A 65nm Dual-mode Baseband and Multimedia Application Processor SoC with Advanced Power and Memory Management
|
|
|
- Jasper Morton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A 65nm Dual-mode Baseband and Multimedia Application Processor SoC with Advanced Power and Memory Management Tatsuya Kamei, Tetsuhiro Yamada, Takao Koike, Masayuki Ito, Takahiro Irita, Kenichi Nitta, Toshihiro Hattori, Shinichi Yoshioka Renesas Technology Corp.
2 2 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Chip Architecture 3. Power Management Static Power (Hierarchical Power Domain) Dynamic Power (Partial Clock Activation) 4. Memory Management IP-MMU 5. Summary
3 Introduction(1) Trend of Mobile phone In a 2G handset, a baseband processor executed applications in addition to modem control. (RTOS) In a high-end 3G handset, applications require High-Level-OS and rich multimedia functions. 3(BB, AP, and MM) processors in a handset. System cost increase 1 chip integration 2G (Conventional) 3G system RF RTOS Baseband Processor Multimedia Accelerator RF 1 chip RTOS Baseband Processor HLOS Application Processor Multimedia Processor 3
4 4 Introduction(2) Challenges Low Power Limited battery capacity No fan High Performance Digital TV Mega-pixel camera 3D graphics for games and UI System Cost Memory capacity (SDRAM, NAND/NOR FLASH) Packaging (SIP, POP)
5 Introduction(3) History of SH-Mobile G 1 st generation SH-Mobile G1 In mass production from M Transistors, 90nm LP Hierarchical Power Domain for leakage reduction 2 nd generation SH-Mobile G2 In mass production from M Transistors, 90nm LP Inter-Connect Buffer for high-performance multimedia 3 rd generation SH-Mobile G3 In mass production from M Transistors, 65nm LP Partial Clock Activation for dynamic power reduction IP-MMU for memory footprint reduction 5
6 6 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Chip Architecture 3. Power Management Static Power (Hierarchical Power Domain) Dynamic Power (Partial Clock Activation) 4. Memory Management IP-MMU 5. Summary
7 SH-Mobile G3 Chip Specifications CPU ARM926EJ-S, 166MHz [ baseband ] 3G/2G modem Multimedia hardware engines I/O ARM1176JZF-S, 500MHz [ application ] SH-X2, 500MHz [ multimedia ] W-CDMA/HSDPA Cat. 8 (up to 7.2 Mbps), GSM/GPRS/EDGE Video Processing Unit(VPU) (MPEG4/H.264/VC-1 D1 size), Sound Processing Unit(SPU), 3D/2D Graphics, GPS, LCDC, Camera interface (up to 12M pixels), 512KBytes MediaRAM(MERAM) 617 pins 7
8 8 Block Diagram (Bus Architecture) C-SHwy RT-SHwy ICB MERAM HSDPA/ WCDMA GSM IP-MMU IP-MMU IP-MMU (RTOS) MMU I$ 32KB SH-X2 D$ 32KB ILRAM 4KB DSP XYRAM 16KB (RTOS) ARM9 (High-Level-OS) MMU I$ 32KB ARM11 D$ 32KB ITCM 8KB VFP JAVA L2$ 256KB Sound Processing Unit DMA DSP P-RAM X-RAM Y-RAM Media IPs I$ 32KB D$ 32KB Peripherals 3DG 2DG Bridge RT-Domain Sys-Domain BB-Domain Bridge AHB ITCM 64KB DTCM 16KB DDR ch.1 Peripherals DDR ch.2
9 9 Die micrograph Die size 9.3mmx9.3mm GSM HSDPA /WCDMA BB- ARM GPS L2$ Hardware accelerators VPU SYS- ARM 3D Graphics RT- SHX2 Process Supply voltage # of TRs, gate, memory 65nm LP 8M(7Cu+1Al) 3Vth CMOS 1.2V(internal), 1.8/2.5/3.3V (I/O) 307M TRs (28.2M Gates, 30.7Mb RAM, 6.4Mb ROM)
10 10 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Chip Architecture 3. Power Management Static Power (Hierarchical Power Domain) Dynamic Power (Partial Clock Activation) 4. Memory Management IP-MMU 5. Summary
11 11 Power Management Both Static and Dynamic Power are very important for mobile application! Static Power Consumption (Leakage) Objective: Standby time Technique: Hierarchical Power Domain (HPD) Dynamic Power Consumption Objective: Operational time Technique: Partial Clock Activation (PCA)
12 Static Power Management Tr. Vth Leakage Frequency HVth Good (Low) Poor (Low) MVth Moderate Moderate LVth Poor (High) Good (High) Triple Vth technology Power Domain Separation (Partial Power-Off) # of domains Pros Cons Few Easy to control Limited Leakage reduction Many Optimal Leakage reduction Difficult to control Hierarchical Power Domain (HPD) 12
13 Hierarchical Power Domain Power area activity: AP BB System Real-time 20 domains in total W-CDMA GSM Almost Power Off ARM1176 ARM1176 (logic) (RAM) SYS Peripheral SH-X2 (logic) 3D Graphics SH-X2 (RAM) RT Peripheral LCDC, MediaRAM Sound related IPs LVDS serial interface GPS BB DSP RAM DSP RAM ARM926 Almost Power On INTC, DDR. cntrl1 INTC, RTSHwy BB- bus & DMAC Always On Common Power Domain C-SHwy, Local Bus, DDR cntrl2 PLL Clock Generators Back-up FFs Repeater cells 13
14 Hierarchical Power Domain Power area activity: AP BB System Real-time 20 domains in total W-CDMA GSM Almost Power Off ARM1176 ARM1176 (logic) (RAM) SYS Peripheral SH-X2 (logic) 3D Graphics SH-X2 (RAM) RT Peripheral Almost Power On INTC, DDR. cntrl1 INTC, RTSHwy LCDC, MediaRAM Sound related IPs LVDS serial interface w/ GPS CLAMP BB DSP RAM BB- bus DSP w/o RAM CLAMP & DMAC ARM926 Right domain must be ON Always On Common Power Domain C-SHwy, Local Bus, DDR cntrl2 PLL Clock Generators Back-up FFs Repeater cells 14
15 15 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Chip Architecture 3. Power Management Static Power (Hierarchical Power Domain) Dynamic Power (Partial Clock Activation) 4. Memory Management IP-MMU 5. Summary
16 Dynamic Power Management At low power scenario (music replay etc.), estimated power would go over the budget. all un-used domains already in power-off Clock gating already applied deeply In this case, Common Power Domain consumed large percentage of whole chip power (60%). ma(1.2v) Common Power Domain Others Clock Bus DSP CPU Leak scene: long time music replay 16
17 Partial Clock Activation: Motivation [Problem cause] Big modules have already been in power-off. But accumulated small power is not negligible. PLL and clock tree (PLL modules) Power-Off common power area pll1_stp PLL1 clk0 Clock Divider CPU_stby 1 st clock driver A 1 st clock driver B clka clkb mstp CPU BUS Always active 1 st clock driver C clkc mstp SPU 17
18 Partial Clock Activation: Diagram Clock tree separation Intermittent activation PLL_cntrl Clock gating control intermittent clock-active region Common Power Domain STOP PLL1 clk1 Clock Divider CPU_stby 1 st clock driver A 1 st clock driver B clka clkb CPU always clock-active BUS region BYPASS PLL2 clk2 Clock Divider 1 st clock driver C clkc SPU 18
19 Partial Clock Activation: Control Clock for SPU and serial IO is slowed down (PLL2 is bypassed.) PLL1 and clock tree is stopped in synchronization with CPU stand-by. They are reactivated in intermittent manner for housekeeping operation. (data copy from SD-card to SPU) PCA enable PLL2_bypass CPU_stby PLL1_stop clk1/a/b clk2/c auto-stop halt intermittent CPU task halt 19
20 Partial Clock Activation: Result Scene: Long time music replay ma(1.2v) x0.6 x common Others Clock Bus DSP CPU Leak 0 Without PCA With PCA PCA: Partial Clock Activation 20
21 21 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Chip Architecture 3. Power Management Static Power (Hierarchical Power Domain) Dynamic Power (Partial Clock Activation) 4. Memory Management IP-MMU 5. Summary
22 Memory Management: Motivation In general, efficient memory management is required for mobile phone due to limited memory capacity. Goal: To reduce system cost by minimizing memory footprint However, 1. HW-IP (Accelerator) requires address-contiguous large memory regions. 2. Memory fragmentation proceeds with application execution. Large memory chunk may not remain after some applications have run (even after exit)! 3. To avoid this fragmentation, large memory regions have to be statically allocated at boot phase. 4. As a result, system footprint on main memory becomes very large although actual memory size in use at the same time is not so large! 22
23 IP-MMU: Concept (a) Without IP-MMU Physical Address Space HW-IP (b) With IP-MMU Virtual Address Space Physical Address Space HW-IP Address Translation by IP-MMU 23
24 24 IP-MMU: Benefit Benefit Large address-contiguous memory regions can be composed of physically fragmented memory chunks. Memory regions can be freed after applications terminated and they can be allocated on demand. Reduction of system footprint HW-IP can see Virtual Address Space like CPU. CPU and HW-IPs can directly share the "pointer" to the memory. Easy development of applications utilizing HW-IPs
25 IP-MMU : Address Space View First half (2GB): TLB (Translation Look-aside Buffer) Dynamically allocated by OS (4KB granularity) Shared with a software process on OS Second half (2GB): PMB (Physical-address Mapping Buffer) Statically allocated at boot time (always alive) (e.g. LCDC frame buffer) Access window to arbitrary physical address HW-IP1 Virtual Address Space ([31]=0:TLB mapping) V Address 1(1) V Address 1(2) Physical Memory P Address 1(1) P Address 2 P Address 1(2) HW-IP2 P' Address 2 P Address 3 P' Address 3 Pseudo-Physical Address Space ([31]=1:PMB mapping) 25
26 IP-MMU: Implementation (Basic) Bus request Bus response Address space judgment virtual address VA PA physical address µtlb (8 ent.) Replacer PMB (16 entries, full-assoc) 64MB page TLB RAM main TLB (64 entries, 2-way) Hardware Page Table Walker Response filter Bus request Bus response 26
27 IP-MMU: Problem Inter-Connect Buffer (ICB) is the bus bridge that buffers data with 512 KBytes MediaRAM for inter-ip communication. [Problem1] Inserting IP-MMU at bus I/F(1) may degrade performance. [Problem2] Inserting IP-MMU to each IP side(2) is costly because 16 IP- MMUs are needed for ICB. Multimedia IPs Buff. Off IP #0 IP #15 ICB control Buff. On Buff. cntrl Bus I/F On chip bus 2 Media RAM 512KB 1 27
28 IP-MMU : Solution High data throughput Multimedia IPs common PMB main TLB TLB RAM HW PTW IP #2 W IP #2 R IP #1 W IP #0 R IP indep. µtlb #0 - #2 2 ent. x4 IP #3 ICB access control IP comm. µtlb #3 - #15 20 ent. Bus interface On chip bus IP #15 Buff. cntrl Buff. µtlb 2 ent. IPs that share µtlb Media RAM 512KB Buff. on #0-#15 30 µtlb entries in total 28
29 IP-MMU: Evaluation results Statically allocated memory size 53MB Camera, display (35MB) Graphics (18MB) 43MB free (-81%) Camera, display 10MB Note: All IP are used with IP-MMU. Performance evaluation Degradation is negligible. Video camcorder application performance: 30 for MPEG4/AVC format on G3 29
30 Summary The SH-Mobile G3 integrates a dual-mode (3G/2G) baseband processor, an application processor, and a multimedia processor with 65nm LP for mobile phone. Hierarchical Power Domain architecture separates the chip into 20 power domains and reduces leakage in many use cases. Partial Clock Activation reduces power even in low power scenario. It achieved more than 40% reduction of chip power in long time music replay scene. IP-MMU enables HW-IPs to use physically fragmented memory. By using this, more than 80% of statically allocated memory can be freed in the actual system without performance degradation. 30
SH-MobileG1: A Single-Chip Application and Dual-mode Baseband Processor
 SH-MobileG1: A Single-Chip Application and Dual-mode Baseband Processor Masayuki Ito 1, Takahiro Irita 1, Eiji Yamamoto 1, Kunihiko Nishiyama 1, Takao Koike 1, Yoshihiko Tsuchihashi 1, Hiroyuki Asano 1,
SH-MobileG1: A Single-Chip Application and Dual-mode Baseband Processor Masayuki Ito 1, Takahiro Irita 1, Eiji Yamamoto 1, Kunihiko Nishiyama 1, Takao Koike 1, Yoshihiko Tsuchihashi 1, Hiroyuki Asano 1,
MPSoC Approaches for Low-power Embedded Soc's
 MPSoC Approaches for Low-power Embedded Soc's Development Dept. 1 Toshihiro Hattori, June 26, 2007 Outline Approaches for Embedded MPSoC SH-MobileG1 : AP+BB Onechip SH-X3: SuperH SH-4A Quad-Core EXREAL
MPSoC Approaches for Low-power Embedded Soc's Development Dept. 1 Toshihiro Hattori, June 26, 2007 Outline Approaches for Embedded MPSoC SH-MobileG1 : AP+BB Onechip SH-X3: SuperH SH-4A Quad-Core EXREAL
SH-Mobile3: Application Processor for 3G Cellular Phones on a Low-Power SoC Design Platform
 SH-Mobile3: Application Processor for 3G Cellular Phones on a Low-Power SoC Design Platform H. Mizuno, N. Irie, K. Uchiyama, Y. Yanagisawa 1, S. Yoshioka 1, I. Kawasaki 1, and T. Hattori 2 Hitachi Ltd.,
SH-Mobile3: Application Processor for 3G Cellular Phones on a Low-Power SoC Design Platform H. Mizuno, N. Irie, K. Uchiyama, Y. Yanagisawa 1, S. Yoshioka 1, I. Kawasaki 1, and T. Hattori 2 Hitachi Ltd.,
SH-X3 Flexible SuperH Multi-core for High-performance and Low-power Embedded Systems
 SH-X3 Flexible SuperH Multi-core for High-performance and Low-power Embedded Systems Shinichi Shibahara 1, Masashi Takada 2, Tatsuya Kamei 1, Kiyoshi Hayase 1, Yutaka Yoshida 1, Osamu Nishii 1, Toshihiro
SH-X3 Flexible SuperH Multi-core for High-performance and Low-power Embedded Systems Shinichi Shibahara 1, Masashi Takada 2, Tatsuya Kamei 1, Kiyoshi Hayase 1, Yutaka Yoshida 1, Osamu Nishii 1, Toshihiro
Multimedia in Mobile Phones. Architectures and Trends Lund
 Multimedia in Mobile Phones Architectures and Trends Lund 091124 Presentation Henrik Ohlsson Contact: henrik.h.ohlsson@stericsson.com Working with multimedia hardware (graphics and displays) at ST- Ericsson
Multimedia in Mobile Phones Architectures and Trends Lund 091124 Presentation Henrik Ohlsson Contact: henrik.h.ohlsson@stericsson.com Working with multimedia hardware (graphics and displays) at ST- Ericsson
Product Technical Brief S3C2413 Rev 2.2, Apr. 2006
 Product Technical Brief Rev 2.2, Apr. 2006 Overview SAMSUNG's is a Derivative product of S3C2410A. is designed to provide hand-held devices and general applications with cost-effective, low-power, and
Product Technical Brief Rev 2.2, Apr. 2006 Overview SAMSUNG's is a Derivative product of S3C2410A. is designed to provide hand-held devices and general applications with cost-effective, low-power, and
Cannon Mountain Dr Longmont, CO LS6410 Hardware Design Perspective
 LS6410 Hardware Design Perspective 1. S3C6410 Introduction The S3C6410X is a 16/32-bit RISC microprocessor, which is designed to provide a cost-effective, lowpower capabilities, high performance Application
LS6410 Hardware Design Perspective 1. S3C6410 Introduction The S3C6410X is a 16/32-bit RISC microprocessor, which is designed to provide a cost-effective, lowpower capabilities, high performance Application
Intelop. *As new IP blocks become available, please contact the factory for the latest updated info.
 A FPGA based development platform as part of an EDK is available to target intelop provided IPs or other standard IPs. The platform with Virtex-4 FX12 Evaluation Kit provides a complete hardware environment
A FPGA based development platform as part of an EDK is available to target intelop provided IPs or other standard IPs. The platform with Virtex-4 FX12 Evaluation Kit provides a complete hardware environment
AT-501 Cortex-A5 System On Module Product Brief
 AT-501 Cortex-A5 System On Module Product Brief 1. Scope The following document provides a brief description of the AT-501 System on Module (SOM) its features and ordering options. For more details please
AT-501 Cortex-A5 System On Module Product Brief 1. Scope The following document provides a brief description of the AT-501 System on Module (SOM) its features and ordering options. For more details please
System-on-Chip Architecture for Mobile Applications. Sabyasachi Dey
 System-on-Chip Architecture for Mobile Applications Sabyasachi Dey Email: sabyasachi.dey@gmail.com Agenda What is Mobile Application Platform Challenges Key Architecture Focus Areas Conclusion Mobile Revolution
System-on-Chip Architecture for Mobile Applications Sabyasachi Dey Email: sabyasachi.dey@gmail.com Agenda What is Mobile Application Platform Challenges Key Architecture Focus Areas Conclusion Mobile Revolution
Product Technical Brief S3C2416 May 2008
 Product Technical Brief S3C2416 May 2008 Overview SAMSUNG's S3C2416 is a 32/16-bit RISC cost-effective, low power, high performance micro-processor solution for general applications including the GPS Navigation
Product Technical Brief S3C2416 May 2008 Overview SAMSUNG's S3C2416 is a 32/16-bit RISC cost-effective, low power, high performance micro-processor solution for general applications including the GPS Navigation
Oberon M2M IoT Platform. JAN 2016
 Oberon M2M IoT Platform JAN 2016 www.imgtec.com Contents Iot Segments and Definitions Targeted Use Cases for IoT Oberon targeted use cases IoT Differentiators IoT Power Management IoT Security Integrated
Oberon M2M IoT Platform JAN 2016 www.imgtec.com Contents Iot Segments and Definitions Targeted Use Cases for IoT Oberon targeted use cases IoT Differentiators IoT Power Management IoT Security Integrated
The Use Of Virtual Platforms In MP-SoC Design. Eshel Haritan, VP Engineering CoWare Inc. MPSoC 2006
 The Use Of Virtual Platforms In MP-SoC Design Eshel Haritan, VP Engineering CoWare Inc. MPSoC 2006 1 MPSoC Is MP SoC design happening? Why? Consumer Electronics Complexity Cost of ASIC Increased SW Content
The Use Of Virtual Platforms In MP-SoC Design Eshel Haritan, VP Engineering CoWare Inc. MPSoC 2006 1 MPSoC Is MP SoC design happening? Why? Consumer Electronics Complexity Cost of ASIC Increased SW Content
Development of Low Power and High Performance Application Processor (T6G) for Multimedia Mobile Applications
 Session 8D-2 Development of Low Power and High Performance Application Processor (T6G) for Multimedia Mobile Applications Yoshiyuki Kitasho, Yu Kikuchi, Takayoshi Shimazawa, Yasuo Ohara, Masafumi Takahashi,
Session 8D-2 Development of Low Power and High Performance Application Processor (T6G) for Multimedia Mobile Applications Yoshiyuki Kitasho, Yu Kikuchi, Takayoshi Shimazawa, Yasuo Ohara, Masafumi Takahashi,
Product Technical Brief S3C2412 Rev 2.2, Apr. 2006
 Product Technical Brief S3C2412 Rev 2.2, Apr. 2006 Overview SAMSUNG's S3C2412 is a Derivative product of S3C2410A. S3C2412 is designed to provide hand-held devices and general applications with cost-effective,
Product Technical Brief S3C2412 Rev 2.2, Apr. 2006 Overview SAMSUNG's S3C2412 is a Derivative product of S3C2410A. S3C2412 is designed to provide hand-held devices and general applications with cost-effective,
Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) Devices
 Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) Devices 1 Contents Altera FPGAs and CPLDs CPLDs FPGAs with embedded processors ACEX FPGAs Cyclone I,II FPGAs APEX FPGAs Stratix FPGAs Stratix II,III FPGAs Xilinx FPGAs
Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) Devices 1 Contents Altera FPGAs and CPLDs CPLDs FPGAs with embedded processors ACEX FPGAs Cyclone I,II FPGAs APEX FPGAs Stratix FPGAs Stratix II,III FPGAs Xilinx FPGAs
High-Speed NAND Flash
 High-Speed NAND Flash Design Considerations to Maximize Performance Presented by: Robert Pierce Sr. Director, NAND Flash Denali Software, Inc. History of NAND Bandwidth Trend MB/s 20 60 80 100 200 The
High-Speed NAND Flash Design Considerations to Maximize Performance Presented by: Robert Pierce Sr. Director, NAND Flash Denali Software, Inc. History of NAND Bandwidth Trend MB/s 20 60 80 100 200 The
An Evaluation of an Energy Efficient Many-Core SoC with Parallelized Face Detection
 An Evaluation of an Energy Efficient Many-Core SoC with Parallelized Face Detection Hiroyuki Usui, Jun Tanabe, Toru Sano, Hui Xu, and Takashi Miyamori Toshiba Corporation, Kawasaki, Japan Copyright 2013,
An Evaluation of an Energy Efficient Many-Core SoC with Parallelized Face Detection Hiroyuki Usui, Jun Tanabe, Toru Sano, Hui Xu, and Takashi Miyamori Toshiba Corporation, Kawasaki, Japan Copyright 2013,
Age nda. Intel PXA27x Processor Family: An Applications Processor for Phone and PDA applications
 Intel PXA27x Processor Family: An Applications Processor for Phone and PDA applications N.C. Paver PhD Architect Intel Corporation Hot Chips 16 August 2004 Age nda Overview of the Intel PXA27X processor
Intel PXA27x Processor Family: An Applications Processor for Phone and PDA applications N.C. Paver PhD Architect Intel Corporation Hot Chips 16 August 2004 Age nda Overview of the Intel PXA27X processor
Chapter 5B. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5B Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy One Transistor Dynamic RAM 1-T DRAM Cell word access transistor V REF TiN top electrode (V REF ) Ta 2 O 5 dielectric bit Storage capacitor (FET gate,
Chapter 5B Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy One Transistor Dynamic RAM 1-T DRAM Cell word access transistor V REF TiN top electrode (V REF ) Ta 2 O 5 dielectric bit Storage capacitor (FET gate,
Achieves excellent performance of 1,920 MIPS and a single-chip solution for nextgeneration car information systems
 Renesas Technology to Release SH7776 (SH-Navi3), Industry s First Dual-Core SoC with Built-in Image Recognition Processing Function for Car Information Terminals Achieves excellent performance of 1,920
Renesas Technology to Release SH7776 (SH-Navi3), Industry s First Dual-Core SoC with Built-in Image Recognition Processing Function for Car Information Terminals Achieves excellent performance of 1,920
Techniques for Optimizing Performance and Energy Consumption: Results of a Case Study on an ARM9 Platform
 Techniques for Optimizing Performance and Energy Consumption: Results of a Case Study on an ARM9 Platform BL Standard IC s, PL Microcontrollers October 2007 Outline LPC3180 Description What makes this
Techniques for Optimizing Performance and Energy Consumption: Results of a Case Study on an ARM9 Platform BL Standard IC s, PL Microcontrollers October 2007 Outline LPC3180 Description What makes this
RZ Embedded Microprocessors
 Next Generation HMI Solutions RZ Embedded Microprocessors www.renesas.eu 2013.11 The RZ Family Embedded Microprocessors The RZ is a new family of embedded microprocessors that retains the ease-of-use of
Next Generation HMI Solutions RZ Embedded Microprocessors www.renesas.eu 2013.11 The RZ Family Embedded Microprocessors The RZ is a new family of embedded microprocessors that retains the ease-of-use of
Software Defined Modem A commercial platform for wireless handsets
 Software Defined Modem A commercial platform for wireless handsets Charles F Sturman VP Marketing June 22 nd ~ 24 th Brussels charles.stuman@cognovo.com www.cognovo.com Agenda SDM Separating hardware from
Software Defined Modem A commercial platform for wireless handsets Charles F Sturman VP Marketing June 22 nd ~ 24 th Brussels charles.stuman@cognovo.com www.cognovo.com Agenda SDM Separating hardware from
Introduction to ASIC Design
 Introduction to ASIC Design Victor P. Nelson ELEC 5250/6250 CAD of Digital ICs Design & implementation of ASICs Oops Not these! Application-Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC) Developed for a specific application
Introduction to ASIC Design Victor P. Nelson ELEC 5250/6250 CAD of Digital ICs Design & implementation of ASICs Oops Not these! Application-Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC) Developed for a specific application
High-Performance 32-bit
 High-Performance 32-bit Microcontroller with Built-in 11-Channel Serial Interface and Two High-Speed A/D Converter Units A 32-bit microcontroller optimal for digital home appliances that integrates various
High-Performance 32-bit Microcontroller with Built-in 11-Channel Serial Interface and Two High-Speed A/D Converter Units A 32-bit microcontroller optimal for digital home appliances that integrates various
Course Introduction. Purpose: Objectives: Content: Learning Time:
 Course Introduction Purpose: This course provides an overview of the Renesas SuperH series of 32-bit RISC processors, especially the microcontrollers in the SH-2 and SH-2A series Objectives: Learn the
Course Introduction Purpose: This course provides an overview of the Renesas SuperH series of 32-bit RISC processors, especially the microcontrollers in the SH-2 and SH-2A series Objectives: Learn the
Intel s s Memory Strategy for the Wireless Phone
 Intel s s Memory Strategy for the Wireless Phone Stefan Lai VP and Co-Director, CTM Intel Corporation Nikkei Microdevices Memory Symposium January 26 th, 2005 Agenda Evolution of Memory Requirements Evolution
Intel s s Memory Strategy for the Wireless Phone Stefan Lai VP and Co-Director, CTM Intel Corporation Nikkei Microdevices Memory Symposium January 26 th, 2005 Agenda Evolution of Memory Requirements Evolution
Copyright 2016 Xilinx
 Zynq Architecture Zynq Vivado 2015.4 Version This material exempt per Department of Commerce license exception TSU Objectives After completing this module, you will be able to: Identify the basic building
Zynq Architecture Zynq Vivado 2015.4 Version This material exempt per Department of Commerce license exception TSU Objectives After completing this module, you will be able to: Identify the basic building
Memory Management. Mobile Hardware Resources. Address Space and Process. Memory Management Overview. Memory Management Concepts
 Mobile Hardware Resources Memory Management Symbian Operating System 275078 Eka Ardianto 263416 Ikrimach M. 292964 Jumadi 275057 Muji Syukur 293082 Prisa M. Kusumantara 292301 Sheila Nurul Huda Moblie
Mobile Hardware Resources Memory Management Symbian Operating System 275078 Eka Ardianto 263416 Ikrimach M. 292964 Jumadi 275057 Muji Syukur 293082 Prisa M. Kusumantara 292301 Sheila Nurul Huda Moblie
Flash Storage Trends & Ecosystem
 Flash Storage Trends & Ecosystem Hung Vuong Qualcomm Inc. Introduction Trends Agenda Wireless Industry Trends Memory & Storage Trends Opportunities Summary Cellular Products Group (CPG) Wireless Handsets
Flash Storage Trends & Ecosystem Hung Vuong Qualcomm Inc. Introduction Trends Agenda Wireless Industry Trends Memory & Storage Trends Opportunities Summary Cellular Products Group (CPG) Wireless Handsets
2D/3D Graphics Accelerator for Mobile Multimedia Applications. Ramchan Woo, Sohn, Seong-Jun Song, Young-Don
 RAMP-IV: A Low-Power and High-Performance 2D/3D Graphics Accelerator for Mobile Multimedia Applications Woo, Sungdae Choi, Ju-Ho Sohn, Seong-Jun Song, Young-Don Bae,, and Hoi-Jun Yoo oratory Dept. of EECS,
RAMP-IV: A Low-Power and High-Performance 2D/3D Graphics Accelerator for Mobile Multimedia Applications Woo, Sungdae Choi, Ju-Ho Sohn, Seong-Jun Song, Young-Don Bae,, and Hoi-Jun Yoo oratory Dept. of EECS,
New STM32 F7 Series. World s 1 st to market, ARM Cortex -M7 based 32-bit MCU
 New STM32 F7 Series World s 1 st to market, ARM Cortex -M7 based 32-bit MCU 7 Keys of STM32 F7 series 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 First. ST is first to sample a fully functional Cortex-M7 based 32-bit MCU : STM32
New STM32 F7 Series World s 1 st to market, ARM Cortex -M7 based 32-bit MCU 7 Keys of STM32 F7 series 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 First. ST is first to sample a fully functional Cortex-M7 based 32-bit MCU : STM32
SIMULTANEOUS BASEBAND PROCESSING CONSIDERATIONS IN A MULTI-MODE HANDSET USING THE SANDBLASTER BASEBAND PROCESSOR
 SIMULTANEOUS BASEBAND PROCESSING CONSIDERATIONS IN A MULTI-MODE HANDSET USING THE SANDBLASTER BASEBAND PROCESSOR Babak Beheshti, b.beheshti@ieee.org Sanjay Jinturkar, Sandbridge Technologies, sanjay.jinturkar@sandbridgetech.com
SIMULTANEOUS BASEBAND PROCESSING CONSIDERATIONS IN A MULTI-MODE HANDSET USING THE SANDBLASTER BASEBAND PROCESSOR Babak Beheshti, b.beheshti@ieee.org Sanjay Jinturkar, Sandbridge Technologies, sanjay.jinturkar@sandbridgetech.com
A 1-GHz Configurable Processor Core MeP-h1
 A 1-GHz Configurable Processor Core MeP-h1 Takashi Miyamori, Takanori Tamai, and Masato Uchiyama SoC Research & Development Center, TOSHIBA Corporation Outline Background Pipeline Structure Bus Interface
A 1-GHz Configurable Processor Core MeP-h1 Takashi Miyamori, Takanori Tamai, and Masato Uchiyama SoC Research & Development Center, TOSHIBA Corporation Outline Background Pipeline Structure Bus Interface
DevKit8000 Evaluation Kit
 DevKit8000 Evaluation Kit TI OMAP3530 Processor based on 600MHz ARM Cortex-A8 core Memory supporting 256MByte DDR SDRAM and 256MByte NAND Flash UART, USB Host/OTG, Ethernet, Camera, Audio, SD, Keyboard,
DevKit8000 Evaluation Kit TI OMAP3530 Processor based on 600MHz ARM Cortex-A8 core Memory supporting 256MByte DDR SDRAM and 256MByte NAND Flash UART, USB Host/OTG, Ethernet, Camera, Audio, SD, Keyboard,
Silicon Motion s Graphics Display SoCs
 WHITE PAPER Silicon Motion s Graphics Display SoCs Enable 4K High Definition and Low Power Power and bandwidth: the twin challenges of implementing a solution for bridging any computer to any high-definition
WHITE PAPER Silicon Motion s Graphics Display SoCs Enable 4K High Definition and Low Power Power and bandwidth: the twin challenges of implementing a solution for bridging any computer to any high-definition
Design and Implementation of an AHB SRAM Memory Controller
 Design and Implementation of an AHB SRAM Memory Controller 1 Module Overview Learn the basics of Computer Memory; Design and implement an AHB SRAM memory controller, which replaces the previous on-chip
Design and Implementation of an AHB SRAM Memory Controller 1 Module Overview Learn the basics of Computer Memory; Design and implement an AHB SRAM memory controller, which replaces the previous on-chip
Product Technical Brief S3C2440X Series Rev 2.0, Oct. 2003
 Product Technical Brief S3C2440X Series Rev 2.0, Oct. 2003 S3C2440X is a derivative product of Samsung s S3C24XXX family of microprocessors for mobile communication market. The S3C2440X s main enhancement
Product Technical Brief S3C2440X Series Rev 2.0, Oct. 2003 S3C2440X is a derivative product of Samsung s S3C24XXX family of microprocessors for mobile communication market. The S3C2440X s main enhancement
Computer Architecture. Introduction. Lynn Choi Korea University
 Computer Architecture Introduction Lynn Choi Korea University Class Information Lecturer Prof. Lynn Choi, School of Electrical Eng. Phone: 3290-3249, 공학관 411, lchoi@korea.ac.kr, TA: 윤창현 / 신동욱, 3290-3896,
Computer Architecture Introduction Lynn Choi Korea University Class Information Lecturer Prof. Lynn Choi, School of Electrical Eng. Phone: 3290-3249, 공학관 411, lchoi@korea.ac.kr, TA: 윤창현 / 신동욱, 3290-3896,
ARM Processors for Embedded Applications
 ARM Processors for Embedded Applications Roadmap for ARM Processors ARM Architecture Basics ARM Families AMBA Architecture 1 Current ARM Core Families ARM7: Hard cores and Soft cores Cache with MPU or
ARM Processors for Embedded Applications Roadmap for ARM Processors ARM Architecture Basics ARM Families AMBA Architecture 1 Current ARM Core Families ARM7: Hard cores and Soft cores Cache with MPU or
HotChips An innovative HD video and digital image processor for low-cost digital entertainment products. Deepu Talla.
 HotChips 2007 An innovative HD video and digital image processor for low-cost digital entertainment products Deepu Talla Texas Instruments 1 Salient features of the SoC HD video encode and decode using
HotChips 2007 An innovative HD video and digital image processor for low-cost digital entertainment products Deepu Talla Texas Instruments 1 Salient features of the SoC HD video encode and decode using
Overview. Memory Classification Read-Only Memory (ROM) Random Access Memory (RAM) Functional Behavior of RAM. Implementing Static RAM
 Memories Overview Memory Classification Read-Only Memory (ROM) Types of ROM PROM, EPROM, E 2 PROM Flash ROMs (Compact Flash, Secure Digital, Memory Stick) Random Access Memory (RAM) Types of RAM Static
Memories Overview Memory Classification Read-Only Memory (ROM) Types of ROM PROM, EPROM, E 2 PROM Flash ROMs (Compact Flash, Secure Digital, Memory Stick) Random Access Memory (RAM) Types of RAM Static
See K600. Product Specification
 ID : Golden See K600 Product Specification Product Highlights 4G Android smartphone operating system, WiFi, BT, camera, GPS, gsensor, OTG, back touch, compass, fingerprint identification, etc. Technical
ID : Golden See K600 Product Specification Product Highlights 4G Android smartphone operating system, WiFi, BT, camera, GPS, gsensor, OTG, back touch, compass, fingerprint identification, etc. Technical
Department of Computer Science, Institute for System Architecture, Operating Systems Group. Real-Time Systems '08 / '09. Hardware.
 Department of Computer Science, Institute for System Architecture, Operating Systems Group Real-Time Systems '08 / '09 Hardware Marcus Völp Outlook Hardware is Source of Unpredictability Caches Pipeline
Department of Computer Science, Institute for System Architecture, Operating Systems Group Real-Time Systems '08 / '09 Hardware Marcus Völp Outlook Hardware is Source of Unpredictability Caches Pipeline
A 50Mvertices/s Graphics Processor with Fixed-Point Programmable Vertex Shader for Mobile Applications
 A 50Mvertices/s Graphics Processor with Fixed-Point Programmable Vertex Shader for Mobile Applications Ju-Ho Sohn, Jeong-Ho Woo, Min-Wuk Lee, Hye-Jung Kim, Ramchan Woo, Hoi-Jun Yoo Semiconductor System
A 50Mvertices/s Graphics Processor with Fixed-Point Programmable Vertex Shader for Mobile Applications Ju-Ho Sohn, Jeong-Ho Woo, Min-Wuk Lee, Hye-Jung Kim, Ramchan Woo, Hoi-Jun Yoo Semiconductor System
SpiNNaker - a million core ARM-powered neural HPC
 The Advanced Processor Technologies Group SpiNNaker - a million core ARM-powered neural HPC Cameron Patterson cameron.patterson@cs.man.ac.uk School of Computer Science, The University of Manchester, UK
The Advanced Processor Technologies Group SpiNNaker - a million core ARM-powered neural HPC Cameron Patterson cameron.patterson@cs.man.ac.uk School of Computer Science, The University of Manchester, UK
Fujitsu System Applications Support. Fujitsu Microelectronics America, Inc. 02/02
 Fujitsu System Applications Support 1 Overview System Applications Support SOC Application Development Lab Multimedia VoIP Wireless Bluetooth Processors, DSP and Peripherals ARM Reference Platform 2 SOC
Fujitsu System Applications Support 1 Overview System Applications Support SOC Application Development Lab Multimedia VoIP Wireless Bluetooth Processors, DSP and Peripherals ARM Reference Platform 2 SOC
ISSCC 2003 / SESSION 14 / MICROPROCESSORS / PAPER 14.5
 ISSCC 2003 / SESSION 14 / MICROPROCESSORS / PAPER 14.5 14.5 A 600MHz Single-Chip Multiprocessor with 4.8GB/s Internal Shared Pipelined Bus and 512kB Internal Memory Satoshi Kaneko, Katsunori Sawai, Norio
ISSCC 2003 / SESSION 14 / MICROPROCESSORS / PAPER 14.5 14.5 A 600MHz Single-Chip Multiprocessor with 4.8GB/s Internal Shared Pipelined Bus and 512kB Internal Memory Satoshi Kaneko, Katsunori Sawai, Norio
SoC for Car Navigation Systems with a 53.3 GOPS Image Recognition Engine
 Session 5D : Designer s Forum : State-of-the-art SoCs 5D-4 SoC for Car Navigation Systems with a 53.3 GOPS Image Recognition Engine Jan. 20. 2010 Hiroyuki Hamasaki*, Yasuhiko Hoshi*, Atsushi Nakamura *,
Session 5D : Designer s Forum : State-of-the-art SoCs 5D-4 SoC for Car Navigation Systems with a 53.3 GOPS Image Recognition Engine Jan. 20. 2010 Hiroyuki Hamasaki*, Yasuhiko Hoshi*, Atsushi Nakamura *,
CENG4480 Lecture 09: Memory 1
 CENG4480 Lecture 09: Memory 1 Bei Yu byu@cse.cuhk.edu.hk (Latest update: November 8, 2017) Fall 2017 1 / 37 Overview Introduction Memory Principle Random Access Memory (RAM) Non-Volatile Memory Conclusion
CENG4480 Lecture 09: Memory 1 Bei Yu byu@cse.cuhk.edu.hk (Latest update: November 8, 2017) Fall 2017 1 / 37 Overview Introduction Memory Principle Random Access Memory (RAM) Non-Volatile Memory Conclusion
ELEC 5200/6200 Computer Architecture and Design Spring 2017 Lecture 7: Memory Organization Part II
 ELEC 5200/6200 Computer Architecture and Design Spring 2017 Lecture 7: Organization Part II Ujjwal Guin, Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Auburn University, Auburn,
ELEC 5200/6200 Computer Architecture and Design Spring 2017 Lecture 7: Organization Part II Ujjwal Guin, Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Auburn University, Auburn,
Crusoe Processor Model TM5800
 Model TM5800 Crusoe TM Processor Model TM5800 Features VLIW processor and x86 Code Morphing TM software provide x86-compatible mobile platform solution Processors fabricated in latest 0.13µ process technology
Model TM5800 Crusoe TM Processor Model TM5800 Features VLIW processor and x86 Code Morphing TM software provide x86-compatible mobile platform solution Processors fabricated in latest 0.13µ process technology
Accelerating Innovation
 Accelerating Innovation In the Era of Exponentials Dr. Chi-Foon Chan President and co-chief Executive Officer, Synopsys, Inc. August 27, 2013 ASQED 1 Accelerating Technology Innovation Exciting time to
Accelerating Innovation In the Era of Exponentials Dr. Chi-Foon Chan President and co-chief Executive Officer, Synopsys, Inc. August 27, 2013 ASQED 1 Accelerating Technology Innovation Exciting time to
Design Techniques for Implementing an 800MHz ARM v5 Core for Foundry-Based SoC Integration. Faraday Technology Corp.
 Design Techniques for Implementing an 800MHz ARM v5 Core for Foundry-Based SoC Integration Faraday Technology Corp. Table of Contents 1 2 3 4 Faraday & FA626TE Overview Why We Need an 800MHz ARM v5 Core
Design Techniques for Implementing an 800MHz ARM v5 Core for Foundry-Based SoC Integration Faraday Technology Corp. Table of Contents 1 2 3 4 Faraday & FA626TE Overview Why We Need an 800MHz ARM v5 Core
Last Time. Making correct concurrent programs. Maintaining invariants Avoiding deadlocks
 Last Time Making correct concurrent programs Maintaining invariants Avoiding deadlocks Today Power management Hardware capabilities Software management strategies Power and Energy Review Energy is power
Last Time Making correct concurrent programs Maintaining invariants Avoiding deadlocks Today Power management Hardware capabilities Software management strategies Power and Energy Review Energy is power
IMEC CORE CMOS P. MARCHAL
 APPLICATIONS & 3D TECHNOLOGY IMEC CORE CMOS P. MARCHAL OUTLINE What is important to spec 3D technology How to set specs for the different applications - Mobile consumer - Memory - High performance Conclusions
APPLICATIONS & 3D TECHNOLOGY IMEC CORE CMOS P. MARCHAL OUTLINE What is important to spec 3D technology How to set specs for the different applications - Mobile consumer - Memory - High performance Conclusions
A 167-processor Computational Array for Highly-Efficient DSP and Embedded Application Processing
 A 167-processor Computational Array for Highly-Efficient DSP and Embedded Application Processing Dean Truong, Wayne Cheng, Tinoosh Mohsenin, Zhiyi Yu, Toney Jacobson, Gouri Landge, Michael Meeuwsen, Christine
A 167-processor Computational Array for Highly-Efficient DSP and Embedded Application Processing Dean Truong, Wayne Cheng, Tinoosh Mohsenin, Zhiyi Yu, Toney Jacobson, Gouri Landge, Michael Meeuwsen, Christine
CORRIGENDUM ISSUED FOR NATIONAL COMPETITIVE BIDDING UNDER TEQIP PHASE-II
 CORRIGENDUM ISSUED FOR NATIONAL COMPETITIVE BIDDING UNDER TEQIP PHASE-II The prebid meeting for the packages to be purchased under national competitive bidding for TEQIP Phase II was held on 15/10/2013
CORRIGENDUM ISSUED FOR NATIONAL COMPETITIVE BIDDING UNDER TEQIP PHASE-II The prebid meeting for the packages to be purchased under national competitive bidding for TEQIP Phase II was held on 15/10/2013
DevKit7000 Evaluation Kit
 DevKit7000 Evaluation Kit Samsung S5PV210 Processor based on 1GHz ARM Cortex-A8 core Onboard 512MByte DDR2 and 512MByte NAND Flash 4 UART, 4 USB Host, USB Device, Ethernet, Audio, TF, RTC,... Supports
DevKit7000 Evaluation Kit Samsung S5PV210 Processor based on 1GHz ARM Cortex-A8 core Onboard 512MByte DDR2 and 512MByte NAND Flash 4 UART, 4 USB Host, USB Device, Ethernet, Audio, TF, RTC,... Supports
Total IP Solution for Mobile Storage UFS & NAND Controllers
 Total IP Solution for Mobile Storage UFS & NAND Controllers Yuping Chung Arasan Chip Systems San Jose, CA Mobile Forum Taiwan & Korea 2012 Fast Growing NAND Storage Markets GB(M) 15 10 5 Mobile SSD Tablet
Total IP Solution for Mobile Storage UFS & NAND Controllers Yuping Chung Arasan Chip Systems San Jose, CA Mobile Forum Taiwan & Korea 2012 Fast Growing NAND Storage Markets GB(M) 15 10 5 Mobile SSD Tablet
MYD-IMX28X Development Board
 MYD-IMX28X Development Board MYC-IMX28X CPU Module as Controller Board Two 1.27mm pitch 80-pin SMT Male Connectors for Board-to-Board Connections 454MHz Freescale i.mx28 Series ARM926EJ-S Processors 128MB
MYD-IMX28X Development Board MYC-IMX28X CPU Module as Controller Board Two 1.27mm pitch 80-pin SMT Male Connectors for Board-to-Board Connections 454MHz Freescale i.mx28 Series ARM926EJ-S Processors 128MB
Growth outside Cell Phone Applications
 ARM Introduction Growth outside Cell Phone Applications ~1B units shipped into non-mobile applications Embedded segment now accounts for 13% of ARM shipments Automotive, microcontroller and smartcards
ARM Introduction Growth outside Cell Phone Applications ~1B units shipped into non-mobile applications Embedded segment now accounts for 13% of ARM shipments Automotive, microcontroller and smartcards
Hello, and welcome to this presentation of the STM32 Flash memory interface. It covers all the new features of the STM32F7 Flash memory.
 Hello, and welcome to this presentation of the STM32 Flash memory interface. It covers all the new features of the STM32F7 Flash memory. 1 STM32F7 microcontrollers embed up to 2 Mbytes of Flash memory.
Hello, and welcome to this presentation of the STM32 Flash memory interface. It covers all the new features of the STM32F7 Flash memory. 1 STM32F7 microcontrollers embed up to 2 Mbytes of Flash memory.
Using the i.mx RT FlexRAM
 NXP Semiconductors Document Number: AN12077 Application Note Rev. 0, 10/2017 Using the i.mx RT FlexRAM 1. Introduction This document describes the flexible memory array available on the i.mx RT MCUs. The
NXP Semiconductors Document Number: AN12077 Application Note Rev. 0, 10/2017 Using the i.mx RT FlexRAM 1. Introduction This document describes the flexible memory array available on the i.mx RT MCUs. The
Memory Needs. Technology DDR/SRAM DDR/SRAM/Flash EEPROM/Flash HD/SSD/SD/Flash HD/SSD/SD/Flash
 Memory Systems Memory Needs Function Description Volatility Size Speed Access Portable Data Temp data/operand store for programs V Direct N Instructions Opcode storage for executing programs V/NV Direct
Memory Systems Memory Needs Function Description Volatility Size Speed Access Portable Data Temp data/operand store for programs V Direct N Instructions Opcode storage for executing programs V/NV Direct
Memory Management. Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1
 Memory Management Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1 CPU management Roadmap Process, thread, synchronization, scheduling Memory management Virtual memory Disk
Memory Management Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1 CPU management Roadmap Process, thread, synchronization, scheduling Memory management Virtual memory Disk
Reduce Your System Power Consumption with Altera FPGAs Altera Corporation Public
 Reduce Your System Power Consumption with Altera FPGAs Agenda Benefits of lower power in systems Stratix III power technology Cyclone III power Quartus II power optimization and estimation tools Summary
Reduce Your System Power Consumption with Altera FPGAs Agenda Benefits of lower power in systems Stratix III power technology Cyclone III power Quartus II power optimization and estimation tools Summary
Review Questions on Computer Basics
 Review Questions on Computer Basics 1. Distinguish between and define (see glossary in Maxfield and Brown s Bebop Bytes Back for the definition of terms not found in Andrews A Guide to Managing and Maintaining
Review Questions on Computer Basics 1. Distinguish between and define (see glossary in Maxfield and Brown s Bebop Bytes Back for the definition of terms not found in Andrews A Guide to Managing and Maintaining
The Mobile Internet: The Potential of Handhelds to Bring Internet to the Masses. April 2008
 The Mobile Internet: The Potential of Handhelds to Bring Internet to the Masses April 2008 Agenda Today s Mobile Internet Market Mobile Convergence Products Internet Browsing on a Handheld Separating Fact
The Mobile Internet: The Potential of Handhelds to Bring Internet to the Masses April 2008 Agenda Today s Mobile Internet Market Mobile Convergence Products Internet Browsing on a Handheld Separating Fact
When Less Is More: Bigger & Faster Memory in Shrinking Packages for the Mobile Market
 When Less Is More: Bigger & Faster Memory in Shrinking Packages for the Mobile Market Kathy Choe Thomas, Flash Product Mktg Samsung Semiconductor, Inc. Living in the Connected World Like it or Not, We
When Less Is More: Bigger & Faster Memory in Shrinking Packages for the Mobile Market Kathy Choe Thomas, Flash Product Mktg Samsung Semiconductor, Inc. Living in the Connected World Like it or Not, We
Low-Power Processor Solutions for Always-on Devices
 Low-Power Processor Solutions for Always-on Devices Pieter van der Wolf MPSoC 2014 July 7 11, 2014 2014 Synopsys, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Always-on Mobile Devices Mobile devices on the move Mobile
Low-Power Processor Solutions for Always-on Devices Pieter van der Wolf MPSoC 2014 July 7 11, 2014 2014 Synopsys, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Always-on Mobile Devices Mobile devices on the move Mobile
On-chip Networks Enable the Dark Silicon Advantage. Drew Wingard CTO & Co-founder Sonics, Inc.
 On-chip Networks Enable the Dark Silicon Advantage Drew Wingard CTO & Co-founder Sonics, Inc. Agenda Sonics history and corporate summary Power challenges in advanced SoCs General power management techniques
On-chip Networks Enable the Dark Silicon Advantage Drew Wingard CTO & Co-founder Sonics, Inc. Agenda Sonics history and corporate summary Power challenges in advanced SoCs General power management techniques
Computer Architecture. Memory Hierarchy. Lynn Choi Korea University
 Computer Architecture Memory Hierarchy Lynn Choi Korea University Memory Hierarchy Motivated by Principles of Locality Speed vs. Size vs. Cost tradeoff Locality principle Temporal Locality: reference to
Computer Architecture Memory Hierarchy Lynn Choi Korea University Memory Hierarchy Motivated by Principles of Locality Speed vs. Size vs. Cost tradeoff Locality principle Temporal Locality: reference to
New Embedded NVM architectures
 New Embedded NVM architectures for Secure & Low Power Microcontrollers Jean DEVIN, Bruno LECONTE Microcontrollers, Memories & Smartcard Group STMicroelectronics 11 th LETI Annual review, June 24th, 2009
New Embedded NVM architectures for Secure & Low Power Microcontrollers Jean DEVIN, Bruno LECONTE Microcontrollers, Memories & Smartcard Group STMicroelectronics 11 th LETI Annual review, June 24th, 2009
D Demonstration of disturbance recording functions for PQ monitoring
 D6.3.7. Demonstration of disturbance recording functions for PQ monitoring Final Report March, 2013 M.Sc. Bashir Ahmed Siddiqui Dr. Pertti Pakonen 1. Introduction The OMAP-L138 C6-Integra DSP+ARM processor
D6.3.7. Demonstration of disturbance recording functions for PQ monitoring Final Report March, 2013 M.Sc. Bashir Ahmed Siddiqui Dr. Pertti Pakonen 1. Introduction The OMAP-L138 C6-Integra DSP+ARM processor
KeyStone C665x Multicore SoC
 KeyStone Multicore SoC Architecture KeyStone C6655/57: Device Features C66x C6655: One C66x DSP Core at 1.0 or 1.25 GHz C6657: Two C66x DSP Cores at 0.85, 1.0, or 1.25 GHz Fixed and Floating Point Operations
KeyStone Multicore SoC Architecture KeyStone C6655/57: Device Features C66x C6655: One C66x DSP Core at 1.0 or 1.25 GHz C6657: Two C66x DSP Cores at 0.85, 1.0, or 1.25 GHz Fixed and Floating Point Operations
Effective System Design with ARM System IP
 Effective System Design with ARM System IP Mentor Technical Forum 2009 Serge Poublan Product Marketing Manager ARM 1 Higher level of integration WiFi Platform OS Graphic 13 days standby Bluetooth MP3 Camera
Effective System Design with ARM System IP Mentor Technical Forum 2009 Serge Poublan Product Marketing Manager ARM 1 Higher level of integration WiFi Platform OS Graphic 13 days standby Bluetooth MP3 Camera
Memory management units
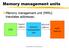 Memory management units Memory management unit (MMU) translates addresses: CPU logical address memory management unit physical address main memory Computers as Components 1 Access time comparison Media
Memory management units Memory management unit (MMU) translates addresses: CPU logical address memory management unit physical address main memory Computers as Components 1 Access time comparison Media
CS/COE0447: Computer Organization
 CS/COE0447: Computer Organization and Assembly Language Terminology and Concepts Sangyeun Cho Dept. of Computer Science Five classic components I am like a control tower I am like a pack of file folders
CS/COE0447: Computer Organization and Assembly Language Terminology and Concepts Sangyeun Cho Dept. of Computer Science Five classic components I am like a control tower I am like a pack of file folders
Memory management. Last modified: Adaptation of Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne slides for the textbook Applied Operating Systems Concepts
 Memory management Last modified: 26.04.2016 1 Contents Background Logical and physical address spaces; address binding Overlaying, swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of
Memory management Last modified: 26.04.2016 1 Contents Background Logical and physical address spaces; address binding Overlaying, swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Segmentation Paging Structure of
Memory Systems IRAM. Principle of IRAM
 Memory Systems 165 other devices of the module will be in the Standby state (which is the primary state of all RDRAM devices) or another state with low-power consumption. The RDRAM devices provide several
Memory Systems 165 other devices of the module will be in the Standby state (which is the primary state of all RDRAM devices) or another state with low-power consumption. The RDRAM devices provide several
Contents of this presentation: Some words about the ARM company
 The architecture of the ARM cores Contents of this presentation: Some words about the ARM company The ARM's Core Families and their benefits Explanation of the ARM architecture Architecture details, features
The architecture of the ARM cores Contents of this presentation: Some words about the ARM company The ARM's Core Families and their benefits Explanation of the ARM architecture Architecture details, features
CS5460: Operating Systems Lecture 14: Memory Management (Chapter 8)
 CS5460: Operating Systems Lecture 14: Memory Management (Chapter 8) Important from last time We re trying to build efficient virtual address spaces Why?? Virtual / physical translation is done by HW and
CS5460: Operating Systems Lecture 14: Memory Management (Chapter 8) Important from last time We re trying to build efficient virtual address spaces Why?? Virtual / physical translation is done by HW and
Gigascale Integration Design Challenges & Opportunities. Shekhar Borkar Circuit Research, Intel Labs October 24, 2004
 Gigascale Integration Design Challenges & Opportunities Shekhar Borkar Circuit Research, Intel Labs October 24, 2004 Outline CMOS technology challenges Technology, circuit and μarchitecture solutions Integration
Gigascale Integration Design Challenges & Opportunities Shekhar Borkar Circuit Research, Intel Labs October 24, 2004 Outline CMOS technology challenges Technology, circuit and μarchitecture solutions Integration
Introduction to Microprocessor
 Introduction to Microprocessor Slide 1 Microprocessor A microprocessor is a multipurpose, programmable, clock-driven, register-based electronic device That reads binary instructions from a storage device
Introduction to Microprocessor Slide 1 Microprocessor A microprocessor is a multipurpose, programmable, clock-driven, register-based electronic device That reads binary instructions from a storage device
Memory Management. Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1
 Memory Management Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1 CPU management Roadmap Process, thread, synchronization, scheduling Memory management Virtual memory Disk
Memory Management Disclaimer: some slides are adopted from book authors slides with permission 1 CPU management Roadmap Process, thread, synchronization, scheduling Memory management Virtual memory Disk
Chapter 1 Computer System Overview
 Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 1 Computer System Overview Seventh Edition By William Stallings Course Outline & Marks Distribution Hardware Before mid Memory After mid Linux
Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 1 Computer System Overview Seventh Edition By William Stallings Course Outline & Marks Distribution Hardware Before mid Memory After mid Linux
TQ2440 Development Platform Manual
 TQ2440 Development Platform Manual 0 Directory Directory... 1 Chapter 1 Introduction... 7 11Appearance of TQ2440 development platform... 7 12Hardware resource of TQ2440... 7 13Software introduction of
TQ2440 Development Platform Manual 0 Directory Directory... 1 Chapter 1 Introduction... 7 11Appearance of TQ2440 development platform... 7 12Hardware resource of TQ2440... 7 13Software introduction of
Title: Using low-power dual-port for inter processor communication in next generation mobile handsets
 Title: Using low-power dual-port for inter processor communication in next generation mobile handsets Abstract: The convergence of mobile phones and other consumer-driven devices such as PDAs, MP3 players,
Title: Using low-power dual-port for inter processor communication in next generation mobile handsets Abstract: The convergence of mobile phones and other consumer-driven devices such as PDAs, MP3 players,
Chapter 8 Main Memory
 COP 4610: Introduction to Operating Systems (Spring 2014) Chapter 8 Main Memory Zhi Wang Florida State University Contents Background Swapping Contiguous memory allocation Paging Segmentation OS examples
COP 4610: Introduction to Operating Systems (Spring 2014) Chapter 8 Main Memory Zhi Wang Florida State University Contents Background Swapping Contiguous memory allocation Paging Segmentation OS examples
NanoMind Z7000. Datasheet On-board CPU and FPGA for space applications
 NanoMind Z7000 Datasheet On-board CPU and FPGA for space applications 1 Table of Contents 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS... 2 2 OVERVIEW... 3 2.1 HIGHLIGHTED FEATURES... 3 2.2 BLOCK DIAGRAM... 4 2.3 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION...
NanoMind Z7000 Datasheet On-board CPU and FPGA for space applications 1 Table of Contents 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS... 2 2 OVERVIEW... 3 2.1 HIGHLIGHTED FEATURES... 3 2.2 BLOCK DIAGRAM... 4 2.3 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION...
Memory classification:- Topics covered:- types,organization and working
 Memory classification:- Topics covered:- types,organization and working 1 Contents What is Memory? Cache Memory PC Memory Organisation Types 2 Memory what is it? Usually we consider this to be RAM, ROM
Memory classification:- Topics covered:- types,organization and working 1 Contents What is Memory? Cache Memory PC Memory Organisation Types 2 Memory what is it? Usually we consider this to be RAM, ROM
MYD-IMX28X Development Board
 MYD-IMX28X Development Board MYC-IMX28X CPU Module as Controller Board Two 1.27mm pitch 80-pin SMT Connectors for Board-to-Board Connections 454MHz Freescale i.mx28 Series ARM926EJ-S Processors 128MB DDR2
MYD-IMX28X Development Board MYC-IMX28X CPU Module as Controller Board Two 1.27mm pitch 80-pin SMT Connectors for Board-to-Board Connections 454MHz Freescale i.mx28 Series ARM926EJ-S Processors 128MB DDR2
NS9210/NS9215. Overview. Block Diagram. NS µ CMOS, 265-pin BGA. Features/Benefits. Platforms and Services.
 NS9210/NS9215 32-bit NET+ARM Processor Family Cost-efficient, small footprint ARM926EJ-S processor with integrated encryption and unique interface flexibility. Overview The NS9210/NS9215 processor family
NS9210/NS9215 32-bit NET+ARM Processor Family Cost-efficient, small footprint ARM926EJ-S processor with integrated encryption and unique interface flexibility. Overview The NS9210/NS9215 processor family
Memory Management. Dr. Yingwu Zhu
 Memory Management Dr. Yingwu Zhu Big picture Main memory is a resource A process/thread is being executing, the instructions & data must be in memory Assumption: Main memory is infinite Allocation of memory
Memory Management Dr. Yingwu Zhu Big picture Main memory is a resource A process/thread is being executing, the instructions & data must be in memory Assumption: Main memory is infinite Allocation of memory
Nevis ADC Design. Jaroslav Bán. Columbia University. June 4, LAr ADC Review. LAr ADC Review. Jaroslav Bán
 Nevis ADC Design Columbia University June 4, 2014 Outline The goals of the project Introductory remarks The road toward the design Components developed in Nevis09, Nevis10 and Nevis12 Nevis13 chip Architecture
Nevis ADC Design Columbia University June 4, 2014 Outline The goals of the project Introductory remarks The road toward the design Components developed in Nevis09, Nevis10 and Nevis12 Nevis13 chip Architecture
SPEAr: an HW/SW reconfigurable multi processor architecture
 Welcome to the «SPEAr Age» Structured Processor Enhanced Architecture SPEAr: an HW/SW reconfigurable multi processor architecture COMPUTER PERIPHERAL GROUP Outline Economics of Moore s law and market view
Welcome to the «SPEAr Age» Structured Processor Enhanced Architecture SPEAr: an HW/SW reconfigurable multi processor architecture COMPUTER PERIPHERAL GROUP Outline Economics of Moore s law and market view
Chapter 11: Input/Output Organisation. Lesson 15: Standard I/O bus PCI
 Chapter 11: Input/Output Organisation Lesson 15: Standard I/O bus PCI Objective Familiar with I/O bus and standard I/O interfaces parallel bus PCI (Peripheral Connect Interface) for a synchronous parallel
Chapter 11: Input/Output Organisation Lesson 15: Standard I/O bus PCI Objective Familiar with I/O bus and standard I/O interfaces parallel bus PCI (Peripheral Connect Interface) for a synchronous parallel
Computer Science 146. Computer Architecture
 Computer Architecture Spring 2004 Harvard University Instructor: Prof. dbrooks@eecs.harvard.edu Lecture 18: Virtual Memory Lecture Outline Review of Main Memory Virtual Memory Simple Interleaving Cycle
Computer Architecture Spring 2004 Harvard University Instructor: Prof. dbrooks@eecs.harvard.edu Lecture 18: Virtual Memory Lecture Outline Review of Main Memory Virtual Memory Simple Interleaving Cycle
