Logic synthesis and Place and Route Tutorial Page 1
|
|
|
- Ellen Powers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Logic synthesis and Place and Route Tutorial Page 1 Standard Cell ASIC Design flow: A designer uses predesigned logic cells such as AND gate, NOR gate, etc. These gates are called Standard Cells. The advantage of Standard Cell ASIC s is that the designers save time, money and reduce the risk by using a predesigned and pre-tested Standard Cell Library. We will be using Cadence RTL compiler to synthesize our design. Logic synthesis is a process by which an abstract form of desired circuit behavior, typically register transfer level (RTL), is turned into a design implementation in terms of logic gates. Common examples of this process include synthesis of HDLs, including VHDL and Verilog. Logic synthesis is one aspect of electronic design automation. After logic synthesis, in a typical ASIC design, a Place and Route tool is used to place the standard cells and then route the nets between them and produce an optimized design. We will be using Cadence Soc Encounter to place and route our design. This tutorial will help you to learn a typical ASIC design flow. We will be using the following flow in our Labs. Build the Schematic of Design using Virtuoso Simulate for rise and fall times and Propagation delays Generate a HDL netlist Logic Synthesis Place and Route Import the Placed n Routed Design in Virtuoso Run DRC and LVS Extract the design for parasitics and generate a netlist Simulate for rise and fall times and Propagation delays
2 Logic synthesis and Place and Route Tutorial Page 2 I. Generation of a Verilog Netlist using NC-Verilog 1. Go to Launch Simulation NC-Verilog Fig A window will pop up.
3 Logic synthesis and Place and Route Tutorial Page 3 Fig Go to Commands Initialize Design. 4. After Initializing the design, Go to Setup Netlist. A window will appear. On the Netlisting Mode, click Entire design. Click Netlist Explicitly In the Global Power Nets change the value to vdd In the Global Ground Nets change the value to gnd 5. The form window should like
4 Logic synthesis and Place and Route Tutorial Page 4 Fig Click OK. 7. Go to Commands Generate Netlist 8. The status should be Netlist Succeeded. 9. Go to Results Netlist. A GUI-form will open up. Fig. 4
5 Logic synthesis and Place and Route Tutorial Page Click on the library name which has your design. Click on any Cell name and click View. You will see the verilog netlist of the design you made and also the netlist of instances that were used in your design. So for example, If the top level design is a 4 bit adder, it will show you the netlist of a 4 bit adder with four 1 bit full adders instantiated. Then there will be another netlist of a 1 bit full adder containing the XOR, AND and OR cells instantiated. 11. When you open the netlist. Go to File Save as. Save all the netlist files in directory where you will be invoking the PnR tool. The file name should be same as the module name. This is very important. 12. In the netlist containing the top-level design module, copy the contents of all the low level design modules. So for example if the top-level HDL is 4 bit adder, copy the whole HDL definition of module 1bit adder in the top level HDL file. 13. Make sure you remove all the specify and endspecify staments An example file will look like module add_4bit ( Cout, Sbus0, Sbus1, Sbus2, Sbus3, Abus0, Abus1, Abus2, Abus3, Bbus0, Bbus1, Bbus2, Bbus3, Cin, gnd, vdd ); output Cout, Sbus0, Sbus1, Sbus2, Sbus3; input Abus0, Abus1, Abus2, Abus3, Bbus0, Bbus1, Bbus2, Bbus3, Cin, gnd, vdd; adder I3 (.cout(cout),.sum(sbus3),.a(abus3),.b(bbus3),.c(net24),.gnd(gnd),.vdd(vdd)); adder I2 (.cout(net24),.sum(sbus2),.a(abus2),.b(bbus2),.c(net32),.gnd(gnd),.vdd(vdd)); adder I1 (.cout(net32),.sum(sbus1),.a(abus1),.b(bbus1),.c(net40),.gnd(gnd),.vdd(vdd)); adder I0 (.cout(net40),.sum(sbus0),.a(abus0),.b(bbus0),.c(cin),.gnd(gnd),.vdd(vdd)); endmodule module adder ( Cout, Sum, gnd, vdd, A, B, Cin ); output Cout, Sum; input A, B, Cin, gnd, vdd; XOR2X1 I4 (.A(A),.B(B),.Y(net22),.gnd(gnd),.vdd(vdd)); XOR2X1 I5 (.A(net22),.B(Cin),.Y(Sum),.gnd(gnd),.vdd(vdd)); AND2X1 I3 (.A(A),.B(B),.Y(net27),.gnd(gnd),.vdd(vdd)); AND2X1 I2 (.A(net22),.B(Cin),.Y(net32),.gnd(gnd),.vdd(vdd)); OR2X1 I6 (.A(net32),.B(net27),.Y(Cout),.gnd(gnd),.vdd(vdd)); endmodule
6 Logic synthesis and Place and Route Tutorial Page 6 II. Logic Synthesis and Place n Route Tutorial This part is totally automated by a perl script PR.pl. The script removes gnd and vdd definitions from your HDL input and gives it to synthesis tool. The RTL compiler takes logic gates from it s own library gscl45nm.v and builds your circuit and then optimizes it. Then the Encounter tool places the standard cells between rows and routes the nets to produce an ASIC design. 1. Go to the directory where you have saved the HDL file and all the encounter files should be present. 2. In the command line,type perl PR.pl Your_HDL_file_name.v Again make sure the HDL file name is same as top level module name. 3. The script runs the cadence RTL compiler, synthesizes the design in logic gates and outputs a file Your_HDL_file_name.vh 4. It will also output following files i) rc.log --- This is the log file of the synthesis tool. The file shouldn t have any errors or any unexpected warnings. If there is an error, the whole flow will exit with an error. A successful synthesis run should look like Incremental optimization status =============================== Worst DRC Total Total Neg Max Operation Area Slack Cap Worst Path init_delay Bbus0 --> Sbus3 init_drc Bbus0 --> Sbus3 init_area Bbus0 --> Sbus3 Done mapping add_sub4bit Synthesis succeeded. rc:/> rc:/> Tracing clock networks. Levelizing the circuit. Applying wireload models. Computing net loads. Computing delays. Computing arrivals and requireds. rc:/> rc:/> rc:/> rc:/> rc:/> rc:/> rc:/> rc:/> Synthesis Finished! rc:/> Check timing.rep, area.rep, gate.rep and power.rep for synthesis results
7 Logic synthesis and Place and Route Tutorial Page 7 ii) rc.cmd ---- this is the cmd file which is generated by RTL compiler. It contains all the internal commands which are run in a typical logic synthesis flow. iii) Files with extension.rep are generated which contain the timing and power information of the design. 5. The output.vh file is given as input to Soc Encounter by the script itself and it starts running in background. 6. The Encounter runs an encounter.tcl file. If you are interested you can open the file and see the internal commands. 7. The Encounter flow should also run without any errors. Open the encounter.log. The end of the file should look like this <CMD> verifygeometry *** Starting Verify Geometry (MEM: 580.5) *** VERIFY GEOMETRY... Starting Verification VERIFY GEOMETRY... Initializing VERIFY GEOMETRY... Deleting Existing Violations VERIFY GEOMETRY... Creating Sub-Areas... bin size: 2080 VERIFY GEOMETRY... SubArea : 1 of 1 VERIFY GEOMETRY... Cells : 0 Viols. VERIFY GEOMETRY... SameNet : 0 Viols. VERIFY GEOMETRY... Wiring : 0 Viols. VERIFY GEOMETRY... Antenna : 0 Viols. VERIFY GEOMETRY... Sub-Area : 1 complete 0 Viols. 0 Wrngs. VG: elapsed time: 2.00 Begin Summary... Cells : 0 SameNet : 0 Wiring : 0 Antenna : 0 Short : 0 Overlap : 0 End Summary Verification Complete : 0 Viols. 0 Wrngs. **********End: VERIFY GEOMETRY********** *** verify geometry (CPU: 0:00:01.2 MEM: 78.7M) <CMD> verifyconnectivity -type all ******** Start: VERIFY CONNECTIVITY ******** Start Time: Thu Jan 27 04:26: Design Name: add_sub4bit Database Units: 2000 Design Boundary: (0.0000, ) ( , ) Error Limit = 1000; Warning Limit = 50 Check all nets VC Elapsed Time: 0:00:00.0 Begin Summary Found no problems or warnings. End Summary ******** End: VERIFY CONNECTIVITY ******** Verification Complete : 0 Viols. 0 Wrngs.
8 Logic synthesis and Place and Route Tutorial Page 8 8. The Design Window should look like Fig Go to the File Save DEF OK. The DEF file will be saved with your design name and will be your final design output. 10. You can close the Encounter Window now. A HDL file final.v is also saved in the current directory. This file is the HDL version of your design. We will use this file later for our LVS check.
9 Logic synthesis and Place and Route Tutorial Page 9 III. Back Annotation of Design in Cadence Virtuoso 1. Open the ICFB window. Go to File Import DEF. A form will open up. Give the path to your DEF file Give the Target Library Name Ref. Technology Libraries should be NCSU_TechLib_FreePDK45 From the Drop-Down Menu of Technology From Library Select the NCSU_Techlib_FreePDK45. If you are not able to select anything from drop-down menu, click Use Template file and the again click Use GUI Fields Give the Target Cell Name Give the Target View Name as layout Give the Master Library List as freepdk45_cells 2. Click OK. Fig 6.
10 Logic synthesis and Place and Route Tutorial Page In the ICFB window you will see the DEF import. The DEF import will complete with some errors as shown below. This error ROW_CORE_ROW are generated due to Place and Route boundaries. You shouldn t worry about them. However, if you are seeing some other type of error, then probably the DEF import wasn t correct. ERROR: (OALEFDEF-50096): /u/vbakshi/desktop/cadencesetup/encounter/flow/add_sub4bit.def(24) : ROW CORE_ROW_0: The sitedef CoreSite was not found. This row was ignored. Ensure that the site is defined in the technology database. ******************************************************************************** Product : Virtuoso(R) DEF In Program defin.exe version /10/ :51 (cds23100) $ SubVersion: sub-version IC Started at: 28-Jan :56:59 User Name : vbakshi Host Name : nemo.ece.pdx.edu Directory : /u/vbakshi/desktop/cadencesetup/cadence610 DB Version: (SJ) CADENCE Design Systems, Inc. ******************************************************************************** ERROR: (OALEFDEF-50096): /u/vbakshi/desktop/cadencesetup/encounter/flow/add_sub4bit.def(26) : ROW CORE_ROW_1: The sitedef CoreSite was not found. This row was ignored. Ensure that the site is defined in the technology database. ERROR: (OALEFDEF-50096): /u/vbakshi/desktop/cadencesetup/encounter/flow/add_sub4bit.def(28) : ROW CORE_ROW_2: The sitedef CoreSite was not found. This row was ignored. Ensure that the site is defined in the technology database. ERROR: (OALEFDEF-50096): /u/vbakshi/desktop/cadencesetup/encounter/flow/add_sub4bit.def(30) : ROW CORE_ROW_3: The sitedef CoreSite was not found. This row was ignored. Ensure that the site is defined in the technology database. Elapsed Time: 5.3s defin translation completed (errors: 4, warnings: 0) 4. Go to the Library Manager and you will be able to see the layout of your design. 5. You will notice all the Boundaries. On the keyboard press ctrl + A. The design will get selected. Move the Design from these boundaries and you will be able to see a design like Fig 7 below.
11 Logic synthesis and Place and Route Tutorial Page 11 Fig Press shift + S. Click Add criteria and fill in the forms as shown below.
12 Logic synthesis and Place and Route Tutorial Page After you have filled the form, click Apply and then Select All. 8. Press Q. This will open up the property form. Click attribute and then Common. Change the View as layout. Click OK. Fig Now you have to put the labels on all the input and output pins. For each net put a label on all the pins including vdd and gnd. Make sure that the label is of same metal layer as the net and of type ll(label) as shown in the figure. The labels are added to layout explicitly as LVS cannot detect pins. So during layout extraction it converts the labels to pins.
13 Logic synthesis and Place and Route Tutorial Page 13 Fig Run DRC. It should come clean. 11. Open LVS form. Go to the Inputs section and then the netlist tab. Choose the format as verilog and browse to get the final.v which you had saved in the PnR flow. Refer to figure below.
14 Logic synthesis and Place and Route Tutorial Page 14 Fig The output of the LVS will come incorrect because of different number of nets and instances. That is OK. However the results should not be NOT COMPARED. This means there was some error. 13. Go to Calibre Run Pex. A form will open up. Again go to Input Tab. Go to Netlist Tab. Again select the verilog file final.v and format as VERILOG. It should look like the Fig Go to Output tab. Change the extraction to Transistor level, Extraction type as R + C and No Inductance 15. Choose the format as SPECTRE and use names from Layout. Refer to Fig Click Run Pex.
15 Logic synthesis and Place and Route Tutorial Page 15 Fig After some time, the PEX will complete with no errors. It will also show you the netlist. Make sure all the input and output pins are declared including vdd and gnd. 16. The PEX outputs three files as the extracted netlist. These are: {design name}.netlist {design name}.pex {design name}.pxi The starting part of.netlist should look like below. Make sure all the input and output pins are showing in the netlist. This netlist contains all the extracted transistors, resistance and capacitances.
16 Logic synthesis and Place and Route Tutorial Page 16 // File: add_sub4bit.pex.netlist // Created: Fri Jan 28 04:06: // Program "Calibre xrc" // Version "v2007.1_24.22" // include "add_sub4bit.pex.netlist.pex" subckt ADD_SUB4BIT ( C4 SBUS0 SBUS1 SBUS2 SBUS3 ABUS0 ABUS1 ABUS2 ABUS3 BBUS0 \ BBUS1 BBUS2 BBUS3 CIN INST VDD GND ) // // SBUS0 SBUS0 // SBUS3 SBUS3 // ABUS0 ABUS0 // ABUS1 ABUS1 // BBUS0 BBUS0 // BBUS1 BBUS1 // ABUS2 ABUS2 // ABUS3 ABUS3 // BBUS2 BBUS2 // BBUS3 BBUS3 // C4 C4 // CIN CIN // SBUS1 SBUS1 // SBUS2 SBUS2 // GND GND // VDD VDD
17 Logic synthesis and Place and Route Tutorial Page 17 IV. Simulating an PEX extracted netlist Couple of hacks to done before we are ready for simulating our extracted netlist. 1. On the command line, > mkdir spectre.run1/ 2. Copy your all three extracted netlist files in this directory. 3. Rename the.netlist file as netlist. On the command line write > mv *.netlist netlist 4. In the spectre.run1/ directory type on the command line > cp./netlist./input.scs This input.scs file will be input to your ocean script. Open input.scs in gedit. This will be your new input.scs When you simulated your schematic, a directory called simulation is formed in the current running directory. The directory contains an input.scs file. An example of the path will be like: /u/username/desktop/cadence610/simulation/add_sub4bit_test/spectre/schematic/netlist Go to this directory and open the input.scs file in gedit. Remember this is your old input.scs file in which you simulated your schematic. Now you have two input.scs file open, one is the old version (the one which simulated your schematic) and another will be your new version. Do not get confused by two input.scs files In Old input.scs, you will see the starting lines something like below: simulator lang=spectre global 0 include "/u/vbakshi/desktop/cadencesetup/cadence610/50nmodels.m" // Library name: freepdk45_cells // Cell name: XOR2X1 // View name: schematic //
18 Logic synthesis and Place and Route Tutorial Page Copy these first three lines at the top of your new input.scs file. 6. Again at the end of your old input.scs file after the End of subcircuit Definition, you will notice all instantiation of your circuit, voltage sources and ground definitions will be there. An example will be // End of subcircuit definition. // Library name: lab_test2 // Cell name: add_sub4bit_test // View name: schematic I0 (net29 net29 net27 net27 net25 net25 net23 net23 C4 0 0 Sbus0 Sbus1 \ Sbus2 Sbus3 0 net31) add_sub4bit V6 (net23 0) vsource type=pwl wave=[ n n 0 30n n 1.2 \ 45n 1.2 ] V5 (net25 0) vsource type=pwl wave=[ n n n n 0 \ 35n 0 ] V1 (net27 0) vsource type=pwl wave=[ n n 0 30n n 1.2 \ 45n 1.2 ] V0 (net29 0) vsource type=pwl wave=[ n n n n 0 \ 35n 0 ] V4 (net31 0) vsource type=dc dc=1.2 simulatoroptions options reltol=1e-3 vabstol=1e-6 iabstol=1e-12 temp=27 \ tnom=27 scalem=1.0 scale=1.0 gmin=1e-12 rforce=1 maxnotes=5 maxwarns=5 \ digits=5 cols=80 pivrel=1e-3 sensfile="../psf/sens.output" \ checklimitdest=psf tran tran stop=100n write="spectre.ic" writefinal="spectre.fc" \ annotate=status maxiters=5 finaltimeop info what=oppoint where=rawfile modelparameter info what=models where=rawfile element info what=inst where=rawfile outputparameter info what=output where=rawfile designparamvals info what=parameters where=rawfile primitives info what=primitives where=rawfile subckts info what=subckts where=rawfile saveoptions options save=allpub 7. Copy all the lines after End of subcircuit Definition in your new input.scs file. 8. Close the old input.scs file 9. In your new input.scs file, notice that the subcircuit has been instantiated like subckt ADD_SUB4BIT ( C4 SBUS0 SBUS1 SBUS2 SBUS3 ABUS0 ABUS1 ABUS2 ABUS3 BBUS0 \ BBUS1 BBUS2 BBUS3 CIN INST VDD GND ) Then at end of subcircuit definitions, you will notice the instantiation of your subcircuit I0 (net29 net29 net27 net27 net25 net25 net23 net23 C4 0 0 Sbus0 Sbus1 \ Sbus2 Sbus3 0 net31) add_sub4bit
19 Logic synthesis and Place and Route Tutorial Page 19 These nets should be in the same order as the subcircuit definition. You will notice that order is not correct above. Edit it to make connections in proper order. An example of proper order will be: I0 (C4 Sbus0 Sbus1 Sbus2 Sbus3 net29 net29 net27 net27 net25 net25 net23 net23 \ 0 0 net31 0) ADD_SUB4BIT. 10. One final hack Open the.pex netlist file and at the top of the file include this line simulator lang=spectre 11. Now you are ready for some simulation!!! Download the Ocean Script from the website. Edit the Ocean Script to give proper paths. The input file will be your spectre.run1/netlist Run the Ocean script.
20 Logic synthesis and Place and Route Tutorial Page 20 V. Direct Place and Route tutorial 1. Go to the Encounter/flow Directory. 2. Before coming to this stage, make sure you have run a synthesis and place and route design flow. In the flow directory you see there will two files HDL_name.v and HDL_name.vh HDL_name.v is your verilog file created by NC-verilog from your schematic. This is your un-optimized design. HDL_name.vh is the optimized design produced by logic synthesis and given as input to Encounter which places and routes the standard cells. 3. Delete the.vh extension file. On the command line > rm HDL_name.vh 4. Rename the original verilog file as.vh file. On the command line write > mv HDL_name.v HDL_name.vh 5. This file will become input to your encounter tool and it will place and route your original design. On the command line write > encounter init encounter.tcl You have to use the new encounter.tcl for this. 6. The rest of the flow is same. After the encounter finishes, save the DEF file and import into cadence virtuoso. Extract the netlist with parasitics and simulate it.
Laboratory 3. EE 342 (VLSI Circuit Design) - Using Spectre netlist and Calculator for simulation
 EE 342 (VLSI Circuit Design) Laboratory 3 - Using Spectre netlist and Calculator for simulation By Mulong Li, 2013 1 Background knowledge Spectre: is a SPICE-class circuit simulator. It provides the basic
EE 342 (VLSI Circuit Design) Laboratory 3 - Using Spectre netlist and Calculator for simulation By Mulong Li, 2013 1 Background knowledge Spectre: is a SPICE-class circuit simulator. It provides the basic
RC Extraction. of an Inverter Circuit
 RC Extraction of an Inverter Circuit Santa Clara University Department of Electrical Engineering Under Guidance of Dr Samiha Mourad & Dr Shoba Krishnan Date of Last Revision: February 1, 2010 Copyright
RC Extraction of an Inverter Circuit Santa Clara University Department of Electrical Engineering Under Guidance of Dr Samiha Mourad & Dr Shoba Krishnan Date of Last Revision: February 1, 2010 Copyright
ESE 570 Cadence Lab Assignment 2: Introduction to Spectre, Manual Layout Drawing and Post Layout Simulation (PLS)
 ESE 570 Cadence Lab Assignment 2: Introduction to Spectre, Manual Layout Drawing and Post Layout Simulation (PLS) Objective Part A: To become acquainted with Spectre (or HSpice) by simulating an inverter,
ESE 570 Cadence Lab Assignment 2: Introduction to Spectre, Manual Layout Drawing and Post Layout Simulation (PLS) Objective Part A: To become acquainted with Spectre (or HSpice) by simulating an inverter,
The following is a procedure for extracting a layout, doing a layout vs. schematic check, and then simulating the extracted layout with Cadence.
 The following is a procedure for extracting a layout, doing a layout vs. schematic check, and then simulating the extracted layout with Cadence. (This might not be the best way, but it works!) 1) Realize
The following is a procedure for extracting a layout, doing a layout vs. schematic check, and then simulating the extracted layout with Cadence. (This might not be the best way, but it works!) 1) Realize
EE 330 Laboratory Experiment Number 11
 EE 330 Laboratory Experiment Number 11 Design and Simulation of Digital Circuits using Hardware Description Languages Fall 2017 Contents Purpose:... 3 Background... 3 Part 1: Inverter... 4 1.1 Simulating
EE 330 Laboratory Experiment Number 11 Design and Simulation of Digital Circuits using Hardware Description Languages Fall 2017 Contents Purpose:... 3 Background... 3 Part 1: Inverter... 4 1.1 Simulating
Extraction of Parasitic Capacitance and Resistances for HSPICE Simulation
 Extraction of Parasitic Capacitance and Resistances for HSPICE Simulation Make the layout window active and select Calibre > Run PEX from the top menu bar to start a Parasitic EXtraction. You will need
Extraction of Parasitic Capacitance and Resistances for HSPICE Simulation Make the layout window active and select Calibre > Run PEX from the top menu bar to start a Parasitic EXtraction. You will need
CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #4, Standard cell design flow (from verilog to layout, 8-bit accumulator)
 CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #4, Standard cell design flow (from verilog to layout, 8-bit accumulator) Joel Wilder, Aleksandar Milenkovic, ECE Dept., The University of Alabama in Huntsville
CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #4, Standard cell design flow (from verilog to layout, 8-bit accumulator) Joel Wilder, Aleksandar Milenkovic, ECE Dept., The University of Alabama in Huntsville
Creating LEF File. Abstract Generation: Creating LEF Tutorial File Release Date: 01/13/2004. Export GDS:
 Creating LEF Tutorial 1-1 - Creating LEF File Abstract Generation: Export GDS: Abstract generator comes as a part of the Silicon Ensemble package. As such, it cannot directly read ICFB library databases.
Creating LEF Tutorial 1-1 - Creating LEF File Abstract Generation: Export GDS: Abstract generator comes as a part of the Silicon Ensemble package. As such, it cannot directly read ICFB library databases.
Tutorial for Encounter
 Tutorial for Encounter STEP 1: Login to the Linux system on Linuxlab server. Start a terminal (the shell prompt). (If you don t know how to login to Linuxlab server, look at here) Click here to open a
Tutorial for Encounter STEP 1: Login to the Linux system on Linuxlab server. Start a terminal (the shell prompt). (If you don t know how to login to Linuxlab server, look at here) Click here to open a
CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #3, Standard cell design flow (from schematic to layout, 8-bit accumulator)
 CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #3, Standard cell design flow (from schematic to layout, 8-bit accumulator) Joel Wilder, Aleksandar Milenkovic, ECE Dept., The University of Alabama in Huntsville
CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #3, Standard cell design flow (from schematic to layout, 8-bit accumulator) Joel Wilder, Aleksandar Milenkovic, ECE Dept., The University of Alabama in Huntsville
EE434 ASIC & Digital Systems. From Layout to SPICE Simulation (Virtuoso, Calibre, HSpice) Spring 2017 Dae Hyun Kim
 EE434 ASIC & Digital Systems From Layout to SPICE Simulation (Virtuoso, Calibre, HSpice) Spring 2017 Dae Hyun Kim daehyun@eecs.wsu.edu 1 Preparation for Lab2 Download the following file into your working
EE434 ASIC & Digital Systems From Layout to SPICE Simulation (Virtuoso, Calibre, HSpice) Spring 2017 Dae Hyun Kim daehyun@eecs.wsu.edu 1 Preparation for Lab2 Download the following file into your working
TUTORIAL II ECE 555 / 755 Updated on September 11 th 2006 CADENCE LAYOUT AND PARASITIC EXTRACTION
 TUTORIAL II ECE 555 / 755 Updated on September 11 th 2006 CADENCE LAYOUT AND PARASITIC EXTRACTION After finishing a schematic of your design (Tutorial-I), the next step is creating masks which are for
TUTORIAL II ECE 555 / 755 Updated on September 11 th 2006 CADENCE LAYOUT AND PARASITIC EXTRACTION After finishing a schematic of your design (Tutorial-I), the next step is creating masks which are for
Laboratory 6. - Using Encounter for Automatic Place and Route. By Mulong Li, 2013
 CME 342 (VLSI Circuit Design) Laboratory 6 - Using Encounter for Automatic Place and Route By Mulong Li, 2013 Reference: Digital VLSI Chip Design with Cadence and Synopsys CAD Tools, Erik Brunvand Background
CME 342 (VLSI Circuit Design) Laboratory 6 - Using Encounter for Automatic Place and Route By Mulong Li, 2013 Reference: Digital VLSI Chip Design with Cadence and Synopsys CAD Tools, Erik Brunvand Background
Virtuoso Layout Editor
 This tutorial will cover the basic steps involved in using the Cadence layout editor called Virtuoso, extracting layout, and running simulation on the layout. The inverter layout is used as an example
This tutorial will cover the basic steps involved in using the Cadence layout editor called Virtuoso, extracting layout, and running simulation on the layout. The inverter layout is used as an example
Abstract Editor (Last updated: Oct. 23, 2008)
 Abstract Editor (Last updated: Oct. 23, 2008) Abstract Editor Tutorial This tutorial has been created to discuss all of the steps needed to create an abstract Library Exchange Format (LEF) file for custom
Abstract Editor (Last updated: Oct. 23, 2008) Abstract Editor Tutorial This tutorial has been created to discuss all of the steps needed to create an abstract Library Exchange Format (LEF) file for custom
EE 330 Laboratory Experiment Number 11 Design and Simulation of Digital Circuits using Hardware Description Languages
 EE 330 Laboratory Experiment Number 11 Design and Simulation of Digital Circuits using Hardware Description Languages Fall 2015 Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to develop methods for using Hardware
EE 330 Laboratory Experiment Number 11 Design and Simulation of Digital Circuits using Hardware Description Languages Fall 2015 Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to develop methods for using Hardware
CADENCE TUTORIAL. San Diego State University, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Amith Dharwadkar and Ashkan Ashrafi
 CADENCE TUTORIAL San Diego State University, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Amith Dharwadkar and Ashkan Ashrafi 1 Contents 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) Introduction 3 Connecting to the Volta server..4
CADENCE TUTORIAL San Diego State University, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Amith Dharwadkar and Ashkan Ashrafi 1 Contents 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) Introduction 3 Connecting to the Volta server..4
Cadence Virtuoso Schematic Design and Circuit Simulation Tutorial
 Cadence Virtuoso Schematic Design and Circuit Simulation Tutorial Introduction This tutorial is an introduction to schematic capture and circuit simulation for ENGN1600 using Cadence Virtuoso. These courses
Cadence Virtuoso Schematic Design and Circuit Simulation Tutorial Introduction This tutorial is an introduction to schematic capture and circuit simulation for ENGN1600 using Cadence Virtuoso. These courses
EECE 285 VLSI Design. Cadence Tutorial EECE 285 VLSI. By: Kevin Dick Co-author: Jeff Kauppila Co-author: Dr. Arthur Witulski
 Cadence Tutorial EECE 285 VLSI By: Kevin Dick Co-author: Jeff Kauppila Co-author: Dr. Arthur Witulski 1 Table of Contents Purpose of Cadence 1) The Purpose of Cadence pg. 4 Linux 1) The Purpose of Linux
Cadence Tutorial EECE 285 VLSI By: Kevin Dick Co-author: Jeff Kauppila Co-author: Dr. Arthur Witulski 1 Table of Contents Purpose of Cadence 1) The Purpose of Cadence pg. 4 Linux 1) The Purpose of Linux
CMOS Design Lab Manual
 CMOS Design Lab Manual Developed By University Program Team CoreEl Technologies (I) Pvt. Ltd. 1 Objective Objective of this lab is to learn the Mentor Graphics HEP2 tools as well learn the flow of the
CMOS Design Lab Manual Developed By University Program Team CoreEl Technologies (I) Pvt. Ltd. 1 Objective Objective of this lab is to learn the Mentor Graphics HEP2 tools as well learn the flow of the
CMOS VLSI Design Lab 3: Controller Design and Verification
 CMOS VLSI Design Lab 3: Controller Design and Verification The controller for your MIPS processor is responsible for generating the signals to the datapath to fetch and execute each instruction. It lacks
CMOS VLSI Design Lab 3: Controller Design and Verification The controller for your MIPS processor is responsible for generating the signals to the datapath to fetch and execute each instruction. It lacks
Cadence Tutorial C: Simulating DC and Timing Characteristics 1
 Cadence Tutorial C: Simulating DC and Timing Characteristics Created for the MSU VLSI program by Professor A. Mason and the AMSaC lab group Last updated by Patrick O Hara SS15 Document Contents Introduction
Cadence Tutorial C: Simulating DC and Timing Characteristics Created for the MSU VLSI program by Professor A. Mason and the AMSaC lab group Last updated by Patrick O Hara SS15 Document Contents Introduction
CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #3, Standard cell design flow (from schematic to layout, 8-bit accumulator)
 CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #3, Standard cell design flow (from schematic to layout, 8-bit accumulator) Joel Wilder, Aleksandar Milenkovic, ECE Dept., The University of Alabama in Huntsville
CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #3, Standard cell design flow (from schematic to layout, 8-bit accumulator) Joel Wilder, Aleksandar Milenkovic, ECE Dept., The University of Alabama in Huntsville
Amplifier Simulation Tutorial. Design Kit: Cadence 0.18μm CMOS PDK (gpdk180) (Cadence Version 6.1.5)
 Amplifier Simulation Tutorial Design Kit: Cadence 0.18μm CMOS PDK (gpdk180) (Cadence Version 6.1.5) Yongsuk Choi, Marvin Onabajo This tutorial provides a quick introduction to the use of Cadence tools
Amplifier Simulation Tutorial Design Kit: Cadence 0.18μm CMOS PDK (gpdk180) (Cadence Version 6.1.5) Yongsuk Choi, Marvin Onabajo This tutorial provides a quick introduction to the use of Cadence tools
The IIT standard cell library Version 2.1
 The IIT standard cell library Version 2.1 Highlights - Support for AMI 0.35um library, including pads - Added Primetime and Pathmill support to IIT ASIC Flow - Support for stacked vias (for Virtuoso and
The IIT standard cell library Version 2.1 Highlights - Support for AMI 0.35um library, including pads - Added Primetime and Pathmill support to IIT ASIC Flow - Support for stacked vias (for Virtuoso and
Cadence Tutorial A: Schematic Entry and Functional Simulation Created for the MSU VLSI program by Andrew Mason and the AMSaC lab group.
 Cadence Tutorial A: Schematic Entry and Functional Simulation Created for the MSU VLSI program by Andrew Mason and the AMSaC lab group. Revision Notes: Aug. 2003 update and edit A. Mason add intro/revision/contents
Cadence Tutorial A: Schematic Entry and Functional Simulation Created for the MSU VLSI program by Andrew Mason and the AMSaC lab group. Revision Notes: Aug. 2003 update and edit A. Mason add intro/revision/contents
Cadence Tutorial. Introduction to Cadence 0.18um, Implementation and Simulation of an inverter. A. Moradi, A. Miled et M. Sawan
 Cadence Tutorial Introduction to Cadence 0.18um, Implementation and Simulation of an inverter A. Moradi, A. Miled et M. Sawan Section 1: Introduction to Cadence You will see how to create a new library
Cadence Tutorial Introduction to Cadence 0.18um, Implementation and Simulation of an inverter A. Moradi, A. Miled et M. Sawan Section 1: Introduction to Cadence You will see how to create a new library
EE 330 Laboratory Experiment Number 11 Design, Simulation and Layout of Digital Circuits using Hardware Description Languages
 EE 330 Laboratory Experiment Number 11 Design, Simulation and Layout of Digital Circuits using Hardware Description Languages Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to develop methods for using Hardware
EE 330 Laboratory Experiment Number 11 Design, Simulation and Layout of Digital Circuits using Hardware Description Languages Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to develop methods for using Hardware
ECE425: Introduction to VLSI System Design Machine Problem 3 Due: 11:59pm Friday, Dec. 15 th 2017
 ECE425: Introduction to VLSI System Design Machine Problem 3 Due: 11:59pm Friday, Dec. 15 th 2017 In this MP, you will use automated tools to synthesize the controller module from your MP2 project into
ECE425: Introduction to VLSI System Design Machine Problem 3 Due: 11:59pm Friday, Dec. 15 th 2017 In this MP, you will use automated tools to synthesize the controller module from your MP2 project into
CMOS VLSI Design Lab 3: Controller Design and Verification
 CMOS VLSI Design Lab 3: Controller Design and Verification The controller for your MIPS processor is responsible for generating the signals to the datapath to fetch and execute each instruction. It lacks
CMOS VLSI Design Lab 3: Controller Design and Verification The controller for your MIPS processor is responsible for generating the signals to the datapath to fetch and execute each instruction. It lacks
Revision Notes: July2004 Generate tutorial for single transistor analysis. Based on existing schematic entry tutorial developed for ECE410
 Cadence Analog Tutorial 1: Schematic Entry and Transistor Characterization Created for the MSU VLSI program by Professor A. Mason and the AMSaC lab group. Revision Notes: July2004 Generate tutorial for
Cadence Analog Tutorial 1: Schematic Entry and Transistor Characterization Created for the MSU VLSI program by Professor A. Mason and the AMSaC lab group. Revision Notes: July2004 Generate tutorial for
An overview of standard cell based digital VLSI design
 An overview of standard cell based digital VLSI design Implementation of the first generation AsAP processor Zhiyi Yu and Tinoosh Mohsenin VCL Laboratory UC Davis Outline Overview of standard cellbased
An overview of standard cell based digital VLSI design Implementation of the first generation AsAP processor Zhiyi Yu and Tinoosh Mohsenin VCL Laboratory UC Davis Outline Overview of standard cellbased
Synthesis and APR Tools Tutorial
 Synthesis and APR Tools Tutorial (Last updated: Oct. 26, 2008) Introduction This tutorial will get you familiarized with the design flow of synthesizing and place and routing a Verilog module. All the
Synthesis and APR Tools Tutorial (Last updated: Oct. 26, 2008) Introduction This tutorial will get you familiarized with the design flow of synthesizing and place and routing a Verilog module. All the
CMOS VLSI Design Lab 3: Controller Design and Verification
 CMOS VLSI Design Lab 3: Controller Design and Verification The controller for your MIPS processor is responsible for generating the signals to the datapath to fetch and execute each instruction. It lacks
CMOS VLSI Design Lab 3: Controller Design and Verification The controller for your MIPS processor is responsible for generating the signals to the datapath to fetch and execute each instruction. It lacks
Cadence Tutorial A: Schematic Entry and Functional Simulation Created for the MSU VLSI program by Professor A. Mason and the AMSaC lab group.
 Cadence Tutorial A: Schematic Entry and Functional Simulation Created for the MSU VLSI program by Professor A. Mason and the AMSaC lab group. Revision Notes: Jan. 2006 Updated for use with spectre simulator
Cadence Tutorial A: Schematic Entry and Functional Simulation Created for the MSU VLSI program by Professor A. Mason and the AMSaC lab group. Revision Notes: Jan. 2006 Updated for use with spectre simulator
Logic Synthesis. Logic Synthesis. Gate-Level Optimization. Logic Synthesis Flow. Logic Synthesis. = Translation+ Optimization+ Mapping
 Logic Synthesis Logic Synthesis = Translation+ Optimization+ Mapping Logic Synthesis 2 Gate-Level Optimization Logic Synthesis Flow 3 4 Design Compiler Procedure Logic Synthesis Input/Output 5 6 Design
Logic Synthesis Logic Synthesis = Translation+ Optimization+ Mapping Logic Synthesis 2 Gate-Level Optimization Logic Synthesis Flow 3 4 Design Compiler Procedure Logic Synthesis Input/Output 5 6 Design
101-1 Under-Graduate Project Digital IC Design Flow
 101-1 Under-Graduate Project Digital IC Design Flow Speaker: Ming-Chun Hsiao Adviser: Prof. An-Yeu Wu Date: 2012/9/25 ACCESS IC LAB Outline Introduction to Integrated Circuit IC Design Flow Verilog HDL
101-1 Under-Graduate Project Digital IC Design Flow Speaker: Ming-Chun Hsiao Adviser: Prof. An-Yeu Wu Date: 2012/9/25 ACCESS IC LAB Outline Introduction to Integrated Circuit IC Design Flow Verilog HDL
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING MULTIMEDIA UNIVERSITY LAB SHEET DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
 FACULTY OF ENGINEERING MULTIMEDIA UNIVERSITY LAB SHEET DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUIT DIC1: Schematic Design Entry, Simulation & Verification DIC2: Schematic Driven Layout Drawing (SDL) Design Rule Check (DRC)
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING MULTIMEDIA UNIVERSITY LAB SHEET DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUIT DIC1: Schematic Design Entry, Simulation & Verification DIC2: Schematic Driven Layout Drawing (SDL) Design Rule Check (DRC)
CS/EE 5720/6720 Analog IC Design Tutorial for Schematic Design and Analysis using Spectre
 CS/EE 5720/6720 Analog IC Design Tutorial for Schematic Design and Analysis using Spectre Introduction to Cadence EDA: The Cadence toolset is a complete microchip EDA (Electronic Design Automation) system,
CS/EE 5720/6720 Analog IC Design Tutorial for Schematic Design and Analysis using Spectre Introduction to Cadence EDA: The Cadence toolset is a complete microchip EDA (Electronic Design Automation) system,
UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO
 UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO UW ASIC DESIGN TEAM: Cadence Tutorial Description: Part I: Layout & DRC of a CMOS inverter. Part II: Extraction & LVS of a CMOS inverter. Part III: Post-Layout Simulation. The Cadence
UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO UW ASIC DESIGN TEAM: Cadence Tutorial Description: Part I: Layout & DRC of a CMOS inverter. Part II: Extraction & LVS of a CMOS inverter. Part III: Post-Layout Simulation. The Cadence
Lab 2. Standard Cell layout.
 Lab 2. Standard Cell layout. The purpose of this lab is to demonstrate CMOS-standard cell design. Use the lab instructions and the cadence manual (http://www.es.lth.se/ugradcourses/cadsys/cadence.html)
Lab 2. Standard Cell layout. The purpose of this lab is to demonstrate CMOS-standard cell design. Use the lab instructions and the cadence manual (http://www.es.lth.se/ugradcourses/cadsys/cadence.html)
Lab. Course Goals. Topics. What is VLSI design? What is an integrated circuit? VLSI Design Cycle. VLSI Design Automation
 Course Goals Lab Understand key components in VLSI designs Become familiar with design tools (Cadence) Understand design flows Understand behavioral, structural, and physical specifications Be able to
Course Goals Lab Understand key components in VLSI designs Become familiar with design tools (Cadence) Understand design flows Understand behavioral, structural, and physical specifications Be able to
EECS 627, Lab Assignment 3
 EECS 627, Lab Assignment 3 1 Introduction In this lab assignment, we will use Cadence ICFB and Calibre to become familiar with the process of DRC/LVS checks on a design. So far, we have placed and routed
EECS 627, Lab Assignment 3 1 Introduction In this lab assignment, we will use Cadence ICFB and Calibre to become familiar with the process of DRC/LVS checks on a design. So far, we have placed and routed
Physical Placement with Cadence SoCEncounter 7.1
 Physical Placement with Cadence SoCEncounter 7.1 Joachim Rodrigues Department of Electrical and Information Technology Lund University Lund, Sweden November 2008 Address for correspondence: Joachim Rodrigues
Physical Placement with Cadence SoCEncounter 7.1 Joachim Rodrigues Department of Electrical and Information Technology Lund University Lund, Sweden November 2008 Address for correspondence: Joachim Rodrigues
DRC and LVS checks using Cadence Virtuoso Version 3.0
 DRC and LVS checks using Cadence Virtuoso Version 3.0 Start virtuoso l l Open a virtuoso session in the directory which contains the required cds.lib and lib.def files. Command : virtuoso & Open the layout
DRC and LVS checks using Cadence Virtuoso Version 3.0 Start virtuoso l l Open a virtuoso session in the directory which contains the required cds.lib and lib.def files. Command : virtuoso & Open the layout
EEC 118 Spring 2011 Lab #5 Manchester Carry-Chain Adder
 EEC 118 Spring 2011 Lab #5 Manchester Carry-Chain Adder Rajeevan Amirtharajah Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, Davis Issued: May 9, 2011 Due: May 20, 2011, 5 PM in
EEC 118 Spring 2011 Lab #5 Manchester Carry-Chain Adder Rajeevan Amirtharajah Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, Davis Issued: May 9, 2011 Due: May 20, 2011, 5 PM in
Cell-Based IC Physical Design & Verification SOC Encounter. Advisor : 李昆忠 Presenter : 蕭智元
 Cell-Based IC Physical Design & Verification SOC Encounter Advisor : 李昆忠 Presenter : 蕭智元 Reference: SOC Encounter Training Manual, 2007, edited by CIC. Introduction We ll use some EDA tools to transform
Cell-Based IC Physical Design & Verification SOC Encounter Advisor : 李昆忠 Presenter : 蕭智元 Reference: SOC Encounter Training Manual, 2007, edited by CIC. Introduction We ll use some EDA tools to transform
CS755 CAD TOOL TUTORIAL
 CS755 CAD TOOL TUTORIAL CREATING SCHEMATIC IN CADENCE Shi-Ting Zhou shi-ting@cs.wisc.edu After you have figured out what you want to design, and drafted some pictures and diagrams, it s time to input schematics
CS755 CAD TOOL TUTORIAL CREATING SCHEMATIC IN CADENCE Shi-Ting Zhou shi-ting@cs.wisc.edu After you have figured out what you want to design, and drafted some pictures and diagrams, it s time to input schematics
Hardware Verification Group. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Concordia University, Montreal, Canada. CAD Tool Tutorial.
 Digital Logic Synthesis and Equivalence Checking Tools Hardware Verification Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Concordia University, Montreal, Canada CAD Tool Tutorial May, 2010
Digital Logic Synthesis and Equivalence Checking Tools Hardware Verification Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Concordia University, Montreal, Canada CAD Tool Tutorial May, 2010
Altera Quartus II Synopsys Design Vision Tutorial
 Altera Quartus II Synopsys Design Vision Tutorial Part III ECE 465 (Digital Systems Design) ECE Department, UIC Instructor: Prof. Shantanu Dutt Prepared by: Xiuyan Zhang, Ouwen Shi In tutorial part II,
Altera Quartus II Synopsys Design Vision Tutorial Part III ECE 465 (Digital Systems Design) ECE Department, UIC Instructor: Prof. Shantanu Dutt Prepared by: Xiuyan Zhang, Ouwen Shi In tutorial part II,
ANALOG MICROELECTRONICS ( A)
 ANALOG MICROELECTRONICS (304-534A) IBM 130 nm CMOS Technology An Introduction to Cadence Virtuoso Layout Tool and the Analog Simulation Environment Prepared By - Azhar A. Chowdhury Updated by Ming Yang
ANALOG MICROELECTRONICS (304-534A) IBM 130 nm CMOS Technology An Introduction to Cadence Virtuoso Layout Tool and the Analog Simulation Environment Prepared By - Azhar A. Chowdhury Updated by Ming Yang
CMOS VLSI Design Lab 2: Datapath Design and Verification
 CMOS VLSI Design Lab 2: Datapath Design and Verification In this lab, you will begin designing an 8-bit MIPS processor. You will first review and simulate a Verilog model of the overall processor. You
CMOS VLSI Design Lab 2: Datapath Design and Verification In this lab, you will begin designing an 8-bit MIPS processor. You will first review and simulate a Verilog model of the overall processor. You
VLSI Lab Tutorial 3. Virtuoso Layout Editing Introduction
 VLSI Lab Tutorial 3 Virtuoso Layout Editing Introduction 1.0 Introduction The purpose of this lab tutorial is to guide you through the design process in creating a custom IC layout for your CMOS inverter
VLSI Lab Tutorial 3 Virtuoso Layout Editing Introduction 1.0 Introduction The purpose of this lab tutorial is to guide you through the design process in creating a custom IC layout for your CMOS inverter
Cell-Based Design Flow. TA : 吳廸優
 Cell-Based Design Flow TA : 吳廸優 dywu@viplab.cs.nctu.edu.tw 1 Outline Overview Design Flow Stage 1 RTL Development Synthesis Gate Level Simulation Design Flow Stage 2 Placement and Routing Post Layout Simulation
Cell-Based Design Flow TA : 吳廸優 dywu@viplab.cs.nctu.edu.tw 1 Outline Overview Design Flow Stage 1 RTL Development Synthesis Gate Level Simulation Design Flow Stage 2 Placement and Routing Post Layout Simulation
EE4111 Advanced Analog Electronics Design. Spring 2009 Experiment #4 April 6 ~ April 17
 EE4111 Advanced Analog Electronics Design Spring 2009 Experiment #4 April 6 ~ April 17 Setup Cadence in VLSI Lab 1) Copy files $ cp r /home/grads/ee4111ta ~/ 2) Edit your.cshrc file -- Include the following
EE4111 Advanced Analog Electronics Design Spring 2009 Experiment #4 April 6 ~ April 17 Setup Cadence in VLSI Lab 1) Copy files $ cp r /home/grads/ee4111ta ~/ 2) Edit your.cshrc file -- Include the following
Tutorial for Cadence SOC Encounter Place & Route
 Tutorial for Cadence SOC Encounter Place & Route For Encounter RTL-to-GDSII System 13.15 T. Manikas, Southern Methodist University, 3/9/15 Contents 1 Preliminary Setup... 1 1.1 Helpful Hints... 1 2 Starting
Tutorial for Cadence SOC Encounter Place & Route For Encounter RTL-to-GDSII System 13.15 T. Manikas, Southern Methodist University, 3/9/15 Contents 1 Preliminary Setup... 1 1.1 Helpful Hints... 1 2 Starting
Cadence Tutorial 2: Layout, DRC/LVS and Circuit Simulation with Extracted Parasitics
 Cadence Tutorial 2: Layout, DRC/LVS and Circuit Simulation with Extracted Parasitics Introduction This tutorial describes how to generate a mask layout in the Cadence Virtuoso Layout Editor. Use of DIVA
Cadence Tutorial 2: Layout, DRC/LVS and Circuit Simulation with Extracted Parasitics Introduction This tutorial describes how to generate a mask layout in the Cadence Virtuoso Layout Editor. Use of DIVA
Fall 2008: EE5323 VLSI Design I using Cadence
 1 of 23 9/17/2008 6:47 PM Fall 2008: EE5323 VLSI Design I using Cadence This tutorial has been adapted from EE5323 offered in Fall 2007. Thanks to Jie Gu, Prof. Chris Kim and Satish Sivaswamy of the University
1 of 23 9/17/2008 6:47 PM Fall 2008: EE5323 VLSI Design I using Cadence This tutorial has been adapted from EE5323 offered in Fall 2007. Thanks to Jie Gu, Prof. Chris Kim and Satish Sivaswamy of the University
This is a brief tutorial about building a Symbol for a Schematic in Cadence IC design tool environment for hierarchical design of schematics.
 This is a brief tutorial about building a Symbol for a Schematic in Cadence IC design tool environment for hierarchical design of schematics. 1. > cd work035 2. > cadsetup ams035 3. > virtuoso& IMPORTANT:
This is a brief tutorial about building a Symbol for a Schematic in Cadence IC design tool environment for hierarchical design of schematics. 1. > cd work035 2. > cadsetup ams035 3. > virtuoso& IMPORTANT:
The original document link is
 Tutorial:Analog Artist with HSPICE The original document link is http://www.eda.ncsu.edu/wiki/tutorial:analog_artist_with_hspice This tutorial will introduce you to the Cadence Environment: specifically
Tutorial:Analog Artist with HSPICE The original document link is http://www.eda.ncsu.edu/wiki/tutorial:analog_artist_with_hspice This tutorial will introduce you to the Cadence Environment: specifically
CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #2, Schematic Capture, DC Analysis, Transient Analysis (Inverter, NAND2)
 CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #2, Schematic Capture, DC Analysis, Transient Analysis (Inverter, NAND2) Joel Wilder, Aleksandar Milenkovic, ECE Dept., The University of Alabama in Huntsville
CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: Tutorial #2, Schematic Capture, DC Analysis, Transient Analysis (Inverter, NAND2) Joel Wilder, Aleksandar Milenkovic, ECE Dept., The University of Alabama in Huntsville
Cadence Schematic Tutorial. EEE5320/EEE4306 Fall 2015 University of Florida ECE
 Cadence Schematic Tutorial EEE5320/EEE4306 Fall 2015 University of Florida ECE 1 Remote access You may access the Linux server directly from the NEB Computer Lab using your GatorLink username and password.
Cadence Schematic Tutorial EEE5320/EEE4306 Fall 2015 University of Florida ECE 1 Remote access You may access the Linux server directly from the NEB Computer Lab using your GatorLink username and password.
EE 330 Spring 2018 Laboratory 2: Basic Boolean Circuits
 EE 330 Spring 2018 Laboratory 2: Basic Boolean Circuits Contents Objective:... 2 Part 1: Introduction... 2 Part 2 Simulation of a CMOS Inverter... 3 Part 2.1 Attaching technology information... 3 Part
EE 330 Spring 2018 Laboratory 2: Basic Boolean Circuits Contents Objective:... 2 Part 1: Introduction... 2 Part 2 Simulation of a CMOS Inverter... 3 Part 2.1 Attaching technology information... 3 Part
EE 330 Spring Laboratory 2: Basic Boolean Circuits
 EE 330 Spring 2013 Laboratory 2: Basic Boolean Circuits Objective: The objective of this experiment is to investigate methods for evaluating the performance of Boolean circuits. Emphasis will be placed
EE 330 Spring 2013 Laboratory 2: Basic Boolean Circuits Objective: The objective of this experiment is to investigate methods for evaluating the performance of Boolean circuits. Emphasis will be placed
HOMEWORK 9 CMPEN 411 Due: 4/12/ :30pm
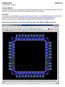 HOMEWORK 9 CMPEN 411 Due: 4/12/2016 11:30pm Learning Objective Complete the full 8 bit RISC microprocessor chip design by placing the processor core design into the 40 pin 'tiny' chip pad frame. Do verify
HOMEWORK 9 CMPEN 411 Due: 4/12/2016 11:30pm Learning Objective Complete the full 8 bit RISC microprocessor chip design by placing the processor core design into the 40 pin 'tiny' chip pad frame. Do verify
DRC and LVS checks using Cadence Virtuoso Version 2.0
 DRC and LVS checks using Cadence Virtuoso Version 2.0 Start virtuoso l l Open a virtuoso session in the directory which contains the required cds.lib and lib.def files. Command : virtuoso & Open the layout
DRC and LVS checks using Cadence Virtuoso Version 2.0 Start virtuoso l l Open a virtuoso session in the directory which contains the required cds.lib and lib.def files. Command : virtuoso & Open the layout
Creating Verilog Tutorial Netlist Release Date: 01/13/2005(Version 2)
 Creating Verilog Tutorial 2-1 - Creating a verilog netlist for a schematic: The verilog netlist is necessary for automatic layout (placement and routing) tools. It contains information about the I/O pins
Creating Verilog Tutorial 2-1 - Creating a verilog netlist for a schematic: The verilog netlist is necessary for automatic layout (placement and routing) tools. It contains information about the I/O pins
EE5323/5324 VLSI Design I/II using Cadence
 1 of 18 2009-1-23 23:58 Spring 2009: EE5323/5324 VLSI Design I/II using Cadence This tutorial has been adapted from EE5323 offered in Fall 2007. Thanks to Jie Gu, Prof. Chris Kim and Satish Sivaswamy of
1 of 18 2009-1-23 23:58 Spring 2009: EE5323/5324 VLSI Design I/II using Cadence This tutorial has been adapted from EE5323 offered in Fall 2007. Thanks to Jie Gu, Prof. Chris Kim and Satish Sivaswamy of
EDA-BASED DESIGN PRACTICAL LABORATORY SESSION No. 3
 LABORATOIRE DE SYSTEMES MICROELECTRONIQUES EPFL STI IMM LSM ELD Station nº 11 CH-1015 Lausanne Téléphone : Fax : E-mail : Site web : +4121 693 6955 +4121 693 6959 lsm@epfl.ch lsm.epfl.ch EDA-BASED DESIGN
LABORATOIRE DE SYSTEMES MICROELECTRONIQUES EPFL STI IMM LSM ELD Station nº 11 CH-1015 Lausanne Téléphone : Fax : E-mail : Site web : +4121 693 6955 +4121 693 6959 lsm@epfl.ch lsm.epfl.ch EDA-BASED DESIGN
INTRODUCTION TO MENTOR GRAPHICS DESIGN TOOLS
 INTRODUCTION TO MENTOR GRAPHICS DESIGN TOOLS 1. RUNNING MENTOR GRAPHICS Erdem S. Erdogan 09.13.2006 Note: These commands can be run remotely via ssh to one of the DSIL machines. If running remotely, ignore
INTRODUCTION TO MENTOR GRAPHICS DESIGN TOOLS 1. RUNNING MENTOR GRAPHICS Erdem S. Erdogan 09.13.2006 Note: These commands can be run remotely via ssh to one of the DSIL machines. If running remotely, ignore
Cadence On-Line Document
 Cadence On-Line Document 1 Purpose: Use Cadence On-Line Document to look up command/syntax in SoC Encounter. 2 Cadence On-Line Document An on-line searching system which can be used to inquire about LEF/DEF
Cadence On-Line Document 1 Purpose: Use Cadence On-Line Document to look up command/syntax in SoC Encounter. 2 Cadence On-Line Document An on-line searching system which can be used to inquire about LEF/DEF
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Lab #2: Layout and Simulation
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Lab #2: Layout and Simulation NTU IC541CA 1 Assumed Knowledge This lab assumes use of the Electric
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Lab #2: Layout and Simulation NTU IC541CA 1 Assumed Knowledge This lab assumes use of the Electric
ECE471/571 Energy Ecient VLSI Design
 ECE471/571 Energy Ecient VLSI Design Project 2 Cadence Setup and Creation of an Inverter Due Date 11:30pm on Friday, January 30 th 2015 Introduction This project will rst walk you through the setup for
ECE471/571 Energy Ecient VLSI Design Project 2 Cadence Setup and Creation of an Inverter Due Date 11:30pm on Friday, January 30 th 2015 Introduction This project will rst walk you through the setup for
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, DAVIS Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. EEC180A DIGITAL SYSTEMS I Winter 2015
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, DAVIS Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EEC180A DIGITAL SYSTEMS I Winter 2015 LAB 1: Introduction to Quartus II Schematic Capture and ModelSim Simulation This
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, DAVIS Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EEC180A DIGITAL SYSTEMS I Winter 2015 LAB 1: Introduction to Quartus II Schematic Capture and ModelSim Simulation This
Actel Libero TM Integrated Design Environment v2.3 Structural Schematic Flow Design Tutorial
 Actel Libero TM Integrated Design Environment v2.3 Structural Schematic Flow Design Tutorial 1 Table of Contents Design Flow in Libero TM IDE v2.3 Step 1 - Design Creation 3 Step 2 - Design Verification
Actel Libero TM Integrated Design Environment v2.3 Structural Schematic Flow Design Tutorial 1 Table of Contents Design Flow in Libero TM IDE v2.3 Step 1 - Design Creation 3 Step 2 - Design Verification
Tutorial 2 Automatic Placement & Routing
 Tutorial 2 Automatic Placement & Routing Please follow the instructions found under Setup on the CADTA main page before starting this tutorial. 1.1. Start Encounter Log on to a VLSI server using your EE
Tutorial 2 Automatic Placement & Routing Please follow the instructions found under Setup on the CADTA main page before starting this tutorial. 1.1. Start Encounter Log on to a VLSI server using your EE
ECE471/571 Energy Efficient VLSI Design Project 2 Cadence Setup and Creation of an Inverter Due Date 11:30 am on Friday, February 2 nd, 2018
 ECE471/571 Energy Efficient VLSI Design Project 2 Cadence Setup and Creation of an Inverter Due Date 11:30 am on Friday, February 2 nd, 2018 Introduction This project will first walk you through the setup
ECE471/571 Energy Efficient VLSI Design Project 2 Cadence Setup and Creation of an Inverter Due Date 11:30 am on Friday, February 2 nd, 2018 Introduction This project will first walk you through the setup
CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: VHDL design simulation, synthesis, and ASIC flow, Laboratory #8,
 CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: VHDL design simulation, synthesis, and ASIC flow, Laboratory #8, Joel Wilder and Aleksandar Milenkovic, ECE Dept., The University of Alabama in Huntsville 1. INTRODUCTION
CPE/EE 427, CPE 527, VLSI Design I: VHDL design simulation, synthesis, and ASIC flow, Laboratory #8, Joel Wilder and Aleksandar Milenkovic, ECE Dept., The University of Alabama in Huntsville 1. INTRODUCTION
EET2141 Project 2: Binary Adder Using Xilinx 7.1i Due Friday April 25
 EET2141 Project 2: Binary Adder Using Xilinx 7.1i Due Friday April 25 Introduction This Xilinx project introduces the characteristics of the ripple carry adder. From the last project, you learned that
EET2141 Project 2: Binary Adder Using Xilinx 7.1i Due Friday April 25 Introduction This Xilinx project introduces the characteristics of the ripple carry adder. From the last project, you learned that
HOMEWORK 10 CMPEN 411 Due: 4/28/ :30pm
 HOMEWORK 10 CMPEN 411 Due: 4/28/2016 11:30pm Instruction First, fabrication ready the full 8 bit RISC microprocessor chip: redesign the chip (its components) to fit the entire chip fitted into the 40 pin
HOMEWORK 10 CMPEN 411 Due: 4/28/2016 11:30pm Instruction First, fabrication ready the full 8 bit RISC microprocessor chip: redesign the chip (its components) to fit the entire chip fitted into the 40 pin
Lab 1: Cadence Custom IC design tools- Setup, Schematic capture and simulation
 Lab 1: Cadence Custom IC design tools- Setup, Schematic capture and simulation Brittany Duffy EE 330- Integrated Electronics Lab Section B Professor Randy Geiger 1/24/13 Introduction The main goal of this
Lab 1: Cadence Custom IC design tools- Setup, Schematic capture and simulation Brittany Duffy EE 330- Integrated Electronics Lab Section B Professor Randy Geiger 1/24/13 Introduction The main goal of this
EE 330 Fall 2017 Lab 1: Cadence Custom IC design tools - Setup, Schematic capture and simulation
 EE 330 Fall 2017 Lab 1: Cadence Custom IC design tools - Setup, Schematic capture and simulation Table of Contents Objective... 2 1. Setup... 2 Set Bash Shell for the account... 2 2. Starting Cadence Custom
EE 330 Fall 2017 Lab 1: Cadence Custom IC design tools - Setup, Schematic capture and simulation Table of Contents Objective... 2 1. Setup... 2 Set Bash Shell for the account... 2 2. Starting Cadence Custom
Cadence Tutorial D: Using Design Variables and Parametric Analysis Document Contents Introduction Using Design Variables Apply Apply
 Cadence Tutorial D: Using Design Variables and Parametric Analysis Created for the MSU VLSI program by Casey Wallace Last Updated by: Patrick O Hara SS15 Document Contents Introduction Using Design Variables
Cadence Tutorial D: Using Design Variables and Parametric Analysis Created for the MSU VLSI program by Casey Wallace Last Updated by: Patrick O Hara SS15 Document Contents Introduction Using Design Variables
EE 330 Spring 2018 Lab 1: Cadence Custom IC design tools Setup, Schematic capture and simulation
 EE 330 Spring 2018 Lab 1: Cadence Custom IC design tools Setup, Schematic capture and simulation Table of Contents Objective... 2 1. Setup... 2 Set Bash Shell for the account... 2 2. Starting Cadence Custom
EE 330 Spring 2018 Lab 1: Cadence Custom IC design tools Setup, Schematic capture and simulation Table of Contents Objective... 2 1. Setup... 2 Set Bash Shell for the account... 2 2. Starting Cadence Custom
HOMEWORK 2 CMPEN 411 Due: 1/31/ :30pm
 HOMEWORK 2 CMPEN 411 Due: 1/31/2011 11:30pm Learning Objective Learn the VLSI CAD tools and chip design concepts by designing 8-bit Ripple Carry Adder (RCA). Instruction Design 8-bit Ripple Carry Adder
HOMEWORK 2 CMPEN 411 Due: 1/31/2011 11:30pm Learning Objective Learn the VLSI CAD tools and chip design concepts by designing 8-bit Ripple Carry Adder (RCA). Instruction Design 8-bit Ripple Carry Adder
CS/EE 6710 Digital VLSI Design Tutorial on Cadence to Synopsys Interface (CSI)
 CS/EE 6710 Digital VLSI Design Tutorial on Cadence to Synopsys Interface (CSI) This tutorial walks you through the Cadence to Synopsys Interface (CSI). This interface lets you take a schematic from composer
CS/EE 6710 Digital VLSI Design Tutorial on Cadence to Synopsys Interface (CSI) This tutorial walks you through the Cadence to Synopsys Interface (CSI). This interface lets you take a schematic from composer
A. Setting Up the Environment a. ~/ece394 % mkdir synopsys b.
 ECE 394 ASIC & FPGA Design Synopsys Design Compiler and Design Analyzer Tutorial A. Setting Up the Environment a. Create a new folder (i.e. synopsys) under your ece394 directory ~/ece394 % mkdir synopsys
ECE 394 ASIC & FPGA Design Synopsys Design Compiler and Design Analyzer Tutorial A. Setting Up the Environment a. Create a new folder (i.e. synopsys) under your ece394 directory ~/ece394 % mkdir synopsys
An Overview of Standard Cell Based Digital VLSI Design
 An Overview of Standard Cell Based Digital VLSI Design With examples taken from the implementation of the 36-core AsAP1 chip and the 1000-core KiloCore chip Zhiyi Yu, Tinoosh Mohsenin, Aaron Stillmaker,
An Overview of Standard Cell Based Digital VLSI Design With examples taken from the implementation of the 36-core AsAP1 chip and the 1000-core KiloCore chip Zhiyi Yu, Tinoosh Mohsenin, Aaron Stillmaker,
Part B. Dengxue Yan Washington University in St. Louis
 Tools Tutorials Part B Dengxue Yan Washington University in St. Louis Tools mainly used in this class Synopsys VCS Simulation Synopsys Design Compiler Generate gate-level netlist Cadence Encounter placing
Tools Tutorials Part B Dengxue Yan Washington University in St. Louis Tools mainly used in this class Synopsys VCS Simulation Synopsys Design Compiler Generate gate-level netlist Cadence Encounter placing
DOWNLOAD PDF CADENCE WAVEFORM CALCULATOR USER GUIDE
 Chapter 1 : CSE / Cadence Tutorial The Cadence Design Communities support Cadence users and technologists interacting to exchange ideas, news, technical information, and best practices to solve problems
Chapter 1 : CSE / Cadence Tutorial The Cadence Design Communities support Cadence users and technologists interacting to exchange ideas, news, technical information, and best practices to solve problems
Place & Route Tutorial #1
 Place & Route Tutorial #1 In this tutorial you will use Synopsys IC Compiler (ICC) to place, route, and analyze the timing and wirelength of two simple designs. This tutorial assumes that you have worked
Place & Route Tutorial #1 In this tutorial you will use Synopsys IC Compiler (ICC) to place, route, and analyze the timing and wirelength of two simple designs. This tutorial assumes that you have worked
More information can be found in the Cadence manuals Virtuoso Layout Editor User Guide and Cadence Hierarchy Editor User Guide.
 Chapter 6 Building with Layout This chapter consists of two parts. The first describes the generation of layout views and the second deals with the various tools used for verifying the layout, both physical
Chapter 6 Building with Layout This chapter consists of two parts. The first describes the generation of layout views and the second deals with the various tools used for verifying the layout, both physical
VIVADO TUTORIAL- TIMING AND POWER ANALYSIS
 VIVADO TUTORIAL- TIMING AND POWER ANALYSIS IMPORTING THE PROJECT FROM ISE TO VIVADO Initially for migrating the same project which we did in ISE 14.7 to Vivado 2016.1 you will need to follow the steps
VIVADO TUTORIAL- TIMING AND POWER ANALYSIS IMPORTING THE PROJECT FROM ISE TO VIVADO Initially for migrating the same project which we did in ISE 14.7 to Vivado 2016.1 you will need to follow the steps
EE115C Digital Electronic Circuits. Tutorial 4: Schematic-driven Layout (Virtuoso XL)
 EE115C Digital Electronic Circuits Tutorial 4: Schematic-driven Layout (Virtuoso XL) This tutorial will demonstrate schematic-driven layout on the example of a 2-input NAND gate. Simple Layout (that won
EE115C Digital Electronic Circuits Tutorial 4: Schematic-driven Layout (Virtuoso XL) This tutorial will demonstrate schematic-driven layout on the example of a 2-input NAND gate. Simple Layout (that won
Cadence Tutorial: Schematic Entry and Circuit Simulation of a CMOS Inverter
 Cadence Tutorial: Schematic Entry and Circuit Simulation of a CMOS Inverter Introduction This tutorial describes the steps involved in the design and simulation of a CMOS inverter using the Cadence Virtuoso
Cadence Tutorial: Schematic Entry and Circuit Simulation of a CMOS Inverter Introduction This tutorial describes the steps involved in the design and simulation of a CMOS inverter using the Cadence Virtuoso
Speaker: Shao-Wei Feng Adviser: Prof. An-Yeu Wu Date: 2010/09/28
 99-1 Under-Graduate Project Verilog Simulation & Debugging Tools Speaker: Shao-Wei Feng Adviser: Prof. An-Yeu Wu Date: 2010/09/28 ACCESS IC LAB Outline Basic Concept of Verilog HDL Gate Level Modeling
99-1 Under-Graduate Project Verilog Simulation & Debugging Tools Speaker: Shao-Wei Feng Adviser: Prof. An-Yeu Wu Date: 2010/09/28 ACCESS IC LAB Outline Basic Concept of Verilog HDL Gate Level Modeling
ENEE245 Digital Circuits and Systems Lab Manual
 ENEE245 Digital Circuits and Systems Lab Manual Department of Engineering, Physical & Computer Sciences Montgomery College Modified Fall 2017 Copyright Prof. Lan Xiang (Do not distribute without permission)
ENEE245 Digital Circuits and Systems Lab Manual Department of Engineering, Physical & Computer Sciences Montgomery College Modified Fall 2017 Copyright Prof. Lan Xiang (Do not distribute without permission)
EE115C Digital Electronic Circuits. Tutorial 2: Hierarchical Schematic and Simulation
 EE115C Digital Electronic Circuits Tutorial 2: Hierarchical Schematic and Simulation The objectives are to become familiar with Virtuoso schematic editor, learn how to create the symbol view of basic primitives,
EE115C Digital Electronic Circuits Tutorial 2: Hierarchical Schematic and Simulation The objectives are to become familiar with Virtuoso schematic editor, learn how to create the symbol view of basic primitives,
ECE 331: Electronics Principles I Fall 2014
 ECE 331: Electronics Principles I Fall 2014 Lab #0: Introduction to Computer Modeling and Laboratory Measurements Report due at your registered lab period on the week of Sept. 8-12 Week 1 Accessing Linux
ECE 331: Electronics Principles I Fall 2014 Lab #0: Introduction to Computer Modeling and Laboratory Measurements Report due at your registered lab period on the week of Sept. 8-12 Week 1 Accessing Linux
Graphics: Alexandra Nolte, Gesine Marwedel, Universität Dortmund. RTL Synthesis
 Graphics: Alexandra Nolte, Gesine Marwedel, 2003 Universität Dortmund RTL Synthesis Purpose of HDLs Purpose of Hardware Description Languages: Capture design in Register Transfer Language form i.e. All
Graphics: Alexandra Nolte, Gesine Marwedel, 2003 Universität Dortmund RTL Synthesis Purpose of HDLs Purpose of Hardware Description Languages: Capture design in Register Transfer Language form i.e. All
