Machine code. Nils Jansen December 12, 2017
|
|
|
- Alvin Walsh
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Machine code Nils Jansen December 12, 2017
2 Overview So far Circuits Memory ALU Data Path Fetch-Decode-Execute Cycle Fetch-decode-execute cycle Today Machine code Stack 2
3 Recap: Execute-phase: Computation flags operands result Program Screen Keyboard Memory Tanenbaum, Structured Computer Organization, Fifth Edition, 2006 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved
4 RUN1718 CPU Fetch-Test-Decode+Execute Several instructions for RUN1718 CPU (in HADES) XOR READ ADD HALT 12
5 Type of Instructions Influence Program Flow HALT Data Transport READ, WRITE, LOADHI Computation ADD, XOR, Stack PUSH, POP 13
6 Machine code: Example 1 (HALT) HALT cond Instruction with condition cond = 1111 Condition is TRUE 14
7 Machine code: Example 2 (LOADHI) LOADHI.NZ 0x3FFFFF, R LOADHI bit const. target register R3: 0011 condition NZ:
8 Systematic Structure for Machine Code instructions of the same type machine codes have similar structures format := group machine codes with similar structure format 1:+0 HALT format 2+3: memory (READ, WRITE) format 4+5: stack operations (PUSH + POP) format 6: LOADHI format 7: computation + JUMP(derived) 16
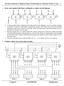
9 All Formats, binary condition bit constant src reg B dest reg condition bit constant src reg A src reg B condition src reg A condition dest reg condition bit constant dest reg condition 0 opc. f src reg A src reg B dest reg condition 0 opc. f 0 10-bit constant src reg B dest reg condition all instructions: conditional uniform structure makes control unit easier 17
10 Example: Format 2 and 3 (READ/WRITE) bit constant src reg B dest reg condition bit constant src reg A src reg B condition READ: WRITE: Memory address: register B + constant READ: result to destination register WRITE: write value from register A 18
11 Design Considerations: Alternative Format condition 1 1 X X dest reg variabel condition 1 0 dest reg variabel condition 0 dest reg variabel condition also possible less uniform structure more complicated control unit more complicated assembler 19
12 More structure Source registers and constant in the same bits as far as possible General machine code X X X X flg nc signed constant src reg A src reg B dest reg condition 20
13 Example: Format 7 (Computation) X X X X flg nc signed constant src reg A src reg B dest reg condition 0 opcode flg src reg A src reg B dest reg condition 0 opcode flg 0 signed constant src reg B dest reg condition variable part: information regarding operands nc = 1: two registers as input nc = 0: constant and register as input 21
14 Example: Format 7 (Computation) X X X X flg nc signed constant src reg A src reg B dest reg condition 0 opcode flg src reg A src reg B dest reg condition 0 opcode flg 0 signed constant src reg B dest reg condition
15 Example: Format 7 (Computation) Constants are assigned 10 bits of space fits exactly. MOVE, JUMP This is the machine code of - MOVE constant, reg OR constant, R0, reg - JUMP label ADD constant, PC, PC 23
16 Derived Instructions Some assembly commands don t have machine code instructions! Example JUMP MOVE CMPf Translated by the assembler! 24
17 Problem: 32-bits-constants To store a 32-bit number in a register, the machine code must at least contain: 32 bits constant 4 bit target register 4 bit condition 1 bit identification of format 41 bits total but each machine code has only 32 bits! 25
18 Solution: LOADHI (calculation) instruction can set the lowest 10 bits of register to an arbitrary value instruction format 3 for the highest 22 bits: LOADHI constant, dest reg stores constant in the highest 22 bits of the dest register sets lowest 10 bits to 0. use LOADHI + ADD together! 26
19 Solution: LOADHI constant (highest 22b) dest reg condition constant (lowest 10b) dest reg dest reg condition 1027 in R1 LOADHI 1, R1 ADD 3, R1, R in R6 LOADHI 1, R6 ADD -24, R6, R6 27
20 Formats 4 and 5 (PUSH/POP) src reg A condition dest reg condition Stack: PUSH POP 28
21 Stack Stack is a data structure Operations: PUSH puts value on top of stack POP retrieves top value of stack Order: LIFO 29
22 Why a stack? Stack is need for: Function call: call stack Local varibales Computation of expressions (store intermediate results) 30
23 Stack Operations in RUN1718 CPU Part of the main memory is reserved for stack Stack pointer SP indicates 'top' of stack (register R14) PUSH Rn - Decrease SP by 4 - Store value in Rn at address [SP] POP Rm - Read value at address [SP] to Rm - Increase SP by 4 31
24 Function Parameterized piece of code that you want to perform several times from different places in the main program Afterwards continue with the main program, at the place where the call occurred So: put call return address on the stack for call function 33
25 Function Call Call Save parameters (on stack or in registers) Put return address on stack Jump to function address Return Save result function (usually in register) Return address from stack Jump to return address 34
26 Format 4 + 5: PUSH and POP src reg A condition dest reg condition Format 4 is PUSH; how do we implement this? subtract 4 from R14 write from A to new R14 Format 5 is POP: READ from R14 to D add 4 to R14 35
27 Format 4: PUSH src reg A condition dest reg condition 4 is PUSH; can we adapt the machine code such that 4 is no special format? bits := 110 (ADD) bits := (-4) 36
28 PUSH, more efficient bit constant src reg A src reg B condition src reg A condition 0 opc. f src reg A src reg B dest reg condition 0 opc. f 0 10-bit constant src reg B dest reg condition 4 is PUSH; now stack increment is handled by standard logic! bits := 110 (ADD) bits := 00 (no flags, constant) bits := (-4) Careful: reg A is not needed in ADD! 37
29 RISC and CISC assembly languages started at the level of the practical assembler better processors -> more and more powerful instructions (for instance memory access at each instruction and multiple operations in one instruction) but also: increasingly complicated processors RISC = Reduced Instruction Set Computer as counter-movement 38
30 Program Languages Higher programming language: abstract, mathematical notation Assembly: mnemonic instruction names can directly be translated to machine code Machine language: bit patterns in memory hard to read easy to make mistakes 39
31 (Dis-)Advantages of Assembly w.r.t machine language + easier to understand + less error-prone w.r.t higher languages + full control of CPU + efficient, smal programs only for specific CPU-type small instructions error-prone 40
32 Preview: What does an Assembler do? translate mnemonic names compute addresses (often) macros pseudo instructions 41
33 Summary: Machine Code Machine codes have a fixed layout per instruction format for all instructions together Assembler resolves derived instructions 43
34 Summary: Stack Stack: data structure (LIFO) Operations: PUSH, POP Applications: function calls, local variables, calculating expressions 44
How does the CPU execute programs? Nils Jansen December 5, 2017 (Based on slides by Jeroen Keiren and Niek Janssen)
 How does the CPU execute programs? Nils Jansen December 5, 2017 (Based on slides by Jeroen Keiren and Niek Janssen) Overview 2 Overview So far Circuits Memory ALU 2 Overview So far Circuits Memory ALU
How does the CPU execute programs? Nils Jansen December 5, 2017 (Based on slides by Jeroen Keiren and Niek Janssen) Overview 2 Overview So far Circuits Memory ALU 2 Overview So far Circuits Memory ALU
Computer Organization CS 206 T Lec# 2: Instruction Sets
 Computer Organization CS 206 T Lec# 2: Instruction Sets Topics What is an instruction set Elements of instruction Instruction Format Instruction types Types of operations Types of operand Addressing mode
Computer Organization CS 206 T Lec# 2: Instruction Sets Topics What is an instruction set Elements of instruction Instruction Format Instruction types Types of operations Types of operand Addressing mode
The von Neumann Architecture. IT 3123 Hardware and Software Concepts. The Instruction Cycle. Registers. LMC Executes a Store.
 IT 3123 Hardware and Software Concepts February 11 and Memory II Copyright 2005 by Bob Brown The von Neumann Architecture 00 01 02 03 PC IR Control Unit Command Memory ALU 96 97 98 99 Notice: This session
IT 3123 Hardware and Software Concepts February 11 and Memory II Copyright 2005 by Bob Brown The von Neumann Architecture 00 01 02 03 PC IR Control Unit Command Memory ALU 96 97 98 99 Notice: This session
Computer Architecture (part 2)
 Computer Architecture (part 2) Topics: Machine Organization Machine Cycle Program Execution Machine Language Types of Memory & Access 2 Chapter 5 The Von Neumann Architecture 1 Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
Computer Architecture (part 2) Topics: Machine Organization Machine Cycle Program Execution Machine Language Types of Memory & Access 2 Chapter 5 The Von Neumann Architecture 1 Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
CHAPTER ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMMING
 CHAPTER 2 8051 ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMMING Registers Register are used to store information temporarily: A byte of data to be processed An address pointing to the data to be fetched The vast majority
CHAPTER 2 8051 ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMMING Registers Register are used to store information temporarily: A byte of data to be processed An address pointing to the data to be fetched The vast majority
UNIT-II. Part-2: CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT
 Page1 UNIT-II Part-2: CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT Stack Organization Instruction Formats Addressing Modes Data Transfer And Manipulation Program Control Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) Introduction:
Page1 UNIT-II Part-2: CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT Stack Organization Instruction Formats Addressing Modes Data Transfer And Manipulation Program Control Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) Introduction:
CPU: SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE INSTRUCTION SET (PART
 General Introduction CPU: SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE INSTRUCTION SET (PART 1) General Introduction (1/5): On Instructions Instruction operate with data or with the flow of the program The following information
General Introduction CPU: SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE INSTRUCTION SET (PART 1) General Introduction (1/5): On Instructions Instruction operate with data or with the flow of the program The following information
Microprogrammed Control Approach
 Microprogrammed Control Approach Considering the FSM for our MIPS subset has 10 states, the complete MIPS instruction set, which contains more than 100 instructions, and considering that these instructions
Microprogrammed Control Approach Considering the FSM for our MIPS subset has 10 states, the complete MIPS instruction set, which contains more than 100 instructions, and considering that these instructions
Computer Architecture and Organization: L09: CPU Organization
 Computer Architecture and Organization: L09: CPU Organization By: A. H. Abdul Hafez Abdul.hafez@hku.edu.tr, ah.abdulhafez@gmail.com, hafez@research.iiit.ac.in 1 CAO, by Dr. A.H. Abdul Hafez, CE Dept. HKU
Computer Architecture and Organization: L09: CPU Organization By: A. H. Abdul Hafez Abdul.hafez@hku.edu.tr, ah.abdulhafez@gmail.com, hafez@research.iiit.ac.in 1 CAO, by Dr. A.H. Abdul Hafez, CE Dept. HKU
Lecture1: introduction. Outline: History overview Central processing unite Register set Special purpose address registers Datapath Control unit
 Lecture1: introduction Outline: History overview Central processing unite Register set Special purpose address registers Datapath Control unit 1 1. History overview Computer systems have conventionally
Lecture1: introduction Outline: History overview Central processing unite Register set Special purpose address registers Datapath Control unit 1 1. History overview Computer systems have conventionally
EC-801 Advanced Computer Architecture
 EC-801 Advanced Computer Architecture Lecture 5 Instruction Set Architecture I Dr Hashim Ali Fall 2018 Department of Computer Science and Engineering HITEC University Taxila!1 Instruction Set Architecture
EC-801 Advanced Computer Architecture Lecture 5 Instruction Set Architecture I Dr Hashim Ali Fall 2018 Department of Computer Science and Engineering HITEC University Taxila!1 Instruction Set Architecture
SOEN228, Winter Revision 1.2 Date: October 25,
 SOEN228, Winter 2003 Revision 1.2 Date: October 25, 2003 1 Contents Flags Mnemonics Basic I/O Exercises Overview of sample programs 2 Flag Register The flag register stores the condition flags that retain
SOEN228, Winter 2003 Revision 1.2 Date: October 25, 2003 1 Contents Flags Mnemonics Basic I/O Exercises Overview of sample programs 2 Flag Register The flag register stores the condition flags that retain
Designing Computers. The Von Neumann Architecture. The Von Neumann Architecture. The Von Neumann Architecture
 Chapter 5.1-5.2 Designing Computers All computers more or less based on the same basic design, the Von Neumann Architecture! Von Neumann Architecture CMPUT101 Introduction to Computing (c) Yngvi Bjornsson
Chapter 5.1-5.2 Designing Computers All computers more or less based on the same basic design, the Von Neumann Architecture! Von Neumann Architecture CMPUT101 Introduction to Computing (c) Yngvi Bjornsson
The Von Neumann Architecture. Designing Computers. The Von Neumann Architecture. CMPUT101 Introduction to Computing - Spring 2001
 The Von Neumann Architecture Chapter 5.1-5.2 Von Neumann Architecture Designing Computers All computers more or less based on the same basic design, the Von Neumann Architecture! CMPUT101 Introduction
The Von Neumann Architecture Chapter 5.1-5.2 Von Neumann Architecture Designing Computers All computers more or less based on the same basic design, the Von Neumann Architecture! CMPUT101 Introduction
CMPUT101 Introduction to Computing - Summer 2002
 7KH9RQ1HXPDQQ$UFKLWHFWXUH Chapter 5.1-5.2 Von Neumann Architecture 'HVLJQLQJ&RPSXWHUV All computers more or less based on the same basic design, the Von Neumann Architecture! CMPUT101 Introduction to Computing
7KH9RQ1HXPDQQ$UFKLWHFWXUH Chapter 5.1-5.2 Von Neumann Architecture 'HVLJQLQJ&RPSXWHUV All computers more or less based on the same basic design, the Von Neumann Architecture! CMPUT101 Introduction to Computing
Chapter 2 Instruction Set Architecture
 Chapter 2 Instruction Set Architecture Course Outcome (CO) - CO2 Describe the architecture and organization of computer systems Program Outcome (PO) PO1 Apply knowledge of mathematics, science and engineering
Chapter 2 Instruction Set Architecture Course Outcome (CO) - CO2 Describe the architecture and organization of computer systems Program Outcome (PO) PO1 Apply knowledge of mathematics, science and engineering
Central Processing Unit
 Central Processing Unit Networks and Embedded Software Module.. by Wolfgang Neff Components () lock diagram Execution Unit Control Unit Registers rithmetic logic unit DD, SU etc. NOT, ND etc. us Interface
Central Processing Unit Networks and Embedded Software Module.. by Wolfgang Neff Components () lock diagram Execution Unit Control Unit Registers rithmetic logic unit DD, SU etc. NOT, ND etc. us Interface
CPU ARCHITECTURE. QUESTION 1 Explain how the width of the data bus and system clock speed affect the performance of a computer system.
 CPU ARCHITECTURE QUESTION 1 Explain how the width of the data bus and system clock speed affect the performance of a computer system. ANSWER 1 Data Bus Width the width of the data bus determines the number
CPU ARCHITECTURE QUESTION 1 Explain how the width of the data bus and system clock speed affect the performance of a computer system. ANSWER 1 Data Bus Width the width of the data bus determines the number
CPU. Fall 2003 CSE 207 Digital Design Project #4 R0 R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6 R7 PC STATUS IR. Control Logic RAM MAR MDR. Internal Processor Bus
 http://www.engr.uconn.edu/~barry/cse207/fa03/project4.pdf Page 1 of 16 Fall 2003 CSE 207 Digital Design Project #4 Background Microprocessors are increasingly common in every day devices. Desktop computers
http://www.engr.uconn.edu/~barry/cse207/fa03/project4.pdf Page 1 of 16 Fall 2003 CSE 207 Digital Design Project #4 Background Microprocessors are increasingly common in every day devices. Desktop computers
When an instruction is initially read from memory it goes to the Instruction register.
 CS 320 Ch. 12 Instruction Sets Computer instructions are written in mnemonics. Mnemonics typically have a 1 to 1 correspondence between a mnemonic and the machine code. Mnemonics are the assembly language
CS 320 Ch. 12 Instruction Sets Computer instructions are written in mnemonics. Mnemonics typically have a 1 to 1 correspondence between a mnemonic and the machine code. Mnemonics are the assembly language
2.2 THE MARIE Instruction Set Architecture
 2.2 THE MARIE Instruction Set Architecture MARIE has a very simple, yet powerful, instruction set. The instruction set architecture (ISA) of a machine specifies the instructions that the computer can perform
2.2 THE MARIE Instruction Set Architecture MARIE has a very simple, yet powerful, instruction set. The instruction set architecture (ISA) of a machine specifies the instructions that the computer can perform
Digital System Design Using Verilog. - Processing Unit Design
 Digital System Design Using Verilog - Processing Unit Design 1.1 CPU BASICS A typical CPU has three major components: (1) Register set, (2) Arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and (3) Control unit (CU) The register
Digital System Design Using Verilog - Processing Unit Design 1.1 CPU BASICS A typical CPU has three major components: (1) Register set, (2) Arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and (3) Control unit (CU) The register
CS 24: INTRODUCTION TO. Spring 2018 Lecture 3 COMPUTING SYSTEMS
 CS 24: INTRODUCTION TO Spring 2018 Lecture 3 COMPUTING SYSTEMS LAST TIME Basic components of processors: Buses, multiplexers, demultiplexers Arithmetic/Logic Unit (ALU) Addressable memory Assembled components
CS 24: INTRODUCTION TO Spring 2018 Lecture 3 COMPUTING SYSTEMS LAST TIME Basic components of processors: Buses, multiplexers, demultiplexers Arithmetic/Logic Unit (ALU) Addressable memory Assembled components
Computer Architecture
 Computer Architecture Slide Sets WS 2013/2014 Prof. Dr. Uwe Brinkschulte M.Sc. Benjamin Betting Part 3 Fundamentals in Computer Architecture Computer Architecture Part 3 page 1 of 55 Prof. Dr. Uwe Brinkschulte,
Computer Architecture Slide Sets WS 2013/2014 Prof. Dr. Uwe Brinkschulte M.Sc. Benjamin Betting Part 3 Fundamentals in Computer Architecture Computer Architecture Part 3 page 1 of 55 Prof. Dr. Uwe Brinkschulte,
CSC 252: Computer Organization Spring 2018: Lecture 11
 CSC 252: Computer Organization Spring 2018: Lecture 11 Instructor: Yuhao Zhu Department of Computer Science University of Rochester Action Items: Assignment 3 is due March 2, midnight Announcement Programming
CSC 252: Computer Organization Spring 2018: Lecture 11 Instructor: Yuhao Zhu Department of Computer Science University of Rochester Action Items: Assignment 3 is due March 2, midnight Announcement Programming
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION & ARCHITECTURE
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION & ARCHITECTURE Instructions Sets Architecture Lesson 5a 1 What are Instruction Sets The complete collection of instructions that are understood by a CPU Can be considered as a functional
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION & ARCHITECTURE Instructions Sets Architecture Lesson 5a 1 What are Instruction Sets The complete collection of instructions that are understood by a CPU Can be considered as a functional
Rui Wang, Assistant professor Dept. of Information and Communication Tongji University.
 Instructions: ti Language of the Computer Rui Wang, Assistant professor Dept. of Information and Communication Tongji University it Email: ruiwang@tongji.edu.cn Computer Hierarchy Levels Language understood
Instructions: ti Language of the Computer Rui Wang, Assistant professor Dept. of Information and Communication Tongji University it Email: ruiwang@tongji.edu.cn Computer Hierarchy Levels Language understood
Microcomputer Architecture and Programming
 IUST-EE (Chapter 1) Microcomputer Architecture and Programming 1 Outline Basic Blocks of Microcomputer Typical Microcomputer Architecture The Single-Chip Microprocessor Microprocessor vs. Microcontroller
IUST-EE (Chapter 1) Microcomputer Architecture and Programming 1 Outline Basic Blocks of Microcomputer Typical Microcomputer Architecture The Single-Chip Microprocessor Microprocessor vs. Microcontroller
4- MACHINE LANGUAGE CODING 4-1THE INSTRUCTION SET:
 4- MACHINE LANGUAGE CODING 4-1THE INSTRUCTION SET: The microprocessor's instruction set defines the basic operations that a programmer can specify to the device to perform. Table 4-1 contains list basic
4- MACHINE LANGUAGE CODING 4-1THE INSTRUCTION SET: The microprocessor's instruction set defines the basic operations that a programmer can specify to the device to perform. Table 4-1 contains list basic
Practical Malware Analysis
 Practical Malware Analysis Ch 4: A Crash Course in x86 Disassembly Revised 1-16-7 Basic Techniques Basic static analysis Looks at malware from the outside Basic dynamic analysis Only shows you how the
Practical Malware Analysis Ch 4: A Crash Course in x86 Disassembly Revised 1-16-7 Basic Techniques Basic static analysis Looks at malware from the outside Basic dynamic analysis Only shows you how the
Chapter 2: Instructions How we talk to the computer
 Chapter 2: Instructions How we talk to the computer 1 The Instruction Set Architecture that part of the architecture that is visible to the programmer - instruction formats - opcodes (available instructions)
Chapter 2: Instructions How we talk to the computer 1 The Instruction Set Architecture that part of the architecture that is visible to the programmer - instruction formats - opcodes (available instructions)
Introduction to Computers - Chapter 4
 Introduction to Computers - Chapter 4 Since the invention of the transistor and the first digital computer of the 1940s, computers have been increasing in complexity and performance; however, their overall
Introduction to Computers - Chapter 4 Since the invention of the transistor and the first digital computer of the 1940s, computers have been increasing in complexity and performance; however, their overall
CISC 662 Graduate Computer Architecture. Lecture 4 - ISA MIPS ISA. In a CPU. (vonneumann) Processor Organization
 CISC 662 Graduate Computer Architecture Lecture 4 - ISA MIPS ISA Michela Taufer http://www.cis.udel.edu/~taufer/courses Powerpoint Lecture Notes from John Hennessy and David Patterson s: Computer Architecture,
CISC 662 Graduate Computer Architecture Lecture 4 - ISA MIPS ISA Michela Taufer http://www.cis.udel.edu/~taufer/courses Powerpoint Lecture Notes from John Hennessy and David Patterson s: Computer Architecture,
CPU Structure and Function
 CPU Structure and Function Chapter 12 Lesson 17 Slide 1/36 Processor Organization CPU must: Fetch instructions Interpret instructions Fetch data Process data Write data Lesson 17 Slide 2/36 CPU With Systems
CPU Structure and Function Chapter 12 Lesson 17 Slide 1/36 Processor Organization CPU must: Fetch instructions Interpret instructions Fetch data Process data Write data Lesson 17 Slide 2/36 CPU With Systems
Address Modes effective address
 Address Modes The MARIE supports only three addressing modes: immediate, direct, and indirect. We are now going to discuss addressing modes in general. Most computers support quite a few of these modes.
Address Modes The MARIE supports only three addressing modes: immediate, direct, and indirect. We are now going to discuss addressing modes in general. Most computers support quite a few of these modes.
CMPUT101 Introduction to Computing - Summer 2002
 7KH9RQ1HXPDQQ$UFKLWHFWXUH 2GGVDQG(QGV Chapter 5.1-5.2 Von Neumann Architecture CMPUT101 Introduction to Computing (c) Yngvi Bjornsson & Vadim Bulitko 1 'HVLJQLQJ&RPSXWHUV All computers more or less based
7KH9RQ1HXPDQQ$UFKLWHFWXUH 2GGVDQG(QGV Chapter 5.1-5.2 Von Neumann Architecture CMPUT101 Introduction to Computing (c) Yngvi Bjornsson & Vadim Bulitko 1 'HVLJQLQJ&RPSXWHUV All computers more or less based
CISC 662 Graduate Computer Architecture. Lecture 4 - ISA
 CISC 662 Graduate Computer Architecture Lecture 4 - ISA Michela Taufer http://www.cis.udel.edu/~taufer/courses Powerpoint Lecture Notes from John Hennessy and David Patterson s: Computer Architecture,
CISC 662 Graduate Computer Architecture Lecture 4 - ISA Michela Taufer http://www.cis.udel.edu/~taufer/courses Powerpoint Lecture Notes from John Hennessy and David Patterson s: Computer Architecture,
The CPU and Memory. How does a computer work? How does a computer interact with data? How are instructions performed? Recall schematic diagram:
 The CPU and Memory How does a computer work? How does a computer interact with data? How are instructions performed? Recall schematic diagram: 1 Registers A register is a permanent storage location within
The CPU and Memory How does a computer work? How does a computer interact with data? How are instructions performed? Recall schematic diagram: 1 Registers A register is a permanent storage location within
Module 3 Instruction Set Architecture (ISA)
 Module 3 Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) I S A L E V E L E L E M E N T S O F I N S T R U C T I O N S I N S T R U C T I O N S T Y P E S N U M B E R O F A D D R E S S E S R E G I S T E R S T Y P E S O
Module 3 Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) I S A L E V E L E L E M E N T S O F I N S T R U C T I O N S I N S T R U C T I O N S T Y P E S N U M B E R O F A D D R E S S E S R E G I S T E R S T Y P E S O
E3940 Microprocessor Systems Laboratory. Introduction to the Z80
 E3940 Microprocessor Systems Laboratory Introduction to the Z80 Andrew T. Campbell comet.columbia.edu/~campbell campbell@comet.columbia.edu E3940 Microprocessor Systems Laboratory Page 1 Z80 Laboratory
E3940 Microprocessor Systems Laboratory Introduction to the Z80 Andrew T. Campbell comet.columbia.edu/~campbell campbell@comet.columbia.edu E3940 Microprocessor Systems Laboratory Page 1 Z80 Laboratory
Instruction Sets: Characteristics and Functions Addressing Modes
 Instruction Sets: Characteristics and Functions Addressing Modes Chapters 10 and 11, William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 th Edition What is an Instruction Set? The complete collection
Instruction Sets: Characteristics and Functions Addressing Modes Chapters 10 and 11, William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 th Edition What is an Instruction Set? The complete collection
CS 261 Fall Machine and Assembly Code. Data Movement and Arithmetic. Mike Lam, Professor
 CS 261 Fall 2018 0000000100000f50 55 48 89 e5 48 83 ec 10 48 8d 3d 3b 00 00 00 c7 0000000100000f60 45 fc 00 00 00 00 b0 00 e8 0d 00 00 00 31 c9 89 0000000100000f70 45 f8 89 c8 48 83 c4 10 5d c3 Mike Lam,
CS 261 Fall 2018 0000000100000f50 55 48 89 e5 48 83 ec 10 48 8d 3d 3b 00 00 00 c7 0000000100000f60 45 fc 00 00 00 00 b0 00 e8 0d 00 00 00 31 c9 89 0000000100000f70 45 f8 89 c8 48 83 c4 10 5d c3 Mike Lam,
Computer Science 324 Computer Architecture Mount Holyoke College Fall Topic Notes: MIPS Instruction Set Architecture
 Computer Science 324 Computer Architecture Mount Holyoke College Fall 2009 Topic Notes: MIPS Instruction Set Architecture vonneumann Architecture Modern computers use the vonneumann architecture. Idea:
Computer Science 324 Computer Architecture Mount Holyoke College Fall 2009 Topic Notes: MIPS Instruction Set Architecture vonneumann Architecture Modern computers use the vonneumann architecture. Idea:
CISC Processor Design
 CISC Processor Design Virendra Singh Indian Institute of Science Bangalore virendra@computer.org Lecture 3 SE-273: Processor Design Processor Architecture Processor Architecture CISC RISC Jan 21, 2008
CISC Processor Design Virendra Singh Indian Institute of Science Bangalore virendra@computer.org Lecture 3 SE-273: Processor Design Processor Architecture Processor Architecture CISC RISC Jan 21, 2008
The Von Neumann Architecture Odds and Ends. Designing Computers. The Von Neumann Architecture. CMPUT101 Introduction to Computing - Spring 2001
 The Von Neumann Architecture Odds and Ends Chapter 5.1-5.2 Von Neumann Architecture CMPUT101 Introduction to Computing (c) Yngvi Bjornsson & Vadim Bulitko 1 Designing Computers All computers more or less
The Von Neumann Architecture Odds and Ends Chapter 5.1-5.2 Von Neumann Architecture CMPUT101 Introduction to Computing (c) Yngvi Bjornsson & Vadim Bulitko 1 Designing Computers All computers more or less
Project - RTL Model. III. Design Decisions. Part 4 - May 17, Jason Nemeth. model is capable of modeling both provided benchmarks.
 Project - RTL Model Part 4 - May 17, 2005 Jason Nemeth I. Introduction The purpose of this assignment was to refine the structural model of the microprocessor into a working RTL-level VHDL implementation.
Project - RTL Model Part 4 - May 17, 2005 Jason Nemeth I. Introduction The purpose of this assignment was to refine the structural model of the microprocessor into a working RTL-level VHDL implementation.
Computer Science 104:! Y86 & Single Cycle Processor Design!
 Computer Science 104: Y86 & Single Cycle Processor Design Alvin R. Lebeck Slides based on those from Randy Bryant 1 CS:APP Administrative Homework #4 My office hours today 11:30-12:30 Reading: text 4.3
Computer Science 104: Y86 & Single Cycle Processor Design Alvin R. Lebeck Slides based on those from Randy Bryant 1 CS:APP Administrative Homework #4 My office hours today 11:30-12:30 Reading: text 4.3
Systems I. Machine-Level Programming V: Procedures
 Systems I Machine-Level Programming V: Procedures Topics abstraction and implementation IA32 stack discipline Procedural Memory Usage void swap(int *xp, int *yp) int t0 = *xp; int t1 = *yp; *xp = t1; *yp
Systems I Machine-Level Programming V: Procedures Topics abstraction and implementation IA32 stack discipline Procedural Memory Usage void swap(int *xp, int *yp) int t0 = *xp; int t1 = *yp; *xp = t1; *yp
CPE 323 MSP430 INSTRUCTION SET ARCHITECTURE (ISA)
 CPE 323 MSP430 INSTRUCTION SET ARCHITECTURE (ISA) Aleksandar Milenković Email: milenka@uah.edu Web: http://www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka Objective Introduce MSP430 Instruction Set Architecture (Class of ISA,
CPE 323 MSP430 INSTRUCTION SET ARCHITECTURE (ISA) Aleksandar Milenković Email: milenka@uah.edu Web: http://www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka Objective Introduce MSP430 Instruction Set Architecture (Class of ISA,
Computer Organization II CMSC 3833 Lecture 33
 Term MARIE Definition Machine Architecture that is Really Intuitive and Easy 4.8.1 The Architecture Figure s Architecture Characteristics: Binary, two s complement Stored program, fixed word length Word
Term MARIE Definition Machine Architecture that is Really Intuitive and Easy 4.8.1 The Architecture Figure s Architecture Characteristics: Binary, two s complement Stored program, fixed word length Word
ELEG3924 Microprocessor
 Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG3924 Microprocessor Ch.2 Assembly Language Programming Dr. Jing Yang jingyang@uark.edu 1 OUTLINE Inside 8051 Introduction to assembly programming
Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG3924 Microprocessor Ch.2 Assembly Language Programming Dr. Jing Yang jingyang@uark.edu 1 OUTLINE Inside 8051 Introduction to assembly programming
ELEG3923 Microprocessor Ch.2 Assembly Language Programming
 Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG3923 Microprocessor Ch.2 Assembly Language Programming Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Inside 8051 Introduction to assembly programming
Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG3923 Microprocessor Ch.2 Assembly Language Programming Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Inside 8051 Introduction to assembly programming
Topic Notes: MIPS Instruction Set Architecture
 Computer Science 220 Assembly Language & Comp. Architecture Siena College Fall 2011 Topic Notes: MIPS Instruction Set Architecture vonneumann Architecture Modern computers use the vonneumann architecture.
Computer Science 220 Assembly Language & Comp. Architecture Siena College Fall 2011 Topic Notes: MIPS Instruction Set Architecture vonneumann Architecture Modern computers use the vonneumann architecture.
Instruction Set II. COMP 212 Computer Organization & Architecture. COMP 212 Fall Lecture 7. Instruction Set. Quiz. What is an Instruction Set?
 COMP 212 Computer Organization & Architecture Quiz COMP 212 Fall 2008 Lecture 7 Fill in your student number only, do NOT write down your name Open book, but NO calculator, NO discussions, Relax and have
COMP 212 Computer Organization & Architecture Quiz COMP 212 Fall 2008 Lecture 7 Fill in your student number only, do NOT write down your name Open book, but NO calculator, NO discussions, Relax and have
Introduction to Computers & Programming
 16.070 Introduction to Computers & Programming Computer Architecture, Machine Language, Program Execution Prof. Kristina Lundqvist Dept. of Aero/Astro, MIT Chapter Summary This chapter introduces the activities
16.070 Introduction to Computers & Programming Computer Architecture, Machine Language, Program Execution Prof. Kristina Lundqvist Dept. of Aero/Astro, MIT Chapter Summary This chapter introduces the activities
VARDHAMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS) Shamshabad, Hyderabad
 Introduction to MS-DOS Debugger DEBUG In this laboratory, we will use DEBUG program and learn how to: 1. Examine and modify the contents of the 8086 s internal registers, and dedicated parts of the memory
Introduction to MS-DOS Debugger DEBUG In this laboratory, we will use DEBUG program and learn how to: 1. Examine and modify the contents of the 8086 s internal registers, and dedicated parts of the memory
CN310 Microprocessor Systems Design
 CN310 Microprocessor Systems Design Micro Architecture Nawin Somyat Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Thammasat University 28 August 2018 Outline Course Contents 1 Introduction 2 Simple
CN310 Microprocessor Systems Design Micro Architecture Nawin Somyat Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Thammasat University 28 August 2018 Outline Course Contents 1 Introduction 2 Simple
Instruction-set Design Issues: what is the ML instruction format(s) ML instruction Opcode Dest. Operand Source Operand 1...
 Instruction-set Design Issues: what is the format(s) Opcode Dest. Operand Source Operand 1... 1) Which instructions to include: How many? Complexity - simple ADD R1, R2, R3 complex e.g., VAX MATCHC substrlength,
Instruction-set Design Issues: what is the format(s) Opcode Dest. Operand Source Operand 1... 1) Which instructions to include: How many? Complexity - simple ADD R1, R2, R3 complex e.g., VAX MATCHC substrlength,
CS 265. Computer Architecture. Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng.
 CS 265 Computer Architecture Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng. Part 3: von Neumann Architecture von Neumann Architecture Our goal: understand the basics of von Neumann architecture, including memory, control unit
CS 265 Computer Architecture Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng. Part 3: von Neumann Architecture von Neumann Architecture Our goal: understand the basics of von Neumann architecture, including memory, control unit
Little Man Computer (LMC)
 Little Man Computer (LMC) A-level Computing Independent Study Project Part Two The Little Man Computer (LMC) is a simulator which models the basic features of a modern computer. It features a central processing
Little Man Computer (LMC) A-level Computing Independent Study Project Part Two The Little Man Computer (LMC) is a simulator which models the basic features of a modern computer. It features a central processing
Problem with Scanning an Infix Expression
 Operator Notation Consider the infix expression (X Y) + (W U), with parentheses added to make the evaluation order perfectly obvious. This is an arithmetic expression written in standard form, called infix
Operator Notation Consider the infix expression (X Y) + (W U), with parentheses added to make the evaluation order perfectly obvious. This is an arithmetic expression written in standard form, called infix
Expectations. Why learn Assembly Language? Administrative Issues. Assignments. CSC 3210 Computer Organization and Programming
 CSC 3210 Computer Organization and Programming Introduction and Overview Dr. Anu Bourgeois (modified by Michael Weeks) Expectations Writing code with loops Base conversions Especially involving decimal
CSC 3210 Computer Organization and Programming Introduction and Overview Dr. Anu Bourgeois (modified by Michael Weeks) Expectations Writing code with loops Base conversions Especially involving decimal
 Chapter 1 Microprocessor architecture ECE 3120 Dr. Mohamed Mahmoud http://iweb.tntech.edu/mmahmoud/ mmahmoud@tntech.edu Outline 1.1 Computer hardware organization 1.1.1 Number System 1.1.2 Computer hardware
Chapter 1 Microprocessor architecture ECE 3120 Dr. Mohamed Mahmoud http://iweb.tntech.edu/mmahmoud/ mmahmoud@tntech.edu Outline 1.1 Computer hardware organization 1.1.1 Number System 1.1.2 Computer hardware
Interfacing Compiler and Hardware. Computer Systems Architecture. Processor Types And Instruction Sets. What Instructions Should A Processor Offer?
 Interfacing Compiler and Hardware Computer Systems Architecture FORTRAN 90 program C++ program Processor Types And Sets FORTRAN 90 Compiler C++ Compiler set level Hardware 1 2 What s Should A Processor
Interfacing Compiler and Hardware Computer Systems Architecture FORTRAN 90 program C++ program Processor Types And Sets FORTRAN 90 Compiler C++ Compiler set level Hardware 1 2 What s Should A Processor
SCRAM Introduction. Philipp Koehn. 19 February 2018
 SCRAM Introduction Philipp Koehn 19 February 2018 This eek 1 Fully work through a computer circuit assembly code Simple but Complete Random Access Machine (SCRAM) every instruction is 8 bit 4 bit for op-code:
SCRAM Introduction Philipp Koehn 19 February 2018 This eek 1 Fully work through a computer circuit assembly code Simple but Complete Random Access Machine (SCRAM) every instruction is 8 bit 4 bit for op-code:
Micro computer Organization
 Micro computer Organization I Base Basic Components CPU SYSTEM BUSES VDD CLK RESET 1 MPU vs MCU Microprocessor Unit (MPU) CPU (called Microprocessor) is a die All components external to die Basically on
Micro computer Organization I Base Basic Components CPU SYSTEM BUSES VDD CLK RESET 1 MPU vs MCU Microprocessor Unit (MPU) CPU (called Microprocessor) is a die All components external to die Basically on
CHAPTER 5 : Introduction to Intel 8085 Microprocessor Hardware BENG 2223 MICROPROCESSOR TECHNOLOGY
 CHAPTER 5 : Introduction to Intel 8085 Hardware BENG 2223 MICROPROCESSOR TECHNOLOGY The 8085A(commonly known as the 8085) : Was first introduced in March 1976 is an 8-bit microprocessor with 16-bit address
CHAPTER 5 : Introduction to Intel 8085 Hardware BENG 2223 MICROPROCESSOR TECHNOLOGY The 8085A(commonly known as the 8085) : Was first introduced in March 1976 is an 8-bit microprocessor with 16-bit address
Assembly Language Programming of 8085
 Assembly Language Programming of 8085 Topics 1. Introduction 2. Programming model of 8085 3. Instruction set of 8085 4. Example Programs 5. Addressing modes of 8085 6. Instruction & Data Formats of 8085
Assembly Language Programming of 8085 Topics 1. Introduction 2. Programming model of 8085 3. Instruction set of 8085 4. Example Programs 5. Addressing modes of 8085 6. Instruction & Data Formats of 8085
ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE MACHINE ORGANIZATION
 ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE MACHINE ORGANIZATION CHAPTER 3 1 Sub-topics The topic will cover: Microprocessor architecture CPU processing methods Pipelining Superscalar RISC Multiprocessing Instruction Cycle Instruction
ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE MACHINE ORGANIZATION CHAPTER 3 1 Sub-topics The topic will cover: Microprocessor architecture CPU processing methods Pipelining Superscalar RISC Multiprocessing Instruction Cycle Instruction
Computer Organization and Technology Processor and System Structures
 Computer Organization and Technology Processor and System Structures Assoc. Prof. Dr. Wattanapong Kurdthongmee Division of Computer Engineering, School of Engineering and Resources, Walailak University
Computer Organization and Technology Processor and System Structures Assoc. Prof. Dr. Wattanapong Kurdthongmee Division of Computer Engineering, School of Engineering and Resources, Walailak University
THE MICROPROCESSOR Von Neumann s Architecture Model
 THE ICROPROCESSOR Von Neumann s Architecture odel Input/Output unit Provides instructions and data emory unit Stores both instructions and data Arithmetic and logic unit Processes everything Control unit
THE ICROPROCESSOR Von Neumann s Architecture odel Input/Output unit Provides instructions and data emory unit Stores both instructions and data Arithmetic and logic unit Processes everything Control unit
CS 101, Mock Computer Architecture
 CS 101, Mock Computer Architecture Computer organization and architecture refers to the actual hardware used to construct the computer, and the way that the hardware operates both physically and logically
CS 101, Mock Computer Architecture Computer organization and architecture refers to the actual hardware used to construct the computer, and the way that the hardware operates both physically and logically
Grundlagen Microcontroller Processor Core. Günther Gridling Bettina Weiss
 Grundlagen Microcontroller Processor Core Günther Gridling Bettina Weiss 1 Processor Core Architecture Instruction Set Lecture Overview 2 Processor Core Architecture Computes things > ALU (Arithmetic Logic
Grundlagen Microcontroller Processor Core Günther Gridling Bettina Weiss 1 Processor Core Architecture Instruction Set Lecture Overview 2 Processor Core Architecture Computes things > ALU (Arithmetic Logic
CHAPTER 5 A Closer Look at Instruction Set Architectures
 CHAPTER 5 A Closer Look at Instruction Set Architectures 5.1 Introduction 5.2 Instruction Formats 5.2.1 Design Decisions for Instruction Sets 5.2.2 Little versus Big Endian 5.2.3 Internal Storage in the
CHAPTER 5 A Closer Look at Instruction Set Architectures 5.1 Introduction 5.2 Instruction Formats 5.2.1 Design Decisions for Instruction Sets 5.2.2 Little versus Big Endian 5.2.3 Internal Storage in the
Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences. Lab 4: Introduction to MARIE
 Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences CS 3401 Assembly Language 4 Lab 4: Introduction to MARIE Objectives: The main objective of this lab is to get you familiarized with MARIE a simple computer
Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences CS 3401 Assembly Language 4 Lab 4: Introduction to MARIE Objectives: The main objective of this lab is to get you familiarized with MARIE a simple computer
TYPES OF INTERRUPTS: -
 There are 3 types of interrupts. TYPES OF INTERRUPTS: - External Interrupts. Internal Interrupts. Software interrupts. Hardware Interrupts (1) External interrupts come from I/O devices, from a timing device
There are 3 types of interrupts. TYPES OF INTERRUPTS: - External Interrupts. Internal Interrupts. Software interrupts. Hardware Interrupts (1) External interrupts come from I/O devices, from a timing device
Instruction Sets: Characteristics and Functions
 Instruction Sets: Characteristics and Functions Chapter 10 Lesson 15 Slide 1/22 Machine instruction set Computer designer: The machine instruction set provides the functional requirements for the CPU.
Instruction Sets: Characteristics and Functions Chapter 10 Lesson 15 Slide 1/22 Machine instruction set Computer designer: The machine instruction set provides the functional requirements for the CPU.
STRUCTURE OF DESKTOP COMPUTERS
 Page no: 1 UNIT 1 STRUCTURE OF DESKTOP COMPUTERS The desktop computers are the computers which are usually found on a home or office desk. They consist of processing unit, storage unit, visual display
Page no: 1 UNIT 1 STRUCTURE OF DESKTOP COMPUTERS The desktop computers are the computers which are usually found on a home or office desk. They consist of processing unit, storage unit, visual display
CPE300: Digital System Architecture and Design
 CPE300: Digital System Architecture and Design Fall 2011 MW 17:30-18:45 CBC C316 Arithmetic Unit 10032011 http://www.egr.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe300/ 2 Outline Recap Chapter 3 Number Systems Fixed Point
CPE300: Digital System Architecture and Design Fall 2011 MW 17:30-18:45 CBC C316 Arithmetic Unit 10032011 http://www.egr.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe300/ 2 Outline Recap Chapter 3 Number Systems Fixed Point
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies Unit - 1
 Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies Unit - 1 1. Draw and explain 4 bit binary arithmetic or adder circuit diagram. A binary parallel adder is digital function that produces
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies Unit - 1 1. Draw and explain 4 bit binary arithmetic or adder circuit diagram. A binary parallel adder is digital function that produces
3.0 Instruction Set. 3.1 Overview
 3.0 Instruction Set 3.1 Overview There are 16 different P8 instructions. Research on instruction set usage was the basis for instruction selection. Each instruction has at least two addressing modes, with
3.0 Instruction Set 3.1 Overview There are 16 different P8 instructions. Research on instruction set usage was the basis for instruction selection. Each instruction has at least two addressing modes, with
(2) Explain the addressing mode of OR What do you mean by addressing mode? Explain diff. addressing mode for 8085 with examples.
 (1) Explain instruction format and Opcode format of 8085 μp with example. OR With help of examples, explain the formation of opcodes of 8085 OR What is an instruction? List type of instruction based on
(1) Explain instruction format and Opcode format of 8085 μp with example. OR With help of examples, explain the formation of opcodes of 8085 OR What is an instruction? List type of instruction based on
Fundamentals of Computer Architecture. 8. Bringing It All Together The Hardware Engineer s Perspective
 Fundamentals of Computer Architecture 8. Bringing It All Together The Hardware Engineer s Perspective 1 CHAPTER OVERVIEW This chapter includes: Assigning tasks to individual processor components; Micro-instructions;
Fundamentals of Computer Architecture 8. Bringing It All Together The Hardware Engineer s Perspective 1 CHAPTER OVERVIEW This chapter includes: Assigning tasks to individual processor components; Micro-instructions;
CPU Design John D. Carpinelli, All Rights Reserved 1
 CPU Design 1997 John D. Carpinelli, All Rights Reserved 1 Outline Register organization ALU design Stacks Instruction formats and types Addressing modes 1997 John D. Carpinelli, All Rights Reserved 2 We
CPU Design 1997 John D. Carpinelli, All Rights Reserved 1 Outline Register organization ALU design Stacks Instruction formats and types Addressing modes 1997 John D. Carpinelli, All Rights Reserved 2 We
Chapter 3 : Control Unit
 3.1 Control Memory Chapter 3 Control Unit The function of the control unit in a digital computer is to initiate sequences of microoperations. When the control signals are generated by hardware using conventional
3.1 Control Memory Chapter 3 Control Unit The function of the control unit in a digital computer is to initiate sequences of microoperations. When the control signals are generated by hardware using conventional
Register-Level Design
 Register-Level Design A digital system can be treated at different level of abstraction or compleity. So far, we have seen it at the gate level and the transistor level. At a higher level than the gate
Register-Level Design A digital system can be treated at different level of abstraction or compleity. So far, we have seen it at the gate level and the transistor level. At a higher level than the gate
session 7. Datapath Design
 General Objective: Determine the hardware requirement of a digital computer based on its instruction set. Specific Objectives: Describe the general concepts in designing the data path of a digital computer
General Objective: Determine the hardware requirement of a digital computer based on its instruction set. Specific Objectives: Describe the general concepts in designing the data path of a digital computer
The Itanium Bit Microprocessor Report
 The Itanium - 1986 8 Bit Microprocessor Report By PRIYANK JAIN (02010123) Group # 11 Under guidance of Dr. J. K. Deka & Dr. S. B. Nair Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology,
The Itanium - 1986 8 Bit Microprocessor Report By PRIYANK JAIN (02010123) Group # 11 Under guidance of Dr. J. K. Deka & Dr. S. B. Nair Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology,
MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER BASED SYSTEMS
 MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER BASED SYSTEMS UNIT I INTRODUCTION TO 8085 8085 Microprocessor - Architecture and its operation, Concept of instruction execution and timing diagrams, fundamentals of
MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER BASED SYSTEMS UNIT I INTRODUCTION TO 8085 8085 Microprocessor - Architecture and its operation, Concept of instruction execution and timing diagrams, fundamentals of
Data Manipulation. Chih-Wei Tang ( 唐之瑋 ) Department of Communication Engineering National Central University JhongLi, Taiwan
 Data Manipulation Chih-Wei Tang ( 唐之瑋 ) Department of Communication Engineering National Central University JhongLi, Taiwan Outline Computer Architecture Machine Language Program Execution Arithmetic/Logic
Data Manipulation Chih-Wei Tang ( 唐之瑋 ) Department of Communication Engineering National Central University JhongLi, Taiwan Outline Computer Architecture Machine Language Program Execution Arithmetic/Logic
Memory General R0 Registers R1 R2. Input Register 1. Input Register 2. Program Counter. Instruction Register
 CPU Organisation Central Processing Unit (CPU) Memory General R0 Registers R1 R2 ALU R3 Output Register Input Register 1 Input Register 2 Internal Bus Address Bus Data Bus Addr. $ 000 001 002 Program Counter
CPU Organisation Central Processing Unit (CPU) Memory General R0 Registers R1 R2 ALU R3 Output Register Input Register 1 Input Register 2 Internal Bus Address Bus Data Bus Addr. $ 000 001 002 Program Counter
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture. Instruction Set Architectures
 COSC 6385 Computer Architecture Instruction Set Architectures Spring 2012 Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) Definition on Wikipedia: Part of the Computer Architecture related to programming Defines set
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture Instruction Set Architectures Spring 2012 Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) Definition on Wikipedia: Part of the Computer Architecture related to programming Defines set
Advanced Parallel Architecture Lesson 3. Annalisa Massini /2015
 Advanced Parallel Architecture Lesson 3 Annalisa Massini - 2014/2015 Von Neumann Architecture 2 Summary of the traditional computer architecture: Von Neumann architecture http://williamstallings.com/coa/coa7e.html
Advanced Parallel Architecture Lesson 3 Annalisa Massini - 2014/2015 Von Neumann Architecture 2 Summary of the traditional computer architecture: Von Neumann architecture http://williamstallings.com/coa/coa7e.html
Problem with Scanning an Infix Expression
 Operator Notation Consider the infix expression (X Y) + (W U), with parentheses added to make the evaluation order perfectly obvious. This is an arithmetic expression written in standard form, called infix
Operator Notation Consider the infix expression (X Y) + (W U), with parentheses added to make the evaluation order perfectly obvious. This is an arithmetic expression written in standard form, called infix
17.1. Unit 17. Instruction Sets Picoblaze Processor
 17.1 Unit 17 Instruction Sets Picoblaze Processor INSTRUCTION SET OVERVIEW 17.2 17.3 Instruction Set Review Defines the software interface of the processor and memory system Instruction set is the vocabulary
17.1 Unit 17 Instruction Sets Picoblaze Processor INSTRUCTION SET OVERVIEW 17.2 17.3 Instruction Set Review Defines the software interface of the processor and memory system Instruction set is the vocabulary
MIPS Instruction Set
 MIPS Instruction Set Prof. James L. Frankel Harvard University Version of 7:12 PM 3-Apr-2018 Copyright 2018, 2017, 2016, 201 James L. Frankel. All rights reserved. CPU Overview CPU is an acronym for Central
MIPS Instruction Set Prof. James L. Frankel Harvard University Version of 7:12 PM 3-Apr-2018 Copyright 2018, 2017, 2016, 201 James L. Frankel. All rights reserved. CPU Overview CPU is an acronym for Central
It is possible to define a number using a character or multiple numbers (see instruction DB) by using a string.
 1 od 5 17. 12. 2017 23:53 (https://github.com/schweigi/assembler-simulator) Introduction This simulator provides a simplified assembler syntax (based on NASM (http://www.nasm.us)) and is simulating a x86
1 od 5 17. 12. 2017 23:53 (https://github.com/schweigi/assembler-simulator) Introduction This simulator provides a simplified assembler syntax (based on NASM (http://www.nasm.us)) and is simulating a x86
Chapter 4. MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer 4.8 MARIE 4.8 MARIE A Discussion on Decoding
 4.8 MARIE This is the MARIE architecture shown graphically. Chapter 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer 2 4.8 MARIE MARIE s Full Instruction Set A computer s control unit keeps things synchronized,
4.8 MARIE This is the MARIE architecture shown graphically. Chapter 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer 2 4.8 MARIE MARIE s Full Instruction Set A computer s control unit keeps things synchronized,
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Computing Layers
 Chapter 5 The LC-3 Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by C. Wilcox, S. Rajopadhye Colorado State University Computing Layers Problems Algorithms Language
Chapter 5 The LC-3 Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by C. Wilcox, S. Rajopadhye Colorado State University Computing Layers Problems Algorithms Language
Computer Organization
 Computer Organization (Instruction set Architecture & Assembly Language Programming) KR Chowdhary Professor & Head Email: kr.chowdhary@gmail.com webpage: krchowdhary.com Department of Computer Science
Computer Organization (Instruction set Architecture & Assembly Language Programming) KR Chowdhary Professor & Head Email: kr.chowdhary@gmail.com webpage: krchowdhary.com Department of Computer Science
