Geol 588. GIS for Geoscientists II. Zonal functions. Feb 22, Zonal statistics. Interpolation. Zonal statistics Sp. Analyst Tools - Zonal.
|
|
|
- Edmund Henderson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Zonal functions Geol 588 GIS for Geoscientists II Feb 22, 2011 Zonal statistics Interpolation Zonal statistics Sp. Analyst Tools - Zonal Choose correct attribute for zones (usually: must be unique ID for each zone) Choose which stat(s) for each zone: get value raster cells that are inside the zone calculate stat(s) of these cells store stat(s) for this zone in a table Tool: Zonal Statistics as Table, creates a standalone table that can be joined to zone layer (ArcMap TOC: list by source to see standalone tables!) Tool: Zonal Statistics: stores 1 type of stat in a new raster new raster will have Nodata outside of the zones inside a zone: all cells have the same value (e.g. the mean of the zone) Value Raster Zones Needs 2 inputs: a zone data: discrete raster or features (polygon, line points) which attribute? a value raster Zones don t need to be continuous! Value: DEM raster Zones: polygon or discrete raster
2 Spatial Interpolation point samples (x,y, value ) fill each cell (center) in raster with an appropriate value Principle: the closer together points are, the more similar their value (should be) (depends on many factors: type of underlying phenomenon, etc.) Examples? in general: distance and sample value matter data\interpolation Exercise Thiessen (Voronoi) polygons Space division scheme Assign each sample its fair share of space around it Raster: fill this space (polygon) with same value Keep in mind for Natural Neighbor interpolation method Raster of point density NOT a value interpolation scheme! decide on a circle (kernel) size (radius, bandwidth ) go through all cells... count how many samples fall within a that circle divide the count by the circle s area assign this density value to the cell next cell Tools: Spatial Analyst - Density Point density Kernel Density Samples: have no value, we only care about their location High density Low density Raster containing the point density
3 Interpolating values super simple: moving averages Irregularly spaced samples! Inverse Distance Weighted (IDW) interpolation Zi is value of known point Dij is distance to known point Zj is the cell value (unknown) n is a user selected exponent or power (often 1,2 or 3) decide on a radius go through all cell centers grab all the point samples within the search radius Sum these points values and divid by their number How does size of radius affect results? Does sample to center distance play any role How could we deal more fairly with farther away samples (9) compared to closer samples (3)? Irregularly spaced samples! grab all the point samples inside a radius When calculation the cell s value, take the sample distances into account ( weight ) Weight of each sample point is an inverse proportion to its distance to the cell The further away the point, the less the weight it gets (contributes less) effect of exponent (1,2,3,..)? exponent n is 1 one 9 10 Effect: samples that are closer to the cell (center) to be estimated, get a larger weight (are more important) The larger the sample to center distance, the less important the sample is (We could use all the samples for each cell s estimation Using a search radius is more efficient (why?) Simple Averaging Higher exponents: less weight to distant points (point that are farther away) (closer point are more important) Use more samples: smoother distribution interpolated value at sample location? linear : exponent = 1 squared : exponent =
4 Tool: Spatial Analyst Interpolation - IDW point features (here: elevation samples) set correct attribute (here: elev) encode the parameters in your output raster s file name: IDW => interpolation method 2 => power Var_12 => Search parameters bar => used barriers IDW: search parameters size of search radius: multiples of cell size variable search radius: grab n (12) closest points, up to a distance of d (default 0, => no distance limit) fixed search radius: grab ALL points within a distance of (250) units, use at least n points (default 0, => use all) IDW: using break lines line features to limit (block) point grabbing samples from the other side of the break line will NOT be used use for: ridges, faults,... Caveats: much slower, some NoData values (extrapolation issues?) Splines smooth surface, non-exact based on minimizing curvature rubber sheet bent around samples can over-shoot / under-shoot ArgGIS: 2 types - regularized and tension ArcGIS: Weight - smoothness tweak factor gotcha: both have different meaning of weight tension (0.1-15): low = smooth, high = coarse) IDW: squared, 12 nearest points Spline 15 16
5 IDW: Z-Value Power 1 Power 2 Distance Z-Value Spline Distance 17
Lesson 5 overview. Concepts. Interpolators. Assessing accuracy Exercise 5
 Interpolation Tools Lesson 5 overview Concepts Sampling methods Creating continuous surfaces Interpolation Density surfaces in GIS Interpolators IDW, Spline,Trend, Kriging,Natural neighbors TopoToRaster
Interpolation Tools Lesson 5 overview Concepts Sampling methods Creating continuous surfaces Interpolation Density surfaces in GIS Interpolators IDW, Spline,Trend, Kriging,Natural neighbors TopoToRaster
Lecture 22 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part 3)
 GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 22 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part 3) Today: Zonal Analysis (statistics) for polygons, lines, points, interpolation (IDW), Effects Toolbar, analysis masks
GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 22 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part 3) Today: Zonal Analysis (statistics) for polygons, lines, points, interpolation (IDW), Effects Toolbar, analysis masks
Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS
 HOUSEKEEPING Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Quizzes Lab 8? WEEK EIGHT Lecture INTERPOLATION & SPATIAL ESTIMATION Joe Wheaton READING FOR TODAY WHAT CAN WE COLLECT AT POINTS?
HOUSEKEEPING Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Quizzes Lab 8? WEEK EIGHT Lecture INTERPOLATION & SPATIAL ESTIMATION Joe Wheaton READING FOR TODAY WHAT CAN WE COLLECT AT POINTS?
What can we represent as a Surface?
 Geography 38/42:376 GIS II Topic 7: Surface Representation and Analysis (Chang: Chapters 13 & 15) DeMers: Chapter 10 What can we represent as a Surface? Surfaces can be used to represent: Continuously
Geography 38/42:376 GIS II Topic 7: Surface Representation and Analysis (Chang: Chapters 13 & 15) DeMers: Chapter 10 What can we represent as a Surface? Surfaces can be used to represent: Continuously
Creating Surfaces. Steve Kopp Steve Lynch
 Steve Kopp Steve Lynch Overview Learn the types of surfaces and the data structures used to store them Emphasis on surface interpolation Learn the interpolation workflow Understand how interpolators work
Steve Kopp Steve Lynch Overview Learn the types of surfaces and the data structures used to store them Emphasis on surface interpolation Learn the interpolation workflow Understand how interpolators work
Spatial Analysis (Vector) II
 Spatial Analysis (Vector) II GEOG 300, Lecture 9 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 A Spatial Network is a set of geographic locations interconnected in a system by a number of routes is a system of linear features
Spatial Analysis (Vector) II GEOG 300, Lecture 9 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 A Spatial Network is a set of geographic locations interconnected in a system by a number of routes is a system of linear features
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 24: Spatial Analyst Continued
 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 24: Spatial Analyst Continued Spatial Analyst - Spatial Analyst is an ArcGIS extension designed to work with raster data - in lecture I went through a series of demonstrations
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 24: Spatial Analyst Continued Spatial Analyst - Spatial Analyst is an ArcGIS extension designed to work with raster data - in lecture I went through a series of demonstrations
Cell based GIS. Introduction to rasters
 Week 9 Cell based GIS Introduction to rasters topics of the week Spatial Problems Modeling Raster basics Application functions Analysis environment, the mask Application functions Spatial Analyst in ArcGIS
Week 9 Cell based GIS Introduction to rasters topics of the week Spatial Problems Modeling Raster basics Application functions Analysis environment, the mask Application functions Spatial Analyst in ArcGIS
Lab 12: Sampling and Interpolation
 Lab 12: Sampling and Interpolation What You ll Learn: -Systematic and random sampling -Majority filtering -Stratified sampling -A few basic interpolation methods Videos that show how to copy/paste data
Lab 12: Sampling and Interpolation What You ll Learn: -Systematic and random sampling -Majority filtering -Stratified sampling -A few basic interpolation methods Videos that show how to copy/paste data
Lab 12: Sampling and Interpolation
 Lab 12: Sampling and Interpolation What You ll Learn: -Systematic and random sampling -Majority filtering -Stratified sampling -A few basic interpolation methods Data for the exercise are in the L12 subdirectory.
Lab 12: Sampling and Interpolation What You ll Learn: -Systematic and random sampling -Majority filtering -Stratified sampling -A few basic interpolation methods Data for the exercise are in the L12 subdirectory.
University of West Hungary, Faculty of Geoinformatics. Béla Márkus. Spatial Analysis 5. module SAN5. 3D analysis
 University of West Hungary, Faculty of Geoinformatics Béla Márkus Spatial Analysis 5. module SAN5 3D analysis SZÉKESFEHÉRVÁR 2010 The right to this intellectual property is protected by the 1999/LXXVI
University of West Hungary, Faculty of Geoinformatics Béla Márkus Spatial Analysis 5. module SAN5 3D analysis SZÉKESFEHÉRVÁR 2010 The right to this intellectual property is protected by the 1999/LXXVI
Esri International User Conference. San Diego, California. Technical Workshops. July Creating Surfaces. Steve Kopp and Steve Lynch
 Esri International User Conference San Diego, California Technical Workshops July 2011 Creating Surfaces Steve Kopp and Steve Lynch Overview Learn the types of surfaces and the data structures used to
Esri International User Conference San Diego, California Technical Workshops July 2011 Creating Surfaces Steve Kopp and Steve Lynch Overview Learn the types of surfaces and the data structures used to
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Spatial Analyst [10] Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri. [10] Spring 2018 GIS Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri Spatial Analyst
![Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Spatial Analyst [10] Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri. [10] Spring 2018 GIS Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri Spatial Analyst Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Spatial Analyst [10] Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri. [10] Spring 2018 GIS Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri Spatial Analyst](/thumbs/80/81171101.jpg) Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Spatial Analyst [10] Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri 1 Preface POINTS, LINES, and POLYGONS are good at representing geographic objects with distinct shapes They are less good
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Spatial Analyst [10] Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri 1 Preface POINTS, LINES, and POLYGONS are good at representing geographic objects with distinct shapes They are less good
Mapping Distance and Density
 Mapping Distance and Density Distance functions allow you to determine the nearest location of something or the least-cost path to a particular destination. Density functions, on the other hand, allow
Mapping Distance and Density Distance functions allow you to determine the nearest location of something or the least-cost path to a particular destination. Density functions, on the other hand, allow
Dijkstra's Algorithm
 Shortest Path Algorithm Dijkstra's Algorithm To find the shortest path from the origin node to the destination node No matrix calculation Floyd s Algorithm To find all the shortest paths from the nodes
Shortest Path Algorithm Dijkstra's Algorithm To find the shortest path from the origin node to the destination node No matrix calculation Floyd s Algorithm To find all the shortest paths from the nodes
Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2)
 GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2) Today: Digital Elevation Models (DEMs), Topographic functions (surface analysis): slope, aspect hillshade, viewshed,
GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2) Today: Digital Elevation Models (DEMs), Topographic functions (surface analysis): slope, aspect hillshade, viewshed,
Raster Data. James Frew ESM 263 Winter
 Raster Data 1 Vector Data Review discrete objects geometry = points by themselves connected lines closed polygons attributes linked to feature ID explicit location every point has coordinates 2 Fields
Raster Data 1 Vector Data Review discrete objects geometry = points by themselves connected lines closed polygons attributes linked to feature ID explicit location every point has coordinates 2 Fields
GIS Tools - Geometry. A GIS stores data as different layers of information Different feature types are stored in individual files.
 A Definition of GIS GIS is a system of hardware, software, and procedures designed to support the capture, management, manipulation, analysis, modeling and display of spatially referenced data for solving
A Definition of GIS GIS is a system of hardware, software, and procedures designed to support the capture, management, manipulation, analysis, modeling and display of spatially referenced data for solving
CPSC 695. Methods for interpolation and analysis of continuing surfaces in GIS Dr. M. Gavrilova
 CPSC 695 Methods for interpolation and analysis of continuing surfaces in GIS Dr. M. Gavrilova Overview Data sampling for continuous surfaces Interpolation methods Global interpolation Local interpolation
CPSC 695 Methods for interpolation and analysis of continuing surfaces in GIS Dr. M. Gavrilova Overview Data sampling for continuous surfaces Interpolation methods Global interpolation Local interpolation
Surface Analysis with 3D Analyst
 2013 Esri International User Conference July 8 12, 2013 San Diego, California Technical Workshop Surface Analysis with 3D Analyst Khalid H. Duri Esri UC2013. Technical Workshop. Why use 3D GIS? Because
2013 Esri International User Conference July 8 12, 2013 San Diego, California Technical Workshop Surface Analysis with 3D Analyst Khalid H. Duri Esri UC2013. Technical Workshop. Why use 3D GIS? Because
Getting Started with Spatial Analyst. Steve Kopp Elizabeth Graham
 Getting Started with Spatial Analyst Steve Kopp Elizabeth Graham Workshop Overview Fundamentals of using Spatial Analyst What analysis capabilities exist and where to find them How to build a simple site
Getting Started with Spatial Analyst Steve Kopp Elizabeth Graham Workshop Overview Fundamentals of using Spatial Analyst What analysis capabilities exist and where to find them How to build a simple site
Surface Creation & Analysis with 3D Analyst
 Esri International User Conference July 23 27 San Diego Convention Center Surface Creation & Analysis with 3D Analyst Khalid Duri Surface Basics Defining the surface Representation of any continuous measurement
Esri International User Conference July 23 27 San Diego Convention Center Surface Creation & Analysis with 3D Analyst Khalid Duri Surface Basics Defining the surface Representation of any continuous measurement
Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis. GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University
 Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University 1 Spatial Data It can be most simply defined as information that describes the distribution
Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University 1 Spatial Data It can be most simply defined as information that describes the distribution
Spatial Analysis with Raster Datasets
 Spatial Analysis with Raster Datasets Francisco Olivera, Ph.D., P.E. Srikanth Koka Lauren Walker Aishwarya Vijaykumar Keri Clary Department of Civil Engineering April 21, 2014 Contents Brief Overview of
Spatial Analysis with Raster Datasets Francisco Olivera, Ph.D., P.E. Srikanth Koka Lauren Walker Aishwarya Vijaykumar Keri Clary Department of Civil Engineering April 21, 2014 Contents Brief Overview of
Spatial Interpolation & Geostatistics
 (Z i Z j ) 2 / 2 Spatial Interpolation & Geostatistics Lag Lag Mean Distance between pairs of points 1 Tobler s Law All places are related, but nearby places are related more than distant places Corollary:
(Z i Z j ) 2 / 2 Spatial Interpolation & Geostatistics Lag Lag Mean Distance between pairs of points 1 Tobler s Law All places are related, but nearby places are related more than distant places Corollary:
Spatial Interpolation - Geostatistics 4/3/2018
 Spatial Interpolation - Geostatistics 4/3/201 (Z i Z j ) 2 / 2 Spatial Interpolation & Geostatistics Lag Distance between pairs of points Lag Mean Tobler s Law All places are related, but nearby places
Spatial Interpolation - Geostatistics 4/3/201 (Z i Z j ) 2 / 2 Spatial Interpolation & Geostatistics Lag Distance between pairs of points Lag Mean Tobler s Law All places are related, but nearby places
Getting Started with Spatial Analyst. Steve Kopp Elizabeth Graham
 Getting Started with Spatial Analyst Steve Kopp Elizabeth Graham Spatial Analyst Overview Over 100 geoprocessing tools plus raster functions Raster and vector analysis Construct workflows with ModelBuilder,
Getting Started with Spatial Analyst Steve Kopp Elizabeth Graham Spatial Analyst Overview Over 100 geoprocessing tools plus raster functions Raster and vector analysis Construct workflows with ModelBuilder,
Lab 12: Sampling and Interpolation
 Lab 12: Sampling and Interpolation What You ll Learn: -Systematic and random sampling -Majority filtering -Stratified sampling -A few basic interpolation methods Data for the exercise are found in the
Lab 12: Sampling and Interpolation What You ll Learn: -Systematic and random sampling -Majority filtering -Stratified sampling -A few basic interpolation methods Data for the exercise are found in the
Lecture 9. Raster Data Analysis. Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University
 Lecture 9 Raster Data Analysis Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Raster Data Model The GIS raster data model represents datasets in which square
Lecture 9 Raster Data Analysis Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Raster Data Model The GIS raster data model represents datasets in which square
Lecture 20 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part1)
 GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 20 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part) 4 lectures on rasters - but won t cover everything (Raster GIS course: Geol 588: GIS II (Spring 20) Today: Raster data,
GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 20 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part) 4 lectures on rasters - but won t cover everything (Raster GIS course: Geol 588: GIS II (Spring 20) Today: Raster data,
DEM Artifacts: Layering or pancake effects
 Outcomes DEM Artifacts: Stream networks & watersheds derived using ArcGIS s HYDROLOGY routines are only as good as the DEMs used. - Both DEM examples below have problems - Lidar and SRTM DEM products are
Outcomes DEM Artifacts: Stream networks & watersheds derived using ArcGIS s HYDROLOGY routines are only as good as the DEMs used. - Both DEM examples below have problems - Lidar and SRTM DEM products are
RASTER ANALYSIS S H A W N L. P E N M A N E A R T H D A T A A N A LY S I S C E N T E R U N I V E R S I T Y O F N E W M E X I C O
 RASTER ANALYSIS S H A W N L. P E N M A N E A R T H D A T A A N A LY S I S C E N T E R U N I V E R S I T Y O F N E W M E X I C O TOPICS COVERED Spatial Analyst basics Raster / Vector conversion Raster data
RASTER ANALYSIS S H A W N L. P E N M A N E A R T H D A T A A N A LY S I S C E N T E R U N I V E R S I T Y O F N E W M E X I C O TOPICS COVERED Spatial Analyst basics Raster / Vector conversion Raster data
Raster model. Raster model. Resolution. Value and data types. Structure and storage. Cell. Values. Data
 Raster model. Resolution. Values and data types 3. Storage. Fitting rasters 5. Map algebra 6. Interpolation 7. Conversion vectorraster 8. Vector vs. raster Raster model Divides the space into a regular
Raster model. Resolution. Values and data types 3. Storage. Fitting rasters 5. Map algebra 6. Interpolation 7. Conversion vectorraster 8. Vector vs. raster Raster model Divides the space into a regular
Buckskin Detachment Surface Interpolation, Southern Lincoln Ranch Basin, Buckskin Mountains, Western Arizona Hal Hundley
 Buckskin Detachment Surface Interpolation, Southern Lincoln Ranch Basin, Buckskin Mountains, Western Arizona Hal Hundley Introduction The Lincoln Ranch basin in Buckskin Mountains in west-central Arizona
Buckskin Detachment Surface Interpolation, Southern Lincoln Ranch Basin, Buckskin Mountains, Western Arizona Hal Hundley Introduction The Lincoln Ranch basin in Buckskin Mountains in west-central Arizona
Crea%ng DEMs From LiDAR Point Cloud Data
 Crea%ng DEMs From LiDAR Point Cloud Data C. Crosby (ccrosby@sdsc.edu) San Diego Supercomputer Center / OpenTopography.org Ramon Arrowsmith SESE, ASU 2009 SCEC LiDAR Short Course Digital ElevaEon Models
Crea%ng DEMs From LiDAR Point Cloud Data C. Crosby (ccrosby@sdsc.edu) San Diego Supercomputer Center / OpenTopography.org Ramon Arrowsmith SESE, ASU 2009 SCEC LiDAR Short Course Digital ElevaEon Models
Review of Cartographic Data Types and Data Models
 Review of Cartographic Data Types and Data Models GIS Data Models Raster Versus Vector in GIS Analysis Fundamental element used to represent spatial features: Raster: pixel or grid cell. Vector: x,y coordinate
Review of Cartographic Data Types and Data Models GIS Data Models Raster Versus Vector in GIS Analysis Fundamental element used to represent spatial features: Raster: pixel or grid cell. Vector: x,y coordinate
RASTER ANALYSIS GIS Analysis Fall 2013
 RASTER ANALYSIS GIS Analysis Fall 2013 Raster Data The Basics Raster Data Format Matrix of cells (pixels) organized into rows and columns (grid); each cell contains a value representing information. What
RASTER ANALYSIS GIS Analysis Fall 2013 Raster Data The Basics Raster Data Format Matrix of cells (pixels) organized into rows and columns (grid); each cell contains a value representing information. What
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 25: 3D Analyst
 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 25: 3D Analyst 3D Analyst - 3D Analyst is an ArcGIS extension designed to work with TIN data (triangulated irregular network) - many of the tools in 3D Analyst also
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 25: 3D Analyst 3D Analyst - 3D Analyst is an ArcGIS extension designed to work with TIN data (triangulated irregular network) - many of the tools in 3D Analyst also
RASTER ANALYSIS GIS Analysis Winter 2016
 RASTER ANALYSIS GIS Analysis Winter 2016 Raster Data The Basics Raster Data Format Matrix of cells (pixels) organized into rows and columns (grid); each cell contains a value representing information.
RASTER ANALYSIS GIS Analysis Winter 2016 Raster Data The Basics Raster Data Format Matrix of cells (pixels) organized into rows and columns (grid); each cell contains a value representing information.
Module 7 Raster operations
 Introduction Geo-Information Science Practical Manual Module 7 Raster operations 7. INTRODUCTION 7-1 LOCAL OPERATIONS 7-2 Mathematical functions and operators 7-5 Raster overlay 7-7 FOCAL OPERATIONS 7-8
Introduction Geo-Information Science Practical Manual Module 7 Raster operations 7. INTRODUCTION 7-1 LOCAL OPERATIONS 7-2 Mathematical functions and operators 7-5 Raster overlay 7-7 FOCAL OPERATIONS 7-8
INTRODUCTION TO GIS WORKSHOP EXERCISE
 111 Mulford Hall, College of Natural Resources, UC Berkeley (510) 643-4539 INTRODUCTION TO GIS WORKSHOP EXERCISE This exercise is a survey of some GIS and spatial analysis tools for ecological and natural
111 Mulford Hall, College of Natural Resources, UC Berkeley (510) 643-4539 INTRODUCTION TO GIS WORKSHOP EXERCISE This exercise is a survey of some GIS and spatial analysis tools for ecological and natural
Statistical surfaces and interpolation. This is lecture ten
 Statistical surfaces and interpolation This is lecture ten Data models for representation of surfaces So far have considered field and object data models (represented by raster and vector data structures).
Statistical surfaces and interpolation This is lecture ten Data models for representation of surfaces So far have considered field and object data models (represented by raster and vector data structures).
Geoprocessing and georeferencing raster data
 Geoprocessing and georeferencing raster data Raster conversion tools Geoprocessing tools ArcCatalog tools ESRI Grid GDB Raster Raster Dataset Raster Catalog Erdas IMAGINE TIFF ArcMap - raster projection
Geoprocessing and georeferencing raster data Raster conversion tools Geoprocessing tools ArcCatalog tools ESRI Grid GDB Raster Raster Dataset Raster Catalog Erdas IMAGINE TIFF ArcMap - raster projection
Steps for Modeling a Proposed New Reservoir in GIS
 Steps for Modeling a Proposed New Reservoir in GIS Requirements: ArcGIS ArcMap, ArcScene, Spatial Analyst, and 3D Analyst There s a new reservoir proposed for Right Hand Fork in Logan Canyon. I wanted
Steps for Modeling a Proposed New Reservoir in GIS Requirements: ArcGIS ArcMap, ArcScene, Spatial Analyst, and 3D Analyst There s a new reservoir proposed for Right Hand Fork in Logan Canyon. I wanted
Raster model. Alexandre Gonçalves, DECivil, IST
 Raster model 1. Resolution 2. Values and data types 3. Storage 4. Fitting rasters 5. Map algebra 6. Interpolation 7. Conversion vector raster 8. Vector vs. raster 1 Raster model Divides the space into
Raster model 1. Resolution 2. Values and data types 3. Storage 4. Fitting rasters 5. Map algebra 6. Interpolation 7. Conversion vector raster 8. Vector vs. raster 1 Raster model Divides the space into
Combine Yield Data From Combine to Contour Map Ag Leader
 Combine Yield Data From Combine to Contour Map Ag Leader Exporting the Yield Data Using SMS Program 1. Data format On Hard Drive. 2. Start program SMS Basic. a. In the File menu choose Open. b. Click on
Combine Yield Data From Combine to Contour Map Ag Leader Exporting the Yield Data Using SMS Program 1. Data format On Hard Drive. 2. Start program SMS Basic. a. In the File menu choose Open. b. Click on
Data Assembly, Part II. GIS Cyberinfrastructure Module Day 4
 Data Assembly, Part II GIS Cyberinfrastructure Module Day 4 Objectives Continuation of effective troubleshooting Create shapefiles for analysis with buffers, union, and dissolve functions Calculate polygon
Data Assembly, Part II GIS Cyberinfrastructure Module Day 4 Objectives Continuation of effective troubleshooting Create shapefiles for analysis with buffers, union, and dissolve functions Calculate polygon
Creating raster DEMs and DSMs from large lidar point collections. Summary. Coming up with a plan. Using the Point To Raster geoprocessing tool
 Page 1 of 5 Creating raster DEMs and DSMs from large lidar point collections ArcGIS 10 Summary Raster, or gridded, elevation models are one of the most common GIS data types. They can be used in many ways
Page 1 of 5 Creating raster DEMs and DSMs from large lidar point collections ArcGIS 10 Summary Raster, or gridded, elevation models are one of the most common GIS data types. They can be used in many ways
Gridding and Contouring in Geochemistry for ArcGIS
 Gridding and Contouring in Geochemistry for ArcGIS The Geochemsitry for ArcGIS extension includes three gridding options: Minimum Curvature Gridding, Kriging and a new Inverse Distance Weighting algorithm.
Gridding and Contouring in Geochemistry for ArcGIS The Geochemsitry for ArcGIS extension includes three gridding options: Minimum Curvature Gridding, Kriging and a new Inverse Distance Weighting algorithm.
Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS
 HOUSEKEEPING Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS CONTOURS! Self-Paced Lab Due Friday! WEEK SIX Lecture RASTER ANALYSES Joe Wheaton YOUR EXCERCISE Integer Elevations Rounded up
HOUSEKEEPING Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS CONTOURS! Self-Paced Lab Due Friday! WEEK SIX Lecture RASTER ANALYSES Joe Wheaton YOUR EXCERCISE Integer Elevations Rounded up
Lab 9. Raster Analyses. Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University
 Lab 9 Raster Analyses Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University How to Interpolate Surface Turn on the Spatial Analyst extension: Tools > Extensions >
Lab 9 Raster Analyses Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University How to Interpolate Surface Turn on the Spatial Analyst extension: Tools > Extensions >
AUTOMATING MANNING S N COEFFICIENT VALUE ASSIGNMENTS FOR HYDRAULIC MODELING
 Imagery Source: Bing Maps via ESRI AUTOMATING MANNING S N COEFFICIENT VALUE ASSIGNMENTS FOR HYDRAULIC MODELING Kyle Gallagher, GISP Black & Veatch Special Projects Corp. Project Overview USACE Tulsa District
Imagery Source: Bing Maps via ESRI AUTOMATING MANNING S N COEFFICIENT VALUE ASSIGNMENTS FOR HYDRAULIC MODELING Kyle Gallagher, GISP Black & Veatch Special Projects Corp. Project Overview USACE Tulsa District
Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment
 Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment Aligning Raster and Vector Data to the Real World Rotation Differential Scaling Distortion Skew Translation 1 The Problem How are geographically unregistered data, either
Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment Aligning Raster and Vector Data to the Real World Rotation Differential Scaling Distortion Skew Translation 1 The Problem How are geographically unregistered data, either
ENGRG Introduction to GIS
 ENGRG 59910 Introduction to GIS Michael Piasecki April 3, 2014 Lecture 11: Raster Analysis GIS Related? 4/3/2014 ENGRG 59910 Intro to GIS 2 1 Why we use Raster GIS In our previous discussion of data models,
ENGRG 59910 Introduction to GIS Michael Piasecki April 3, 2014 Lecture 11: Raster Analysis GIS Related? 4/3/2014 ENGRG 59910 Intro to GIS 2 1 Why we use Raster GIS In our previous discussion of data models,
Maps as Numbers: Data Models
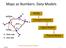 Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices E Reality S E S arcs S E Conceptual Models nodes E Logical Models S Start node E End node S Physical Models 1 The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can
Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices E Reality S E S arcs S E Conceptual Models nodes E Logical Models S Start node E End node S Physical Models 1 The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can
Thoughts on Representing Spatial Objects. William A. Huber Quantitative Decisions Rosemont, PA
 Thoughts on Representing Spatial Objects William A. Huber Quantitative Decisions Rosemont, PA Overview 1. Some Ways to Structure Space 2. What to Put into a Grid 3. Objects and Fields 4. Hybrid Structures
Thoughts on Representing Spatial Objects William A. Huber Quantitative Decisions Rosemont, PA Overview 1. Some Ways to Structure Space 2. What to Put into a Grid 3. Objects and Fields 4. Hybrid Structures
Generating a New Shapefile
 Week 9 Generating a New Shapefile STEPS 1) Select a appropriate folder or folder connection in the Catalog tree. 2) Click on Contents tab and move cursor into that window 3) Right click in that window
Week 9 Generating a New Shapefile STEPS 1) Select a appropriate folder or folder connection in the Catalog tree. 2) Click on Contents tab and move cursor into that window 3) Right click in that window
IMPROVING THE ACCURACY OF DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELS
 STUDIA UNIV. BABEŞ BOLYAI, INFORMATICA, Volume XLV, Number 1, 2000 IMPROVING THE ACCURACY OF DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELS GABRIELA DROJ Abstract. The change from paper maps to GIS, in various kinds of geographical
STUDIA UNIV. BABEŞ BOLYAI, INFORMATICA, Volume XLV, Number 1, 2000 IMPROVING THE ACCURACY OF DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELS GABRIELA DROJ Abstract. The change from paper maps to GIS, in various kinds of geographical
Delineating the Stream Network and Watersheds of the Guadalupe Basin
 Delineating the Stream Network and Watersheds of the Guadalupe Basin Francisco Olivera Department of Civil Engineering Texas A&M University Srikanth Koka Department of Civil Engineering Texas A&M University
Delineating the Stream Network and Watersheds of the Guadalupe Basin Francisco Olivera Department of Civil Engineering Texas A&M University Srikanth Koka Department of Civil Engineering Texas A&M University
DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELLING. Endre Katona University of Szeged Department of Informatics
 DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELLING Endre Katona University of Szeged Department of Informatics katona@inf.u-szeged.hu The problem: data sources data structures algorithms DTM = Digital Terrain Model Terrain function:
DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELLING Endre Katona University of Szeged Department of Informatics katona@inf.u-szeged.hu The problem: data sources data structures algorithms DTM = Digital Terrain Model Terrain function:
Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment 2/13/2018
 Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment The Problem Aligning Raster and Vector Data to the Real World How are geographically unregistered data, either raster or vector, made to align with data that exist in
Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment The Problem Aligning Raster and Vector Data to the Real World How are geographically unregistered data, either raster or vector, made to align with data that exist in
Interpolate Continuous Data From Non-Continuous Data. Examples. Dialog Box
 Interpolate Continuous Data From Non-Continuous Data Examples Dialog Box Interpolating Continuous Elevation Data From Contours Interpolating Continuous Bathymetric Data Using a Mask Map Layer Using the
Interpolate Continuous Data From Non-Continuous Data Examples Dialog Box Interpolating Continuous Elevation Data From Contours Interpolating Continuous Bathymetric Data Using a Mask Map Layer Using the
Spatial Interpolation & Geostatistics
 (Z i Z j ) 2 / 2 Spatial Interpolation & Geostatistics Lag Lag Mean Distance between pairs of points 11/3/2016 GEO327G/386G, UT Austin 1 Tobler s Law All places are related, but nearby places are related
(Z i Z j ) 2 / 2 Spatial Interpolation & Geostatistics Lag Lag Mean Distance between pairs of points 11/3/2016 GEO327G/386G, UT Austin 1 Tobler s Law All places are related, but nearby places are related
Crea%ng DEMs From LiDAR Point Cloud Data
 Crea%ng DEMs From LiDAR Point Cloud Data C. Crosby (ccrosby@sdsc.edu) San Diego Supercomputer Center / OpenTopography.org Ramon Arrowsmith SESE, ASU 2011 SCEC LiDAR Short Course Digital ElevaEon Models
Crea%ng DEMs From LiDAR Point Cloud Data C. Crosby (ccrosby@sdsc.edu) San Diego Supercomputer Center / OpenTopography.org Ramon Arrowsmith SESE, ASU 2011 SCEC LiDAR Short Course Digital ElevaEon Models
Lecture 23 - LiDAR. GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I. Scanning Lidar. 30 m DEM. Lidar representations:
 GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 23 - LiDAR LiDAR - some background (thanks to Chris Kahle, DNR) Converting Lidar point data to a raster Look at online lidar data for Iowa (1m hillshaded)
GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 23 - LiDAR LiDAR - some background (thanks to Chris Kahle, DNR) Converting Lidar point data to a raster Look at online lidar data for Iowa (1m hillshaded)
The Problem. Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment. Nature Of The Problem: For Example: Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment 9/20/2016
 Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment Aligning Raster and Vector Data to the Real World The Problem How are geographically unregistered data, either raster or vector, made to align with data that exist in
Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment Aligning Raster and Vector Data to the Real World The Problem How are geographically unregistered data, either raster or vector, made to align with data that exist in
The Problem. Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment. Nature of the problem: For Example: Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment 2/4/2014
 Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment Aligning Raster and Vector Data to a GIS The Problem How are geographically unregistered data, either raster or vector, made to align with data that exist in geographical
Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment Aligning Raster and Vector Data to a GIS The Problem How are geographically unregistered data, either raster or vector, made to align with data that exist in geographical
Making Yield Contour Maps Using John Deere Data
 Making Yield Contour Maps Using John Deere Data Exporting the Yield Data Using JDOffice 1. Data Format On Hard Drive 2. Start program JD Office. a. From the PC Card menu on the left of the screen choose
Making Yield Contour Maps Using John Deere Data Exporting the Yield Data Using JDOffice 1. Data Format On Hard Drive 2. Start program JD Office. a. From the PC Card menu on the left of the screen choose
Spatial Analysis and Modeling (GIST 4302/5302) Guofeng Cao Department of Geosciences Texas Tech University
 Spatial Analysis and Modeling (GIST 4302/5302) Guofeng Cao Department of Geosciences Texas Tech University 1 Outline of This Week Last topic, we learned: Spatial autocorrelation of areal data Spatial regression
Spatial Analysis and Modeling (GIST 4302/5302) Guofeng Cao Department of Geosciences Texas Tech University 1 Outline of This Week Last topic, we learned: Spatial autocorrelation of areal data Spatial regression
Raster Data Model & Analysis
 Topics: 1. Understanding Raster Data 2. Adding and displaying raster data in ArcMap 3. Converting between floating-point raster and integer raster 4. Converting Vector data to Raster 5. Querying Raster
Topics: 1. Understanding Raster Data 2. Adding and displaying raster data in ArcMap 3. Converting between floating-point raster and integer raster 4. Converting Vector data to Raster 5. Querying Raster
Surface Analysis. Data for Surface Analysis. What are Surfaces 4/22/2010
 Surface Analysis Cornell University Data for Surface Analysis Vector Triangulated Irregular Networks (TIN) a surface layer where space is partitioned into a set of non-overlapping triangles Attribute and
Surface Analysis Cornell University Data for Surface Analysis Vector Triangulated Irregular Networks (TIN) a surface layer where space is partitioned into a set of non-overlapping triangles Attribute and
Introduction to 3D Analysis. Jinwu Ma Jie Chang Khalid Duri
 Introduction to 3D Analysis Jinwu Ma Jie Chang Khalid Duri Area & Volume 3D Analyst Features Detect Change Determine Cut/Fill Calculate Surface Area & Volume Data Management Data Creation Data Conversion
Introduction to 3D Analysis Jinwu Ma Jie Chang Khalid Duri Area & Volume 3D Analyst Features Detect Change Determine Cut/Fill Calculate Surface Area & Volume Data Management Data Creation Data Conversion
Exercise 5. Height above Nearest Drainage Flood Inundation Analysis
 Exercise 5. Height above Nearest Drainage Flood Inundation Analysis GIS in Water Resources, Fall 2018 Prepared by David G Tarboton Purpose The purpose of this exercise is to learn how to calculation the
Exercise 5. Height above Nearest Drainage Flood Inundation Analysis GIS in Water Resources, Fall 2018 Prepared by David G Tarboton Purpose The purpose of this exercise is to learn how to calculation the
Raster Data. James Frew ESM 263 Winter
 Raster Data 1 Vector Data Review discrete objects geometry = points by themselves connected lines closed polygons agributes linked to feature ID explicit localon every point has coordinates 2 Fields in
Raster Data 1 Vector Data Review discrete objects geometry = points by themselves connected lines closed polygons agributes linked to feature ID explicit localon every point has coordinates 2 Fields in
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 02: Feature Types and Data Models
 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 02: Feature Types and Data Models Feature Types and Data Models How Does a GIS Work? - a GIS operates on the premise that all of the features in the real world can
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 02: Feature Types and Data Models Feature Types and Data Models How Does a GIS Work? - a GIS operates on the premise that all of the features in the real world can
Final project: Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2) GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I
 GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2) Talk about class project (copy follow_along_data\ch8a_class_ex into U:\ArcGIS\ if needed) Catch up with lecture 20
GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2) Talk about class project (copy follow_along_data\ch8a_class_ex into U:\ArcGIS\ if needed) Catch up with lecture 20
GEO/GY461 Applied GIS: Environmental Geology of the Cheaha Mountain, AL, 7.5' Quadrangle Project
 Figure 1: Reference points spreadsheet for Cheaha Mt. 7.5' quadrangle (LatLongCalc_24k.xls). Page -1- Figure 2: RMS statistic from the Cheaha Mountain field map georeference. Page -2- Figure 3: Appearance
Figure 1: Reference points spreadsheet for Cheaha Mt. 7.5' quadrangle (LatLongCalc_24k.xls). Page -1- Figure 2: RMS statistic from the Cheaha Mountain field map georeference. Page -2- Figure 3: Appearance
ArcCatalog or the ArcCatalog tab in ArcMap ArcCatalog or the ArcCatalog tab in ArcMap ArcCatalog or the ArcCatalog tab in ArcMap
 ArcGIS Procedures NUMBER OPERATION APPLICATION: TOOLBAR 1 Import interchange file to coverage 2 Create a new 3 Create a new feature dataset 4 Import Rasters into a 5 Import tables into a PROCEDURE Coverage
ArcGIS Procedures NUMBER OPERATION APPLICATION: TOOLBAR 1 Import interchange file to coverage 2 Create a new 3 Create a new feature dataset 4 Import Rasters into a 5 Import tables into a PROCEDURE Coverage
Your Prioritized List. Priority 1 Faulted gridding and contouring. Priority 2 Geoprocessing. Priority 3 Raster format
 Your Prioritized List Priority 1 Faulted gridding and contouring Priority 2 Geoprocessing Priority 3 Raster format Priority 4 Raster Catalogs and SDE Priority 5 Expanded 3D Functionality Priority 1 Faulted
Your Prioritized List Priority 1 Faulted gridding and contouring Priority 2 Geoprocessing Priority 3 Raster format Priority 4 Raster Catalogs and SDE Priority 5 Expanded 3D Functionality Priority 1 Faulted
Creating Digital Elevation Model Using a Mobile Device
 Name : Ali Ihsan Durmaz UnitID : aidurmaz Creating Digital Elevation Model Using a Mobile Device ABSTRACT DEM (Digital Elevation Models) is the best way to interpret topography on the ground. In recent
Name : Ali Ihsan Durmaz UnitID : aidurmaz Creating Digital Elevation Model Using a Mobile Device ABSTRACT DEM (Digital Elevation Models) is the best way to interpret topography on the ground. In recent
Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources. This course consists of 9 lessons, including Power point presentations, demonstrations,
 Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources. This course consists of 9 lessons, including Power point presentations, demonstrations, readings, and hands on GIS lab exercises. Following the last
Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources. This course consists of 9 lessons, including Power point presentations, demonstrations, readings, and hands on GIS lab exercises. Following the last
Point clouds and DEMs
 Point clouds and DEMs J Ramón Arrowsmith School of Earth and Space Exploration Arizona State University Christopher J. Crosby UNAVCO Tutorial notes (April 2016) Point clouds and DEMs 1. Download tahoe.las
Point clouds and DEMs J Ramón Arrowsmith School of Earth and Space Exploration Arizona State University Christopher J. Crosby UNAVCO Tutorial notes (April 2016) Point clouds and DEMs 1. Download tahoe.las
Working with Map Algebra
 Working with Map Algebra While you can accomplish much with the Spatial Analyst user interface, you can do even more with Map Algebra, the analysis language of Spatial Analyst. Map Algebra expressions
Working with Map Algebra While you can accomplish much with the Spatial Analyst user interface, you can do even more with Map Algebra, the analysis language of Spatial Analyst. Map Algebra expressions
L7 Raster Algorithms
 L7 Raster Algorithms NGEN6(TEK23) Algorithms in Geographical Information Systems by: Abdulghani Hasan, updated Nov 216 by Per-Ola Olsson Background Store and analyze the geographic information: Raster
L7 Raster Algorithms NGEN6(TEK23) Algorithms in Geographical Information Systems by: Abdulghani Hasan, updated Nov 216 by Per-Ola Olsson Background Store and analyze the geographic information: Raster
Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images
 Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images Airborne TerrestriaL Applications Sensor (ATLAS) Nine flight paths were recorded over the city of Providence. 1 True color ATLAS image (bands 4, 2, 1 in
Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images Airborne TerrestriaL Applications Sensor (ATLAS) Nine flight paths were recorded over the city of Providence. 1 True color ATLAS image (bands 4, 2, 1 in
Introduction to Geographic Information Science. Some Updates. Last Lecture 4/6/2017. Geography 4103 / Raster Data and Tesselations.
 Geography 43 / 3 Introduction to Geographic Information Science Raster Data and Tesselations Schedule Some Updates Last Lecture We finished DBMS and learned about storage of data in complex databases Relational
Geography 43 / 3 Introduction to Geographic Information Science Raster Data and Tesselations Schedule Some Updates Last Lecture We finished DBMS and learned about storage of data in complex databases Relational
Using GIS to Site Minimal Excavation Helicopter Landings
 Using GIS to Site Minimal Excavation Helicopter Landings The objective of this analysis is to develop a suitability map for aid in locating helicopter landings in mountainous terrain. The tutorial uses
Using GIS to Site Minimal Excavation Helicopter Landings The objective of this analysis is to develop a suitability map for aid in locating helicopter landings in mountainous terrain. The tutorial uses
Geo372 Vertiefung GIScience. Spatial Interpolation
 Geo372 Vertiefung GIScience Spatial Interpolation Herbstsemester Ross Purves Last week We looked at data quality and integration We saw how uncertainty could be introduced by the concepts we chose, by
Geo372 Vertiefung GIScience Spatial Interpolation Herbstsemester Ross Purves Last week We looked at data quality and integration We saw how uncertainty could be introduced by the concepts we chose, by
Geostatistics Predictions with Deterministic Procedures
 Instituto Superior de Estatística e Gestão de Informação Universidade Nova de Lisboa Master of Science in Geospatial Technologies Geostatistics Predictions with Deterministic Procedures Carlos Alberto
Instituto Superior de Estatística e Gestão de Informação Universidade Nova de Lisboa Master of Science in Geospatial Technologies Geostatistics Predictions with Deterministic Procedures Carlos Alberto
GIS Fundamentals: Supplementary Lessons with ArcGIS Pro
 Station Analysis (parts 1 & 2) What You ll Learn: - Practice various skills using ArcMap. - Combining parcels, land use, impervious surface, and elevation data to calculate suitabilities for various uses
Station Analysis (parts 1 & 2) What You ll Learn: - Practice various skills using ArcMap. - Combining parcels, land use, impervious surface, and elevation data to calculate suitabilities for various uses
GIS IN ECOLOGY: MORE RASTER ANALYSES
 GIS IN ECOLOGY: MORE RASTER ANALYSES Contents Introduction... 2 More Raster Application Functions... 2 Data Sources... 3 Tasks... 4 Raster Recap... 4 Viewshed Determining Visibility... 5 Hydrology Modeling
GIS IN ECOLOGY: MORE RASTER ANALYSES Contents Introduction... 2 More Raster Application Functions... 2 Data Sources... 3 Tasks... 4 Raster Recap... 4 Viewshed Determining Visibility... 5 Hydrology Modeling
Analytical and Computer Cartography Winter Lecture 9: Geometric Map Transformations
 Analytical and Computer Cartography Winter 2017 Lecture 9: Geometric Map Transformations Cartographic Transformations Attribute Data (e.g. classification) Locational properties (e.g. projection) Graphics
Analytical and Computer Cartography Winter 2017 Lecture 9: Geometric Map Transformations Cartographic Transformations Attribute Data (e.g. classification) Locational properties (e.g. projection) Graphics
Exercise 5. Height above Nearest Drainage Flood Inundation Analysis
 Exercise 5. Height above Nearest Drainage Flood Inundation Analysis GIS in Water Resources, Fall 2016 Prepared by David G Tarboton Purpose The purpose of this exercise is to illustrate the use of TauDEM
Exercise 5. Height above Nearest Drainage Flood Inundation Analysis GIS in Water Resources, Fall 2016 Prepared by David G Tarboton Purpose The purpose of this exercise is to illustrate the use of TauDEM
Graphic Display of Vector Object
 What is GIS? GIS stands for Geographic Information Systems, although the term Geographic Information Science is gaining popularity. A GIS is a software platform for storing, organizing, viewing, querying,
What is GIS? GIS stands for Geographic Information Systems, although the term Geographic Information Science is gaining popularity. A GIS is a software platform for storing, organizing, viewing, querying,
The Reference Library Generating Low Confidence Polygons
 GeoCue Support Team In the new ASPRS Positional Accuracy Standards for Digital Geospatial Data, low confidence areas within LIDAR data are defined to be where the bare earth model might not meet the overall
GeoCue Support Team In the new ASPRS Positional Accuracy Standards for Digital Geospatial Data, low confidence areas within LIDAR data are defined to be where the bare earth model might not meet the overall
Spatial Analysis Exercise GIS in Water Resources Fall 2011
 Spatial Analysis Exercise GIS in Water Resources Fall 2011 Prepared by David G. Tarboton and David R. Maidment Goal The goal of this exercise is to serve as an introduction to Spatial Analysis with ArcGIS.
Spatial Analysis Exercise GIS in Water Resources Fall 2011 Prepared by David G. Tarboton and David R. Maidment Goal The goal of this exercise is to serve as an introduction to Spatial Analysis with ArcGIS.
Lecture 06. Raster and Vector Data Models. Part (1) Common Data Models. Raster. Vector. Points. Points. ( x,y ) Area. Area Line.
 Lecture 06 Raster and Vector Data Models Part (1) 1 Common Data Models Vector Raster Y Points Points ( x,y ) Line Area Line Area 2 X 1 3 Raster uses a grid cell structure Vector is more like a drawn map
Lecture 06 Raster and Vector Data Models Part (1) 1 Common Data Models Vector Raster Y Points Points ( x,y ) Line Area Line Area 2 X 1 3 Raster uses a grid cell structure Vector is more like a drawn map
B A
 GIS in Water Resources Exercise #3 Solution Part 1. Slope Calculations 1.1 Hand Calculation (Point A only): (i) ESRI Slope Cell Referencing 45.4 46.1 47 48.6 47.7 45 46.1 46.4 B 47.9 47.4 45.1 45.8 46.8
GIS in Water Resources Exercise #3 Solution Part 1. Slope Calculations 1.1 Hand Calculation (Point A only): (i) ESRI Slope Cell Referencing 45.4 46.1 47 48.6 47.7 45 46.1 46.4 B 47.9 47.4 45.1 45.8 46.8
Blacksburg, VA July 24 th 30 th, 2010 Georeferencing images and scanned maps Page 1. Georeference
 George McLeod Prepared by: With support from: NSF DUE-0903270 in partnership with: Geospatial Technician Education Through Virginia s Community Colleges (GTEVCC) Georeference The process of defining how
George McLeod Prepared by: With support from: NSF DUE-0903270 in partnership with: Geospatial Technician Education Through Virginia s Community Colleges (GTEVCC) Georeference The process of defining how
DATA MODELS IN GIS. Prachi Misra Sahoo I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi
 DATA MODELS IN GIS Prachi Misra Sahoo I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi -110012 1. Introduction GIS depicts the real world through models involving geometry, attributes, relations, and data quality. Here the realization
DATA MODELS IN GIS Prachi Misra Sahoo I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi -110012 1. Introduction GIS depicts the real world through models involving geometry, attributes, relations, and data quality. Here the realization
