Computer Vision: Making machines see
|
|
|
- Edith Atkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Computer Vision: Making machines see Roberto Cipolla Department of Engineering Laboratory/
2 Vision: what is where by looking Cognitive Systems Engineering
3 Computer Vision What?
4 Computer Vision What?
5 Real-time application
6 Overview 1. Background: why and how? 2. 3R s of Computer Vision: - Reconstruction - Registration - Recognition
7 1. How to make machines that see?
8 How? Introduction
9 1 Geometry - Perspective
10 2 Probabilistic framework Perception is our best guess as to what is in the world, given our current sensory input and our prior experience. Helmholtz (1988) 1. Deal with the ambiguity of the visual world 2. Are able to fuse information 3. Have the ability to learn
11 3 Machine Learning
12 2 Computer Vision at Cambridge
13 Computer Vision: 3R s Reconstruction Recognition Registration Reconstruction: Recover 3D shape Recognition: Identify objects (example) Registration: Compute their position and pose
14 Computer Vision: 3R s Reconstruction Recognition Registration Reconstruction: Recover 3D shape Recognition: Identify objects (example) Registration: Compute their position and pose
15 Reconstruction? Recovery of 3D shape from images
16 Reconstruction
17 Ambiquity in a single view O
18 Stereo vision O e e' O'
19 Stereo vision 3D point
20 Multi-view stereo p 1 p 4 p 3 p 2 minimize f (R,T,P) p 5 p 6 p 7 Camera 1 Camera 3 R 1,t 1 Camera 2 R 3,t 3 R 2,t 2
21 Structure from motion Input sequence 2D features 2D track 3D points
22 Structure from motion Input sequence 2D features 2D track 3D points
23 Structure from motion Input sequence 2D features 2D track 3D points
24 Structure from motion Input sequence 2D features 2D track 3D points
25 3D MRF for 3D modelling
26 3D Models
27 Large Scale Reconstruction
28 Deformable objects: Real-time photometric stereo using colour lighting
29 Textureless deforming objects a method for reconstructing a textureless deforming object in 2.5d
30 Colour Photometric Stereo
31 Real-time deformable surfaces
32 Sample Reconstructions
33 Registration? Target detection and pose estimation
34 Registration: Expressive Visual Text-to- Speech
35 Registration alignment of training data
36 What is an expressive talking head? > User inputs a sentence which they wish to be uttered > User specifies an emotion Video output is generated
37 Our current talking head
38 Expressive Visual Text to Speech
39 Demo XpressiveTalk
40 3D Registration - Magic Mirrors
41 Registration Body shape
42 Single-shot Body Shape
43 Single-shot Body Shape
44 Single-shot Body Shape
45 Recognition?
46 road Recognition image classification categorical object detection horses airplanes background semantic segmentation tree bicycle building grass dog car sky building road
47 Deep Learning - Class Recognition with CNN feat. of 11x11 size, 2x2 pool size 256 feat. of 5x5 size, 2x2 pool size 512 feat. of 3x3 size 1024 feat. of 3x3 size 1024 feat. of 3x3 size, 2x2 pool size Soft-max classification Layer Convolutional Layer Max pool + Max pool + Max pool + Cat Dog Horse Bird Convolution with features Rectification (non-linearity) Local Pooling & Subsampling Max pool + 2 fully connected layers W W represents the trainable parameters (features) in a layer
48 SegNet Architecture Highlights: Learns to extract features using an encoder network (e.g. VGG16) and maps features to pixel wise labels using a decoder network. Decoders uses the stored pooling indices in the encoding layer to enable upsampling its input to double the resolution. Non-linear upsampling using pooling indices maintains shape of categories, and Reduces the number of parameters in the decoder network by a large margin as compared to other recent architectures.
49 SegNet training from labelled data
50 SegNet predictions on unseen test images - DEMO
51 SegNet Real-time DEMO
52 Why? Applications
53 Summary Computer Vision 1. Background: why and how? 2. 3R s of Computer Vision: - Registration - Reconstruction - Recognition
54 More information Publications: Research demos and code: Research Videos:
Making Machines See. Roberto Cipolla Department of Engineering. Research team
 Making Machines See Roberto Cipolla Department of Engineering Research team http://www.eng.cam.ac.uk/~cipolla/people.html Cognitive Systems Engineering Cognitive Systems Engineering Introduction Making
Making Machines See Roberto Cipolla Department of Engineering Research team http://www.eng.cam.ac.uk/~cipolla/people.html Cognitive Systems Engineering Cognitive Systems Engineering Introduction Making
Computer Vision at Cambridge: Reconstruction,Registration and Recognition
 Computer Vision at Cambridge: Reconstruction,Registration and Recognition Roberto Cipolla Research team http://www.eng.cam.ac.uk/~cipolla/people.html Cognitive Systems Engineering Cognitive Systems Engineering
Computer Vision at Cambridge: Reconstruction,Registration and Recognition Roberto Cipolla Research team http://www.eng.cam.ac.uk/~cipolla/people.html Cognitive Systems Engineering Cognitive Systems Engineering
Why study Computer Vision?
 Computer Vision Why study Computer Vision? Images and movies are everywhere Fast-growing collection of useful applications building representations of the 3D world from pictures automated surveillance
Computer Vision Why study Computer Vision? Images and movies are everywhere Fast-growing collection of useful applications building representations of the 3D world from pictures automated surveillance
Analysis: TextonBoost and Semantic Texton Forests. Daniel Munoz Februrary 9, 2009
 Analysis: TextonBoost and Semantic Texton Forests Daniel Munoz 16-721 Februrary 9, 2009 Papers [shotton-eccv-06] J. Shotton, J. Winn, C. Rother, A. Criminisi, TextonBoost: Joint Appearance, Shape and Context
Analysis: TextonBoost and Semantic Texton Forests Daniel Munoz 16-721 Februrary 9, 2009 Papers [shotton-eccv-06] J. Shotton, J. Winn, C. Rother, A. Criminisi, TextonBoost: Joint Appearance, Shape and Context
Places Challenge 2017
 Places Challenge 2017 Scene Parsing Task CASIA_IVA_JD Jun Fu, Jing Liu, Longteng Guo, Haijie Tian, Fei Liu, Hanqing Lu Yong Li, Yongjun Bao, Weipeng Yan National Laboratory of Pattern Recognition, Institute
Places Challenge 2017 Scene Parsing Task CASIA_IVA_JD Jun Fu, Jing Liu, Longteng Guo, Haijie Tian, Fei Liu, Hanqing Lu Yong Li, Yongjun Bao, Weipeng Yan National Laboratory of Pattern Recognition, Institute
Object Recognition II
 Object Recognition II Linda Shapiro EE/CSE 576 with CNN slides from Ross Girshick 1 Outline Object detection the task, evaluation, datasets Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) overview and history Region-based
Object Recognition II Linda Shapiro EE/CSE 576 with CNN slides from Ross Girshick 1 Outline Object detection the task, evaluation, datasets Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) overview and history Region-based
Arbitrary Style Transfer in Real-Time with Adaptive Instance Normalization. Presented by: Karen Lucknavalai and Alexandr Kuznetsov
 Arbitrary Style Transfer in Real-Time with Adaptive Instance Normalization Presented by: Karen Lucknavalai and Alexandr Kuznetsov Example Style Content Result Motivation Transforming content of an image
Arbitrary Style Transfer in Real-Time with Adaptive Instance Normalization Presented by: Karen Lucknavalai and Alexandr Kuznetsov Example Style Content Result Motivation Transforming content of an image
Contents I IMAGE FORMATION 1
 Contents I IMAGE FORMATION 1 1 Geometric Camera Models 3 1.1 Image Formation............................. 4 1.1.1 Pinhole Perspective....................... 4 1.1.2 Weak Perspective.........................
Contents I IMAGE FORMATION 1 1 Geometric Camera Models 3 1.1 Image Formation............................. 4 1.1.1 Pinhole Perspective....................... 4 1.1.2 Weak Perspective.........................
6. Convolutional Neural Networks
 6. Convolutional Neural Networks CS 519 Deep Learning, Winter 2017 Fuxin Li With materials from Zsolt Kira Quiz coming up Next Thursday (2/2) 20 minutes Topics: Optimization Basic neural networks No Convolutional
6. Convolutional Neural Networks CS 519 Deep Learning, Winter 2017 Fuxin Li With materials from Zsolt Kira Quiz coming up Next Thursday (2/2) 20 minutes Topics: Optimization Basic neural networks No Convolutional
Semantic Segmentation
 Semantic Segmentation UCLA:https://goo.gl/images/I0VTi2 OUTLINE Semantic Segmentation Why? Paper to talk about: Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. J. Long, E. Shelhamer, and T. Darrell,
Semantic Segmentation UCLA:https://goo.gl/images/I0VTi2 OUTLINE Semantic Segmentation Why? Paper to talk about: Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. J. Long, E. Shelhamer, and T. Darrell,
Deep learning for dense per-pixel prediction. Chunhua Shen The University of Adelaide, Australia
 Deep learning for dense per-pixel prediction Chunhua Shen The University of Adelaide, Australia Image understanding Classification error Convolution Neural Networks 0.3 0.2 0.1 Image Classification [Krizhevsky
Deep learning for dense per-pixel prediction Chunhua Shen The University of Adelaide, Australia Image understanding Classification error Convolution Neural Networks 0.3 0.2 0.1 Image Classification [Krizhevsky
What is Computer Vision? Introduction. We all make mistakes. Why is this hard? What was happening. What do you see? Intro Computer Vision
 What is Computer Vision? Trucco and Verri (Text): Computing properties of the 3-D world from one or more digital images Introduction Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 1 Sockman and Shapiro:
What is Computer Vision? Trucco and Verri (Text): Computing properties of the 3-D world from one or more digital images Introduction Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 1 Sockman and Shapiro:
Why study Computer Vision?
 Why study Computer Vision? Images and movies are everywhere Fast-growing collection of useful applications building representations of the 3D world from pictures automated surveillance (who s doing what)
Why study Computer Vision? Images and movies are everywhere Fast-growing collection of useful applications building representations of the 3D world from pictures automated surveillance (who s doing what)
Deep condolence to Professor Mark Everingham
 Deep condolence to Professor Mark Everingham Towards VOC2012 Object Classification Challenge Generalized Hierarchical Matching for Sub-category Aware Object Classification National University of Singapore
Deep condolence to Professor Mark Everingham Towards VOC2012 Object Classification Challenge Generalized Hierarchical Matching for Sub-category Aware Object Classification National University of Singapore
Deep Models for 3D Reconstruction
 Deep Models for 3D Reconstruction Andreas Geiger Autonomous Vision Group, MPI for Intelligent Systems, Tübingen Computer Vision and Geometry Group, ETH Zürich October 12, 2017 Max Planck Institute for
Deep Models for 3D Reconstruction Andreas Geiger Autonomous Vision Group, MPI for Intelligent Systems, Tübingen Computer Vision and Geometry Group, ETH Zürich October 12, 2017 Max Planck Institute for
Learning to generate 3D shapes
 Learning to generate 3D shapes Subhransu Maji College of Information and Computer Sciences University of Massachusetts, Amherst http://people.cs.umass.edu/smaji August 10, 2018 @ Caltech Creating 3D shapes
Learning to generate 3D shapes Subhransu Maji College of Information and Computer Sciences University of Massachusetts, Amherst http://people.cs.umass.edu/smaji August 10, 2018 @ Caltech Creating 3D shapes
Computer Vision Lecture 17
 Computer Vision Lecture 17 Epipolar Geometry & Stereo Basics 13.01.2015 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Announcements Seminar in the summer semester
Computer Vision Lecture 17 Epipolar Geometry & Stereo Basics 13.01.2015 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Announcements Seminar in the summer semester
Yiqi Yan. May 10, 2017
 Yiqi Yan May 10, 2017 P a r t I F u n d a m e n t a l B a c k g r o u n d s Convolution Single Filter Multiple Filters 3 Convolution: case study, 2 filters 4 Convolution: receptive field receptive field
Yiqi Yan May 10, 2017 P a r t I F u n d a m e n t a l B a c k g r o u n d s Convolution Single Filter Multiple Filters 3 Convolution: case study, 2 filters 4 Convolution: receptive field receptive field
Computer Vision Lecture 17
 Announcements Computer Vision Lecture 17 Epipolar Geometry & Stereo Basics Seminar in the summer semester Current Topics in Computer Vision and Machine Learning Block seminar, presentations in 1 st week
Announcements Computer Vision Lecture 17 Epipolar Geometry & Stereo Basics Seminar in the summer semester Current Topics in Computer Vision and Machine Learning Block seminar, presentations in 1 st week
Presented at the FIG Congress 2018, May 6-11, 2018 in Istanbul, Turkey
 Presented at the FIG Congress 2018, May 6-11, 2018 in Istanbul, Turkey Evangelos MALTEZOS, Charalabos IOANNIDIS, Anastasios DOULAMIS and Nikolaos DOULAMIS Laboratory of Photogrammetry, School of Rural
Presented at the FIG Congress 2018, May 6-11, 2018 in Istanbul, Turkey Evangelos MALTEZOS, Charalabos IOANNIDIS, Anastasios DOULAMIS and Nikolaos DOULAMIS Laboratory of Photogrammetry, School of Rural
Deep Learning for Computer Vision with MATLAB By Jon Cherrie
 Deep Learning for Computer Vision with MATLAB By Jon Cherrie 2015 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 Deep learning is getting a lot of attention "Dahl and his colleagues won $22,000 with a deeplearning system. 'We
Deep Learning for Computer Vision with MATLAB By Jon Cherrie 2015 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 Deep learning is getting a lot of attention "Dahl and his colleagues won $22,000 with a deeplearning system. 'We
Object Detection on Self-Driving Cars in China. Lingyun Li
 Object Detection on Self-Driving Cars in China Lingyun Li Introduction Motivation: Perception is the key of self-driving cars Data set: 10000 images with annotation 2000 images without annotation (not
Object Detection on Self-Driving Cars in China Lingyun Li Introduction Motivation: Perception is the key of self-driving cars Data set: 10000 images with annotation 2000 images without annotation (not
Creating Affordable and Reliable Autonomous Vehicle Systems
 Creating Affordable and Reliable Autonomous Vehicle Systems Shaoshan Liu shaoshan.liu@perceptin.io Autonomous Driving Localization Most crucial task of autonomous driving Solutions: GNSS but withvariations,
Creating Affordable and Reliable Autonomous Vehicle Systems Shaoshan Liu shaoshan.liu@perceptin.io Autonomous Driving Localization Most crucial task of autonomous driving Solutions: GNSS but withvariations,
Predicting Depth, Surface Normals and Semantic Labels with a Common Multi-Scale Convolutional Architecture David Eigen, Rob Fergus
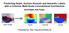 Predicting Depth, Surface Normals and Semantic Labels with a Common Multi-Scale Convolutional Architecture David Eigen, Rob Fergus Presented by: Rex Ying and Charles Qi Input: A Single RGB Image Estimate
Predicting Depth, Surface Normals and Semantic Labels with a Common Multi-Scale Convolutional Architecture David Eigen, Rob Fergus Presented by: Rex Ying and Charles Qi Input: A Single RGB Image Estimate
Internet of things that video
 Video recognition from a sentence Cees Snoek Intelligent Sensory Information Systems Lab University of Amsterdam The Netherlands Internet of things that video 45 billion cameras by 2022 [LDV Capital] 2
Video recognition from a sentence Cees Snoek Intelligent Sensory Information Systems Lab University of Amsterdam The Netherlands Internet of things that video 45 billion cameras by 2022 [LDV Capital] 2
Call for Proposals Media Technology HIRP OPEN 2017
 Call for Proposals HIRP OPEN 2017 1 Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2015-2016. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without
Call for Proposals HIRP OPEN 2017 1 Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2015-2016. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without
CS231N Section. Video Understanding 6/1/2018
 CS231N Section Video Understanding 6/1/2018 Outline Background / Motivation / History Video Datasets Models Pre-deep learning CNN + RNN 3D convolution Two-stream What we ve seen in class so far... Image
CS231N Section Video Understanding 6/1/2018 Outline Background / Motivation / History Video Datasets Models Pre-deep learning CNN + RNN 3D convolution Two-stream What we ve seen in class so far... Image
Video Object Segmentation using Deep Learning
 Video Object Segmentation using Deep Learning Update Presentation, Week 3 Zack While Advised by: Rui Hou, Dr. Chen Chen, and Dr. Mubarak Shah June 2, 2017 Youngstown State University 1 Table of Contents
Video Object Segmentation using Deep Learning Update Presentation, Week 3 Zack While Advised by: Rui Hou, Dr. Chen Chen, and Dr. Mubarak Shah June 2, 2017 Youngstown State University 1 Table of Contents
Computer Vision: Summary and Discussion
 12/05/2011 Computer Vision: Summary and Discussion Computer Vision CS 143, Brown James Hays Many slides from Derek Hoiem Announcements Today is last day of regular class Second quiz on Wednesday (Dec 7
12/05/2011 Computer Vision: Summary and Discussion Computer Vision CS 143, Brown James Hays Many slides from Derek Hoiem Announcements Today is last day of regular class Second quiz on Wednesday (Dec 7
Deep Learning. Deep Learning. Practical Application Automatically Adding Sounds To Silent Movies
 http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09/article/details/8775360 Automatic Colorization of Black and White Images Automatically Adding Sounds To Silent Movies Traditionally this was done by hand with human effort
http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09/article/details/8775360 Automatic Colorization of Black and White Images Automatically Adding Sounds To Silent Movies Traditionally this was done by hand with human effort
Deep Incremental Scene Understanding. Federico Tombari & Christian Rupprecht Technical University of Munich, Germany
 Deep Incremental Scene Understanding Federico Tombari & Christian Rupprecht Technical University of Munich, Germany C. Couprie et al. "Toward Real-time Indoor Semantic Segmentation Using Depth Information"
Deep Incremental Scene Understanding Federico Tombari & Christian Rupprecht Technical University of Munich, Germany C. Couprie et al. "Toward Real-time Indoor Semantic Segmentation Using Depth Information"
List of Accepted Papers for ICVGIP 2018
 List of Accepted Papers for ICVGIP 2018 Paper ID ACM Article Title 3 1 PredGAN - A deep multi-scale video prediction framework for anomaly detection in videos 7 2 Handwritten Essay Grading on Mobiles using
List of Accepted Papers for ICVGIP 2018 Paper ID ACM Article Title 3 1 PredGAN - A deep multi-scale video prediction framework for anomaly detection in videos 7 2 Handwritten Essay Grading on Mobiles using
Lecture 7: Semantic Segmentation
 Semantic Segmentation CSED703R: Deep Learning for Visual Recognition (207F) Segmenting images based on its semantic notion Lecture 7: Semantic Segmentation Bohyung Han Computer Vision Lab. bhhanpostech.ac.kr
Semantic Segmentation CSED703R: Deep Learning for Visual Recognition (207F) Segmenting images based on its semantic notion Lecture 7: Semantic Segmentation Bohyung Han Computer Vision Lab. bhhanpostech.ac.kr
Semantic Video Indexing
 Semantic Video Indexing T-61.6030 Multimedia Retrieval Stevan Keraudy stevan.keraudy@tkk.fi Helsinki University of Technology March 14, 2008 What is it? Query by keyword or tag is common Semantic Video
Semantic Video Indexing T-61.6030 Multimedia Retrieval Stevan Keraudy stevan.keraudy@tkk.fi Helsinki University of Technology March 14, 2008 What is it? Query by keyword or tag is common Semantic Video
Object Detection Lecture Introduction to deep learning (CNN) Idar Dyrdal
 Object Detection Lecture 10.3 - Introduction to deep learning (CNN) Idar Dyrdal Deep Learning Labels Computational models composed of multiple processing layers (non-linear transformations) Used to learn
Object Detection Lecture 10.3 - Introduction to deep learning (CNN) Idar Dyrdal Deep Learning Labels Computational models composed of multiple processing layers (non-linear transformations) Used to learn
Computer Vision. From traditional approaches to deep neural networks. Stanislav Frolov München,
 Computer Vision From traditional approaches to deep neural networks Stanislav Frolov München, 27.02.2018 Outline of this talk What we are going to talk about Computer vision Human vision Traditional approaches
Computer Vision From traditional approaches to deep neural networks Stanislav Frolov München, 27.02.2018 Outline of this talk What we are going to talk about Computer vision Human vision Traditional approaches
Lecture 5: Object Detection
 Object Detection CSED703R: Deep Learning for Visual Recognition (2017F) Lecture 5: Object Detection Bohyung Han Computer Vision Lab. bhhan@postech.ac.kr 2 Traditional Object Detection Algorithms Region-based
Object Detection CSED703R: Deep Learning for Visual Recognition (2017F) Lecture 5: Object Detection Bohyung Han Computer Vision Lab. bhhan@postech.ac.kr 2 Traditional Object Detection Algorithms Region-based
Attributes. Computer Vision. James Hays. Many slides from Derek Hoiem
 Many slides from Derek Hoiem Attributes Computer Vision James Hays Recap: Human Computation Active Learning: Let the classifier tell you where more annotation is needed. Human-in-the-loop recognition:
Many slides from Derek Hoiem Attributes Computer Vision James Hays Recap: Human Computation Active Learning: Let the classifier tell you where more annotation is needed. Human-in-the-loop recognition:
2 OVERVIEW OF RELATED WORK
 Utsushi SAKAI Jun OGATA This paper presents a pedestrian detection system based on the fusion of sensors for LIDAR and convolutional neural network based image classification. By using LIDAR our method
Utsushi SAKAI Jun OGATA This paper presents a pedestrian detection system based on the fusion of sensors for LIDAR and convolutional neural network based image classification. By using LIDAR our method
Encoder-Decoder Networks for Semantic Segmentation. Sachin Mehta
 Encoder-Decoder Networks for Semantic Segmentation Sachin Mehta Outline > Overview of Semantic Segmentation > Encoder-Decoder Networks > Results What is Semantic Segmentation? Input: RGB Image Output:
Encoder-Decoder Networks for Semantic Segmentation Sachin Mehta Outline > Overview of Semantic Segmentation > Encoder-Decoder Networks > Results What is Semantic Segmentation? Input: RGB Image Output:
Does the Brain do Inverse Graphics?
 Does the Brain do Inverse Graphics? Geoffrey Hinton, Alex Krizhevsky, Navdeep Jaitly, Tijmen Tieleman & Yichuan Tang Department of Computer Science University of Toronto The representation used by the
Does the Brain do Inverse Graphics? Geoffrey Hinton, Alex Krizhevsky, Navdeep Jaitly, Tijmen Tieleman & Yichuan Tang Department of Computer Science University of Toronto The representation used by the
RGBd Image Semantic Labelling for Urban Driving Scenes via a DCNN
 RGBd Image Semantic Labelling for Urban Driving Scenes via a DCNN Jason Bolito, Research School of Computer Science, ANU Supervisors: Yiran Zhong & Hongdong Li 2 Outline 1. Motivation and Background 2.
RGBd Image Semantic Labelling for Urban Driving Scenes via a DCNN Jason Bolito, Research School of Computer Science, ANU Supervisors: Yiran Zhong & Hongdong Li 2 Outline 1. Motivation and Background 2.
24 hours of Photo Sharing. installation by Erik Kessels
 24 hours of Photo Sharing installation by Erik Kessels And sometimes Internet photos have useful labels Im2gps. Hays and Efros. CVPR 2008 But what if we want more? Image Categorization Training Images
24 hours of Photo Sharing installation by Erik Kessels And sometimes Internet photos have useful labels Im2gps. Hays and Efros. CVPR 2008 But what if we want more? Image Categorization Training Images
Does the Brain do Inverse Graphics?
 Does the Brain do Inverse Graphics? Geoffrey Hinton, Alex Krizhevsky, Navdeep Jaitly, Tijmen Tieleman & Yichuan Tang Department of Computer Science University of Toronto How to learn many layers of features
Does the Brain do Inverse Graphics? Geoffrey Hinton, Alex Krizhevsky, Navdeep Jaitly, Tijmen Tieleman & Yichuan Tang Department of Computer Science University of Toronto How to learn many layers of features
Object Detection. Part1. Presenter: Dae-Yong
 Object Part1 Presenter: Dae-Yong Contents 1. What is an Object? 2. Traditional Object Detector 3. Deep Learning-based Object Detector What is an Object? Subset of Object Recognition What is an Object?
Object Part1 Presenter: Dae-Yong Contents 1. What is an Object? 2. Traditional Object Detector 3. Deep Learning-based Object Detector What is an Object? Subset of Object Recognition What is an Object?
VISION FOR AUTOMOTIVE DRIVING
 VISION FOR AUTOMOTIVE DRIVING French Japanese Workshop on Deep Learning & AI, Paris, October 25th, 2017 Quoc Cuong PHAM, PhD Vision and Content Engineering Lab AI & MACHINE LEARNING FOR ADAS AND SELF-DRIVING
VISION FOR AUTOMOTIVE DRIVING French Japanese Workshop on Deep Learning & AI, Paris, October 25th, 2017 Quoc Cuong PHAM, PhD Vision and Content Engineering Lab AI & MACHINE LEARNING FOR ADAS AND SELF-DRIVING
Learning Deep Structured Models for Semantic Segmentation. Guosheng Lin
 Learning Deep Structured Models for Semantic Segmentation Guosheng Lin Semantic Segmentation Outline Exploring Context with Deep Structured Models Guosheng Lin, Chunhua Shen, Ian Reid, Anton van dan Hengel;
Learning Deep Structured Models for Semantic Segmentation Guosheng Lin Semantic Segmentation Outline Exploring Context with Deep Structured Models Guosheng Lin, Chunhua Shen, Ian Reid, Anton van dan Hengel;
Deformable Part Models
 CS 1674: Intro to Computer Vision Deformable Part Models Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh November 9, 2016 Today: Object category detection Window-based approaches: Last time: Viola-Jones
CS 1674: Intro to Computer Vision Deformable Part Models Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh November 9, 2016 Today: Object category detection Window-based approaches: Last time: Viola-Jones
Structure from Motion. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 10
 Structure from Motion CSE 152 Lecture 10 Announcements Homework 3 is due May 9, 11:59 PM Reading: Chapter 8: Structure from Motion Optional: Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision, 2nd edition, Hartley
Structure from Motion CSE 152 Lecture 10 Announcements Homework 3 is due May 9, 11:59 PM Reading: Chapter 8: Structure from Motion Optional: Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision, 2nd edition, Hartley
Nonlinear State Estimation for Robotics and Computer Vision Applications: An Overview
 Nonlinear State Estimation for Robotics and Computer Vision Applications: An Overview Arun Das 05/09/2017 Arun Das Waterloo Autonomous Vehicles Lab Introduction What s in a name? Arun Das Waterloo Autonomous
Nonlinear State Estimation for Robotics and Computer Vision Applications: An Overview Arun Das 05/09/2017 Arun Das Waterloo Autonomous Vehicles Lab Introduction What s in a name? Arun Das Waterloo Autonomous
CS 4495 Computer Vision A. Bobick. Motion and Optic Flow. Stereo Matching
 Stereo Matching Fundamental matrix Let p be a point in left image, p in right image l l Epipolar relation p maps to epipolar line l p maps to epipolar line l p p Epipolar mapping described by a 3x3 matrix
Stereo Matching Fundamental matrix Let p be a point in left image, p in right image l l Epipolar relation p maps to epipolar line l p maps to epipolar line l p p Epipolar mapping described by a 3x3 matrix
Deep Learning for Virtual Shopping. Dr. Jürgen Sturm Group Leader RGB-D
 Deep Learning for Virtual Shopping Dr. Jürgen Sturm Group Leader RGB-D metaio GmbH Augmented Reality with the Metaio SDK: IKEA Catalogue App Metaio: Augmented Reality Metaio SDK for ios, Android and Windows
Deep Learning for Virtual Shopping Dr. Jürgen Sturm Group Leader RGB-D metaio GmbH Augmented Reality with the Metaio SDK: IKEA Catalogue App Metaio: Augmented Reality Metaio SDK for ios, Android and Windows
Structured Models in. Dan Huttenlocher. June 2010
 Structured Models in Computer Vision i Dan Huttenlocher June 2010 Structured Models Problems where output variables are mutually dependent or constrained E.g., spatial or temporal relations Such dependencies
Structured Models in Computer Vision i Dan Huttenlocher June 2010 Structured Models Problems where output variables are mutually dependent or constrained E.g., spatial or temporal relations Such dependencies
Learning Semantic Environment Perception for Cognitive Robots
 Learning Semantic Environment Perception for Cognitive Robots Sven Behnke University of Bonn, Germany Computer Science Institute VI Autonomous Intelligent Systems Some of Our Cognitive Robots Equipped
Learning Semantic Environment Perception for Cognitive Robots Sven Behnke University of Bonn, Germany Computer Science Institute VI Autonomous Intelligent Systems Some of Our Cognitive Robots Equipped
Topics to be Covered in the Rest of the Semester. CSci 4968 and 6270 Computational Vision Lecture 15 Overview of Remainder of the Semester
 Topics to be Covered in the Rest of the Semester CSci 4968 and 6270 Computational Vision Lecture 15 Overview of Remainder of the Semester Charles Stewart Department of Computer Science Rensselaer Polytechnic
Topics to be Covered in the Rest of the Semester CSci 4968 and 6270 Computational Vision Lecture 15 Overview of Remainder of the Semester Charles Stewart Department of Computer Science Rensselaer Polytechnic
Multi-View 3D Object Detection Network for Autonomous Driving
 Multi-View 3D Object Detection Network for Autonomous Driving Xiaozhi Chen, Huimin Ma, Ji Wan, Bo Li, Tian Xia CVPR 2017 (Spotlight) Presented By: Jason Ku Overview Motivation Dataset Network Architecture
Multi-View 3D Object Detection Network for Autonomous Driving Xiaozhi Chen, Huimin Ma, Ji Wan, Bo Li, Tian Xia CVPR 2017 (Spotlight) Presented By: Jason Ku Overview Motivation Dataset Network Architecture
INTRODUCTION TO DEEP LEARNING
 INTRODUCTION TO DEEP LEARNING CONTENTS Introduction to deep learning Contents 1. Examples 2. Machine learning 3. Neural networks 4. Deep learning 5. Convolutional neural networks 6. Conclusion 7. Additional
INTRODUCTION TO DEEP LEARNING CONTENTS Introduction to deep learning Contents 1. Examples 2. Machine learning 3. Neural networks 4. Deep learning 5. Convolutional neural networks 6. Conclusion 7. Additional
AUTOMATIC VIDEO INDEXING
 AUTOMATIC VIDEO INDEXING Itxaso Bustos Maite Frutos TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction Methods Key-frame extraction Automatic visual indexing Shot boundary detection Video OCR Index in motion Image processing
AUTOMATIC VIDEO INDEXING Itxaso Bustos Maite Frutos TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction Methods Key-frame extraction Automatic visual indexing Shot boundary detection Video OCR Index in motion Image processing
Joint Inference in Image Databases via Dense Correspondence. Michael Rubinstein MIT CSAIL (while interning at Microsoft Research)
 Joint Inference in Image Databases via Dense Correspondence Michael Rubinstein MIT CSAIL (while interning at Microsoft Research) My work Throughout the year (and my PhD thesis): Temporal Video Analysis
Joint Inference in Image Databases via Dense Correspondence Michael Rubinstein MIT CSAIL (while interning at Microsoft Research) My work Throughout the year (and my PhD thesis): Temporal Video Analysis
Unified, real-time object detection
 Unified, real-time object detection Final Project Report, Group 02, 8 Nov 2016 Akshat Agarwal (13068), Siddharth Tanwar (13699) CS698N: Recent Advances in Computer Vision, Jul Nov 2016 Instructor: Gaurav
Unified, real-time object detection Final Project Report, Group 02, 8 Nov 2016 Akshat Agarwal (13068), Siddharth Tanwar (13699) CS698N: Recent Advances in Computer Vision, Jul Nov 2016 Instructor: Gaurav
Why equivariance is better than premature invariance
 1 Why equivariance is better than premature invariance Geoffrey Hinton Canadian Institute for Advanced Research & Department of Computer Science University of Toronto with contributions from Sida Wang
1 Why equivariance is better than premature invariance Geoffrey Hinton Canadian Institute for Advanced Research & Department of Computer Science University of Toronto with contributions from Sida Wang
Detection III: Analyzing and Debugging Detection Methods
 CS 1699: Intro to Computer Vision Detection III: Analyzing and Debugging Detection Methods Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh November 17, 2015 Today Review: Deformable part models How can
CS 1699: Intro to Computer Vision Detection III: Analyzing and Debugging Detection Methods Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh November 17, 2015 Today Review: Deformable part models How can
Towards Large-Scale Semantic Representations for Actionable Exploitation. Prof. Trevor Darrell UC Berkeley
 Towards Large-Scale Semantic Representations for Actionable Exploitation Prof. Trevor Darrell UC Berkeley traditional surveillance sensor emerging crowd sensor Desired capabilities: spatio-temporal reconstruction
Towards Large-Scale Semantic Representations for Actionable Exploitation Prof. Trevor Darrell UC Berkeley traditional surveillance sensor emerging crowd sensor Desired capabilities: spatio-temporal reconstruction
Machine Learning 13. week
 Machine Learning 13. week Deep Learning Convolutional Neural Network Recurrent Neural Network 1 Why Deep Learning is so Popular? 1. Increase in the amount of data Thanks to the Internet, huge amount of
Machine Learning 13. week Deep Learning Convolutional Neural Network Recurrent Neural Network 1 Why Deep Learning is so Popular? 1. Increase in the amount of data Thanks to the Internet, huge amount of
Semantic RGB-D Perception for Cognitive Robots
 Semantic RGB-D Perception for Cognitive Robots Sven Behnke Computer Science Institute VI Autonomous Intelligent Systems Our Domestic Service Robots Dynamaid Cosero Size: 100-180 cm, weight: 30-35 kg 36
Semantic RGB-D Perception for Cognitive Robots Sven Behnke Computer Science Institute VI Autonomous Intelligent Systems Our Domestic Service Robots Dynamaid Cosero Size: 100-180 cm, weight: 30-35 kg 36
Associating video frames with text
 Associating video frames with text Pinar Duygulu and Howard Wactlar Informedia Project School of Computer Science University Informedia Digital Video Understanding Project IDVL interface returned for "El
Associating video frames with text Pinar Duygulu and Howard Wactlar Informedia Project School of Computer Science University Informedia Digital Video Understanding Project IDVL interface returned for "El
Object Recognition. Lecture 11, April 21 st, Lexing Xie. EE4830 Digital Image Processing
 Object Recognition Lecture 11, April 21 st, 2008 Lexing Xie EE4830 Digital Image Processing http://www.ee.columbia.edu/~xlx/ee4830/ 1 Announcements 2 HW#5 due today HW#6 last HW of the semester Due May
Object Recognition Lecture 11, April 21 st, 2008 Lexing Xie EE4830 Digital Image Processing http://www.ee.columbia.edu/~xlx/ee4830/ 1 Announcements 2 HW#5 due today HW#6 last HW of the semester Due May
Content-Based Image Recovery
 Content-Based Image Recovery Hong-Yu Zhou and Jianxin Wu National Key Laboratory for Novel Software Technology Nanjing University, China zhouhy@lamda.nju.edu.cn wujx2001@nju.edu.cn Abstract. We propose
Content-Based Image Recovery Hong-Yu Zhou and Jianxin Wu National Key Laboratory for Novel Software Technology Nanjing University, China zhouhy@lamda.nju.edu.cn wujx2001@nju.edu.cn Abstract. We propose
3D Scanning. Qixing Huang Feb. 9 th Slide Credit: Yasutaka Furukawa
 3D Scanning Qixing Huang Feb. 9 th 2017 Slide Credit: Yasutaka Furukawa Geometry Reconstruction Pipeline This Lecture Depth Sensing ICP for Pair-wise Alignment Next Lecture Global Alignment Pairwise Multiple
3D Scanning Qixing Huang Feb. 9 th 2017 Slide Credit: Yasutaka Furukawa Geometry Reconstruction Pipeline This Lecture Depth Sensing ICP for Pair-wise Alignment Next Lecture Global Alignment Pairwise Multiple
Multi-Class Segmentation with Relative Location Prior
 Multi-Class Segmentation with Relative Location Prior Stephen Gould, Jim Rodgers, David Cohen, Gal Elidan, Daphne Koller Department of Computer Science, Stanford University International Journal of Computer
Multi-Class Segmentation with Relative Location Prior Stephen Gould, Jim Rodgers, David Cohen, Gal Elidan, Daphne Koller Department of Computer Science, Stanford University International Journal of Computer
CMU Lecture 18: Deep learning and Vision: Convolutional neural networks. Teacher: Gianni A. Di Caro
 CMU 15-781 Lecture 18: Deep learning and Vision: Convolutional neural networks Teacher: Gianni A. Di Caro DEEP, SHALLOW, CONNECTED, SPARSE? Fully connected multi-layer feed-forward perceptrons: More powerful
CMU 15-781 Lecture 18: Deep learning and Vision: Convolutional neural networks Teacher: Gianni A. Di Caro DEEP, SHALLOW, CONNECTED, SPARSE? Fully connected multi-layer feed-forward perceptrons: More powerful
Computer Vision with MATLAB MATLAB Expo 2012 Steve Kuznicki
 Computer Vision with MATLAB MATLAB Expo 2012 Steve Kuznicki 2011 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 Today s Topics Introduction Computer Vision Feature-based registration Automatic image registration Object recognition/rotation
Computer Vision with MATLAB MATLAB Expo 2012 Steve Kuznicki 2011 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 Today s Topics Introduction Computer Vision Feature-based registration Automatic image registration Object recognition/rotation
Depth. Common Classification Tasks. Example: AlexNet. Another Example: Inception. Another Example: Inception. Depth
 Common Classification Tasks Recognition of individual objects/faces Analyze object-specific features (e.g., key points) Train with images from different viewing angles Recognition of object classes Analyze
Common Classification Tasks Recognition of individual objects/faces Analyze object-specific features (e.g., key points) Train with images from different viewing angles Recognition of object classes Analyze
Su et al. Shape Descriptors - III
 Su et al. Shape Descriptors - III Siddhartha Chaudhuri http://www.cse.iitb.ac.in/~cs749 Funkhouser; Feng, Liu, Gong Recap Global A shape descriptor is a set of numbers that describes a shape in a way that
Su et al. Shape Descriptors - III Siddhartha Chaudhuri http://www.cse.iitb.ac.in/~cs749 Funkhouser; Feng, Liu, Gong Recap Global A shape descriptor is a set of numbers that describes a shape in a way that
Colorado School of Mines. Computer Vision. Professor William Hoff Dept of Electrical Engineering &Computer Science.
 Professor William Hoff Dept of Electrical Engineering &Computer Science http://inside.mines.edu/~whoff/ 1 Model Based Object Recognition 2 Object Recognition Overview Instance recognition Recognize a known
Professor William Hoff Dept of Electrical Engineering &Computer Science http://inside.mines.edu/~whoff/ 1 Model Based Object Recognition 2 Object Recognition Overview Instance recognition Recognize a known
Learning and Recognizing Visual Object Categories Without First Detecting Features
 Learning and Recognizing Visual Object Categories Without First Detecting Features Daniel Huttenlocher 2007 Joint work with D. Crandall and P. Felzenszwalb Object Category Recognition Generic classes rather
Learning and Recognizing Visual Object Categories Without First Detecting Features Daniel Huttenlocher 2007 Joint work with D. Crandall and P. Felzenszwalb Object Category Recognition Generic classes rather
CAP 5415 Computer Vision. Fall 2011
 CAP 5415 Computer Vision Fall 2011 General Instructor: Dr. Mubarak Shah Email: shah@eecs.ucf.edu Office: 247-F HEC Course Class Time Tuesdays, Thursdays 12 Noon to 1:15PM 383 ENGR Office hours Tuesdays
CAP 5415 Computer Vision Fall 2011 General Instructor: Dr. Mubarak Shah Email: shah@eecs.ucf.edu Office: 247-F HEC Course Class Time Tuesdays, Thursdays 12 Noon to 1:15PM 383 ENGR Office hours Tuesdays
Vision based autonomous driving - A survey of recent methods. -Tejus Gupta
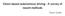 Vision based autonomous driving - A survey of recent methods -Tejus Gupta Presently, there are three major paradigms for vision based autonomous driving: Directly map input image to driving action using
Vision based autonomous driving - A survey of recent methods -Tejus Gupta Presently, there are three major paradigms for vision based autonomous driving: Directly map input image to driving action using
Colorado School of Mines. Computer Vision. Professor William Hoff Dept of Electrical Engineering &Computer Science.
 Professor William Hoff Dept of Electrical Engineering &Computer Science http://inside.mines.edu/~whoff/ 1 Introduction to 2 What is? A process that produces from images of the external world a description
Professor William Hoff Dept of Electrical Engineering &Computer Science http://inside.mines.edu/~whoff/ 1 Introduction to 2 What is? A process that produces from images of the external world a description
Augmenting Reality, Naturally:
 Augmenting Reality, Naturally: Scene Modelling, Recognition and Tracking with Invariant Image Features by Iryna Gordon in collaboration with David G. Lowe Laboratory for Computational Intelligence Department
Augmenting Reality, Naturally: Scene Modelling, Recognition and Tracking with Invariant Image Features by Iryna Gordon in collaboration with David G. Lowe Laboratory for Computational Intelligence Department
Paper Motivation. Fixed geometric structures of CNN models. CNNs are inherently limited to model geometric transformations
 Paper Motivation Fixed geometric structures of CNN models CNNs are inherently limited to model geometric transformations Higher-level features combine lower-level features at fixed positions as a weighted
Paper Motivation Fixed geometric structures of CNN models CNNs are inherently limited to model geometric transformations Higher-level features combine lower-level features at fixed positions as a weighted
Towards Fully-automated Driving. tue-mps.org. Challenges and Potential Solutions. Dr. Gijs Dubbelman Mobile Perception Systems EE-SPS/VCA
 Towards Fully-automated Driving Challenges and Potential Solutions Dr. Gijs Dubbelman Mobile Perception Systems EE-SPS/VCA Mobile Perception Systems 6 PhDs, 1 postdoc, 1 project manager, 2 software engineers
Towards Fully-automated Driving Challenges and Potential Solutions Dr. Gijs Dubbelman Mobile Perception Systems EE-SPS/VCA Mobile Perception Systems 6 PhDs, 1 postdoc, 1 project manager, 2 software engineers
Computer Vision I - Introduction
 Computer Vision I - Introduction Carsten Rother 21/10/2014 Computer Vision I:Introduction Computer Vision I: Introduction 21/10/2014 2 Admin Stuff Language: German/English; Slides: English (all the terminology
Computer Vision I - Introduction Carsten Rother 21/10/2014 Computer Vision I:Introduction Computer Vision I: Introduction 21/10/2014 2 Admin Stuff Language: German/English; Slides: English (all the terminology
Turning an Automated System into an Autonomous system using Model-Based Design Autonomous Tech Conference 2018
 Turning an Automated System into an Autonomous system using Model-Based Design Autonomous Tech Conference 2018 Asaf Moses Systematics Ltd., Technical Product Manager aviasafm@systematics.co.il 1 Autonomous
Turning an Automated System into an Autonomous system using Model-Based Design Autonomous Tech Conference 2018 Asaf Moses Systematics Ltd., Technical Product Manager aviasafm@systematics.co.il 1 Autonomous
SEMANTIC segmentation has a wide array of applications
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON PATTERN ANALYSIS AND MACHINE INTELLIGENCE, VOL. 39, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2017 2481 SegNet: A Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Image Segmentation Vijay Badrinarayanan,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON PATTERN ANALYSIS AND MACHINE INTELLIGENCE, VOL. 39, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2017 2481 SegNet: A Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Image Segmentation Vijay Badrinarayanan,
Stereo. 11/02/2012 CS129, Brown James Hays. Slides by Kristen Grauman
 Stereo 11/02/2012 CS129, Brown James Hays Slides by Kristen Grauman Multiple views Multi-view geometry, matching, invariant features, stereo vision Lowe Hartley and Zisserman Why multiple views? Structure
Stereo 11/02/2012 CS129, Brown James Hays Slides by Kristen Grauman Multiple views Multi-view geometry, matching, invariant features, stereo vision Lowe Hartley and Zisserman Why multiple views? Structure
Vision is inferential. (
 Announcements Final: Thursday, December 15, 8am, here. Review Session, Wednesday, Dec 14, 1pm, AV Williams 4424. Review sheet with practice problems on-line. Hints for Final Focus on core techniques/ideas:
Announcements Final: Thursday, December 15, 8am, here. Review Session, Wednesday, Dec 14, 1pm, AV Williams 4424. Review sheet with practice problems on-line. Hints for Final Focus on core techniques/ideas:
The Hilbert Problems of Computer Vision. Jitendra Malik UC Berkeley & Google, Inc.
 The Hilbert Problems of Computer Vision Jitendra Malik UC Berkeley & Google, Inc. This talk The computational power of the human brain Research is the art of the soluble Hilbert problems, circa 2004 Hilbert
The Hilbert Problems of Computer Vision Jitendra Malik UC Berkeley & Google, Inc. This talk The computational power of the human brain Research is the art of the soluble Hilbert problems, circa 2004 Hilbert
CS 4495 Computer Vision A. Bobick. Motion and Optic Flow. Stereo Matching
 Stereo Matching Fundamental matrix Let p be a point in left image, p in right image l l Epipolar relation p maps to epipolar line l p maps to epipolar line l p p Epipolar mapping described by a 3x3 matrix
Stereo Matching Fundamental matrix Let p be a point in left image, p in right image l l Epipolar relation p maps to epipolar line l p maps to epipolar line l p p Epipolar mapping described by a 3x3 matrix
Multiple Model Estimation : The EM Algorithm & Applications
 Multiple Model Estimation : The EM Algorithm & Applications Princeton University COS 429 Lecture Nov. 13, 2007 Harpreet S. Sawhney hsawhney@sarnoff.com Recapitulation Problem of motion estimation Parametric
Multiple Model Estimation : The EM Algorithm & Applications Princeton University COS 429 Lecture Nov. 13, 2007 Harpreet S. Sawhney hsawhney@sarnoff.com Recapitulation Problem of motion estimation Parametric
Stereo. Outline. Multiple views 3/29/2017. Thurs Mar 30 Kristen Grauman UT Austin. Multi-view geometry, matching, invariant features, stereo vision
 Stereo Thurs Mar 30 Kristen Grauman UT Austin Outline Last time: Human stereopsis Epipolar geometry and the epipolar constraint Case example with parallel optical axes General case with calibrated cameras
Stereo Thurs Mar 30 Kristen Grauman UT Austin Outline Last time: Human stereopsis Epipolar geometry and the epipolar constraint Case example with parallel optical axes General case with calibrated cameras
Solution: filter the image, then subsample F 1 F 2. subsample blur subsample. blur
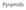 Pyramids Gaussian pre-filtering Solution: filter the image, then subsample blur F 0 subsample blur subsample * F 0 H F 1 F 1 * H F 2 { Gaussian pyramid blur F 0 subsample blur subsample * F 0 H F 1 F 1
Pyramids Gaussian pre-filtering Solution: filter the image, then subsample blur F 0 subsample blur subsample * F 0 H F 1 F 1 * H F 2 { Gaussian pyramid blur F 0 subsample blur subsample * F 0 H F 1 F 1
視覚情報処理論. (Visual Information Processing ) 開講所属 : 学際情報学府水 (Wed)5 [16:50-18:35]
![視覚情報処理論. (Visual Information Processing ) 開講所属 : 学際情報学府水 (Wed)5 [16:50-18:35] 視覚情報処理論. (Visual Information Processing ) 開講所属 : 学際情報学府水 (Wed)5 [16:50-18:35]](/thumbs/95/123948781.jpg) 視覚情報処理論 (Visual Information Processing ) 開講所属 : 学際情報学府水 (Wed)5 [16:50-18:35] Computer Vision Design algorithms to implement the function of human vision 3D reconstruction from 2D image (retinal image)
視覚情報処理論 (Visual Information Processing ) 開講所属 : 学際情報学府水 (Wed)5 [16:50-18:35] Computer Vision Design algorithms to implement the function of human vision 3D reconstruction from 2D image (retinal image)
An Evaluation of Volumetric Interest Points
 An Evaluation of Volumetric Interest Points Tsz-Ho YU Oliver WOODFORD Roberto CIPOLLA Machine Intelligence Lab Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge About this project We conducted the first
An Evaluation of Volumetric Interest Points Tsz-Ho YU Oliver WOODFORD Roberto CIPOLLA Machine Intelligence Lab Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge About this project We conducted the first
Markov Networks in Computer Vision
 Markov Networks in Computer Vision Sargur Srihari srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu 1 Markov Networks for Computer Vision Some applications: 1. Image segmentation 2. Removal of blur/noise 3. Stereo reconstruction
Markov Networks in Computer Vision Sargur Srihari srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu 1 Markov Networks for Computer Vision Some applications: 1. Image segmentation 2. Removal of blur/noise 3. Stereo reconstruction
Recognizing Deformable Shapes. Salvador Ruiz Correa (CSE/EE576 Computer Vision I)
 Recognizing Deformable Shapes Salvador Ruiz Correa (CSE/EE576 Computer Vision I) Input 3-D Object Goal We are interested in developing algorithms for recognizing and classifying deformable object shapes
Recognizing Deformable Shapes Salvador Ruiz Correa (CSE/EE576 Computer Vision I) Input 3-D Object Goal We are interested in developing algorithms for recognizing and classifying deformable object shapes
A Deep Learning Approach to Vehicle Speed Estimation
 A Deep Learning Approach to Vehicle Speed Estimation Benjamin Penchas bpenchas@stanford.edu Tobin Bell tbell@stanford.edu Marco Monteiro marcorm@stanford.edu ABSTRACT Given car dashboard video footage,
A Deep Learning Approach to Vehicle Speed Estimation Benjamin Penchas bpenchas@stanford.edu Tobin Bell tbell@stanford.edu Marco Monteiro marcorm@stanford.edu ABSTRACT Given car dashboard video footage,
Object Detection Based on Deep Learning
 Object Detection Based on Deep Learning Yurii Pashchenko AI Ukraine 2016, Kharkiv, 2016 Image classification (mostly what you ve seen) http://tutorial.caffe.berkeleyvision.org/caffe-cvpr15-detection.pdf
Object Detection Based on Deep Learning Yurii Pashchenko AI Ukraine 2016, Kharkiv, 2016 Image classification (mostly what you ve seen) http://tutorial.caffe.berkeleyvision.org/caffe-cvpr15-detection.pdf
Dynamic Routing Between Capsules. Yiting Ethan Li, Haakon Hukkelaas, and Kaushik Ram Ramasamy
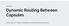 Dynamic Routing Between Capsules Yiting Ethan Li, Haakon Hukkelaas, and Kaushik Ram Ramasamy Problems & Results Object classification in images without losing information about important parts of the picture.
Dynamic Routing Between Capsules Yiting Ethan Li, Haakon Hukkelaas, and Kaushik Ram Ramasamy Problems & Results Object classification in images without losing information about important parts of the picture.
Automatic Thoracic CT Image Segmentation using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Xiao Han, Ph.D.
 Automatic Thoracic CT Image Segmentation using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Xiao Han, Ph.D. Outline Background Brief Introduction to DCNN Method Results 2 Focus where it matters Structure Segmentation
Automatic Thoracic CT Image Segmentation using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Xiao Han, Ph.D. Outline Background Brief Introduction to DCNN Method Results 2 Focus where it matters Structure Segmentation
