programmable Logic Array (PLA) Storage
Lab. Course Goals. Topics. What is VLSI design? What is an integrated circuit? VLSI Design Cycle. VLSI Design Automation
 Course Goals Lab Understand key components in VLSI designs Become familiar with design tools (Cadence) Understand design flows Understand behavioral, structural, and physical specifications Be able to
Course Goals Lab Understand key components in VLSI designs Become familiar with design tools (Cadence) Understand design flows Understand behavioral, structural, and physical specifications Be able to
CMOS VLSI DESIGN ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING CMOS VLSI DESIGN. Dr. Lynn Fuller
 ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING CMOS VLSI DESIGN Dr. Lynn Fuller Webpage: http://people.rit.edu/~lffeee 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604 Tel (585) 475-2035
ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING CMOS VLSI DESIGN Dr. Lynn Fuller Webpage: http://people.rit.edu/~lffeee 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604 Tel (585) 475-2035
Layout and Layout Verification. of an Inverter Circuit
 Layout and Layout Verification of an Inverter Circuit Santa Clara University Department of Electrical Engineering By Piyush Panwar Under Guidance of Dr Samiha Mourad Date of Last Revision: August 7, 2010
Layout and Layout Verification of an Inverter Circuit Santa Clara University Department of Electrical Engineering By Piyush Panwar Under Guidance of Dr Samiha Mourad Date of Last Revision: August 7, 2010
Embedded System Application
 Laboratory Embedded System Application 4190.303C 2010 Spring Semester ROMs, Non-volatile and Flash Memories ELPL Naehyuck Chang Dept. of EECS/CSE Seoul National University naehyuck@snu.ac.kr Revisit Previous
Laboratory Embedded System Application 4190.303C 2010 Spring Semester ROMs, Non-volatile and Flash Memories ELPL Naehyuck Chang Dept. of EECS/CSE Seoul National University naehyuck@snu.ac.kr Revisit Previous
Announcements. Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits. No office hour next Monday. Lecture 2: Scaling Trends
 EE24 - Spring 2008 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 2: Scaling Trends Announcements No office hour next Monday Extra office hours Tuesday and Thursday 2-3pm 2 CMOS Scaling Rules Voltage, V
EE24 - Spring 2008 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 2: Scaling Trends Announcements No office hour next Monday Extra office hours Tuesday and Thursday 2-3pm 2 CMOS Scaling Rules Voltage, V
Memory Arrays. Array Architecture. Chapter 16 Memory Circuits and Chapter 12 Array Subsystems from CMOS VLSI Design by Weste and Harris, 4 th Edition
 Chapter 6 Memory Circuits and Chapter rray Subsystems from CMOS VLSI Design by Weste and Harris, th Edition E E 80 Introduction to nalog and Digital VLSI Paul M. Furth New Mexico State University Static
Chapter 6 Memory Circuits and Chapter rray Subsystems from CMOS VLSI Design by Weste and Harris, th Edition E E 80 Introduction to nalog and Digital VLSI Paul M. Furth New Mexico State University Static
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring Lecture 22: Memery, ROM
 CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2011 Lecture 22: Memery, ROM [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] Sp11 CMPEN 411 L22 S.1
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2011 Lecture 22: Memery, ROM [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] Sp11 CMPEN 411 L22 S.1
Integrated circuits and fabrication
 Integrated circuits and fabrication Motivation So far we have discussed about the various devices that are the heartbeat of core electronics. This modules aims at giving an overview of how these solid
Integrated circuits and fabrication Motivation So far we have discussed about the various devices that are the heartbeat of core electronics. This modules aims at giving an overview of how these solid
Memory Design I. Semiconductor Memory Classification. Read-Write Memories (RWM) Memory Scaling Trend. Memory Scaling Trend
 Array-Structured Memory Architecture Memory Design I Professor hris H. Kim University of Minnesota Dept. of EE chriskim@ece.umn.edu 2 Semiconductor Memory lassification Read-Write Memory Non-Volatile Read-Write
Array-Structured Memory Architecture Memory Design I Professor hris H. Kim University of Minnesota Dept. of EE chriskim@ece.umn.edu 2 Semiconductor Memory lassification Read-Write Memory Non-Volatile Read-Write
AltaSens A5262-4T 4.5 Megapixel CMOS Image Sensor 0.18 µm IBM Process
 AltaSens A5262-4T 4.5 Megapixel CMOS Image Sensor 0.18 µm IBM Process Imager Process Review For comments, questions, or more information about this report, or for any additional technical needs concerning
AltaSens A5262-4T 4.5 Megapixel CMOS Image Sensor 0.18 µm IBM Process Imager Process Review For comments, questions, or more information about this report, or for any additional technical needs concerning
Magic Technology Manual #1: NMOS
 Magic Technology Manual #1: NMOS John Ousterhout Computer Science Division Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California Berkeley, CA 970 (Warning: Process details often change.
Magic Technology Manual #1: NMOS John Ousterhout Computer Science Division Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California Berkeley, CA 970 (Warning: Process details often change.
Integrated Circuit Fabrication
 Integrated Circuit Fabrication Professor Dean Neikirk Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin world wide web: http://weewave.mer.utexas.edu Integrated circuits
Integrated Circuit Fabrication Professor Dean Neikirk Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin world wide web: http://weewave.mer.utexas.edu Integrated circuits
Low Voltage Bandgap References and High PSRR Mechanism
 Low Voltage Bandgap References and High PSRR Mechanism Vahe Arakelyan 2nd year Master Student Synopsys Armenia Educational Department, State Engineering University of Armenia Moscow March 21-24, 2011 Outline
Low Voltage Bandgap References and High PSRR Mechanism Vahe Arakelyan 2nd year Master Student Synopsys Armenia Educational Department, State Engineering University of Armenia Moscow March 21-24, 2011 Outline
More information can be found in the Cadence manuals Virtuoso Layout Editor User Guide and Cadence Hierarchy Editor User Guide.
 Chapter 6 Building with Layout This chapter consists of two parts. The first describes the generation of layout views and the second deals with the various tools used for verifying the layout, both physical
Chapter 6 Building with Layout This chapter consists of two parts. The first describes the generation of layout views and the second deals with the various tools used for verifying the layout, both physical
Victory Advanced Structure Editor. 3D Process Simulator for Large Structures
 Victory Advanced Structure Editor 3D Process Simulator for Large Structures Applications Victory Advanced Structure Editor is designed for engineers who need to create layout driven 3D process based structures
Victory Advanced Structure Editor 3D Process Simulator for Large Structures Applications Victory Advanced Structure Editor is designed for engineers who need to create layout driven 3D process based structures
EE115C Digital Electronic Circuits. Tutorial 4: Schematic-driven Layout (Virtuoso XL)
 EE115C Digital Electronic Circuits Tutorial 4: Schematic-driven Layout (Virtuoso XL) This tutorial will demonstrate schematic-driven layout on the example of a 2-input NAND gate. Simple Layout (that won
EE115C Digital Electronic Circuits Tutorial 4: Schematic-driven Layout (Virtuoso XL) This tutorial will demonstrate schematic-driven layout on the example of a 2-input NAND gate. Simple Layout (that won
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Outline (approximate) Introduction and Motivation The VLSI Design Process Details of the MOS Transistor Device Fabrication Design Rules CMOS
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Outline (approximate) Introduction and Motivation The VLSI Design Process Details of the MOS Transistor Device Fabrication Design Rules CMOS
Microelectronica. Full-Custom Design with Cadence Tutorial
 Área Científica de Electrónica Microelectronica Full-Custom Design with Cadence Tutorial AustriaMicroSystems C35B3 (HIT-Kit 3.70) Marcelino Santos Table of contends 1. Starting Cadence... 3 Starting Cadence
Área Científica de Electrónica Microelectronica Full-Custom Design with Cadence Tutorial AustriaMicroSystems C35B3 (HIT-Kit 3.70) Marcelino Santos Table of contends 1. Starting Cadence... 3 Starting Cadence
Taming the Challenges of 20nm Custom/Analog Design
 Taming the Challenges of 20nm Custom/Analog Design Custom and analog designers will lay the foundation for 20nm IC design. However, they face many challenges that arise from manufacturing complexity. The
Taming the Challenges of 20nm Custom/Analog Design Custom and analog designers will lay the foundation for 20nm IC design. However, they face many challenges that arise from manufacturing complexity. The
Chapter 6. CMOS Functional Cells
 Chapter 6 CMOS Functional Cells In the previous chapter we discussed methods of designing layout of logic gates and building blocks like transmission gates, multiplexers and tri-state inverters. In this
Chapter 6 CMOS Functional Cells In the previous chapter we discussed methods of designing layout of logic gates and building blocks like transmission gates, multiplexers and tri-state inverters. In this
8.3.4 The Four-Transistor (4-T) Cell
 전자회로 II 제 10 주 1 강 8.3.4 The Four-Transistor (4-T) Cell Static memory design has shorter access times than dynamic design 6-T static cell provides a to drive the sense amplifier Figure 8.19 : 4-T dynamic
전자회로 II 제 10 주 1 강 8.3.4 The Four-Transistor (4-T) Cell Static memory design has shorter access times than dynamic design 6-T static cell provides a to drive the sense amplifier Figure 8.19 : 4-T dynamic
+1 (479)
 Memory Courtesy of Dr. Daehyun Lim@WSU, Dr. Harris@HMC, Dr. Shmuel Wimer@BIU and Dr. Choi@PSU http://csce.uark.edu +1 (479) 575-6043 yrpeng@uark.edu Memory Arrays Memory Arrays Random Access Memory Serial
Memory Courtesy of Dr. Daehyun Lim@WSU, Dr. Harris@HMC, Dr. Shmuel Wimer@BIU and Dr. Choi@PSU http://csce.uark.edu +1 (479) 575-6043 yrpeng@uark.edu Memory Arrays Memory Arrays Random Access Memory Serial
TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 PURPOSE INTRODUCTION ESD CHECKS THROUGHOUT IC DESIGN FLOW... 2
 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 PURPOSE... 1 2.0 INTRODUCTION... 1 3.0 ESD CHECKS THROUGHOUT IC DESIGN FLOW... 2 3.1 PRODUCT DEFINITION PHASE... 3 3.2 CHIP ARCHITECTURE PHASE... 4 3.3 MODULE AND FULL IC DESIGN PHASE...
TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 PURPOSE... 1 2.0 INTRODUCTION... 1 3.0 ESD CHECKS THROUGHOUT IC DESIGN FLOW... 2 3.1 PRODUCT DEFINITION PHASE... 3 3.2 CHIP ARCHITECTURE PHASE... 4 3.3 MODULE AND FULL IC DESIGN PHASE...
ELE 455/555 Computer System Engineering. Section 1 Review and Foundations Class 3 Technology
 ELE 455/555 Computer System Engineering Section 1 Review and Foundations Class 3 MOSFETs MOSFET Terminology Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor 4 terminal device Source, Gate, Drain, Body
ELE 455/555 Computer System Engineering Section 1 Review and Foundations Class 3 MOSFETs MOSFET Terminology Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor 4 terminal device Source, Gate, Drain, Body
EEC 116 Fall 2011 Lab #1 Cadence Schematic Capture and Layout Tutorial
 EEC 116 Fall 2011 Lab #1 Cadence Schematic Capture and Layout Tutorial Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, Davis September 26, 2011 Reading: Rabaey Chapters 1, 2, A,
EEC 116 Fall 2011 Lab #1 Cadence Schematic Capture and Layout Tutorial Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, Davis September 26, 2011 Reading: Rabaey Chapters 1, 2, A,
FPGA Programming Technology
 FPGA Programming Technology Static RAM: This Xilinx SRAM configuration cell is constructed from two cross-coupled inverters and uses a standard CMOS process. The configuration cell drives the gates of
FPGA Programming Technology Static RAM: This Xilinx SRAM configuration cell is constructed from two cross-coupled inverters and uses a standard CMOS process. The configuration cell drives the gates of
UNIT 4 INTEGRATED CIRCUIT DESIGN METHODOLOGY E5163
 UNIT 4 INTEGRATED CIRCUIT DESIGN METHODOLOGY E5163 LEARNING OUTCOMES 4.1 DESIGN METHODOLOGY By the end of this unit, student should be able to: 1. Explain the design methodology for integrated circuit.
UNIT 4 INTEGRATED CIRCUIT DESIGN METHODOLOGY E5163 LEARNING OUTCOMES 4.1 DESIGN METHODOLOGY By the end of this unit, student should be able to: 1. Explain the design methodology for integrated circuit.
On the Design of Ultra-High Density 14nm Finfet based Transistor-Level Monolithic 3D ICs
 2016 IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI On the Design of Ultra-High Density 14nm Finfet based Transistor-Level Monolithic 3D ICs Jiajun Shi 1,2, Deepak Nayak 1,Motoi Ichihashi 1, Srinivasa
2016 IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI On the Design of Ultra-High Density 14nm Finfet based Transistor-Level Monolithic 3D ICs Jiajun Shi 1,2, Deepak Nayak 1,Motoi Ichihashi 1, Srinivasa
ECE471/571 Energy Efficient VLSI Design Project 2 Cadence Setup and Creation of an Inverter Due Date 11:30 am on Friday, February 2 nd, 2018
 ECE471/571 Energy Efficient VLSI Design Project 2 Cadence Setup and Creation of an Inverter Due Date 11:30 am on Friday, February 2 nd, 2018 Introduction This project will first walk you through the setup
ECE471/571 Energy Efficient VLSI Design Project 2 Cadence Setup and Creation of an Inverter Due Date 11:30 am on Friday, February 2 nd, 2018 Introduction This project will first walk you through the setup
Q.1. Attempt any TEN of the following: (a) Define the term Noise Margins. Ans: [Define: 2 M]
![Q.1. Attempt any TEN of the following: (a) Define the term Noise Margins. Ans: [Define: 2 M] Q.1. Attempt any TEN of the following: (a) Define the term Noise Margins. Ans: [Define: 2 M]](/thumbs/90/102030632.jpg) Subject Code: 17659 Model Answer Page 1 of 24 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model
Subject Code: 17659 Model Answer Page 1 of 24 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model
VLSI Test Technology and Reliability (ET4076)
 VLSI Test Technology and Reliability (ET4076) Lecture 8(2) I DDQ Current Testing (Chapter 13) Said Hamdioui Computer Engineering Lab Delft University of Technology 2009-2010 1 Learning aims Describe the
VLSI Test Technology and Reliability (ET4076) Lecture 8(2) I DDQ Current Testing (Chapter 13) Said Hamdioui Computer Engineering Lab Delft University of Technology 2009-2010 1 Learning aims Describe the
Printed Circuit Board Prototyping Guide
 Printed Circuit Board Prototyping Guide Shiva 03/12/08 This document has referenced and extracted certain contents in verbatim from Capture CIS Tutorial, Ekarat Laohavalesson, Layout Plus Tutorial, Ekarat
Printed Circuit Board Prototyping Guide Shiva 03/12/08 This document has referenced and extracted certain contents in verbatim from Capture CIS Tutorial, Ekarat Laohavalesson, Layout Plus Tutorial, Ekarat
E40M. MOS Transistors, CMOS Logic Circuits, and Cheap, Powerful Computers. M. Horowitz, J. Plummer, R. Howe 1
 E40M MOS Transistors, CMOS Logic Circuits, and Cheap, Powerful Computers M. Horowitz, J. Plummer, R. Howe 1 Reading Chapter 4 in the reader For more details look at A&L 5.1 Digital Signals (goes in much
E40M MOS Transistors, CMOS Logic Circuits, and Cheap, Powerful Computers M. Horowitz, J. Plummer, R. Howe 1 Reading Chapter 4 in the reader For more details look at A&L 5.1 Digital Signals (goes in much
Design Rule Optimization of Regular layout for Leakage Reduction in Nanoscale Design
 Design Rule Optimization of Regular layout for Leakage Reduction in Nanoscale Design Anupama R. Subramaniam, Ritu Singhal, Chi-Chao Wang, Yu Cao Department of Electrical Engineering, Arizona State University,
Design Rule Optimization of Regular layout for Leakage Reduction in Nanoscale Design Anupama R. Subramaniam, Ritu Singhal, Chi-Chao Wang, Yu Cao Department of Electrical Engineering, Arizona State University,
New Layout Scheme to Improve ESD Robustness of I/O Buffers in Fully-Silicided CMOS Process
 New Layout Scheme to Improve ESD Robustness of I/O Buffers in Fully-Silicided CMOS Process Ming-Dou Ker (1, 2), Wen-Yi Chen (1), Wuu-Trong Shieh (3), and I-Ju Wei (3) (1) Institute of Electronics, National
New Layout Scheme to Improve ESD Robustness of I/O Buffers in Fully-Silicided CMOS Process Ming-Dou Ker (1, 2), Wen-Yi Chen (1), Wuu-Trong Shieh (3), and I-Ju Wei (3) (1) Institute of Electronics, National
28F K (256K x 8) FLASH MEMORY
 28F020 2048K (256K x 8) FLASH MEMOR SmartDie Product Specification Flash Electrical Chip Erase 2 Second Typical Chip Erase Quick-Pulse Programming Algorithm 10 ms Typical Byte Program 4 Second Chip Program
28F020 2048K (256K x 8) FLASH MEMOR SmartDie Product Specification Flash Electrical Chip Erase 2 Second Typical Chip Erase Quick-Pulse Programming Algorithm 10 ms Typical Byte Program 4 Second Chip Program
Industrial Example I Semiconductor Manufacturing Photolithography Can you tell me anything about this data!
 Can you tell me anything about this data! 1 In Semiconductor Manufacturing the Photolithography process steps are very critical to ensure proper circuit and device performance. Without good CD (critical
Can you tell me anything about this data! 1 In Semiconductor Manufacturing the Photolithography process steps are very critical to ensure proper circuit and device performance. Without good CD (critical
11 Patent Number: 5,519,242 Avery 45) Date of Patent: May 21, 1996
 United States Patent (19) I I USOO5519242A 11 Patent Number: 5,519,242 Avery 45) Date of Patent: May 21, 1996 54 ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,357,126 10/1994 Jimenez... 257/173 PROTECTION CIRCUIT FOR A NMOS
United States Patent (19) I I USOO5519242A 11 Patent Number: 5,519,242 Avery 45) Date of Patent: May 21, 1996 54 ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,357,126 10/1994 Jimenez... 257/173 PROTECTION CIRCUIT FOR A NMOS
Design Methodologies
 Design Methodologies 1981 1983 1985 1987 1989 1991 1993 1995 1997 1999 2001 2003 2005 2007 2009 Complexity Productivity (K) Trans./Staff - Mo. Productivity Trends Logic Transistor per Chip (M) 10,000 0.1
Design Methodologies 1981 1983 1985 1987 1989 1991 1993 1995 1997 1999 2001 2003 2005 2007 2009 Complexity Productivity (K) Trans./Staff - Mo. Productivity Trends Logic Transistor per Chip (M) 10,000 0.1
Announcements. Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits. No office hour next Monday. Lecture 2: Scaling Trends
 EE4 - Spring 008 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture : Scaling Trends Announcements No office hour next Monday Extra office hours Tuesday and Thursday -3pm CMOS Scaling Rules Voltage, V / α tox/α
EE4 - Spring 008 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture : Scaling Trends Announcements No office hour next Monday Extra office hours Tuesday and Thursday -3pm CMOS Scaling Rules Voltage, V / α tox/α
Power IC 용 ESD 보호기술. 구용서 ( Yong-Seo Koo ) Electronic Engineering Dankook University, Korea
 Power IC 용 ESD 보호기술 구용서 ( Yong-Seo Koo ) Electronic Engineering Dankook University, Korea yskoo@dankook.ac.kr 031-8005-3625 Outline Introduction Basic Concept of ESD Protection Circuit ESD Technology Issue
Power IC 용 ESD 보호기술 구용서 ( Yong-Seo Koo ) Electronic Engineering Dankook University, Korea yskoo@dankook.ac.kr 031-8005-3625 Outline Introduction Basic Concept of ESD Protection Circuit ESD Technology Issue
Regularity for Reduced Variability
 Regularity for Reduced Variability Larry Pileggi Carnegie Mellon pileggi@ece.cmu.edu 28 July 2006 CMU Collaborators Andrzej Strojwas Slava Rovner Tejas Jhaveri Thiago Hersan Kim Yaw Tong Sandeep Gupta
Regularity for Reduced Variability Larry Pileggi Carnegie Mellon pileggi@ece.cmu.edu 28 July 2006 CMU Collaborators Andrzej Strojwas Slava Rovner Tejas Jhaveri Thiago Hersan Kim Yaw Tong Sandeep Gupta
A Transistor-Level Placement Tool for Asynchronous Circuits
 A Transistor-Level Placement Tool for Asynchronous Circuits M Salehi, H Pedram, M Saheb Zamani, M Naderi, N Araghi Department of Computer Engineering, Amirkabir University of Technology 424, Hafez Ave,
A Transistor-Level Placement Tool for Asynchronous Circuits M Salehi, H Pedram, M Saheb Zamani, M Naderi, N Araghi Department of Computer Engineering, Amirkabir University of Technology 424, Hafez Ave,
Electromagnetic Compatibility ( EMC )
 Electromagnetic Compatibility ( EMC ) ESD Strategies in IC and System Design 8-1 Agenda ESD Design in IC Level ( ) Design Guide Lines CMOS Design Process Level Method Circuit Level Method Whole Chip Design
Electromagnetic Compatibility ( EMC ) ESD Strategies in IC and System Design 8-1 Agenda ESD Design in IC Level ( ) Design Guide Lines CMOS Design Process Level Method Circuit Level Method Whole Chip Design
memories The world of Memories DEEP SUBMICRON CMOS DESIGN 10. Memories
 10 Memories This chapter described the memory cell architecture. After a general introduction, we detail the principles and implementation of static RAM, dynamic RAM, read-only memories, electrically erasable
10 Memories This chapter described the memory cell architecture. After a general introduction, we detail the principles and implementation of static RAM, dynamic RAM, read-only memories, electrically erasable
Transistor Flaring in Deep Submicron Design Considerations
 Transistor Flaring in Deep Submicron Design Considerations Vipul Singhal, Keshav C.B., Sumanth K.G., P.R. Suresh Abstract - The deep sub-micron regime has broughtup several manufacturing issues which impact
Transistor Flaring in Deep Submicron Design Considerations Vipul Singhal, Keshav C.B., Sumanth K.G., P.R. Suresh Abstract - The deep sub-micron regime has broughtup several manufacturing issues which impact
University of California, Davis College of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. EEC118 EXPERIMENT No.
 I. OBJECTIVE University of California, Davis College of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EEC118 EXPERIMENT No. 1 MAGIC TUTORIAL The objective of this experiment is to learn
I. OBJECTIVE University of California, Davis College of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EEC118 EXPERIMENT No. 1 MAGIC TUTORIAL The objective of this experiment is to learn
