CSE 2021 Computer Organization. Hugh Chesser, CSEB 1012U W9-W
|
|
|
- Tabitha Singleton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CSE 22 Computer Organization Hugh Chesser, CSEB 2U
2 Agenda Topics:. Single Cycle Review (Sample Exam/Quiz Q) 2. ultiple cycle implementation Patterson: Section 4.5 Reminder: Quiz #2 Next Wednesday (November ) 2
3 ain Control (4) 4 Add [3 26] Control RegDst Branch em emtoreg Op em Src Reg Shift left 2 Add result PCSrc PC address memory [3 ] [25 2] [2 6] [5 ] [5 ] 2 Registers 2 6 Sign 32 extend control Zero result Address Data memory [5 ] 3
4 Activity (Sample Quiz, Exam Q) We wish to add jr(jump ) to the single cycle pathfrom the previous slide. Add the necessary connections to the single cycle pathblock diagram to implement the jrinstruction. Also, append the table below to add the necessary control signals needed for the jr instruction. RegDst Src emtoreg Reg em em Branch Op Op R-format lw sw beq 4
5 Answer (Part ): odify the path as shown 5
6 Answer (Part 2): append the table below to add the necessary control signals needed for the jr instruction. RegDst Src emtoreg Reg em em Branch JumpReg Op Op R-format lw sw beq jr 6
7 Why single-cycle implementation is not used? Assuming no delay at adder, sign extension unit, shift left unit, PC, control unit, and U: Load cycle requires 5 functional units: instruction fetch, access,, memory access, access Store cycle requires 4 functional units: instruction fetch, access,, memory access R-type instruction cycle requires 4 functional units: instruction fetch, access,, access Path for a branch instruction requires 3 functional units: instruction fetch, access, Path for a jump instruction requires functional unit: instruction fetch Using a clock cycle of equal duration for each instruction is a waste of resources. 7
8 Why ulticycle? Example: Assume that the operation times for major functional unit in a microprocessor are: emory unit ~ 2ns, and adders ~ 2ns, Register file ~ ns Compare the performance of the following instruction mix Loads: 24%; Stores: 2%; instructions: 44%; Branches: 8%; Jumps: 2% on the two implementations Implementation I: All instructions operate in clock cycle Implementation II: Each instruction is as long as it needs to be. Class Functional units used (Steps involved) type fetch Register Access Register Access 6ns Load word fetch Register Access emory Access Register Access 8ns Store word fetch Register Access emory Access 7ns Branch fetch Register Access 5ns Branch fetch 2ns Average time per instruction: Implementation : ~ 8ns Implementation 2: ~.24(8)+.2(7)+.44(6)+.8(5)+.2(2) = 6.34ns 8
9 ulticycle Implementation : Execution of each instruction is broken into different steps Each step requires clock cycle Each instruction takes multiple clock cycles Functional Unit: Can be used more than once in an instruction (but still only once in a clock cycle) Advantages: Functional units can be shared and adder is combined Single memory is used for instructions and 9
10 ulticycle Implementation: Abstract Diagram PC Address emory Data or emory Data Register # Registers Register # Register # A B Out One is used for incrementing PC and for arithmetic operations Data memory and memory are combined 5 additional s are added. An instruction (IR) to hold instructions before distributing to file or 2. A memory (DR) to hold before distributing to file or 3. Registers A and B that hold before the 4. Register out that hold computed by
11 ulticycle Implementation: ultiplexers added PC u x Address emory emdata [25 2] [2 6] [5 ] [5 ] emory [5 ] u x u x 6 2 Registers Sign extend 2 32 Shift left 2 A B 4 u x u 2 x 3 Zero result Out Because functional units are shared, multiplexers are added to select between different devices. U before memory selects either the PC output (fetch instruction) or output (storing ) 2. U before write selects write- number (instruction [5-] or instruction[2-6]) 3. U before write selects from Out (R-type instruction) or emdata (lw instruction) 4. Upper U before selects PC output (increment PC) or (R-type instruction) 5. Lower U before selects 2, or sign extended instruction[5-] or shift left sign extended instruction[5-], or 4
12 ulticycle Implementation: Controls added IorD em em IR RegDst Reg SrcA PC Address emory emdata [25 2] [2 6] [5 ] [5 ] [5 ] 2 Registers 2 A B Zero result Out emory 6 Sign extend 32 Shift left 2 control [5 ] emtoreg SrcB Op Because functional units are shared, multiplexers are added to select between different devices. U before memory selects either the PC output (fetch instruction) or output (storing ) 2. U before write selects write- number (instruction [5-] or instruction[2-6]) 2
13 ulticycle Implementation: Control Units added PC Address emory emdata [3-26] [25 2] [2 6] [5 ] [5 ] PCCond PC IorD em em emtoreg IR [25 ] [5 ] Outputs Control Op [5 ] PCSource Op SrcB SrcA Reg RegDst 2 Registers 2 A B Shift 28 left 2 PC [3-28] Zero result Jump address [3-] Out 2 emory 6 Sign extend 32 Shift left 2 control [5 ] 3
14 Action of -bit Control Signals Control Input IorD em em IR RegDst Reg SrcA emtoreg PC PCCond PC supplies address to memory (instruction fetch) None None None None Effect when Deasserted () Register specified by [2-6] (lw) PC is the first operand in (increment PC) Data of the file comes from Out Operation at PC depends on PCCond and zero output of Operation at PC depends on PC Effect when asserted () out supplies address to memory (lw/sw) emory content specified by address is placed on em o/p (lw/any instruction) I/p is stored at specified address (sw) emdata o/p is written on IR (instruction fetch) Register specified by [5-] (R-type) Data from Data i/p is written on the specified by Register number Register A is the first operand in Data of the file comes from DR PC is written; Source is determined by PCSource PC is written if zero o/p of = ; Source is determined by PCSource 4
15 Action of 2-bit Control Signals Control Input Op SrcB PCSource Value performs an add operation performs a subtract operation The second operand of = 4 The second operand of is sign extended [5-] The second operand of is sign extended, 2-bit left shifted [5- ] Output of (PC + 4) is sent to PC Effect The function field of defines the operation of The second operand of comes from Register B Contents of Out (branch target address = PC x offset) is sent to PC Contents of [25-], shift left by 2, and concatenated with the SB 4- bits of PC is sent to PC (jump instruction) 5
CSE 2021 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION
 CSE 22 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION HUGH CHESSER CHESSER HUGH CSEB 2U 2U CSEB Agenda Topics:. Sample Exam/Quiz Q - Review 2. Multiple cycle implementation Patterson: Section 4.5 Reminder: Quiz #2 Next Wednesday
CSE 22 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION HUGH CHESSER CHESSER HUGH CSEB 2U 2U CSEB Agenda Topics:. Sample Exam/Quiz Q - Review 2. Multiple cycle implementation Patterson: Section 4.5 Reminder: Quiz #2 Next Wednesday
CSE 2021 Computer Organization. Hugh Chesser, CSEB 1012U W12-M
 CSE 22 Computer Organization Hugh Chesser, CSEB 2U W2- Graphical Representation Time 2 6 8 add $s, $t, $t IF ID E E Decode / Execute emory Back fetch from / stage into the instruction register file. Shading
CSE 22 Computer Organization Hugh Chesser, CSEB 2U W2- Graphical Representation Time 2 6 8 add $s, $t, $t IF ID E E Decode / Execute emory Back fetch from / stage into the instruction register file. Shading
CSE 2021 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION
 CSE 2021 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION HUGH LAS CHESSER 1012U HUGH CHESSER CSEB 1012U W10-M Agenda Topics: 1. Multiple cycle implementation review 2. State Machine 3. Control Unit implementation for Multi-cycle
CSE 2021 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION HUGH LAS CHESSER 1012U HUGH CHESSER CSEB 1012U W10-M Agenda Topics: 1. Multiple cycle implementation review 2. State Machine 3. Control Unit implementation for Multi-cycle
CSE 2021 Computer Organization. Hugh Chesser, CSEB 1012U W10-M
 CSE 22 Computer Organization Hugh Chesser, CSEB 2U Agenda Topics:. ultiple cycle implementation - complete Patterson: Appendix C, D 2 Breaking the Execution into Clock Cycles Execution of each instruction
CSE 22 Computer Organization Hugh Chesser, CSEB 2U Agenda Topics:. ultiple cycle implementation - complete Patterson: Appendix C, D 2 Breaking the Execution into Clock Cycles Execution of each instruction
ECE 313 Computer Organization EXAM 2 November 9, 2001
 ECE 33 Computer Organization EA 2 November 9, 2 This exam is open book and open notes. You have 5 minutes. Credit for problems requiring calculation will be given only if you show your work. Choose and
ECE 33 Computer Organization EA 2 November 9, 2 This exam is open book and open notes. You have 5 minutes. Credit for problems requiring calculation will be given only if you show your work. Choose and
Lecture 5: The Processor
 Lecture 5: The Processor CSCE 26 Computer Organization Instructor: Saraju P. ohanty, Ph. D. NOTE: The figures, text etc included in slides are borrowed from various books, websites, authors pages, and
Lecture 5: The Processor CSCE 26 Computer Organization Instructor: Saraju P. ohanty, Ph. D. NOTE: The figures, text etc included in slides are borrowed from various books, websites, authors pages, and
comp 180 Lecture 25 Outline of Lecture The ALU Control Operation & Design The Datapath Control Operation & Design HKUST 1 Computer Science
 Outline of Lecture The Control Operation & Design The Datapath Control Operation & Design HKST 1 Computer Science Control After the design of partial single IPS datapath, we need to add the control unit
Outline of Lecture The Control Operation & Design The Datapath Control Operation & Design HKST 1 Computer Science Control After the design of partial single IPS datapath, we need to add the control unit
Multi-cycle Approach. Single cycle CPU. Multi-cycle CPU. Requires state elements to hold intermediate values. one clock cycle or instruction
 Multi-cycle Approach Single cycle CPU State element Combinational logic State element clock one clock cycle or instruction Multi-cycle CPU Requires state elements to hold intermediate values State Element
Multi-cycle Approach Single cycle CPU State element Combinational logic State element clock one clock cycle or instruction Multi-cycle CPU Requires state elements to hold intermediate values State Element
CO Computer Architecture and Programming Languages CAPL. Lecture 18 & 19
 CO2-3224 Computer Architecture and Programming Languages CAPL Lecture 8 & 9 Dr. Kinga Lipskoch Fall 27 Single Cycle Disadvantages & Advantages Uses the clock cycle inefficiently the clock cycle must be
CO2-3224 Computer Architecture and Programming Languages CAPL Lecture 8 & 9 Dr. Kinga Lipskoch Fall 27 Single Cycle Disadvantages & Advantages Uses the clock cycle inefficiently the clock cycle must be
Processor Design CSCE Instructor: Saraju P. Mohanty, Ph. D. NOTE: The figures, text etc included in slides are borrowed
 Lecture 3: General Purpose Processor Design CSCE 665 Advanced VLSI Systems Instructor: Saraju P. ohanty, Ph. D. NOTE: The figures, tet etc included in slides are borrowed from various books, websites,
Lecture 3: General Purpose Processor Design CSCE 665 Advanced VLSI Systems Instructor: Saraju P. ohanty, Ph. D. NOTE: The figures, tet etc included in slides are borrowed from various books, websites,
CPE 335. Basic MIPS Architecture Part II
 CPE 335 Computer Organization Basic MIPS Architecture Part II Dr. Iyad Jafar Adapted from Dr. Gheith Abandah slides http://www.abandah.com/gheith/courses/cpe335_s08/index.html CPE232 Basic MIPS Architecture
CPE 335 Computer Organization Basic MIPS Architecture Part II Dr. Iyad Jafar Adapted from Dr. Gheith Abandah slides http://www.abandah.com/gheith/courses/cpe335_s08/index.html CPE232 Basic MIPS Architecture
Multiple Cycle Data Path
 Multiple Cycle Data Path CS 365 Lecture 7 Prof. Yih Huang CS365 1 Multicycle Approach Break up the instructions into steps, each step takes a cycle balance the amount of work to be done restrict each cycle
Multiple Cycle Data Path CS 365 Lecture 7 Prof. Yih Huang CS365 1 Multicycle Approach Break up the instructions into steps, each step takes a cycle balance the amount of work to be done restrict each cycle
RISC Design: Multi-Cycle Implementation
 RISC Design: Multi-Cycle Implementation Virendra Singh Associate Professor Computer Architecture and Dependable Systems Lab Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay http://www.ee.iitb.ac.in/~viren/
RISC Design: Multi-Cycle Implementation Virendra Singh Associate Professor Computer Architecture and Dependable Systems Lab Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay http://www.ee.iitb.ac.in/~viren/
ECE473 Computer Architecture and Organization. Processor: Combined Datapath
 Computer Architecture and Organization Processor: Combined path Lecturer: Prof. Yifeng Zhu Fall, 2014 Portions of these slides are derived from: Dave Patterson CB 1 Where are we? Want to build a processor
Computer Architecture and Organization Processor: Combined path Lecturer: Prof. Yifeng Zhu Fall, 2014 Portions of these slides are derived from: Dave Patterson CB 1 Where are we? Want to build a processor
Computer Science 141 Computing Hardware
 Computer Science 4 Computing Hardware Fall 6 Harvard University Instructor: Prof. David Brooks dbrooks@eecs.harvard.edu Upcoming topics Mon, Nov th MIPS Basic Architecture (Part ) Wed, Nov th Basic Computer
Computer Science 4 Computing Hardware Fall 6 Harvard University Instructor: Prof. David Brooks dbrooks@eecs.harvard.edu Upcoming topics Mon, Nov th MIPS Basic Architecture (Part ) Wed, Nov th Basic Computer
Processor: Multi- Cycle Datapath & Control
 Processor: Multi- Cycle Datapath & Control (Based on text: David A. Patterson & John L. Hennessy, Computer Organization and Design: The Hardware/Software Interface, 3 rd Ed., Morgan Kaufmann, 27) COURSE
Processor: Multi- Cycle Datapath & Control (Based on text: David A. Patterson & John L. Hennessy, Computer Organization and Design: The Hardware/Software Interface, 3 rd Ed., Morgan Kaufmann, 27) COURSE
Computer Organization & Design The Hardware/Software Interface Chapter 5 The processor : Datapath and control
 Computer Organization & Design The Hardware/Software Interface Chapter 5 The processor : Datapath and control Qing-song Shi http://.24.26.3 Email: zjsqs@zju.edu.cn Chapter 5 The processor : Datapath and
Computer Organization & Design The Hardware/Software Interface Chapter 5 The processor : Datapath and control Qing-song Shi http://.24.26.3 Email: zjsqs@zju.edu.cn Chapter 5 The processor : Datapath and
LECTURE 6. Multi-Cycle Datapath and Control
 LECTURE 6 Multi-Cycle Datapath and Control SINGLE-CYCLE IMPLEMENTATION As we ve seen, single-cycle implementation, although easy to implement, could potentially be very inefficient. In single-cycle, we
LECTURE 6 Multi-Cycle Datapath and Control SINGLE-CYCLE IMPLEMENTATION As we ve seen, single-cycle implementation, although easy to implement, could potentially be very inefficient. In single-cycle, we
Processor (multi-cycle)
 CS359: Computer Architecture Processor (multi-cycle) Yanyan Shen Department of Computer Science and Engineering Five Instruction Steps ) Instruction Fetch ) Instruction Decode and Register Fetch 3) R-type
CS359: Computer Architecture Processor (multi-cycle) Yanyan Shen Department of Computer Science and Engineering Five Instruction Steps ) Instruction Fetch ) Instruction Decode and Register Fetch 3) R-type
Midterm. Sticker winners: if you got >= 50 / 67
 CSC258 Week 8 Midterm Class average: 4.2 / 67 (6%) Highest mark: 64.5 / 67 Tests will be return in office hours. Make sure your midterm mark is correct on MarkUs Solution posted on the course website.
CSC258 Week 8 Midterm Class average: 4.2 / 67 (6%) Highest mark: 64.5 / 67 Tests will be return in office hours. Make sure your midterm mark is correct on MarkUs Solution posted on the course website.
CPE 335 Computer Organization. Basic MIPS Architecture Part I
 CPE 335 Computer Organization Basic MIPS Architecture Part I Dr. Iyad Jafar Adapted from Dr. Gheith Abandah slides http://www.abandah.com/gheith/courses/cpe335_s8/index.html CPE232 Basic MIPS Architecture
CPE 335 Computer Organization Basic MIPS Architecture Part I Dr. Iyad Jafar Adapted from Dr. Gheith Abandah slides http://www.abandah.com/gheith/courses/cpe335_s8/index.html CPE232 Basic MIPS Architecture
ECE 313 Computer Organization Name SOLUTION EXAM 2 November 3, Floating Point 20 Points
 ECE Computer Organization Name SOLTION EA November, This exam is open book and open notes. Credit for problems requiring calculation will be given only if you show your work.. Floating Point Points Translate
ECE Computer Organization Name SOLTION EA November, This exam is open book and open notes. Credit for problems requiring calculation will be given only if you show your work.. Floating Point Points Translate
LECTURE 5. Single-Cycle Datapath and Control
 LECTURE 5 Single-Cycle Datapath and Control PROCESSORS In lecture 1, we reminded ourselves that the datapath and control are the two components that come together to be collectively known as the processor.
LECTURE 5 Single-Cycle Datapath and Control PROCESSORS In lecture 1, we reminded ourselves that the datapath and control are the two components that come together to be collectively known as the processor.
The extra single-cycle adders
 lticycle Datapath As an added bons, we can eliminate some of the etra hardware from the single-cycle path. We will restrict orselves to sing each fnctional nit once per cycle, jst like before. Bt since
lticycle Datapath As an added bons, we can eliminate some of the etra hardware from the single-cycle path. We will restrict orselves to sing each fnctional nit once per cycle, jst like before. Bt since
COMP303 - Computer Architecture Lecture 10. Multi-Cycle Design & Exceptions
 COP33 - Computer Architecture Lecture ulti-cycle Design & Exceptions Single Cycle Datapath We designed a processor that requires one cycle per instruction RegDst busw 32 Clk RegWr Rd ux imm6 Rt 5 5 Rs
COP33 - Computer Architecture Lecture ulti-cycle Design & Exceptions Single Cycle Datapath We designed a processor that requires one cycle per instruction RegDst busw 32 Clk RegWr Rd ux imm6 Rt 5 5 Rs
Pipelined Datapath. One register file is enough
 ipelined path The goal of pipelining is to allow multiple instructions execute at the same time We may need to perform several operations in a cycle Increment the and add s at the same time. Fetch one
ipelined path The goal of pipelining is to allow multiple instructions execute at the same time We may need to perform several operations in a cycle Increment the and add s at the same time. Fetch one
Lab 8: Multicycle Processor (Part 1) 0.0
 Lab 8: ulticycle Processor (Part ). Introduction In this lab and the next, you will design and build your own multicycle IPS processor! Your processor should match the design from the text reprinted below
Lab 8: ulticycle Processor (Part ). Introduction In this lab and the next, you will design and build your own multicycle IPS processor! Your processor should match the design from the text reprinted below
Single-Cycle Examples, Multi-Cycle Introduction
 Single-Cycle Examples, ulti-cycle Introduction 1 Today s enu Single cycle examples Single cycle machines vs. multi-cycle machines Why multi-cycle? Comparative performance Physical and Logical Design of
Single-Cycle Examples, ulti-cycle Introduction 1 Today s enu Single cycle examples Single cycle machines vs. multi-cycle machines Why multi-cycle? Comparative performance Physical and Logical Design of
Topic #6. Processor Design
 Topic #6 Processor Design Major Goals! To present the single-cycle implementation and to develop the student's understanding of combinational and clocked sequential circuits and the relationship between
Topic #6 Processor Design Major Goals! To present the single-cycle implementation and to develop the student's understanding of combinational and clocked sequential circuits and the relationship between
Lecture 5 and 6. ICS 152 Computer Systems Architecture. Prof. Juan Luis Aragón
 ICS 152 Computer Systems Architecture Prof. Juan Luis Aragón Lecture 5 and 6 Multicycle Implementation Introduction to Microprogramming Readings: Sections 5.4 and 5.5 1 Review of Last Lecture We have seen
ICS 152 Computer Systems Architecture Prof. Juan Luis Aragón Lecture 5 and 6 Multicycle Implementation Introduction to Microprogramming Readings: Sections 5.4 and 5.5 1 Review of Last Lecture We have seen
Review Multicycle: What is Happening. Controlling The Multicycle Design
 Review lticycle: What is Happening Reslt Zero Op SrcA SrcB Registers Reg Address emory em Data Sign etend Shift left Sorce A B Ot [-6] [5-] [-6] [5-] [5-] Instrction emory IR RegDst emtoreg IorD em em
Review lticycle: What is Happening Reslt Zero Op SrcA SrcB Registers Reg Address emory em Data Sign etend Shift left Sorce A B Ot [-6] [5-] [-6] [5-] [5-] Instrction emory IR RegDst emtoreg IorD em em
EEC 483 Computer Organization
 EEC 483 Compter Organization Chapter 4.4 A Simple Implementation Scheme Chans Y The Big Pictre The Five Classic Components of a Compter Processor Control emory Inpt path Otpt path & Control 2 path and
EEC 483 Compter Organization Chapter 4.4 A Simple Implementation Scheme Chans Y The Big Pictre The Five Classic Components of a Compter Processor Control emory Inpt path Otpt path & Control 2 path and
CC 311- Computer Architecture. The Processor - Control
 CC 311- Computer Architecture The Processor - Control Control Unit Functions: Instruction code Control Unit Control Signals Select operations to be performed (ALU, read/write, etc.) Control data flow (multiplexor
CC 311- Computer Architecture The Processor - Control Control Unit Functions: Instruction code Control Unit Control Signals Select operations to be performed (ALU, read/write, etc.) Control data flow (multiplexor
Multicycle conclusion
 Multicycle conclusion The last few lectures covered a lot of material! We introduced a multicycle datapath, where different instructions take different numbers of cycles to execute. A multicycle unit is
Multicycle conclusion The last few lectures covered a lot of material! We introduced a multicycle datapath, where different instructions take different numbers of cycles to execute. A multicycle unit is
Review: Abstract Implementation View
 Review: Abstract Implementation View Split memory (Harvard) model - single cycle operation Simplified to contain only the instructions: memory-reference instructions: lw, sw arithmetic-logical instructions:
Review: Abstract Implementation View Split memory (Harvard) model - single cycle operation Simplified to contain only the instructions: memory-reference instructions: lw, sw arithmetic-logical instructions:
CSE 2021: Computer Organization Fall 2010 Solution to Assignment # 3: Multicycle Implementation
 CSE 2021: Computer Organization Fall 2010 Solution to Assignment # 3: Multicycle Implementation Note that these questions are taken from the previous final exmas of CSE2021 and should serve as practice
CSE 2021: Computer Organization Fall 2010 Solution to Assignment # 3: Multicycle Implementation Note that these questions are taken from the previous final exmas of CSE2021 and should serve as practice
CSE 141 Computer Architecture Spring Lectures 11 Exceptions and Introduction to Pipelining. Announcements
 CSE 4 Computer Architecture Spring 25 Lectures Exceptions and Introduction to Pipelining May 4, 25 Announcements Reading Assignment Sections 5.6, 5.9 The Processor Datapath and Control Section 6., Enhancing
CSE 4 Computer Architecture Spring 25 Lectures Exceptions and Introduction to Pipelining May 4, 25 Announcements Reading Assignment Sections 5.6, 5.9 The Processor Datapath and Control Section 6., Enhancing
Processor (I) - datapath & control. Hwansoo Han
 Processor (I) - datapath & control Hwansoo Han Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count - Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time - Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two
Processor (I) - datapath & control Hwansoo Han Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count - Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time - Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two
Computer and Information Sciences College / Computer Science Department The Processor: Datapath and Control
 Computer and Information Sciences College / Computer Science Department The Processor: Datapath and Control Chapter 5 The Processor: Datapath and Control Big Picture: Where are We Now? Performance of a
Computer and Information Sciences College / Computer Science Department The Processor: Datapath and Control Chapter 5 The Processor: Datapath and Control Big Picture: Where are We Now? Performance of a
Systems Architecture I
 Systems Architecture I Topics A Simple Implementation of MIPS * A Multicycle Implementation of MIPS ** *This lecture was derived from material in the text (sec. 5.1-5.3). **This lecture was derived from
Systems Architecture I Topics A Simple Implementation of MIPS * A Multicycle Implementation of MIPS ** *This lecture was derived from material in the text (sec. 5.1-5.3). **This lecture was derived from
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 14: One Cycle MIPs Datapath Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB R-Format Instructions Read two register operands Perform
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 14: One Cycle MIPs Datapath Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB R-Format Instructions Read two register operands Perform
Mark Redekopp and Gandhi Puvvada, All rights reserved. EE 357 Unit 15. Single-Cycle CPU Datapath and Control
 EE 37 Unit Single-Cycle CPU path and Control CPU Organization Scope We will build a CPU to implement our subset of the MIPS ISA Memory Reference Instructions: Load Word (LW) Store Word (SW) Arithmetic
EE 37 Unit Single-Cycle CPU path and Control CPU Organization Scope We will build a CPU to implement our subset of the MIPS ISA Memory Reference Instructions: Load Word (LW) Store Word (SW) Arithmetic
CSEN 601: Computer System Architecture Summer 2014
 CSEN 601: Computer System Architecture Summer 2014 Practice Assignment 5 Solutions Exercise 5-1: (Midterm Spring 2013) a. What are the values of the control signals (except ALUOp) for each of the following
CSEN 601: Computer System Architecture Summer 2014 Practice Assignment 5 Solutions Exercise 5-1: (Midterm Spring 2013) a. What are the values of the control signals (except ALUOp) for each of the following
PART I: Adding Instructions to the Datapath. (2 nd Edition):
 EE57 Instrctor: G. Pvvada ===================================================================== Homework #5b De: check on the blackboard =====================================================================
EE57 Instrctor: G. Pvvada ===================================================================== Homework #5b De: check on the blackboard =====================================================================
ELEC 5200/6200 Computer Architecture and Design Spring 2017 Lecture 4: Datapath and Control
 ELEC 52/62 Computer Architecture and Design Spring 217 Lecture 4: Datapath and Control Ujjwal Guin, Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Auburn University, Auburn, AL 36849
ELEC 52/62 Computer Architecture and Design Spring 217 Lecture 4: Datapath and Control Ujjwal Guin, Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Auburn University, Auburn, AL 36849
The Processor. Z. Jerry Shi Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Connecticut. CSE3666: Introduction to Computer Architecture
 The Processor Z. Jerry Shi Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Connecticut CSE3666: Introduction to Computer Architecture Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count
The Processor Z. Jerry Shi Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Connecticut CSE3666: Introduction to Computer Architecture Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count
CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems
 CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Tajana Simunic Rosing Announcements and Outline Check webct grades, make sure everything is there and is correct Pick up graded d homework at
CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Tajana Simunic Rosing Announcements and Outline Check webct grades, make sure everything is there and is correct Pick up graded d homework at
RISC Processor Design
 RISC Processor Design Single Cycle Implementation - MIPS Virendra Singh Indian Institute of Science Bangalore virendra@computer.org Lecture 13 SE-273: Processor Design Feb 07, 2011 SE-273@SERC 1 Courtesy:
RISC Processor Design Single Cycle Implementation - MIPS Virendra Singh Indian Institute of Science Bangalore virendra@computer.org Lecture 13 SE-273: Processor Design Feb 07, 2011 SE-273@SERC 1 Courtesy:
The single-cycle design from last time
 lticycle path Last time we saw a single-cycle path and control nit for or simple IPS-based instrction set. A mlticycle processor fies some shortcomings in the single-cycle CPU. Faster instrctions are not
lticycle path Last time we saw a single-cycle path and control nit for or simple IPS-based instrction set. A mlticycle processor fies some shortcomings in the single-cycle CPU. Faster instrctions are not
ENGN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 04: Single-Cycle Processor Design
 ENGN64: Design of Computing Systems Topic 4: Single-Cycle Processor Design Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University
ENGN64: Design of Computing Systems Topic 4: Single-Cycle Processor Design Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University
Systems Architecture
 Systems Architecture Lecture 15: A Simple Implementation of MIPS Jeremy R. Johnson Anatole D. Ruslanov William M. Mongan Some or all figures from Computer Organization and Design: The Hardware/Software
Systems Architecture Lecture 15: A Simple Implementation of MIPS Jeremy R. Johnson Anatole D. Ruslanov William M. Mongan Some or all figures from Computer Organization and Design: The Hardware/Software
Lecture Topics. Announcements. Today: Single-Cycle Processors (P&H ) Next: continued. Milestone #3 (due 2/9) Milestone #4 (due 2/23)
 Lecture Topics Today: Single-Cycle Processors (P&H 4.1-4.4) Next: continued 1 Announcements Milestone #3 (due 2/9) Milestone #4 (due 2/23) Exam #1 (Wednesday, 2/15) 2 1 Exam #1 Wednesday, 2/15 (3:00-4:20
Lecture Topics Today: Single-Cycle Processors (P&H 4.1-4.4) Next: continued 1 Announcements Milestone #3 (due 2/9) Milestone #4 (due 2/23) Exam #1 (Wednesday, 2/15) 2 1 Exam #1 Wednesday, 2/15 (3:00-4:20
CENG 3420 Lecture 06: Datapath
 CENG 342 Lecture 6: Datapath Bei Yu byu@cse.cuhk.edu.hk CENG342 L6. Spring 27 The Processor: Datapath & Control q We're ready to look at an implementation of the MIPS q Simplified to contain only: memory-reference
CENG 342 Lecture 6: Datapath Bei Yu byu@cse.cuhk.edu.hk CENG342 L6. Spring 27 The Processor: Datapath & Control q We're ready to look at an implementation of the MIPS q Simplified to contain only: memory-reference
Lecture 10 Multi-Cycle Implementation
 Lecture 10 ulti-cycle Implementation 1 Today s enu ulti-cycle machines Why multi-cycle? Comparative performance Physical and Logical Design of Datapath and Control icroprogramming 2 ulti-cycle Solution
Lecture 10 ulti-cycle Implementation 1 Today s enu ulti-cycle machines Why multi-cycle? Comparative performance Physical and Logical Design of Datapath and Control icroprogramming 2 ulti-cycle Solution
Major CPU Design Steps
 Datapath Major CPU Design Steps. Analyze instruction set operations using independent RTN ISA => RTN => datapath requirements. This provides the the required datapath components and how they are connected
Datapath Major CPU Design Steps. Analyze instruction set operations using independent RTN ISA => RTN => datapath requirements. This provides the the required datapath components and how they are connected
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN. The Hardware/Software Interface. Chapter 4. The Processor: A Based on P&H
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface Chapter 4 The Processor: A Based on P&H Introduction We will examine two MIPS implementations A simplified version A more realistic pipelined
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface Chapter 4 The Processor: A Based on P&H Introduction We will examine two MIPS implementations A simplified version A more realistic pipelined
The final datapath. M u x. Add. 4 Add. Shift left 2. PCSrc. RegWrite. MemToR. MemWrite. Read data 1 I [25-21] Instruction. Read. register 1 Read.
![The final datapath. M u x. Add. 4 Add. Shift left 2. PCSrc. RegWrite. MemToR. MemWrite. Read data 1 I [25-21] Instruction. Read. register 1 Read. The final datapath. M u x. Add. 4 Add. Shift left 2. PCSrc. RegWrite. MemToR. MemWrite. Read data 1 I [25-21] Instruction. Read. register 1 Read.](/thumbs/77/75626003.jpg) The final path PC 4 Add Reg Shift left 2 Add PCSrc Instrction [3-] Instrction I [25-2] I [2-6] I [5 - ] register register 2 register 2 Registers ALU Zero Reslt ALUOp em Data emtor RegDst ALUSrc em I [5
The final path PC 4 Add Reg Shift left 2 Add PCSrc Instrction [3-] Instrction I [25-2] I [2-6] I [5 - ] register register 2 register 2 Registers ALU Zero Reslt ALUOp em Data emtor RegDst ALUSrc em I [5
CS3350B Computer Architecture Quiz 3 March 15, 2018
 CS3350B Computer Architecture Quiz 3 March 15, 2018 Student ID number: Student Last Name: Question 1.1 1.2 1.3 2.1 2.2 2.3 Total Marks The quiz consists of two exercises. The expected duration is 30 minutes.
CS3350B Computer Architecture Quiz 3 March 15, 2018 Student ID number: Student Last Name: Question 1.1 1.2 1.3 2.1 2.2 2.3 Total Marks The quiz consists of two exercises. The expected duration is 30 minutes.
CS/COE0447: Computer Organization
 CS/COE0447: Computer Organization and Assembly Language Datapath and Control Sangyeun Cho Dept. of Computer Science A simple MIPS We will design a simple MIPS processor that supports a small instruction
CS/COE0447: Computer Organization and Assembly Language Datapath and Control Sangyeun Cho Dept. of Computer Science A simple MIPS We will design a simple MIPS processor that supports a small instruction
CS/COE0447: Computer Organization
 A simple MIPS CS/COE447: Computer Organization and Assembly Language Datapath and Control Sangyeun Cho Dept. of Computer Science We will design a simple MIPS processor that supports a small instruction
A simple MIPS CS/COE447: Computer Organization and Assembly Language Datapath and Control Sangyeun Cho Dept. of Computer Science We will design a simple MIPS processor that supports a small instruction
CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design. Lecture 06: MIPS Processor - I. Bei Yu
 CENG 342 Computer Organization and Design Lecture 6: MIPS Processor - I Bei Yu CEG342 L6. Spring 26 The Processor: Datapath & Control q We're ready to look at an implementation of the MIPS q Simplified
CENG 342 Computer Organization and Design Lecture 6: MIPS Processor - I Bei Yu CEG342 L6. Spring 26 The Processor: Datapath & Control q We're ready to look at an implementation of the MIPS q Simplified
ﻪﺘﻓﺮﺸﻴﭘ ﺮﺗﻮﻴﭙﻣﺎﻛ يرﺎﻤﻌﻣ MIPS يرﺎﻤﻌﻣ data path and ontrol control
 معماري كامپيوتر پيشرفته معماري MIPS data path and control abbasi@basu.ac.ir Topics Building a datapath support a subset of the MIPS-I instruction-set A single cycle processor datapath all instruction actions
معماري كامپيوتر پيشرفته معماري MIPS data path and control abbasi@basu.ac.ir Topics Building a datapath support a subset of the MIPS-I instruction-set A single cycle processor datapath all instruction actions
Points available Your marks Total 100
 CSSE 3 Computer Architecture I Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology Computer Science and Software Engineering Department Exam Name: Section: 3 This exam is closed book. You are allowed to use the reference
CSSE 3 Computer Architecture I Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology Computer Science and Software Engineering Department Exam Name: Section: 3 This exam is closed book. You are allowed to use the reference
Multicycle Approach. Designing MIPS Processor
 CSE 675.2: Introduction to Computer Architecture Multicycle Approach 8/8/25 Designing MIPS Processor (Multi-Cycle) Presentation H Slides by Gojko Babić and Elsevier Publishing We will be reusing functional
CSE 675.2: Introduction to Computer Architecture Multicycle Approach 8/8/25 Designing MIPS Processor (Multi-Cycle) Presentation H Slides by Gojko Babić and Elsevier Publishing We will be reusing functional
CS2214 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE & ORGANIZATION SPRING 2014
 CS COPTER ARCHITECTRE & ORGANIZATION SPRING DE : arch 6, HOEWORK III READ : i) Related portions of Chapter (except Sections. through.) ii) Related portions of Appendix A iii) Related portions of Appendix
CS COPTER ARCHITECTRE & ORGANIZATION SPRING DE : arch 6, HOEWORK III READ : i) Related portions of Chapter (except Sections. through.) ii) Related portions of Appendix A iii) Related portions of Appendix
Chapter 3 & Appendix C Pipelining Part A: Basic and Intermediate Concepts
 CS359: Computer Architecture Chapter 3 & Appendix C Pipelining Part A: Basic and Intermediate Concepts Yanyan Shen Department of Computer Science and Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University Parallel
CS359: Computer Architecture Chapter 3 & Appendix C Pipelining Part A: Basic and Intermediate Concepts Yanyan Shen Department of Computer Science and Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University Parallel
Note- E~ S. \3 \S U\e. ~ ~s ~. 4. \\ o~ (fw' \i<.t. (~e., 3\0)
 5.4 A Multicycle Implementation 377 Similarly, if we had a machine with more powerful operations and addressing modes, instructions could vary from three or four functional unit delays to tens or even
5.4 A Multicycle Implementation 377 Similarly, if we had a machine with more powerful operations and addressing modes, instructions could vary from three or four functional unit delays to tens or even
ECE 313 Computer Organization FINAL EXAM December 14, This exam is open book and open notes. You have 2 hours.
 This exam is open book and open notes. You have 2 hours. Problems 1-4 refer to a proposed MIPS instruction lwu (load word - update) which implements update addressing an addressing mode that is used in
This exam is open book and open notes. You have 2 hours. Problems 1-4 refer to a proposed MIPS instruction lwu (load word - update) which implements update addressing an addressing mode that is used in
Chapter 5: The Processor: Datapath and Control
 Chapter 5: The Processor: Datapath and Control Overview Logic Design Conventions Building a Datapath and Control Unit Different Implementations of MIPS instruction set A simple implementation of a processor
Chapter 5: The Processor: Datapath and Control Overview Logic Design Conventions Building a Datapath and Control Unit Different Implementations of MIPS instruction set A simple implementation of a processor
Outline. Combinational Element. State (Sequential) Element. Clocking Methodology. Input/Output of Elements
 Outline ombinational Element ombinational & sequential logic Single-cycle PU ulti-cycle PU Examples of ombinational Elements State (Sequential) Element! "#$$$ #$$ #$$ #$ # & & ) *.// * - + #3, * + - locking
Outline ombinational Element ombinational & sequential logic Single-cycle PU ulti-cycle PU Examples of ombinational Elements State (Sequential) Element! "#$$$ #$$ #$$ #$ # & & ) *.// * - + #3, * + - locking
EECS 322 Computer Architecture Improving Memory Access: the Cache
 EECS 322 Computer Architecture Improving emory Access: the Cache Instructor: Francis G. Wolff wolff@eecs.cwru.edu Case Western Reserve University This presentation uses powerpoint animation: please viewshow
EECS 322 Computer Architecture Improving emory Access: the Cache Instructor: Francis G. Wolff wolff@eecs.cwru.edu Case Western Reserve University This presentation uses powerpoint animation: please viewshow
Register Transfer Level (RTL) Design
 CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Register Transfer Level (RTL) Design Instructor: Mohsen Imani Slides from Tajana Simunic Rosing CAPE CAPEs are out!!! https://cape.ucsd.edu/students/
CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Register Transfer Level (RTL) Design Instructor: Mohsen Imani Slides from Tajana Simunic Rosing CAPE CAPEs are out!!! https://cape.ucsd.edu/students/
Chapter 4. The Processor
 Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS implementations A simplified
Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS implementations A simplified
Design of Digital Circuits 2017 Srdjan Capkun Onur Mutlu (Guest starring: Frank K. Gürkaynak and Aanjhan Ranganathan)
 Microarchitecture Design of Digital Circuits 27 Srdjan Capkun Onur Mutlu (Guest starring: Frank K. Gürkaynak and Aanjhan Ranganathan) http://www.syssec.ethz.ch/education/digitaltechnik_7 Adapted from Digital
Microarchitecture Design of Digital Circuits 27 Srdjan Capkun Onur Mutlu (Guest starring: Frank K. Gürkaynak and Aanjhan Ranganathan) http://www.syssec.ethz.ch/education/digitaltechnik_7 Adapted from Digital
The multicycle datapath. Lecture 10 (Wed 10/15/2008) Finite-state machine for the control unit. Implementing the FSM
 Lectre (Wed /5/28) Lab # Hardware De Fri Oct 7 HW #2 IPS programming, de Wed Oct 22 idterm Fri Oct 2 IorD The mlticycle path SrcA Today s objectives: icroprogramming Etending the mlti-cycle path lti-cycle
Lectre (Wed /5/28) Lab # Hardware De Fri Oct 7 HW #2 IPS programming, de Wed Oct 22 idterm Fri Oct 2 IorD The mlticycle path SrcA Today s objectives: icroprogramming Etending the mlti-cycle path lti-cycle
Computer Architecture, IFE CS and T&CS, 4 th sem. Single-Cycle Architecture
 Single-Cycle Architecture Data flow Data flow is synchronized with clock (edge) in sequential systems Architecture Elements - assumptions Program (Instruction) memory: All instructions & buses are 32-bit
Single-Cycle Architecture Data flow Data flow is synchronized with clock (edge) in sequential systems Architecture Elements - assumptions Program (Instruction) memory: All instructions & buses are 32-bit
ENE 334 Microprocessors
 ENE 334 Microprocessors Lecture 6: Datapath and Control : Dejwoot KHAWPARISUTH Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, 3 th & 4 th Edition, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005/2008, Elsevier (MK) http://webstaff.kmutt.ac.th/~dejwoot.kha/
ENE 334 Microprocessors Lecture 6: Datapath and Control : Dejwoot KHAWPARISUTH Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, 3 th & 4 th Edition, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005/2008, Elsevier (MK) http://webstaff.kmutt.ac.th/~dejwoot.kha/
Inf2C - Computer Systems Lecture 12 Processor Design Multi-Cycle
 Inf2C - Computer Systems Lecture 12 Processor Design Multi-Cycle Boris Grot School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Previous lecture: single-cycle processor Inf2C Computer Systems - 2017-2018. Boris
Inf2C - Computer Systems Lecture 12 Processor Design Multi-Cycle Boris Grot School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Previous lecture: single-cycle processor Inf2C Computer Systems - 2017-2018. Boris
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN. 5 th Edition. The Hardware/Software Interface. Chapter 4. The Processor
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle
The overall datapath for RT, lw,sw beq instrucution
 Designing The Main Control Unit: Remember the three instruction classes {R-type, Memory, Branch}: a) R-type : Op rs rt rd shamt funct 1.src 2.src dest. 31-26 25-21 20-16 15-11 10-6 5-0 a) Memory : Op rs
Designing The Main Control Unit: Remember the three instruction classes {R-type, Memory, Branch}: a) R-type : Op rs rt rd shamt funct 1.src 2.src dest. 31-26 25-21 20-16 15-11 10-6 5-0 a) Memory : Op rs
Review. A single-cycle MIPS processor
 Review If three instrctions have opcodes, 7 and 5 are they all of the same type? If we were to add an instrction to IPS of the form OD $t, $t2, $t3, which performs $t = $t2 OD $t3, what wold be its opcode?
Review If three instrctions have opcodes, 7 and 5 are they all of the same type? If we were to add an instrction to IPS of the form OD $t, $t2, $t3, which performs $t = $t2 OD $t3, what wold be its opcode?
The Processor: Datapath and Control. Jin-Soo Kim Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 The Processor: Datapath and Control Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined
The Processor: Datapath and Control Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined
Chapter 4. The Processor. Computer Architecture and IC Design Lab
 Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors CPI Clock Cycle Time Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS
Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors CPI Clock Cycle Time Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS
ECE369. Chapter 5 ECE369
 Chapter 5 1 State Elements Unclocked vs. Clocked Clocks used in synchronous logic Clocks are needed in sequential logic to decide when an element that contains state should be updated. State element 1
Chapter 5 1 State Elements Unclocked vs. Clocked Clocks used in synchronous logic Clocks are needed in sequential logic to decide when an element that contains state should be updated. State element 1
ALUOut. Registers A. I + D Memory IR. combinatorial block. combinatorial block. combinatorial block MDR
 Microprogramming Exceptions and interrupts 9 CMPE Fall 26 A. Di Blas Fall 26 CMPE CPU Multicycle From single-cycle to Multicycle CPU with sequential control: Finite State Machine Textbook Edition: 5.4,
Microprogramming Exceptions and interrupts 9 CMPE Fall 26 A. Di Blas Fall 26 CMPE CPU Multicycle From single-cycle to Multicycle CPU with sequential control: Finite State Machine Textbook Edition: 5.4,
CS 251, Spring 2018, Assignment 3.0 3% of course mark
 CS 25, Spring 28, Assignment 3. 3% of corse mark De onday, Jne 25th, 5:3 P. (5 points) Consider the single-cycle compter shown on page 6 of this assignment. Sppose the circit elements take the following
CS 25, Spring 28, Assignment 3. 3% of corse mark De onday, Jne 25th, 5:3 P. (5 points) Consider the single-cycle compter shown on page 6 of this assignment. Sppose the circit elements take the following
Chapter 4. The Processor
 Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware 4.1 Introduction We will examine two MIPS implementations
Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware 4.1 Introduction We will examine two MIPS implementations
THE HONG KONG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Computer Organization (COMP 2611) Spring Semester, 2014 Final Examination
 THE HONG KONG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Computer Organization (COMP 2611) Spring Semester, 2014 Final Examination May 23, 2014 Name: Email: Student ID: Lab Section Number: Instructions: 1. This
THE HONG KONG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Computer Organization (COMP 2611) Spring Semester, 2014 Final Examination May 23, 2014 Name: Email: Student ID: Lab Section Number: Instructions: 1. This
Inf2C - Computer Systems Lecture Processor Design Single Cycle
 Inf2C - Computer Systems Lecture 10-11 Processor Design Single Cycle Boris Grot School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Previous lectures Combinational circuits Combinations of gates (INV, AND, OR,
Inf2C - Computer Systems Lecture 10-11 Processor Design Single Cycle Boris Grot School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Previous lectures Combinational circuits Combinations of gates (INV, AND, OR,
Block diagram view. Datapath = functional units + registers
 Computer design an application of digital logic design procedures Computer = processing unit + memory system Processing unit = control + datapath Control = finite state machine inputs = machine instruction,
Computer design an application of digital logic design procedures Computer = processing unit + memory system Processing unit = control + datapath Control = finite state machine inputs = machine instruction,
Designing a Pipelined CPU
 Designing a Pipelined CPU CSE 4, S2'6 Review -- Single Cycle CPU CSE 4, S2'6 Review -- ultiple Cycle CPU CSE 4, S2'6 Review -- Instruction Latencies Single-Cycle CPU Load Ifetch /Dec Exec em Wr ultiple
Designing a Pipelined CPU CSE 4, S2'6 Review -- Single Cycle CPU CSE 4, S2'6 Review -- ultiple Cycle CPU CSE 4, S2'6 Review -- Instruction Latencies Single-Cycle CPU Load Ifetch /Dec Exec em Wr ultiple
ECE 30, Lab #8 Spring 2014
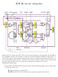 ECE 30, Lab #8 Spring 20 Shown above is a multi-cycle CPU. There are six special registers in this datapath: PC, IR, MDR, A, B, and ALUOut. Of these, PC and IR are enabled to change when PCWr and IRWr
ECE 30, Lab #8 Spring 20 Shown above is a multi-cycle CPU. There are six special registers in this datapath: PC, IR, MDR, A, B, and ALUOut. Of these, PC and IR are enabled to change when PCWr and IRWr
EECE 417 Computer Systems Architecture
 EECE 417 Computer Systems Architecture Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Howard University Charles Kim Spring 2007 1 Computer Organization and Design (3 rd Ed) -The Hardware/Software Interface
EECE 417 Computer Systems Architecture Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Howard University Charles Kim Spring 2007 1 Computer Organization and Design (3 rd Ed) -The Hardware/Software Interface
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE232: Harware Organization an Design ectre 11: Introction to IPs path apte from Compter Organization an Design, Patterson & Hennessy, CB IPS-lite processor Compter Want to bil a processor for a sbset
ECE232: Harware Organization an Design ectre 11: Introction to IPs path apte from Compter Organization an Design, Patterson & Hennessy, CB IPS-lite processor Compter Want to bil a processor for a sbset
ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture. Designing a Multiple Cycle Controller
 ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture Designing a Multiple Cycle Controller ECE468 multicontroller Review of a Multiple Cycle Implementation The root of the single cycle processor s problems: The
ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture Designing a Multiple Cycle Controller ECE468 multicontroller Review of a Multiple Cycle Implementation The root of the single cycle processor s problems: The
EE 457 Unit 6a. Basic Pipelining Techniques
 EE 47 Unit 6a Basic Pipelining Techniques 2 Pipelining Introduction Consider a drink bottling plant Filling the bottle = 3 sec. Placing the cap = 3 sec. Labeling = 3 sec. Would you want Machine = Does
EE 47 Unit 6a Basic Pipelining Techniques 2 Pipelining Introduction Consider a drink bottling plant Filling the bottle = 3 sec. Placing the cap = 3 sec. Labeling = 3 sec. Would you want Machine = Does
1048: Computer Organization
 48: Compter Organization Lectre 5 Datapath and Control Lectre5A - simple implementation (cwli@twins.ee.nct.ed.tw) 5A- Introdction In this lectre, we will try to implement simplified IPS which contain emory
48: Compter Organization Lectre 5 Datapath and Control Lectre5A - simple implementation (cwli@twins.ee.nct.ed.tw) 5A- Introdction In this lectre, we will try to implement simplified IPS which contain emory
Lecture 8: Control COS / ELE 375. Computer Architecture and Organization. Princeton University Fall Prof. David August
 Lecture 8: Control COS / ELE 375 Computer Architecture and Organization Princeton University Fall 2015 Prof. David August 1 Datapath and Control Datapath The collection of state elements, computation elements,
Lecture 8: Control COS / ELE 375 Computer Architecture and Organization Princeton University Fall 2015 Prof. David August 1 Datapath and Control Datapath The collection of state elements, computation elements,
EC 413 Computer Organization - Fall 2017 Problem Set 3 Problem Set 3 Solution
 EC 413 Computer Organization - Fall 2017 Problem Set 3 Problem Set 3 Solution Important guidelines: Always state your assumptions and clearly explain your answers. Please upload your solution document
EC 413 Computer Organization - Fall 2017 Problem Set 3 Problem Set 3 Solution Important guidelines: Always state your assumptions and clearly explain your answers. Please upload your solution document
CS232 Final Exam May 5, 2001
 CS232 Final Exam May 5, 2 Name: This exam has 4 pages, including this cover. There are six questions, worth a total of 5 points. You have 3 hours. Budget your time! Write clearly and show your work. State
CS232 Final Exam May 5, 2 Name: This exam has 4 pages, including this cover. There are six questions, worth a total of 5 points. You have 3 hours. Budget your time! Write clearly and show your work. State
