Parallel Method for Dasymetric Mapping. Sam Zhang
|
|
|
- Wesley Marshall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Parallel Method for Dasymetric Mapping Sam Zhang
2 Overview Dasymetric mapping is a commonlyapplied algorithm in GIS that can determine the population distribution in a high resolution level. It maps the population data with a coarse resolution with a high-resolution ancillary-level data! (most of the time, it s land type data).! However, for a large-scale problem,! it may take a long time to do this! process. So we will propose a parallel! method for this problem. And we will! use this method to perform dasymetric! mapping on Tennessee. If the result is successful, we can expand the source area to the whole U.S.!
3 Size of District Units Three levels of district units are included. The largest one is state, the second largest is block group, the smallest is 30m*30m grid. U.S. contains block groups. Thus a state will contain about 4000 block groups. There are about 10^10 grids in the U.S. Thus there are about grids in a block group.
4 Datasets NLCD dataset: A x matrix in.img format. (raster file) The value of each entry corresponds to a land type. Boundary data of block groups are polygons(vector file) They represent the shape of different block groups in a state. ACS Summary File stores the estimate of population in every block group.
5 Two Stages From tables/raw data to matrices NLCD Data extract Matrix A Boundary File for block groups rasterize QGIS/GDAL Matrix B ACS Summary File Table extract Array x From matrices to result A x B C
6 What is A,B and x? The first step is needed because the three datasets are on different enumeration unit and are in different format. Our output will produce two matrices and an array. They are all on the state level, and the entries of both matrices are on the level of 30*30 grids. So matrix A is the statelevel NLCD matrix. Matrix B is the state-level block group matrix(each entry corresponds to a region on the map, indicating which block group this region belongs to). Array x tells the population in each block group in this state.
7 Matrix A 11-Open water 21-Developed, Low Intensity 22-Developed, Medium Intensity 51-Dwarf scrub Matrix B 1-Block group 1 2-Block group 2 3-Block group 3
8 Matrices Matrix A Matrix B
9 Second stage The second stage is to get matrix C: A matrix that stores how many people are there in each 30*30 grid. First of all, we have to assign weights according to the land type. Each land type will be given a weight according to their ability to reside people. This weight is determined by some regression method. This step changes matrix A to another weight matrix(w) of the same size. We can count the total weights in a block group and store this total-weight in another array y(same length as x).
10 Regression Method Now we have the land type data for Tennessee, however, it cannot be used directly to determine population distribution. However, it can be used to give a brief estimate of population density in each 30m*30m grid. We can use a linear regression model to model the relation between land type and density:!!! where is the population of zone S; is the intercept term; is the coefficient for land cover c; is the area of land cover c within zone s; C is the number of populated land cover types occurring within study region; and is a random error term.! It can also be written as:! where and are vectors. Negative population totals can also be avoided by using Poisson regression:!!! Here S(source zone) is a block group. The values in are the estimated population density for cells with different land types.!
11 Matrix A Matrix W 11-Open water 21-Developed, Low Intensity 22-Developed, Medium Intensity 51-Dwarf scrub
12 Second stage(cont.) Now we can easily get our result. For example, given a grid, we know it s from block group a, its weight in W is W1, the total weight of a is W*, total population in block group a is P, then population in this grid will be estimated as W1*P/(W*). All the values in a grid can be computed in this way.
13 Result
14 Parallel Method We would like to use distributed memory to implement the parallel method, so a state will be cut into several boxes. Two parts will be different from serial method. The first part is in determining the brief estimate of population density. Each box will calculate the for itself. The values in can be different for different boxes. Also, in the regression process, we need the total area of land cover c within zone s for every block group. However, for those block groups on the intersection between boxes, we cannot know this value for them. Thus we will find these block groups and make sure they will not participate in the regression. The second part is that we need to transfer the weight of cells of block groups on the intersection between boxes to its neighbourhood to get the total weight of that block group.!! Due to more than 90% or more block groups will be internal area(not on the intersection), and their population density can be calculated using the same method as the serial one inside each box, the data transferring on the boundary will not take a long time in general.!
15 Future Work For sure, the method above is not the only method. We can try polygon method instead of grid method. Also we plan to implement Prof. Nagle s PMEDM Method for dasymetric mapping and adapt it to become parallel. We will also extend our studying area into the whole U.S. After that, we will make analysis on the improvement of efficiency using parallel computing compared to doing serially.!
Review of Cartographic Data Types and Data Models
 Review of Cartographic Data Types and Data Models GIS Data Models Raster Versus Vector in GIS Analysis Fundamental element used to represent spatial features: Raster: pixel or grid cell. Vector: x,y coordinate
Review of Cartographic Data Types and Data Models GIS Data Models Raster Versus Vector in GIS Analysis Fundamental element used to represent spatial features: Raster: pixel or grid cell. Vector: x,y coordinate
EAT 233/3 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM (GIS)
 EAT 233/3 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM (GIS) CO3: Ability to produce detail mapping using geographic information systems (GIS) BY : AYU WAZIRA AZHARI SPATIAL DATA & THE MODELLING Spatial Data in GIS Spatial
EAT 233/3 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM (GIS) CO3: Ability to produce detail mapping using geographic information systems (GIS) BY : AYU WAZIRA AZHARI SPATIAL DATA & THE MODELLING Spatial Data in GIS Spatial
GIS Data Models. 4/9/ GIS Data Models
 GIS Data Models 1 Conceptual models of the real world The real world can be described using two conceptually different models: 1. As discrete objects, possible to represent as points, lines or polygons.
GIS Data Models 1 Conceptual models of the real world The real world can be described using two conceptually different models: 1. As discrete objects, possible to represent as points, lines or polygons.
Cell based GIS. Introduction to rasters
 Week 9 Cell based GIS Introduction to rasters topics of the week Spatial Problems Modeling Raster basics Application functions Analysis environment, the mask Application functions Spatial Analyst in ArcGIS
Week 9 Cell based GIS Introduction to rasters topics of the week Spatial Problems Modeling Raster basics Application functions Analysis environment, the mask Application functions Spatial Analyst in ArcGIS
LECTURE 2 SPATIAL DATA MODELS
 LECTURE 2 SPATIAL DATA MODELS Computers and GIS cannot directly be applied to the real world: a data gathering step comes first. Digital computers operate in numbers and characters held internally as binary
LECTURE 2 SPATIAL DATA MODELS Computers and GIS cannot directly be applied to the real world: a data gathering step comes first. Digital computers operate in numbers and characters held internally as binary
Measure the Perimeter of Polygons Over a Surface. Operations. What Do I Need?
 Measure the Perimeter of Polygons Over a Surface Operations What Do I Need? Incremental Frontage Score To measure the perimeter of polygons over a surface you need to have two input map layers. The first
Measure the Perimeter of Polygons Over a Surface Operations What Do I Need? Incremental Frontage Score To measure the perimeter of polygons over a surface you need to have two input map layers. The first
Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis. GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University
 Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University 1 Spatial Data It can be most simply defined as information that describes the distribution
Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University 1 Spatial Data It can be most simply defined as information that describes the distribution
Remote Sensing and GIS. GIS Spatial Overlay Analysis
 Subject Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Geology Remote Sensing and GIS GIS Spatial Overlay Analysis RS & GIS XXXI Principal Investigator Co-Principal Investigator Co-Principal Investigator
Subject Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Geology Remote Sensing and GIS GIS Spatial Overlay Analysis RS & GIS XXXI Principal Investigator Co-Principal Investigator Co-Principal Investigator
Tips for a Good Meshing Experience
 Tips for a Good Meshing Experience Meshes are very powerful and flexible for modeling 2D overland flows in a complex urban environment. However, complex geometries can be frustrating for many modelers
Tips for a Good Meshing Experience Meshes are very powerful and flexible for modeling 2D overland flows in a complex urban environment. However, complex geometries can be frustrating for many modelers
Lecture 7 Digitizing. Dr. Zhang Spring, 2017
 Lecture 7 Digitizing Dr. Zhang Spring, 2017 Model of the course Using and making maps Navigating GIS maps Map design Working with spatial data Geoprocessing Spatial data infrastructure Digitizing File
Lecture 7 Digitizing Dr. Zhang Spring, 2017 Model of the course Using and making maps Navigating GIS maps Map design Working with spatial data Geoprocessing Spatial data infrastructure Digitizing File
PART 1. Answers module 6: 'Transformations'
 Answers module 6: 'Transformations' PART 1 1 a A nominal measure scale refers to data that are in named categories. There is no order among these categories. That is, no category is better or more than
Answers module 6: 'Transformations' PART 1 1 a A nominal measure scale refers to data that are in named categories. There is no order among these categories. That is, no category is better or more than
Unit 3, Lesson 3.1 Creating and Graphing Equations Using Standard Form
 Unit 3, Lesson 3.1 Creating and Graphing Equations Using Standard Form Imagine the path of a basketball as it leaves a player s hand and swooshes through the net. Or, imagine the path of an Olympic diver
Unit 3, Lesson 3.1 Creating and Graphing Equations Using Standard Form Imagine the path of a basketball as it leaves a player s hand and swooshes through the net. Or, imagine the path of an Olympic diver
Introduction to Geographic Information Science. Some Updates. Last Lecture 4/6/2017. Geography 4103 / Raster Data and Tesselations.
 Geography 43 / 3 Introduction to Geographic Information Science Raster Data and Tesselations Schedule Some Updates Last Lecture We finished DBMS and learned about storage of data in complex databases Relational
Geography 43 / 3 Introduction to Geographic Information Science Raster Data and Tesselations Schedule Some Updates Last Lecture We finished DBMS and learned about storage of data in complex databases Relational
How to Research Chemicals Using
 Tool Kit Item # 5 How to Research Chemicals Using ChemTRAC TK5.1 Tool Kit Item # 5 how to research chemicals using chemtrac You have a right to know about the various chemical substances that are used
Tool Kit Item # 5 How to Research Chemicals Using ChemTRAC TK5.1 Tool Kit Item # 5 how to research chemicals using chemtrac You have a right to know about the various chemical substances that are used
AUTOMATING MANNING S N COEFFICIENT VALUE ASSIGNMENTS FOR HYDRAULIC MODELING
 Imagery Source: Bing Maps via ESRI AUTOMATING MANNING S N COEFFICIENT VALUE ASSIGNMENTS FOR HYDRAULIC MODELING Kyle Gallagher, GISP Black & Veatch Special Projects Corp. Project Overview USACE Tulsa District
Imagery Source: Bing Maps via ESRI AUTOMATING MANNING S N COEFFICIENT VALUE ASSIGNMENTS FOR HYDRAULIC MODELING Kyle Gallagher, GISP Black & Veatch Special Projects Corp. Project Overview USACE Tulsa District
Spatial Analysis (Vector) II
 Spatial Analysis (Vector) II GEOG 300, Lecture 9 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 A Spatial Network is a set of geographic locations interconnected in a system by a number of routes is a system of linear features
Spatial Analysis (Vector) II GEOG 300, Lecture 9 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 A Spatial Network is a set of geographic locations interconnected in a system by a number of routes is a system of linear features
AN INTRODUCTION TO GRID ANALYSIS: HOTSPOT DETECTION
 AN INTRODUCTION TO GRID ANALYSIS: HOTSPOT DETECTION etraining Introduction Use the Grid Analysis commands of GeoMedia to extract hotspot locations from a feature class containing a collection of incident
AN INTRODUCTION TO GRID ANALYSIS: HOTSPOT DETECTION etraining Introduction Use the Grid Analysis commands of GeoMedia to extract hotspot locations from a feature class containing a collection of incident
Spatial Data Models. Raster uses individual cells in a matrix, or grid, format to represent real world entities
 Spatial Data Models Raster uses individual cells in a matrix, or grid, format to represent real world entities Vector uses coordinates to store the shape of spatial data objects David Tenenbaum GEOG 7
Spatial Data Models Raster uses individual cells in a matrix, or grid, format to represent real world entities Vector uses coordinates to store the shape of spatial data objects David Tenenbaum GEOG 7
A population grid for Andalusia Year Institute of Statistics and Cartography of Andalusia (IECA) Sofia (BU), 24 th October 2013
 A population grid for Andalusia Year 2013 Institute of Statistics and Cartography of Andalusia (IECA) Sofia (BU), 24 th October 2013 IECA project. Population grid cells sized 250 x 250m for Andalusia 1.
A population grid for Andalusia Year 2013 Institute of Statistics and Cartography of Andalusia (IECA) Sofia (BU), 24 th October 2013 IECA project. Population grid cells sized 250 x 250m for Andalusia 1.
Lecturer 2: Spatial Concepts and Data Models
 Lecturer 2: Spatial Concepts and Data Models 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Models of Spatial Information 2.3 Three-Step Database Design 2.4 Extending ER with Spatial Concepts 2.5 Summary Learning Objectives Learning
Lecturer 2: Spatial Concepts and Data Models 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Models of Spatial Information 2.3 Three-Step Database Design 2.4 Extending ER with Spatial Concepts 2.5 Summary Learning Objectives Learning
Section 1.4 Equations and Graphs of Polynomial Functions soln.notebook September 25, 2017
 Section 1.4 Equations and Graphs of Polynomial Functions Sep 21 8:49 PM Factors tell us... the zeros of the function the roots of the equation the x intercepts of the graph Multiplicity (of a zero) > The
Section 1.4 Equations and Graphs of Polynomial Functions Sep 21 8:49 PM Factors tell us... the zeros of the function the roots of the equation the x intercepts of the graph Multiplicity (of a zero) > The
v Importing Rasters SMS 11.2 Tutorial Requirements Raster Module Map Module Mesh Module Time minutes Prerequisites Overview Tutorial
 v. 11.2 SMS 11.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial teaches how to import a Raster, view elevations at individual points, change display options for multiple views of the data, show the 2D profile plots,
v. 11.2 SMS 11.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial teaches how to import a Raster, view elevations at individual points, change display options for multiple views of the data, show the 2D profile plots,
Steps for Modeling a Proposed New Reservoir in GIS
 Steps for Modeling a Proposed New Reservoir in GIS Requirements: ArcGIS ArcMap, ArcScene, Spatial Analyst, and 3D Analyst There s a new reservoir proposed for Right Hand Fork in Logan Canyon. I wanted
Steps for Modeling a Proposed New Reservoir in GIS Requirements: ArcGIS ArcMap, ArcScene, Spatial Analyst, and 3D Analyst There s a new reservoir proposed for Right Hand Fork in Logan Canyon. I wanted
RASTER ANALYSIS S H A W N L. P E N M A N E A R T H D A T A A N A LY S I S C E N T E R U N I V E R S I T Y O F N E W M E X I C O
 RASTER ANALYSIS S H A W N L. P E N M A N E A R T H D A T A A N A LY S I S C E N T E R U N I V E R S I T Y O F N E W M E X I C O TOPICS COVERED Spatial Analyst basics Raster / Vector conversion Raster data
RASTER ANALYSIS S H A W N L. P E N M A N E A R T H D A T A A N A LY S I S C E N T E R U N I V E R S I T Y O F N E W M E X I C O TOPICS COVERED Spatial Analyst basics Raster / Vector conversion Raster data
Building Vector Layers
 Building Vector Layers in QGIS Introduction: Spatially referenced data can be separated into two categories, raster and vector data. This week, we focus on the building of vector features. Vector shapefiles
Building Vector Layers in QGIS Introduction: Spatially referenced data can be separated into two categories, raster and vector data. This week, we focus on the building of vector features. Vector shapefiles
Course Number 432/433 Title Algebra II (A & B) H Grade # of Days 120
 Whitman-Hanson Regional High School provides all students with a high- quality education in order to develop reflective, concerned citizens and contributing members of the global community. Course Number
Whitman-Hanson Regional High School provides all students with a high- quality education in order to develop reflective, concerned citizens and contributing members of the global community. Course Number
Classification (or thematic) accuracy assessment. Lecture 8 March 11, 2005
 Classification (or thematic) accuracy assessment Lecture 8 March 11, 2005 Why and how Remote sensing-derived thematic information are becoming increasingly important. Unfortunately, they contain errors.
Classification (or thematic) accuracy assessment Lecture 8 March 11, 2005 Why and how Remote sensing-derived thematic information are becoming increasingly important. Unfortunately, they contain errors.
Multidimensional Data and Modelling
 Multidimensional Data and Modelling 1 Problems of multidimensional data structures l multidimensional (md-data or spatial) data and their implementation of operations between objects (spatial data practically
Multidimensional Data and Modelling 1 Problems of multidimensional data structures l multidimensional (md-data or spatial) data and their implementation of operations between objects (spatial data practically
REVIEW FOR THE FIRST SEMESTER EXAM
 Algebra II Honors @ Name Period Date REVIEW FOR THE FIRST SEMESTER EXAM You must NEATLY show ALL of your work ON SEPARATE PAPER in order to receive full credit! All graphs must be done on GRAPH PAPER!
Algebra II Honors @ Name Period Date REVIEW FOR THE FIRST SEMESTER EXAM You must NEATLY show ALL of your work ON SEPARATE PAPER in order to receive full credit! All graphs must be done on GRAPH PAPER!
Algorithms for GIS csci3225
 Algorithms for GIS csci3225 Laura Toma Bowdoin College Spatial data types and models Spatial data in GIS satellite imagery planar maps surfaces networks point cloud (LiDAR) Spatial data in GIS satellite
Algorithms for GIS csci3225 Laura Toma Bowdoin College Spatial data types and models Spatial data in GIS satellite imagery planar maps surfaces networks point cloud (LiDAR) Spatial data in GIS satellite
Calculator Basics TI-83, TI-83 +, TI-84. Index Page
 Calculator Basics TI-83, TI-83 +, TI-84 Index Page Getting Started Page 1 Graphing Page 2 Evaluating Functions page 4 Minimum and Maximum Values Page 5 Table of Values Page 6 Graphing Scatter Plots Page
Calculator Basics TI-83, TI-83 +, TI-84 Index Page Getting Started Page 1 Graphing Page 2 Evaluating Functions page 4 Minimum and Maximum Values Page 5 Table of Values Page 6 Graphing Scatter Plots Page
Understanding Geospatial Data Models
 Understanding Geospatial Data Models 1 A geospatial data model is a formal means of representing spatially referenced information. It is a simplified view of physical entities and a conceptualization of
Understanding Geospatial Data Models 1 A geospatial data model is a formal means of representing spatially referenced information. It is a simplified view of physical entities and a conceptualization of
v SMS Tutorials Working with Rasters Prerequisites Requirements Time Objectives
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Objectives Learn how to import a Raster, view elevations at individual points, change display options for multiple views of the data, show the 2D profile plots, and interpolate
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Objectives Learn how to import a Raster, view elevations at individual points, change display options for multiple views of the data, show the 2D profile plots, and interpolate
CS 664 Segmentation. Daniel Huttenlocher
 CS 664 Segmentation Daniel Huttenlocher Grouping Perceptual Organization Structural relationships between tokens Parallelism, symmetry, alignment Similarity of token properties Often strong psychophysical
CS 664 Segmentation Daniel Huttenlocher Grouping Perceptual Organization Structural relationships between tokens Parallelism, symmetry, alignment Similarity of token properties Often strong psychophysical
v Working with Rasters SMS 12.1 Tutorial Requirements Raster Module Map Module Mesh Module Time minutes Prerequisites Overview Tutorial
 v. 12.1 SMS 12.1 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial teaches how to import a Raster, view elevations at individual points, change display options for multiple views of the data, show the 2D profile plots,
v. 12.1 SMS 12.1 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial teaches how to import a Raster, view elevations at individual points, change display options for multiple views of the data, show the 2D profile plots,
Attribute Accuracy. Quantitative accuracy refers to the level of bias in estimating the values assigned such as estimated values of ph in a soil map.
 Attribute Accuracy Objectives (Entry) This basic concept of attribute accuracy has been introduced in the unit of quality and coverage. This unit will teach a basic technique to quantify the attribute
Attribute Accuracy Objectives (Entry) This basic concept of attribute accuracy has been introduced in the unit of quality and coverage. This unit will teach a basic technique to quantify the attribute
Name: Date: June 27th, 2011 GIS Boot Camps For Educators Lecture_3
 Name: Date: June 27th, 2011 GIS Boot Camps For Educators Lecture_3 Practical: Creating and Editing Shapefiles Using Straight, AutoComplete and Cut Polygon Tools Use ArcCatalog to copy data files from:
Name: Date: June 27th, 2011 GIS Boot Camps For Educators Lecture_3 Practical: Creating and Editing Shapefiles Using Straight, AutoComplete and Cut Polygon Tools Use ArcCatalog to copy data files from:
Exercise 5: Import Tabular GPS Data and Digitizing
 Exercise 5: Import Tabular GPS Data and Digitizing You can create NEW GIS data layers by digitizing on screen with an aerial photograph or other image as a back-drop. You can also digitize using imported
Exercise 5: Import Tabular GPS Data and Digitizing You can create NEW GIS data layers by digitizing on screen with an aerial photograph or other image as a back-drop. You can also digitize using imported
UNDERSTAND HOW TO SET UP AND RUN A HYDRAULIC MODEL IN HEC-RAS CREATE A FLOOD INUNDATION MAP IN ARCGIS.
 CE 412/512, Spring 2017 HW9: Introduction to HEC-RAS and Floodplain Mapping Due: end of class, print and hand in. HEC-RAS is a Hydrologic Modeling System that is designed to describe the physical properties
CE 412/512, Spring 2017 HW9: Introduction to HEC-RAS and Floodplain Mapping Due: end of class, print and hand in. HEC-RAS is a Hydrologic Modeling System that is designed to describe the physical properties
Class #2. Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures
 Class #2 Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures Role of a Data Model Levels of Data Model Abstraction GIS as Digital
Class #2 Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures Role of a Data Model Levels of Data Model Abstraction GIS as Digital
GIS in agriculture scale farm level - used in agricultural applications - managing crop yields, monitoring crop rotation techniques, and estimate
 Types of Input GIS in agriculture scale farm level - used in agricultural applications - managing crop yields, monitoring crop rotation techniques, and estimate soil loss from individual farms or agricultural
Types of Input GIS in agriculture scale farm level - used in agricultural applications - managing crop yields, monitoring crop rotation techniques, and estimate soil loss from individual farms or agricultural
Esri International User Conference. July San Diego Convention Center. Lidar Solutions. Clayton Crawford
 Esri International User Conference July 23 27 San Diego Convention Center Lidar Solutions Clayton Crawford Outline Data structures, tools, and workflows Assessing lidar point coverage and sample density
Esri International User Conference July 23 27 San Diego Convention Center Lidar Solutions Clayton Crawford Outline Data structures, tools, and workflows Assessing lidar point coverage and sample density
Geographic Information Systems. using QGIS
 Geographic Information Systems using QGIS 1 - INTRODUCTION Generalities A GIS (Geographic Information System) consists of: -Computer hardware -Computer software - Digital Data Generalities GIS softwares
Geographic Information Systems using QGIS 1 - INTRODUCTION Generalities A GIS (Geographic Information System) consists of: -Computer hardware -Computer software - Digital Data Generalities GIS softwares
Logan City GIS Master Plan. Term Project. Colton Smith. David Tarboton CEE 6440
 Logan City GIS Master Plan Term Project Colton Smith David Tarboton CEE 6440 November 29, 2012 Introduction Logan City has lots of data available for streets, canals, trails, zoning maps, and municipalities.
Logan City GIS Master Plan Term Project Colton Smith David Tarboton CEE 6440 November 29, 2012 Introduction Logan City has lots of data available for streets, canals, trails, zoning maps, and municipalities.
Overview.! Manual Digitizing! Heads-up Digitizing! Common Errors! Summary! Heads-up Digitizing Tutorial
 Digitizing Overview! Manual Digitizing! Heads-up Digitizing! Common Errors! Summary! Heads-up Digitizing Tutorial Manual Digitizing! Simplest, easiest, and cheapest method of capturing vector data from
Digitizing Overview! Manual Digitizing! Heads-up Digitizing! Common Errors! Summary! Heads-up Digitizing Tutorial Manual Digitizing! Simplest, easiest, and cheapest method of capturing vector data from
THE TOOLS OF AUTOMATED GENERALIZATION AND BUILDING GENERALIZATION IN AN ArcGIS ENVIRONMENT
 Vol. XIX, 2011, No. 1, 1 7, DOI: 10.2478/v10189-011-0001-4 V. DROPPOVÁ THE TOOLS OF AUTOMATED GENERALIZATION AND BUILDING GENERALIZATION IN AN ArcGIS ENVIRONMENT Veronika Droppová email: veronika.droppova@gmail.com
Vol. XIX, 2011, No. 1, 1 7, DOI: 10.2478/v10189-011-0001-4 V. DROPPOVÁ THE TOOLS OF AUTOMATED GENERALIZATION AND BUILDING GENERALIZATION IN AN ArcGIS ENVIRONMENT Veronika Droppová email: veronika.droppova@gmail.com
Undo Button Clicking this tool will undo the last action. Clicking on this tool multiple times will undo all subsequent changes that were made.
 SMS Featured Icons: Editor Window This document includes a brief description of the tools in the SMS Desktop Software Editor windows, as well as showing you the toolbar shortcuts to easily access these
SMS Featured Icons: Editor Window This document includes a brief description of the tools in the SMS Desktop Software Editor windows, as well as showing you the toolbar shortcuts to easily access these
Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources. This course consists of 9 lessons, including Power point presentations, demonstrations,
 Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources. This course consists of 9 lessons, including Power point presentations, demonstrations, readings, and hands on GIS lab exercises. Following the last
Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources. This course consists of 9 lessons, including Power point presentations, demonstrations, readings, and hands on GIS lab exercises. Following the last
Combine Yield Data From Combine to Contour Map Ag Leader
 Combine Yield Data From Combine to Contour Map Ag Leader Exporting the Yield Data Using SMS Program 1. Data format On Hard Drive. 2. Start program SMS Basic. a. In the File menu choose Open. b. Click on
Combine Yield Data From Combine to Contour Map Ag Leader Exporting the Yield Data Using SMS Program 1. Data format On Hard Drive. 2. Start program SMS Basic. a. In the File menu choose Open. b. Click on
Channel Conditions in the Onion Creek Watershed. Integrating High Resolution Elevation Data in Flood Forecasting
 Channel Conditions in the Onion Creek Watershed Integrating High Resolution Elevation Data in Flood Forecasting Lukas Godbout GIS in Water Resources CE394K Fall 2016 Introduction Motivation Flooding is
Channel Conditions in the Onion Creek Watershed Integrating High Resolution Elevation Data in Flood Forecasting Lukas Godbout GIS in Water Resources CE394K Fall 2016 Introduction Motivation Flooding is
UNIT 5: GEOMETRIC AND ALGEBRAIC CONNECTIONS. Apply Geometric Concepts in Modeling Situations
 UNIT 5: GEOMETRIC AND ALGEBRAIC CONNECTIONS This unit investigates coordinate geometry. Students look at equations for circles and use given information to derive equations for representations of these
UNIT 5: GEOMETRIC AND ALGEBRAIC CONNECTIONS This unit investigates coordinate geometry. Students look at equations for circles and use given information to derive equations for representations of these
1.1 Pearson Modeling and Equation Solving
 Date:. Pearson Modeling and Equation Solving Syllabus Objective:. The student will solve problems using the algebra of functions. Modeling a Function: Numerical (data table) Algebraic (equation) Graphical
Date:. Pearson Modeling and Equation Solving Syllabus Objective:. The student will solve problems using the algebra of functions. Modeling a Function: Numerical (data table) Algebraic (equation) Graphical
layers in a raster model
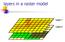 layers in a raster model Layer 1 Layer 2 layers in an vector-based model (1) Layer 2 Layer 1 layers in an vector-based model (2) raster versus vector data model Raster model Vector model Simple data structure
layers in a raster model Layer 1 Layer 2 layers in an vector-based model (1) Layer 2 Layer 1 layers in an vector-based model (2) raster versus vector data model Raster model Vector model Simple data structure
v CMS-Wave Analysis SMS 12.2 Tutorial Prerequisites Requirements Time Objectives
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Objectives This workshop gives a brief introduction to the CMS-Wave interface and model. This model is similar to STWAVE and the tutorial for the models is similar. As with the
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Objectives This workshop gives a brief introduction to the CMS-Wave interface and model. This model is similar to STWAVE and the tutorial for the models is similar. As with the
Topic 5: Raster and Vector Data Models
 Geography 38/42:286 GIS 1 Topic 5: Raster and Vector Data Models Chapters 3 & 4: Chang (Chapter 4: DeMers) 1 The Nature of Geographic Data Most features or phenomena occur as either: discrete entities
Geography 38/42:286 GIS 1 Topic 5: Raster and Vector Data Models Chapters 3 & 4: Chang (Chapter 4: DeMers) 1 The Nature of Geographic Data Most features or phenomena occur as either: discrete entities
Developing an Interactive GIS Tool for Stream Classification in Northeast Puerto Rico
 Developing an Interactive GIS Tool for Stream Classification in Northeast Puerto Rico Lauren Stachowiak Advanced Topics in GIS Spring 2012 1 Table of Contents: Project Introduction-------------------------------------
Developing an Interactive GIS Tool for Stream Classification in Northeast Puerto Rico Lauren Stachowiak Advanced Topics in GIS Spring 2012 1 Table of Contents: Project Introduction-------------------------------------
Terms and definitions * keep definitions of processes and terms that may be useful for tests, assignments
 Lecture 1 Core of GIS Thematic layers Terms and definitions * keep definitions of processes and terms that may be useful for tests, assignments Lecture 2 What is GIS? Info: value added data Data to solve
Lecture 1 Core of GIS Thematic layers Terms and definitions * keep definitions of processes and terms that may be useful for tests, assignments Lecture 2 What is GIS? Info: value added data Data to solve
Accuracy, Support, and Interoperability. Michael F. Goodchild University of California Santa Barbara
 Accuracy, Support, and Interoperability Michael F. Goodchild University of California Santa Barbara The traditional view Every object has a true position and set of attributes with enough time and resources
Accuracy, Support, and Interoperability Michael F. Goodchild University of California Santa Barbara The traditional view Every object has a true position and set of attributes with enough time and resources
George Mason University Department of Civil, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering. Dr. Celso Ferreira Prepared by Lora Baumgartner
 George Mason University Department of Civil, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering Dr. Celso Ferreira Prepared by Lora Baumgartner Exercise Topic: Getting started with HEC GeoRAS Objective: Create
George Mason University Department of Civil, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering Dr. Celso Ferreira Prepared by Lora Baumgartner Exercise Topic: Getting started with HEC GeoRAS Objective: Create
Sedimentation in Aquilla Lake Hill County, Texas
 Sedimentation in Aquilla Lake Hill County, Texas by Lorena Roque Martinez, GIS and GPS Applications in Earth Sciences (GEO 327G) Introduction The Texas Water Development Board (TWDB) is in charge of offering
Sedimentation in Aquilla Lake Hill County, Texas by Lorena Roque Martinez, GIS and GPS Applications in Earth Sciences (GEO 327G) Introduction The Texas Water Development Board (TWDB) is in charge of offering
YRERFS GIS WORKFLOW AND MODELING PROCESS
 YRERFS GIS WORKFLOW AND MODELING PROCESS Presenter Name Presenter Title Duty Location Date of Presentation US Army Corps of Engineers YRERFS Downy Woodpecker Riparian Forest (RF) Habitat Determination
YRERFS GIS WORKFLOW AND MODELING PROCESS Presenter Name Presenter Title Duty Location Date of Presentation US Army Corps of Engineers YRERFS Downy Woodpecker Riparian Forest (RF) Habitat Determination
Lab 5: Image Analysis with ArcGIS 10 Unsupervised Classification
 Lab 5: Image Analysis with ArcGIS 10 Unsupervised Classification Peter E. Price TerraView 2010 Peter E. Price All rights reserved Revised 03/2011 Revised for Geob 373 by BK Feb 28, 2017. V3 The information
Lab 5: Image Analysis with ArcGIS 10 Unsupervised Classification Peter E. Price TerraView 2010 Peter E. Price All rights reserved Revised 03/2011 Revised for Geob 373 by BK Feb 28, 2017. V3 The information
ENGRG Introduction to GIS
 ENGRG 59910 Introduction to GIS Michael Piasecki April 3, 2014 Lecture 11: Raster Analysis GIS Related? 4/3/2014 ENGRG 59910 Intro to GIS 2 1 Why we use Raster GIS In our previous discussion of data models,
ENGRG 59910 Introduction to GIS Michael Piasecki April 3, 2014 Lecture 11: Raster Analysis GIS Related? 4/3/2014 ENGRG 59910 Intro to GIS 2 1 Why we use Raster GIS In our previous discussion of data models,
Basic Queries Exercise - Haiti
 Basic Queries Exercise - Haiti Written by Barbara Parmenter, revised by Carolyn Talmadge on September 18, 2016 SETTING UP... 1 WHERE ARE THE HOSPITALS THAT ARE STILL OPERATING? (SELECT BY ATTRIBUTE )...
Basic Queries Exercise - Haiti Written by Barbara Parmenter, revised by Carolyn Talmadge on September 18, 2016 SETTING UP... 1 WHERE ARE THE HOSPITALS THAT ARE STILL OPERATING? (SELECT BY ATTRIBUTE )...
Example 1: Given below is the graph of the quadratic function f. Use the function and its graph to find the following: Outputs
 Quadratic Functions: - functions defined by quadratic epressions (a 2 + b + c) o the degree of a quadratic function is ALWAYS 2 - the most common way to write a quadratic function (and the way we have
Quadratic Functions: - functions defined by quadratic epressions (a 2 + b + c) o the degree of a quadratic function is ALWAYS 2 - the most common way to write a quadratic function (and the way we have
d = (x 2 - x 1 ) 2 + (y 2 - y 1 ) 2 Student Name: Date: Teacher Name: Sunil Dudeja Score:
 Geometry EOC (GSE) Quiz Answer Key Equations and Measurement - (MGSE9 12.G.GPE.4) Use Coordinates For Theorems, (MGSE9 12.G.GPE.5 ) Prove Slope Criteria, (MGSE9 12.G.GPE.6) Find The Point, (MGSE9 12.G.GPE.7
Geometry EOC (GSE) Quiz Answer Key Equations and Measurement - (MGSE9 12.G.GPE.4) Use Coordinates For Theorems, (MGSE9 12.G.GPE.5 ) Prove Slope Criteria, (MGSE9 12.G.GPE.6) Find The Point, (MGSE9 12.G.GPE.7
Geometry Pre AP Graphing Linear Equations
 Geometry Pre AP Graphing Linear Equations Name Date Period Find the x- and y-intercepts and slope of each equation. 1. y = -x 2. x + 3y = 6 3. x = 2 4. y = 0 5. y = 2x - 9 6. 18x 42 y = 210 Graph each
Geometry Pre AP Graphing Linear Equations Name Date Period Find the x- and y-intercepts and slope of each equation. 1. y = -x 2. x + 3y = 6 3. x = 2 4. y = 0 5. y = 2x - 9 6. 18x 42 y = 210 Graph each
NRM435 Spring 2017 Accuracy Assessment of GIS Data
 Accuracy Assessment Lab Page 1 of 18 NRM435 Spring 2017 Accuracy Assessment of GIS Data GIS data always contains errors hopefully the errors are so small that will do not significantly affect the results
Accuracy Assessment Lab Page 1 of 18 NRM435 Spring 2017 Accuracy Assessment of GIS Data GIS data always contains errors hopefully the errors are so small that will do not significantly affect the results
Using ArcGIS for Landcover Classification. Presented by CORE GIS May 8, 2012
 Using ArcGIS for Landcover Classification Presented by CORE GIS May 8, 2012 How to use ArcGIS for Image Classification 1. Find and download the right data 2. Have a look at the data (true color/false color)
Using ArcGIS for Landcover Classification Presented by CORE GIS May 8, 2012 How to use ArcGIS for Image Classification 1. Find and download the right data 2. Have a look at the data (true color/false color)
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 18: Spatial Modeling
 Spatial Analysis in GIS (cont d) GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 18: Spatial Modeling - the basic types of analysis that can be accomplished with a GIS are outlined in The Esri Guide to GIS Analysis
Spatial Analysis in GIS (cont d) GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 18: Spatial Modeling - the basic types of analysis that can be accomplished with a GIS are outlined in The Esri Guide to GIS Analysis
Geography 281 Map Making with GIS Project Three: Viewing Data Spatially
 Geography 281 Map Making with GIS Project Three: Viewing Data Spatially This activity introduces three of the most common thematic maps: Choropleth maps Dot density maps Graduated symbol maps You will
Geography 281 Map Making with GIS Project Three: Viewing Data Spatially This activity introduces three of the most common thematic maps: Choropleth maps Dot density maps Graduated symbol maps You will
Lidar and GIS: Applications and Examples. Dan Hedges Clayton Crawford
 Lidar and GIS: Applications and Examples Dan Hedges Clayton Crawford Outline Data structures, tools, and workflows Assessing lidar point coverage and sample density Creating raster DEMs and DSMs Data area
Lidar and GIS: Applications and Examples Dan Hedges Clayton Crawford Outline Data structures, tools, and workflows Assessing lidar point coverage and sample density Creating raster DEMs and DSMs Data area
Raster model. Raster model. Resolution. Value and data types. Structure and storage. Cell. Values. Data
 Raster model. Resolution. Values and data types 3. Storage. Fitting rasters 5. Map algebra 6. Interpolation 7. Conversion vectorraster 8. Vector vs. raster Raster model Divides the space into a regular
Raster model. Resolution. Values and data types 3. Storage. Fitting rasters 5. Map algebra 6. Interpolation 7. Conversion vectorraster 8. Vector vs. raster Raster model Divides the space into a regular
Representing Geography
 Data models and axioms Chapters 3 and 7 Representing Geography Road map Representing the real world Conceptual models: objects vs fields Implementation models: vector vs raster Vector topological model
Data models and axioms Chapters 3 and 7 Representing Geography Road map Representing the real world Conceptual models: objects vs fields Implementation models: vector vs raster Vector topological model
Data handling 3: Alter Process
 Introduction Geo information Science (GRS 10306) Data handling 3: Alter Process 2009/2010 CGI GIRS 2 Alter / process / analysis / operations definition Query a data handling class of operators which doesn
Introduction Geo information Science (GRS 10306) Data handling 3: Alter Process 2009/2010 CGI GIRS 2 Alter / process / analysis / operations definition Query a data handling class of operators which doesn
How the DSS Works. August 14. Version 1
 How the DSS Works August 14 2009 Note: This document is incomplete and may be incorrect. It is constantly being revised and updated. It is for general information purposes only, and should not be regarded
How the DSS Works August 14 2009 Note: This document is incomplete and may be incorrect. It is constantly being revised and updated. It is for general information purposes only, and should not be regarded
Using GIS To Estimate Changes in Runoff and Urban Surface Cover In Part of the Waller Creek Watershed Austin, Texas
 Using GIS To Estimate Changes in Runoff and Urban Surface Cover In Part of the Waller Creek Watershed Austin, Texas Jordan Thomas 12-6-2009 Introduction The goal of this project is to understand runoff
Using GIS To Estimate Changes in Runoff and Urban Surface Cover In Part of the Waller Creek Watershed Austin, Texas Jordan Thomas 12-6-2009 Introduction The goal of this project is to understand runoff
Matrix Multiplication
 Systolic Arrays Matrix Multiplication Is used in many areas of signal processing, graph theory, graphics, machine learning, physics etc Implementation considerations are based on precision, storage and
Systolic Arrays Matrix Multiplication Is used in many areas of signal processing, graph theory, graphics, machine learning, physics etc Implementation considerations are based on precision, storage and
Classification. Vladimir Curic. Centre for Image Analysis Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala University
 Classification Vladimir Curic Centre for Image Analysis Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala University Outline An overview on classification Basics of classification How to choose appropriate
Classification Vladimir Curic Centre for Image Analysis Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala University Outline An overview on classification Basics of classification How to choose appropriate
USING GEOMEDIA 3D: HOTSPOT DETECTION AND VISUALIZATION
 USING GEOMEDIA 3D: HOTSPOT DETECTION AND VISUALIZATION etraining Introduction Use GeoMedia and GeoMedia 3D for hotspot detection and visualization. Software GeoMedia and GeoMedia 3D Data QuickBird-2 image
USING GEOMEDIA 3D: HOTSPOT DETECTION AND VISUALIZATION etraining Introduction Use GeoMedia and GeoMedia 3D for hotspot detection and visualization. Software GeoMedia and GeoMedia 3D Data QuickBird-2 image
Exercise 4.1. Create New Variables in a Shapefile. GIS Techniques for Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS and Related Programs
 GIS Techniques for Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS and Related Programs Exercise 4.1 Create New Variables in a Shapefile *This training was developed as part of a joint effort between MEASURE Evaluation
GIS Techniques for Monitoring and Evaluation of HIV/AIDS and Related Programs Exercise 4.1 Create New Variables in a Shapefile *This training was developed as part of a joint effort between MEASURE Evaluation
3x 2 + 7x + 2. A 8-6 Factor. Step 1. Step 3 Step 4. Step 2. Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4
 A 8-6 Factor. Step 1 3x 2 + 7x + 2 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 3x 2 + 7x + 2 3x 2 + 7x + 2 Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 Factor. 1. 3x 2 + 4x +1 = 2. 3x 2 +10x + 3 = 3. 3x 2 +13x + 4 = A 8-6 Name BDFM? Why? Factor.
A 8-6 Factor. Step 1 3x 2 + 7x + 2 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 3x 2 + 7x + 2 3x 2 + 7x + 2 Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 Factor. 1. 3x 2 + 4x +1 = 2. 3x 2 +10x + 3 = 3. 3x 2 +13x + 4 = A 8-6 Name BDFM? Why? Factor.
Neighbourhood Operations Specific Theory
 Neighbourhood Operations Specific Theory Neighbourhood operations are a method of analysing data in a GIS environment. They are especially important when a situation requires the analysis of relationships
Neighbourhood Operations Specific Theory Neighbourhood operations are a method of analysing data in a GIS environment. They are especially important when a situation requires the analysis of relationships
v Overview SMS Tutorials Prerequisites Requirements Time Objectives
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Overview Objectives This tutorial describes the major components of the SMS interface and gives a brief introduction to the different SMS modules. Ideally, this tutorial should
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Overview Objectives This tutorial describes the major components of the SMS interface and gives a brief introduction to the different SMS modules. Ideally, this tutorial should
Math 7 Glossary Terms
 Math 7 Glossary Terms Absolute Value Absolute value is the distance, or number of units, a number is from zero. Distance is always a positive value; therefore, absolute value is always a positive value.
Math 7 Glossary Terms Absolute Value Absolute value is the distance, or number of units, a number is from zero. Distance is always a positive value; therefore, absolute value is always a positive value.
Lecture 06. Raster and Vector Data Models. Part (1) Common Data Models. Raster. Vector. Points. Points. ( x,y ) Area. Area Line.
 Lecture 06 Raster and Vector Data Models Part (1) 1 Common Data Models Vector Raster Y Points Points ( x,y ) Line Area Line Area 2 X 1 3 Raster uses a grid cell structure Vector is more like a drawn map
Lecture 06 Raster and Vector Data Models Part (1) 1 Common Data Models Vector Raster Y Points Points ( x,y ) Line Area Line Area 2 X 1 3 Raster uses a grid cell structure Vector is more like a drawn map
Systems of Inequalities and Linear Programming 5.7 Properties of Matrices 5.8 Matrix Inverses
 5 5 Systems and Matrices Systems and Matrices 5.6 Systems of Inequalities and Linear Programming 5.7 Properties of Matrices 5.8 Matrix Inverses Sections 5.6 5.8 2008 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights
5 5 Systems and Matrices Systems and Matrices 5.6 Systems of Inequalities and Linear Programming 5.7 Properties of Matrices 5.8 Matrix Inverses Sections 5.6 5.8 2008 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights
Community Resilience Scenario Planning Model
 Community Resilience Scenario Planning Model Technical User Guide American Planning Association Making Great Communities Happen This Technical User Guide was developed by Focused Planning Solutions, Inc.,
Community Resilience Scenario Planning Model Technical User Guide American Planning Association Making Great Communities Happen This Technical User Guide was developed by Focused Planning Solutions, Inc.,
Making Yield Contour Maps Using John Deere Data
 Making Yield Contour Maps Using John Deere Data Exporting the Yield Data Using JDOffice 1. Data Format On Hard Drive 2. Start program JD Office. a. From the PC Card menu on the left of the screen choose
Making Yield Contour Maps Using John Deere Data Exporting the Yield Data Using JDOffice 1. Data Format On Hard Drive 2. Start program JD Office. a. From the PC Card menu on the left of the screen choose
Overview. Frequency Distributions. Chapter 2 Summarizing & Graphing Data. Descriptive Statistics. Inferential Statistics. Frequency Distribution
 Chapter 2 Summarizing & Graphing Data Slide 1 Overview Descriptive Statistics Slide 2 A) Overview B) Frequency Distributions C) Visualizing Data summarize or describe the important characteristics of a
Chapter 2 Summarizing & Graphing Data Slide 1 Overview Descriptive Statistics Slide 2 A) Overview B) Frequency Distributions C) Visualizing Data summarize or describe the important characteristics of a
Automatic Discretization and Parameterization of Watersheds using a Digital Elevation Model
 Automatic Discretization and Parameterization of Watersheds using a Digital Elevation Model Ellen Hachborn, Karen Finney, Rob James, Nandana Perera, Tiehong Xiao WaterTech 2017 Computational Hydraulics
Automatic Discretization and Parameterization of Watersheds using a Digital Elevation Model Ellen Hachborn, Karen Finney, Rob James, Nandana Perera, Tiehong Xiao WaterTech 2017 Computational Hydraulics
YRERFS GIS WORKFLOW AND MODELING PROCESS
 YRERFS GIS WORKFLOW AND MODELING PROCESS Presenter Name Presenter Title Duty Location Date of Presentation US Army Corps of Engineers YRERFS Yellow Warbler Riparian Scrub Shrub (RSS) Habitat Determination
YRERFS GIS WORKFLOW AND MODELING PROCESS Presenter Name Presenter Title Duty Location Date of Presentation US Army Corps of Engineers YRERFS Yellow Warbler Riparian Scrub Shrub (RSS) Habitat Determination
SuRVoS Workbench. Super-Region Volume Segmentation. Imanol Luengo
 SuRVoS Workbench Super-Region Volume Segmentation Imanol Luengo Index - The project - What is SuRVoS - SuRVoS Overview - What can it do - Overview of the internals - Current state & Limitations - Future
SuRVoS Workbench Super-Region Volume Segmentation Imanol Luengo Index - The project - What is SuRVoS - SuRVoS Overview - What can it do - Overview of the internals - Current state & Limitations - Future
Outline. 14. Query, Measurement, and Transformation. Spatial analysis. Definitions. The Snow map. What is spatial analysis?
 Outline 14. Query, Measurement, and Transformation What is spatial analysis? Transformations Geographic Information Systems and Science SECOND EDITION Paul A. Longley, Michael F. Goodchild, David J. Maguire,
Outline 14. Query, Measurement, and Transformation What is spatial analysis? Transformations Geographic Information Systems and Science SECOND EDITION Paul A. Longley, Michael F. Goodchild, David J. Maguire,
Integrating Travel Demand Management into the Long-Range Planning Process 2017 AMPO
 Integrating Travel Demand Management into the Long-Range Planning Process 2017 AMPO October 19, 2017 Chattanooga 2045 RTP Chattanooga 2045 RTP addresses both transportation supply and demand Continued
Integrating Travel Demand Management into the Long-Range Planning Process 2017 AMPO October 19, 2017 Chattanooga 2045 RTP Chattanooga 2045 RTP addresses both transportation supply and demand Continued
We have already studied equations of the line. There are several forms:
 Chapter 13-Coordinate Geometry extended. 13.1 Graphing equations We have already studied equations of the line. There are several forms: slope-intercept y = mx + b point-slope y - y1=m(x - x1) standard
Chapter 13-Coordinate Geometry extended. 13.1 Graphing equations We have already studied equations of the line. There are several forms: slope-intercept y = mx + b point-slope y - y1=m(x - x1) standard
notes13.1inclass May 01, 2015
 Chapter 13-Coordinate Geometry extended. 13.1 Graphing equations We have already studied equations of the line. There are several forms: slope-intercept y = mx + b point-slope y - y1=m(x - x1) standard
Chapter 13-Coordinate Geometry extended. 13.1 Graphing equations We have already studied equations of the line. There are several forms: slope-intercept y = mx + b point-slope y - y1=m(x - x1) standard
Using HEC-RAS and HEC-GeoRAS for River Modeling Adapted by E. Maurer, using an exercise by V. Merwade, Purdue Univ.
 Introduction Using HEC-RAS and HEC-GeoRAS for River Modeling Adapted by E. Maurer, using an exercise by V. Merwade, Purdue Univ. This tutorial uses the output from HEC_GeoRAS from a prior exercise as input
Introduction Using HEC-RAS and HEC-GeoRAS for River Modeling Adapted by E. Maurer, using an exercise by V. Merwade, Purdue Univ. This tutorial uses the output from HEC_GeoRAS from a prior exercise as input
THE DEPTH-BUFFER VISIBLE SURFACE ALGORITHM
 On-Line Computer Graphics Notes THE DEPTH-BUFFER VISIBLE SURFACE ALGORITHM Kenneth I. Joy Visualization and Graphics Research Group Department of Computer Science University of California, Davis To accurately
On-Line Computer Graphics Notes THE DEPTH-BUFFER VISIBLE SURFACE ALGORITHM Kenneth I. Joy Visualization and Graphics Research Group Department of Computer Science University of California, Davis To accurately
3.1 INTRODUCTION TO THE FAMILY OF QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS
 3.1 INTRODUCTION TO THE FAMILY OF QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Finding the Zeros of a Quadratic Function Examples 1 and and more Find the zeros of f(x) = x x 6. Solution by Factoring f(x) = x x 6 = (x 3)(x + )
3.1 INTRODUCTION TO THE FAMILY OF QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Finding the Zeros of a Quadratic Function Examples 1 and and more Find the zeros of f(x) = x x 6. Solution by Factoring f(x) = x x 6 = (x 3)(x + )
