DesignSpark Mechanical 4.0
|
|
|
- Lynette Rice
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DesignSpark Mechanical 4.0 Release Notes
2 Table of Contents DesignSpark Mechanical 4.0 Enhancements Overview... 3 Sketch... 4 Facets... 6 Pull... 7 Move Split Body Split Blend Fill Curve/Edge Vertex Dragging Graphics/UI/Layout/Selection UI/Graphics Core... 63
3 DesignSpark Mechanical 4.0 Enhancements Overview This release of DesignSpark Mechanical contains many modeling improvements to the software; these are described in the following changelog. Apart from the listed, user experience improvements have been made on several fronts: 1. Revamped registration/activation system and more informative start page 2. Prepare your 3D model for printing with a seamless integration to the popular & open-source Ultimaker Cura slicing software 3. Get instant production & delivery quotes for your 3D designs from the 3D hubs global printing marketplace. 4. Know when new versions of DSM are introduced at the click of a button (in the Help/Resources tab). 5. Check out possible upgrade paths for more advanced features from our own DesignSpark Mechanical add-ons or the ANSYS software suite. 6. Ability to right-click structure tree item and analyze your solid body geometry for errors and how to fix them. 7. FOR DSM ADD-ON users: NEW STEP AP242 (including manufacturing part information) format support 8. Switch between multiple graphics rendering drivers and modes. 9. Export 3D geometry in DreamWorks open-source OpenVDB file format K and Ultra HD monitor support, updated UI elements & look. Enhanced rendering options for high end GPUs. Page 3
4 Sketch You can now use the Ctrl key to round several corners at once. To round several corners 1. Sketch some curves with several vertices (e.g. a rectangle). 2. Enter the Create Rounded Corner tool. 3. Click a corner vertex and drag to preview the round. 4. Press and hold the Ctrl key The preview disappears Page 4
5 5. While holding Ctrl, click and drag another corner vertex to preview BOTH rounds. 6. Press and hold the Ctrl key The preview disappears 7. Repeat for the remaining corners. 8. On the last corner (meaning no more Ctrl key selection), you will see all rounds previewing simultaneously. 9. Click to place the rounds or enter a radius value Page 5
6 Facets In the Subtract tool, once the Target is selected, you can now use box-select to select multiple cutters. You can now use the Pull tool to offset an entire faceted body. Select the faceted Mesh body in the Structure Tree, or triple-click on the facet mesh. Page 6
7 Pull In the Pull tool, the Pull Both Sides option now works for Helices. Page 7
8 Curve Color: When extruding sketch curves into surfaces, the following rules apply to the resulting surface color. If all curves being pulled ARE the same color, AND the curve colors override their layer color, the surface is the same color as the curves. If all curves being pulled ARE the same color, AND the curves take their color from a layer that is NOT the Active layer, the surface is the color of the Active layer and NOT the color of the curves. If all curves are NOT the same color, the surface uses the Active Layer color. If all curves are NOT the same color AND take their colors from different layers, the surface uses the Active Layer color. Page 8
9 Variable Radius Rounds: The Variable Radius Round Handles have been enhanced and redesigned. Instead of double arrows, the radius handles have a drag (ball) handle. The center Radius Handle cannot be dragged. It adjusts all radii values at once. Click the ball and drag to add, and place, a new radius handle. Page 9
10 Up To: The selection used for Up To can come from the Structure Tree, if it can be determined. A single-face surface is an example of an Up To selection in the Structure Tree. Page 10
11 Draft: Draft neutral faces can now be selected in the Structure Tree. Chamfers: Stop Chamfers have conical stop faces that mimic the effect of an angled cutting tool rotating and coming-to-a-stop in the middle of an edge. With an edge selected, when you click the Chamfer option in the Pull tool, the edge ends switch to yellow cones that can be dragged. This is like the Pull Edge user-interface in Sheet Metal and sets the point where the simulated cutter will stop. Notice the conical stop face created at the chamfer s end. Page 11
12 You can move both ends to create stop faces at both ends of the chamfer. Reverse Chamfer Stop has been added to Chamfer options. This flips the direction of the conical Stop Face. Page 12
13 Here it is reversed or flipped 90. An Apex offset input box has been added to Chamfer options to offset the cone apex (the lowest point of the cone) past the furthest extent of the intersection of the virtual cutter with the material. Apex offset = 0 Page 13
14 Apex offset = 1 Apex offset = 2 For circular edges, you will see a linear dimension when you set the extent of the chamfer. The linear dimension in the image refers to the arc length of the un-chamfered part of the original edge. Page 14
15 Move You can now create a circular pattern, using the Up To tool guide in the Move tool, by rotating up to a linear entity passing through the Move Handle origin. The image below shows an example. Relocate the Move Handle to the axis of the cylinder. Then choose the rotation handle about the cylinder s axis. When you click on Up To and select the horizontal axis, the pattern is created. Move Up To this axis An exciting enhancement has been made to the Move Handle. It greatly speeds up the process of moving Curve/Beam endpoints to a single point. To illustrate, consider the model shown here. Radial Move now allows you to select the Axis in the Structure Tree. Page 15
16 Move in Sketch: You can now snap the Move Handle Anchor to circle quadrants and tangents. Page 16
17 Split Body In the Split Body tool, you can now use Local Slicing to split a solid with a cylindrical surface! Previously, only planar faces, datum planes, and their edge loops were selectable. There is also a new Create split surfaces option, which (instead of cutting the solid) creates surfaces at the intersection of the target and cutter. Page 17
18 An interesting consequence of this enhancement is that, when you are NOT using Local Slicing, you can use a Full-Round face to carve out a cylinder. Page 18
19 Split The Split Face tool is now the Split tool. The reason for the change is that it now works on Edges. Curves and Beams will be added later. With the Split Edge tool guide active, the cursor changes indicate that only Edges are selectable. to When you click on an edge, you can adjust the Split location by: Dragging the yellow ball Entering a Percentage Press the Tab key twice and enter a length Page 19
20 You can also press the Tab key and enter a Count (i.e. number of Split Pieces) Page 20
21 With a chain of tangent faces selected, the Split now propagates across entire chain, when using the Select UV Cutter Point tool guide. To have the split propagate, you need to select a Cutter Point on one of the end edges or any of the interior tangent edges and set a percentage along the edge. This sets the parameterization for the split, which is then progressively applied to each tangent face in the chain. In the image to the right, the parameterization is set to 50%, which is then applied to each of the three tangent faces. The Split tool works on Beams and Curves, with editable split dimensions. Page 21
22 Blend You can create blends between points, edges, or faces. To create a blend 1. Enter the Blend tool 2. Select a point, edge, or face 3. Ctrl+Select a corresponding point, edge, or face 4. You can select more than two objects 5. The blend is previewed as you select 6. Complete the blend Options The following options are available in the Blend tool Options panel when you select the appropriate geometry for a blend. Rotational blend: Create cylinders and cones whenever possible during the creation of a blend. You must have selected faces, points, or edges that can be rotated around a common axis. Periodic blend: Go all the way around when blending. The blend will begin and end at the first selected object. You must have selected three or more faces, points, or edges that can be rotated around a common axis, and that also span an arc greater than 180 degrees. (Blending between 3 equal-radius circle faces creates a torus.) Ruled sections: Create straight edges when you blend. When you blend between faces, this option has the same affect as selecting the face and its edges. Local guides: Selected guide curves only influence areas near to them. Clocked guides: Guide curves are oriented relative to the face edges instead being simply translated from vertex to vertex. Sheet metal blend: Forces the tool to create developable surfaces. A developable surface is defined in mathematics as a surface with zero Gaussian Curvature (i.e. a surface that can be flattened into a plane). The tool attempts to create planes, cylinders, and cones, in that order to maximize the planar areas. It is restricted to blending between two parallel planes. Normal to Centerline: When on by default, Normal to Centerline forces the Blend algorithm to keep sections normal to the centerline. When off, the algorithm has more freedom to adjust sections so that a surface can be created. Show UV grid: This option is ON by default to help visualize contours by displaying a grid on the preview. Use the dropdown slider to increase or decrease the density of the grid. Adding Tangency Make the blend tangent to adjacent faces by Alt+Selecting them. In the image below right, the blue face was Alt+selected to make the blend surface tangent to it. Page 22
23 In the Blend tool, the system of Tangency and guide constraints sets up a system of equations that DesignSpark Mechanical solves to produce the Blend result. Certain cases create a system of equations which is Inconsistent, meaning the equations produce a contradiction and have no solution. In some cases, when Blending with a combination of Tangency and Guide constraints, conflicts between the constraints can occur. In these cases, the conflicted geometry will highlight and an error message will be displayed. Swept blends A Swept Blend is a blend between two or more edges without local guide influence. The entire blend is swept along the guide curve, as shown below. If you check the Local guide option, the guide curve has a local effect on the blend. Swept blends are different from sweeps. Swept blends need at least two profiles, while sweeps use a single profile. Sweeps give you limited control over the orientation and angle of the section along the trajectory, or at the end cap, because it is always determined by sweeping the profile along the trajectory. With swept blends, you specify the section shape and orientation explicitly at the ends and at specific points along the trajectory (guide curve). When you select more than one guide curve, the additional guide curves give you more control over the final shape of the blend. Each guide curve affects entities in the profile that are closest to the curve. Vertices between guide curves are controlled by curves blended between the neighboring guide curves. The behavior for Local Guides has been improved for cases with additional tangency references. If neighboring faces are selected as tangency references, Local Guides is forced when Guide Curves are selected. Page 23
24 In this example, a Blend will be created to fill in the middle of the surface. Create the initial Blend. Now add a Guide Curve. Notice that the opposite side is influenced as well, indicating that Local Guides is NOT active. Page 24
25 This side is influenced by the Guide Curve on the opposite side If you select the tangency references first and then add the Guide Curve, you see that the effect is localized. Previously, you would still see the opposite side influenced. Page 25
26 Tangency In the Blend tool, the system of Tangency and guide constraints sets up a system of equations that DesignSpark Mechanical solves to produce the Blend result. Certain cases create a system of equations which is Inconsistent, which means they produce a contradiction and have no solution. In this example, an inconsistency is created and an error is issued, when you select the guide at the bottom Page 26
27 You can now Blend open and closed sections to a Point. Some simple examples are shown here. Centerline Blends: The Blend tool allows you to select a centerline path for the blend to follow between two planar profiles. The centerline does not have to touch either of the profiles, but the extension of the curves must pass through the profile. Also, although it is called a centerline, the path does not need to pass through the center of each profile. Centerline distinguishes itself from guide curves, which must touch the profile edges. Multi-segmented curves or edges can be used as centerline blends provided they meet end-to-end without gaps and are piece-wise continuous or tangent. Page 27
28 The centerline consists of three lines and two tangent arcs. Select the oval and circle faces to preview the default Blend. Select the Centerline tool and double-click the centerline to select the curve chain. The preview updates to show the Centerline Blend. Normal to Centerline: When on by default, Normal to Centerline forces the Blend algorithm to keep sections normal to the centerline. When off, the algorithm has more freedom to adjust sections so that a surface can be created. Page 28
29 Normal to centerline on Normal to centerline off The centerline can pass through the profiles. In these examples, the centerline has been changed to a spline. You can extend the spline using the Pull tool to pull it beyond the profile plane. Page 29
30 The Blend can be created using the extended spline. The spline can be shortened so it does not touch the profile planes. The centerline can be moved normal to the original plane. In this example, the spline was moved to the right, which is normal to its original sketch plane. Page 30
31 Fill The Fill tool now uses curve color when curves are filled to make a surface. Fill The Fill tool can now account for holes in missing faces. An example is shown below. The top face is missing but there are holes in the part. Select the edges of the outside boundary and the interior holes and execute the Fill command. Fill Page 31
32 When you use the Fill tool in Action-Object mode, there is an updated Options panel with two, radio buttons. Extend Fill Fills selected edges by extending the neighboring faces. Patch Fill Fills the selected edges using the initial tangency of neighboring faces to create a smooth patch. Page 32
33 In the Fill tool, using the Patch option, you can now Fill multiple areas at once using Altselected tangency influences and Preview the changes. In the example below, the two loops are being filled simultaneously and previewed. Notice the preview change when a different Point is Alt-selected. Page 33
34 Fill works on multiple-selected, disconnected edge loops in surfaces. It s a shortcut to filling them all individually. Page 34
35 Curve/Edge Vertex Dragging Exciting changes are being made to curve vertex dragging. Now, when you hover and pre-highlight a vertex, the curve to which it belongs is highlighted. Using the mouse wheel, you can scroll through the other curves. This is consistent with vertices on solids. Previously, in the example shown on the right, only the vertex would highlight. The highlighting is important because it enables changes to what happens when you drag a vertex shared by more than one curve. When several curves vertices are in the same location and there is a Drag action, ALL curve vertices are dragged together, pivoting about their other endpoints. This is existing behavior. Page 35
36 Now, you can Alt-drag to move only the vertex of a specific curve. This is made possible by the curve highlighting described above, where the parent curve highlights when hovering over a vertex. The cursor changes to the Move cursor when the mouse is over a vertex. Pressing the Alt key changes the Move cursor to the Detach-and-Move cursor. You do not need to hold the Alt key throughout dragging. You can release it once you start dragging. Drag the vertex straight down Page 36
37 Drag a copy of the curve using Ctrl+Alt-drag. Copy In the images above, notice the source-generated dotted lines extending from the other curve. This is borrowed from similar behavior in Sketch Mode for aligning and snapping the vertex. By default, the system generates them extending from ALL curves that intersect at the selected-andmoving vertex. If the vertex is far enough away from the extension, the dotted line is not displayed. Example images are below. Three curves intersecting at 90 to each other (as in the corner of a box). Page 37
38 Drag the vertex vertically. The extension line for the affected curve is shown as well as the extension for the vertical curve. Drag the vertex away from the vertical curve. The vertical extension line disappears, the affected curve extension stays and the extension for the third curve appears. Unlike Sketch, which only allows snapping in the plane, Curve Dragging allows snapping in 3D. Green dot Snap Indicator Page 38
39 Any straight line or edge that you hover over, while dragging a vertex, will generate a dotted vector. That allows you to snap to the extension of any existing line or edge. Since you do not have to hold the Alt or Ctrl key, your hand is free for Shift-hovering over other objects. This displays extension lines for other lines or edges. The default, source-generated dotted lines are erased, when you Shift-hover over an object. Press Shift Page 39
40 Sequentially Shift-hovering on converging lines or edges let you snap to their virtual intersection. In the image below, the top horizontal line is a single curve but with two sub-curves because the vertical curve s endpoint lies somewhere along its length. Even though there is only one horizontal curve, it can be treated as split, for the purposes of dragging other vertices to these sub-curve endpoints or midpoints. Two Subcurves Page 40
41 Sub-curve midpoints are available for snapping, if you Shift-hover over the parent curve. NOTE: The cursor is turned off in this image to better display the snap indicators. Green balls display at the endpoints of the sub-curve and a triangle displays at the midpoint. This helps in determining which portion of the curve is being snapped to, in cases where it may have been ambuiguous to the user. The virtual intersection of the horizontal and slanted lines is available for snapping if you Shift-hover over both. Page 41
42 Curve intersections (for both straight and arc-shaped curves) are available for snapping and displayed with a + sign. Page 42
43 Face selection does not override edge extension snapping. In this example, the extension line is above the face. If the face had a higher priority, you could not snap to the extension line without reorienting the view. Previously, the endpoint would snap to the face. You can now snap a vertex to a 3D Point. Page 43
44 You can snap a vertex to the virtual intersections of extend solid edges. Snap indicators now display when dragging entire surfaces and solids by their vertices. An example is shown below. In the image on the right, the image is enlarged and the cursor is turned off to better display the snap indicator. Drag the surface and snap to the solid corner Page 44
45 Graphics/UI/Layout/Selection Design Window Scrollbars: A Scrollbar option has been added to File>Options>Popular. It is now OFF by default. When checked, it adds scroll bars to the Design window. Page 45
46 Status Window: Status icons have been added for Warnings and Info, with the ability for mouse-over tooltips. A column has been added to show the number of objects affected. A new Zoom option has been added to the Status popup window. If it is checked ON, which is the default, when you double-click on a status message, the graphics will zoom-and fit to any associated objects. Status Bar: The Status Bar measurement numeric format has changed to show separators in numbers greater than 999 and a space has been added between the measurement and the units. The Status Bar selection count numeric format has changed to show separators in counts greater than 999. Previously this length and count would look like this. Alt + Z: Alt+Z is the new shortcut for Box Zoom. Page 46
47 Popular Options: In DesignSpark Mechanical Popular options, the Adaptive faceting sub-option for Multi-threaded faceting has been removed. The option had automatically determined when to use Multi-threaded faceting based on the geometry, and now has proven to be sufficiently robust. Renderer: DesignSpark Mechanical Options>Advanced options you can now change the Renderer. This is in addition to the Ctrl+Alt+Shift+R shortcut. The Void option is for Running without graphics. Equivalent to the command line argument /renderer= void Cases of failed 3D Graphics Initialization (old driver, old hardware, etc.). If you set Void as the Renderer option, you see this in the graphics window. Clip with Plane: Union is now ON by default when clipping with more than one Plane. Union unites the selected planes and treats them as a whole. In the image on the right, all three planes are selected and united to clip away 1/8 of the block. Page 47
48 Previously, as shown on the right, planes were not united by default. Each plane clips the model individually. So, in this example, the first plane cuts the block in half. The second cuts the remainder in half. That result is cut in half by the third plane, leaving 1/8 of the block visible. Clip with Volume: A new command has been added to the Clip with Volume RMB menu. Extract Geometry caps off the clipped boundaries, according to the Clip type (Spherical volume or by Planes), and show a closed solid, if it starts with a solid. Page 48
49 For intersections with surface models, Extract Geometry also creates a geometry snapshot, but displays the surfaces with a more opaque, solid look. Page 49
50 Tool Guides: Within an active group of Tool Guides, you can now use the Tab key to cycle through them. As soon as the tool guide switches, the cursor changes to reflect the active guide. RMB Menu: Delete is disabled when none of the selected objects can be deleted. For example, the root item in the Structure Tree cannot be deleted. If some of the objects in the current selection CAN be deleted and some of them cannot, only those that can be deleted will be deleted. The others are ignored. Model Orientation: Drag now works for in-plane rotation using the Orientation gizmo. By default, the scene will rotate in 5-degree increments. Page 50
51 Press and hold the Shift key to rotate smoothly. Units: Units now default to the following: Imperial = 3 digits Metric = 2 digits Object Renaming: Multiple bodies selected in the Structure Tree can now be renamed at once. The new name applies to the body for which it was entered. Page 51
52 The remaining bodies are numerically incremented. This also applies for multiple components selected in the Structure Tree. DesignSpark Mechanical Options>Popular options has a new setting for controlling the number of files in the MRU list. The new default is 8. Page 52
53 UI/Graphics Zoom Legend: A Zoom Legend can now be displayed using the Show menu in the Design ribbon. The Zoom Legend can be moved using LMB-drag. It highlights on mouse-over, indicating that it can be selected and dragged to a new location in screen space. New Status Bar: The Status bar has a new look as shown below. There are new buttons for Rotate 90 CW and CCW in the pull-up menu on the Spin Button. Page 53
54 You can now select length measurements and assorted other text displayed in the Status Bar for Copy-Paste. The Selection Filter is collapsed by default, if Smart selection is checked ON. If Smart selection is checked OFF, the Selection Filter is expanded to show all of the choices. Another addition is that the Annotations item has been expanded to include Notes, Dimensions, and all the rest of the annotations that can be selected. Page 54
55 Show Vertices: You can now show body Vertices using the Show menu in the Display tab. Vertices shows all vertices in the model. It works on a per-window basis. Vertices are NOT shown on closed periodic edges (e.g. A cylinder). Top View Direction: You can now change the Top View direction in the Advanced page of DesignSpark Mechanical Options. X is added to comply with manufacturing conventions. Page 55
56 Shortcuts: Ctrl+Shift+H has been removed so Change Highlighting Scheme now has no shortcut Ctrl+Shift+H is now Show All (It used to be Change Highlighting Scheme) Ctrl+Shift+A is now Activate Component Alt+H is now Hide Others Power Select: You can now Power Select based on surface area for surface models. Structure Tree: Mesh bodies are now called Facets in the Structure tree. Page 56
57 BOM s: You can now group BOM rows according to a selected Custom Property. Page 57
58 You can change the numbering of the grouped components by setting the Start groups from property, which is set to Number items sequentially in the image below. Page 58
59 The Print Preview dialog box has been enhanced. There are new Orient icons as shown below, as well as standard MMB and Wheel navigation controls. Page 59
60 A Navigate button has been added to allow you to move the print window when zoomed in. The images below show an example. Page 60
61 Zoom Box In has been added. The cursor switches to a zoom cursor when you click Zoom Box In. Preview for Patch Fill and Blend has been sped up and Show UV grid option has been to both tools. Show UV grid displays a grid on the preview geometry to make it easier to visualize. Use the slider to adjust the density of the grid. Show UV grid is only enabled when Patch is checked ON in the Fill tool. Page 61
62 Split Tool: In the Split tool, you can now select a Plane to split a selected edge or curve. The plane is selected after selecting the edge/curve to split. Page 62
63 Core Recovery Assistant A recovery assistant has been added in the options to ensure data is not lost if the program stops responding. With Backup, you can save your files automatically, helping to reduce the risk or impact of data loss in case of a crash or freeze. The default Backup time interval is 10 minutes, but you can select a time interval from 1 to 100 minutes. Once you select a time interval, you can enter or click the browse button to select a location for the Backup files on your computer. By default, DesignSpark Mechanical stores Backup files on your C: drive in your Users folder. If you save your file before your session ends, your Backup files are purged. When you relaunch DesignSpark Mechanical after a crash or freeze, an information box displays to notify you that Backup files are available. To recover them, click Recover from the File menu and select the file you want to open. Save As: Changes have been made to Save As to give control over when to overwrite modified external components. If you save the assembly using Save As, a new dialog opens with options for handling External components. The following assembly will be used to clarify the behavior for each option. The Block and the Hexagon are both external components and the Cylinder is an internal component. The names are changed manually for clarity the clue to the user as to external vs internal status is the structure tree icon for the component File icon behind the block denotes External. Page 63
64 Save every external document as a new version saves ALL external documents, regardless of their modified status. The images below show the assembly BEFORE the Save As. Notice that the Block has been modified and the Hexagon has not. This can also be seen in the structure tree image at left in that the modified document has an asterisk next to the component name. It is also important to note that the assembly is Not marked as changed (no asterisk) because the modified component is external. The file list at right shows the files on disk BEFORE the Save As. File List The images below show the assembly AFTER the Save As. The assembly has been saved as Design4_NEW and both the Block AND the Hexagon have new versions in the Structure Tree and file list, even though the Block was the only external component modified. Page 64
65 File List Save only modified external documents as a new version saves Only Modified external documents. The images below show the assembly BEFORE the Save As. Notice that the Block has been modified and the Hexagon has not. This can also be seen in the structure tree image at left in that the modified document has an asterisk next to the component name. It is also important to note that the assembly is Not marked as changed (no asterisk) because the modified component is external. The file list at right shows the files on disk BEFORE the Save As. File List Page 65
66 The images below show the assembly AFTER the Save As. The assembly has been saved as Design4_NEW and ONLY the Block has a new version in the Structure Tree and file list, because it was the only Modified external component. File List File List Overwrite any modified external documents saves Only Modified external documents by overwriting the existing files. The images below show the assembly BEFORE the Save As. Notice that the Block and the Hexagon have been modified. This can also be seen in the structure tree image at left in that the modified documents have an asterisk next to their component name. It is also important to note that the assembly is Not marked as changed (no asterisk) because the modified components are external. The file list at right shows the files on disk BEFORE the Save As. Page 66
67 File List The images below show the assembly AFTER the Save As. The assembly has been saved as Design4_NEW and NONE of the external components have version numbers in the Structure Tree or file list because they have been overwritten. File List Page 67
68 Multi-level external components have a different behavior when the solid is modified. A multilevel component consists of a component which has multiple levels of sub-components. An example is shown below. The Top level design contains a component called BB with a subcomponent CCC, which contains a sub-component DDDD that contains the solid block. All of the components are External. File List Page 68
69 Modifying the block by rounding an edge also modifies the parent component. This impacts the behavior of the options as described below. Save every external document as a new version saves ALL the components as new versions. The top level assembly has been saved as A_NEW and all of the sub-components have been saved as new versions. File List Save only modified external documents as a new version has the same behavior as the first option because all the parents of the solid are modified when the solid is modified. Page 69
70 File List Overwrite any modified external documents overwrites the existing files of modified components. The top level assembly has been saved as A_NEW and all of the sub-components have been overwritten. File List Page 70
71 Bodies can now be split by any edge that is planar, even if it is not a closed loop. An example is shown below. The edge is an arc (that could have been selected and used to create a plane using the Plane tool) so it therefore can be used to split the solid Page 71
72 Hide Faces With faces selected, the Context menu now contains a Face section. Use Right-Mouse-Button > Face > Hide Face to hide the selected faces. Hidden faces allow selection of objects behind them without using the scroll wheel. Page 72
73 Use Right-Mouse-Button > Face > Inverse Face Visibility to invert the current Hide Face state. Hidden Faces (even if they are hidden By Body) become visible Visible Faces become Hidden Use Right-Mouse-Button > Face > Hide Other Faces to hide all faces besides the selected faces. Page 73
74 Use Right-Mouse-Button > Face > Show All Faces to restore the visibility of all hidden faces, whether they were set By Face or by By Body. A new Body icon has been added to the Structure Tree to indicate which solid or surface bodies have hidden faces. Page 74
75 A Face submenu has been added to the Body context menu in the Structure Tree. Inverse Visibility for Bodies: An Inverse Visibility option has been added when you right-click on a body. Page 75
76 Transparency can now be applied per face. This allows you to hide individual faces, but still select objects behind the faces. To apply per-face transparency: 1. Select a face 2. Open the Color dropdown in the Display tab 3. Set the Transparency of the face 4. View the Properties of the selected face 5. By default, the Style property will be By Color, By Style Page 76
77 6. This means the Body Style overrides the Face style so the Transparency is overridden 7. Open the Style Override dropdown menu in the Display tab and notice that Opaque is the active Body Style. 8. Click the active style to disable it 9. This disables the Style Override as evidenced by the buttons appearance 10. The face transparency now displays. Page 77
78 Rendering Quality: Rendering Quality now has 10 as the highest level. Values above 7 are shown in red to indicate that performance will be affected. The highly-zoomed-in images show the effect of moving Rendering Quality from 7 to 10. Please be warned that values above 7 require significantly more resources, which will greatly impact performance. It is strongly suggested that you do not select a value greater than 7. Page 78
79 Document-level Undo/Redo is on by default and there are separate Undo Stacks for each independent DesignSpark Mechanical window tab. Undo and redo allows you to have multiple models open and move between them making changes. You can return to any window where you have been working and undo changes from the last time you worked in the window. Dependencies created between windows, however, will permanently merge the Undo operations for those windows. For example, if you open a component of an assembly in a second window, a model dependent on the first window, the Undo operations will be merged. Making changes in the first window and then choosing to Undo those changes in the second window will undo the changes in both windows. Trim Away: In the Trim Away tool, segments to be removed are now shown in red. Previously, they were green. Page 79
Solidworks 2006 Surface-modeling
 Solidworks 2006 Surface-modeling (Tutorial 2-Mouse) Surface-modeling Solid-modeling A- 1 Assembly Design Design with a Master Model Surface-modeling Tutorial 2A Import 2D outline drawing into Solidworks2006
Solidworks 2006 Surface-modeling (Tutorial 2-Mouse) Surface-modeling Solid-modeling A- 1 Assembly Design Design with a Master Model Surface-modeling Tutorial 2A Import 2D outline drawing into Solidworks2006
SpaceClaim 2016 Beta Release Notes. SpaceClaim 2016 Beta. Release Notes
 SpaceClaim 2016 Beta Release Notes Table of Contents Table of Contents... 2 SpaceClaim 2016 Enhancements Overview... 1 Beta Items... 2 Skin Surface... 2 Pull... 19 Move... 22 Split Body... 25 Split...
SpaceClaim 2016 Beta Release Notes Table of Contents Table of Contents... 2 SpaceClaim 2016 Enhancements Overview... 1 Beta Items... 2 Skin Surface... 2 Pull... 19 Move... 22 Split Body... 25 Split...
SOLIDWORKS 2016: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate Users
 SOLIDWORKS 2016: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate Users The premium provider of learning products and solutions www.cadartifex.com Table of Contents Dedication... 3 Preface... 15 Part 1. Introducing
SOLIDWORKS 2016: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate Users The premium provider of learning products and solutions www.cadartifex.com Table of Contents Dedication... 3 Preface... 15 Part 1. Introducing
Alibre Design Tutorial - Simple Revolve Translucent Glass Lamp Globe
 Alibre Design Tutorial - Simple Revolve Translucent Glass Lamp Globe Part Tutorial Exercise 2: Globe-1 In this Exercise, We will set System Parameters first. Then, in sketch mode, we will first Outline
Alibre Design Tutorial - Simple Revolve Translucent Glass Lamp Globe Part Tutorial Exercise 2: Globe-1 In this Exercise, We will set System Parameters first. Then, in sketch mode, we will first Outline
Exercise Guide. Published: August MecSoft Corpotation
 VisualCAD Exercise Guide Published: August 2018 MecSoft Corpotation Copyright 1998-2018 VisualCAD 2018 Exercise Guide by Mecsoft Corporation User Notes: Contents 2 Table of Contents About this Guide 4
VisualCAD Exercise Guide Published: August 2018 MecSoft Corpotation Copyright 1998-2018 VisualCAD 2018 Exercise Guide by Mecsoft Corporation User Notes: Contents 2 Table of Contents About this Guide 4
4) Finish the spline here. To complete the spline, double click the last point or select the spline tool again.
 1) Select the line tool 3) Move the cursor along the X direction (be careful to stay on the X axis alignment so that the line is perpendicular) and click for the second point of the line. Type 0.5 for
1) Select the line tool 3) Move the cursor along the X direction (be careful to stay on the X axis alignment so that the line is perpendicular) and click for the second point of the line. Type 0.5 for
Module 1: Basics of Solids Modeling with SolidWorks
 Module 1: Basics of Solids Modeling with SolidWorks Introduction SolidWorks is the state of the art in computer-aided design (CAD). SolidWorks represents an object in a virtual environment just as it exists
Module 1: Basics of Solids Modeling with SolidWorks Introduction SolidWorks is the state of the art in computer-aided design (CAD). SolidWorks represents an object in a virtual environment just as it exists
Selective Space Structures Manual
 Selective Space Structures Manual February 2017 CONTENTS 1 Contents 1 Overview and Concept 4 1.1 General Concept........................... 4 1.2 Modules................................ 6 2 The 3S Generator
Selective Space Structures Manual February 2017 CONTENTS 1 Contents 1 Overview and Concept 4 1.1 General Concept........................... 4 1.2 Modules................................ 6 2 The 3S Generator
SpaceClaim 2009 SP1. Release Notes
 SpaceClaim 2009 SP1 Release Notes Table of contents General... 4 Licensing... 4 Navigation... 5 Structure tree... 5 Copy and Paste... 6 Select... 6 General selection... 6 Select temporary objects... 7
SpaceClaim 2009 SP1 Release Notes Table of contents General... 4 Licensing... 4 Navigation... 5 Structure tree... 5 Copy and Paste... 6 Select... 6 General selection... 6 Select temporary objects... 7
Lesson 1: Creating T- Spline Forms. In Samples section of your Data Panel, browse to: Fusion 101 Training > 03 Sculpt > 03_Sculpting_Introduction.
 3.1: Sculpting Sculpting in Fusion 360 allows for the intuitive freeform creation of organic solid bodies and surfaces by leveraging the T- Splines technology. In the Sculpt Workspace, you can rapidly
3.1: Sculpting Sculpting in Fusion 360 allows for the intuitive freeform creation of organic solid bodies and surfaces by leveraging the T- Splines technology. In the Sculpt Workspace, you can rapidly
Lesson 14 Blends. For Resources go to > click on the Creo Parametric 2.0 Book cover
 Lesson 14 Blends Figure 14.1 Cap OBJECTIVES Create a Parallel Blend feature Use the Shell Tool Create a Hole Pattern REFERENCES AND RESOURCES For Resources go to www.cad-resources.com > click on the Creo
Lesson 14 Blends Figure 14.1 Cap OBJECTIVES Create a Parallel Blend feature Use the Shell Tool Create a Hole Pattern REFERENCES AND RESOURCES For Resources go to www.cad-resources.com > click on the Creo
SOLIDWORKS 2016 and Engineering Graphics
 SOLIDWORKS 2016 and Engineering Graphics An Integrated Approach Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following
SOLIDWORKS 2016 and Engineering Graphics An Integrated Approach Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following
Skateboard. Hanger. in the Feature Manager and click Sketch on the Context toolbar, Fig. 1. Fig. 2
 Chapter 3 Skateboard Hanger A. Sketch1 Lines. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part Metric and OK. Step 2. Click Right Plane in the Feature Manager and click Sketch on the Context toolbar, Fig. 1.
Chapter 3 Skateboard Hanger A. Sketch1 Lines. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part Metric and OK. Step 2. Click Right Plane in the Feature Manager and click Sketch on the Context toolbar, Fig. 1.
Autodesk Fusion 360 Training: The Future of Making Things Attendee Guide
 Autodesk Fusion 360 Training: The Future of Making Things Attendee Guide Abstract After completing this workshop, you will have a basic understanding of editing 3D models using Autodesk Fusion 360 TM to
Autodesk Fusion 360 Training: The Future of Making Things Attendee Guide Abstract After completing this workshop, you will have a basic understanding of editing 3D models using Autodesk Fusion 360 TM to
3D Design with 123D Design
 3D Design with 123D Design Introduction: 3D Design involves thinking and creating in 3 dimensions. x, y and z axis Working with 123D Design 123D Design is a 3D design software package from Autodesk. A
3D Design with 123D Design Introduction: 3D Design involves thinking and creating in 3 dimensions. x, y and z axis Working with 123D Design 123D Design is a 3D design software package from Autodesk. A
Inventor 201. Work Planes, Features & Constraints: Advanced part features and constraints
 Work Planes, Features & Constraints: 1. Select the Work Plane feature tool, move the cursor to the rim of the base so that inside and outside edges are highlighted and click once on the bottom rim of the
Work Planes, Features & Constraints: 1. Select the Work Plane feature tool, move the cursor to the rim of the base so that inside and outside edges are highlighted and click once on the bottom rim of the
Introduction to SolidWorks Basics Materials Tech. Wood
 Introduction to SolidWorks Basics Materials Tech. Wood Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 Book End... 2 Introduction... 2 Learning Intentions... 2 Modelling the Base... 3 Modelling the Front... 10
Introduction to SolidWorks Basics Materials Tech. Wood Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 Book End... 2 Introduction... 2 Learning Intentions... 2 Modelling the Base... 3 Modelling the Front... 10
Google SketchUp. and SketchUp Pro 7. The book you need to succeed! CD-ROM Included! Kelly L. Murdock. Master SketchUp Pro 7 s tools and features
 CD-ROM Included! Free version of Google SketchUp 7 Trial version of Google SketchUp Pro 7 Chapter example files from the book Kelly L. Murdock Google SketchUp and SketchUp Pro 7 Master SketchUp Pro 7 s
CD-ROM Included! Free version of Google SketchUp 7 Trial version of Google SketchUp Pro 7 Chapter example files from the book Kelly L. Murdock Google SketchUp and SketchUp Pro 7 Master SketchUp Pro 7 s
CO2 Rail Car. Wheel Rear Px. on the Command Manager toolbar.
 Chapter 6 CO2 Rail Car Wheel Rear Px A. Sketch Construction Lines. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part Metric and OK. Step 2. Click Front (plane) in the Feature Manager (left panel), Fig. 1. Step
Chapter 6 CO2 Rail Car Wheel Rear Px A. Sketch Construction Lines. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part Metric and OK. Step 2. Click Front (plane) in the Feature Manager (left panel), Fig. 1. Step
SpaceClaim 2009 SP2. Release Notes
 SpaceClaim 2009 SP2 Release Notes Table of contents General... 3 SpaceClaim 2009 SP2 Highlights... 3 Print... 4 Groups... 4 Object, document, component properties... 4 Structure tree... 4 Select... 6 Designing
SpaceClaim 2009 SP2 Release Notes Table of contents General... 3 SpaceClaim 2009 SP2 Highlights... 3 Print... 4 Groups... 4 Object, document, component properties... 4 Structure tree... 4 Select... 6 Designing
XPEL DAP SUPPORT. DAP Tool List & Overview DESCRIPTION ICON/TOOL (SHORTCUT)
 Pointer (S) Left-click on individual entities to add them to the current selection (selected entities will turn red). If the entity selected is a member of a group, the entire group will be added to the
Pointer (S) Left-click on individual entities to add them to the current selection (selected entities will turn red). If the entity selected is a member of a group, the entire group will be added to the
Revit Architecture 2015 Basics
 Revit Architecture 2015 Basics From the Ground Up Elise Moss Authorized Author SDC P U B L I C AT I O N S Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit
Revit Architecture 2015 Basics From the Ground Up Elise Moss Authorized Author SDC P U B L I C AT I O N S Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit
SolidWorks 2½D Parts
 SolidWorks 2½D Parts IDeATe Laser Micro Part 1b Dave Touretzky and Susan Finger 1. Create a new part In this lab, you ll create a CAD model of the 2 ½ D key fob below to make on the laser cutter. Select
SolidWorks 2½D Parts IDeATe Laser Micro Part 1b Dave Touretzky and Susan Finger 1. Create a new part In this lab, you ll create a CAD model of the 2 ½ D key fob below to make on the laser cutter. Select
Glider. Wing. Top face click Sketch. on the Standard Views. (S) on the Sketch toolbar.
 Chapter 5 Glider Wing 4 Panel Tip A. Open and Save As "WING 4 PANEL". Step 1. Open your WING BLANK file. Step 2. Click File Menu > Save As. Step 3. Key-in WING 4 PANEL for the filename and press ENTER.
Chapter 5 Glider Wing 4 Panel Tip A. Open and Save As "WING 4 PANEL". Step 1. Open your WING BLANK file. Step 2. Click File Menu > Save As. Step 3. Key-in WING 4 PANEL for the filename and press ENTER.
SolidWorks 2013 and Engineering Graphics
 SolidWorks 2013 and Engineering Graphics An Integrated Approach Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Visit the following
SolidWorks 2013 and Engineering Graphics An Integrated Approach Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Visit the following
Module 4B: Creating Sheet Metal Parts Enclosing The 3D Space of Right and Oblique Pyramids With The Work Surface of Derived Parts
 Inventor (5) Module 4B: 4B- 1 Module 4B: Creating Sheet Metal Parts Enclosing The 3D Space of Right and Oblique Pyramids With The Work Surface of Derived Parts In Module 4B, we will learn how to create
Inventor (5) Module 4B: 4B- 1 Module 4B: Creating Sheet Metal Parts Enclosing The 3D Space of Right and Oblique Pyramids With The Work Surface of Derived Parts In Module 4B, we will learn how to create
SolidWorks Implementation Guides. User Interface
 SolidWorks Implementation Guides User Interface Since most 2D CAD and SolidWorks are applications in the Microsoft Windows environment, tool buttons, toolbars, and the general appearance of the windows
SolidWorks Implementation Guides User Interface Since most 2D CAD and SolidWorks are applications in the Microsoft Windows environment, tool buttons, toolbars, and the general appearance of the windows
User Guide. mk Config
 User Guide mk Config mk Config Register 1.1. CD-Start 4 1.2. Installation 5 1.3. Start 6 1.4. Layout of user interface and functions 7 1.4.1. Overview 7 1.4.2. Part buttons 8 1.4.3. Menus 9 1.4.3.1. Export
User Guide mk Config mk Config Register 1.1. CD-Start 4 1.2. Installation 5 1.3. Start 6 1.4. Layout of user interface and functions 7 1.4.1. Overview 7 1.4.2. Part buttons 8 1.4.3. Menus 9 1.4.3.1. Export
CO 2 Shell Car. Body. in the Feature Manager and click Sketch from the context toolbar, Fig. 1. on the Standard Views toolbar.
 CO 2 Shell Car Chapter 2 Body A. Save as "BODY". Step 1. If necessary, open your BLANK file. Step 2. Click File Menu > Save As. Step 3. Key-in BODY for the filename and press ENTER. B. FRONT Wheel Shell.
CO 2 Shell Car Chapter 2 Body A. Save as "BODY". Step 1. If necessary, open your BLANK file. Step 2. Click File Menu > Save As. Step 3. Key-in BODY for the filename and press ENTER. B. FRONT Wheel Shell.
StickFont Editor v1.01 User Manual. Copyright 2012 NCPlot Software LLC
 StickFont Editor v1.01 User Manual Copyright 2012 NCPlot Software LLC StickFont Editor Manual Table of Contents Welcome... 1 Registering StickFont Editor... 3 Getting Started... 5 Getting Started...
StickFont Editor v1.01 User Manual Copyright 2012 NCPlot Software LLC StickFont Editor Manual Table of Contents Welcome... 1 Registering StickFont Editor... 3 Getting Started... 5 Getting Started...
Module 4A: Creating the 3D Model of Right and Oblique Pyramids
 Inventor (5) Module 4A: 4A- 1 Module 4A: Creating the 3D Model of Right and Oblique Pyramids In Module 4A, we will learn how to create 3D solid models of right-axis and oblique-axis pyramid (regular or
Inventor (5) Module 4A: 4A- 1 Module 4A: Creating the 3D Model of Right and Oblique Pyramids In Module 4A, we will learn how to create 3D solid models of right-axis and oblique-axis pyramid (regular or
Constructing treatment features
 Constructing treatment features Publication Number spse01530 Constructing treatment features Publication Number spse01530 Proprietary and restricted rights notice This software and related documentation
Constructing treatment features Publication Number spse01530 Constructing treatment features Publication Number spse01530 Proprietary and restricted rights notice This software and related documentation
SolidWorks Intro Part 1b
 SolidWorks Intro Part 1b Dave Touretzky and Susan Finger 1. Create a new part We ll create a CAD model of the 2 ½ D key fob below to make on the laser cutter. Select File New Templates IPSpart If the SolidWorks
SolidWorks Intro Part 1b Dave Touretzky and Susan Finger 1. Create a new part We ll create a CAD model of the 2 ½ D key fob below to make on the laser cutter. Select File New Templates IPSpart If the SolidWorks
To familiarize of 3ds Max user interface and adapt a workflow based on preferences of navigating Autodesk 3D Max.
 Job No: 01 Duration: 8H Job Title: User interface overview Objective: To familiarize of 3ds Max user interface and adapt a workflow based on preferences of navigating Autodesk 3D Max. Students should be
Job No: 01 Duration: 8H Job Title: User interface overview Objective: To familiarize of 3ds Max user interface and adapt a workflow based on preferences of navigating Autodesk 3D Max. Students should be
Lesson 14 Blends. For Resources go to > click on the Creo Parametric Book cover
 Lesson 14 Blends Figure 14.1 Cap OBJECTIVES Create a Parallel Blend feature Use the Shell Tool Create a Swept Blend REFERENCES AND RESOURCES For Resources go to www.cad-resources.com > click on the Creo
Lesson 14 Blends Figure 14.1 Cap OBJECTIVES Create a Parallel Blend feature Use the Shell Tool Create a Swept Blend REFERENCES AND RESOURCES For Resources go to www.cad-resources.com > click on the Creo
Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals
 2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Extruded Solid Models Understand the Basic Parametric Modeling Procedure Create 2-D Sketches Understand the Shape before Size Approach Use the
2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Extruded Solid Models Understand the Basic Parametric Modeling Procedure Create 2-D Sketches Understand the Shape before Size Approach Use the
Module 1B: Parallel-Line Flat Pattern Development of Sheet- Metal Folded Model Wrapping the 3D Space of A Truncated Right Prism
 Inventor (5) Module 1B: 1B- 1 Module 1B: Parallel-Line Flat Pattern Development of Sheet- Metal Folded Model Wrapping the 3D Space of A Truncated Right Prism In this Module, we will learn how to create
Inventor (5) Module 1B: 1B- 1 Module 1B: Parallel-Line Flat Pattern Development of Sheet- Metal Folded Model Wrapping the 3D Space of A Truncated Right Prism In this Module, we will learn how to create
Introduction to ANSYS DesignModeler
 Lecture 5 Modeling 14. 5 Release Introduction to ANSYS DesignModeler 2012 ANSYS, Inc. November 20, 2012 1 Release 14.5 Preprocessing Workflow Geometry Creation OR Geometry Import Geometry Operations Meshing
Lecture 5 Modeling 14. 5 Release Introduction to ANSYS DesignModeler 2012 ANSYS, Inc. November 20, 2012 1 Release 14.5 Preprocessing Workflow Geometry Creation OR Geometry Import Geometry Operations Meshing
Beaumont Middle School Design Project April May 2014 Carl Lee and Craig Schroeder
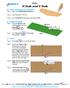
 Beaumont Middle School Design Project April May 2014 Carl Lee and Craig Schroeder 1 2 SketchUp 1. SketchUp is free, and you can download it from the website www.sketchup.com. For some K12 use, see www.sketchup.com/3dfor/k12-education.
Beaumont Middle School Design Project April May 2014 Carl Lee and Craig Schroeder 1 2 SketchUp 1. SketchUp is free, and you can download it from the website www.sketchup.com. For some K12 use, see www.sketchup.com/3dfor/k12-education.
Autodesk Inventor 6 Essentials Instructor Guide Chapter Four: Creating Placed Features Chapter Outline This chapter provides instruction on the follow
 Chapter Four: Creating Placed Features Chapter Outline This chapter provides instruction on the following topics and provides exercises for students to practice their skills. Day Two Topic: How to create
Chapter Four: Creating Placed Features Chapter Outline This chapter provides instruction on the following topics and provides exercises for students to practice their skills. Day Two Topic: How to create
Autodesk Inventor Design Exercise 2: F1 Team Challenge Car Developed by Tim Varner Synergis Technologies
 Autodesk Inventor Design Exercise 2: F1 Team Challenge Car Developed by Tim Varner Synergis Technologies Tim Varner - 2004 The Inventor User Interface Command Panel Lists the commands that are currently
Autodesk Inventor Design Exercise 2: F1 Team Challenge Car Developed by Tim Varner Synergis Technologies Tim Varner - 2004 The Inventor User Interface Command Panel Lists the commands that are currently
User Guide. for. JewelCAD Professional Version 2.0
 User Guide Page 1 of 121 User Guide for JewelCAD Professional Version 2.0-1 - User Guide Page 2 of 121 Table of Content 1. Introduction... 7 1.1. Purpose of this document... 7 2. Launch JewelCAD Professional
User Guide Page 1 of 121 User Guide for JewelCAD Professional Version 2.0-1 - User Guide Page 2 of 121 Table of Content 1. Introduction... 7 1.1. Purpose of this document... 7 2. Launch JewelCAD Professional
AUTODESK FUSION 360 Designing a RC Car Body
 AUTODESK FUSION 360 Designing a RC Car Body Abstract This project explores how to use the sculpting tools available in Autodesk Fusion 360 Ultimate to design the body of a RC car. John Helfen john.helfen@autodesk.com
AUTODESK FUSION 360 Designing a RC Car Body Abstract This project explores how to use the sculpting tools available in Autodesk Fusion 360 Ultimate to design the body of a RC car. John Helfen john.helfen@autodesk.com
Luana Valentini InternetGIS course
 Google SketchUp - A brief introduction - Luana Valentini InternetGIS course - 2011 Create 3D models and share them with the world Google SketchUp is software that allows you to create 3D models of anything
Google SketchUp - A brief introduction - Luana Valentini InternetGIS course - 2011 Create 3D models and share them with the world Google SketchUp is software that allows you to create 3D models of anything
Delta Dart. Propeller. in the Feature Manager and click Sketch from the Content toolbar, Fig. 1. on the Sketch toolbar.
 Chapter 8 Delta Dart Propeller A. Base for Blade. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part Metric and OK. Step 2. Click Top Plane in the Feature Manager and click Sketch from the Content toolbar, Fig.
Chapter 8 Delta Dart Propeller A. Base for Blade. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part Metric and OK. Step 2. Click Top Plane in the Feature Manager and click Sketch from the Content toolbar, Fig.
Equipment Support Structures
 Equipment Support Structures Overview Conventions What's New? Getting Started Setting Up Your Session Creating a Simple Structural Frame Creating Non-uniform Columns Creating Plates with Openings Bracing
Equipment Support Structures Overview Conventions What's New? Getting Started Setting Up Your Session Creating a Simple Structural Frame Creating Non-uniform Columns Creating Plates with Openings Bracing
H Stab and V Stab. Chapter 6. Glider. A. Open and Save as "H STAB". Step 1. Open your STABILIZER BLANK file.
 Chapter 6 Glider H Stab and V Stab A. Open and Save as "H STAB". Step 1. Open your STABILIZER BLANK file. Step 2. Click File Menu > Save As. Step 3. Key-in H STAB for the filename and press ENTER. B. Sketch
Chapter 6 Glider H Stab and V Stab A. Open and Save as "H STAB". Step 1. Open your STABILIZER BLANK file. Step 2. Click File Menu > Save As. Step 3. Key-in H STAB for the filename and press ENTER. B. Sketch
Equipment Support Structures
 Page 1 Equipment Support Structures Preface Using This Guide Where to Find More Information Conventions What's New? Getting Started Setting Up Your Session Creating a Simple Structural Frame Creating Non-uniform
Page 1 Equipment Support Structures Preface Using This Guide Where to Find More Information Conventions What's New? Getting Started Setting Up Your Session Creating a Simple Structural Frame Creating Non-uniform
Create Complex Surfaces
 Create Complex Surfaces In this lesson, you will be introduced to the functionalities available in the Generative Surface Design workbench. Lesson content: Case Study: Surface Design Design Intent Stages
Create Complex Surfaces In this lesson, you will be introduced to the functionalities available in the Generative Surface Design workbench. Lesson content: Case Study: Surface Design Design Intent Stages
Sheet Metal Overview. Chapter. Chapter Objectives
 Chapter 1 Sheet Metal Overview This chapter describes the terminology, design methods, and fundamental tools used in the design of sheet metal parts. Building upon these foundational elements of design,
Chapter 1 Sheet Metal Overview This chapter describes the terminology, design methods, and fundamental tools used in the design of sheet metal parts. Building upon these foundational elements of design,
Chapter 6. Concept Modeling. ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary Inventory # May 11, ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 6 Concept Modeling 6-1 Contents Concept Modeling Creating Line Bodies Modifying i Line Bodies Cross Sections Cross Section Alignment Cross Section Offset Surfaces From Lines Surfaces From Sketches
Chapter 6 Concept Modeling 6-1 Contents Concept Modeling Creating Line Bodies Modifying i Line Bodies Cross Sections Cross Section Alignment Cross Section Offset Surfaces From Lines Surfaces From Sketches
Feature-Based Modeling and Optional Advanced Modeling. ENGR 1182 SolidWorks 05
 Feature-Based Modeling and Optional Advanced Modeling ENGR 1182 SolidWorks 05 Today s Objectives Feature-Based Modeling (comprised of 2 sections as shown below) 1. Breaking it down into features Creating
Feature-Based Modeling and Optional Advanced Modeling ENGR 1182 SolidWorks 05 Today s Objectives Feature-Based Modeling (comprised of 2 sections as shown below) 1. Breaking it down into features Creating
It is a good idea to practice View Control tools for 5 minutes at the start of every 3D session, before doing any other work.
 3D View Control Module Overview All the 2D view controls, such as Fit View, Zoom In and Out, Window Area, and Pan, can be used in 3D. As in 2D, elements to the left, right, above, or below can be excluded
3D View Control Module Overview All the 2D view controls, such as Fit View, Zoom In and Out, Window Area, and Pan, can be used in 3D. As in 2D, elements to the left, right, above, or below can be excluded
SpaceClaim 2015 Release Notes. SpaceClaim 2015 SP1. Release Notes
 SpaceClaim 2015 Release Notes SpaceClaim 2015 SP1 Release Notes Table of Contents SpaceClaim 2015 Release Notes SpaceClaim 2015 Enhancements Overview... 1 Notes... 2 SP1 Items... 3 STL Modeling... 3 Vectorize
SpaceClaim 2015 Release Notes SpaceClaim 2015 SP1 Release Notes Table of Contents SpaceClaim 2015 Release Notes SpaceClaim 2015 Enhancements Overview... 1 Notes... 2 SP1 Items... 3 STL Modeling... 3 Vectorize
LAB # 2 3D Modeling, Properties Commands & Attributes
 COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Electrical Engineering Department (Islamabad Campus) LAB # 2 3D Modeling, Properties Commands & Attributes Designed by Syed Muzahir Abbas 1 1. Overview of the
COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Electrical Engineering Department (Islamabad Campus) LAB # 2 3D Modeling, Properties Commands & Attributes Designed by Syed Muzahir Abbas 1 1. Overview of the
3D ModelingChapter1: Chapter. Objectives
 Chapter 1 3D ModelingChapter1: The lessons covered in this chapter familiarize you with 3D modeling and how you view your designs as you create them. You also learn the coordinate system and how you can
Chapter 1 3D ModelingChapter1: The lessons covered in this chapter familiarize you with 3D modeling and how you view your designs as you create them. You also learn the coordinate system and how you can
Swept Blend Creates a quilt using swept blend geometry.
 Swept Blend Creates a quilt using swept blend geometry. 1 A surface can be defined by a set of cross-sections located at various points along a controlling Spine Curve. In Pro/SURFACE, this is known as
Swept Blend Creates a quilt using swept blend geometry. 1 A surface can be defined by a set of cross-sections located at various points along a controlling Spine Curve. In Pro/SURFACE, this is known as
CATIA V5 Parametric Surface Modeling
 CATIA V5 Parametric Surface Modeling Version 5 Release 16 A- 1 Toolbars in A B A. Wireframe: Create 3D curves / lines/ points/ plane B. Surfaces: Create surfaces C. Operations: Join surfaces, Split & Trim
CATIA V5 Parametric Surface Modeling Version 5 Release 16 A- 1 Toolbars in A B A. Wireframe: Create 3D curves / lines/ points/ plane B. Surfaces: Create surfaces C. Operations: Join surfaces, Split & Trim
Skateboard. Hanger. in the Feature Manager and click Sketch. (S) on the Sketch. Line
 Chapter 3 Skateboard Hanger A. Sketch 1. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part Metric and OK. Step 2. Click Right Plane from the Content toolbar, Fig. 1. in the Feature Manager and click Sketch Step
Chapter 3 Skateboard Hanger A. Sketch 1. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part Metric and OK. Step 2. Click Right Plane from the Content toolbar, Fig. 1. in the Feature Manager and click Sketch Step
USING THE TRIBALL FOR POSITIONING
 USING THE TRIBALL FOR POSITIONING Although many important positioning tools are available, none are as versatile as the TriBall tool. This TriBall tool offers complete repositioning of many items: Shapes
USING THE TRIBALL FOR POSITIONING Although many important positioning tools are available, none are as versatile as the TriBall tool. This TriBall tool offers complete repositioning of many items: Shapes
A Comprehensive Introduction to SolidWorks 2011
 A Comprehensive Introduction to SolidWorks 2011 Godfrey Onwubolu, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation Chapter 2 Geometric Construction Tools Objectives: When
A Comprehensive Introduction to SolidWorks 2011 Godfrey Onwubolu, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation Chapter 2 Geometric Construction Tools Objectives: When
GraphWorX64 Productivity Tips
 Description: Overview of the most important productivity tools in GraphWorX64 General Requirement: Basic knowledge of GraphWorX64. Introduction GraphWorX64 has a very powerful development environment in
Description: Overview of the most important productivity tools in GraphWorX64 General Requirement: Basic knowledge of GraphWorX64. Introduction GraphWorX64 has a very powerful development environment in
Press the Plus + key to zoom in. Press the Minus - key to zoom out. Scroll the mouse wheel away from you to zoom in; towards you to zoom out.
 Navigate Around the Map Interactive maps provide many choices for displaying information, searching for more details, and moving around the map. Most navigation uses the mouse, but at times you may also
Navigate Around the Map Interactive maps provide many choices for displaying information, searching for more details, and moving around the map. Most navigation uses the mouse, but at times you may also
Lesson 3: Surface Creation
 Lesson 3: Surface Creation In this lesson, you will learn how to create surfaces from wireframes. Lesson Contents: Case Study: Surface Creation Design Intent Stages in the Process Choice of Surface Sweeping
Lesson 3: Surface Creation In this lesson, you will learn how to create surfaces from wireframes. Lesson Contents: Case Study: Surface Creation Design Intent Stages in the Process Choice of Surface Sweeping
Assembly Design: A Hands-On Experience
 Mark Thompson Sr. Application Engineer Assembly Design: A Hands-On Experience Solid Edge University 2014 May 12-14, Atlanta, GA, USA SOLID EDGE UNIVERSITY 2014 Re-imagine What s Possible #SEU14 Agenda
Mark Thompson Sr. Application Engineer Assembly Design: A Hands-On Experience Solid Edge University 2014 May 12-14, Atlanta, GA, USA SOLID EDGE UNIVERSITY 2014 Re-imagine What s Possible #SEU14 Agenda
Publication Number spse01695
 XpresRoute (tubing) Publication Number spse01695 XpresRoute (tubing) Publication Number spse01695 Proprietary and restricted rights notice This software and related documentation are proprietary to Siemens
XpresRoute (tubing) Publication Number spse01695 XpresRoute (tubing) Publication Number spse01695 Proprietary and restricted rights notice This software and related documentation are proprietary to Siemens
TRAINING SESSION Q2 2016
 There are 8 main topics in this training session which focus on the Sketch tools in IRONCAD. Content Sketch... 2 3D Scene Background Settings... 3 Creating a new empty Sketch... 4 Foam with cut out for
There are 8 main topics in this training session which focus on the Sketch tools in IRONCAD. Content Sketch... 2 3D Scene Background Settings... 3 Creating a new empty Sketch... 4 Foam with cut out for
Getting started with Solid Edge with Synchronous Technology
 Getting started with Solid Edge with Synchronous Technology Publication Number MU29000-ENG-1000 Proprietary and Restricted Rights Notice This software and related documentation are proprietary to Siemens
Getting started with Solid Edge with Synchronous Technology Publication Number MU29000-ENG-1000 Proprietary and Restricted Rights Notice This software and related documentation are proprietary to Siemens
This is the opening view of blender.
 This is the opening view of blender. Note that interacting with Blender is a little different from other programs that you may be used to. For example, left clicking won t select objects on the scene,
This is the opening view of blender. Note that interacting with Blender is a little different from other programs that you may be used to. For example, left clicking won t select objects on the scene,
Input CAD Solid Model Assemblies - Split into separate Part Files. DXF, IGES WMF, EMF STL, VDA, Rhino Parasolid, ACIS
 General NC File Output List NC Code Post Processor Selection Printer/Plotter Output Insert Existing Drawing File Input NC Code as Geometry or Tool Paths Input Raster Image Files Report Creator and Designer
General NC File Output List NC Code Post Processor Selection Printer/Plotter Output Insert Existing Drawing File Input NC Code as Geometry or Tool Paths Input Raster Image Files Report Creator and Designer
GDL Toolbox 2 Reference Manual
 Reference Manual Archi-data Ltd. Copyright 2002. New Features Reference Manual New Save GDL command Selected GDL Toolbox elements can be exported into simple GDL scripts. During the export process, the
Reference Manual Archi-data Ltd. Copyright 2002. New Features Reference Manual New Save GDL command Selected GDL Toolbox elements can be exported into simple GDL scripts. During the export process, the
Introduction And Overview ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary
 Introduction And Overview 2006 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary The ANSYS Workbench represents more than a general purpose engineering tool. It provides a highly integrated engineering
Introduction And Overview 2006 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary The ANSYS Workbench represents more than a general purpose engineering tool. It provides a highly integrated engineering
Technique or Feature Where Introduced
 Part 6: Keypad 4 Mirrored features Patterned features First extrusion Rounded corners In the earpiece part, you defined a radial pattern, one that created new instances of a feature at intervals around
Part 6: Keypad 4 Mirrored features Patterned features First extrusion Rounded corners In the earpiece part, you defined a radial pattern, one that created new instances of a feature at intervals around
Introduction to SolidWorks for Technology. No1: Childs Toy
 Introduction to SolidWorks for Technology No1: Childs Toy Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 Introduction... 2 Part Modelling: Cab... 3 Part Modelling: Base... 6 Part Modelling: Wheel... 12 Assembly:
Introduction to SolidWorks for Technology No1: Childs Toy Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1 Introduction... 2 Part Modelling: Cab... 3 Part Modelling: Base... 6 Part Modelling: Wheel... 12 Assembly:
Modeling a Gear Standard Tools, Surface Tools Solid Tool View, Trackball, Show-Hide Snaps Window 1-1
 Modeling a Gear This tutorial describes how to create a toothed gear. It combines using wireframe, solid, and surface modeling together to create a part. The model was created in standard units. To begin,
Modeling a Gear This tutorial describes how to create a toothed gear. It combines using wireframe, solid, and surface modeling together to create a part. The model was created in standard units. To begin,
Delta Dart. Socket. (L) on the Sketch toolbar. Fig. 1. (S) on the Sketch toolbar. on the Sketch toolbar. on the Standard Views toolbar.
 Chapter 6 Delta Dart Socket A. Sketch. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part Metric and OK. Step 2. Click Front Plane in the Feature Manager and click Sketch from the Content toolbar, Fig. 1. Step
Chapter 6 Delta Dart Socket A. Sketch. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part Metric and OK. Step 2. Click Front Plane in the Feature Manager and click Sketch from the Content toolbar, Fig. 1. Step
Additional Surface Tools
 Additional Surface Tools Several additional surface tools, techniques, and related functions are available. This supplement provides a brief introduction to those functions. Panel Part Features Replace
Additional Surface Tools Several additional surface tools, techniques, and related functions are available. This supplement provides a brief introduction to those functions. Panel Part Features Replace
Piping Design. Site Map Preface Getting Started Basic Tasks Advanced Tasks Customizing Workbench Description Index
 Piping Design Site Map Preface Getting Started Basic Tasks Advanced Tasks Customizing Workbench Description Index Dassault Systèmes 1994-2001. All rights reserved. Site Map Piping Design member member
Piping Design Site Map Preface Getting Started Basic Tasks Advanced Tasks Customizing Workbench Description Index Dassault Systèmes 1994-2001. All rights reserved. Site Map Piping Design member member
Mechanical Design V5R19 Update
 CATIA V5 Training Foils Mechanical Design V5R19 Update Version 5 Release 19 August 2008 EDU_CAT_EN_MD2_UF_V5R19 1 About this course Objectives of the course Upon completion of this course you will be able
CATIA V5 Training Foils Mechanical Design V5R19 Update Version 5 Release 19 August 2008 EDU_CAT_EN_MD2_UF_V5R19 1 About this course Objectives of the course Upon completion of this course you will be able
Using the CMA Warp Editor
 Using the CMA Warp Editor Overview The Warp Editor feature lets you adjust Axon HD, Axon HD Pro, DLHD or MMS100 output to match complex projection surfaces. These forms allow the projection to match irregular
Using the CMA Warp Editor Overview The Warp Editor feature lets you adjust Axon HD, Axon HD Pro, DLHD or MMS100 output to match complex projection surfaces. These forms allow the projection to match irregular
Pipe Networks CHAPTER INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES
 CHAPTER 11 Pipe Networks INTRODUCTION Pipe networks are integral to a site-design solution. The piping system s complexity can vary from simple culverts to several storm and sanitary networks that service
CHAPTER 11 Pipe Networks INTRODUCTION Pipe networks are integral to a site-design solution. The piping system s complexity can vary from simple culverts to several storm and sanitary networks that service
Workbench Tutorial Minor Losses, Page 1 Tutorial Minor Losses using Pointwise and FLUENT
 Workbench Tutorial Minor Losses, Page 1 Tutorial Minor Losses using Pointwise and FLUENT Introduction This tutorial provides instructions for meshing two internal flows. Pointwise software will be used
Workbench Tutorial Minor Losses, Page 1 Tutorial Minor Losses using Pointwise and FLUENT Introduction This tutorial provides instructions for meshing two internal flows. Pointwise software will be used
AutoCAD 2009 User InterfaceChapter1:
 AutoCAD 2009 User InterfaceChapter1: Chapter 1 The AutoCAD 2009 interface has been enhanced to make AutoCAD even easier to use, while making as much screen space available as possible. In this chapter,
AutoCAD 2009 User InterfaceChapter1: Chapter 1 The AutoCAD 2009 interface has been enhanced to make AutoCAD even easier to use, while making as much screen space available as possible. In this chapter,
1 - Introduction Training Guide Objectives WorkXplore Environment Importing and Opening CAD Files 5
 Table Of Contents 1.1 - Training Guide Objectives Table Of Contents 1 - Introduction 3 1.1 - Training Guide Objectives... 3 1.2 - WorkXplore Environment... 3 2 - Importing and Opening CAD Files 5 2.1 -
Table Of Contents 1.1 - Training Guide Objectives Table Of Contents 1 - Introduction 3 1.1 - Training Guide Objectives... 3 1.2 - WorkXplore Environment... 3 2 - Importing and Opening CAD Files 5 2.1 -
Publication Number spse01695
 XpresRoute (tubing) Publication Number spse01695 XpresRoute (tubing) Publication Number spse01695 Proprietary and restricted rights notice This software and related documentation are proprietary to Siemens
XpresRoute (tubing) Publication Number spse01695 XpresRoute (tubing) Publication Number spse01695 Proprietary and restricted rights notice This software and related documentation are proprietary to Siemens
Elise Moss Revit Architecture 2017 Basics From the Ground Up SDC. Better Textbooks. Lower Prices.
 Elise Moss Revit Architecture 2017 Basics From the Ground Up SDC P U B L I C AT I O N S Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites
Elise Moss Revit Architecture 2017 Basics From the Ground Up SDC P U B L I C AT I O N S Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites
Parametric Modeling with UGS NX 4
 Parametric Modeling with UGS NX 4 Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com 2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling
Parametric Modeling with UGS NX 4 Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com 2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling
Autodesk Inventor 2019 and Engineering Graphics
 Autodesk Inventor 2019 and Engineering Graphics An Integrated Approach Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the
Autodesk Inventor 2019 and Engineering Graphics An Integrated Approach Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the
Threaded Hex Bolt Tutorial
 1-(800) 877-2745 www.ashlar-vellum.com Tutorial Using Cobalt, Xenon, Argon Copyright 2009-2014 Vellum Investment Partners, LLC, DBA Ashlar-Vellum. All rights reserved. Ashlar-Vellum Cobalt, Xenon & Argon
1-(800) 877-2745 www.ashlar-vellum.com Tutorial Using Cobalt, Xenon, Argon Copyright 2009-2014 Vellum Investment Partners, LLC, DBA Ashlar-Vellum. All rights reserved. Ashlar-Vellum Cobalt, Xenon & Argon
3D Modeling and Design Glossary - Beginner
 3D Modeling and Design Glossary - Beginner Align: to place or arrange (things) in a straight line. To use the Align tool, select at least two objects by Shift left-clicking on them or by dragging a box
3D Modeling and Design Glossary - Beginner Align: to place or arrange (things) in a straight line. To use the Align tool, select at least two objects by Shift left-clicking on them or by dragging a box
Tutorial 01 Quick Start Tutorial
 Tutorial 01 Quick Start Tutorial Homogeneous single material slope No water pressure (dry) Circular slip surface search (Grid Search) Intro to multi scenario modeling Introduction Model This quick start
Tutorial 01 Quick Start Tutorial Homogeneous single material slope No water pressure (dry) Circular slip surface search (Grid Search) Intro to multi scenario modeling Introduction Model This quick start
NURBS modeling for Windows. Training Manual Level 1
 NURBS modeling for Windows Training Manual Level 1 Rhino Level 1 Training 2nd Ed.doc Robert McNeel & Associates 1997-2000 All Rights Reserved. Printed in U.S.A. Copyright by Robert McNeel & Associates.
NURBS modeling for Windows Training Manual Level 1 Rhino Level 1 Training 2nd Ed.doc Robert McNeel & Associates 1997-2000 All Rights Reserved. Printed in U.S.A. Copyright by Robert McNeel & Associates.
Roadway Alignments and Profiles
 NOTES Module 15 Roadway Alignments and Profiles In this module, you learn how to create horizontal alignments, surface profiles, layout (design) profiles, and profile views in AutoCAD Civil 3D. This module
NOTES Module 15 Roadway Alignments and Profiles In this module, you learn how to create horizontal alignments, surface profiles, layout (design) profiles, and profile views in AutoCAD Civil 3D. This module
Autodesk Inventor 2016 Learn by doing. Tutorial Books
 Autodesk Inventor 2016 Learn by doing Tutorial Books Copyright 2015 Kishore This book may not be duplicated in any way without the express written consent of the publisher, except in the form of brief
Autodesk Inventor 2016 Learn by doing Tutorial Books Copyright 2015 Kishore This book may not be duplicated in any way without the express written consent of the publisher, except in the form of brief
Tetra4D Reviewer. Version 5.1. User Guide. Details on how to use Tetra4D Reviewer.
 Tetra4D Reviewer Version 5.1 User Guide Details on how to use Tetra4D Reviewer. ii Contents Chapter 1: Work area... 7 Looking at the work area... 7 Toolbars and toolbar presets... 8 About toolbars and
Tetra4D Reviewer Version 5.1 User Guide Details on how to use Tetra4D Reviewer. ii Contents Chapter 1: Work area... 7 Looking at the work area... 7 Toolbars and toolbar presets... 8 About toolbars and
CHAPTER 1 COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Finding Your Way in the Inventor Interface
 CHAPTER 1 Finding Your Way in the Inventor Interface COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL Understanding Inventor s interface behavior Opening existing files Creating new files Modifying the look and feel of Inventor Managing
CHAPTER 1 Finding Your Way in the Inventor Interface COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL Understanding Inventor s interface behavior Opening existing files Creating new files Modifying the look and feel of Inventor Managing
Profile Modeler Profile Modeler ( A SuperControl Product )
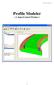 Profile Modeler ( A SuperControl Product ) - 1 - Index Overview... 3 Terminology... 3 Launching the Application... 4 File Menu... 4 Loading a File:... 4 To Load Multiple Files:... 4 Clearing Loaded Files:...
Profile Modeler ( A SuperControl Product ) - 1 - Index Overview... 3 Terminology... 3 Launching the Application... 4 File Menu... 4 Loading a File:... 4 To Load Multiple Files:... 4 Clearing Loaded Files:...
Shape Sculptor Version 5 Release 13. Shape Sculptor
 Shape Sculptor Page 1 Overview Using This Guide Where to Find More Information What's New? Getting Started Entering the Workbench Importing a Polygonal Mesh Decimating a Polygonal Mesh User Tasks Input
Shape Sculptor Page 1 Overview Using This Guide Where to Find More Information What's New? Getting Started Entering the Workbench Importing a Polygonal Mesh Decimating a Polygonal Mesh User Tasks Input
Doctor Walt s Solid Edge Version 19 Workbook 137
 Still using the SMART DIMENSION Tool, click on the left vertical edge of the sketch. Move the cursor to the left and click to set the text position. Type 1.5 for the value and hit the ENTER Key. Next,
Still using the SMART DIMENSION Tool, click on the left vertical edge of the sketch. Move the cursor to the left and click to set the text position. Type 1.5 for the value and hit the ENTER Key. Next,
ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR CS3
 ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR CS3 Chapter 2 Creating Text and Gradients Chapter 2 1 Creating type Create and Format Text Create text anywhere Select the Type Tool Click the artboard and start typing or click and drag
ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR CS3 Chapter 2 Creating Text and Gradients Chapter 2 1 Creating type Create and Format Text Create text anywhere Select the Type Tool Click the artboard and start typing or click and drag
